Mechanism of Fluorescence Characteristics and Application of Zinc-Doped Carbon Dots Synthesized by Using Zinc Citrate Complexes as Precursors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Animals
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Synthesis of Zinc-Doped CDs
2.2.2. Yield and Zinc Content
2.2.3. Physiochemical Characterization of Zinc-Doped CDs
2.2.4. Acute Toxicity of Zinc-Doped CDs
2.2.5. Applications of Zinc-Doped CDs
2.2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Yields and Zinc Contents of TC-Zn, Zn@C-210, and Zn@C-260
3.2. Characterization of TC-Zn, Zn@C-210, and Zn@C-260
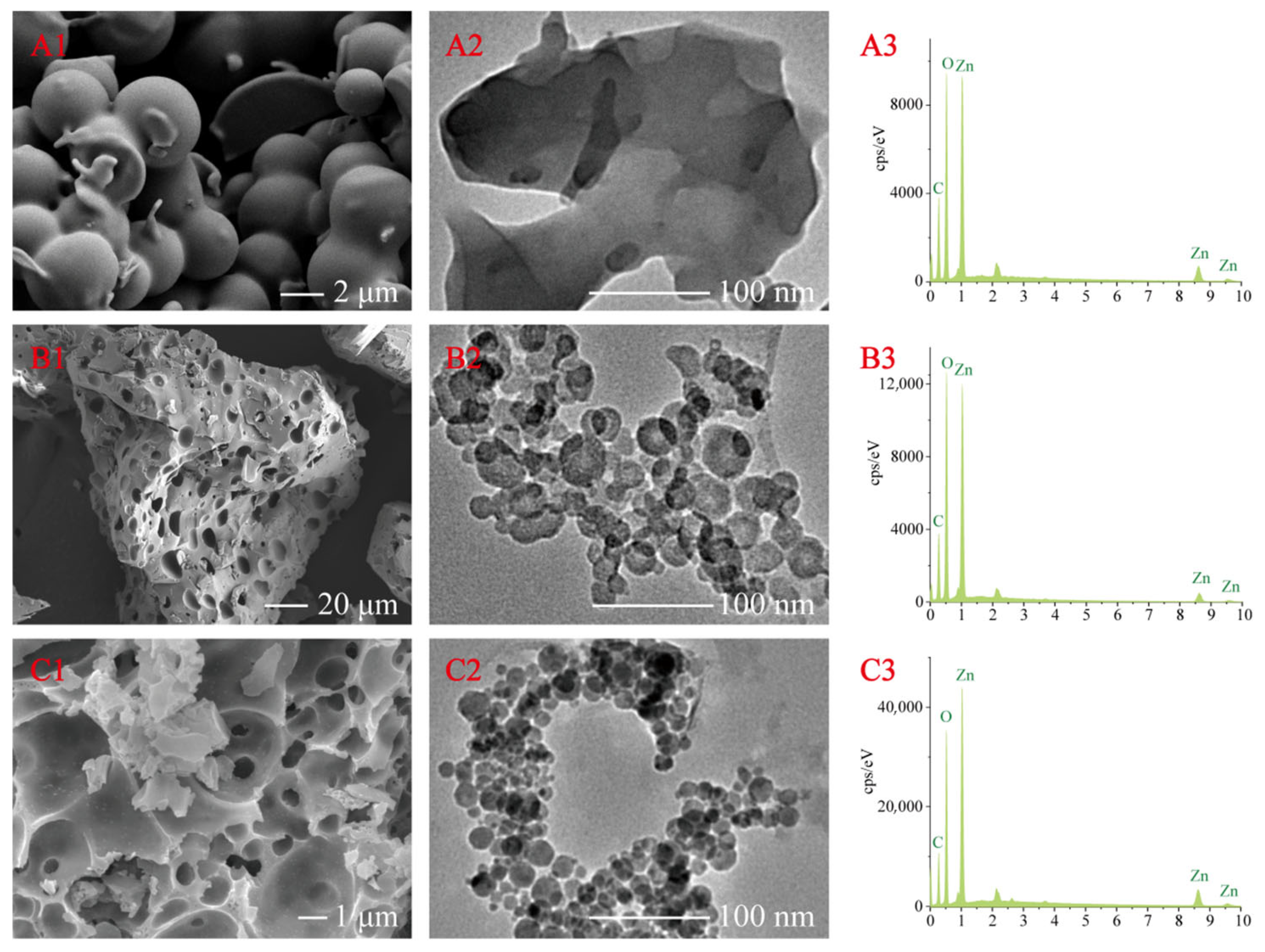
3.2.1. Morphology by SEM and TEM
3.2.2. FT-IR
3.2.3. XRD
3.2.4. XPS
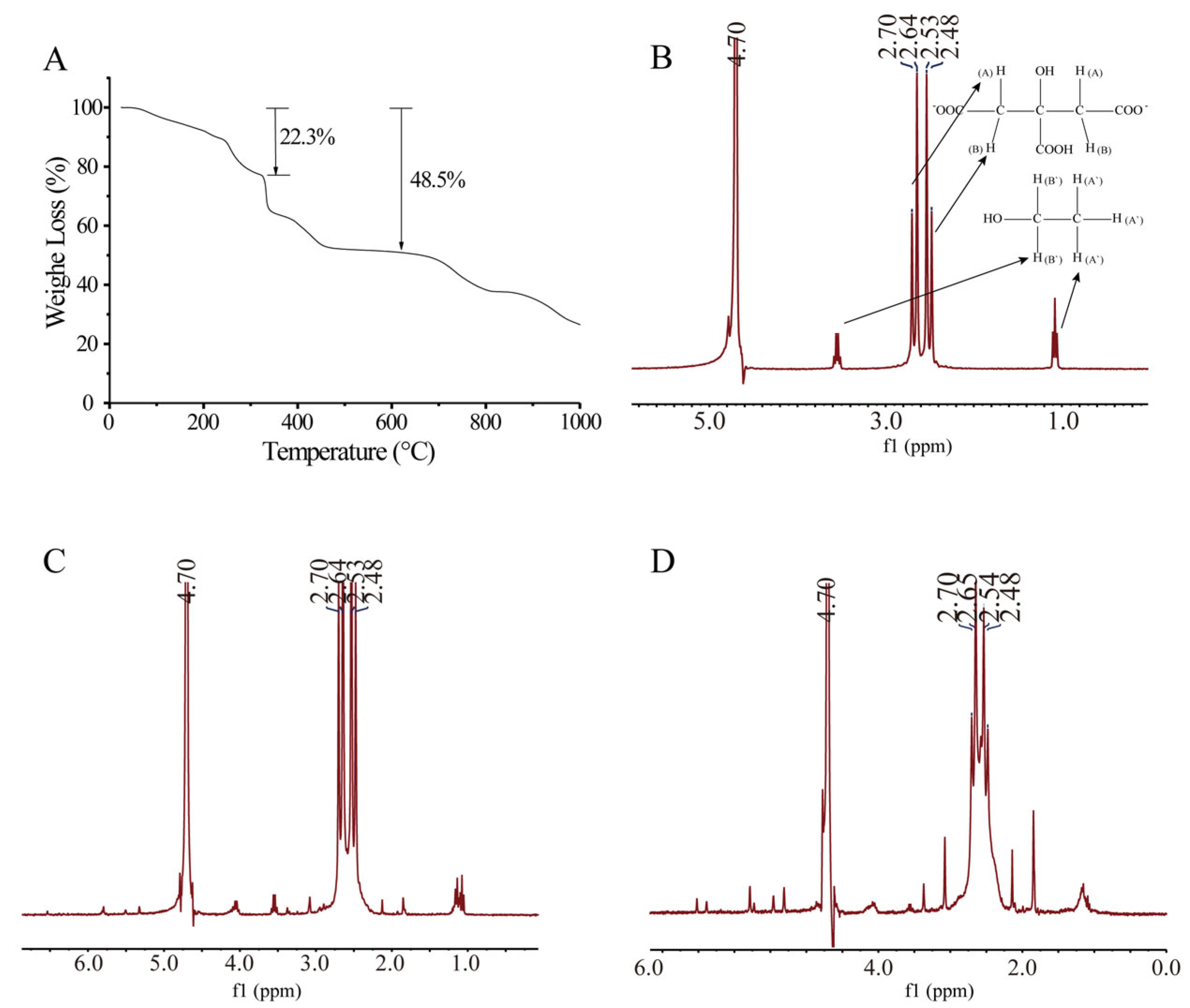
3.2.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.2.6. 1H NMR Analysis
3.3. Formation of Zn@C-210 and Zn@C-260
3.4. Fluorescence Analysis
3.4.1. Temperature Effects
3.4.2. Excitation Wavelength Effects
3.4.3. pH Effects
3.4.4. Anion Solution Effects
3.4.5. Stability of CDs
3.4.6. Fluorescence Lifetime
3.5. Mechanism of Fluorescence
3.6. Acute Toxicity
3.7. Applications of Zn@C-210 and Zn@C-260
3.7.1. Fluorescence Labeling by Zn@C-210
3.7.2. Detection of Folic Acid by Zn@C-260
3.7.3. Biological Imaging by Zn@C-260
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sen, S.; Bose, A. Carbon dots: A review of innovations, applications, challenges, and future prospects. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2025, 173, 113852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.J.; Kim, J.; Park, C.B. Photonic carbon dots as an emerging nanoagent for biomedical and healthcare applications. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 4005–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, K.; Ge, J.; Wang, P. Emerging metal doped carbon dots for promising theranostic applications. Biomed. Mater. 2022, 17, 065001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejwan, N.; Saini, A.K.; Sharma, A.; Singh, T.A.; Kumar, N.; Das, J. Metal-doped and hybrid carbon dots: A comprehensive review on their synthesis and biomedical applications. J. Control. Release 2021, 330, 132–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Tang, B.; Wang, L.; Bao, H.; Lu, Y.; Guan, C.; Zhang, L.; Le, M.; Liu, Z.; Wu, M. Machine learning driven synthesis of carbon dots with enhanced quantum yields. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 1475–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Q.; He, M.; Liao, X.; Wan, Q.; Zhan, W.; Kong, L.; Li, L. A novel strategy to enhance the photostability of InP/ZnSe/ZnS quantum dots with Zr doping. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Huang, J.; Ruan, Y.; Li, H.; Gong, P.; Wang, F.; Tang, Q.; Jiang, Y. Unraveling the structure transition and peroxidase mimic activity of copper sites over atomically dispersed copper-doped carbonized polymer dots. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202214042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, S.; Xiao, J.; Lan, M.; Wang, B.; Zhang, K.; Song, X.; Zeng, L. Metal ions-doped carbon dots: Synthesis, properties, and applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 430, 133101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Tu, H.; Feng, J.; Fan, X.; Mi, Z.; Han, H.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Z. Bismuth/manganese-doped carbon dots in calcium phosphate matrix: Dynamic conformational nanoparticles enhancing tumor accumulation, deep penetration, and radiosensitivity. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 504, 158683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, M.A.A.; Elagamy, S.H.; Gamal, A.; Mansour, F.R. Eco-friendly cobalt-doped carbon quantum dots for spectrofluorometric determination of pregabalin in pharmaceutical capsules. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2024, 248, 116270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, R.; He, P.; Qin, F.; Ma, J.; Xu, C.; Qin, L.; Gao, W. Light on multi-mode optical properties of carbon dots through rational surface engineering tuning strategies. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 484, 149459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Shen, Z.; Shi, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Lei, B. Carbon dots-mediated plant adaptive responses to abiotic stress. Mater. Res. Bull. 2025, 182, 113137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yang, Q.; Liu, X.; Jiang, F.; Xiong, J.; Jiang, P.; Liu, Y. Zn-doped Cu2S quantum dots as new high-efficiency inhibitors against human insulin fibrillation based on specific electrostatic interaction with oligomers. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 179, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashritha, K.S.S.; Rufuss, D.D.W. Carbon quantum dots for sustainable water treatment: A critical review on synthesis, properties, challenges and applications in forward osmosis desalination technologies. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 514, 163059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Cai, W.; Zhang, M.; Su, R.; Ye, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Y.; Yu, Z.; Li, S.; et al. Photoluminescence mechanism and applications of Zn-doped carbon dots. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 17254–17262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, M.; Xie, B.; Li, B.; Huang, H. Zn-doped carbon dots-based versatile bioanalytical probe for precise estimation of antioxidant activity index of multiple samples via fenton chemistry. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 363, 131558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolekar, A.G.; Nille, O.S.; Koparde, S.V.; Patil, A.S.; Waghmare, R.D.; Sohn, D.; Anbhule, P.V. Green, facial zinc doped hydrothermal synthesis of cinnamon derived fluorescent carbon dots (Zn-Cn-CDs) for highly selective and sensitive Cr6+ and Mn7+ metal ion sensing application. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2024, 304, 123413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gao, X.; Pan, Y.G.; Xu, N.; Jia, L. Toxicology and immunology of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides in Kunming mice and Wistar rats. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 85, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Gao, J.; Zheng, Y. Confined synthesis of phosphorus, nitrogen co-doped carbon dots with green luminescence and anion recognition performance. Polyhedron 2019, 171, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Khan, M.Z.H.; Ma, F.; Liu, X. A novel zinc complex with antibacterial and antioxidant activity. BMC Chem. 2021, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Hu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhong, X.; He, Z.; Geng, Z.; Gan, S. Demystifying the Influence of Precursor Structure on S-Doped Hard Carbon Anode: Taking Glucose, Carbon Dots, and Carbon Fibers as Examples. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2403648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, R.; Kamiya, Y.; Wahyuningsih, T.D.; Kartini, I. Tailoring plastic bag derived carbon dots by sulfur-nitrogen passivation for highly selective Fe (III) ion sensing. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2025, 175, 114187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Xie, X.; Shi, Q.; Feng, J.; Zhang, D.; Huang, X. Nitrogen/sulfur-doped dual-emission carbon dots with tunable fluorescence for ratiometric sensing of ferric ions and cell membrane imaging. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 572, 151447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, A.; Batool, M.; Akram, S.; Malik, A.H.; Khanday, W.A.; Wani, W.A.; Sheikh, R.A. Functionalized Graphene Quantum Dots (FGQDs): A review of their synthesis, properties, and emerging biomedical applications. Carbon Trends 2025, 18, 100442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, T.; Khan, R.; Ghosh, A.; Hussien, M.; Kumar, Y.A.; Reddy, N.P.; Moniruzzaman, M. Sustainable carbon electrode materials from biomass for redox flow batteries. Biomass Bioenergy 2025, 198, 107846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, N.S.; Fernandez, M.J.F.; Balanay, M.P. Upcycling biomass waste into luminescent solid-state carbon dots. Next Mater. 2024, 3, 100155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Xu, S.; Miao, Y.; Xu, N.; Wang, H.; Song, X.; Gao, L.; Xiao, G. A highly active and stable Zn@C/HZSM-5 catalyst using Zn@C derived from ZIF-8 as a template for conversion of glycerol to aromatics. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 739–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Xu, S.; Miao, Y.; Xu, N.; Wang, H.; Song, X.; Gao, L.; Xiao, G. Biologically active dual functional zinc-doped biomass-derived carbon dots. RSC Sustain. 2024, 2, 3114–3122. [Google Scholar]
- Mazrad, Z.A.I.; Kang, E.B.; Nuraeni; Lee, G.; In, I.; Park, S.Y. Temperature-sensitive carbon dots derived from poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) for fluorescence on-off properties. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 11149–11157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, H.K.; Parab, D. Green synthesis of carbon quantum dots and applications: An insight. Next Mater. 2025, 8, 100527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozyurt, D.; Al Kobaisi, M.; Hocking, R.K.; Fox, B. Properties, synthesis, and applications of carbon dots: A review. Carbon Trends 2023, 12, 100276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammina, S.K.; Wan, Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Yang, Y. Synthesis of N, Zn-doped carbon dots for the detection of Fe3+ ions and bactericidal activity against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2020, 202, 111734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, G.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Xie, A.; Dong, W. Dramatic red fluorescence enhancement and emission red shift of carbon dots following Zn/ZnO decoration. Luminescence 2019, 34, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Yu, S.; Wei, J.; Xiong, H. Full-Color Light-Emitting Carbon Dots with a Surface-State-Controlled Luminescence Mechanism. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; Ganguly, S.; Bose, M.; Mondal, S.; Choudhary, S.; Gangopadhyay, S.; Das, A.K.; Banerjee, S.; Das, N.C. Zinc and nitrogen ornamented bluish white luminescent carbon dots for engrossing bacteriostatic activity and Fenton based bio-sensor. Mat. Sci. Eng. C Mater. 2018, 88, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, R.; Xing, X.; Yang, C.; Xu, Y.; Wu, D. Correction: Highly photoluminescent nitrogen-rich carbon dots from melamine and citric acid for the selective detection of iron(iii) ion. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 16257–16265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaisare, M.L.; Talib, A.; Khan, M.S.; Pandey, S.; Wu, H. Synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots via microwave carbonization of citric acid in presence of tetraoctylammonium ion, and their application to cellular bioimaging. Microchim. Acta 2015, 182, 2173–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ma, C.; Ma, J.; Guo, W. Promoting potential direct interspecies electron transfer (DIET) and methanogenesis with nitrogen and zinc doped carbon quantum dots. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 410, 124886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, F.S.; Razavi, Z.S.; Shahsavari, H. Advanced synthesis and biomedical applications of colloidal quantum dots: Innovations in Imaging, drug delivery, and theranostics. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2025, 178, 114533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Chowdhury, P. Tunable dual photoluminescence from synthesized urea-based carbon quantum dots: A DFT based simulation on structural insights. Opt. Mater. 2024, 153, 115617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, X.; Ma, M. Preparation and performance study of dye-based carbon quantum dots. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 150, 110541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbarlou, S.; Kahforoushan, D.; Abdollahi, H.; Zarrintaj, P.; Alomar, A.; Villanueva, C.; Davachi, S.M. Advances in quantum dot-based fluorescence sensors for environmental and biomedical detection. Talanta 2025, 294, 128176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quang, N.K.; Hieu, N.N.; Bao, V.V.Q.; Phuoc, V.T.; Ngoc, L.X.D.; Doc, L.Q.; Tri, N.M.; Son, L.V.T. Hydrothermal synthesis of carbon nanodots from waste wine cork and their use in biocompatible fluorescence imaging. New Carbon Mater. 2022, 37, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arul, E.; Chandrasekaran, P.; Sivaraman, G.; Sethuraman, M.G. Biogenic preparation of undoped and heteroatoms doped carbon dots: Effect of heteroatoms doping in fluorescence, catalytic ability and multicolour in-vitro bio-imaging applications–A comparative study. Mater. Res. Bull. 2023, 162, 112204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promcharoen, P.; Chumkaeo, P.; Charoenchaidet, S.; Somsook, E. PET-derived heteroatom-doped carbon quantum dots as color-modulated solid-state fluorescent materials. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 14420–14427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Abbas, A.; Qamar, T.H.; Hassan, S.U.; Jamali, S.B.; Deng, L. Highly efficient, ultralong-lifetime, phosphorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots via multi-confinement for anticounterfeiting applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1013, 178586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Samples | Yield | Zinc Content | -C=C-/-C–C- | -C–O- | -C=O- |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 284.8 eV | 286.4 eV | 288.5 eV | |||
| TC-Zn | 53.15 ± 0.15 | 15.58 ± 0.08 | 43.67 | 22.19 | 34.14 |
| Zn@C-210 | 42.58 ± 0.06 | 18.73 ± 0.12 | 52.26 | 13.44 | 34.30 |
| Zn@C-260 | 40.31 ± 0.06 | 19.22 ± 0.03 | 50.56 | 13.73 | 35.71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Sun, K.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Zhu, J.; Khan, M.Z.H. Mechanism of Fluorescence Characteristics and Application of Zinc-Doped Carbon Dots Synthesized by Using Zinc Citrate Complexes as Precursors. C 2025, 11, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/c11030048
Zhang Y, Guo Y, Sun K, Li X, Liu X, Zhu J, Khan MZH. Mechanism of Fluorescence Characteristics and Application of Zinc-Doped Carbon Dots Synthesized by Using Zinc Citrate Complexes as Precursors. C. 2025; 11(3):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/c11030048
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yun, Yiwen Guo, Kaibo Sun, Xiaojing Li, Xiuhua Liu, Jinhua Zhu, and Md. Zaved Hossain Khan. 2025. "Mechanism of Fluorescence Characteristics and Application of Zinc-Doped Carbon Dots Synthesized by Using Zinc Citrate Complexes as Precursors" C 11, no. 3: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/c11030048
APA StyleZhang, Y., Guo, Y., Sun, K., Li, X., Liu, X., Zhu, J., & Khan, M. Z. H. (2025). Mechanism of Fluorescence Characteristics and Application of Zinc-Doped Carbon Dots Synthesized by Using Zinc Citrate Complexes as Precursors. C, 11(3), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/c11030048







