Abstract
Harmful cyanobacterial blooms (HABs), primarily composed of toxic cyanobacteria like Microcystis aeruginosa, pose a significant threat to aquatic ecosystems and human health. Algicidal bacteria had emerged as a promising strategy for HAB control due to their safety and efficacy. In this study, the algicidal bacterium Streptomyces violaceorubidus lzh-14, isolated from Cha Lake in Dezhou, China, exhibited strong algicidal activity against M. aeruginosa. When bacterial culture was added to algal cultures at a final volume ratio of 10% (v/v), the algicidal activity reached 94.5% ± 1.8% after 72 h. Moreover, S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 showed varying degrees of algicidal activity against other tested cyanobacterial species. Microscopic observation revealed that M. aeruginosa cells treated with lzh-14 became deformed and ruptured, resulting in the leakage of cellular contents. The algicidal substance extracted from S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 demonstrated strong stability under varying temperatures and pH conditions. Based on these findings, algicidal powder was preliminarily developed. This study confirms that S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 and its active substance have potential as effective biocontrol agents against HABs.
1. Introduction
Harmful cyanobacterial blooms (HABs) have been recognized as a global issue in freshwater systems. Their adverse effects are twofold. Firstly, they cause severe environmental degradation, such as elevated turbidity, oxygen depletion, foul odors, and loss of aquatic diversity [1]. Secondly, the associated cyanotoxins pose a direct threat to drinking water safety and human health [2,3]. Over the past three decades, toxic cyanobacterial bloom intensity has increased substantially, degrading water quality in coastal and freshwater systems globally [4]. HABs competitively displace phytoplankton communities for nutrient resources, progressively dominating aquatic ecosystems [5,6]. Microcystis aeruginosa is one of the most common and widespread HABs globally [7,8,9,10]. It frequently dominates toxic blooms in freshwater ecosystems, causing significant ecological and public health hazards. This notoriously destructive cyanobacterium induces severe, often near-annual HABs in regions such as China, Canada, Korea, and Japan. The increasing frequency of these blooms represents a critical ecological problem worldwide [11,12]. Consequently, developing urgently needed efficient HAB control technologies is imperative.
Physical and chemical measures were implemented to mitigate HAB damages [13]. Physical HAB mitigation strategies, which involve environmental manipulation (e.g., water mixing, aeration, barriers), are often limited by cost and scale. In contrast, chemical methods rely on algicides, ranging from traditional oxidants like H2O2 to newer, more selective compounds, but face challenges with residual effects and specificity. Consequently, exploiting competitive/inhibitory biotic interactions, particularly involving Actinomycetes, has emerged as an environmentally prioritized strategy for mitigating HABs [14,15]. Actinomycetes secrete diverse algicidal substances during growth, establishing them as potent biocontrol agents against HABs in eutrophic waters [16,17]. Among algicidal Actinomycetes, the genus Streptomyces are the most extensively reported [14,18,19]. For example, S. globisporus G9 kills M. aeruginosa exclusively through direct cell-to-cell contact, a novel mechanism unreported in Streptomyces, by entangling cyanobacterial cells with hyphae, causing lysis without secreting diffusible algicides [14]. S. amritsarensis HG-16 simultaneously lyses M. aeruginosa and suppresses microcystin synthesis via light-dependent bioactive metabolites [18]. Likewise, S. enissocaesilis M35 exhibits potent algicidal activity against the toxic cyanobacterium Phormidium angustissimum through direct contact and bioactive metabolites, achieving >94% removal efficiency under optimized bioreactor conditions [19].
In general, algicidal bacteria typically inhibit algae through two primary mechanisms: direct contact with algal cells or indirect competition for nutrients or the secretion of extracellular active compounds [20,21,22,23,24]. S. violaceorubidus, as a species within the genus Streptomyces, was identified early on [25,26,27]. However, most studies for S. violaceorubidus have been limited to genomic identification; its their functional roles remain largely unexplored, particularly their inhibitory effects against HABs.
In this study, the algicidal bacterium S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 was isolated from Cha Lake in Dezhou, China and demonstrated significant algicidal activity against M. aeruginosa. However, the stability of its algicidal metabolites remains poorly characterized. To address this gap, we further investigated the algicidal activity, target range, the mode of action, and the compound stability of S. violaceorubidus lzh-14. Based on these findings, algicidal powders were subsequently developed for the future management of M. aeruginosa blooms.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Algicidal Cultures
The indicator microalgae species were obtained from the Freshwater Algae Culture Collection of the Institute of Hydrobiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China (FACHB). The microalgae species included Synechococcus sp. FACHB-805, M. aeruginosa FACHB-915, Chlorella FACHB-8, Xanthophyta, Tribonema FACHB-1786. The algae were cultured in BG11 medium, which was sterilized by autoclaving at 121 °C for 20 min. The cultures were maintained at 25 °C under a 12 h/12 h light/dark cycle, illuminated with cool white fluorescent lamps at an intensity of 100 μmol photons·m−2·s−1. The flasks were shaken manually three times per day.
2.2. Algicidal Cultures Isolation, and Identification of Bacterium lzh-14
Water samples were collected from Cha Lake in Dezhou, Shandong, China (37°43′44.84″ N, 117°13′32.99″ E). Algicidal bacterium was isolated following a previously described method [28]. After serial dilution with sterile water, a 0.1 mL sample was spread on Gause’s medium containing 15 g/L soluble starch, 1 g/L NaNO3, 0.5 g/L K2HPO4, 0.5 g/L MgSO4·7H2O, and 0.01 g/L ferrous sulfate. The medium was prepared using deionized water and sterilized prior to use. After inoculation, the plates were incubated at 28 °C for 24 h. Colonies exhibiting distinct morphologies were repeatedly purified to obtain axenic cultures. These pure cultures were stored at –80 °C in 20% (v/v) glycerol. Strain lzh-14 was cultivated in Gauze’s Synthetic Medium No. 1 at 28 °C with shaking at 125 rpm, unless otherwise stated.
To identify the algicidal bacterium lzh-14, it was subjected to taxonomic analysis using conventional physiological and biochemical tests. Genomic DNA was extracted from the bacterium using the TIANamp Bacterial DNA kit (TIANGEN, Beijing, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The 16S rRNA gene was amplified by polymerase chain reactions (PCR) using the universal primers 27F (5′-AGAGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG-3′) and 1492R (5′-GATTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3′) [29]. PCR amplification was performed using a Thermo PCR Thermal Cycler (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The 50 µL reaction mixture consisted of 1 µL (approximately 20 ng) of template DNA, 1.5 µL of each primer (10 µM), 25 µL of PCR master mix (TaKaRa Bio Inc., Dalian, China), and 21 µL of double-distilled water. The thermocycling protocol included an initial denaturation at 95 °C for 5 min; 35 cycles of denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, annealing at 58 °C for 30 s, and extension at 72 °C for 90 s; followed by a final extension at 72 °C for 7 min. PCR products were analyzed by electrophoresis on 1% (w/v) agarose gel stained with GelGreen, and visualized under UV light. The resulting sequences were assembled and compared with reference sequences in the rRNA/ITS databases using BLAST v2.17 analysis (NCBI, Bethesda, MD, USA) [30].
2.3. Growth Curve of Algicidal Bacterium lzh-14
The growth curve of bacterium lzh-14 was determined turbidimetrically. Bacterium lzh-14 was inoculated into LB liquid medium at an initial concentration of approximately 106 CFU/mL and incubated at 28 °C with shaking at 180 rpm. The optical density (OD) of the bacteria culture was measured at 6 h intervals using a spectrophotometer UV2600 (Techcomp, Shanghai, China) for a total duration of 36 h. The growth curve was plotted with OD600 on the y-axis and time on the x-axis. Experiments included three independent biological replicates.
2.4. Algicidal Activity of Bacterium lzh-14 Against M. aeruginosa
Bacterium lzh-14 was inoculated in Gauze’s Synthetic Medium No. 1 and incubated for 3 days at 28 °C. To assess algicidal activity, bacterial cultures (2 × 103 cells/mL) were added to M. aeruginosa FACHB-915 suspensions (4.6 × 107 cells/mL) at a volume ratio of 10% (v/v). A control group was prepared by adding an equal volume of sterile medium to the algal culture without the bacteria. All co-culture systems were incubated under the same conditions used for algal cultivation. Algicidal activity against M. aeruginosa FACHB-915 was evaluated at 0, 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, and 72 h. Algal cells were counted using a Sail Brand hemocytometer (Mshot, Guangzhou, China) under a light microscope at 40× magnification. The algicidal activity was calculated using the following formula: Algicidal activity (%) = (1 − Nt/Nc) × 100%, where Nt and Nc represent the cell densities of M. aeruginosa FACHB-915 in the treatment and control groups, respectively [31]. Experiments were performed in three independent biological replicates.
2.5. Algicidal Activity of Bacterium lzh-14 Against M. aeruginosa at Different Growth Phase
For each 40 mL sample of M. aeruginosa culture (initial cell density: 4.6 × 107 cells/mL) from four distinct growth phases (lag, logarithmic growth, stable, and decline), 4 mL of lzh-14 culture (initial cell density: 2 × 106 cells/mL) was added (n = 3). The mixtures were incubated under the same conditions, and algicidal activity (%) was determined as described above [31]. All experiments were conducted with three independent biological replicates.
2.6. Algicidal Range of Bacterium lzh-14
To determine the algicidal spectrum, an exponential-phase culture of the algicidal bacterium was added to a final concentration of 10% (v/v) to test algal cultures (initial algal density: 4.6 × 107 cells/mL) of the following bacteria: M. aeruginosa FACHB-915, FACHB-911, FACHB-977; Synechococcus sp. FACHB-805; Anabaena sp. FACHB-175; Chlorella sp. FACHB-5; Chlorococcum humicola FACHB-21; Scenedesmus sp. FACHB-489; Tribonema utriculosum FACHB-2216; and Cystodinium bataviense FACHB-1839. A control was prepared by adding an equal volume of Gauze’s Synthetic Medium No. 1 to the algal culture. Cellular density was measured 24 h after bacterial inoculation. We repeated each experiment three times independently.
2.7. Algicidal Mode of Bacterium lzh-14
To investigate the algicidal mode of action, 400 mL of the bacterium lzh-14 culture was extracted with ethyl acetate. The extract was then evaporated to dryness and reconstituted in 200 μL of deionized water. The lzh-14 extract, lzh-14 pelleted cells from the fermented culture, and sterile water were separately added into M. aeruginosa culture. Cyanobacterial cell density was measured at the indicated time points post-treatment. Experiments included three independent biological replicates.
2.8. Observation on Cell Morphology of Cyanobacteria Attacked by Bacterium lzh-14
Bacterium lzh-14 was added to M. aeruginosa FACHB-915 at a ratio of 10% (v/v). Cyanobacterial cells treated for 72 h with either the cell-free filtrate or the whole culture of bacterium lzh-14 were collected by centrifugation at 1000× g for 10 min at 25 °C. The harvested cells were subsequently prepared for light microscope observation. Experiments were performed in three independent biological replicates.
2.9. Stability of the Algicidal Compounds
The cell-free filtrates were exposed to temperatures of −80, −20, 0, 20, 50, 70, and 100 °C for 2 h and then returned to room temperature. Each temperature-treated filtrate was added to algal cultures at a final volume ratio of 10.0% (v/v) and incubated for 72 h to assess algicidal activity. Separately, the pH of cell-free filtrates was adjusted to 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11 using acid or alkali, held for 2 h, and then neutralized back to the original pH. These pH-adjusted filtrates were also introduced into algal cultures at 10.0% (v/v) and incubated for 72 h to evaluate algicidal activity. All experiments were performed in triplicate.
2.10. Algicidal Powder Production and Application
Sawdust was selected as the carrier for immobilizing bacteriumlzh-14. Briefly, the sawdust was sterilized twice, dried, and used as the carrier material. It was then introduced into a stationary-phase culture of bacterium lzh-14 at a concentration of 15% (w/v) and incubated at 28 °C with shaking at 125 rpm for 6 h to facilitate bacterial adsorption. After incubation, the unadsorbed culture was removed by sieving, and the bacterium-loaded sawdust was transferred to a glass Petri dish and freeze-dried for 24 h. The resulting lyophilized powder was stored at 4 °C.
To assess the algicidal efficacy of the powder, 0.1 g of the powder was added to 50 mL of pre-cultured algal suspension (cell density: 105 cells/mL). A control was prepared using the same amount of sterile sawdust without bacteria. All treatments were performed in triplicate during the light phase under 25 °C. Algal cell counts were determined after 12 h of treatment, and the algicidal activity was calculated as previously described [31]. Experiments included three independent biological replicates.
2.11. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using two distinct methods to evaluate different aspects of the data. First, one-way ANOVA followed by Fisher’s Least Significant Difference (LSD) test was conducted using GraphPad Prism 8 software to compare differences among multiple groups; results are marked with different lowercase letters (p < 0.05), with post hoc comparisons carried out in SPSS Statistics 21. Second, Student’s t-test was applied to assess significant differences between each treatment and the control group, *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, and * p < 0.05, “ns” represents no significance. All data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD).
3. Results
3.1. Identification of S. violaceorubidus lzh-14
In our study, we have screened bacterium with potential algicidal activity and named it bacterium lzh-14. The biochemical characteristics of bacterium lzh-14 are summarized in Table S1. The bacterium is Gram-Positive and forms purplish-red colonies that are difficult to isolate; these colonies developed folds on agar plates after 24 h of incubation in Gause’s medium (Figure S1). Bacterium lzh-14 was able to grow at temperatures ranging from 10 °C to 40 °C, but not below 5 °C or above 45 °C. Additionally, it did not grow at pH levels below 5 or above 10 (Table S1). Phylogenetic analysis based on the 16S rRNA gene sequence (GenBank accession number: MN099143) revealed that bacterium lzh-14 is closely related to S. amritsarensis and was identified as S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 (Figure S2). The growth curve of S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 is shown in Figure 1. Three distinct growth phases were observed: a lag phase (0–6 h), an exponential phase (6–24 h), and a stationary phase (24–36 h). Interestingly, the growth curve shows an exponential rise at 30–36 h.
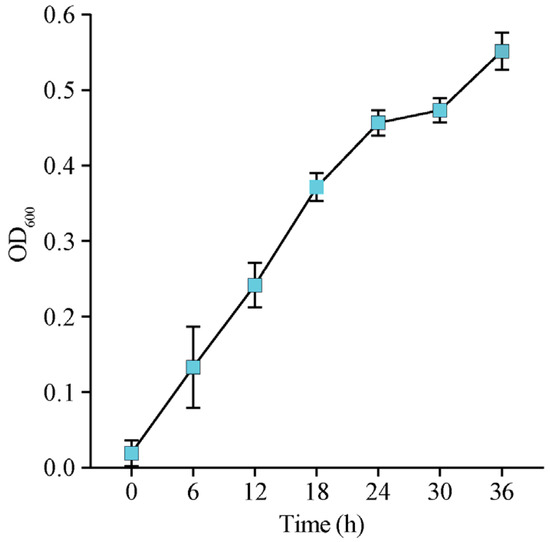
Figure 1.
Growth curve of the algicidal bacterium Streptomyces violaceorubidus lzh-14. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 3).
3.2. Algicidal Activity of S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 Against M. aeruginosa
S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 demonstrated a significant algicidal effect against M. aeruginosa FACHB-915 (Figure 2A,B). After application to the algal culture, algicidal activity reached 94.5% ± 1.8% after 72 h. To investigate the algicidal mechanism, both cell-free supernatant and washed bacterial cells resuspended in water were added to the algal cultures and their algicidal activities were evaluated. The results showed that the cell-free supernatant exhibited significantly higher algicidal activity than the resuspended cells (Figure 2C).
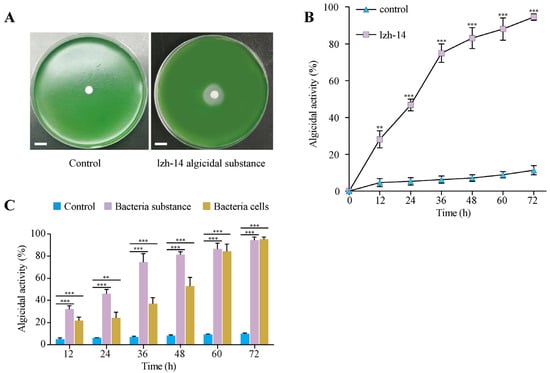
Figure 2.
The algicidal effect of Streptomyces violaceorubidus lzh-14 algicidal substance against Microcystis aeruginosa FACHB-915. (A) The algicidal effects of S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 on M. aeruginosa FACHB-915 were detected using algal plate. Bar: 1 cm. (B) The algicidal activities of S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 on M. aeruginosa FACHB-915 were determined at different times after treatment. (C) Comparison of algicidal activities among different fractions of the algicidal substance from S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 and whole bacterial cells, based on algal cell density and algicidal rate. Bars represent the mean ± SD (n = 3). Significant differences compared to the control group were determined by Student’s t-test, *** p < 0.001 and ** p < 0.01.
3.3. Analysis of Optimal Application Timing for S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 to Achieve Maximum Algicidal Effect
S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 exhibited significant algicidal activity against M. aeruginosa, with its efficacy being influenced by its own growth phase, the co-cultivation time, and the growth stage of the algal culture. As shown in Figure 3A, bacterial cultures harvested during the stationary phase (24–36 h) demonstrated the highest algicidal rate (96.3%), outperforming those from the lag (0–6 h) and exponential (6–24 h) phases. Furthermore, the algicidal activity of S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 varied according to its growth phase, reaching a maximum of 98.3% on the 8th day of co-cultivation when stationary phase cells were applied (Figure 3B). Under the same conditions, the algicidal rates for logarithmic growth phase and stationary phases cultures were approximately 85.5% and 96.2%, respectively. The susceptibility of M. aeruginosa to S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 was also dependent on the algal growth stage. After 4 days of co-culture, the highest algicidal activity (96%) was observed against lag phase algae, followed by logarithmic growth phase (73.2%) and stationary phase (50.4%). No significant algicidal effect was detected against decline phase algae, which is likely attributable to natural cell mortality (Figure 3C).
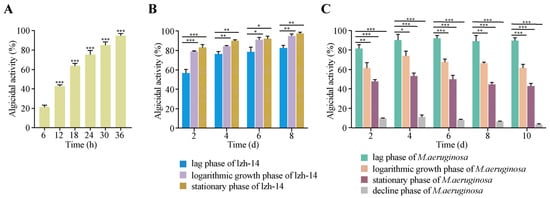
Figure 3.
Effect of culture duration of Streptomyces violaceorubidus lzh-14 at different growth stages on Microcystis aeruginosa FACHB-915. (A) Algicidal activity of S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 against M. aeruginosa FACHB-915 was determined at different time points (0, 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, and 36 h), showing a positive correlation between incubation time and algicidal efficacy. (B) Algicidal activity, expressed as the algal-lysing rate, was compared across different growth phases of S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 (lag phase, logarithmic growth phase, stationary phase). (C) Effect of the growth stage of M. aeruginosa FACHB-915 on the algicidal activity of S. violaceorubidus lzh-14. Bars represent the mean ± SD (n = 3). Significant differences compared to the control group were determined by Student’s t-test, *** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, and * p < 0.05.
3.4. Broad-Spectrum Algicidal Activity of S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 Against Harmful Cyanobacteria
To evaluate the algicidal spectrum of S. violaceorubidus lzh-14, a total of 10 different algal species were selected for the experiment. The results of co-culture assays testing its algicidal activity against various harmful algal species are presented in Table 1. After 72 h of co-cultivation, S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 exhibited algicidal activity exceeding 90% against nearly all tested cyanobacterial species, including M. aeruginosa FACHB-915, FACHB-911, and FACHB-977. These results indicate that S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 is a broad-spectrum algicidal bacterium against HABs. In contrast, its algicidal effects on T. utriculosum FACHB-2216 and C. bataviense FACHB-1839 were not significant.

Table 1.
Algicidal activity of Streptomyces violaceorubidus lzh-14 toward various algal bacteria. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 3).
3.5. Morphological Alterations in M. aeruginosa Cells Induced by S. violaceorubidus lzh-14
Microscopic analysis revealed that S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 significantly altered the morphology of M. aeruginosa cells. As shown in Figure 4A, at the beginning of the treatment, M. aeruginosa FACHB-915 cells exhibited a spherical and plump morphology with smooth and intact cell surfaces. After 36 h of exposure to the cell-free filtrate from S. violaceorubidus lzh-14, the cells lost structural integrity in both the cell wall and plasma membrane (Figure 4B). Following 72 h of treatment, cell rupture and the release of intracellular components were observed, suggesting that S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 likely kills and decomposes algal cells by secreting extracellular active compounds (Figure 4C).
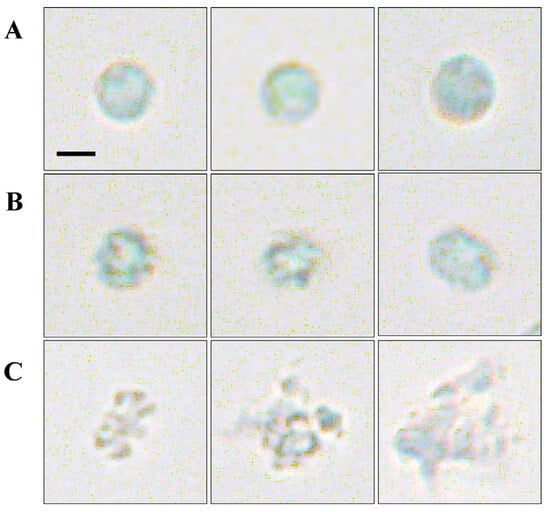
Figure 4.
Morphological changes in Microcystis aeruginosa FACHB-915 following treatment with the algicidal substance from Streptomyces violaceorubidus lzh-14. (A) Normal M. aeruginosa FACHB-915 cell. (B) M. aeruginosa FACHB-915 cells treated with S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 algicidal substance for 36 h. (C) M. aeruginosa FACHB-915 cells treated with S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 algicidal substance for 72 h. Bar: 100 μm.
3.6. Stability of Algicidal Compounds from S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 Under Various Environmental Conditions
To evaluate the algicidal stability of the active compounds produced by S. violaceorubidus lzh-14, their thermal and pH stability were tested (Figure 5). The algicidal activity of the compounds from S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 against M. aeruginosa was assessed across a range of temperatures (Figure 5A). Although minor variations were observed among treatments, the algicidal rates consistently exceeded 80%, indicating high thermal stability. In addition, we also found that the active compounds retained strong algicidal efficacy under both acidic and alkaline conditions (Figure 5B). Furthermore, the activity was largely unaffected by repeated freeze–thaw cycles, with no significant differences observed between the control and treated groups (Figure 5C). These results confirm that the algicidal compounds produced by S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 are relatively stable under diverse environmental conditions.
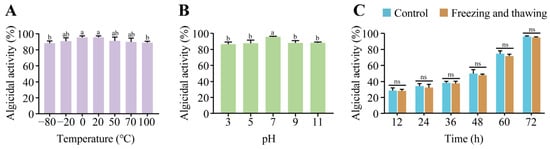
Figure 5.
Algicidal stability of the algicidal substance from Streptomyces violaceorubidus lzh-14 against Microcystis aeruginosa FACHB-915. (A) Temperature stability. (B) pH stability. (C) Stability after repeated freeze–thaw cycles. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three biological replicates. Different lowercase letters denote statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) as determined by one-way ANOVA. “ns” represents no significance.
3.7. Algicide Production and Application of S. violaceorubidus lzh-14
The algicidal powder derived from S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 was applied to a M. aeruginosa culture medium to assess its efficacy. The powder exhibited pronounced algicidal activity at a final concentration of 2% (v/v) (Figure 6). A complete algicidal effect (100%) was achieved within 24 h. These results not only confirm the strong algicidal capacity of the powder but also validate the feasibility of its production method.
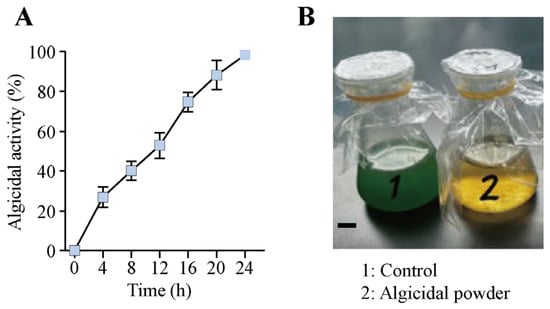
Figure 6.
Algicidal effect of a 2% (final concentration) powder derived from Streptomyces violaceorubidus lzh-14 on Microcystis aeruginosa FACHB-915 after 24 h of continuous treatment. (A) Algicidal activity of the powder. (B) Efficacy of the powder against M. aeruginosa FACHB-915. Data are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 3). Bar: 1 cm.
4. Discussion
Cyanobacterial blooms are global environmental issues that threatens freshwater ecosystems worldwide [32]. The toxic cyanobacterium M. aeruginosa has a widespread global distribution and is one of the most common bloom-forming species. It frequently dominates HABs in freshwater ecosystems, raising significant ecological and public health concerns [7,8,9,10,33]. In efforts to control HABs, algicidal bacteria have gained increasing attention due to their advantageous low-cost and species-specific characteristics [34]. Numerous algicidal bacteria targeting HABs have been isolated and characterized from various environments. For instance, Qipengyuania sp. 3-20A1M lyses the harmful alga Margalefidinium polykrikoides via the secretion of pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid [35]. Similarly, novel cyclic lipopeptide surfactins from Bacillus tequilensis D8 exhibit potent algicidal activity against Heterosigma akashiwo blooms by disrupting cell membranes and photosynthetic functions [36]. Furthermore, the algicidal bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. LD-B6 achieves 90.5% lysis of Noctiluca scintillans within 12 h by secreting heat-stable, non-protein extracellular compounds [37]. In this study, we isolated and identified a highly efficient algicidal bacterium, S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 (Figure 1). Based on the observed exponential rise in the growth curve of S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 between 30 and 36 h, we propose that this phenomenon might represent a diauxic growth pattern, commonly seen in Streptomyces [38,39,40,41], where a lag phase for the activation of enzymes to decompose complex secondary substrates follows the depletion of a preferred carbon source, leading to a renewed increase in OD. Furthermore, compared to the control, S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 exhibited a significant algicidal effect, with its algicidal compounds achieving an activity of 94.5% against M. aeruginosa after 72 h of co-cultivation (Figure 2 and Figure 3). These results suggest that S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 is a promising agent against HABs.
Algicidal bacteria primarily employed two distinct modes of action: direct and indirect algicidal strategies [32,42]. The direct mode requires physical contact or even invasion between the bacterial and algal cells. A notable example is Aeromonas bestiarum HYD0802-MK36, which acts as a specialized direct attacker, exhibiting high specificity toward M. aeruginosa through cell-to-cell contact [43]. In contrast, the indirect algicidal mode does not require physical interaction; instead, bacteria secrete extracellular compounds that inhibit algal growth, induce cell death, or compete with algae for essential resources. For instance, Enterobacter hormaechei F2 demonstrates effective algicidal activity against M. aeruginosa by producing the red pigment prodigiosin and employing the quorum-sensing molecule PQS (Pseudomonas Quinolone Signal) [44]. In our study, S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 exhibited significant algicidal activity against M. aeruginosa, primarily mediated by extracellular compounds released into the supernatant (Figure 2). The cell-free filtrate of S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 induced loss of structural integrity in the cell wall and plasma membrane of M. aeruginosa within 36 h (Figure 4). Previous studies have indicated that S. amritsarensis HG-16 produces proteinase K-resistant active substances that exhibit algicidal activity against M. aeruginosa [18]. Furthermore, an active algicidal triterpenoid saponin from Streptomyces sp. L74 was shown to disrupt the antioxidant systems of M. aeruginosa cells [40]. These results indicate that S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 likely employs an indirect algicidal strategy by secreting active metabolites to kill M. aeruginosa.
Algicidal bacteria have been widely reported to exhibit strong algicidal activity [45,46,47]. However, studies on the stability of these active bacterial substances remain limited. Our findings revealed that the algicidal compounds of S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 were resistant to both acidic and alkaline conditions and remained stable under varying temperature treatments (Figure 5). This observation is consistent with the report by Zhu et al., which showed that the algicidal activity of Microbulbifer sp. YX04 supernatant retained stability after exposure to temperatures ranging from −80 °C to 100 °C and pH values between 4 and 12 for 2 h [48]. These results suggest algicidal compounds produced by S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 possess remarkable stability under a wide range of extreme environmental conditions. Additionally, existing studies have indicated that aminoclay, as a non-proteinaceous and chemically stable algicide, can disrupt algal cell membranes through electrostatic interactions, leading to rapid cell lysis and thereby exerting algicidal effects [49]. Therefore, given the thermal stability of the algicidal compounds produced by S. violaceorubidus Izh-14, they are unlikely to be proteins. This stability, combined with the algicidal potential of these compounds, makes them promising agents for controlling HABs. Moreover, S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 demonstrated efficacy against several harmful algal bloom (HAB) species, including Synechococcus, Anabaena, and Chlorella (Table 1), indicating a broad-spectrum algicidal activity and potential utility in controlling HABs caused by these organisms.
A growing number of algicidal agents have been developed for bloom mitigation [30,50]. In this study, the algicidal powder derived from S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 exhibited high efficacy against M. aeruginosa, achieving 100% algicidal activity within 24 h, confirming both its potent activity and the feasibility of the production process (Figure 6). For future research, it will be essential to isolate and characterize the specific algicidal compounds, and to develop targeted application strategies tailored to specific environmental conditions, such as adapting to variable salinity, temperature, and pH, to enhance practicality and efficiency [51]. Further research should also focus on identifying the effective bioactive compounds produced by S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 using mass spectrometry techniques [52,53,54], and investigating the potential non-target impacts of lzh-14’s algicidal metabolites on beneficial microbial communities, such as plant-growth-promoting bacteria [55,56].
5. Conclusions
S. violaceorubidus lzh-14 exhibits potent, broad-spectrum algicidal activity against M. aeruginosa and other bloom-forming cyanobacteria via extracellular compounds, demonstrating high stability across extreme environmental conditions. The successful development of an efficacious algicidal powder underscores its practical potential for HAB control. Future work should prioritize compound identification and field-applicable formulation strategies to enhance real-world utility.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/fermentation11100596/s1, Figure S1: Colony of Streptomyces violaceorubidus lzh-14 after 24 h of incubation. Bar: 1 cm; Figure S2: Phylogenetic tree based on 16S rRNA gene sequences of Streptomyces violaceorubidus lzh-14 and related reference bacteria retrieved from GenBank, constructed using the neighbor-joining method; Table S1: Phenotypic characteristics of Streptomyces violaceorubidus lzh-14.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.L., and J.W.; Data curation, Z.Z., D.Z., and Y.W.; Formal analysis, Z.Z.; Visualization, Z.Z., Y.Z., J.Q., and L.F.; Methodology, Y.Z.; Validation, F.L., W.Z., and J.G.; Funding acquisition, Z.L.; Writing—original draft, Z.Z., D.Z., and Y.W.; Writing—review & editing, Z.L., and J.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31800106, 62071085), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (ZR2019BC027, ZR2025QC337), Doctoral Research Foundation for Doctoral of Dezhou University (2024xjrc121), The Experimental Technology Project of Dezhou University (SYJS25020). The foundation of Dezhou University (HXKT2024312, HXKT2024027, 202511A0050).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article and Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Saraf, S.R.; Frenkel, A.; Harke, M.J.; Jankowiak, J.G.; Gobler, C.J.; McElroy, A.E. Effects of Microcystis on development of early life stage Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes): Comparative toxicity of natural blooms, cultured Microcystis and microcystin-LR. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 194, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji-Prasath, B.; Wang, Y.; Su, Y.; Chen, M.; Zheng, Y. Algicidal properties of microbial fermentation products on inhibiting the growth of harmful dinoflagellate species. Fermentation 2022, 8, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutoti, M.; Gumbo, J.; Jideani, A.I.O. Occurrence of cyanobacteria in water used for food production: A review. Phys. Chem. Earth 2022, 125, 103101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukenik, A.; Kaplan, A. Cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms in aquatic ecosystems: A comprehensive outlook on current and emerging mitigation and control approaches. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyne, K.J.; Wang, Y.; Johnson, G. Algicidal bacteria: A review of current knowledge and applications to control harmful algal blooms. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 871177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Gao, H.; Yang, Y.; Deng, Y.; Ju, F. Fungi as a critical component of lake microbiota in response to cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 11167–11180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harke, M.J.; Steffen, M.M.; Gobler, C.J.; Otten, T.G.; Wilhelm, S.W.; Wood, S.A.; Paerl, H.W. A review of the global ecology, genomics, and biogeography of the toxic cyanobacterium, Microcystis spp. Harmful Algae 2016, 54, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Li, P.; Du, Y.; Cao, L.; Yan, Z. Inhibitory effects of Artemisia argyi extracts on Microcystis aeruginosa: Anti-algal mechanisms and main allelochemicals. Biology 2025, 14, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Zhu, Y.F.; Yang, Y.C.; Xiao, Y.Z.; Zhu, S.N.; Yang, W.D.; Li, H.Y.; Wang, X. Butylparaben-loaded aged polystyrene nanoplastics amplify its toxicity in Microcystis aeruginosa via quorum sensing suppression and enhanced Microcystin-LR release. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 19195–19207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Sha, J.; Jia, Y.; Ma, J.; Huang, L.; Dai, G.; Song, L. Differential photosynthetic and metabolic susceptibility of Microcystis aeruginosa and Raphidocelis subcapitata to environmentally relevant levels of Diuron. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 158, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W.; Fulton, R.S., 3rd; Moisander, P.H.; Dyble, J. Harmful freshwater algal blooms, with an emphasis on cyanobacteria. Sci. World J. 2001, 1, 76–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhu, H.; Wang, H.; Shutes, B.; Niu, T. Effect of butachlor on Microcystis aeruginosa: Cellular and molecular mechanisms of toxicity. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 449, 131042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo-Rodríguez, J.J.; Astuya-Villalón, A.; Llanos-Rivera, A.; Avello-Fontalba, V.; Ulloa-Jofré, V. A critical review on control methods for harmful algal blooms. Rev. Aquac. 2019, 11, 661–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, C.; Ding, M.; Hamilton, P.B.; Zhang, X.; Yang, C.; Zhnag, L.; Dai, X. A Streptomyces globisporus strain kills Microcystis aeruginosa via cell-to-cell contact. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 144489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morón-López, J.; Font-Nájera, A.; Kokociński, M.; Jarosiewicz, P.; Jurczak, T.; Mankiewicz-Boczek, J. Influence of bloom stage on the effectiveness of algicidal bacteria in controlling harmful cyanobacteria: A microcosm study. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 374, 126261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemesheva, V.; Islamova, R.; Stepchenkova, E.; Shenfeld, A.; Birkemeyer, C.; Tarakhovskaya, E. Antibacterial, antifungal and algicidal activity of phlorotannins, as principal biologically active components of ten species of brown algae. Plants 2023, 12, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Peng, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, H.; Yu, Z.; Zheng, W.; Zheng, T. Effects of marine actinomycete on the removal of a toxicity alga Phaeocystis globose in eutrophication waters. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Luo, F.; Dai, X. An algicidal Streptomyces amritsarensis strain against Microcystis aeruginosa strongly inhibits microcystin synthesis simultaneously. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butsat, W.; Somdee, T.; Somdee, T. A novel actinomycete Streptomyces enissocaesilis exhibiting algicidal activity against the toxic cyanobacterium Phormidium angustissimum. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 66897–66911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, F.; Lei, S.; Shao, S.; Wang, C.; Li, G.; An, T. Efficient inactivation of harmful algae K. mikimotoi by a novel algicidal bacterium via a rare direct contact pathway: Performances and mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chen, S.; Bai, X.; Ma, X.; Xie, Z.; Xu, H. Effect and mechanism of the algicidal bacterium sulfitobacter porphyrae zfx1 on the mitigation of harmful algal blooms caused by prorocentrum donghaiense. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Ding, G.; Lin, S.; Chen, J. Isolation of an algicidal bacterium and its effects against the harmful-algal- bloom dinoflagellate Prorocentrum donghaiense (Dinophyceae). Harmful Algae 2018, 80, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.J.; Xu, Y.; Su, H.C.; Xu, W.J.; Wang, L.H.; Xu, Y.N.; Li, Z.J.; Cao, Y.C.; Wen, G.L. Algicidal bacterium CZBC1 inhibits the growth of Oscillatoria chlorina, Oscillatoria tenuis, and Oscillatoria planctonica. AMB Express 2019, 9, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishu, S.D.; Kang, Y.; Han, I.; Jung, T.Y.; Lee, T.K. Nutritional status regulates algicidal activity of Aeromonas sp. L23 against cyanobacteria and green algae. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0213370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouizgarne, B.; Lanoot, B.; Loqman, S.; Spröer, C.; Klenk, H.P.; Swings, J.; Ouhdouch, Y. Streptomyces marokkonensis sp. nov., isolated from rhizosphere soil of Argania spinosa L. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59, 2857–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pridham, T.G.; Hesseltine, C.W.; Benedict, R.G. A guide for the classification of Streptomycetes according to selected groups. Appl. Microbiol. 1958, 6, 52–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouioui, I.; Carro, L.; García-López, M.; Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Woyke, T.; Kyrpides, N.C.; Pukall, R.; Klenk, H.P.; Goodfellow, M.; Göker, M. Genome-based taxonomic classification of the phylum actinobacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, W.; Zheng, L.; He, C.; Han, B.; Zheng, M.; Gao, W.; Sun, C.; Zhou, G.; Gao, X. Quorum sensing of microalgae associated marine Ponticoccus sp. pd-2 and its algicidal function regulation. AMB Express 2017, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, S.; Woese, C.R. A definition of the domains archaea, bacteria and eucarya in terms of small subunit ribosomal rna characteristics. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1991, 14, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Haga, M.; Imai, I.; Sakai, R.; Fujita, M.J. Function of the algicidal bacterium Pseudomonas sp. Go58 isolated from the biofilm on a water plant, and its active compounds, pyoluteorins. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 872, 162088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, L.; Pan, J.; Yang, H. The algicidal activity of Aeromonas sp. strain GLY-2107 against bloom-forming Microcystis aeruginosa is regulated by N-acyl homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 3867–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, R.; Oon, Y.L.; Oon, Y.S.; Bi, Y.; Mi, W.; Song, G.; Gao, Y. Diverse interactions between bacteria and microalgae: A review for enhancing harmful algal bloom mitigation and biomass processing efficiency. Heliyon 2024, 10, e36503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybalchenko, N.; Kharkhota, M.; Avdeeva, L.; Kharchuk, M.; Rybalchenko, T.; Matviienko, N. Algicidal strain of Bacillus velezensis imv b-7571 for controlling harmful algal blooms. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2025, 45, 101990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, H.; Cao, H.; Sun, M.; Wang, C.; Ye, R.; Lu, L.; An, J.; Chen, B. A potential algicidal bacterium against Spirogyra gracilisblooms: Identification, algicidal activity, algicidal mode, and metabolomic profiling. J. Appl. Phycol. 2024, 36, 3829–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.R.; Van Le, V.; Srivastava, A.; Kang, M.; Oh, H.M.; Ahn, C.Y. Algicidal activity of a novel bacterium, Qipengyuania sp. 3-20A1M, against harmful Margalefidinium polykrikoides: Effects of its active compound. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 186, 114397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, X.; Xie, W.; Liang, Y.; Luo, G.; Li, L.; Zheng, W.; Xu, Q.; Xu, H. Algicidal characteristics of novel algicidal compounds, cyclic lipopeptide surfactins from Bacillus tequilensis strain D8, in eliminating Heterosigma akashiwo blooms. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1066747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yin, X.; Xu, M.; Chen, Y.; Ji, N.; Gu, H.; Cai, Y.; Shen, X. Isolation and characterization of a high-efficiency algicidal bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. ID-B6 against the harmful dinoflagellate noctiluca scintillans. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1091561. [Google Scholar]
- Kearns, D.B.; Russell, J.B. Catabolite regulation in a diauxic strain and a nondiauxic strain of Streptococcus bovis. Curr. Microbiol. 1996, 33, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chater, K.F. Recent advances in understanding Streptomyces. F1000Research 2016, 5, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Wang, Y.; Tang, S.; Liang, J.; Lin, W.; Luo, L. Isolation and identification of algicidal compound from Streptomyces and algicidal mechanism to Microcystis aeruginosa. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Chen, M.; Fei, X.; Zhang, R.; Zhong, Y.; Ni, W.; Tao, X.; He, X.; Zhang, E.; Yong, B.; et al. Complete genome sequence and characterization of a polyethylene biodegradation strain, Streptomyces albogriseolus LBX-2. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demuez, M.; González-Fernández, C.; Ballesteros, M. Algicidal microorganisms and secreted algicides: New tools to induce microalgal cell disruption. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 1615–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.S.; Park, C.S.; Shin, Y.; Yoon, S.; Han, M.S.; Kang, Y.H. Different algicidal modes of the two bacteria aeromonas bestiarum hyd0802-mk36 and pseudomonas syringae kacc10292T against harmful cyanobacteria Microcystis aeruginosa. Toxins 2022, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Yang, Y.; Xie, W.; He, W.; Xie, J.; Liu, W. Identifying algicides of enterobacter hormaechei f2 for control of the harmful alga Microcystis aeruginosa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 7556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.I.; Kim, S.; Choi, K.Y.; Lee, C.; Park, Y.; Choi, Y.E. Control of a toxic cyanobacterial bloom species, Microcystis aeruginosa, using the peptide HPA3NT3-A2. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 32255–32265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.; Yan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, T.; Zhang, X.; Dai, X.; Igarashi, Y.; Luo, F.; Yang, C. An insight into algicidal characteristics of Bacillus altitudinis G3 from dysfunctional photosystem and overproduction of reactive oxygen species. Chemosphere 2023, 310, 136767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Lu, J.; Zhang, J.; Jin, Y.; Ren, L.; Xu, H.; Zhao, M.; Ma, Z. Algicidal mechanism and algicidal active metabolites of alteromonas abrolhosensis against harmful dinoflagellates karenia mikimotoi. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 490, 137815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, S.; Luo, G.; Zheng, W.; Tian, Y.; Lei, X.; Yao, L.; Wu, C.; Xu, H. A novel algicidal bacterium, Microbulbifer sp. YX04, triggered oxidative damage and autophagic cell death in phaeocystis globosa, which causes harmful algal blooms. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0093421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.C.; Jin, E.; Jung, S.W.; Kim, Y.M.; Chang, K.S.; Yang, J.W.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, Y.O.; Shin, H.J. Utilizing the algicidal activity of aminoclay as a practical treatment for toxic red tides. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Jin, Y.; Ma, J.; Zheng, N.; Zhang, J.; Peng, X.; Xie, B. Isolation and characterization of algicidal bacteria from freshwater aquatic environments in china. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1156291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, M.; Yesankar, P.J.; Dwivedi, A.; Qureshi, A. Biotic control of harmful algal blooms (habs): A brief review. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 268, 110687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Parveen; Raj, N.; Khatoon, S.; Fakhri, K.U.; Kumar, P.; Alamri, M.A.; Kamal, M.; Manzoor, N.; Harsha; et al. In-silico and in-vitro evaluation of antifungal bioactive compounds from Streptomyces sp. strain 130 against Aspergillus flavus. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2025, 43, 6045–6063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Kundu, A.; Kumar, M.; Solanki, R.; Kapur, M.K. Exploitation of potential bioactive compounds from two soil derived actinomycetes, Streptomyces sp. strain 196 and RI.24. Microbiol. Res. 2019, 229, 126312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanthasena, P.; Hua, Y.; Rosyidah, A.; Pathom-Aree, W.; Limphirat, W.; Nantapong, N. Isolation and identification of bioactive compounds from Streptomyces actinomycinicus PJ85 and their in vitro antimicrobial activities against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Xue, J.; Ma, J.; Feng, X.; Ying, H.; Xu, H. Streptomyces lydicus M01 regulates soil microbial community and alleviates foliar disease caused by Alternaria alternata on cucumbers. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Spor, A.; Sadeghi, A.; Safaie, N. Streptomyces strains modulate dynamics of soil bacterial communities and their efficacy in disease suppression caused by Phytophthora capsici. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).