Residual Gas for Ethanol Production by Clostridium carboxidivorans in a Dual Impeller Stirred Tank Bioreactor (STBR)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Strain, Culture Medium, and Inoculum Preparation
2.3. Syngas Fermentation in Serum Glass Bottles
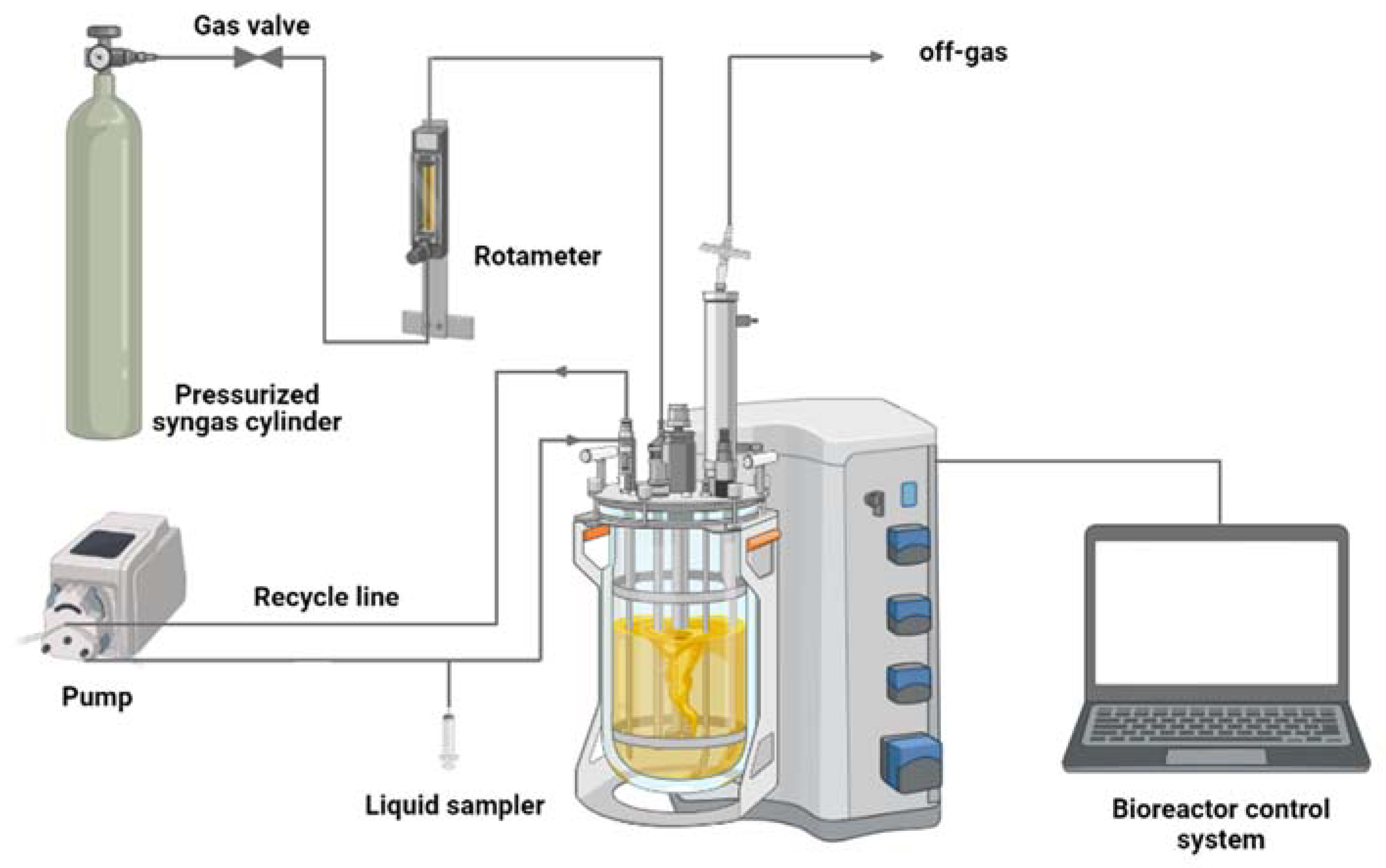
2.4. Syngas Fermentation in Stirred Tank Bioreactor
2.5. Analytical Methods
2.5.1. Dry Weight Cell
2.5.2. Metabolites Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Serum Bottles Fermentation
3.1.1. Cell Growth
3.1.2. Metabolites Production
3.2. Stirred Tank Bioreactor Fermentation
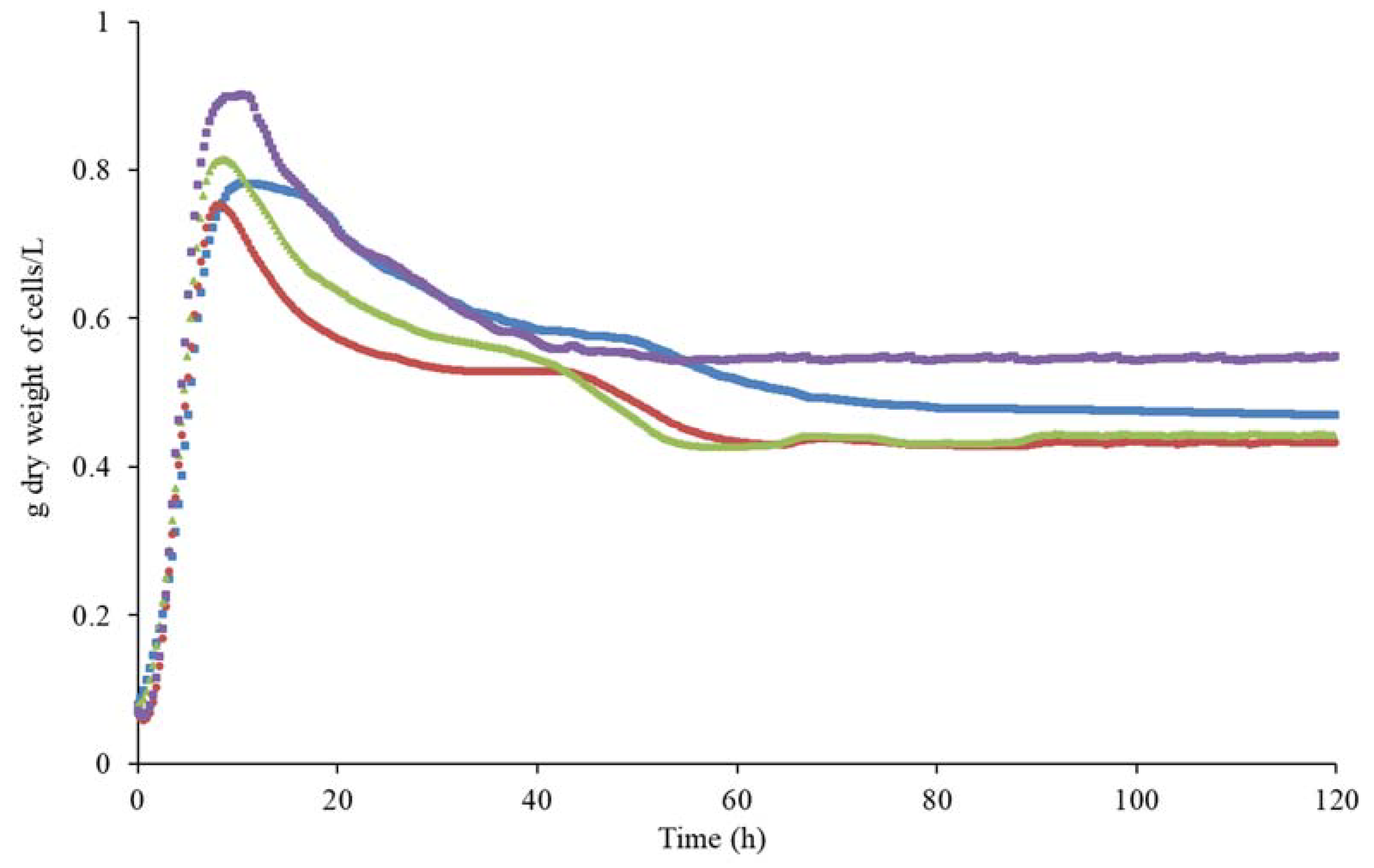
3.2.1. Cell Growth
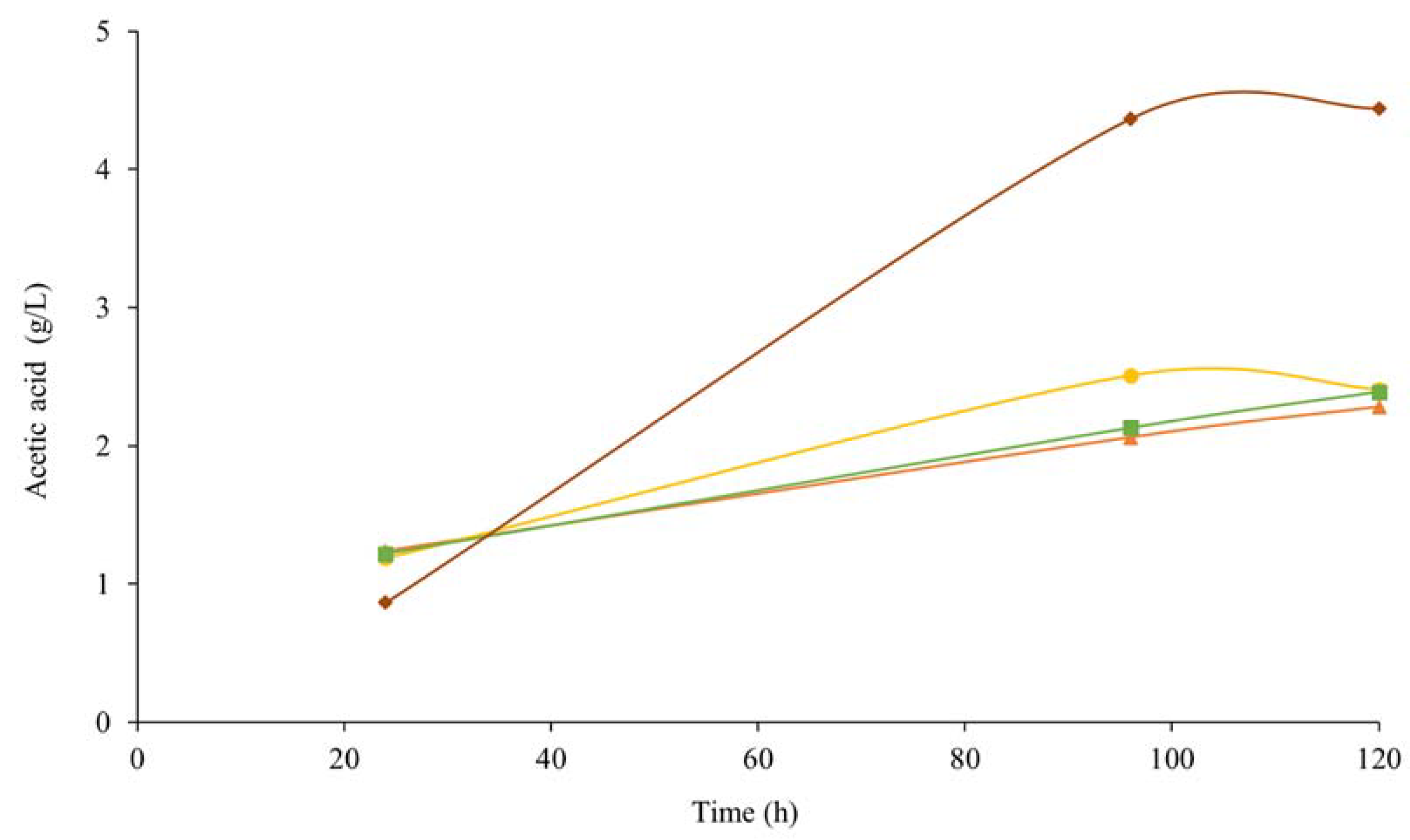
3.2.2. Metabolites Production
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EIA with Projections to 2050. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/outlooks/aeo/ (accessed on 12 August 2021).
- Gildemyn, S.; Molitor, B.; Usack, J.G.; Nguyen, M.; Rabaey, K.; Angenent, L.T. Upgrading syngas fermentation effluent using Clostridium kluyveri in a continuous fermentation. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2017, 10, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, M.; Najafpour, G.D.; Younesi, H.; Lahijani, P.; Uzir, M.H.; Mohamed, A.R. Bioconversion of synthesis gas to second generation biofuels: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2011, 15, 4255–4273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ukpong, M.N.; Atiyeh, H.K.; De Lorme, M.J.M.; Liu, K.; Zhu, X.; Tanner, R.S.; Wilkins, M.R.; Stevenson, B.S. Physiological response of Clostridium carboxidivorans during conversion of synthesis gas to solvents in a gas-fed bioreactor. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 2720–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benevenuti, C.; Botelho, A.; Ribeiro, R.; Branco, M.; Pereira, A.; Vieira, A.C.; Ferreira, T.; Amaral, P. Experimental Design to Improve Cell Growth and Ethanol Production in Syngas Fermentation by Clostridium carboxidivorans. Catalysts 2020, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munasinghe, P.C.; Khanal, S.K. Biomass-derived syngas fermentation into biofuels. Biofuels 2011, 101, 79–98. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Cheng, J. Hydrolysis of lignocellulosic materials for ethanol production: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 83, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boboescu, I.Z.; Gélinas, M.; Beigbeder, J.B.; Lavoie, J.M. A two-step optimization strategy for 2nd generation ethanol production using softwood hemicellulosic hydrolysate as fermentation substrate. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datar, R.P.; Shenkman, R.M.; Cateni, B.G.; Huhnke, R.L.; Lewis, R.S. Fermentation of biomass-generated producer gas to ethanol. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2004, 86, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.S.; Tanner, R.S.; Huhnke, R.L. Huhnke Indirect or Direct Fermentation of Biomass to Fuel Alcohol. U.S. Patent No. 11/441,392, 25 May 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Atiyeh, H.K.; Zhang, H.; Tanner, R.S.; Huhnke, R.L. Enhanced ethanol production from syngas by Clostridium ragsdalei in continuous stirred tank reactor using medium with poultry litter biochar. Appl. Energy 2019, 236, 1269–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Brown, R.; Wen, Z. Syngas fermentation of Clostridium carboxidivoran P7 in a hollow fiber membrane biofilm reactor: Evaluating the mass transfer coefficient and ethanol production performance. Biochem. Eng. J. 2014, 85, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberato, V.; Benevenuti, C.; Coelho, F.; Botelho, A.; Amaral, P.; Pereira, N.; Ferreira, T. Chemicals production in a biorefinery context. Catalysts 2019, 9, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, K.; Rückel, A.; Kämpf, P.; Wende, M.; Weuster-Botz, D. Two stirred-tank bioreactors in series enable continuous production of alcohols from carbon monoxide with Clostridium carboxidivorans. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 41, 1403–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dürre, P.; Eikmanns, B.J. C1-carbon sources for chemical and fuel production by microbial gas fermentation. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 35, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennes, D.; Abubackar, H.N.; Diaz, M.; Veiga, M.C.; Kennes, C. Bioethanol production from biomass: Carbohydrate vs. syngas fermentation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 91, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Taylor, S.; Wang, Y. Effects of end products on fermentation profiles in Clostridium carboxidivorans P7 for syngas fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 218, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundiyana, D.K.; Huhnke, R.L.; Wilkins, M.R. Syngas fermentation in a 100-L pilot scale fermentor: Design and process considerations. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2010, 109, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, H.; Martin, M.E.; Angenent, L.T. A two-stage continuous fermentation system for conversion of syngas into ethanol. Energies 2013, 6, 3987–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, F.M.B.; Botelho, A.M.; Ivo, O.F.; Amaral, P.F.F.; Ferreira, T.F. Volumetric mass transfer coefficient for carbon monoxide in a dual impeller stirred tank reactor considering a perfluorocarbon–water mixture as liquid phase. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2019, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, J.R.; Huhnke, R.L.; Atiyeh, H.K. Syngas fermentation: A microbial conversion process of gaseous substrates to various products. Fermentation 2017, 3, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Naveira, Á.; Veiga, M.C.; Kennes, C. Effect of salinity on C1-gas fermentation by Clostridium carboxidivorans producing acids and alcohols. AMB Express 2019, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Y.; Brown, R.; Wen, Z. Enhancing mass transfer and ethanol production in syngas fermentation of Clostridium carboxidivorans P7 through a monolithic biofilm reactor. Appl. Energy 2014, 136, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, F.M.B.; Nele, M.; Ribeiro, R.R.; Ferreira, T.F.; Amaral, P.F.F. Clostridium carboxidivorans’ surface characterization using contact angle measurement (CAM). In Proceedings of the IConBM2016 2nd International Conference on BIOMASS, Sicily, Italy, 19–22 June 2016; Volume 50, pp. 277–282. [Google Scholar]
- Devarapalli, M.; Lewis, R.S.; Atiyeh, H.K. Continuous ethanol production from synthesis gas by Clostridium ragsdalei in a trickle-bed reactor. Fermentation 2017, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Brown, R.C.; Wen, Z. Syngas fermentation by Clostridium carboxidivorans P7 in a horizontal rotating packed bed biofilm reactor with enhanced ethanol production. Appl. Energy 2017, 187, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldric, J.M.; Gillet, S.; Delvigne, F.; Blecker, C.; Lebeau, F.; Wathelet, J.P.; Manigat, G.; Thonart, P. Effect of surfactants and biomass on the gas / liquid mass transfer in an aqueous-silicone oil two-phase partitioning bioreactor using Rhodococcus erythropolis T902. 1 to remove VOCs from gaseous effluents. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 1274–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, F.; Medley, G.J.D.; Bandulasena, H.; Zimmerman, W.B.J. Fluidic oscillator-mediated microbubble generation to provide cost effective mass transfer and mixing ef fi ciency to the wastewater treat- ment plants. Environ. Res. 2015, 137, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bredwell, M.D.; Telgenhoff, I.M.D.; Barnard, I.S.; Worden, R.M.I. Effect of surfactants on carbon monoxide fermentations by butyribacterium methylotroph icum. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1997, 63–65, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myung, J.; Kim, M.; Pan, M.; Criddle, C.S.; Tang, S.K.Y. Bioresource technology low energy emulsion-based fermentation enabling accelerated methane mass transfer and growth of poly (3-hydroxybutyrate) -accumulating methanotrophs. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 207, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, C.K.; Kjems, J.; Mygind, T.; Snabe, T.; Meyer, R.L. Effects of tween 80 on growth and biofilm formation in laboratory media. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskandani, M.; Hamishehkar, H.; Dolatabadi, J.E.N. Cyto/genotoxicity study of polyoxyethylene (20) sorbitan monolaurate (tween 20). DNA Cell Biol. 2013, 32, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasin, M.; Park, S.; Jeong, Y.; Lee, E.Y.; Lee, J.; Chang, I.S. Effect of internal pressure and gas/liquid interface area on the CO mass transfer coefficient using hollow fibre membranes as a high mass transfer gas diffusing system for microbial syngas fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, V.; Alberto, C.; Cosenza, N.; Barros, C.F.; Krykhtine, F.; Netto, E.; Fortes, S.; Alberto, C.; Cosenza, N.; Barros, C.F. Tratamento de resíduos sólidos urbanos e produção de energia: Análise de legislação para viabilidade econômica de soluçoes. In Proceedings of the XI Simpósio de Excelência em Gestão e Tecnologia—SEGeT, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 22–24 October 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, R.R.; Coelho, F.; Ferreira, T.F.; Amaral, P.F.F. A new strategy for acetogenic bacteriacell growth and metabolites production using syngas in lab scale. IOSR J. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2017, 03, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Naveira, Á.; Abubackar, H.N.; Veiga, M.C.; Kennes, C. Carbon monoxide bioconversion to butanol-ethanol by Clostridium carboxidivorans: Kinetics and toxicity of alcohols. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 4231–4240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Naveira, Á.; Abubackar, H.N.; Veiga, M.C.; Kennes, C. Efficient butanol-ethanol (B-E) production from carbon monoxide fermentation by Clostridium carboxidivorans. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 3361–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata, S. Morphological changes during conversion of clostridium saccharoperbutylacetonicum to protoplasts by sucrose-induced autolysis. Microbiol. Immunol. 1980, 24, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniell, J.; Köpke, M.; Simpson, S.D. Commercial biomass syngas fermentation. Energies 2012, 5, 5372–5417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Naveira, Á.; Veiga, M.C.; Kennes, C. Glucose bioconversion profile in the syngas-metabolizing species Clostridium carboxidivorans. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 244, 552–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Gu, Y.; Chai, C.; Jiang, W.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, Y. Enhanced alcohol titre and ratio in carbon monoxide-rich off-gas fermentation of Clostridium carboxidivorans through combination of trace metals optimization with variable-temperature cultivation. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 239, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, J.M.T.; Rodrigues, J.M.L.; Orvalho, S.C.P.; Alves, S.S.; Mendes, R.L.; Reis, A. Effect of contaminants on mass transfer coefficients in bubble column and airlift contactors. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2003, 58, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, A.; García-Abuín, A.; Gómez-Díaz, D.; Navaza, J.M. Hydrodynamic and absorption studies of carbon dioxide absorption in aqueous amide solutions using a bubble column contactor. Brazilian J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 30, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Belo, I.; García-Abuín, A.; Gómez-Díaz, D.; Navaza, J.M.J.M.; Vidal-Tato, I. Effect of tween 80 on bubble size and mass transfer in a bubble contactor. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2011, 34, 1790–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Naveira, Á.; Veiga, M.C.; Kennes, C. Effect of pH control on the anaerobic H-B-E fermentation of syngas in bioreactors. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 1178–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarapalli, M.; Atiyeh, H.K.; Phillips, J.R.; Lewis, R.S.; Huhnke, R.L. Ethanol production during semi-continuous syngas fermentation in a trickle bed reactor using Clostridium ragsdalei. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 209, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-naveira, Á.; Veiga, M.C.; Kennes, C. Selective anaerobic fermentation of syngas into either C2–C6 organic acids or ethanol and higher alcohols. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 280, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, B.; Dutta, A.; Basu, P. Ethanol production by syngas fermentation in a continuous stirred tank bioreactor using Clostridium ljungdahlii. Biofuels 2019, 10, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anggraini, I.D.; Kery, K.; Bandung, P.N.; Kresnowati, P.; Purwadi, R. Bioethanol production via syngas fermentation of clostridium ljungdahlii in a hollow fiber membrane supported bioreactor. Chem. Eng. 2019, 10, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Chandramohan, V.P.; Mathimani, T.; Pugazhendhi, A. Recent advances in thermochemical methods for the conversion of algal biomass to energy. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 144608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Culture Medium | µ (h−1) |
|---|---|
| ATCC® 2713 | 0.310 ± 0.13 |
| ATCC® 2713 + 0.07% Tween® 80 | 0.359 ± 0.12 |
| ATCC® 2713 + 0.15% Tween® 80 | 0.350 ± 0.06 |
| ATCC® 2713 + 0.3% Tween® 80 | 0.414 ± 0.04 |
| Culture Medium | CGQ Measurement | Direct Cell Dry Weight |
|---|---|---|
| ATCC® 2713 | 0.477 ± 0.023 | 0.433 ± 0.156 |
| ATCC® 2713 + 0.07% Tween® 80 | 0.390 ± 0.003 | 0.413 ± 0.065 |
| ATCC® 2713 + 0.15% Tween® 80 | 0.475 ± 0.054 | 0.443 ± 0.075 |
| ATCC® 2713 + 0.3% Tween® 80 | 0.520 ± 0.019 | 0.477 ± 0.015 |
| Biocatalysts | Reactor a | CO:H2:CO2:N2:CH4 | Ethanol (g/L) | Ethanol Productivity (g/L.h) | Fermentation Period (h) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clostridium ragsdalei | CSTR | 40:30:30:0:0 | 13.2 | 0.044 | 300 | [11] |
| TBR | 38:28:28:5:0 | 5.7 | 0.003 | 1662 | [46] | |
| TBR | 38:28:28:5:0 | 13.2 | 0.158 | 84 | [25] | |
| Clostridium carboxidivorans | CSTR | 20:10:20:50:0 | 2.7 | 0.008 | 340 | [45] |
| CSTR | 100:0:0:0:0 | 5.6 | 0.023 | 245 | [36] | |
| CSTR | 20:10:20:50:0 | 2.34 | 0.011 | 210 | [45] | |
| CSTR | 30:20:10:40:0 | 5.9 | 0.032 | 185 | [47] | |
| CSTR | 20:5:15:60:0 | 2.1 | 0.082 | 25 | [26] | |
| h-RPB | 20:5:15:60:0 | 7 | 0.279 | 25 | [26] | |
| CSTR | 80:0:20:0:0 | 6 | 0.03 | 200 | [14] | |
| STBR | 25:44:10:10:11 | 1.2 | 0.050 | 24 | This study | |
| Clostridium ljungdahli | CSTR | 65:30:5:0:0 | 3.8 | 0.005 | 730 | [48] |
| HFM | 25:15:25:40:0 | 1.09 | 0.005 | 216 | [49] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Benevenuti, C.; Branco, M.; do Nascimento-Correa, M.; Botelho, A.; Ferreira, T.; Amaral, P. Residual Gas for Ethanol Production by Clostridium carboxidivorans in a Dual Impeller Stirred Tank Bioreactor (STBR). Fermentation 2021, 7, 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7030199
Benevenuti C, Branco M, do Nascimento-Correa M, Botelho A, Ferreira T, Amaral P. Residual Gas for Ethanol Production by Clostridium carboxidivorans in a Dual Impeller Stirred Tank Bioreactor (STBR). Fermentation. 2021; 7(3):199. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7030199
Chicago/Turabian StyleBenevenuti, Carolina, Marcelle Branco, Mariana do Nascimento-Correa, Alanna Botelho, Tatiana Ferreira, and Priscilla Amaral. 2021. "Residual Gas for Ethanol Production by Clostridium carboxidivorans in a Dual Impeller Stirred Tank Bioreactor (STBR)" Fermentation 7, no. 3: 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7030199
APA StyleBenevenuti, C., Branco, M., do Nascimento-Correa, M., Botelho, A., Ferreira, T., & Amaral, P. (2021). Residual Gas for Ethanol Production by Clostridium carboxidivorans in a Dual Impeller Stirred Tank Bioreactor (STBR). Fermentation, 7(3), 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation7030199








