The Effects of Essential Oils from Coriander Seed, Tarragon and Orange Peel on Lipid Production by Yarrowia lipolytica Strains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material
2.2. The Extraction of Essential Oils and the Composition of Growth Medium
2.3. The Determination of Biomass
2.4. The Determination of Lipid Production and Lipid Yield
2.5. The Determination of Fatty Acid Composition
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Donot, F.; Fontana, A.; Baccou, J.C.; Strub, C.; Schorr-Galindo, S. Single cell oils (SCOs) from oleaginous yeasts and moulds: Production and genetics. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 68, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koreti, D.; Kosre, A.; Jadhav, S.K.; Chandrawanshi, N.K. A comprehensive review on oleaginous bacteria: An alternative source for biodiesel production. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2022, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevenieau, F.; Nicaud, J.M. Microorganisms as sources of oils. OCL 2013, 20, D603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laribi, A.; Zieniuk, B.; Bouchedja, D.N.; Hafid, K.; Elmechta, L.; Becila, S. Valorization of olive mill wastewater via Yarrowia lipolytica: Sustainable production of high-value metabolites and biocompounds—A Review. Fermentation 2025, 11, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saygün, A.; Şahin-Yeşilçubuk, N.; Aran, N. Effects of different oil sources and residues on biomass and metabolite production by Yarrowia lipolytica YB 423-12. JACS 2014, 91, 1521–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, X.; Han, Y.; Li, Z.; Lu, X.; Shi, H.; Zhang, C.; Wong, A.; Yu, A. Sustainable biosynthesis of squalene from waste cooking oil by the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica. Metab. Eng. Commun. 2024, 18, e00240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayın, B.; Polat, Z.; Kaban, G. Enhanced lipid yield from olive-mill wastewater by Yarrowia lipolytica NRRL YB-423. J. Agric. Product. 2025, 6, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, G.; Jagtap, S.; Kumar, V.R.; RaviKumar, A. Enhancing lipid content of oleaginous Yarrowia lipolytica biomass grown on waste cooking oil and its conversion to biodiesel by statistical optimization. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2025, 15, 2007–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarris, D.; Tsouko, E.; Kothri, M.; Anagnostou, M.; Karageorgiou, E.; Papanikolaou, S. Upgrading biodiesel and olive-mill waste streams with Yarrowia lipolytica strains. Fermentation 2023, 9, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sestric, R.; Munch, G.; Cicek, N.; Sparling, R.; Levin, D.B. Growth and lipid synthesis by Yarrowia lipolytica on various carbon substrates. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 164, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colacicco, M.; Ciliberti, C.; Agrimi, G.; Biundo, A.; Pisano, I. Towards understanding Yarrowia lipolytica growth and lipase production using waste cooking oils. Energies 2022, 15, 5217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Fan, P. Effect of carbon source on lipid accumulation and biodiesel production of Yarrowia lipolytica. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 31234–31242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaaeldin, R.; Sayin, B.; Polat, Z.; Kaya, M.; Kaban, G. Effect of argan oil on lipid production by Yarrowia lipolytica NRRL YB-423. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2025, 35, e2410052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayadi, I.; Gargouri, A.; Guerfali, M. Sustainable valorization of olive mill wastewater via oleaginous yeasts: Single-cell oil production and effluent detoxification. Waste Biomass Valor. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggelis, G.; Athanassopoulos, N.; Paliogianni, A.; Komaitis, M. Effect of a Teucrium polium L. extract on the growth and fatty acid composition of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Yarrowia lipolytica. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 1998, 73, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggelis, G.; Komaitis, M. Enhancement of single cell oil production by Yarrowia lipolytica growing in the presence of Teuchrium polium L. aqueous extract. Biotechnol. Lett. 1999, 21, 747–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karanika, M.S.; Komaitis, M.; Aggelis, G. Effect of aqueous extracts of some plants of Lamiaceae family on the growth of Yarrowia lipolytica. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2001, 64, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Gortzi, O.; Margeli, E.; Chinou, I.; Galiotou-Panayotou, M.; Lalas, S. Effect of Citrus essential oil addition upon growth and cellular lipids of Yarrowia lipolytica yeast. Eur. J. Lip. Sci. Technol. 2008, 110, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzifragkou, A.; Petrou, I.; Gardeli, C.; Komaitis, M.; Papanikolaou, S. Effect of Origanum vulgare L. essential oil on growth and lipid profile of Yarrowia lipolytica cultivated on glycerol-based media. JAOCS 2011, 88, 1955–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozinou, E.; Athanasiadis, V.; Chatzimitakos, T.; Ganos, C.; Gortzi, O.; Diamantopoulou, P.; Papanikolaou, S.; Chinou, I.; Lalas, S.I. Essential oil of Greek citrus sinensis cv new hall-citrus aurantium pericarp: Effect upon cellular lipid composition and growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and antimicrobial activity against bacteria, fungi, and human pathogenic microorganisms. Processes 2023, 11, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, Ö.; Kaban, G.; Kaya, M. Tarhun ve kişniş tohumunun uçucu yağ bileşenleri. Bayburt Üniv. Fen Bil. Derg. 2019, 2, 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Enshaeieh, M.; Nahvi, I.; Madani, M. Improving microbial oil production with standard and native oleaginous yeasts by using Taguchi design. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalfe, L.D.; Schmitz, A.A. The rapid preparation of fatty acid esters for gas chromatographic analysis. Anal. Chem. 1961, 33, 363–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ChiPlot. Available online: https://www.chiplot.online/ (accessed on 30 August 2025).
- Kordali, S.; Kotan, R.; Mavi, A.; Cakir, A.; Ala, A.; Yildirim, A. Determination of the chemical composition and antioxidant activity of the essential oil of Artemisia dracunculus and of the antifungal and antibacterial activities of Turkish Artemisia absinthium, A. dracunculus, Artemisia santonicum, and Artemisia spicigera essential oils. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 9452–9458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Céspedes, C.L.; Avila, J.G.; Martínez, A.; Serrato, B.; Calderón-Mugica, J.C.; Salgado-Garciglia, R. Antifungal and antibacterial activities of Mexican tarragon (Tagetes lucida). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3521–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freires, I.D.A.; Murata, R.M.; Furletti, V.F.; Sartoratto, A.; Alencar, S.M.D.; Figueira, G.M.; Rodrigues, J.A.d.O.; Duarte, M.C.T.; Rosalen, P.L. Coriandrum sativum L.(coriander) essential oil: Antifungal activity and mode of action on Candida spp., and molecular targets affected in human whole-genome expression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Joshi, S.C.; Bhadauria, S. Chemical constituents, toxicity, and antifungal potential of Coriandrum sativum L. seed essential oil and their fractions against fungi causing ringworm infection in human. J. Essent. Oil-Bear. Plants. 2023, 26, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Galiotou-Panayotou, M.; Chevalot, I.; Komaitis, M.; Marc, I.; Aggelis, G. Influence of glucose and saturated free-fatty acid mixtures on citric acid and lipid production by Yarrowia lipolytica. Curr. Microbiol. 2006, 52, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Chatzifragkou, A.; Fakas, S.; Galiotou-Panayotou, M.; Komaitis, M.; Nicaud, J.M.; Aggelis, G. Biosynthesis of lipids and organic acids by Yarrowia lipolytica strains cultivated on glucose. Eur. J. Lip. Sci. Technol. 2009, 111, 1221–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Chevalot, I.; Komaitis, M.; Marc, I.; Aggelis, G. Single cell oil production by Yarrowia lipolytica growing on an industrial derivative of animal fat in batch cultures. App. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 58, 308–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Aggelis, G. Lipid production by Yarrowia lipolytica growing on industrial glycerol in a single-stage continuous culture. Bioresour. Technol. 2002, 82, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakicka, M.; Lazar, Z.; Dulermo, T.; Fickers, P.; Nicau, J.M. Lipid production by the oleaginous yeast Yarrowia lipolytica using industrial by-products under different culture conditions. Biotechnol. Biofuels. 2015, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uprety, B.K.; Rakshit, S.K. Use of essential oils from various plants to change the fatty acids profiles of lipids obtained from oleaginous yeasts. JAOCS 2018, 95, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moustogianni, A.; Bellou, S.; Triantaphyllidou, I.E.; Aggelis, G. Alterations in fatty acid composition of Cunninghamella echinulata lipids induced by orange essential oil. Environ. Biotechnol. 2014, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helal, G.A.; Sarhan, M.M.; Abu Shahla, A.N.K.; Abou El-Khair, E.K. Effects of Cymbopogon citratus L. essential oil on the growth, lipid content and morphogenesis of Aspergillus niger ML2-strain. J. Basic Microbiol. 2006, 46, 456–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moustogianni, A.; Bellou, S.; Triantaphyllidou, I.E.; Aggelis, G. Feasibility of raw glycerol conversion into single cell oil by zygomycetes under non-aseptic conditions. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2015, 112, 827–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreton, R.S. Modification of fatty acid composition of lipid accumulating yeasts with cyclopropene fatty acid desaturase inhibitors. App. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1985, 22, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, S.; Akimoto, K.; Shinmen, Y.; Kawashima, H.; Sugano, M.; Yamada, H. Sesamin is a potent and specific inhibitor of Δ5 desaturase in polyunsaturated fatty acid biosynthesis. Lipids 1991, 26, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaguchi, A.; Franaszek, N.; O’Neill, K.; Lee, S.; Sitepu, I.; Boundy-Mills, K.; Blenner, M. Identification of oleaginous yeasts that metabolize aromatic compounds. J. Indust. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 47, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, S.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, D.; Syed, N.; Gupta, M.; Chanotiya, C.S.; Rout, P.K.; Khare, S.K. An innovative Prosopis cineraria pod aqueous waste as natural inhibitor for enhancing unsaturated lipids production in yeast cell using banana peel. Waste Biomass Valor. 2022, 13, 3113–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Chaturvedi, S.; Syed, N.; Rastogi, D.; Kumar, P.; Sharma, P.K.; Kumar, D.; Sahoo, D.; Srivastava, N.; Nannaware, A.D.; et al. Production of fatty acids from distilled aromatic waste biomass using oleaginous yeast. Biomass Bioenergy 2024, 185, 107213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Muniglia, L.; Chevalot, I.; Aggelis, G.; Marc, I. Accumulation of a cocoa-butter-like lipid by Yarrowia lipolytica cultivated on agro-industrial residues. Curr. Microbiol. 2003, 46, 0124–0130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitepu, I.R.; Sestric, R.; Ignatia, L.; Levin, D.; German, J.B.; Gillies, L.A.; Almada, L.A.G.; Boundy-Mills, K.L. Manipulation of culture conditions alters lipid content and fatty acid profiles of a wide variety of known and new oleaginous yeast species. Biores. Technol. 2013, 144, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parfene, G.; Horincar, V.; Tyagi, A.K.; Malik, A.; Bahrim, G. Production of medium chain saturated fatty acids with enhanced antimicrobial activity from crude coconut fat by solid state cultivation of Yarrowia lipolytica. Food Chem. 2013, 136, 1345–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Jackson, E.N. Production of omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids by metabolic engineering of Yarrowia lipolytica. ACOS Lipid Library. 2015. Available online: http://lipidlibrary.aocs.org/Biochemistry/content.cfm?ItemNumber=41268 (accessed on 25 July 2025).
- Xie, D.; Miller, E.; Sharpe, P.; Jackson, E.; Zhu, Q. Omega-3 production by fermentation of Yarrowia lipolytica: From fed-batch to continuous. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 114, 798–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.K.; Dulermo, T.; Ledesma-Amaro, R.; Nicaud, J.M. Optimization of odd chain fatty acid production by Yarrowia lipolytica. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieliszek, M.; Dourou, M. Effect of selenium on the growth and lipid accumulation of Yarrowia lipolytica yeast. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 1611–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konzock, O.; Matsushita, Y.; Zaghen, S.; Sako, A.; Norbeck, J. Altering the fatty acid profile of Yarrowia lipolytica to mimic cocoa butter by genetic engineering of desaturases. Micro. Cell Fact. 2022, 21, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Sun, M.L.; Lin, L.; Ledesma-Amaro, R.; Wang, K.; Ji, X.J.; Huang, H. Dynamic regulation combined with systematic metabolic engineering for high-level palmitoleic acid accumulation in oleaginous yeast. Metab. Eng. 2025, 89, 33–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
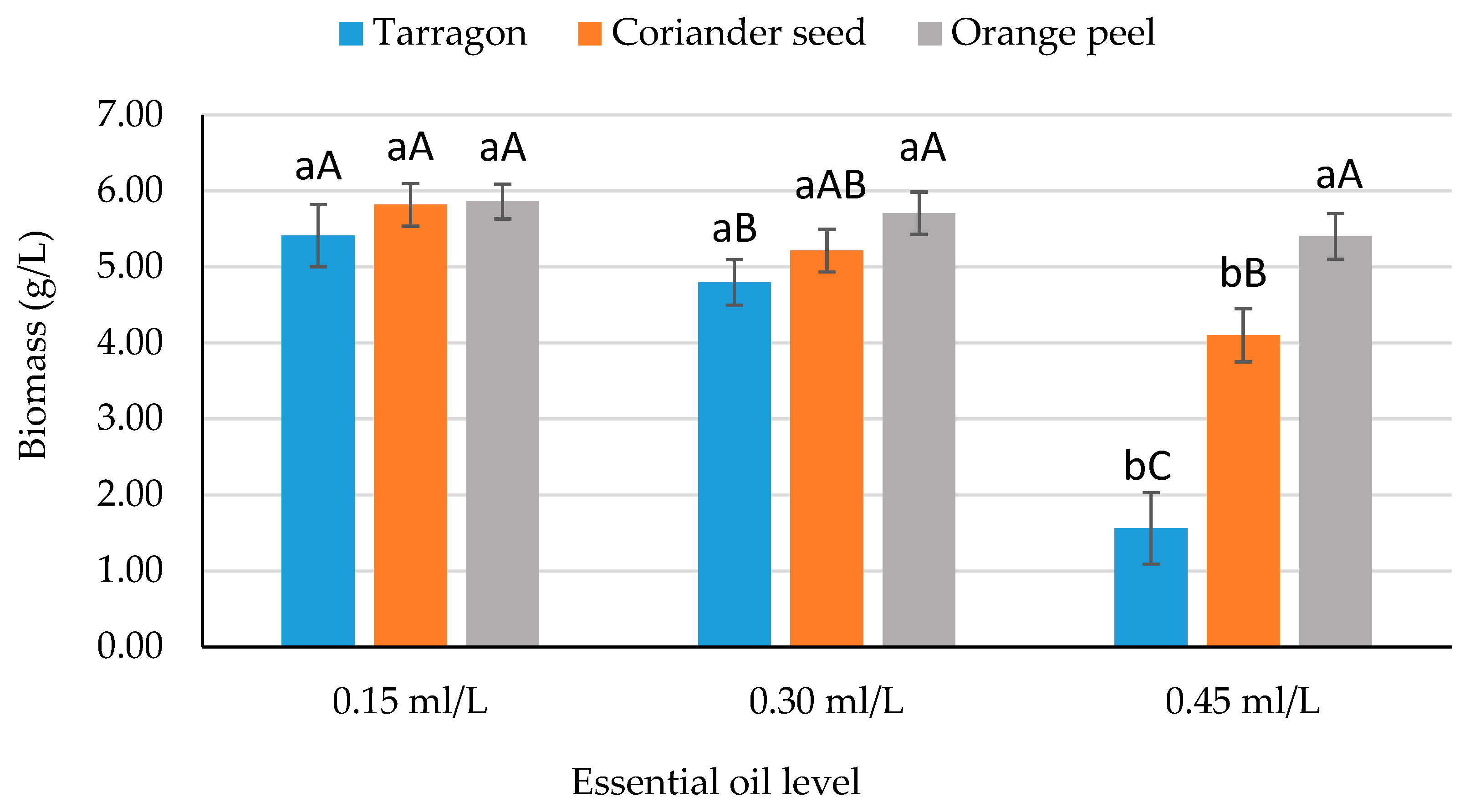
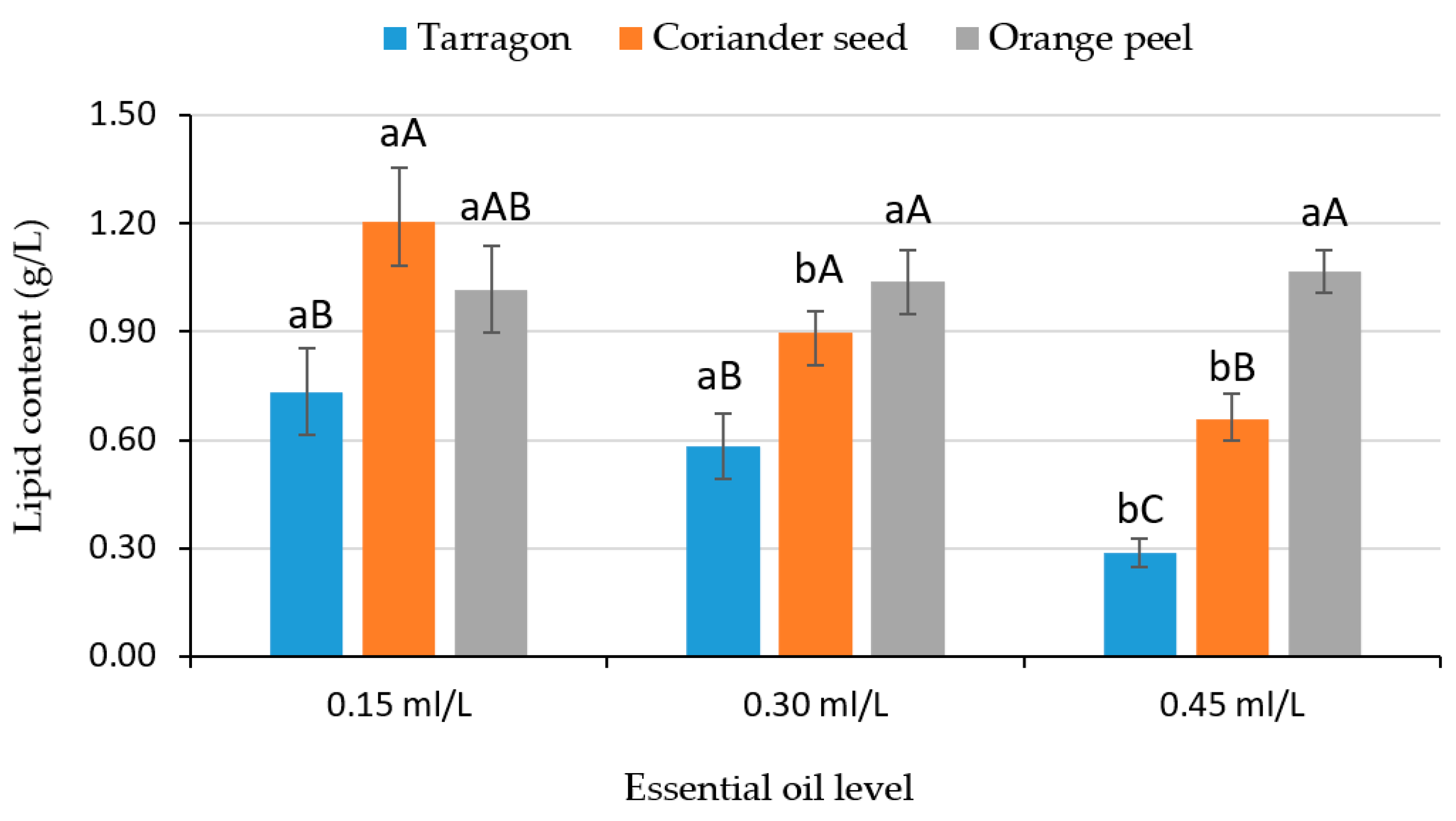
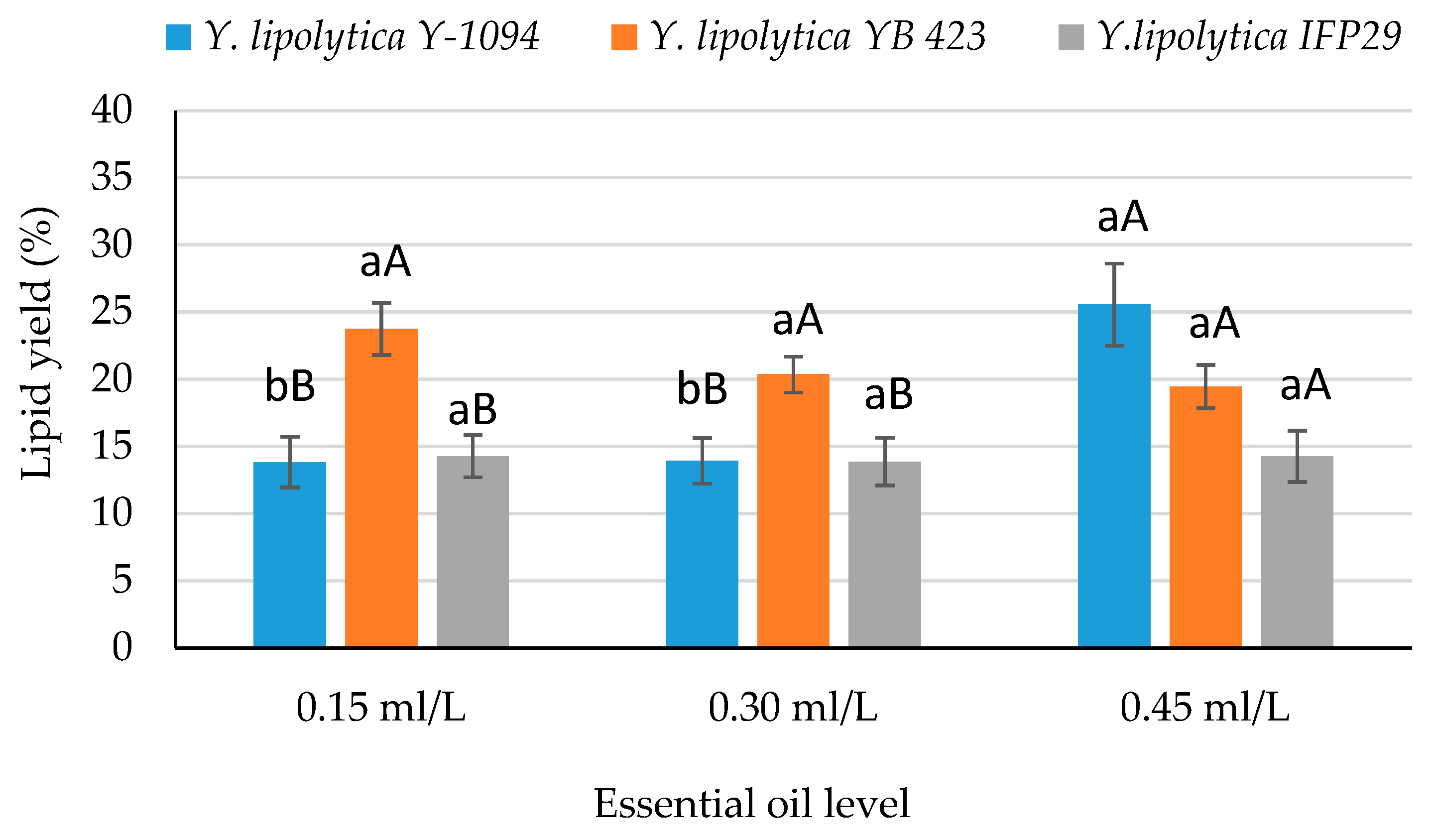
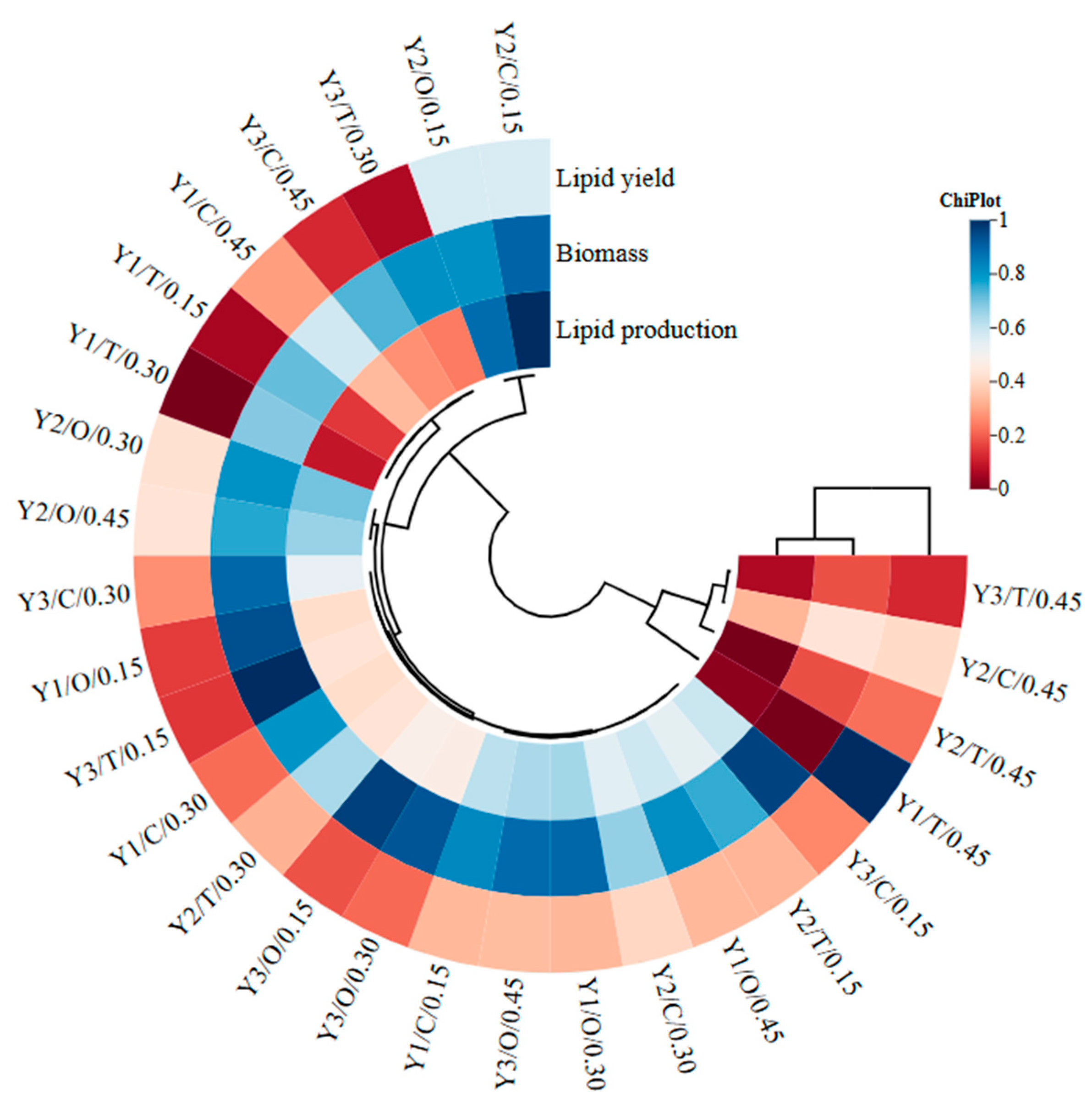
| Factors | Biomass (g/L) | Lipid Content (g/L) | Lipid Yield (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strain (S) | |||
| Y. lipolytica Y-1094 | 4.71 ± 0.18 b | 0.72 ± 0.04 b | 17.76 ± 0.91 ab |
| Y. lipolytica YB 423 | 4.52 ± 0.18 b | 0.98 ± 0.04 a | 21.18 ± 0.91 a |
| Y. lipolytica IFP29 | 5.38 ± 0.18 a | 0.78 ± 0.04 b | 14.13 ± 0.91 b |
| Significance | ** | ** | ** |
| Essential oil level (EOL) | |||
| 0.15 mL/L | 5.69 ± 0.15 a | 0.98 ± 0.04 a | 17.28 ± 0.95 a |
| 0.30 mL/L | 5.24 ± 0.15 a | 0.83 ± 0.04 b | 16.04 ± 0.95 a |
| 0.45 mL/L | 3.68 ± 0.15 b | 0.67 ± 0.04 c | 19.75 ± 0.95 a |
| Significance | ** | ** | NS |
| Essential oil source (EOS) | |||
| Tarragon | 3.92 ± 0.16 c | 0.53 ± 0.04 b | 16.08 ± 0.96 a |
| Coriander seed | 5.04 ± 0.16 b | 0.92 ± 0.04 a | 18.27 ± 0.96 a |
| Orange peel | 5.65 ± 0.16 a | 1.04 ± 0.04 a | 18.71 ± 0.96 a |
| Significance | ** | ** | NS |
| Interactions | |||
| S × EOL | NS | NS | * |
| S × EOS | NS | NS | NS |
| EOS × EOL | ** | * | NS |
| S × EOS × EOL | NS | NS | * |
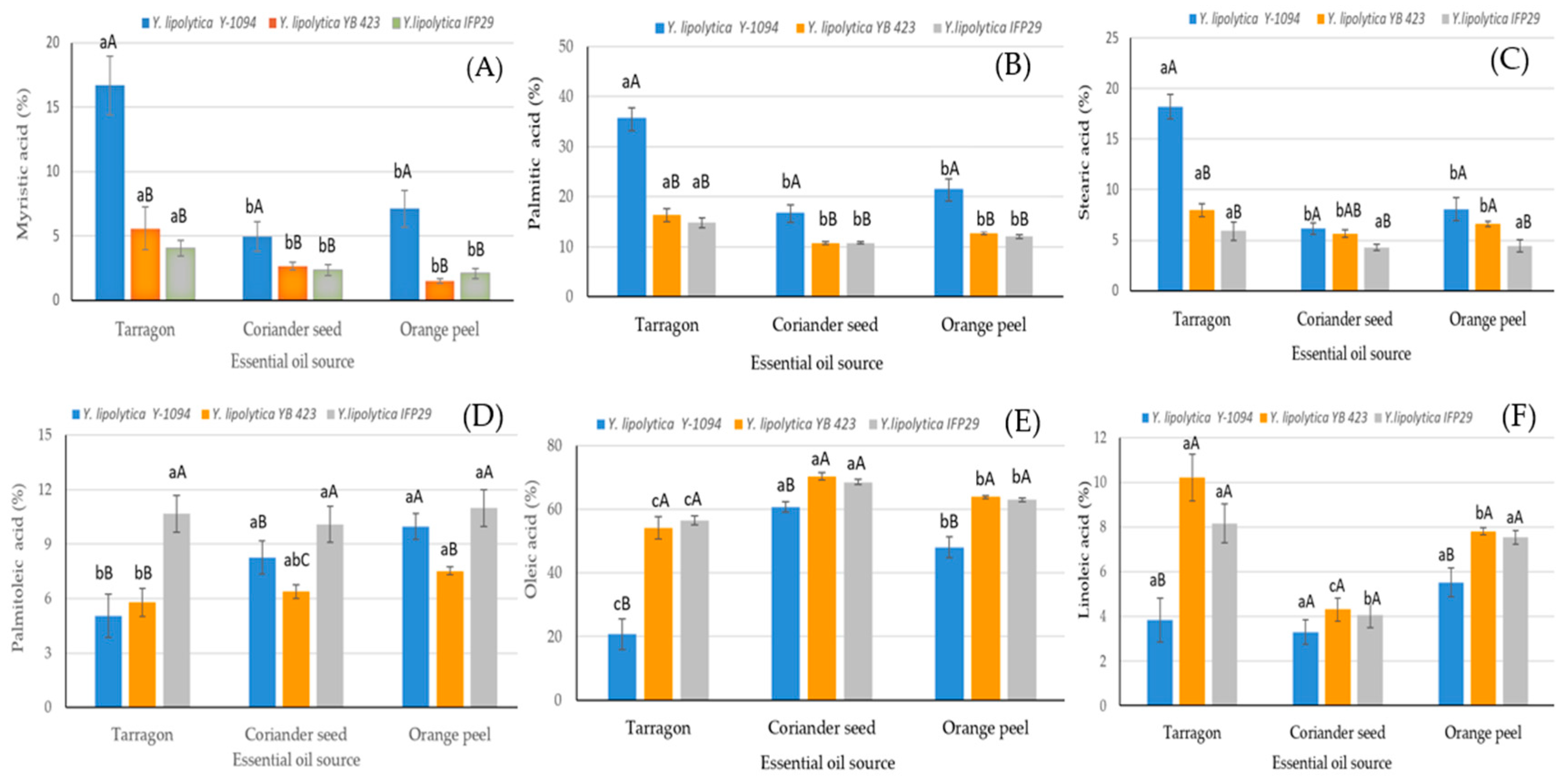
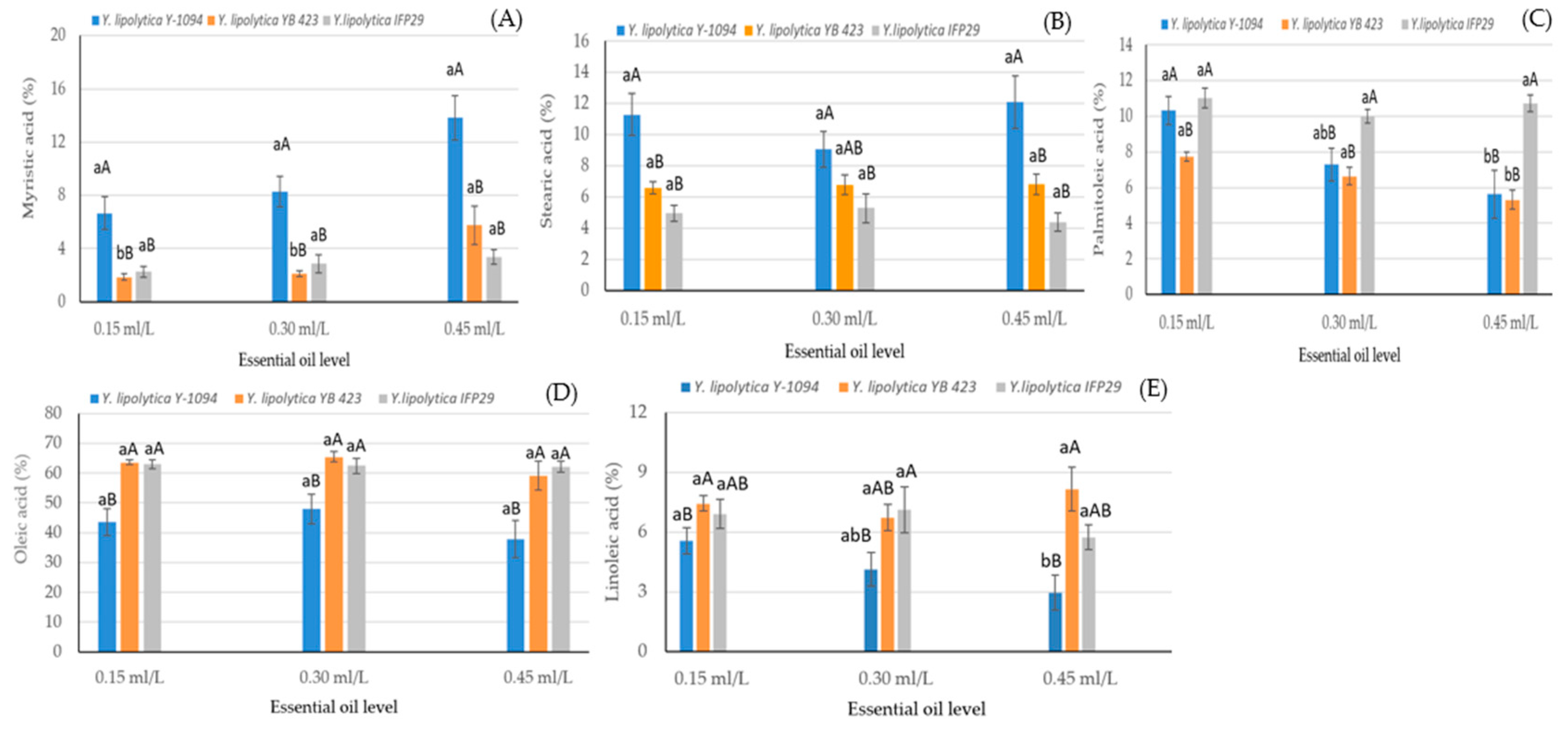
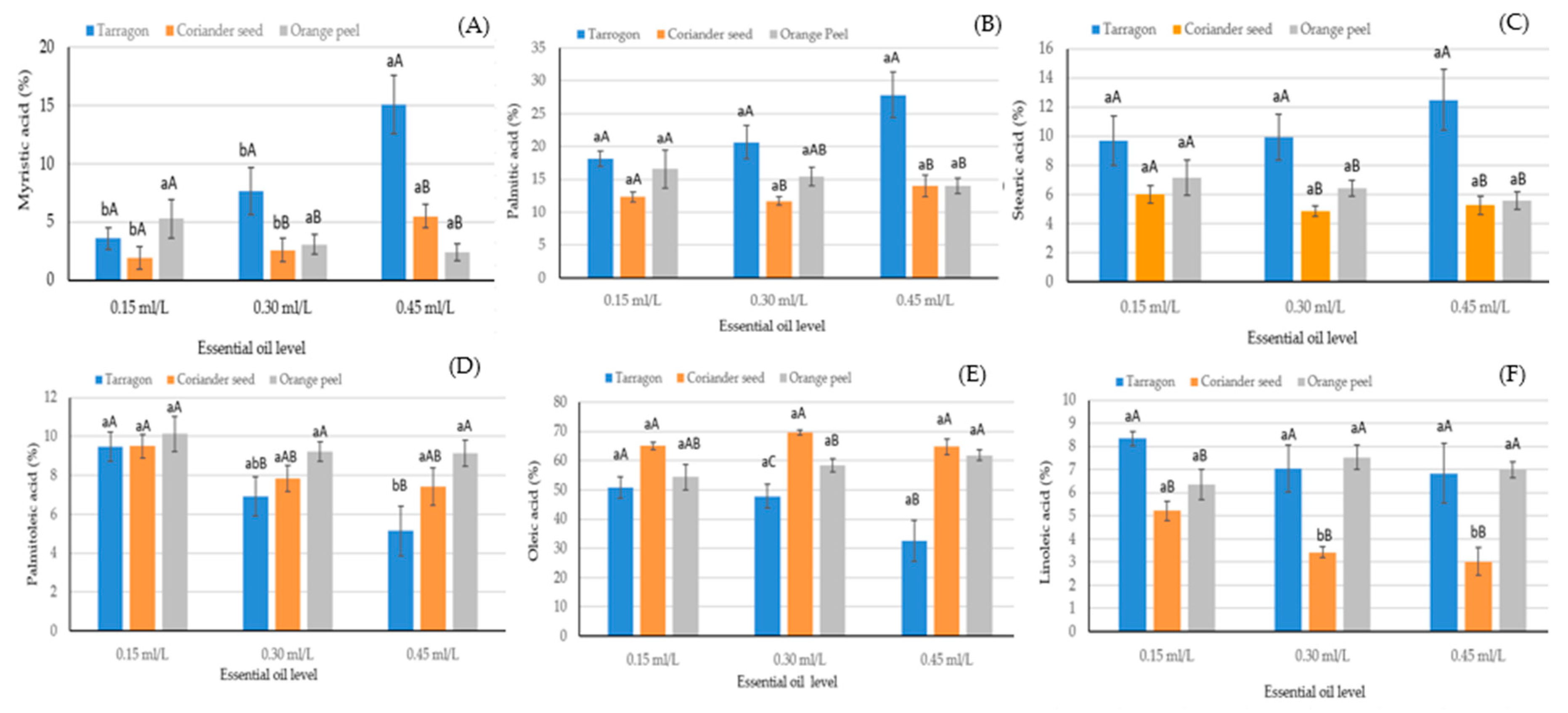
| Factors | Myristic Acid C14:0 | Palmitic Acid C16:0 | Palmitoleic Acid C16:1 | Stearic Acid C18:0 | Oleic Acid C18:1n9c | Linoleic Acid C18:2n6c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain (S) | ||||||
| Y. lipolytica Y-1094 | 9.59 ± 0.52 a | 24.48 ± 0.71 a | 7.75 ± 0.27 b | 10.81 ± 0.43 a | 43.14 ± 1.45 b | 4.21 ± 0.31 c |
| Y. lipolytica YB 423 | 3.25 ± 0.52 b | 13.28 ± 0.71 b | 6.56 ± 0.27 c | 6.73 ± 0.43 b | 62.74 ± 1.45 a | 7.44 ± 0.31 a |
| Y. lipolytica IFP29 | 2.82 ± 0.52 b | 12.52 ± 0.71 b | 10.58 ± 0.27 a | 4.89 ± 0.43 c | 62.57 ± 1.45 a | 6.59 ± 0.31 b |
| Significance | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| Essential oil source (EOS) | ||||||
| Tarragon | 8.77 ± 0.61 a | 22.21 ± 0.83 a | 7.16 ± 0.31 c | 10.69 ± 0.44 a | 43.74 ± 1.43 c | 7.40 ± 0.29 a |
| Coriander seed | 3.31 ± 0.61 b | 12.69 ± 0.83 c | 8.24 ± 0.31 b | 5.37 ± 0.44 b | 66.48 ± 1.43 a | 3.89 ± 0.29 b |
| Orange peel | 3.57 ± 0.61 b | 15.32 ± 0.83 b | 9.49 ± 0.31 a | 6.38 ± 0.44 b | 58.23 ± 1.43 b | 6.95 ± 0.29 a |
| Significance | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| Essential oil level (EOL) | ||||||
| 0.15 mL/L | 3.59 ± 0.64 b | 15.68 ± 0.93 b | 9.69 ± 0.31 a | 7.61 ± 0.51 a | 56.73 ± 1.77 b | 6.63 ± 0.34 a |
| 0.30 mL/L | 4.42 ± 0.64 b | 15.91 ± 0.93 b | 7.98 ± 0.31 b | 7.05 ± 0.51 a | 58.63 ± 1.77 a | 5.99 ± 0.34 ab |
| 0.45 mL/L | 7.65 ± 0.64 a | 18.62 ± 0.93 a | 7.22 ± 0.31 b | 7.77 ± 0.51 a | 53.10 ± 1.77 c | 5.61 ± 0.34 b |
| Significance | ** | ** | ** | NS | ** | * |
| Interaction | ||||||
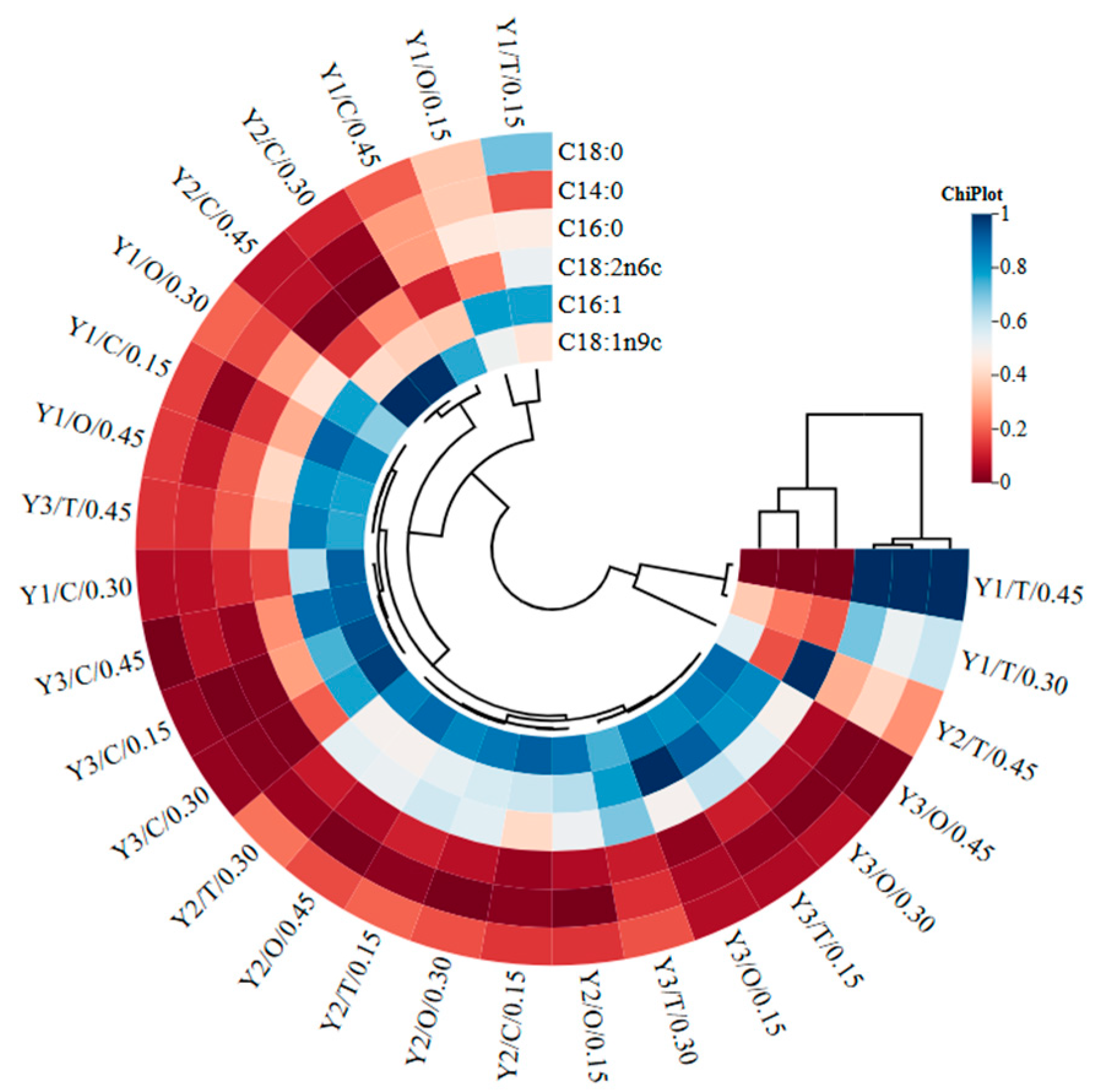
| S × EOS | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** |
| S × EOL | ** | NS | ** | * | ** | ** |
| EOS × EOL | ** | ** | * | * | ** | * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yılmaz, Ö.; Kaban, G.; Kaya, M. The Effects of Essential Oils from Coriander Seed, Tarragon and Orange Peel on Lipid Production by Yarrowia lipolytica Strains. Fermentation 2025, 11, 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11100597
Yılmaz Ö, Kaban G, Kaya M. The Effects of Essential Oils from Coriander Seed, Tarragon and Orange Peel on Lipid Production by Yarrowia lipolytica Strains. Fermentation. 2025; 11(10):597. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11100597
Chicago/Turabian StyleYılmaz, Özlem, Güzin Kaban, and Mükerrem Kaya. 2025. "The Effects of Essential Oils from Coriander Seed, Tarragon and Orange Peel on Lipid Production by Yarrowia lipolytica Strains" Fermentation 11, no. 10: 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11100597
APA StyleYılmaz, Ö., Kaban, G., & Kaya, M. (2025). The Effects of Essential Oils from Coriander Seed, Tarragon and Orange Peel on Lipid Production by Yarrowia lipolytica Strains. Fermentation, 11(10), 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11100597








