High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals the Microbial Community Succession Process During the Fermentation of Traditional Daizhou Huangjiu
Abstract
1. Introduction
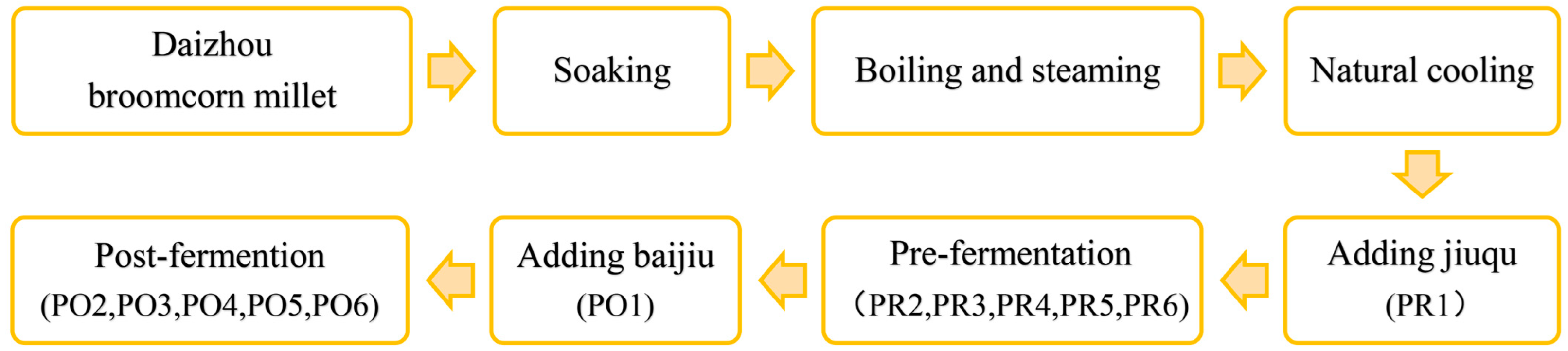
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. DNA Extraction
2.3. Amplicon Sequencing
2.4. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
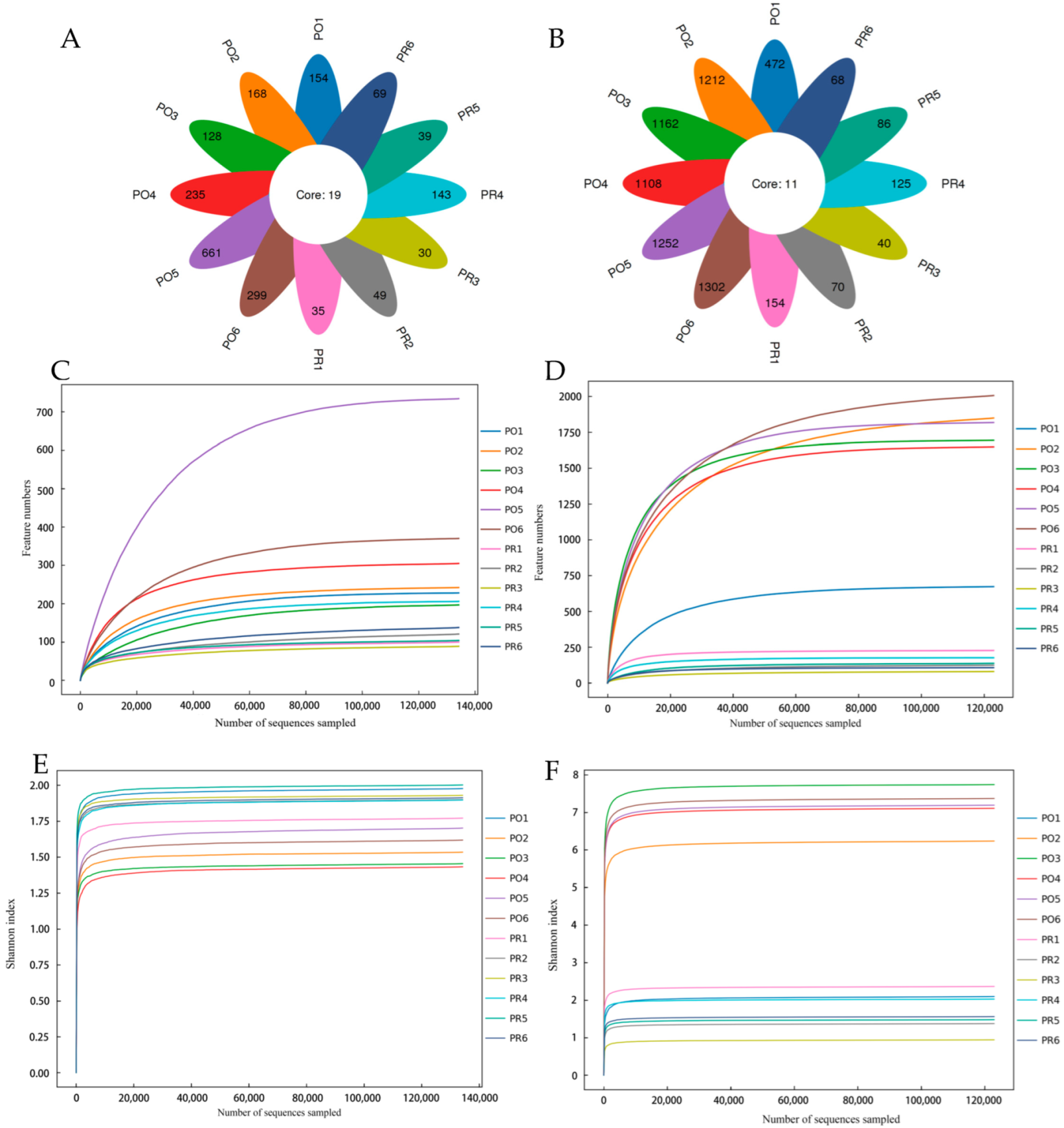
3.1. High-Throughput Sequencing Results
3.2. Alpha Diversity Analysis
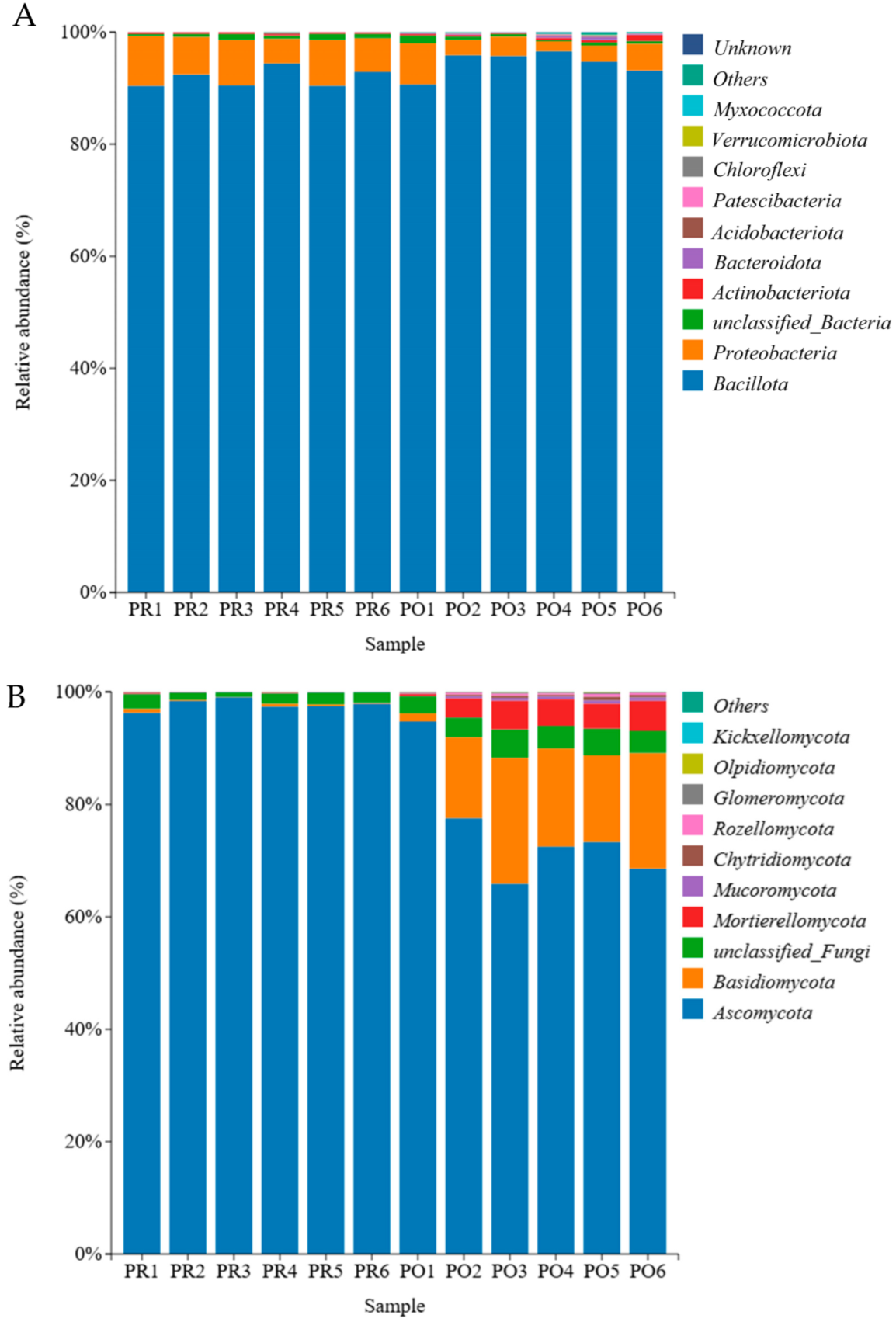
3.3. Microbial Community Analysis at the Phylum Level
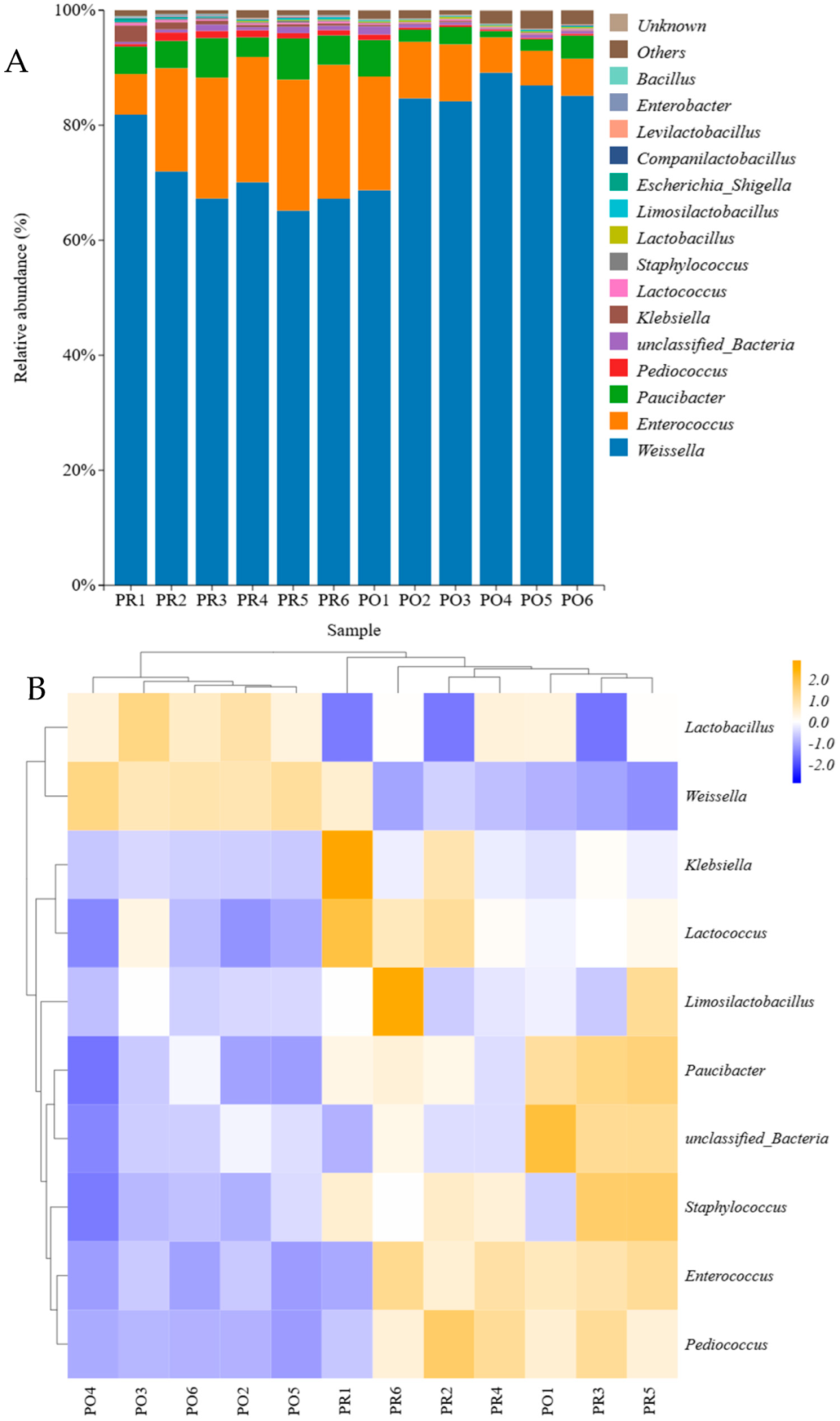
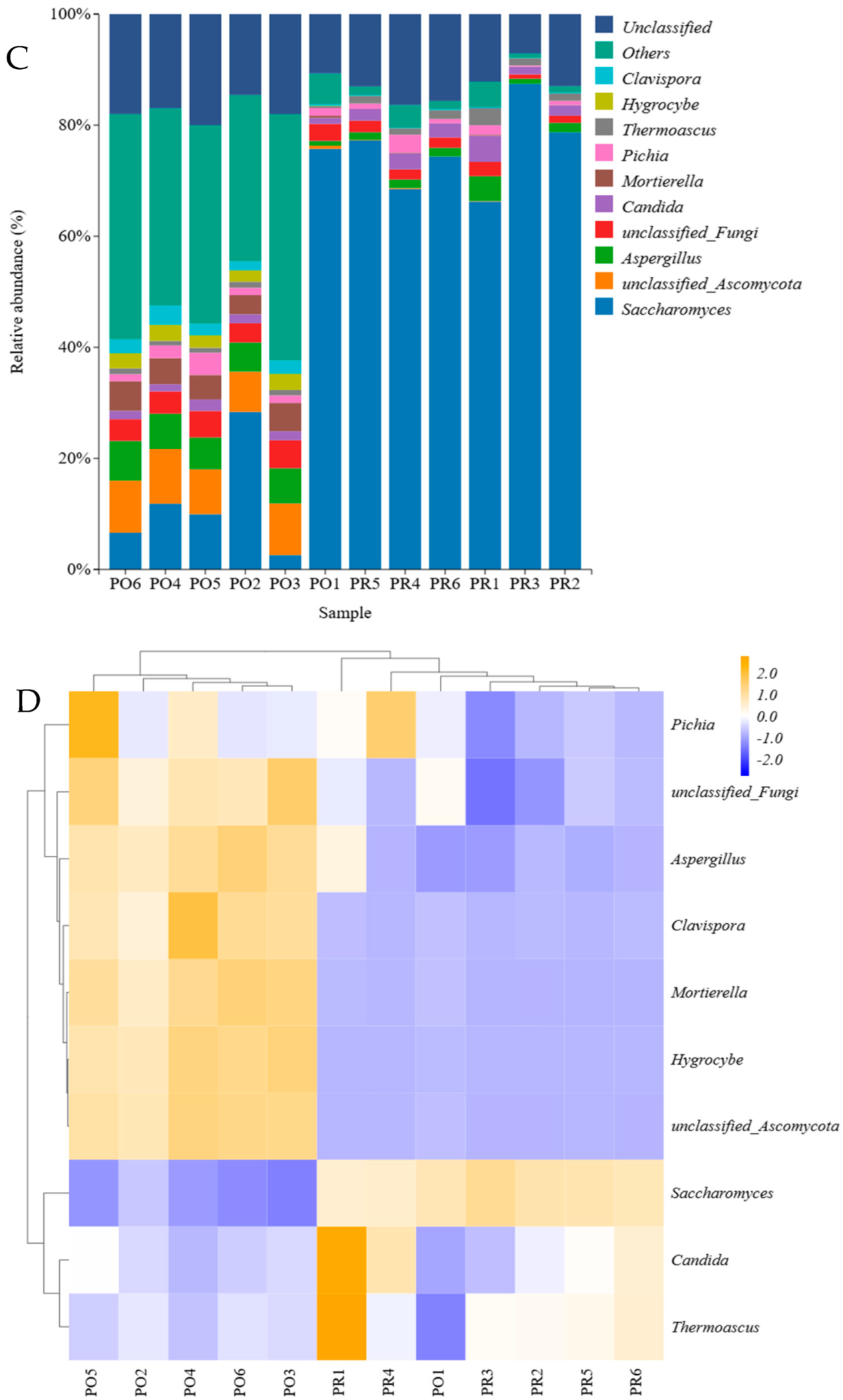
3.4. Microbial Community Analysis at the Genus Level
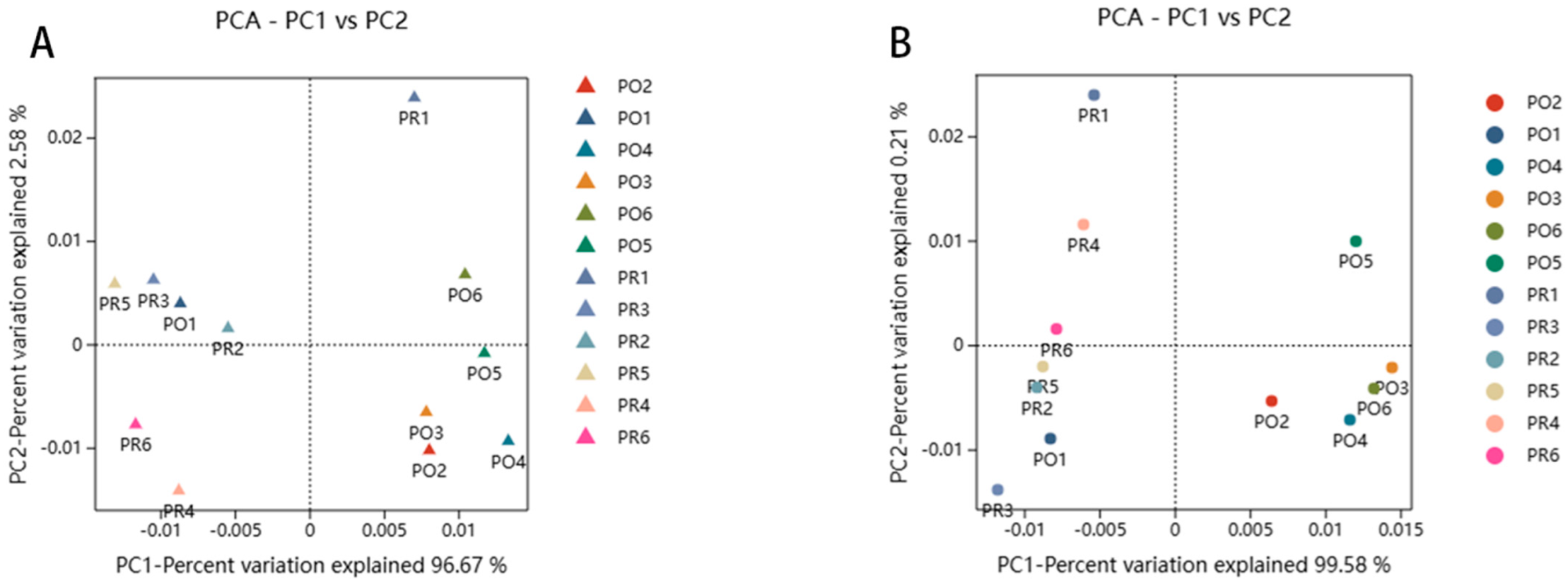
3.5. Beta Diversity Analysis
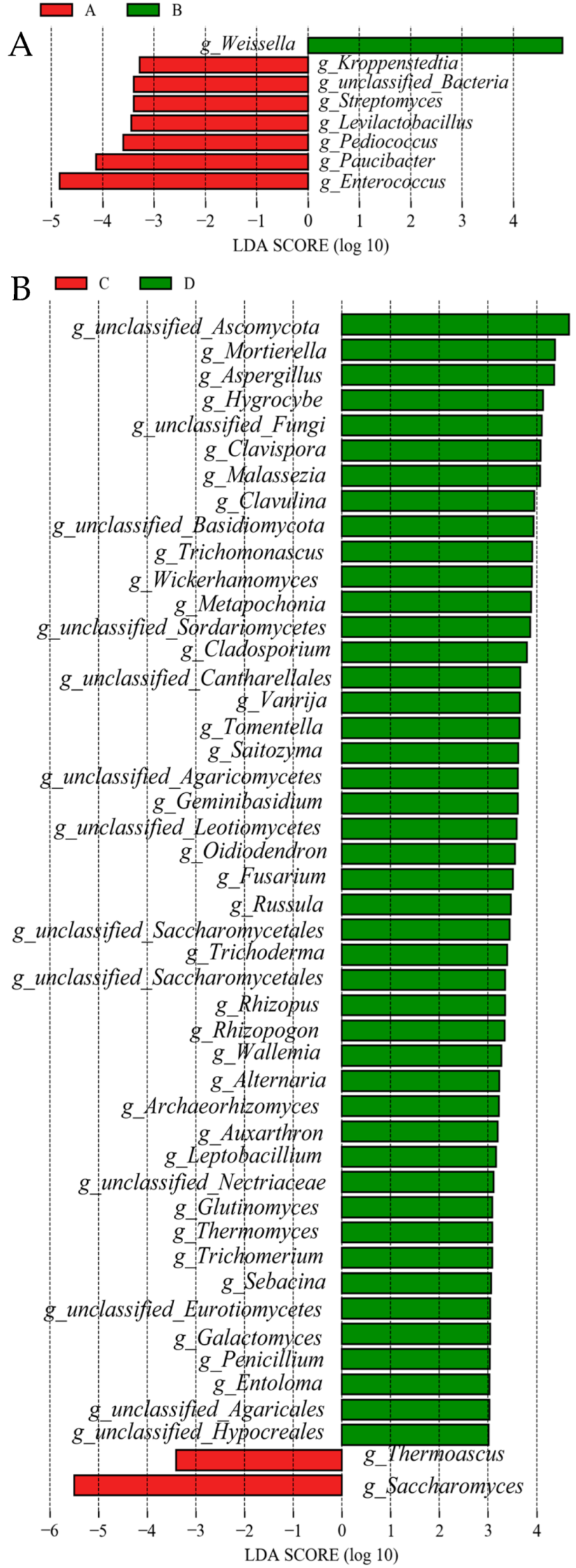
3.6. Significant Differences Between Groups of Analysis
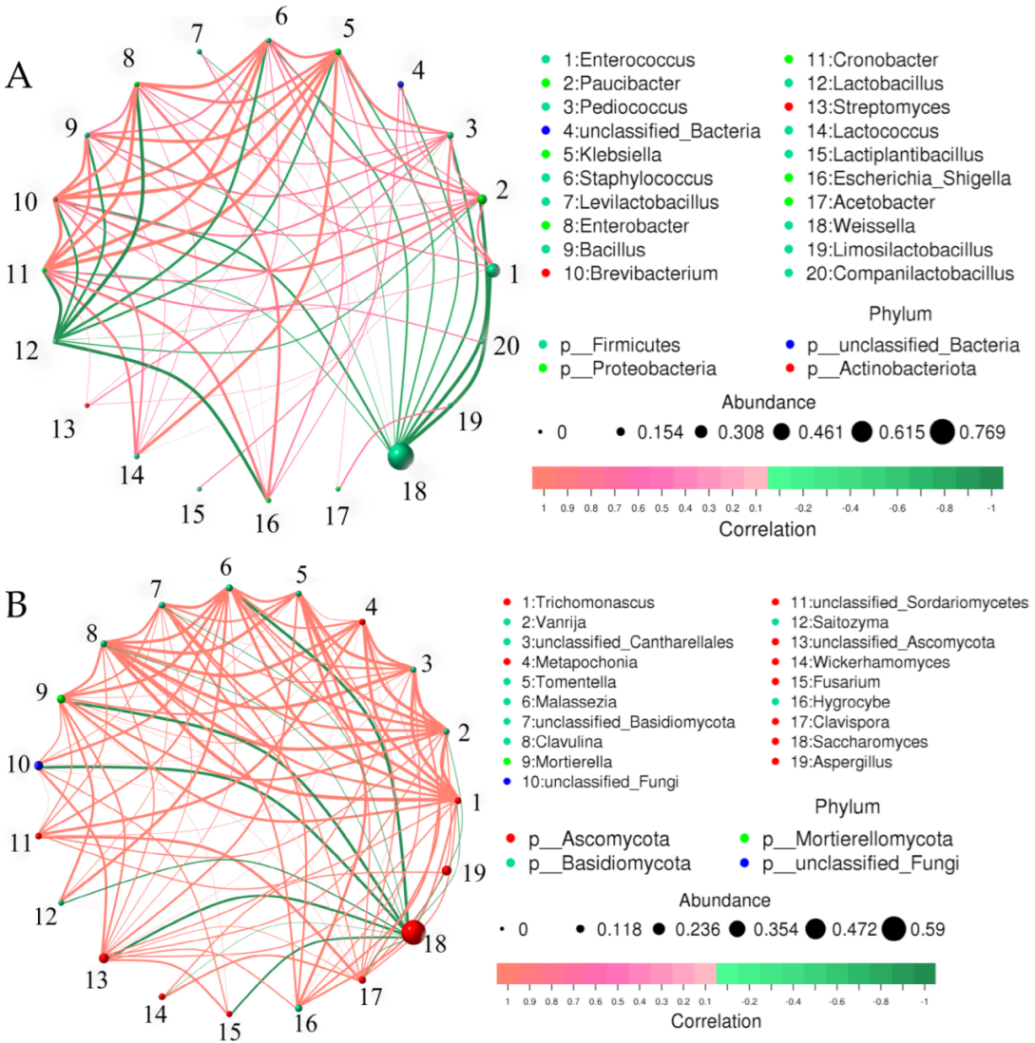
3.7. Correlation Analysis at Genus Level
3.8. Bacteria Gene Function Prediction
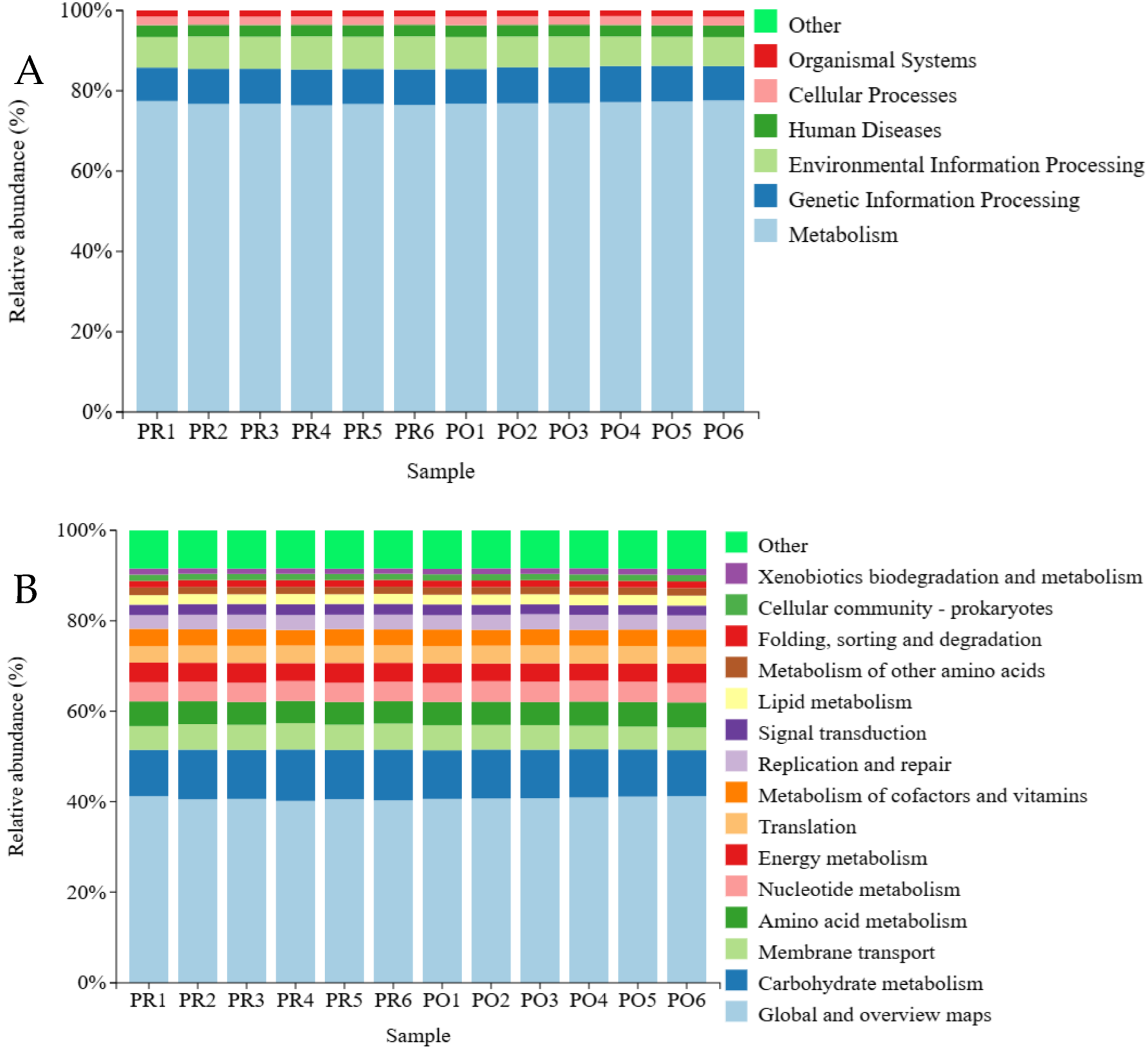
3.8.1. KEGG Metabolic Pathway Analysis
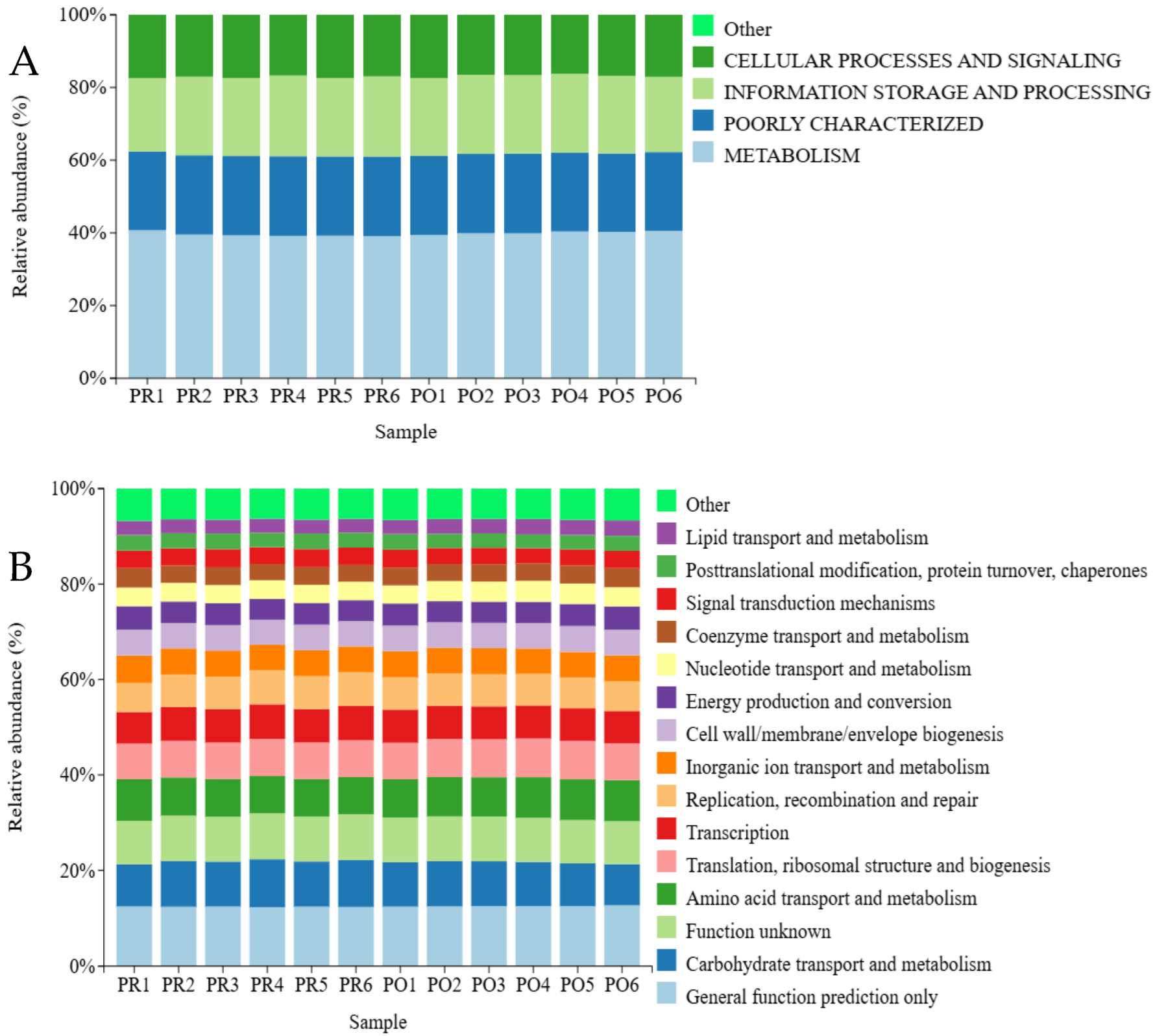
3.8.2. COG Functional Annotation Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zheng, C.Q.; Chen, C.; Jiang, Y.J.; Zhang, L.; Xie, G.F. Studies on Yellow Rice Wine Technology Using Mixed Fermentation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Hansenula anomala. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 24, 146–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.W. Determination of 9 Nutrient Elements and 5 Pollution Elements in Millet Huangjiu by ICP-MS. Liquor-Mak. Sci. Technol. 2023, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Zheng, H.; Qiu, Z.; Lin, Z.; Peng, Q.; Dula Bealu, G.; Elsheery, N.I.; Lu, Y.; Shen, C.; Fu, J.; et al. Study on relationship between bacterial diversity and quality of Huangjiu (Chinese Rice Wine) fermentation. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 9, 3885–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Zheng, H.; Meng, K.; Yu, H.; Xie, G.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, J.; Xu, Z.; Lin, Z.; et al. Quantitative study on core bacteria producing flavor substances in Huangjiu (Chinese yellow rice wine). LWT 2022, 168, 113900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wu, H.J.; Wang, J.X.; Ren, Q. Microbiota Composition during Fermentation of Broomcorn Millet Huangjiu and Their Effects on Flavor Quality. Foods 2023, 12, 2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, S.; Huang, M.Q.; Wang, J.X.; Liu, B.; Ren, Q. Microbial Community Dynamics and the Correlation between Specific Bacterial Strains and Higher Alcohols Production in Tartary Buckwheat Huangjiu Fermentation. Foods 2023, 12, 2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, M.; Zhan, P.; Wang, P.; He, W.Y.; Tian, H.L. A quality comparison for Xiecun Huangjiu with different aging stages based on chemical profile, aroma composition and microbial succession. Food Chem. X 2024, 21, 101132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.Y.; Cen, D.Y.; Liang, L.Y.; Bai, Y.Z.; Liu, M.C.; Wang, C.Y. Correlation analysis between volatile flavor compounds and microbial community of Nanyang red-millet Huangjiu during fermentation process. China Brew. 2023, 42, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Tan, Y.; Wang, H.; Yang, F.; Chen, L.; Hao, F.; Lv, X.; Du, H.; Xu, Y. Effect of Pichia on shaping the fermentation microbial community of sauce-flavor Baijiu. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 336, 108898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.D.; Liu, Y.L.; Xi, X.L.; Chen, Z.Z.; Ma, Y.L.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, S. Microbial Diversity in Six Kinds of Huangjiu Koji Based on High-Throughput Sequencing Techniques. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2022, 43, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.X.; Li, T.; Zou, G.; Wei, Y.J.; Qu, L.B. Advancements and Future Directions in Yellow Rice Wine Production Research. Fermentation 2024, 10, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Dai, Y.J. Analysis of microbial community diversity in Danyang Huangjiu Jiuqu based on Illumina MiSeq high-throughput sequencing technique. China Brew. 2024, 43, 141–145. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Li, Q.; Guo, W.; Chen, C.; Ai, L.; Tian, H. Dynamic analysis of volatile metabolites and microbial community and their correlations during the fermentation process of traditional Huangjiu (Chinese rice wine) produced around Winter Solstice. Food Chem. X 2023, 18, 100620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Chen, H.; Sun, L.; Zhang, W.; Lu, X.; Li, Z.; Xu, J.; Ren, Q. The changes of microbial diversity and flavor compounds during the fermentation of millet Huangjiu, a traditional Chinese beverage. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e262353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhang, C.H.; Liao, H.; Luo, Y.C.; Huang, X.L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Xia, X.L. Integrative metagenomics, volatilomics and chemometrics for deciphering the microbial structure and core metabolic network during Chinese rice wine (Huangjiu) fermentation in different regions. Food Microbiol. 2024, 122, 104569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.F.; Wang, L.; Gao, Q.K.; Yu, W.J.; Hong, X.T.; Zhao, L.Y.; Zou, H.J. Microbial community structure in fermentation process of Shaoxing rice wine by Illumina-based metagenomic sequencing. J. Sci. Food. Agric. 2013, 93, 3121–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.P.; Yu, J.J.; Jia, F.C.; Ma, W.R.; Jin, Y.L.; Zhu, Z.J.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, H.P.; Zhang, Y.H.; Xue, J. Macrogenomics-based analysis of the relationship between microbial diversity and flavour formation during the fermentation of Tibetan highland barley wine. Food Ferment. Ind. 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Yang, X.; Zhou, G.Y.; Guo, Y.Q.; Zhu, L.; Zheng, Y. High-throughput Sequencing Analysis of Microbial Community Diversity in Xiangzao of Made from Huangjiu (Yellow Rice Wine) Vinasse during Spontaneous Fermentation. Food Sci. 2023, 44, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Zheng, H.; Li, S.; Meng, K.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, L.; Xu, Z.; Xie, G.; et al. Analysis on driving factors of microbial community succession in Jiuyao of Shaoxing Huangjiu (Chinese yellow rice wine). Food Res. Int. 2023, 172, 113144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Su, W.; Mu, Y.C.; Jiang, L.; Mu, Y. Correlations between microbiota with physicochemical properties and volatile flavor components in black glutinous rice wine fermentation. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Q.; Sun, L.P.; Sun, Z.B.; Liu, Q.S.; Lu, X.; Li, Z.P.; Xu, J.L. Bacterial succession and the dynamics of flavor compounds in the Huangjiu fermented from corn. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Li, W.; Yuan, Y.; Liang, Z.; Yan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ni, L.; Lv, X. Metagenomic Insights into the Regulatory Effects of Microbial Community on the Formation of Biogenic Amines and Volatile Flavor Components during the Brewing of Hongqu Rice Wine. Foods 2023, 12, 3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.H.; Feng, Z.T.; He, P.; Liu, P.P.; Jian, Y.; Xu, Y.T. Microbial Community Structure and Diversity of Highland Barley Koji in Tibet. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 24, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.J.; Peng, P.; Yu, L.; Wan, B.; Liang, X.T.; Liu, P.L. Metagenomic analysis reveals the correlations between microbial communities and flavor compounds during the brewing of traditional Fangxian huangjiu. Food Biosci. 2024, 58, 103816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, D.J.; Chen, X.G.; Xiang, H.Y.; Ouyang, L.; Yang, B. Isolation, Identification and Characterization of a Microcystin-degrading Bacterium Paucibacter sp. Strain CH. Environ. Sci. 2014, 35, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.P. Culturing the Baijiu Microorganism from Fermentation Vinasse and Pit Mud with Culturomics and Amplicon-Based Metagenomic Approaches. Master’s Thesis, Beijing Technology and Business University, Beijing, China, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, A.; Malfeito-Ferreira, M.; Loureiro, V. The microbial ecology of wine grape berries. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2012, 153, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Hao, L.F.; Lin, Q.; Bao, Y.Y. Effects of Different Fermentation Methods on the Quality and Microbial Diversity of Passion Fruit Wine. Fermentation 2023, 9, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.L.; Zhang, X.R.; Yan, Y.H.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.Y.; Xu, H. Relationship between flavor compounds and changes of microbial community in the solid fermented vinegar. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2022, 86, 1581–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Z.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, W.G. Correlation between changes in flavor compounds and microbial community ecological succession in the liquid fermentation of rice wine. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 40, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Cai, G.L.; Wu, D.H.; Lu, J. Correlation between the bacterial community succession and purine compound changes during Huangjiu fermentation. Food Microbiol. 2024, 121, 104522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Yan, X.; Li, S.; Ni, L.; Zhang, H.; Ni, B.; Ai, L. Insights into whereby raw wheat Qu contributes to the flavor quality of Huangjiu during brewing. LWT 2023, 178, 114619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Hu, W.; Tao, L.; Liu, H.; Xie, C.; Bai, W.; Ai, L. Soaking induced discrepancies in oenological properties, flavor profiles, microbial community and sensory characteristic of Huangjiu (Chinese rice wine). LWT 2020, 139, 110575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, N. Diversity Analysis of Baijiu-Making Microorganisms. Liquor-Mak. Sci. Technol. 2022, 3, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.P.; Chen, Q.L.; Zou, H.J.; Yu, Y.J.; Zhou, Z.L.; Mao, J.; Zhang, S. A metagenomic analysis of the relationship between microorganisms and flavor development in Shaoxing mechanized huangjiu fermentation mashes. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 303, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Chen, L.Q.; Xu, Y. Yeast community associated with the solid state fermentation of traditional Chinese Maotai-flavor liquor. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2013, 166, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Chen, L.Q. Diversity of yeast species during fermentative process contributing to Chinese Maotai-flavour liquor making. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 55, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Hu, W.Y.; Xia, Y.J.; Mu, Z.Y.; Tao, L.R.; Song, X. Flavor Formation in Chinese Rice Wine (Huangjiu): Impacts of the Flavor-Active Microorganisms, Raw Materials, and Fermentation Technology. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 580247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wu, Q.; Xu, Y. Filamentous fungal diversity and community structure associated with the solid state fermentation of Chinese Maotai-flavor liquor. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 179, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diganta, N.; Nitesh, B.; Ashis, B.; Takashi, O.; Hideto, T. Community structure and metabolic potentials of the traditional rice beer starter ‘emao’. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.G.; Chen, Y.Q.; Wu, G.Q.; Yang, G.H.; Zhang, X.K.; Huang, P.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, X.L. Analysis of Yeast Strains in Fermented Grains during Stacking Fermentation of Jiang-flavor Liquor. Liquor-Mak. Sci. Technol. 2013, 6, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Sun, L.; Xing, X.; Wu, H.; Lu, X.; Zhang, W.; Xu, J.; Ren, Q. Microbial succession and exploration of higher alcohols-producing core bacteria in northern Huangjiu fermentation. Amb Express 2022, 12, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.C.; Su, H.; Lin, X.Z.; He, Z.G.; Li, W.X.; Deng, D.L. Microbial communities and amino acids during the fermentation of Wuyi Hong Qu Huangjiu. LWT 2020, 130, 109743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.W. Study on Microbial Community and Functional Genes Diversity in Starters of Huangjiu Based on Metagenomic Approach. Master’s Thesis, Shanghai Institute of Technology, Shanghai, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
| Sample | Alcohol Content (% vol) | Sample | Alcohol Content (% vol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PR1 | 3.00 ± 0.10 | PO1 | 23.30 ± 0.20 |
| PR2 | 7.80 ± 0.10 | PO2 | 23.10 ± 0.20 |
| PR3 | 9.80 ± 0.20 | PO3 | 22.40 ± 0.10 |
| PR4 | 10.80 ± 0.10 | PO4 | 22.80 ± 0.10 |
| PR5 | 10.80 ± 0.10 | PO5 | 23.05 ± 0.05 |
| PR6 | 11.00 ± 0.10 | PO6 | 22.60 ± 0.10 |
| Type | Amplification Region | Primer Name | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|---|
| bacteria | bacteria 16SV3 + V4 | 338F | 5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCA-3′ |
| 806R | 5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′ | ||
| fungi | fungi ITS1 | ITS1F | 5′-CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA-3′ |
| ITS2 | 5′-GCTGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC-3′ |
| Sample Number | OTUs | ACE Index | Chao1 Index | Simpson Index | Shannon Index | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria | Fungi | Bacteria | Fungi | Bacteria | Fungi | Bacteria | Fungi | Bacteria | Fungi | |
| PR1 | 100 | 227 | 102 | 227 | 107 | 227 | 0.4495 | 0.5494 | 1.7714 | 2.3647 |
| PR2 | 121 | 124 | 121 | 125 | 121 | 125 | 0.5396 | 0.3722 | 1.9007 | 1.3745 |
| PR3 | 89 | 80 | 90 | 81 | 99 | 80.6 | 0.5739 | 0.2399 | 1.9300 | 0.9415 |
| PR4 | 206 | 176 | 206 | 176 | 206 | 176 | 0.5461 | 0.5058 | 1.8970 | 2.0268 |
| PR5 | 104 | 137 | 105 | 138 | 107 | 142 | 0.5923 | 0.3939 | 2.0016 | 1.4793 |
| PR6 | 138 | 107 | 141 | 107 | 142 | 107 | 0.5686 | 0.4316 | 1.9128 | 1.5614 |
| PO1 | 228 | 673 | 228 | 674 | 228 | 674 | 0.5630 | 0.4238 | 1.9757 | 2.0964 |
| PO2 | 242 | 1850 | 242 | 1885 | 242 | 1877 | 0.3976 | 0.9030 | 1.5339 | 6.2342 |
| PO3 | 197 | 1694 | 197 | 1695 | 199 | 1697 | 0.3963 | 0.9749 | 1.4520 | 7.7386 |
| PO4 | 305 | 1649 | 305 | 1651 | 306 | 1650 | 0.3373 | 0.9625 | 1.4293 | 7.1064 |
| PO5 | 734 | 1818 | 734 | 1820 | 735 | 1821 | 0.3722 | 0.9592 | 1.7018 | 7.1900 |
| PO6 | 370 | 2007 | 370 | 2038 | 370 | 2029 | 0.3883 | 0.9703 | 1.6185 | 7.3695 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, T.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Gao, G. High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals the Microbial Community Succession Process During the Fermentation of Traditional Daizhou Huangjiu. Fermentation 2025, 11, 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11030138
Cui L, Zhu J, Zhang T, Li Q, Li Y, Gao G. High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals the Microbial Community Succession Process During the Fermentation of Traditional Daizhou Huangjiu. Fermentation. 2025; 11(3):138. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11030138
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Linhua, Jiaying Zhu, Ting Zhang, Qi Li, Yunlong Li, and Guoqiang Gao. 2025. "High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals the Microbial Community Succession Process During the Fermentation of Traditional Daizhou Huangjiu" Fermentation 11, no. 3: 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11030138
APA StyleCui, L., Zhu, J., Zhang, T., Li, Q., Li, Y., & Gao, G. (2025). High-Throughput Sequencing Reveals the Microbial Community Succession Process During the Fermentation of Traditional Daizhou Huangjiu. Fermentation, 11(3), 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11030138





