Biochar Enhanced Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure by Mitigating Ammonium Inhibition and Improving Methane Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sources and Characteristics of Chicken Manure and Inoculum
2.2. Sources and Characteristics of Biochar
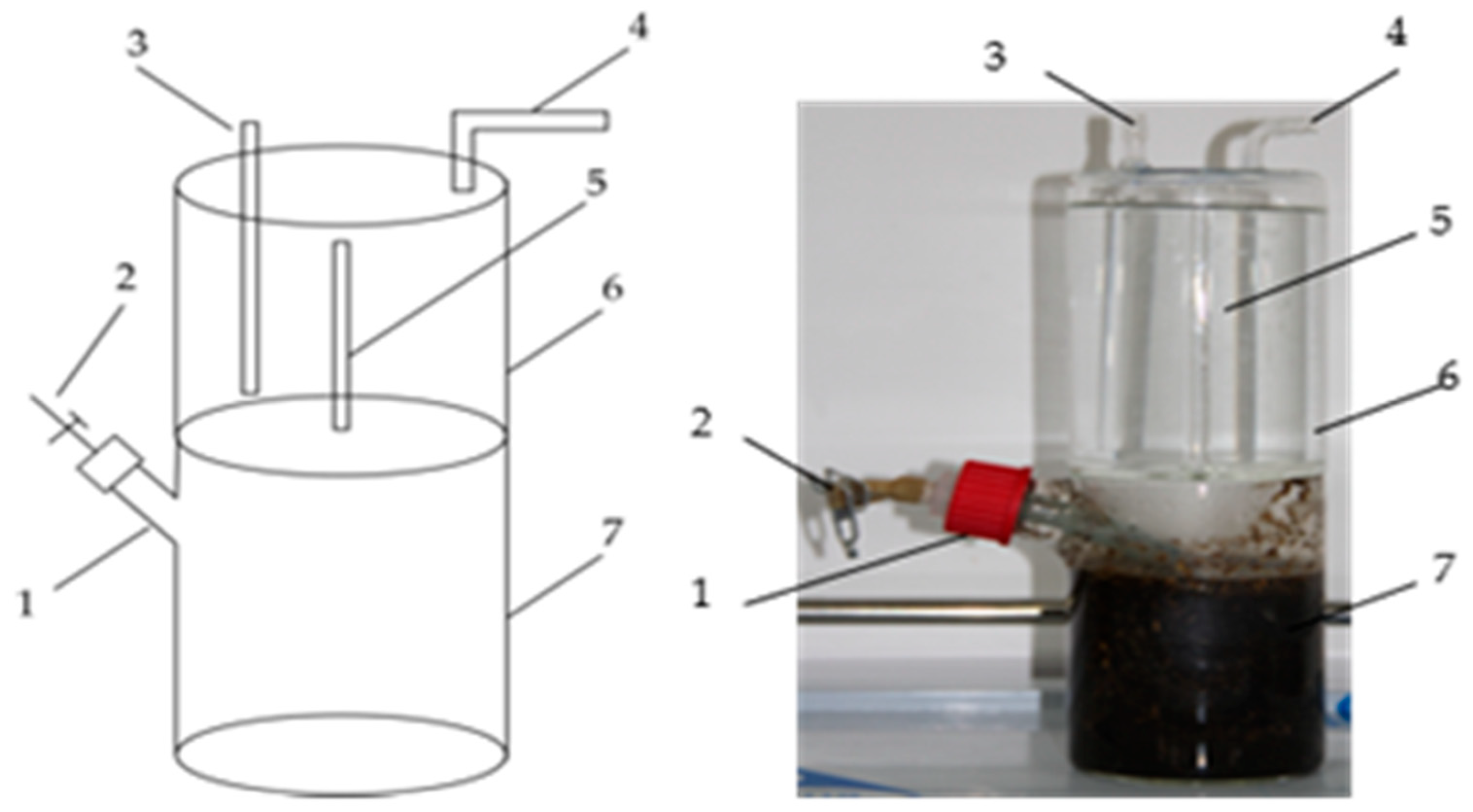
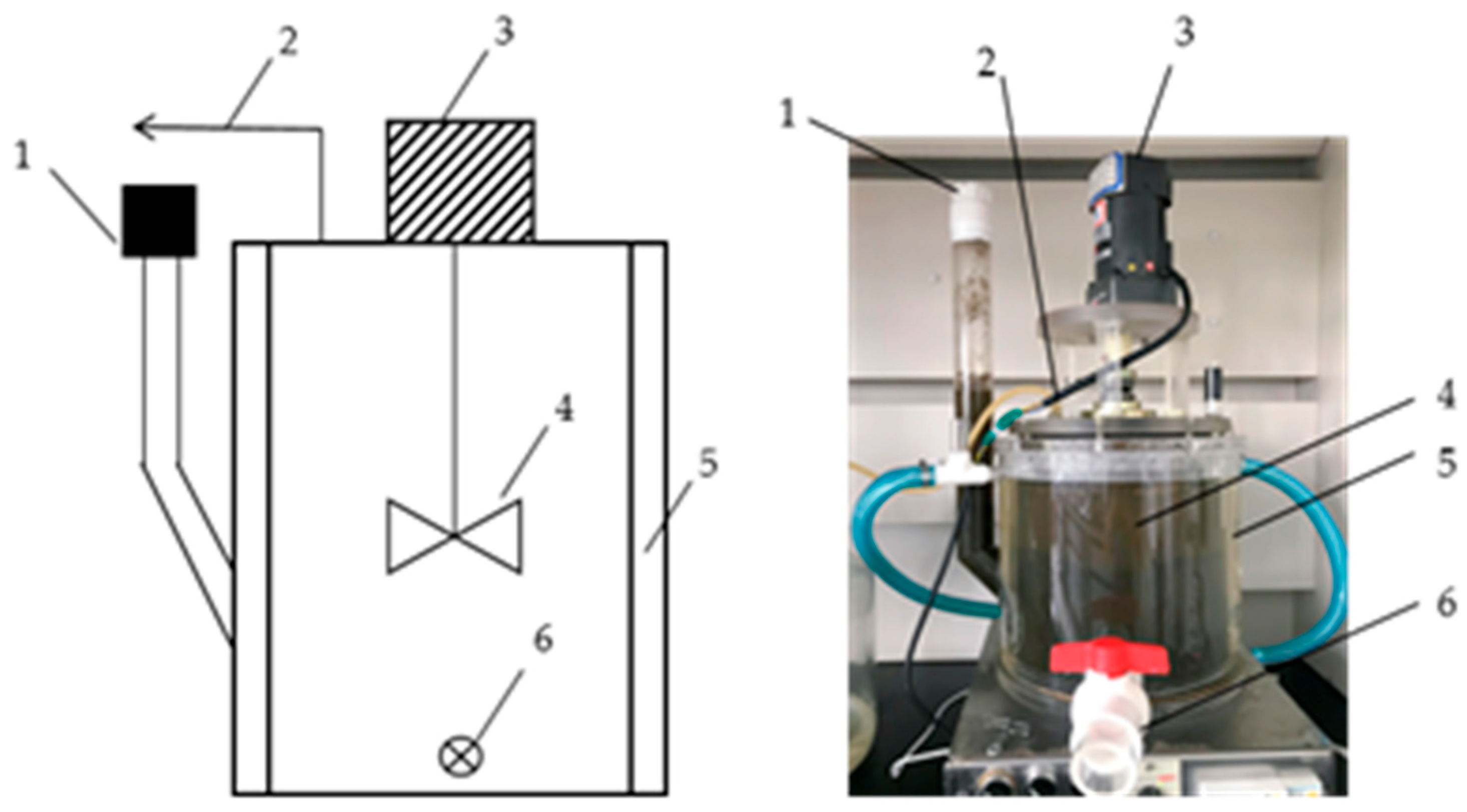
2.3. Experimental Device
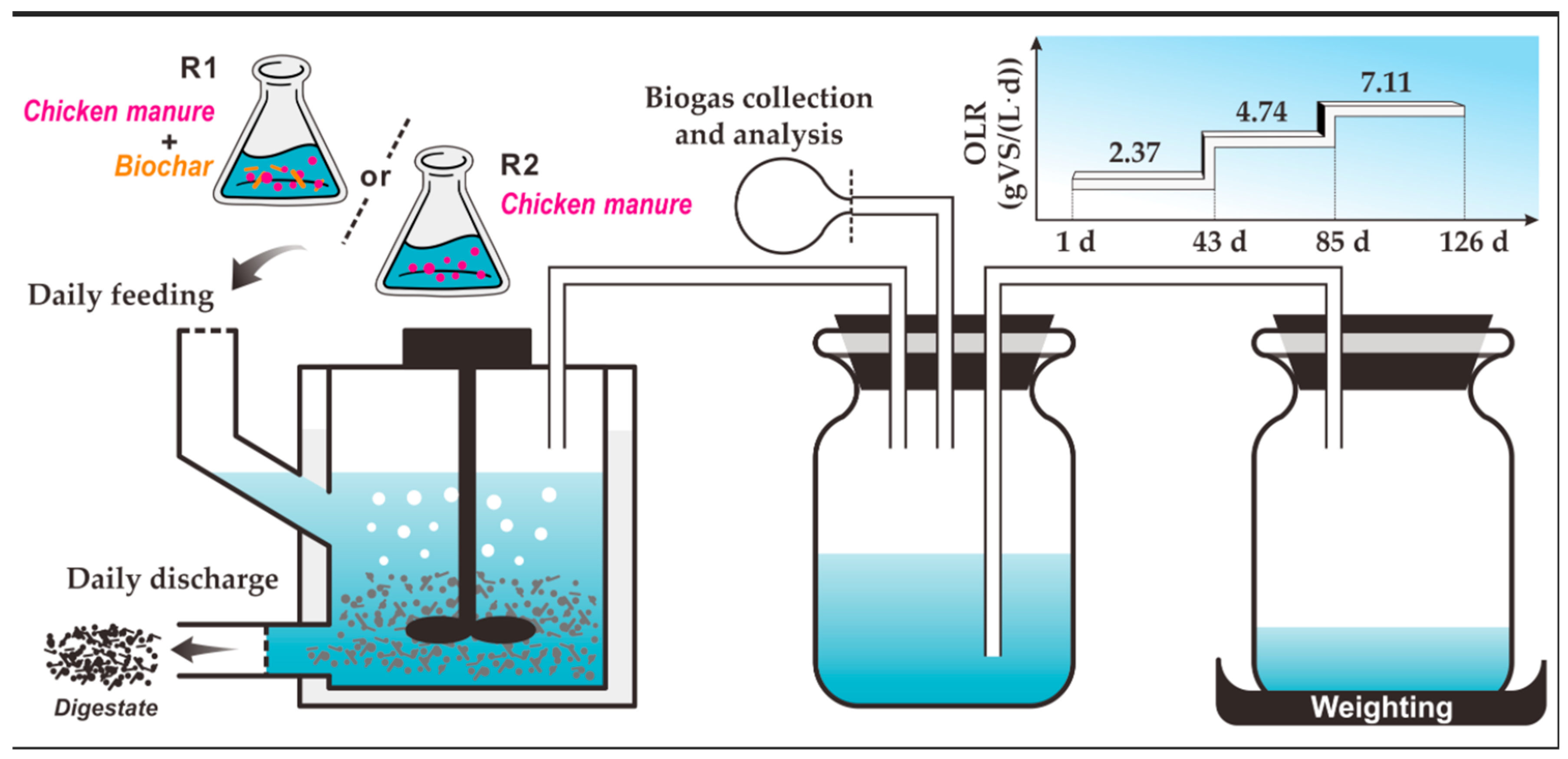
2.4. Experimental Design
2.4.1. Batch Experiment
2.4.2. Continuous Experiment
2.5. Analytical Methods and Calculations
2.5.1. Biogas Production
2.5.2. Methane Content
2.5.3. Methane Production
2.5.4. Biochar
2.5.5. CM, Inoculum, and Digestate
2.5.6. Methanogen Community Analysis
2.6. Kinetic Analysis of Methane Production
2.7. Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
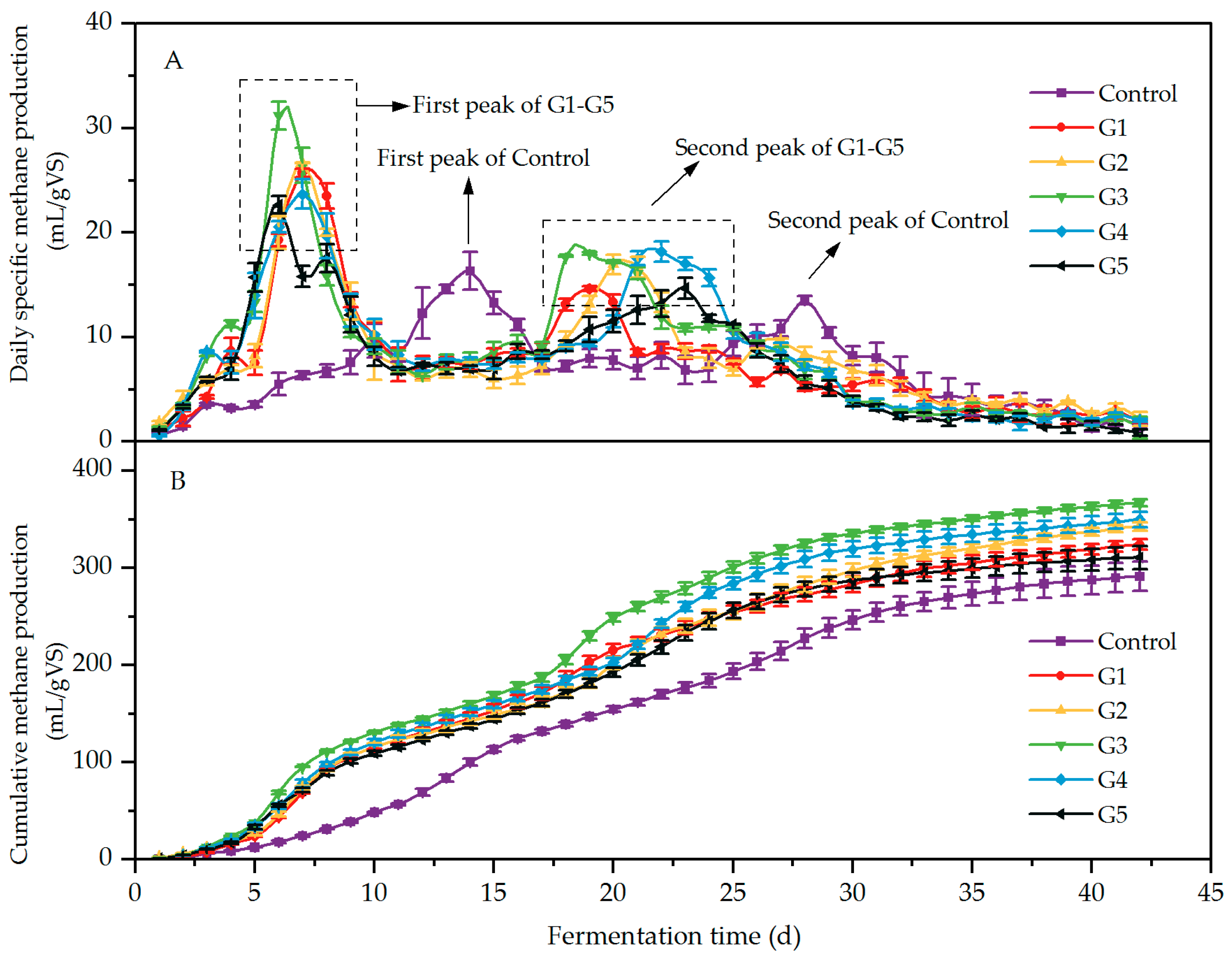
3.1. Batch Experiment
3.1.1. Effect of Different Biochar Ratios on pH, Total Ammonium Nitrogen (TAN), and Free Ammonia Nitrogen (FAN)
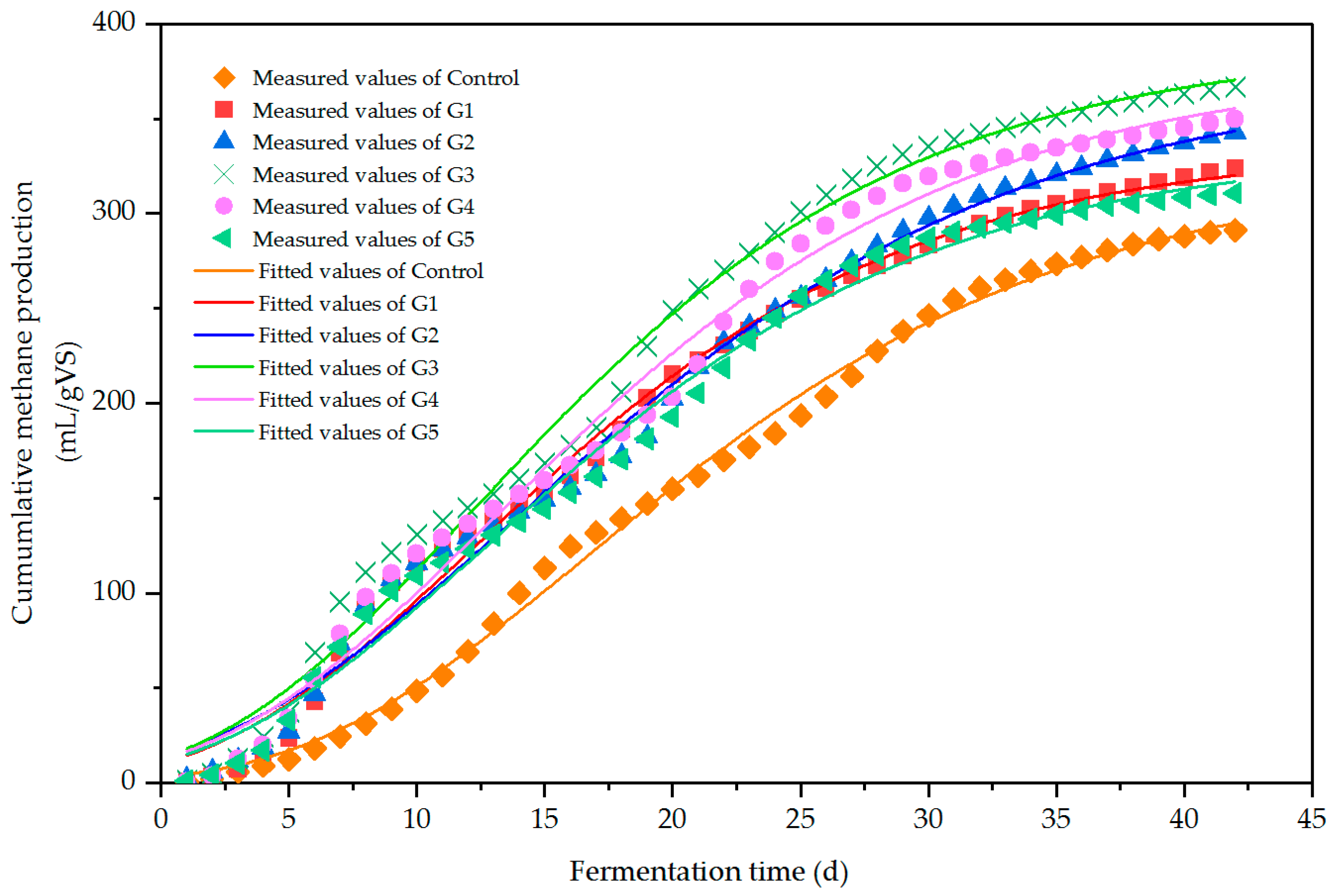
3.1.2. Effect of Different Biochar Ratios on Methane Production
3.2. Continuous Experiment
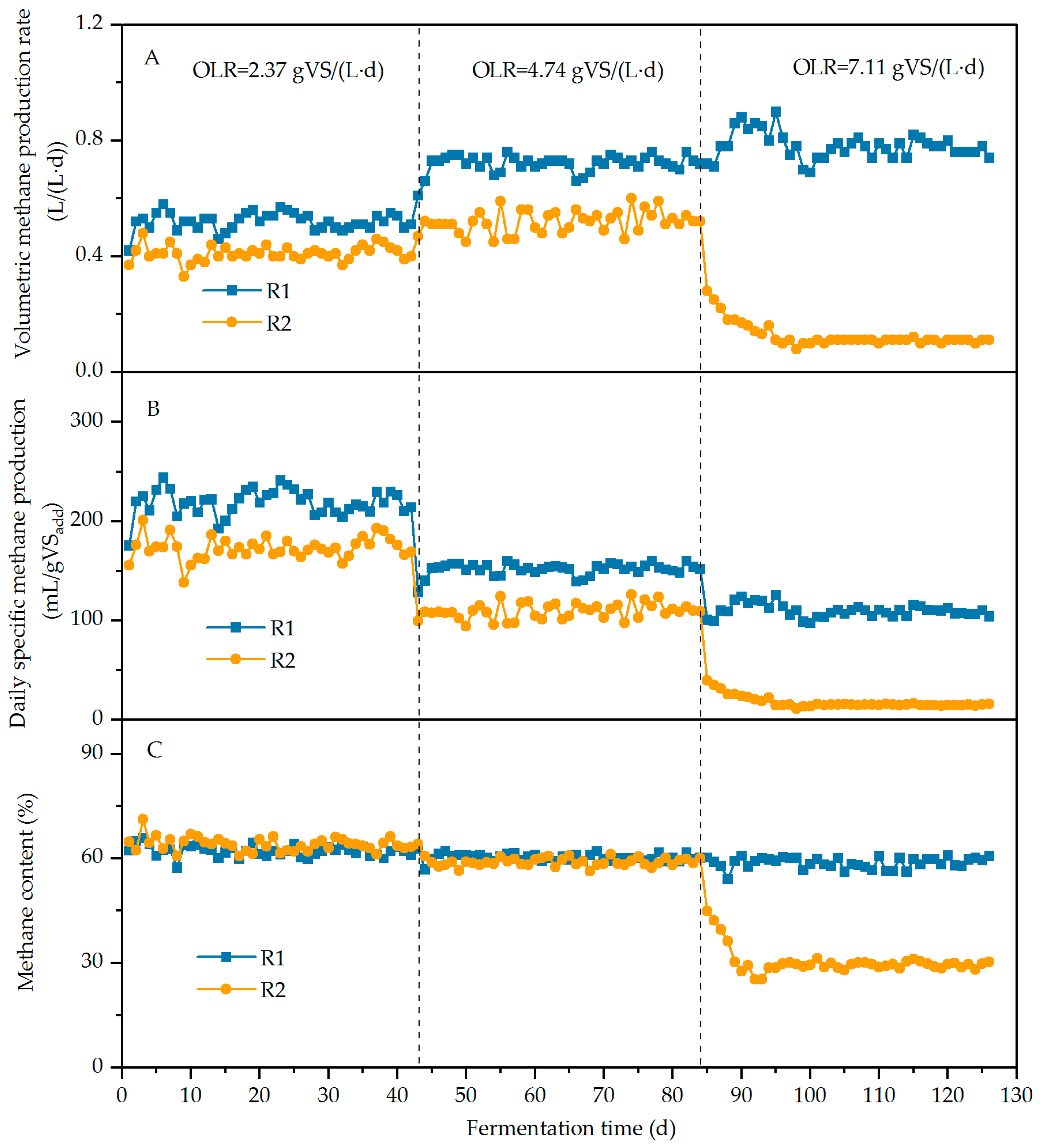
3.2.1. Methane Production
3.2.2. TAN and FAN
3.2.3. pH, VFAs, and Total Alkalinity (TA)
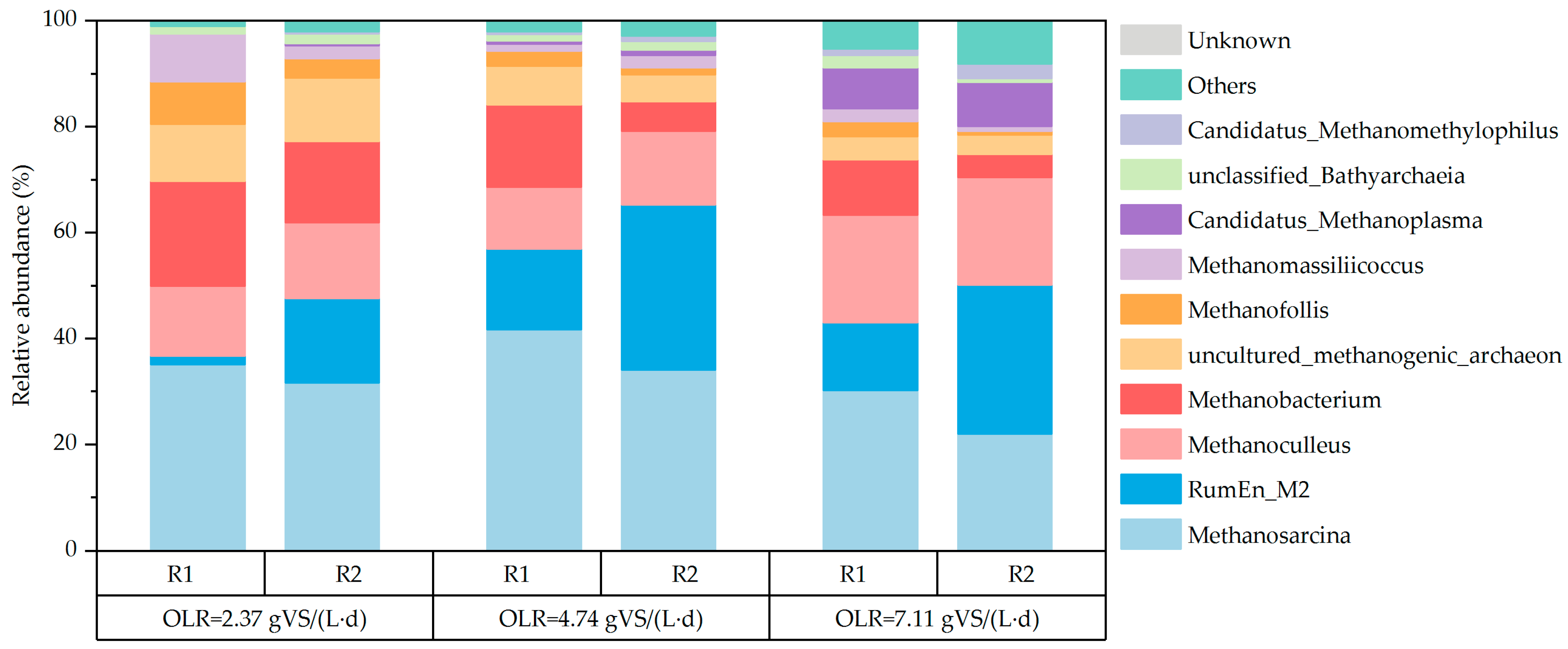
3.2.4. Microbial Community Analysis
4. Further Prospects
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ngo, T.; Khudur, L.S.; Krohn, C.; Hassan, S.; Jansriphibul, K.; Hakeem, I.G.; Shah, K.; Surapaneni, A.; Ball, A.S. Wood biochar enhances methanogenesis in the anaerobic digestion of chicken manure under ammonia inhibition conditions. Heliyon 2023, 9, e21100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Q.; Qiao, W.; Qiang, H.; Hojo, T.; Li, Y. Mesophilic methane fermentation of chicken manure at a wide range of ammonia concentration: Stability, inhibition and recovery. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 137, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.; Jacobi, H.F.; Strach, K.; Xu, C.; Zhou, H.; Liebetrau, J. Mono-fermentation of chicken manure: Ammonia inhibition and recirculation of the digestate. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 178, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazzino, F.; Frontera, P.; Malara, A.; Pedullà, A.; Calabrò, P.S. Effects of carbon-based conductive materials on semi-continuous anaerobic co-digestion of organic fraction of municipal solid waste and waste activated sludge. Chemosphere 2024, 357, 142077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; He, J.; Xin, X.; Li, L.; Zou, X.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cui, X. Characteristics of digested sludge-derived biochar for promoting methane production during anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 384, 129245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Yang, L.; Ren, Y.; Tang, C.; Zhou, A.; Liu, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, A.; He, Z. Insights into the roles and mechanisms of a green-prepared magnetic biochar in anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 896, 165170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casabella-Font, O.; Zahedi, S.; Gros, M.; Balcazar, J.; Radjenovic, J.; Pijuan, M. Graphene oxide addition to anaerobic digestion of waste activated sludge: Impact on methane production and removal of emerging contaminants. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 324, 121343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalantzis, D.; Daskaloudis, I.; Lacoere, T.; Stasinakis, A.S.; Lekkas, D.F.; VriezeJo, D.; Fountoulakis, M.S. Granular activated carbon stimulates biogas production in pilot-scale anaerobic digester treating agro-industrial wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 376, 128908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Lim, E.; Loh, K.; Ok, Y.; Lee, J.; Shen, Y.; Wang, C.; Dai, Y.; Tong, Y. Biochar enhanced thermophilic anaerobic digestion of food waste: Focusing on biochar particle size, microbial community analysis and pilot-scale application. Energy Convers. Manag. 2020, 209, 112654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, W.; He, S.; Lin, Y.; Cheng, J.; Yang, C. Functional biochar in enhanced anaerobic digesiton: Synthesis, performances, and mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappero, M.; Norouzi, O.; Hu, M.; Demichelis, F.; Berruti, F.; Di Maria, F.; Mašek, O.; Fiore, S. Review of biochar role as additive in anaerobic digestion processes. Renew. Sust. Energy Rev. 2020, 131, 110037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Ma, J.; Liu, X.; Zhai, L.; Ouyang, X.; Liu, H. Effects of different types of biochar on the anaerobic digestion of chicken manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, L.; Wang, F.; Li, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, D.; Yi, W.; Shen, X. Influence of nano-Fe3O4 biochar on the methanation pathway during anaerobic digestion of chicken manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 377, 128979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, T.; Khudur, L.; Hassan, S.; Jansriphibul, K.; Ball, A.S. Enhancing microbial viability with biochar for increased methane production during the anaerobic digestion of chicken manure. Fuel 2024, 368, 131603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunyoto, N.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, D. Effect of biochar addition on hydrogen and methane production in two-phase anaerobic digestion of aqueous carbohydrates food waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 219, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, N.; Wang, T.; Chen, S.; Hu, Q.; Cheng, X.; Sun, D.; Vupputuri, S.; Qiu, B.; Liu, H. Conductive polyaniline hydrogel enhanced methane production from anaerobic wastewater treatment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 581, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Linville, J.; Urgun-Demirtas, M.; Schoene, R.; Snyder, S. Producing pipeline-quality biomethane via anaerobic digestion of sludge amended with corn stover biochar with in-situ CO2 removal. Appl. Energy 2015, 158, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Effect and Mechanism of Different Organic Amendments on Soil Aggregates and Splash Erosion. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Xianyang, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, J.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shi, X.; Wang, X.; Li, Y. Enhancement of Fermentation Performance in the Anaerobic Co-Digestion of Chicken Manure and Corn Straw under Biogas Slurry Reflux via Air Stripping of the Digestate. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdoba, V.; Fernández, M.; Santalla, E. The effect of substrate/inoculum ratio on the kinetics of methane production in swine wastewater anaerobic digestion. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 21308–21317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Qiu, L.; Guo, X. Combined effects of liquid digestate recirculation and biochar on methane yield, enzyme activity, and microbial community during semi-continuous anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 364, 128042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, J.; Achinas, S.; Zhang, Z.; Krooneman, J.; Willem, G. The biomethanation of cow manure in a continuous anaerobic digester can be boosted via a bioaugmentation culture containing Bathyarchaeota. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 141042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Li, Z.; Feng, J.; Zhao, L.; Yu, J. Effects of digestate recirculation ratios on biogas production and methane yield of continuous dry anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 316, 123963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; Tang, Y.; Shi, X.; Anwar, S.; Wang, J.; Gao, L.; Zhang, J. Impact of varying mass concentrations of ammonia nitrogen on biogas production and system stability of anaerobic fermentation. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y. Detection Technology of Biogas Fermentation; Metallurgical Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- APHA. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association and Water Environment Federation: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; McAdam, E.; Zhang, Y.; Heaven, S.; Banks, C.; Longhurst, P. Ammonia inhibition and toxicity in anaerobic digestion: A critical review. J. Water Process. Eng. 2019, 32, 100899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yellezuome, D.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, R. Mitigation of ammonia inhibition in anaerobic digestion of nitrogen-rich substrates for biogas production by ammonia stripping: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 157, 112043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, T.V.; Keesman, K.J.; Zeeman, G.; Van Lier, J.B. Effect of ammonia on the anaerobic hydrolysis of cellulose and tributyrin. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 47, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, L.; Ho, G. Mitigating ammonia inhibition of thermophilic anaerobic treatment of digested piggery wastewater: Use of pH reduction, zeolite, biomass and humic acid. Water Res. 2012, 46, 4339–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Qiao, W.; Qiang, H.; Li, Y. Microbial community shifts and biogas conversion computation during steady, inhibited and recovered stages of thermophilic methane fermentation on chicken manure with a wide variation of ammonia. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 146, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Ni, P.; Li, J.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.; Luo, H.; Dach, J.; Dong, R. Integrated approach to sustain biogas production in anaerobic digestion of chicken manure under recycled utilization of liquid digestate: Dynamics of ammonium accumulation and mitigation control. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 205, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagbohungbe, M.; Herbert, B.; Hurst, L.; Li, H.; Usmani, S.; Semple, K. Impact of biochar on the anaerobic digestion of citrus peel waste. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Ma, J.; Qiu, L.; Guo, X.; Gao, T. The performance of biochar-mediated anaerobic digestion of chicken manure. China Environ. Sci. 2016, 36, 2716–2721. [Google Scholar]
- Kizito, S.; Jiagwe, J.; Mdondo, S.W.; Nagawa, C.B.; Bah, H.; Tumutegyereize, P. Synergetic effects of biochar addition on mesophilic and high total solids anaerobic digestion of chicken manure. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 315, 115192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, Q.; Gao, X.; Wang, X. Synergetic promotion of syntrophic methane production from anaerobic digestion of complex organic wastes by biochar: Performance and associated mechanisms. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 812–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, W.; Li, L.; Tang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Yang, P.; Peng, X.; Zhen, F. Biochar and modified magnetic biochar enhanced anaerobic digestion of swine wastewater under ammonia stress: Performance and microbial dynamics. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 111969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Zhang, J.; Chulu, B.; Yang, M.; Nopens, I.; Wei, Y. Ammonia stress decreased biomarker genes of acetoclastic methanogenesis and second peak of production rates during anaerobic digestion of swine manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 317, 124012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akindele, A.A.; Sartaj, M. The toxicity effects of ammonia on anaerobic digestion of organic fraction of municipal solid waste. Waste Manag. 2018, 71, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Cheng, J.; Creamer, K. Inhibition of anaerobic digestion process: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4044–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Liu, S.; Mi, L.; Li, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Yan, Z.; Liu, X. Effects of feedstock ratio and organic loading rate on the anaerobic mesophilic co-digestion of rice straw and cow manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 189, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelidaki, I.; Ahring, B.K. Thermophilic anaerobic-digestion of livestock waste-the effect of ammonia. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1993, 38, 560–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Liu, X.; Chen, C.; Xiao, X.; Feng, L.; He, Y.; Liu, G. Evaluating methane production from anaerobic mono- and co-digestion of kitchen waste, corn stover, and chicken manure. Energy Fuels 2013, 27, 2085–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AJohnravindar, D.; Wong, J.W.C.; Chakraboty, D.; Bodedla, G.; Kaur, G. Food waste and sewage sludge co-digestion amended with different biochars: VFA kinetics, methane yield and digestate quality assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 290, 112457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnürer, A.; Nordberg, Å. Ammonia, a selective agent for methane production by syntrophic acetate oxidation at mesophilic temperature. Water Sci. Technol. 2008, 57, 735–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, D.; Wen, H.; Feng, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, X. Screening of early warming indicators of instability in anaerobic digestion of vegetable waste under mesophilic condition. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 225–230. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Qiao, F.; Fan, J.; Bai, D.; Xu, G. Effect of Thermal Hydrolysis Pretreatment on Anaerobic Digestion of Protein-Rich Biowaste: Process Performance and Microbial Community Structures Shift. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 9, 805078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faisal, S.; Almutairi, A.; Saif, I.; Ting, L.; Wang, Q.; Mustafa, A.; Ebaid, R. Seaweed valorization as anaerobic co-substrate with fat, oil, and grease: Biomethane potential and microbial dynamics. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 421, 132155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Yin, L.; Jin, W.; Cheng, Y.; Zhu, W. Progress of Methanomassiliicoccales in the rumen. Acta Microbiol. Sin. 2020, 60, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- DeVrieze, J.; Arends, J.; Verbeeck, K.; Gildemyn, S.; Rabaey, K. Interfacing anaerobic digestion with (bio)electrochemical systems: Potentials and challenges. Water Res. 2018, 146, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Hou, Z.; Liang, B.; Wang, L.; Zhou, L.; Shou, L.; Lin, D.; Yang, S.; et al. Long-Term cultivation and meta-omics reveal methylotrophic methanogenesis in hydrocarbon-impacted habitats. Engineering 2023, 24, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conrad, R. Importance of hydrogenotrophic, aceticlastic and methylotrophic methanogenesis for methane production in terrestrial, aquatic and other anoxic environments: A mini review. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnravindar, D.; Kaur, G.; Liang, J.; Lou, L.; Zhao, J.; Manu, M.K.; Kumar, R.; Varjani, S.; Wong, J. Impact of total solids content on biochar amended co-digestion of food waste and sludge: Microbial community dynamics, methane production and digestate quality assessment. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 361, 127682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassani, I.; Kougias, P.G.; Treu, L.; Angelidaki, I. Biogas upgrading via hydrogenotrophic methanogenesis in two-stage continuous stirred tank reactors at mesophilic and thermophilic conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12585–12593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.; Zhang, J.; Wei, Y.; Shen, P. Effects of ferric oxide on the microbial community and functioning during anaerobic digestion of swine manure. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 287, 121393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, H.; Wu, J.; Chen, C.; Ding, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Y. Rethinking the biochar impact on the anaerobic digestion of food waste in bench-scale digester: Spatial distribution and biogas production. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 420, 132115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Materials | pH | TS/% | VS/% | TOC/% | TN/% | C/N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chicken manure | 7.73 ± 0.02 | 25.84 ± 0.23 | 16.41 ± 0.38 | 29.64 ± 0.31 | 2.41 ± 0.07 | 12.30 |
| Inoculum | 7.66 ± 0.04 | 7.85 ± 0.51 | 3.56 ± 0.27 | ND | ND | ND |
| pH | EC /(ms/cm) | C/% | H/% | O/% | N/% | S/% | TOC /% | AC/% | SSA /(m2/g) | APD /nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.35 ± 0.04 | 0.42 ± 0.03 | 71.31 ± 0.83 | 2.09 ± 0.02 | 21.24 ± 0.03 | 0.38 ± 0.03 | 0.02 ± 0.002 | 19.57 ± 0.11 | 4.96 ± 0.09 | 187 ± 9.12 | 3.27 ± 0.09 |
| Digester | HRT/d | Biochar Addition | OLR/g VS/(L·d) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1~42 d | 43~84 d | 85~126 d | |||
| R1 | 21 | Y | 2.37 | 4.74 | 7.11 |
| R2 | 21 | N | 2.37 | 4.74 | 7.11 |
| Treatment | G1 | G2 | G3 | G4 | G5 | Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Y0/mL/g VS | 335.49 | 374.66 | 389.45 | 378.85 | 335.26 | 324.78 |
| Rmax/mL/(g VS·d) | 12.64 | 11.94 | 14.39 | 13.22 | 12.03 | 11.04 |
| r/d | 2.40 | 2.26 | 2.22 | 2.47 | 2.36 | 5.86 |
| R 2 | 0.992 | 0.991 | 0.990 | 0.989 | 0.990 | 0.997 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Tang, Y.; Li, Y. Biochar Enhanced Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure by Mitigating Ammonium Inhibition and Improving Methane Production. Fermentation 2025, 11, 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11100549
Zhu J, Meng Q, Zhang X, Zhang X, Tang Y, Li Y. Biochar Enhanced Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure by Mitigating Ammonium Inhibition and Improving Methane Production. Fermentation. 2025; 11(10):549. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11100549
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Jiaoning, Qiyuzhou Meng, Xiaoyuan Zhang, Xiaochen Zhang, Yun Tang, and Yongping Li. 2025. "Biochar Enhanced Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure by Mitigating Ammonium Inhibition and Improving Methane Production" Fermentation 11, no. 10: 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11100549
APA StyleZhu, J., Meng, Q., Zhang, X., Zhang, X., Tang, Y., & Li, Y. (2025). Biochar Enhanced Anaerobic Digestion of Chicken Manure by Mitigating Ammonium Inhibition and Improving Methane Production. Fermentation, 11(10), 549. https://doi.org/10.3390/fermentation11100549





