Production of Nutritional Protein Hydrolysates by Fermentation of Black Soldier Fly Larvae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
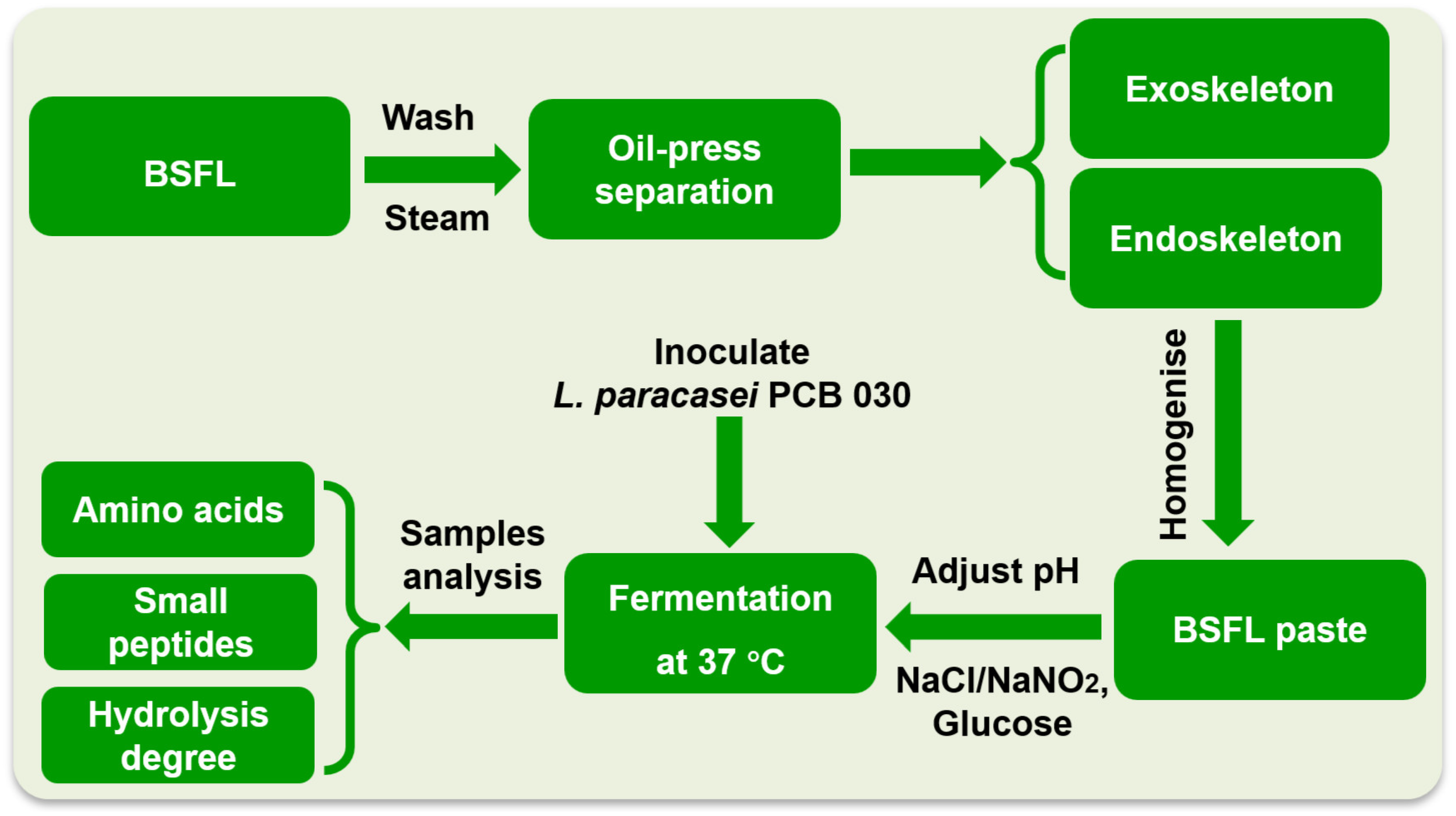
2.2. BSFL Paste Preparation
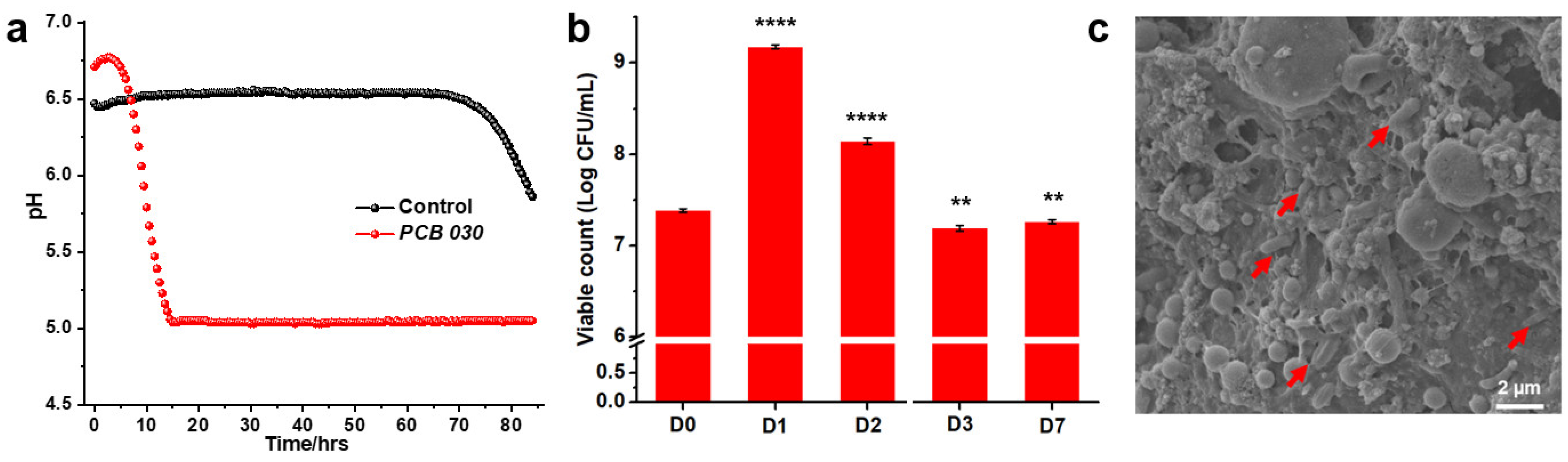
2.3. Online pH Measurement
2.4. Viable Counts
2.5. L. paracasei PCB 030 Fermented BSFL Paste Morphology
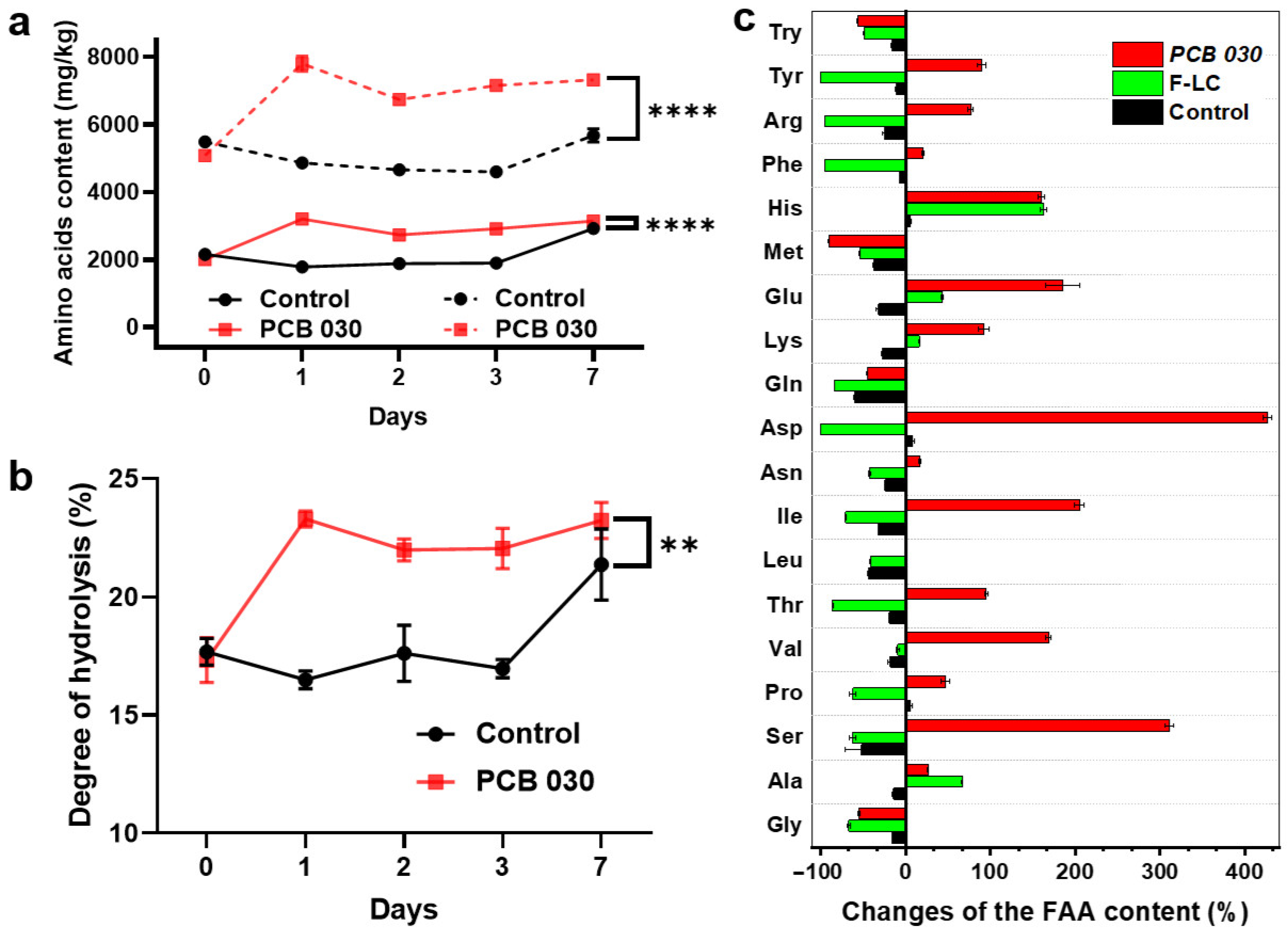
2.6. Degree of Hydrolysis
2.7. Quantification of Free Amino Acids
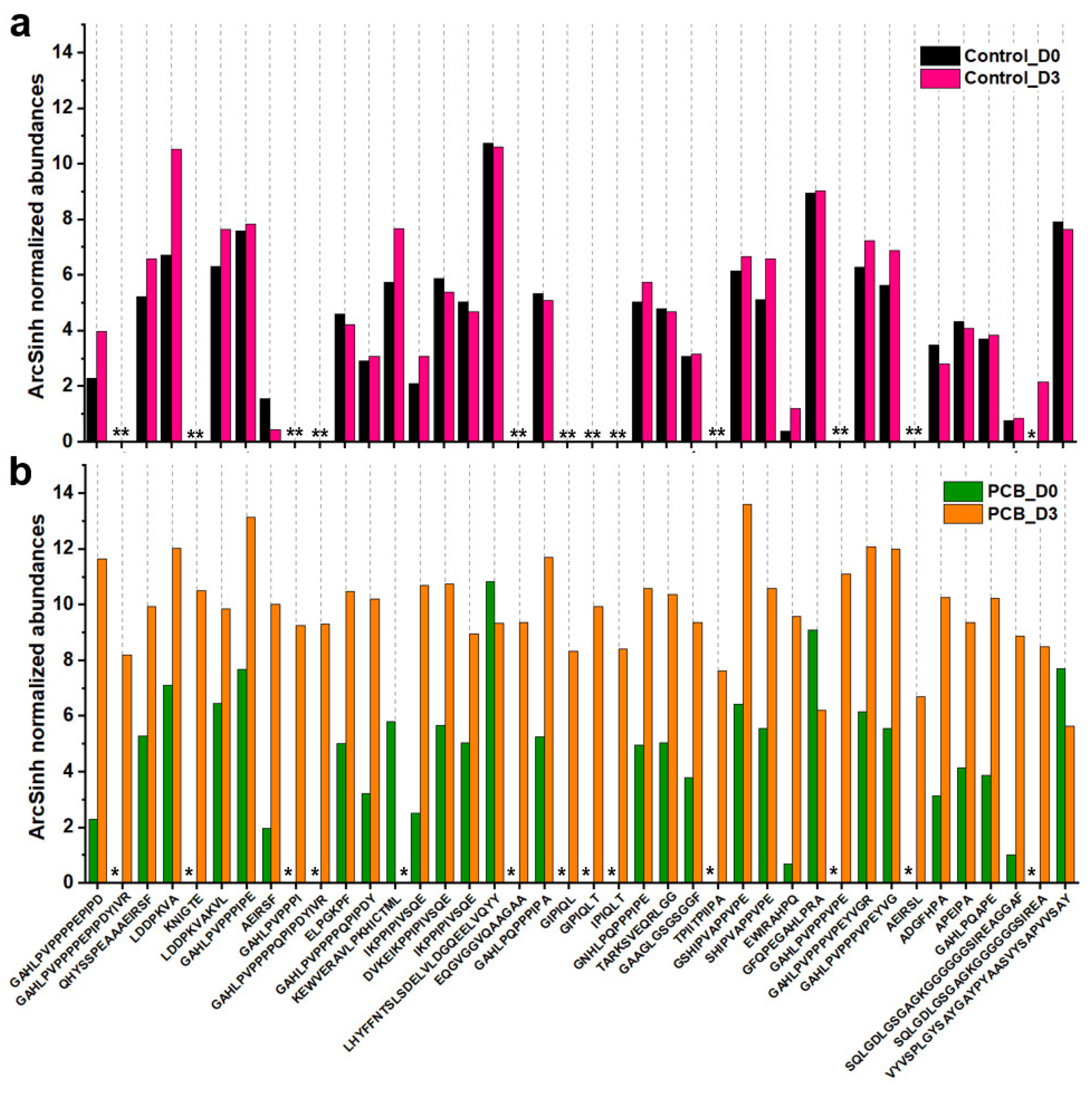
2.8. Small Peptides Analysis by LC-MS/MS
2.9. Fat Content Measurement
2.10. Ash Content Measurement
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. BSFL Pre-Processing and Fermentation Condition
3.2. Phenotypic Characterizations of the Fermentation Process
3.3. Hydrolysate Assessment
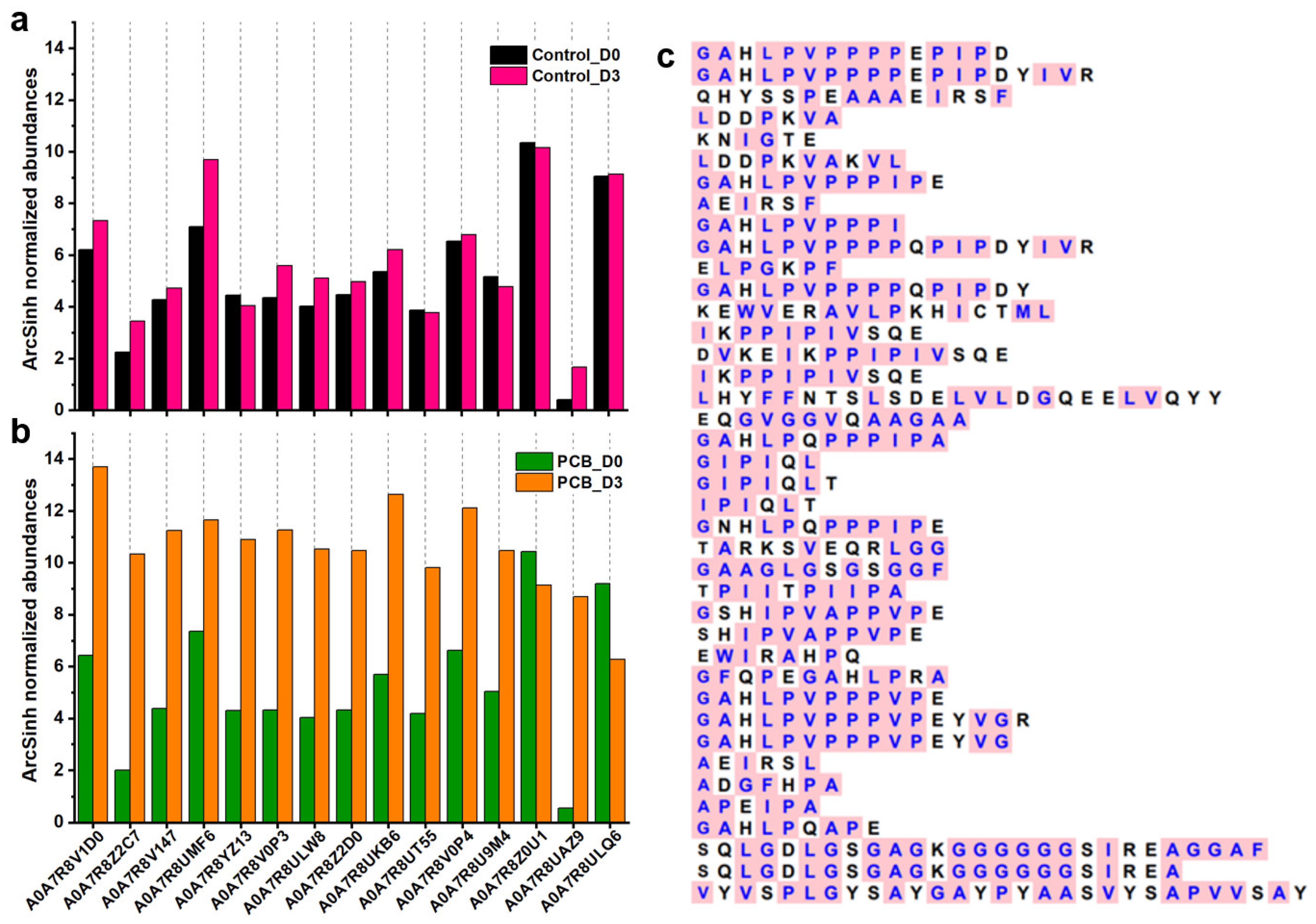
3.4. Small Peptides Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.-S.; Shelomi, M. Review of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) as Animal Feed and Human Food. Foods 2017, 6, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahuddin, M.; Abdel-Wareth, A.A.A.; Hiramatsu, K.; Tomberlin, J.K.; Luza, D.; Lohakare, J. Flight toward Sustainability in Poultry Nutrition with Black Soldier Fly Larvae. Animals 2024, 14, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liland, N.S.; Biancarosa, I.; Araujo, P.; Biemans, D.; Bruckner, C.G.; Waagbo, R.; Torstensen, B.E.; Lock, E.J. Modulation of nutrient composition of black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae by feeding seaweed-enriched media. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finke, M.D. Complete nutrient content of four species of feeder insects. Zoo Biol 2013, 32, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Souza-Vilela, J.; Andrew, N.; Ruhnke, I. Insect protein in animal nutrition. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2019, 59, 2029–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finke, M.D.; Rojo, S.; Roos, N.; van Huis, A.; Yen, A. The European Food Safety Authority scientific opinion on a risk profile related to production and consumption of insects as food and feed. J. Insects Food Feed. 2015, 1, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, M.; Hoffman, L.; Pieterse, E. Artificial diets for neonatal black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae. J. Insects Food Feed 2019, 5, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brulé, L.; Misery, B.; Baudouin, G.; Yan, X.; Guidou, C.; Trespeuch, C.; Foltyn, C.; Anthoine, V.; Moriceau, N.; Federighi, M.; et al. Evaluation of the Microbial Quality of Hermetia illucens Larvae for Animal Feed and Human Consumption: Study of Different Type of Rearing Substrates. Foods 2024, 13, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbeke, W. Profiling consumers who are ready to adopt insects as a meat substitute in a Western society. Food Qual. Prefer. 2015, 39, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, C.; Siegrist, M. Consumer perception and behaviour regarding sustainable protein consumption: A systematic review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 61, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.S.G.; Fischer, A.R.; Tinchan, P.; Stieger, M.; Steenbekkers, L.; van Trijp, H.C. Insects as food: Exploring cultural exposure and individual experience as determinants of acceptance. Food Qual. Prefer. 2015, 42, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemme, A.; Klüber, P. Rethinking Amino Acid Nutrition of Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens) Based on Insights from an Amino Acid Reduction Trial. Insects 2024, 15, 862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadoun, J.H.; Ricci, A.; Cirlini, M.; Bancalari, E.; Bernini, V.; Galaverna, G.; Neviani, E.; Lazzi, C. Production and recovery of volatile compounds from fermented fruit by-products with Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus. Food Bioprod. Process. 2021, 128, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luparelli, A.V.; Saadoun, J.H.; Lolli, V.; Lazzi, C.; Sforza, S.; Caligiani, A. Dynamic changes in molecular composition of black soldier fly prepupae and derived biomasses with microbial fermentation. Food Chem X 2022, 14, 100327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, D.; Sugrue, I.; Tobin, C.; Hill, C.; Stanton, C.; Ross, R.P. The Lactobacillus casei group: History and health related applications. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunelli, L.; Perotti, S.; Gargari, G.; De Vitis, V.; Mantegazza, G.; Ferrari, R.; Minuzzo, M.; Pierallini, E.; Ricci, G.; Fiore, W.; et al. Genetic and phenotypic stability of Lacticaseibacillus paracasei DG (DSM 34154) over 10 years of industrial production. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2025, 91, e02394-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colautti, A.; Ginaldi, F.; Camprini, L.; Comi, G.; Reale, A.; Iacumin, L. Investigating Safety and Technological Traits of a Leading Probiotic Species: Lacticaseibacillus paracasei. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieliszek, M.; Pobiega, K.; Piwowarek, K.; Kot, A.M. Characteristics of the Proteolytic Enzymes Produced by Lactic Acid Bacteria. Molecules 2021, 26, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satılmış, M.K.; Öztürk, H.İ.; Demirci, T.; Denktaş, B.; Akın, N. Revealing the proteolytic characteristics of lactobacillus, lacticaseibacillus, and lactiplantibacillus isolates by in vitro and in situ perspectives. Food Biosci. 2023, 55, 103086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solieri, L.; Sola, L.; Vaccalluzzo, A.; Randazzo, C.L.; Martini, S.; Tagliazucchi, D. Characterization of Cell-Envelope Proteinases from Two Lacticaseibacillus casei Strains Isolated from Parmigiano Reggiano Cheese. Biology 2022, 11, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batish, I.; Brits, D.; Valencia, P.; Miyai, C.; Rafeeq, S.; Xu, Y.; Galanopoulos, M.; Sismour, E.; Ovissipour, R. Effects of Enzymatic Hydrolysis on the Functional Properties, Antioxidant Activity and Protein Structure of Black Soldier Fly (Hermetia illucens) Protein. Insects 2020, 11, 876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakawa, D.P.; Goosen, N.J. Protein recovery from black soldier fly larvae using enzymatic hydrolysis and alkaline extraction. J. Insects Food Feed 2025, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, R.; Spinelli, R.; Neri, P.; Pini, M.; Barbi, S.; Montorsi, M.; Maistrello, L.; Marseglia, A.; Caligiani, A.; Ferrari, A.M. Life Cycle Assessment of Chemical vs Enzymatic-Assisted Extraction of Proteins from Black Soldier Fly Prepupae for the Preparation of Biomaterials for Potential Agricultural Use. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 14752–14764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Ma, L.; Xu, J.; Rong, K.; Peng, N.; Zhao, S. Effect of enzyme-assisted fermentation on quality, safety, and microbial community of black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens L.) as a novel protein source. Food Res. Int. 2023, 174, 113624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadj Saadoun, J.; Luparelli, A.V.; Caligiani, A.; Macavei, L.I.; Maistrello, L.; Neviani, E.; Galaverna, G.; Sforza, S.; Lazzi, C. Antimicrobial Biomasses from Lactic Acid Fermentation of Black Soldier Fly Prepupae and Related By-Products. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyle, N.T.; Merrltt, J.H. Quality of Fish Protein Hydrolysates from Herring (Clupea harengus). J. Food Sci. 1994, 59, 76–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, A.P.F.; Daroit, D.J.; Coelho, J.; Meira, S.M.; Lopes, F.C.; Segalin, J.; Risso, P.H.; Brandelli, A. Antioxidant, antihypertensive and antimicrobial properties of ovine milk caseinate hydrolyzed with a microbial protease. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 2247–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuso, A.; Barbi, S.; Macavei, L.I.; Luparelli, A.V.; Maistrello, L.; Montorsi, M.; Sforza, S.; Caligiani, A. Effect of the Rearing Substrate on Total Protein and Amino Acid Composition in Black Soldier Fly. Foods 2021, 10, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, Q.; ur Rehman, K.; Li, W.; Cai, M.; Li, Q.; Mazza, L.; Zhang, J. Dynamic changes of nutrient composition throughout the entire life cycle of black soldier fly. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintah, B.K.; He, R.; Agyekum, A.A.; Dabbour, M.; Golly, M.K.; Ma, H. Edible insect protein for food applications: Extraction, composition, and functional properties. J. Food Process Eng. 2020, 43, e13362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Ramos, J.A.; Rojas, M.G.; Shelby, K.S.; Coudron, T.A. Nutritional value of pupae versus larvae of Tenebrio molitor (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae) as food for rearing Podisus maculiventris (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2016, 109, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutkins, R.W. Meat Fermentation. In Microbiology and Technology of Fermented Foods; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006; pp. 207–232. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, C.-L.; Jin, W.-Z.; Tao, X.-H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, J.; Feng, S.-Y.; Xu, X.-H.; Li, H.-Y.; Wang, Z.-H.; Zhang, Z.-J. Black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens) strengthen the metabolic function of food waste biodegradation by gut microbiome. Microb. Biotechnol. 2019, 12, 528–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, F.; Verluyten, J.; De Vuyst, L. Functional meat starter cultures for improved sausage fermentation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 106, 270–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandeweyer, D.; Crauwels, S.; Lievens, B.; Van Campenhout, L. Microbial counts of mealworm larvae (Tenebrio molitor) and crickets (Acheta domesticus and Gryllodes sigillatus) from different rearing companies and different production batches. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 242, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.-L.; Chen, C.-C.; Lin, Y.-T.; Wu, W.-K.; Chang, L.-C.; Lai, C.-H.; Wu, M.-S.; Kuo, C.-H. Evaluation and Optimization of Sample Handling Methods for Quantification of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Human Fecal Samples by GC–MS. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 1948–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H.; Lee, K.D.; Choi, K.C. Role of LAB in silage fermentation: Effect on nutritional quality and organic acid production—An overview. AIMS Agric. Food 2021, 6, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.J.; Schieber, A.; Gänzle, M.G. Formation of taste-active amino acids, amino acid derivatives and peptides in food fermentations–A review. Food Res. Int. 2016, 89, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, F.; Fan, M.; Zheng, J.; Cai, M.; Zheng, L.; Huang, F.; Yu, Z.; Zhang, J. Enhanced protein degradation by black soldier fly larvae (Hermetia illucens L.) and its gut microbes. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1095025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.C.; Hansen, A.M.; Lauritsen, F.R. Catabolism of leucine to branched-chain fatty acids in Staphylococcus xylosus. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 96, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freiding, S.; Gutsche, K.A.; Ehrmann, M.A.; Vogel, R.F. Genetic screening of Lactobacillus sakei and Lactobacillus curvatus strains for their peptidolytic system and amino acid metabolism, and comparison of their volatilomes in a model system. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 34, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irmler, S.; Bavan, T.; Oberli, A.; Roetschi, A.; Badertscher, R.; Guggenbühl, B.; Berthoud, H. Catabolism of serine by Pediococcus acidilactici and Pediococcus pentosaceus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattanasiritham, L.; Theerakulkait, C.; Wickramasekara, S.; Maier, C.S.; Stevens, J.F. Isolation and identification of antioxidant peptides from enzymatically hydrolyzed rice bran protein. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendis, E.; Rajapakse, N.; Byun, H.-G.; Kim, S.-K. Investigation of jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) skin gelatin peptides for their in vitro antioxidant effects. Life Sci. 2005, 77, 2166–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimchan, T.; Hamzeh, A.; Siringan, P.; Thumanu, K.; Hanboonsong, Y.; Yongsawatdigul, J. Antibacterial peptides from black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens) larvae: Mode of action and characterization. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 26469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praseatsook, K.; Vachiraarunwong, A.; Taya, S.; Setthaya, P.; Sato, K.; Wanibuchi, H.; Wongpoomchai, R.; Dejkriengkraikul, P.; Gi, M.; Yodkeree, S. Anticancer and Antioxidant Effects of Bioactive Peptides from Black Soldier Fly Larvae (Hermetia illucens). Nutrients 2025, 17, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, P.; Seow, K.; Wein, L.; Steven, R.; Case, R.J.; Wang, Y.; Conway, P.L. Production of Nutritional Protein Hydrolysates by Fermentation of Black Soldier Fly Larvae. Fermentation 2025, 11, 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11090524
Zhang P, Seow K, Wein L, Steven R, Case RJ, Wang Y, Conway PL. Production of Nutritional Protein Hydrolysates by Fermentation of Black Soldier Fly Larvae. Fermentation. 2025; 11(9):524. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11090524
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Penghui, Kelyn Seow, Leo Wein, Rachel Steven, Rebecca J. Case, Yulan Wang, and Patricia L. Conway. 2025. "Production of Nutritional Protein Hydrolysates by Fermentation of Black Soldier Fly Larvae" Fermentation 11, no. 9: 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11090524
APA StyleZhang, P., Seow, K., Wein, L., Steven, R., Case, R. J., Wang, Y., & Conway, P. L. (2025). Production of Nutritional Protein Hydrolysates by Fermentation of Black Soldier Fly Larvae. Fermentation, 11(9), 524. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11090524







