Synergistic Effect of Microorganisms and Enzymes on Nutritional Value of Corn Stover and Wheat Straw
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Substrates, Microorganisms, and Enzymes
2.2. Treatment with Microorganisms and Enzymes
2.3. Determination of Nutritional Components and Fermentation Products
2.4. In Vitro Rumen Fermentation and Determination of Fermentation Parameters
2.5. Fiber Structure Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Nutritional Composition
3.2. Fermentation Products
3.3. Mycotoxins
3.4. In Vitro Rumen Fermentation Parameters
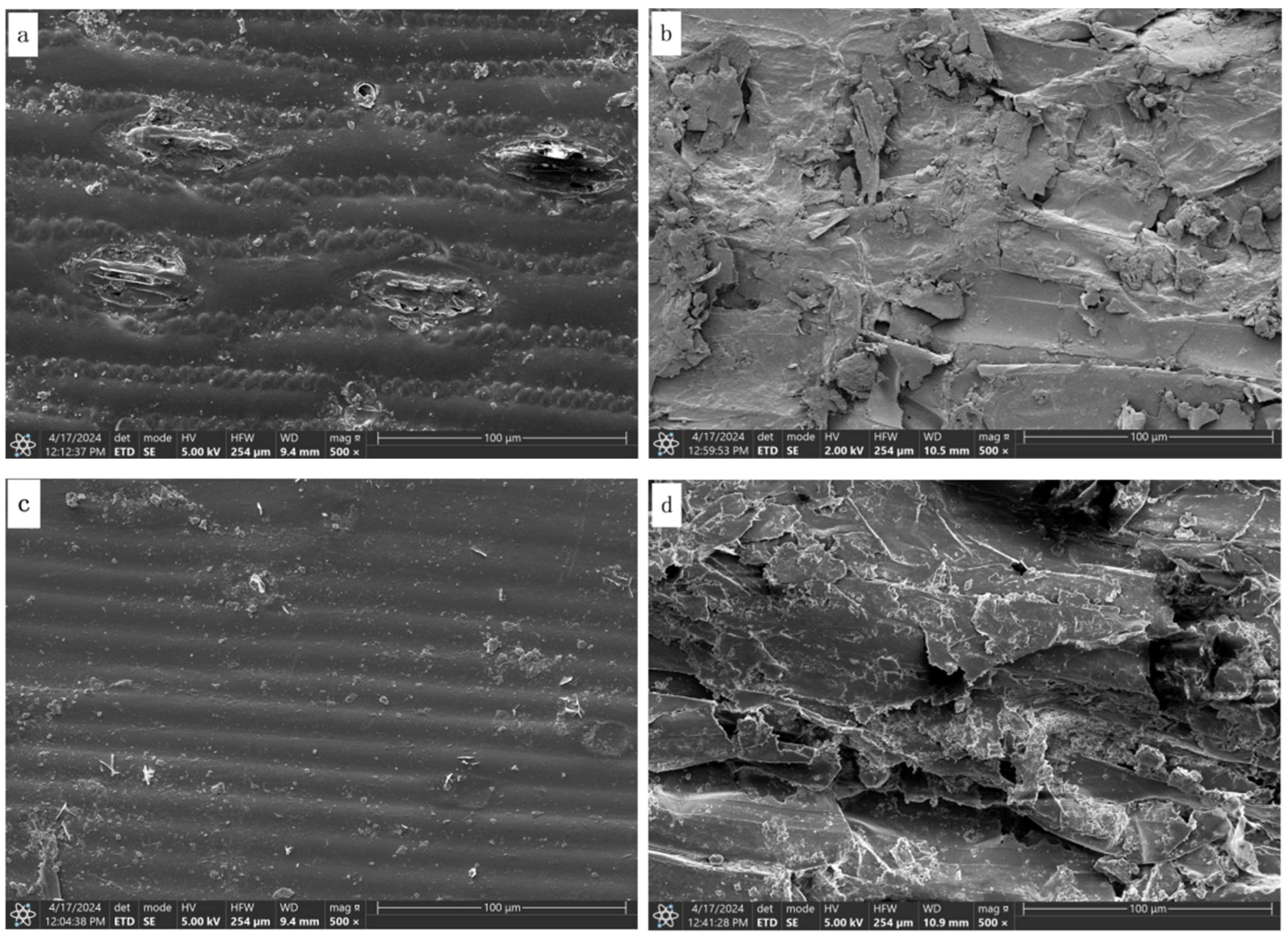
3.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Microorganisms and Enzymes on the Nutritional Composition of Corn Stover and Wheat Straw
4.2. Effects of Microorganisms and Enzymes on Fermentation Products of Corn Stover and Wheat Straw
4.3. Effects of Microorganisms and Enzymes on Mycotoxin Production in Corn Stover and Wheat Straw
4.4. In Vitro Rumen Fermentation of Straw Treated with Microorganism–Enzyme Combinations
4.5. Effects of Microorganisms and Enzymes on the Fiber Structure of Corn Stover and Wheat Straw
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CFU | Colony-forming units |
| DM | Dry matter |
| OM | Organic matter |
| CP | Crude protein |
| NDF | Neutral detergent fiber |
| ADF | Acid detergent fiber |
| NH3-N | Ammonia nitrogen |
| VFAs | Volatile fatty acids |
| TVFAs | Total volatile fatty acids |
| A/P | Acetate/Propionate |
| DMD | Dry matter degradation rate |
| AFB1 | Aflatoxin B1 |
| ZON | Zearalenone |
| DON | Deoxynivalenol |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
References
- Ma, Y.; Shen, Y.; Liu, Y. State of the art of straw treatment technology: Challenges and solutions forward. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 313, 123656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masłowski, M.; Miedzianowska, J.; Strzelec, K. The potential application of cereal straw as a bio-filler for elastomer composites. Polym. Bull. 2020, 77, 2021–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Q.; Li, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, Q.; Chen, Y.; Peng, Q.; Yuan, S.; Li, H.; Huang, R.; et al. An integrated method to produce fermented liquid feed and biologically modified biochar as cadmium adsorbents using corn stalks. Waste Manag. 2021, 127, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Lee, Y.Y.; Kim, T.H. A review on alkaline pretreatment technology for bioconversion of lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 199, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yat, S.C.; Berger, A.; Shonnard, D.R. Kinetic characterization for dilute sulfuric acid hydrolysis of timber varieties and switchgrass. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3855–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Gong, Z.; Wang, G.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, M. Alkaline organosolv pretreatment of corn stover for enhancing the enzymatic digestibility. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 265, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liu, C.; Chang, J.; Yin, Q.; Huang, W.; Liu, Y.; Dang, X.; Gao, T.; Lu, F. Effect of physicochemical pretreatments plus enzymatic hydrolysis on the composition and morphologic structure of corn straw. Renew. Energy 2019, 138, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusănescu, C.; Ciobanu, M.; Rusănescu, M.; Dinculoiu, R. Pretreatments applied to wheat straw to obtain bioethanol. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, B.; Qureshi, N.; Kennedy, G.; Cotta, M. Biological pretreatment of corn stover with white-rot fungus for improved enzymatic hydrolysis. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 109, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, R.; Satlewal, A.; Gaur, R.; Mathur, A.; Kumar, R.; Gupta, R.; Tuli, D. Pilot scale pretreatment of wheat straw and comparative evaluation of commercial enzyme preparations for biomass saccharification and fermentation. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 102, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, H.; Liu, G.; Gong, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, Y. Compound probiotics producing cellulase could replace cellulase preparations during solid-state fermentation of millet bran. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 385, 129457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilić, N.; Milić, M.; Beluhan, S.; Dimitrijević-Branković, S. Cellulases: From lignocellulosic biomass to improved production. Energies 2023, 16, 3598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walia, A.; Guleria, S.; Mehta, P.; Chauhan, A.; Parkash, J. Microbial xylanases and their industrial application in pulp and paper biobleaching: A review. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Pei, X.; Zhou, W.; Zhao, Y.; Gu, P.; Li, Y.; Gao, J. Research and application progress of microbial β-mannanases: A mini-review. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Shen, G.; Yuan, Y.; Yan, L.; Tang, H.; Wang, W. Isolation and characterization of a novel laccase for lignin degradation, LacZ1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 87, e0135521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Sun, Y.; Kang, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhang, H.; Cai, Y.; Zhu, W.; Yuan, X.; Cui, Z. An innovative strategy to enhance the ensiling quality and methane production of excessively wilted wheat straw: Using acetic acid or hetero-fermentative lactic acid bacterial community as additives. Waste Manag. 2022, 149, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntara, C.; Cherdthong, A.; Uriyapongson, S.; Wanapat, M.; Chanjula, P. Comparison effects of ruminal crabtree-negative yeasts and crabtree-positive yeasts for improving ensiled rice straw quality and ruminal digestion using in vitro gas production. J. Fungi 2020, 6, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Dong, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Bai, Y.; Jia, Y.; Shao, T. Ensiling as pretreatment of rice straw: The effect of hemicellulase and Lactobacillus plantarum on hemicellulose degradation and cellulose conversion. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 266, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; He, Y.; Gao, S.; Liao, Z.; Lai, T.; Zhou, H.; Chen, Q.; Li, L.; Gao, H.; Lu, W. The effect of a diet based on rice straw co-fermented with probiotics and enzymes versus a fresh corn Stover-based diet on the rumen bacterial community and metabolites of beef cattle. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Liu, C.; Li, X.; Chang, J.; Jin, S.; Yin, Q.; Zhu, Q. Effect of corn straw treated with Lactobacillus plantarum and cellulase on ruminal fermentation and microbiota of Hu sheep. Fermentation 2024, 10, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Desta, S.; Zhang, J.; Shao, T. Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and fibrolytic enzyme on the fermentation quality and in vitro digestibility of total mixed rations silage including rape straw. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 2087–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Oficial Methods of Analysis; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Arlington, TX, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Li, X.; Guan, H.; Huang, L.; Ma, X.; Peng, Y.; Li, Z.; Nie, G.; Zhou, J.; Yang, W.; et al. Microbial community and fermentation characteristic of Italian ryegrass silage prepared with corn stover and lactic acid bacteria. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 279, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, W.; Liu, S.; Xia, W.; Liu, Z.; Yi, L.; Jiang, Z. Synergistic effect of cellulase and xylanase during hydrolysis of natural lignocellulosic substrates. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broderick, G.; Kang, J. Automated simultaneous determination of ammonia and total amino acids in ruminal fluid and in vitro media. J. Dairy Sci. 1980, 63, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y. Rumen fermentation and microbial diversity of sheep fed a high-concentrate diet supplemented with hydroethanolic extract of walnut green husks. Anim. Biosci. 2024, 37, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhu, W. The Process and matters needing attention of in vitro fermentation of rumen microorganisms. In Microbiome Protocols Ebook; Bio-protocol LLC: Sunnyvale, CA, USA, 2021; Volume Bio-101, p. e2003663, (In Chinese). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yan, H.; Chen, J.; Duan, C.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, S. Correlation of ruminal fermentation parameters and rumen bacterial community by comparing those of the goat, sheep, and cow in vitro. Fermentation 2022, 8, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Research Methods of Ruminant Nutrition; Modern Education Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- GB 13078-2017; Hygienical Standard for Feeds. National Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Liu, X.; Wang, A.; Zhu, L.; Guo, W.; Guo, X.; Zhu, B.; Yang, M. Effect of additive cellulase on fermentation quality of whole-plant corn silage ensiling by a Bacillus inoculant and dynamic microbial community analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1330538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Wang, P.; Zhou, C.; Li, P.; Tang, H.; Zhang, J.; Cai, Y. Chemical composition and in vitro digestibility of corn stover during field exposure and their fermentation characteristics of silage prepared with microbial additives. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 32, 1854–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaeinasab, Y.; Rouzbehan, Y.; Fazaeli, H.; Rezaei, J. Chemical composition, silage fermentation characteristics, and in vitro ruminal fermentation parameters of potato-wheat straw silage treated with molasses and lactic acid bacteria and corn silage. J. Anim. Sci. 2015, 93, 4377–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhou, W.; Wang, C.; Yang, F.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Effect of cellulase and Lactobacillus casei on ensiling characteristics, chemical composition, antioxidant activity, and digestibility of mulberry leaf silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 9919–9931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Christensen, D.A.; McKinnon, J.J. In situ rumen degradation kinetics of timothy and alfalfa as affected by cultivar and stage of maturity. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2004, 84, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinritz, S.N.; Martens, S.D.; Avila, P.; Hoedtke, S. The effect of inoculant and sucrose addition on the silage quality of tropical forage legumes with varying ensilability. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2012, 174, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Fan, X.; Ma, Z.; Huang, X.; Tang, M.; Yin, F.; Zhao, Z.; Gan, S. Silage additives improve fermentation quality, aerobic stability and rumen degradation in mixed silage composed of amaranth and corn straw. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1189747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Schmidt, R.; McDonell, E.; Klingerman, C.; Kung, L. The effect of Lactobacillus buchneri 40788 or Lactobacillus plantarum MTD-1 on the fermentation and aerobic stability of corn silages ensiled at two dry matter contents. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 3907–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Fan, X.; Zhang, H.; Ai, F.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z. Pretreatment of corn stover by torrefaction for improving reducing sugar and biohydrogen production. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 351, 126905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Jiang, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Jing, Y.; Lu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, C.; Zhang, Q. Lignin removal, reducing sugar yield and photo-fermentative biohydrogen production capability of corn stover: Effects of different pretreatments. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 346, 126437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muck, R.; Nadeau, E.; McAllister, T.; Contreras-Govea, F.; Santos, M.; Kung, L. Silage review: Recent advances and future uses of silage additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 3980–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolosa, J.; Rodríguez-Carrasco, Y.; Ruiz, M.; Vila-Donat, P. Multi-mycotoxin occurrence in feed, metabolism and carry-over to animal-derived food products: A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 158, 112661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, W.; Chen, S.; Shao, T.; Tao, X.; Yuan, X. Effect of lactic acid bacteria on the fermentation quality and mycotoxins concentrations of corn silage infested with mycotoxigenic fungi. Toxins 2021, 13, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlberg, S.; Joutsjoki, V.; Korhonen, H. Potential of lactic acid bacteria in aflatoxin risk mitigation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 207, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froetschel, M.; Amos, H. Effects of dietary fiber and feeding frequency on ruminal fermentation, digesta water-holding capacity, and fractional turnover of contents. J. Anim. Sci. 1991, 69, 1312–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Wu, H.; Liu, S.; Chai, S.; Meng, Q.; Zhou, Z. Dynamic alterations in yak rumen bacteria community and metabolome characteristics in response to feed type. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, D.; Hendriks, W.; Xiong, B.; Pellikaan, W. Starch and cellulose degradation in the rumen and applications of metagenomics on ruminal microorganisms. Animals 2022, 12, 3020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Ma, Y.; Khan, M.; Xiao, J.; Alugongo, G.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Z. A combination of lactic acid bacteria and molasses improves fermentation quality, chemical composition, physicochemical structure, in vitro degradability and rumen microbiota colonization of rice straw. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 900764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Crop Stalks | Variety | Harvesting Date | Maturity Stage | DM (%) | ADF (%) | NDF (%) | CP (%) | Reducing Sugars (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn stover | XF806 | 2023.09 | Late collection period | 96.02 | 63.92 | 31.44 | 5.40 | 8.04 |
| Wheat straw | XM1807 | 2023.08 | Late collection period | 96.27 | 61.15 | 34.91 | 5.45 | 4.34 |
| Microorganisms and Enzymes | Groups | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | |
| C. utilis (%) | - | 5.0 | 15.0 | 25.0 | 5.0 | 15.0 | 25.0 |
| L. plantarum (%) | - | 5.0 | 15.0 | 25.0 | 5.0 | 15.0 | 25.0 |
| Cellulase (%) | - | 45.0 | 35.0 | 25.0 | - | - | - |
| Laccase (%) | - | 45.0 | 35.0 | 25.0 | 22.5 | 17.5 | 12.5 |
| β-glucanase (%) | - | - | - | - | 22.5 | 17.5 | 12.5 |
| Xylanase (%) | - | - | - | - | 22.5 | 17.5 | 12.5 |
| Mannanase (%) | - | - | - | - | 22.5 | 17.5 | 12.5 |
| Roughage | Items | C | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | SEM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn stover | OM (%) | 90.26 a | 89.92 ab | 89.93 ab | 89.04 bc | 88.22 c | 88.79 c | 88.69 c | 0.183 | <0.001 |
| CP (%) | 7.37 c | 7.75 bc | 7.85 bc | 8.24 ab | 8.09 ab | 8.27 ab | 8.48 a | 0.087 | <0.001 | |
| NDF (%) | 64.39 a | 55.00 bc | 57.44 b | 51.9 c | 53.73 c | 54.02 c | 52.56 c | 0.917 | <0.001 | |
| ADF (%) | 33.94 a | 30.89 b | 32.67 ab | 30.76 b | 29.99 b | 31.01 b | 34.17 a | 0.442 | 0.021 | |
| Wheat straw | OM (%) | 85.65 | 85.60 | 84.65 | 85.39 | 85.20 | 85.09 | 84.29 | 0.216 | 0.658 |
| CP (%) | 3.61 b | 6.62 a | 6.67 a | 6.74 a | 6.52 a | 6.61 a | 6.51 a | 0.242 | <0.001 | |
| NDF (%) | 70.00 a | 66.75 bc | 65.92 c | 66.05 c | 67.00 b | 66.46 bc | 62.16 d | 0.483 | <0.001 | |
| ADF (%) | 41.43 a | 37.78 c | 37.14 cd | 36.26 d | 37.54 c | 38.93 b | 32.48 e | 0.573 | <0.001 |
| Roughage | Items | C | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | SEM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn stover | pH | 4.89 | 4.50 | 4.42 | 4.58 | 4.73 | 4.68 | 4.29 | 0.057 | 0.060 |
| Reducing sugars (mg/g) | 17.50 b | 27.03 a | 13.35 bc | 12.71 bc | 12.42 bc | 9.38 c | 9.50 c | 1.408 | <0.001 | |
| Lactate (mM) | 4.14 b | 7.46 a | 6.18 ab | 8.59 a | 7.39 a | 7.18 a | 7.33 a | 0.386 | 0.041 | |
| Acetate (mM) | 8.64 | 8.42 | 7.70 | 8.55 | 7.63 | 7.64 | 8.10 | 0.342 | 0.977 | |
| Propionate (mM) | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | ND | - | - | |
| NH3-N (mM) | 2.61 c | 7.02 ab | 5.22 b | 9.28 a | 5.93 b | 6.36 b | 5.85 b | 0.484 | 0.002 | |
| Wheat straw | pH | 4.86 a | 4.27 cd | 4.35 c | 4.36 c | 4.61 b | 4.07 e | 4.22 d | 0.056 | <0.001 |
| Reducing sugars (mg/g) | 5.87 cd | 11.33 a | 8.50 b | 7.75 bc | 5.63 cd | 6.26 bc | 5.22 d | 0.502 | <0.001 | |
| Lactate (mM) | 5.28 cd | 8.23 ab | 7.80 ab | 9.32 a | 7.02 bc | 5.25 cd | 4.85 d | 0.401 | <0.001 | |
| Acetate (mM) | 6.87 | 9.82 | 6.41 | 6.94 | 6.17 | 4.71 | 6.65 | 0.467 | 0.136 | |
| Propionate (μM) | 91.70 | 21.20 | 11.30 | 12.00 | 4.80 | 20.30 | 41.50 | 0.012 | 0.604 | |
| NH3-N (mM) | 1.68 | 2.82 | 2.36 | 2.65 | 2.48 | 3.07 | 1.17 | 0.257 | 0.488 |
| Roughage | Mycotoxins | C | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | SEM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn stover | AFB1 (ug/kg) | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | 3.45 | - | - |
| ZON (ug/kg) | 47.37 b | 36.53 b | 32.62 b | 43.29 b | 39.63 b | 35.07 b | 151.84 a | 9.159 | <0.001 | |
| DON (ug/kg) | <100 | <100 | <100 | <100 | <100 | <100 | <100 | - | - | |
| Wheat straw | AFB1 (ug/kg) | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | <1 | - | - |
| ZON (ug/kg) | 39.48 a | 20.10 cd | 28.80 abcd | 33.66 ab | 17.53 d | 30.81 abc | 21.94 bcd | 2.043 | 0.011 | |
| DON (ug/kg) | <100 | <100 | <100 | <100 | <100 | <100 | <100 | - | - |
| Roughage | Parameters | C | T1 | T2 | T3 | T4 | T5 | T6 | SEM | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Corn stover | pH | 6.43 | 6.62 | 6.51 | 6.48 | 6.46 | 6.45 | 6.51 | 0.022 | 0.265 |
| DMD (%) | 76.76 | 73.07 | 72.95 | 71.72 | 72.61 | 72.01 | 74.15 | 0.557 | 0.227 | |
| NH3-N (mM) | 22.08 ab | 21.79 ab | 19.22 bc | 24.46 a | 20.45 b | 25.24 a | 16.43 c | 0.586 | <0.001 | |
| Protozoa (lg counts/mL) | 5.96 | 5.74 | 5.89 | 6.02 | 5.99 | 5.98 | 5.76 | 0.042 | 0.447 | |
| Acetate (mM) | 35.93 cd | 42.17 abc | 39.72 bc | 48.69 ab | 36.70 cd | 50.08 a | 29.09 d | 1.471 | <0.001 | |
| Propionate (mM) | 9.81 cd | 11.34 bc | 10.75 c | 13.44 ab | 10.10 cd | 13.79 a | 8.05 d | 0.375 | <0.001 | |
| Isobutyrate (mM) | 0.80 bc | 0.93 ab | 0.83 bc | 1.10 a | 0.81 bc | 1.09 a | 0.65 c | 0.031 | <0.001 | |
| Butyrate (mM) | 5.47 cd | 6.49 bc | 5.94 cd | 7.53 ab | 5.72 cd | 7.89 a | 4.76 d | 0.207 | <0.001 | |
| Isovalerate (mM) | 1.61 bc | 1.89 ab | 1.71 bc | 2.27 a | 1.67 bc | 2.30 a | 1.34 c | 0.067 | <0.001 | |
| Valerate (mM) | 0.69 bc | 0.80 b | 0.74 bc | 0.99 a | 0.72 bc | 1.01 a | 0.58 c | 0.030 | <0.001 | |
| TVFAs (mM) | 54.30 bc | 63.63 ab | 59.69 b | 74.01 a | 55.71 bc | 76.16 a | 44.47 c | 2.174 | <0.001 | |
| A/P | 3.65 | 3.70 | 3.70 | 3.62 | 3.57 | 3.62 | 3.60 | 0.020 | 0.540 | |
| Wheat straw | pH | 6.57 bc | 6.58 abc | 6.61 ab | 6.56 c | 6.58 bc | 6.62 a | 6.62 a | 0.005 | 0.002 |
| DMD (%) | 76.91 | 75.13 | 76.48 | 75.85 | 75.35 | 75.55 | 77.52 | 0.375 | 0.602 | |
| NH3-N (mM) | 9.47 cd | 11.76 a | 10.23 bc | 10.88 abc | 11.58 ab | 10.95 abc | 8.79 d | 0.20126 | <0.001 | |
| Protozoa (lg counts/mL) | 5.70 | 5.82 | 5.86 | 5.86 | 5.70 | 5.83 | 5.76 | 0.025 | 0.332 | |
| Acetate (mM) | 24.37 ab | 24.89 a | 20.54 bc | 25.27 a | 26.18 a | 23.86 ab | 17.37 c | 0.561 | <0.001 | |
| Propionate (mM) | 6.54 ab | 6.99 a | 5.65 bc | 7.17 a | 7.27 a | 6.64 ab | 4.84 c | 0.162 | <0.001 | |
| Isobutyrate (mM) | 0.40 ab | 0.41 ab | 0.35 b | 0.41 ab | 0.43 a | 0.39 ab | 0.28 c | 0.009 | <0.001 | |
| Butyrate (mM) | 2.46 ab | 0.73 a | 2.21 bc | 2.59 ab | 2.60 ab | 2.46 ab | 1.97 c | 0.053 | <0.001 | |
| Isovalerate (mM) | 0.55 a | 0.58 a | 0.49 a | 0.56 a | 0.59 a | 0.53 a | 0.39 b | 0.014 | <0.001 | |
| Valerate (mM) | 0.17 a | 0.20 a | 0.15 ab | 0.19 a | 0.19 a | 0.18 a | 0.11 b | 0.006 | <0.001 | |
| TVFAs (mM) | 34.49 ab | 35.81 a | 29.39 bc | 36.19 a | 37.26 a | 34.05 ab | 24.95 c | 0.800 | <0.001 | |
| A/P | 3.74 | 3.57 | 3.63 | 3.56 | 3.60 | 3.61 | 3.62 | 0.018 | 0.118 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, B.; Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Zhang, H.; Li, X.; Tian, C.; Chen, Y. Synergistic Effect of Microorganisms and Enzymes on Nutritional Value of Corn Stover and Wheat Straw. Fermentation 2025, 11, 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040210
Chen B, Liu J, Liu M, Zhang H, Li X, Tian C, Chen Y. Synergistic Effect of Microorganisms and Enzymes on Nutritional Value of Corn Stover and Wheat Straw. Fermentation. 2025; 11(4):210. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040210
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Binglong, Jiancheng Liu, Mengjian Liu, Huiling Zhang, Xuanyue Li, Congcong Tian, and Yong Chen. 2025. "Synergistic Effect of Microorganisms and Enzymes on Nutritional Value of Corn Stover and Wheat Straw" Fermentation 11, no. 4: 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040210
APA StyleChen, B., Liu, J., Liu, M., Zhang, H., Li, X., Tian, C., & Chen, Y. (2025). Synergistic Effect of Microorganisms and Enzymes on Nutritional Value of Corn Stover and Wheat Straw. Fermentation, 11(4), 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11040210





