Adding Digestive Enzymes to Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Cattle Manure and Industrial Corn Grain Waste †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Inoculum and Feedstock
2.3. Semi-Continuous Biodigester Description
2.4. Treatment Descriptions
| Treatments | Substrate Composition | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CM (g) | CG (g) | Water (g) | Enzyme (mL) | |
| CM | 163 | - | 837 | - |
| CM + E | 163 | - | 837 | 1 |
| CM + CG | 114 | 12 | 874 | - |
| CM + CG + E | 114 | 12 | 874 | 1 |
2.5. Laboratory Analyses
2.6. Biogas Monitoring
2.7. Statistical Analysis
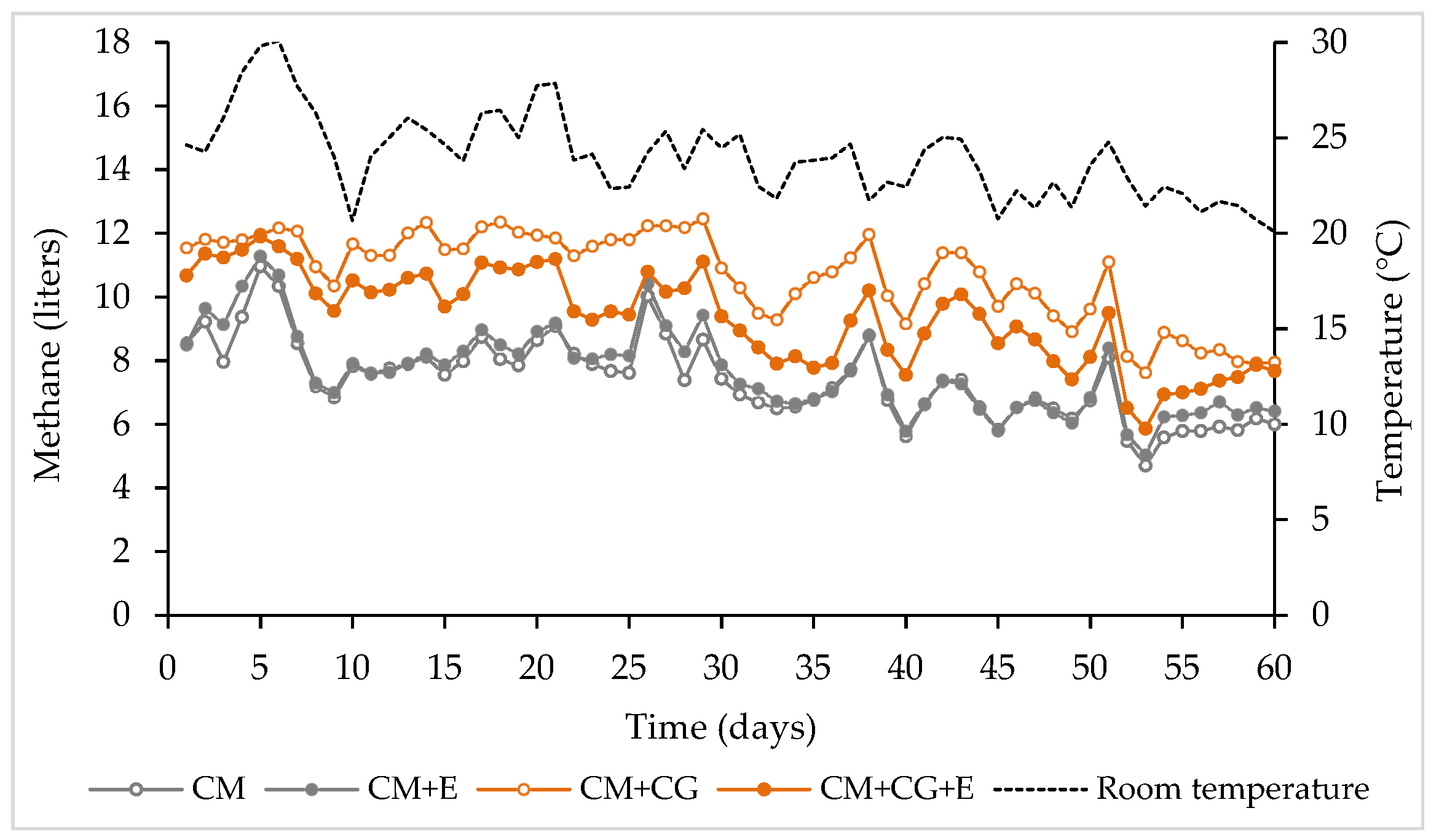
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mendes, F.B.; Volpi, M.P.C.; da Silva Clementino, W.; Albarracin, L.T.; de Souza Moraes, B. An Overview of the Integrated Biogas Production through Agro-Industrial and Livestock Residues in the Brazilian São Paulo State. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Energy Environ. 2023, 12, e494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Mahur, B.K.; Izrayeel, A.M.D.; Ahuja, A.; Rastogi, V.K. Biomass Conversion of Agricultural Waste Residues for Different Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 73622–73647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, L.J.M. Dia Nacional Do Milho—A Importância Do Milho Para o Agronegócio Brasileiro. Embrapa Milho e Sorgo. Available online: https://www.embrapa.br/busca-de-noticias/-/noticia/89583335/artigo-dia-nacional-do-milho---a-importancia-do-milho-para-o-agronegocio-brasileiro (accessed on 18 May 2024).
- Allesina, G.; Pedrazzi, S.; Guidetti, L.; Tartarini, P. Modeling of Coupling Gasification and Anaerobic Digestion Processes for Maize Bioenergy Conversion. Biomass Bioenergy 2015, 81, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, F.B.; Lima, B.V.d.M.; Volpi, M.P.C.; Albarracin, L.T.; Lamparelli, R.A.C.; Moraes, B.d.S. Brazilian Agricultural and Livestock Substrates Used in Co-Digestion for Energy Purposes: Composition Analysis and Valuation Aspects. Biofuels Bioprod. Biorefining 2023, 17, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, D.J.C.; Machado, A.V.; Vilarinho, M.C.L.G. Availability and Suitability of Agroindustrial Residues as Feedstock for Cellulose-Based Materials: Brazil Case Study. Waste Biomass Valorization 2019, 10, 2863–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Khoshnevisan, B.; Duan, N. Meta-Analysis of Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Livestock Manure in Last Decade: Identification of Synergistic Effect and Optimization Synergy Range. Appl. Energy 2021, 282, 116128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnane, I.; Taoumi, H.; Elouahabi, K.; Lahrech, K.; Oulmekki, A. Valorization of Crop Residues and Animal Wastes: Anaerobic Co-Digestion Technology. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Xing, W.; Li, R.; Yang, T.; Yao, N.; Lv, D. Links between Synergistic Effects and Microbial Community Characteristics of Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste, Cattle Manure and Corn Straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 329, 124919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, R.; Jo, S.; Lee, J.; Khanthong, K.; Jang, H.; Park, J. A Review on the Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Livestock Manures in the Context of Sustainable Waste Management. Energies 2024, 17, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tufaner, F.; Avşar, Y. Effects of Co-Substrate on Biogas Production from Cattle Manure: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 13, 2303–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhao, H.; Yu, H.; Chen, D.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Piao, R.; Cui, Z. Evaluation of Biogas Production Performance and Archaeal Microbial Dynamics of Corn Straw during Anaerobic Co-Digestion with Cattle Manure Liquid. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varol, A.; Ugurlu, A. Comparative Evaluation of Biogas Production from Dairy Manure and Co-Digestion with Maize Silage by CSTR and New Anaerobic Hybrid Reactor. Eng. Life Sci. 2017, 17, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Kong, T.; Xing, W.; Li, R.; Yang, T.; Yao, N.; Lv, D. Links between Carbon/Nitrogen Ratio, Synergy and Microbial Characteristics of Long-Term Semi-Continuous Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Food Waste, Cattle Manure and Corn Straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 343, 126094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Güiza, M.S.; Vila, J.; Mata-Alvarez, J.; Chimenos, J.M.; Astals, S. The Role of Additives on Anaerobic Digestion: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 58, 1486–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Z.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Cai, Y.; Ying, H. A Comprehensive Review of the Strategies to Improve Anaerobic Digestion: Their Mechanism and Digestion Performance. Methane 2024, 3, 227–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brémond, U.; de Buyer, R.; Steyer, J.P.; Bernet, N.; Carrere, H. Biological Pretreatments of Biomass for Improving Biogas Production: An Overview from Lab Scale to Full-Scale. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 90, 583–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroyen, M.; Vervaeren, H.; Van Hulle, S.W.H.; Raes, K. Impact of Enzymatic Pretreatment on Corn Stover Degradation and Biogas Production. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 173, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, S.; Li, Z.; Men, Y.; Wu, J. Impacts of Cellulase and Amylase on Enzymatic Hydrolysis and Methane Production in the Anaerobic Digestion of Corn Straw. Sustainability 2020, 12, 5453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Saino, M.; Bai, X. Study on the Bio-Methane Yield and Microbial Community Structure in Enzyme Enhanced Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Cow Manure and Corn Straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weide, T.; Baquero, C.D.; Schomaker, M.; Brügging, E.; Wetter, C. Effects of Enzyme Addition on Biogas and Methane Yields in the Batch Anaerobic Digestion of Agricultural Waste (Silage, Straw, and Animal Manure). Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 132, 105442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamine, L.A.; Passini, R.; Sousa, J.A.S.; Fernandes, A.; de Moraes, M.J. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Cattle Manure and Brewer’s Residual Yeast: Process Stability and Methane and Hydrogen Sulfide Production. Fermentation 2023, 9, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, A.C.d.; Steinmetz, R.L.R.; Kunz, A. Os Biodigestores. In Fundamentos da Digestão Anaeróbia, Purificação do Biogás, Uso e Tratamento do Digestato; Kunz, A., Steinmetz, R.L.R., Amaral, A.C.d., Eds.; Sbera, Embrapa Suínos e Aves: Concórdia, Brazil, 2022; pp. 43–70. [Google Scholar]
- IAL. Métodos Físico-Químicos Para Análise de Alimentos; Instituto Adolfo Lutz: São Paulo, Brazil, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Methods for Examinations of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Water Works Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Carmo, D.L.d.; Silva, C.A. Métodos de Quantificação de Carbono e Matéria Orgânica Em Resíduos Orgânicos. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Do Solo 2012, 36, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IAL. Métodos Químicos e Físicos Para Análises de Alimentos; Instituto Adolfo Lutz: São Paulo, Brazil, 1985; Volume 121. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, D. Sisvar: A Computer Statistical Analysis System. Ciênc. Agrotecnol. 2014, 35, 1039–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernicharo, C.A.d.L. Anaerobic Reactors: Biological Wastewater Treatment Series, 1st ed.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2007; Volume 4, ISBN 9781843391647. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, G.; Ndegwa, P.; Harrison, J.H.; Chen, Y. Methane Yields during Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Animal Manure with Other Feedstocks: A Meta-Analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eliasson, K.A.; Singh, A.; Isaksson, S.; Schnürer, A. Co-Substrate Composition is Critical for Enrichment of Functional Key Species and for Process Efficiency during Biogas Production from Cattle Manure. Microb. Biotechnol. 2023, 16, 350–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, A.; Montoro, S.B.; Akamine, L.A.; Branco, P.M.P.; Sousa, J.A.S.; Lucas Júnior, J.d. Viabilidade Técnica e Econômica de Aditivos in Situ Na Digestão Anaeróbia de Dejetos de Bovinos. Rev. Ibero-Am. Ciênc. Ambient. 2021, 12, 530–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deublein, D.; Steinhauser, A. Gas Preparation. In Biogas from Waste and Renewable Resources; Deublein, D., Steinhauser, A., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008; pp. 333–355. ISBN 978-3-527-31841-4. [Google Scholar]
- Zarkadas, I.S.; Sofikiti, A.S.; Voudrias, E.A.; Pilidis, G.A. Thermophilic Anaerobic Digestion of Pasteurised Food Wastes and Dairy Cattle Manure in Batch and Large Volume Laboratory Digesters: Focussing on Mixing Ratios. Renew. Energy 2015, 80, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Khalid, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Liu, G.; Chen, C.; Thorin, E. Methane Production through Anaerobic Digestion: Participation and Digestion Characteristics of Cellulose, Hemicellulose and Lignin. Appl. Energy 2018, 226, 1219–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharathiraja, B.; Sudharsanaa, T.; Bharghavi, A.; Jayamuthunagai, J.; Praveenkumar, R. Biohydrogen and Biogas—An Overview on Feedstocks and Enhancement Process. Fuel 2016, 185, 810–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyi-Loh, C.E.; Lues, R. Anaerobic Digestion of Lignocellulosic Biomass: Substrate Characteristics (Challenge) and Innovation. Fermentation 2023, 9, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, L.; Kretzschmar, J.; Pröter, J.; Liebetrau, J.; Nelles, M.; Scholwin, F. Does the Addition of Proteases Affect the Biogas Yield from Organic Material in Anaerobic Digestion? Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 203, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, A.C.d.; Steinmetz, R.L.R.; Kunz, A. O Processo de Biodigestão. In Fundamentos da Digestão Anaeróbia, Purificação do Biogás, Uso e Tratamento do Digestato; Kunz, A., Steinmetz, R.L.R., Amaral, A.C.d., Eds.; Sbera, Embrapa Suínos e Aves: Concórdia, Brazil, 2022; pp. 15–28. ISBN 978-65-88155-02-8. [Google Scholar]
- Akhiar, A.; Battimelli, A.; Torrijos, M.; Carrere, H. Comprehensive Characterization of the Liquid Fraction of Digestates from Full-Scale Anaerobic Co-Digestion. Waste Manag. 2017, 59, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Bi, G.; Liu, X.; Yu, Q.; Li, D.; Yuan, H.; Chen, Y.; Xie, J. Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Sugarcane Leaves, Cow Dung and Food Waste: Focus on Methane Yield and Synergistic Effects. Fermentation 2022, 8, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Component | Unit | Fresh Cattle Manure | Corn Grains |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | pH unit | 7.41 | 5.75 |
| Total solids (TS) | % (NM) | 18.35 | 75.23 |
| Volatile solids | % of the TS | 79.43 | 93.97 |
| Ash | % of the TS | 20.57 | 6.03 |
| Total organic carbon | % of the TS | 44.13 | 52.20 |
| Total Kjeldahl nitrogen | % of the TS | 3.10 | 2.05 |
| C/N | - | 14.23 | 25.46 |
| Crude Protein | % of the TS | 15.00 | 20.00 |
| Crude fiber | % of the TS | 23.70 | 9.30 |
| Neutral detergent fiber | % of the TS | 56.40 | 71.20 |
| Acid detergent fiber | % of the TS | 35.40 | 22.40 |
| Hemicellulose | % of the TS | 21.00 | 48.80 |
| Non-structural carbohydrates | % of the TS | 9.70 | 0.90 |
| EE | % of the TS | 1.50 | 1.30 |
| Parameters | Treatments | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CM | CM + E | CM + CG | CM + CG + E | |||
| Total solids | g L−1 | Influ. | 30.51 Ab | 29.76 Bb | 30.38 Ab | 32.25 Aa |
| Efflu. | 13.93 Ab | 13.32 Bb | 13.78 Ab | 16.09 Aa | ||
| Volatile solids | g L−1 | Influ. | 22.76 Ab | 22.30 Bb | 22.98 Ab | 24.82 Aa |
| Efflu. | 6.74 Ab | 7.49 Bb | 7.20 Ab | 9.11 Aa | ||
| VS/TS | - | Influ. | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.76 | 0.77 |
| Efflu. | 0.48 | 0.56 | 0.52 | 0.57 | ||
| C/N ratio | - | Influ. | 13.40 | 13.40 | 16.01 | 16.01 |
| Efflu. | 8.65 | 10.43 | 9.35 | 11.29 | ||
| Nitrogen Kjeldahl total | % of the TS | Influ. | 3.10 | 3.10 | 2.79 | 2.79 |
| Efflu. | 3.10 | 3.00 | 3.10 | 2.80 | ||
| Total organic carbon | % of the TS | Influ. | 41.55 | 41.55 | 44.68 | 44.68 |
| Efflu. | 26.80 | 31.30 | 29.00 | 31.60 | ||
| % | Red. | 35.50 | 24.67 | 35.09 | 29.27 | |
| Crude protein | % of the TS | Influ. | 20.00 | 20.00 | 19.35 | 19.35 |
| Efflu. | 20.00 | 19.70 | 20.00 | 17.50 | ||
| % | Red. | - | 1.50 | - | 9.56 | |
| Crude fiber | % of the TS | Influ. | 10.90 | 10.90 | 12.55 | 12.55 |
| Efflu. | 4.60 | 8.40 | 6.40 | 4.20 | ||
| % | Red. | 57.80 | 22.94 | 49.00 | 66.53 | |
| Neutral detergent fiber | % of the TS | Influ. | 38.70 | 38.70 | 47.15 | 47.15 |
| Efflu. | 28.40 | 27.20 | 26.60 | 24.80 | ||
| % | Red. | 26.61 | 29.72 | 43.59 | 47.41 | |
| Acid detergent fiber | % of the TS | Influ. | 22.40 | 22.40 | 22.54 | 22.54 |
| Efflu. | 24.80 | 20.00 | 15.20 | 21.00 | ||
| % | Red. | - | 10.71 | 32.57 | 6.84 | |
| Hemicellulose | % of the TS | Influ. | 16.30 | 16.30 | 24.61 | 24.61 |
| Efflu. | 3.60 | 7.20 | 11.40 | 3.80 | ||
| % | Red. | 77.91 | 55.83 | 53.68 | 84.56 | |
| Non-structural carbohydrates | % of the TS | Influ. | 16.40 | 16.40 | 11.85 | 11.85 |
| Efflu. | 10.60 | 9.70 | 7.60 | 12.70 | ||
| % | Red. | 35.37 | 40.85 | 35.84 | - | |
| Ether extract | % of the TS | Influ. | 1.35 | 1.35 | 1.25 | 1.25 |
| Efflu. | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.70 | 1.00 | ||
| % | Red. | 25.93 | 25.93 | - | 20.00 | |
| Substrate | pH | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influent | Effluent | |||
| Without enzyme | With enzyme | Without enzyme | With enzyme | |
| CM | 7.30 | 7.11 | 7.52 | 7.45 |
| CM + CG | 7.42 | 7.13 | 7.56 | 7.51 |
| Substrate | Partial alkalinity (mg CaCO3 L−1) | |||
| Influent | Effluent | |||
| Without enzyme | With enzyme | Without enzyme | With enzyme | |
| CM | 1585.0 Aa | 1860.0 Aa | 3537.5 Ab | 4337.5 Aa |
| CM + CG | 1380.0 Aa | 1435.0 Ba | 3455.0 Aa | 3477.5 Ba |
| CV (%) | 13.24 | 5.10 | ||
| Intermediate alkalinity (mg CaCO3 L−1) | ||||
| CM | 1830.0 Aa | 1830.0 Aa | 485.0 Ab | 777.5 Aa |
| CM + CG | 1785.0 Aa | 1850.0 Aa | 485.0 Aa | 477.5 Ba |
| CV (%) | 12.54 | 14.89 | ||
| AI/AP | ||||
| CM | 1.15 | 0.98 | 0.14 | 0.18 |
| CM + CG | 1.29 | 1.29 | 0.14 | 0.14 |
| CV (%) | 10.14 | 5.13 | ||
| Total alkalinity (mg CaCO3 L−1) | ||||
| CM | 3415.0 Ab | 3690.0 Aa | 4022.5 Ab | 5115.0 Aa |
| CM + CG | 3165.0 Ba | 3285.0 Ba | 3940.0 Aa | 3955.0 Ba |
| CV (%) | 2.68 | 4.05 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cintra, L.M.; Passini, R.; Akamine, L.A.; de Sousa, K.D.; Capuchinho, F.F.; de Oliveira, S.B.; Duarte, S.R.R. Adding Digestive Enzymes to Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Cattle Manure and Industrial Corn Grain Waste. Fermentation 2025, 11, 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11120696
Cintra LM, Passini R, Akamine LA, de Sousa KD, Capuchinho FF, de Oliveira SB, Duarte SRR. Adding Digestive Enzymes to Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Cattle Manure and Industrial Corn Grain Waste. Fermentation. 2025; 11(12):696. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11120696
Chicago/Turabian StyleCintra, Laís Medeiros, Roberta Passini, Luana Alves Akamine, Kedinna Dias de Sousa, Frank Freire Capuchinho, Sérgio Botelho de Oliveira, and Silvia Robles Reis Duarte. 2025. "Adding Digestive Enzymes to Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Cattle Manure and Industrial Corn Grain Waste" Fermentation 11, no. 12: 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11120696
APA StyleCintra, L. M., Passini, R., Akamine, L. A., de Sousa, K. D., Capuchinho, F. F., de Oliveira, S. B., & Duarte, S. R. R. (2025). Adding Digestive Enzymes to Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Cattle Manure and Industrial Corn Grain Waste. Fermentation, 11(12), 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11120696






