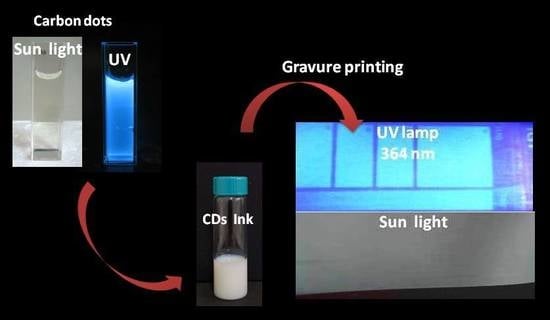
Fluorescent Carbon Dots Ink for Gravure Printing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Gravure Ink
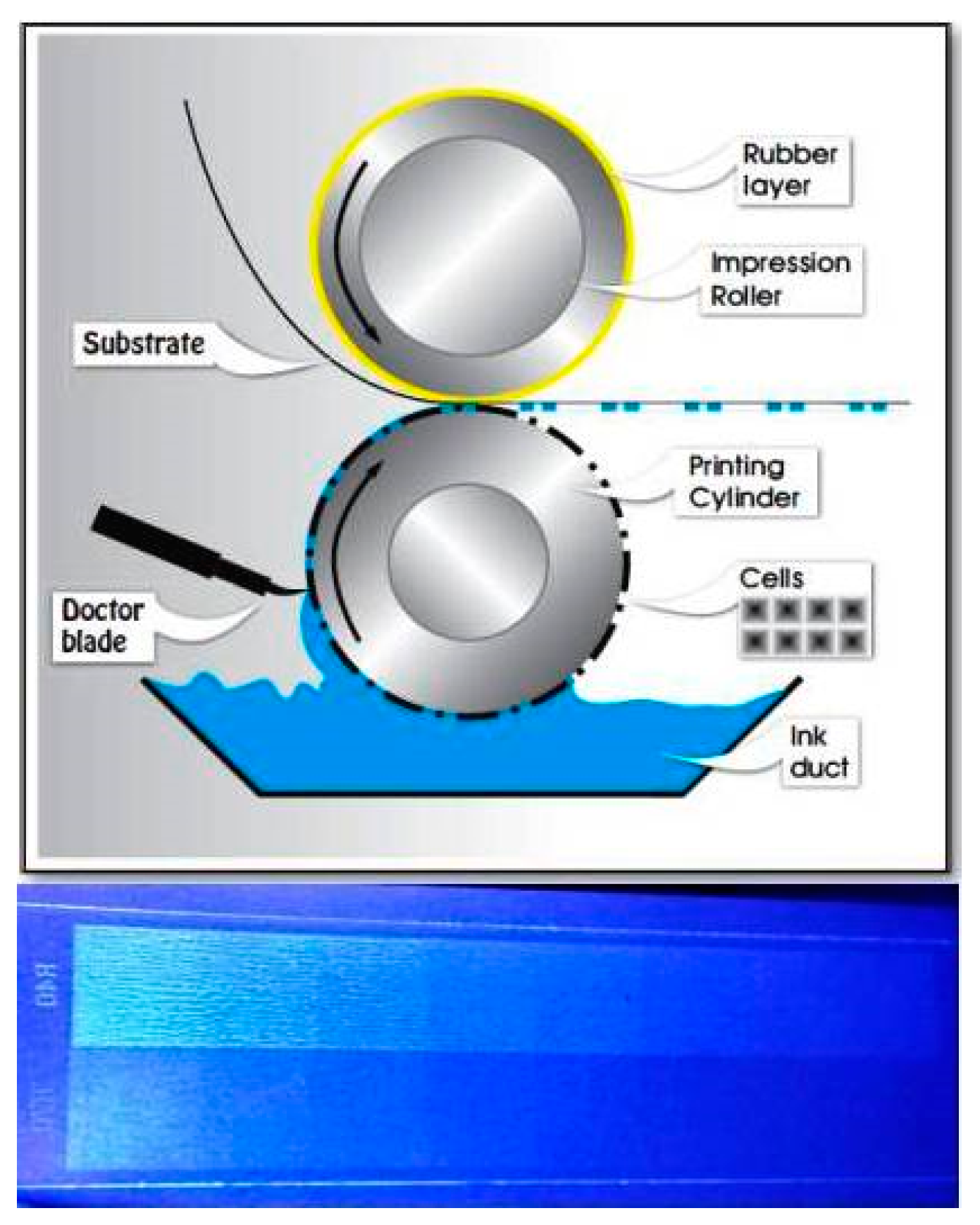
2.3. Gravure Printing
2.4. Instrumentation
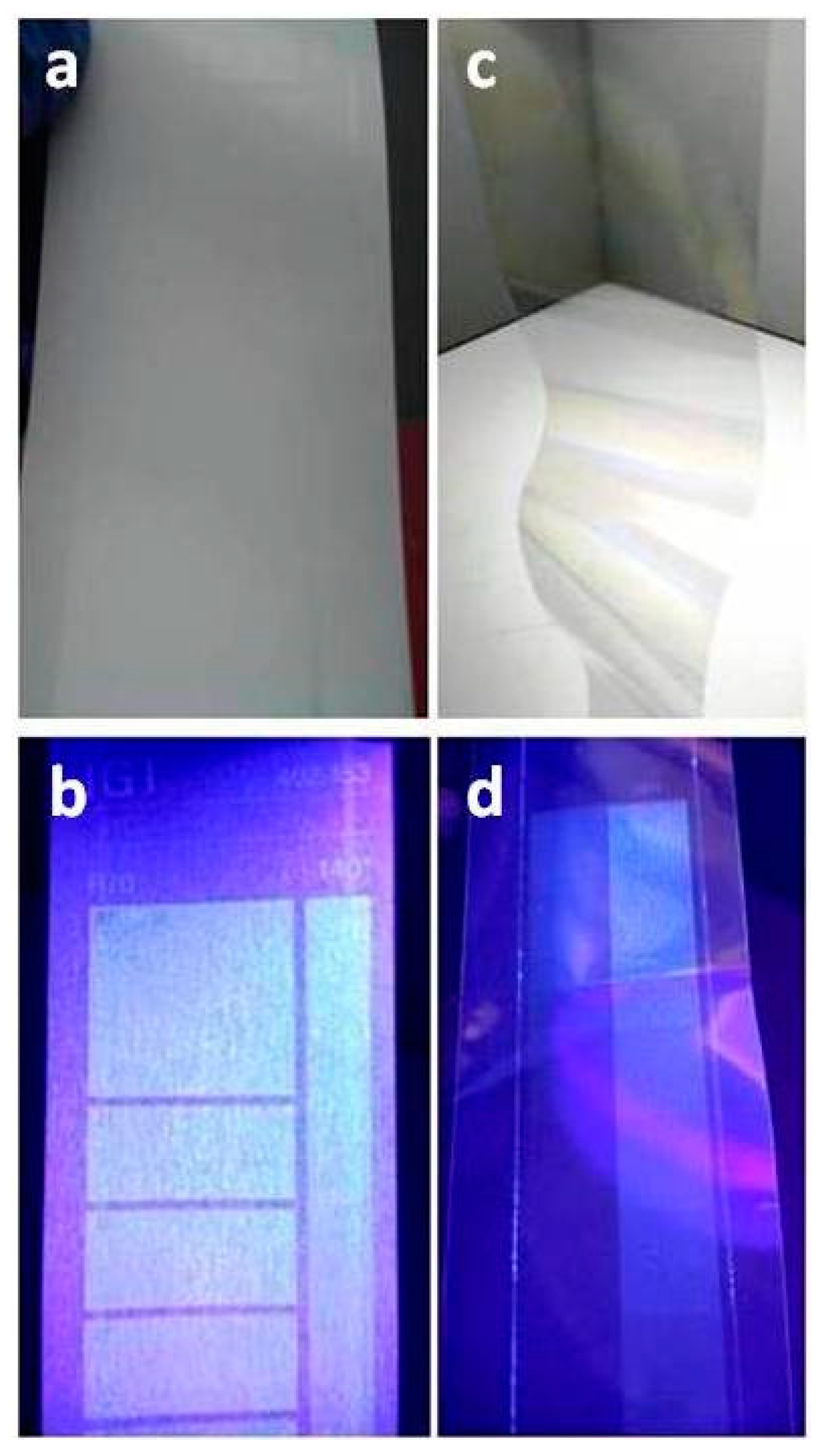
2.5. Adhesion of Ink on Polymeric Substrates
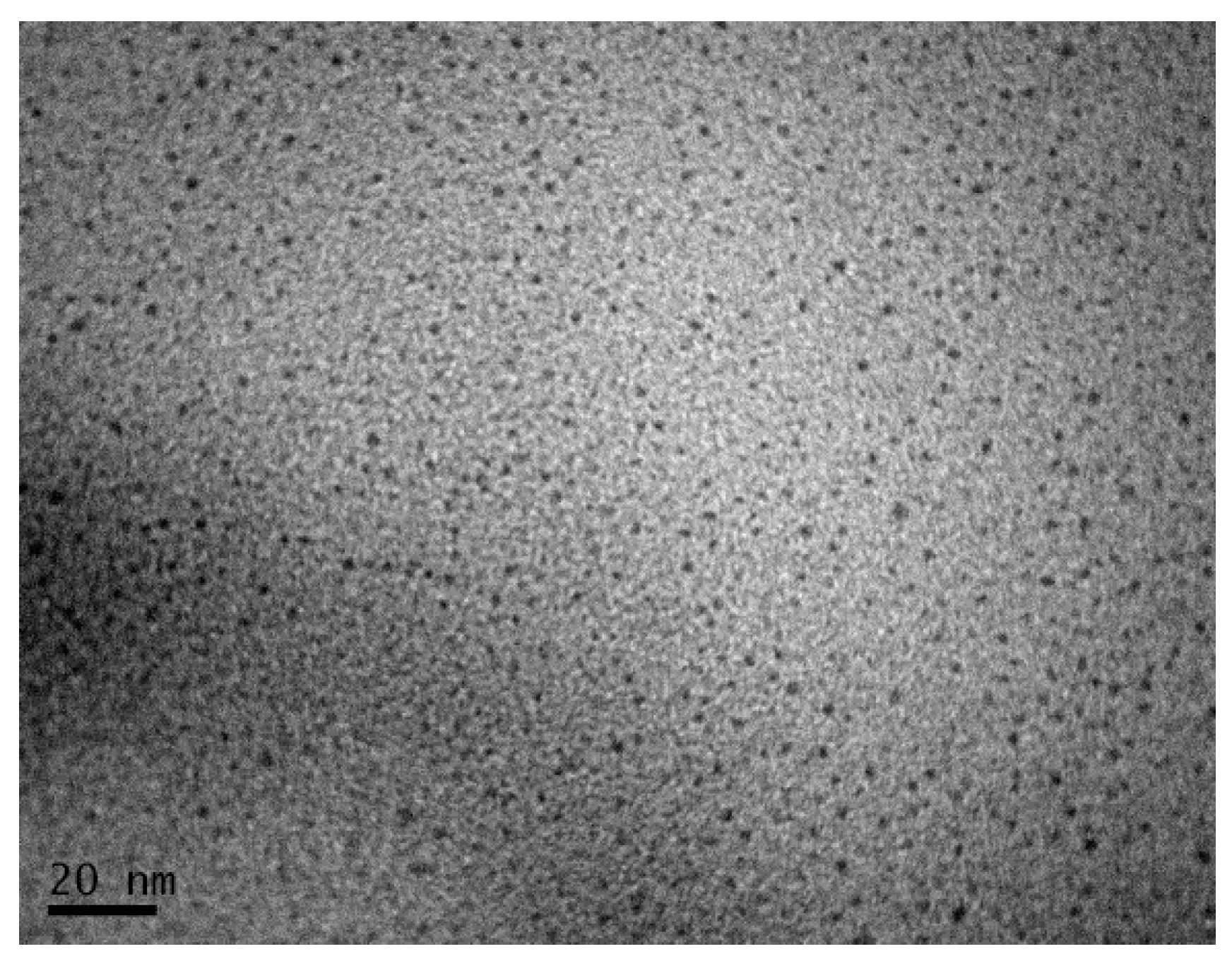
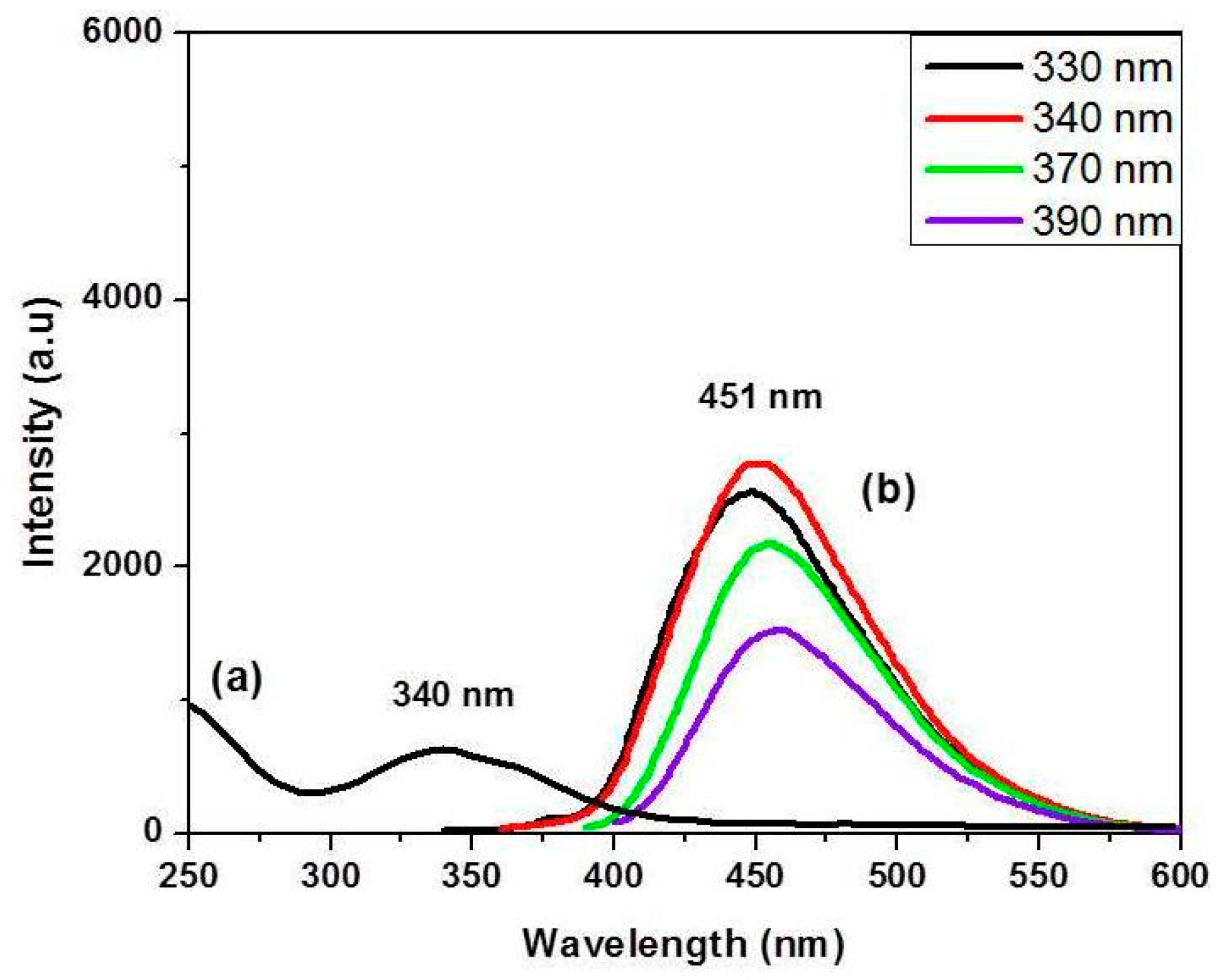
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ying, L.S.; Shen, W.; Gao, Z. Carbon quantum dots and their applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 362–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgakilas, V.; Perman, J.A.; Tucek, J.; Zboril, R. Broad family of carbon nanoallotropes: Classification, chemistry, and applications of fullerenes, carbon dots, nanotubes, graphene, nanodiamonds, and combined superstructures. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4744–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, A.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, C.; Gao, N.; Ren, J.; Qu, X. Recent advances in bioapplications of C-dots. Carbon 2015, 85, 309–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, V.; Patil, A.; Thakur, S.; Kesharwani, P. Carbon dots: Emerging theranostic nanoarchitectures. Drug Discov. Today 2018, 23, 1219–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.L.; Liu, Z.X.; Yuan, Y.H. Carbon dots: Materials, synthesis, properties and approaches to long-wavelength and multicolor emission. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 3794–3809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Zhu, S.; Lu, S.; Song, Y.; Feng, T.; Tao, S.; Liu, J.; Yang, B. Recent progress on the photocatalysis of carbon dots: Classification, mechanism and applications. Nano Today 2018, 19, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabaev, T. Doped carbon dots for sensing and bioimaging applications: A minireview. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourlinos, A.B.; Stassinopoulos, A.; Anglos, D.; Zboril, R.; Georgakilas, V.; Giannelis, E.P. Photoluminescent carbogenic dots. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 4539–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsioukis, A.; Akouros, A.; Zboril, R.; Georgakilas, V. Solid phase extraction for the purification of violet, blue, green and yellow emitted Carbon dots. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 11293–11296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Hu, Q.; Paau, M.C.; Zhang, Y.; Shuang, S.; Dong, C.; Choi, M.M. Red-green-blue fluorescent hollow carbon nanoparticles isolated from chromatographic fractions for cellular imaging. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 8162–8170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Li, Y.; Deng, R.; Zhang, H. Highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots with excellent thermal and photo stability applied as invisible ink for loading important information and anti-counterfeiting. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sk, M.P.; Chattopadhyay, A. Induction coil heater prepared highly fluorescent carbon dots as invisible ink and explosive sensor. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 31994–31999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Kang, J.; Ng, L.W.; Zhu, X.; Howe, R.C.; Jones, C.G.; Hersham, M.C.; Hasan, T. Functional inks and printing of two-dimensional materials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 3265–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Wang, C. Graphene and the related conductive inks for flexible electronics. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 7193–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Lee, J.; Seong, B.; Jang, H.S.; Byun, D. Printing Conductive Micro-Web Structures via Capillary Transport of Elastomeric Ink for Highly Stretchable Strain Sensors. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 3, 1700228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaccorso, F.; Bartolotta, A.; Coleman, J.N.; Backes, C. 2D-Crystal-Based Functional Inks. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 6136–6166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsioukis, A.; Georgakilas, V.; Belessi, V.; Zboril, R. Highly Conductive Water-Based Polymer/Graphene Nanocomposites for Printed Electronics. Chemistry 2017, 23, 8268–8274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiannidis, P.G.; Hodge, S.A.; Lombardi, L.; Tomarchio, F.; Decorde, N.; Milana, S.; Leary, R.K.; Midgley, P.A.; Pugno, N.M.; Torrisi, F.; et al. Microfluidization of graphite and formulation of graphene-based conductive inks. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 2742–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Sun, H. Novel properties and applications of carbon nanodots. Nanoscale Horizons 2018, 3, 565–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalytchuk, S.; Wang, Y.; Poláková, K.; Zboril, R. Carbon Dot Fluorescence-Lifetime-Encoded Anti-Counterfeiting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 29902–29908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Meng, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y.; Jin, H.; Zhang, K.; Yang, B.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; et al. Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 4045–4049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yu, S.H. Carbon dots: Large-scale synthesis, sensing and bioimaging. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, B.; Liu, Y.; Yang, W.; Liu, C.Y. Down-and up-conversion luminescent carbon dot fluid: Inkjet printing and gel glass fabrication. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 3818–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.F.; Cheng, R.; Ji, W.Q.; Ma, K.; Ling, L.; Chen, S. Recognition of Latent Fingerprints and Ink-Free Printing Derived from Interfacial Segregation of Carbon Dots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 39205–39213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yao, W.; Liu, J.; Tian, Q.; Liu, L.; Ding, J.; Xue, Q.; Lu, Q.; Wu, W. Facile synthesis and screen printing of dual-mode luminescent NaYF 4: Er, Yb (Tm)/carbon dots for anti-counterfeiting applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 6512–6520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.S.; Wang, C.F.; Li, C.X.; Wang, J.; Mao, L.H.; Chen, S. Hair-derived carbon dots toward versatile multidimensional fluorescent materials. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 6477–6483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipphan, H. (Ed.) Handbook of Print Media—Technologies and Production Methods, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001; pp. 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Kahn, B.E. Patterning Processes for Flexible Electronics. Proc. IEEE 2015, 103, 497–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilakopoulou, A.; Georgakilas, V.; Koutselas, I. Encapsulation and protection of carbon dots within MCM-41 material. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 82, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassilakopoulou, A.; Georgakilas, V.; Vainos, N.; Koutselas, I. Successful entrapment of carbon dots within flexible free-standing transparent mesoporous organic-inorganic silica hybrid films for photonic applications. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2017, 103, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, I.; Mihić, J.; Radić Seleš, V.; Vuksanović, A. Analysis of Samples Treated by Resistance Test Method Exposed to Accelerated Aging. Acta Graph. 2015, 26, 23–30. [Google Scholar]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koutsioukis, A.; Belessi, V.; Georgakilas, V. Fluorescent Carbon Dots Ink for Gravure Printing. C 2019, 5, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/c5010012
Koutsioukis A, Belessi V, Georgakilas V. Fluorescent Carbon Dots Ink for Gravure Printing. C. 2019; 5(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/c5010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoutsioukis, Apostolos, Vassiliki Belessi, and Vasilios Georgakilas. 2019. "Fluorescent Carbon Dots Ink for Gravure Printing" C 5, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/c5010012
APA StyleKoutsioukis, A., Belessi, V., & Georgakilas, V. (2019). Fluorescent Carbon Dots Ink for Gravure Printing. C, 5(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/c5010012