The Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide on Biogas and Methane Produced from Batch Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Spent Coffee Grounds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Characteristics
2.2. Oxidative Pretreatment
2.3. Biochemical Methane Production (BMP) Tests
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.5. Kinetic Study
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide Pretreatment on the Chemical Composition of SCG
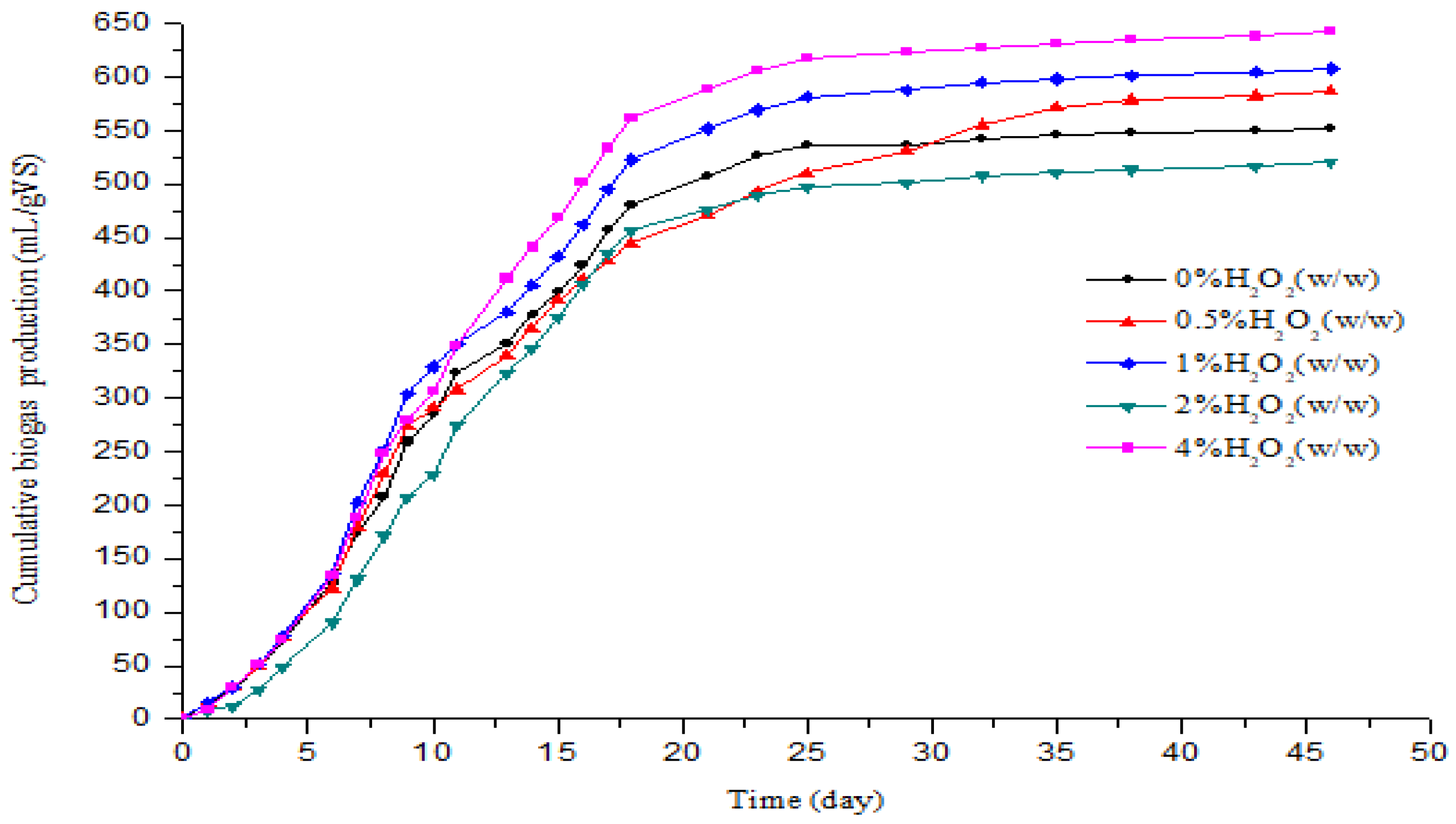
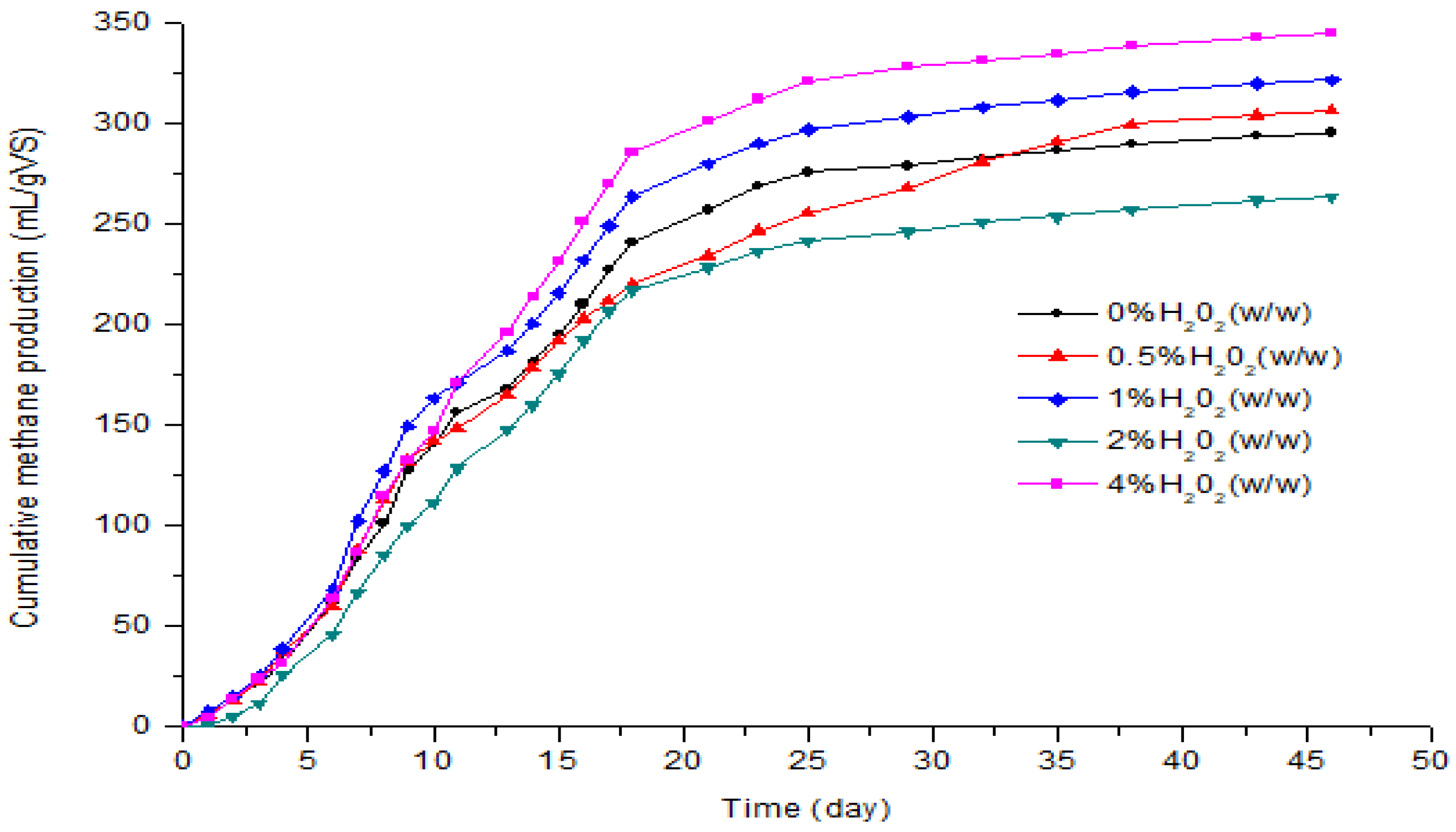
3.2. Effect of H2O2 Pretreatment on the Biogas and Methane Production
3.3. Kinetic Study Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ravindran, R.; Jaiswal, S.; Abu-Ghannam, N.; Jaiswal, A.K. Evaluation of ultrasound assisted potassium permanganate pre-treatment of spent coffee waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 224, 680–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosek, R.; Tun, M.M.; Juchelkova, D. Energy Utilization of Spent Coffee Grounds in the Form of Pellets. Energies 2020, 13, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangri, S.; Derbal, K.; Policastro, G.; Panico, A.; Contestabile, P.; Pontoni, L.; Race, M.; Fabbricino, M. Combining pretreatments and co-fermentation as successful approach to improve biohydrogen production from dairy cow manure. Environ. Res. 2024, 246, 118118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchareb, E.M.; Kerroum, D.; Bezirhan Arikan, E.; Isik, Z.; Dizge, N. Production of bio-hydrogen from bulgur processing industry wastewater. Energy Sources Part Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codignole Luz, F.; Volpe, M.; Fiori, L.; Manni, A.; Cordiner, S.; Mulone, V.; Rocco, V. Spent coffee enhanced biomethane potential via an integrated hydrothermal carbonization-anaerobic digestion process. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 256, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olatunji, K.O.; Ahmed, N.A.; Ogunkunle, O. Optimization of biogas yield from lignocellulosic materials with different pretreatment methods: A review. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2021, 14, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata, T.M.; Martins, A.A.; Caetano, N.S. Bio-refinery approach for spent coffee grounds valorization. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 247, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomfim, A.S.C.D.; De Oliveira, D.M.; Walling, E.; Babin, A.; Hersant, G.; Vaneeckhaute, C.; Dumont, M.-J.; Rodrigue, D. Spent Coffee Grounds Characterization and Reuse in Composting and Soil Amendment. Waste 2022, 1, 2–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazzino, F.; Folino, A.; Mauriello, F.; Pedullà, A.; Calabrò, P.S. Biofuel production from fruit and vegetable market waste and mature landfill leachate by an active filter-anaerobic digestion integrated system. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2021, 12, 100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battista, F.; Barampouti, E.M.; Mai, S.; Bolzonella, D.; Malamis, D.; Moustakas, K.; Loizidou, M. Added-value molecules recovery and biofuels production from spent coffee grounds. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 131, 110007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongcumpou, C.; Usapein, P.; Tuntiwiwattanapun, N. Complete utilization of wet spent coffee grounds waste as a novel feedstock for antioxidant, biodiesel, and bio-char production. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 138, 111484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passadis, K.; Fragoulis, V.; Stoumpou, V.; Novakovic, J.; Barampouti, E.M.; Mai, S.; Moustakas, K.; Malamis, D.; Loizidou, M. Study of Valorisation Routes of Spent Coffee Grounds. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 5295–5306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grammatikos, C.; Stoumpou, V.; Barampouti, E.M.; Mai, S.; Malamis, D.; Loizidou, M. Emerging synergies on the co-treatment of spent coffee grounds and brewer’s spent grains for ethanol production. Waste Biomass Valorization 2022, 13, 877–891. [Google Scholar]
- Vítěz, T.; Koutný, T.; Šotnar, M.; Chovanec, J. On the Spent Coffee Grounds Biogas Production. Acta Univ. Agric. Silvic. Mendel. Brun. 2016, 64, 1279–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luz, F.C.; Cordiner, S.; Manni, A.; Mulone, V.; Rocco, V. Anaerobic digestion of coffee grounds soluble fraction at laboratory scale: Evaluation of the biomethane potential. Appl. Energy 2017, 207, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ning, Z.; Khalid, H.; Zhang, R.; Liu, G.; Chen, C. Enhancement of methane production from Cotton Stalk using different pretreatment techniques. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Baek, G.; Kim, J.; Lee, C. Energy production from different organic wastes by anaerobic co-digestion: Maximizing methane yield versus maximizing synergistic effect. Renew. Energy 2019, 136, 683–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okolie, J.A.; Tabat, M.E.; Gunes, B.; Epelle, E.I.; Mukherjee, A.; Nanda, S.; Dalai, A.K. A techno-economic assessment of biomethane and bioethanol production from crude glycerol through integrated hydrothermal gasification, syngas fermentation and biomethanation. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2021, 12, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awedem Wobiwo, F.; Ercoli Balbuena, J.-L.; Nicolay, T.; Larondelle, Y.; Gerin, P.A. Valorization of spent coffee ground with wheat or miscanthus straw: Yield improvement by the combined conversion to mushrooms and biomethane. Energy Sustain. Dev. 2018, 45, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballesteros, L.F.; Teixeira, J.A.; Mussatto, S.I. Chemical, Functional, and Structural Properties of Spent Coffee Grounds and Coffee Silverskin. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 3493–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katukuri, N.R.; Fu, S.; He, S.; Xu, X.; Yuan, X.; Yang, Z.; Guo, R.-B. Enhanced methane production of Miscanthus floridulus by hydrogen peroxide pretreatment. Fuel 2017, 199, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-H.; Ho, K.-Y.; Lee, K.-T.; Ding, L.; Andrew Lin, K.-Y.; Rajendran, S.; Singh, Y.; Chang, J.-S. Dual pretreatment of mixing H2O2 followed by torrefaction to upgrade spent coffee grounds for fuel production and upgrade level identification of H2O2 pretreatment. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girotto, F.; Pivato, A.; Cossu, R.; Nkeng, G.E.; Lavagnolo, M.C. The broad spectrum of possibilities for spent coffee grounds valorisation. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2018, 20, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwietering, M.H.; Jongenburger, I.; Rombouts, F.M.; Van ’T Riet, K. Modeling of the Bacterial Growth Curve. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1990, 56, 1875–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjørve, K.M.C.; Tjørve, E. The use of Gompertz models in growth analyses, and new Gompertz-model approach: An addition to the Unified-Richards family. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Qiao, W.; Wang, X.; Takayanagi, K.; Shofie, M.; Li, Y.-Y. Kinetic characterization of thermophilic and mesophilic anaerobic digestion for coffee grounds and waste activated sludge. Waste Manag. 2015, 36, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donoso-Bravo, A.; Pérez-Elvira, S.I.; Fdz-Polanco, F. Application of simplified models for anaerobic biodegradability tests. Evaluation of pre-treatment processes. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 160, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, N.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Gao, M.; Yu, N.; Liu, Y. Performance assessment on anaerobic co-digestion of Cannabis ruderalis and blackwater: Ultrasonic pretreatment and kinetic analysis. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 169, 105506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Baek, G.; Lee, C. Anaerobic co-digestion of spent coffee grounds with different waste feedstocks for biogas production. Waste Manag. 2017, 60, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labatut, R.A.; Pronto, J.L. Chapter 4—Sustainable Waste-to-Energy Technologies: Anaerobic Digestion. In Sustainable Food Waste-To-energy Systems; Trabold, T.A., Babbitt, C.W., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 47–67. ISBN 978-0-12-811157-4. [Google Scholar]
- Ouahabi, Y.R.; Bensadok, K.; Ouahabi, A. Optimization of the Biomethane Production Process by Anaerobic Digestion of Wheat Straw Using Chemical Pretreatments Coupled with Ultrasonic Disintegration. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, E.; Atabani, A.E.; Badruddin, I.A. Valorization of spent coffee grounds for biogas production: A circular bioeconomy approach for a biorefinery. Fuel 2022, 328, 125296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, A.; Papirio, S.; Esposito, G.; Lens, P.N.L. Ultrasounds application for nut and coffee wastes valorisation via biomolecules solubilisation and methane production. Waste Manag. 2022, 150, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girotto, F.; Lavagnolo, M.C.; Pivato, A. Spent Coffee Grounds Alkaline Pre-treatment as Biorefinery Option to Enhance their Anaerobic Digestion Yield. Waste Biomass Valorization 2018, 9, 2565–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, F.; Ünşar, E.K.; Perendeci, N.A.; Sahinkaya, E. Energy generation from multifarious wastes of alcohol distillery raki production process: Kinetic modeling of methane production. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xiao, B.; Zhang, K.; Chen, H.; Guo, X. Effects of mixing ratios on anaerobic co-digestion of swine manure and rice straw: Methane production and kinetics. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2021, 13, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainardis, M.; Flaibani, S.; Trigatti, M.; Goi, D. Techno-economic feasibility of anaerobic digestion of cheese whey in small Italian dairies and effect of ultrasound pre-treatment on methane yield. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 246, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, S.; Sharma, H.B.; Dubey, B.K. Anaerobic co-digestion of food waste with pretreated yard waste: A comparative study of methane production, kinetic modeling and energy balance. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 243, 118480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abudi, Z.N.; Hu, Z.; Abood, A.R. Anaerobic co-digestion of mango leaves and pig manure: Performance assessment and kinetic analysis. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2022, 12, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Parameter | Unit | SCG | Inoculum |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total solids (TS) | g/L | 899.856 ± 7.41 | 37.536 ± 1.365 |
| Total volatile solids (TVS) | g/L | 889.833 ± 7.562 | 18.5363 ± 0.353 |
| TVS/TS | % | 98.886 | 49.383 |
| pH | / | 5.68 ± 0.025 | 6.7 ± 0.175 |
| Total chemical oxygen demand (COD) | go2/L | 44.792 ± 4.886 | 14.461 ± 0.121 |
| Soluble chemical oxygen demand (SCOD) | go2/L | 4.322 ± 0.141 | 0.373 ± 0.005 |
| Total nitrogen Kjeldahl (TKN) | g/kg | 2.216 ± 0.126 | 2.282 ± 0.042 |
| ammonium nitrogen (N-NH4+) | mg/L | 1.002 ± 0.026 | 0.043 ± 0.001 |
| Protein | g/kg | 13.850 ± 0.602 | 14.263 ± 0.262 |
| Total alkalinity | mgCaCO3/L | 327.61 ± 8.452 | 1178.31 ± 81.691 |
| Parameters | Spent Coffee Grounds’s Pretreatments | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [H2O2] (% w/w) | 0% | 0.5% | 1% | 2% | 4% |
| Total solids (g/L) | 22.06 ± 0.15 | 18.81 ± 1.57 | 16.47 ± 0.94 | 21.06 ± 2.97 | 17.54 ± 0.27 |
| Total volatile solids (TVS) (g/L) | 21.33 ± 0.16 | 18.17 ± 1.70 | 16.04 ± 0.91 | 20.95 ± 2.77 | 17.43 ± 0.34 |
| % volatile solids (%) | 96.73 | 96.52 | 97.41 | 98.84 | 99.39 |
| Soluble chemical oxygen demand (SCOD) (go2/L) | 13.59 ± 0.65 | 89.14 ± 4.94 | 94.43 ± 3.41 | 109.63 ± 0.89 | 110.48 ± 6.99 |
| Total nitrogen Kjeldahl (TKN) (mg/g) | 2.22 ± 0.13 | 2.02 ± 0.10 | 2.15 ± 0.28 | 2.08 ± 0.22 | 2.03 ± 0.16 |
| Ammonium nitrogen (N-NH4+) (mg/L) | 1.00 ± 0.03 | 1.16 ± 0.02 | 1.17 ± 0.03 | 1.31 ± 0.02 | 1.1 ± 0.02 |
| Protein (mg/g) | 13.85 ± 0.60 | 12.59 ± 0.89 | 13.41 ± 1.74 | 13 ± 1.38 | 12.69 ± 1.00 |
| Total alkalinity (mgCaCO3/L) | 327.61 ± 8.45 | 354.76 ± 12.05 | 318.56 ± 10.08 | 257.02 ± 11.82 | 264.26 ± 9.97 |
| Total soluble sugars mg/L | 0.05 ± 0.00 | 0.40 ± 0.00 | 0.39 ± 0.00 | 0.42 ± 0.00 | 0.41 ± 0.00 |
| Model | Parameter | Treatment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0% H2O2 (w/w) | 0.5% H2O2 (w/w) | 1% H2O2 (w/w) | 2% H2O2 (w/w) | 4% H2O2 (w/w) | ||
| A (mL/g VS) | 292.990 ± 2.747 | 297.174 ± 4.970 | 317.332 ± 3.658 | 259.455 ± 2.040 | 342.510 ± 2.220 | |
| µm (mL/g VS/day) | 17.221 ± 0.493 | 14.779 ± 0.658 | 18.667 ± 0.661 | 16.252 ± 0.408 | 21.065 ± 0.430 | |
| Modified Gompertez model | λ (day) | 2.315 ± 0.238 | 1.359 ± 0.423 | 1.906 ± 0.295 | 3.144 ± 0.197 | 2.958 ± 0.162 |
| R2 | 0.996 | 0.991 | 0.994 | 0.998 | 0.998 | |
| RMSE | 6.223 | 10.016 | 8.393 | 4.728 | 5.105 | |
| A (mL/g VS) | 286.451 ± 4.236 | 288.052 ± 6.631 | 310.473 ± 5.325 | 253.589 ± 3.280 | 334.740 ± 3.797 | |
| µm (mL/g VS/day) | 17.331 ± 0.884 | 14.861 ± 1.076 | 18.594 ± 1.107 | 16.611 ± 0.767 | 21.485 ± 0.862 | |
| Logistic Function model | λ (day) | 2.8478 ± 0.456 | 1.860 ± 0.744 | 2.351 ± 0.539 | 3.770 ± 0.383 | 3.572 ± 0.339 |
| R2 | 0.989 | 0.975 | 0.984 | 0.992 | 0.994 | |
| RMSE | 11.003 | 15.926 | 13.917 | 8.702 | 10.016 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sayoud, S.; Derbal, K.; Panico, A.; Pontoni, L.; Fabbricino, M.; Pirozzi, F.; Benalia, A. The Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide on Biogas and Methane Produced from Batch Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Spent Coffee Grounds. Fermentation 2025, 11, 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11020060
Sayoud S, Derbal K, Panico A, Pontoni L, Fabbricino M, Pirozzi F, Benalia A. The Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide on Biogas and Methane Produced from Batch Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Spent Coffee Grounds. Fermentation. 2025; 11(2):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11020060
Chicago/Turabian StyleSayoud, Siham, Kerroum Derbal, Antonio Panico, Ludovico Pontoni, Massimiliano Fabbricino, Francesco Pirozzi, and Abderrezzaq Benalia. 2025. "The Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide on Biogas and Methane Produced from Batch Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Spent Coffee Grounds" Fermentation 11, no. 2: 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11020060
APA StyleSayoud, S., Derbal, K., Panico, A., Pontoni, L., Fabbricino, M., Pirozzi, F., & Benalia, A. (2025). The Effect of Hydrogen Peroxide on Biogas and Methane Produced from Batch Mesophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Spent Coffee Grounds. Fermentation, 11(2), 60. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11020060









