Structural Modifications and Novel Protein-Binding Sites in Pre-miR-675—Explaining Its Regulatory Mechanism in Carcinogenesis
Abstract
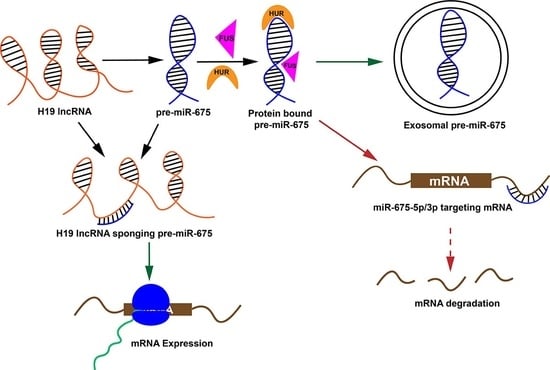
1. Introduction
2. Results
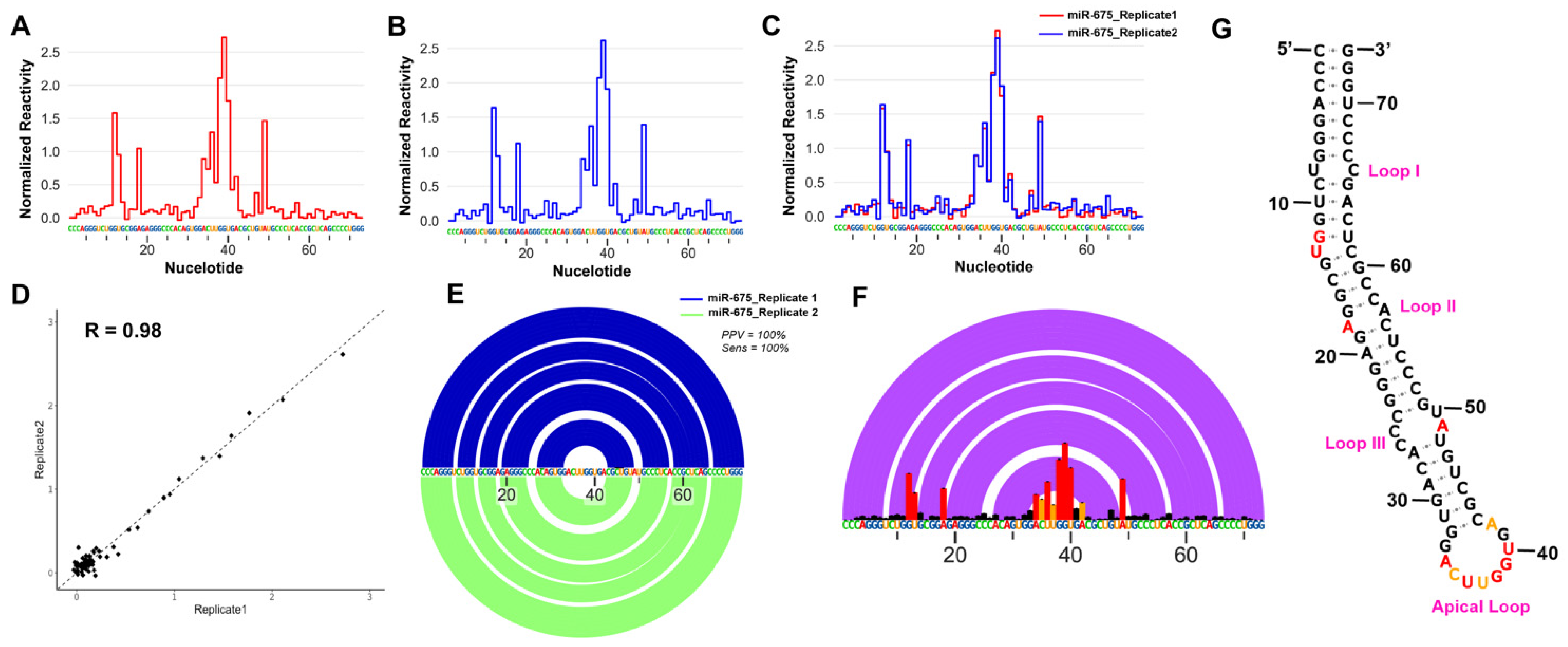
2.1. Secondary Structure of Pre-miR-675 Represents Canonical Stem Loop Helical Conformation
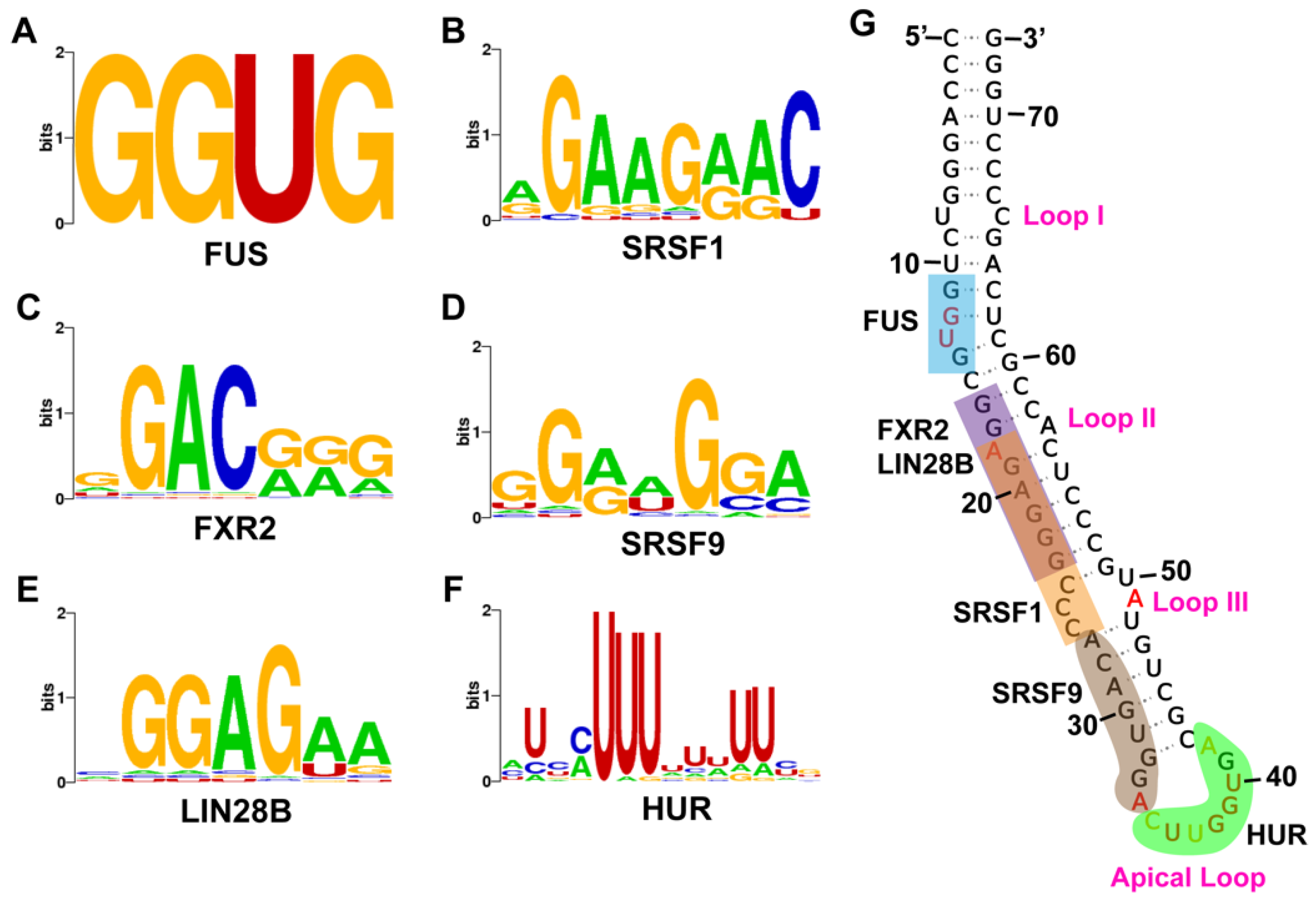
2.2. Pre-miR-675 Acts as a Hotspot for Many RNA-Binding Protein
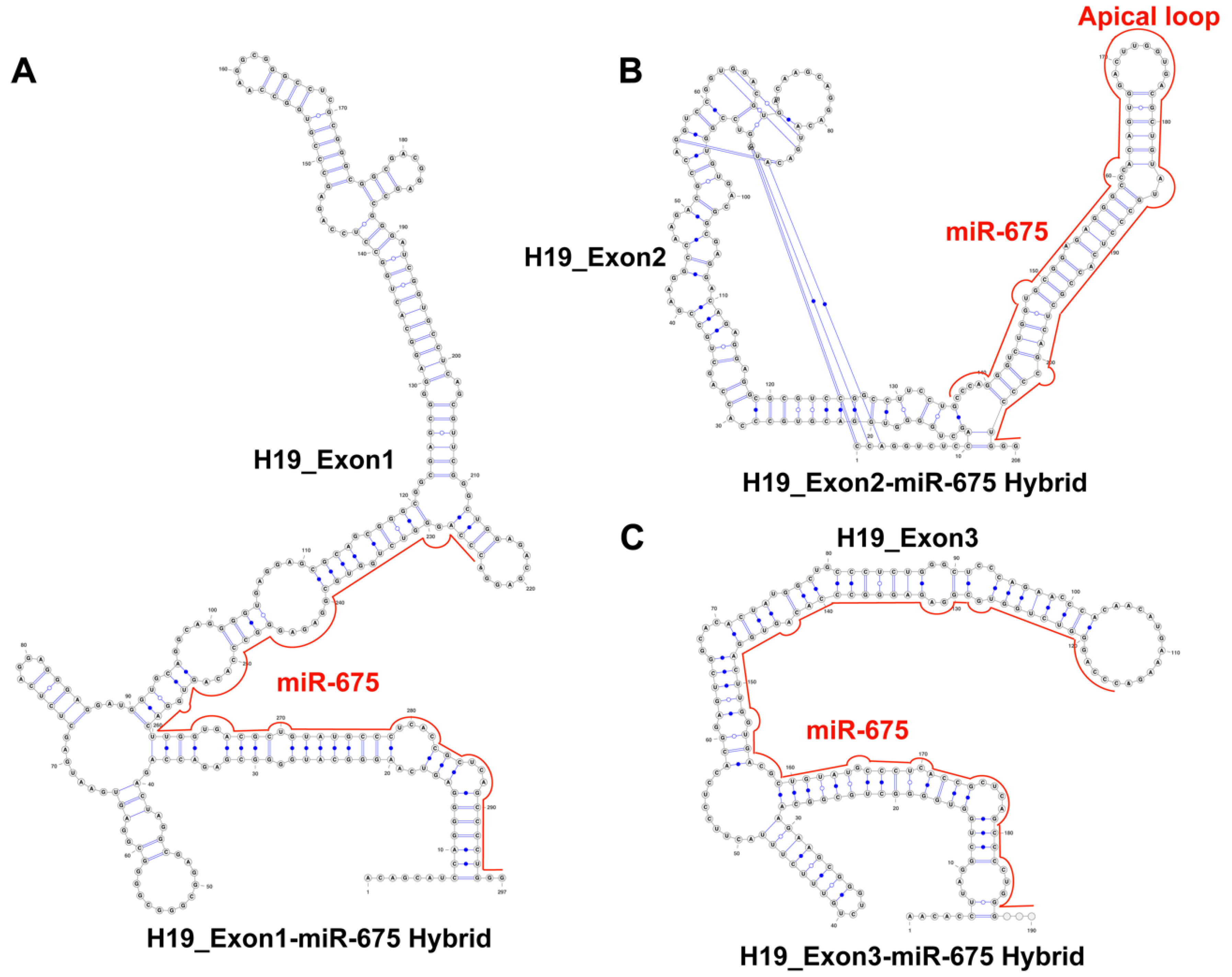
2.3. H19 Long Noncoding RNA (lncRNA) Sequester Pre-miR-675 by Modifying Its Conformation
3. Discussion and Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Pre-miR-675 Conformation Analysis Using Selective 2′ Hydroxyl Acylation Analysed by Primer Extension (SHAPE) Assay
4.2. Identification of Protein-Binding Sites on Pre-miR-675
4.3. RNA Co-Fold Analysis
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
This Article Bears NIPER-R Communication Number
References
- Yang, J.; Qi, M.; Fei, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, K. LncRNA H19: A novel oncogene in multiple cancers. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 3188–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.C.; Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.H. Comprehensive upstream and downstream regulatory analyses identify miR-675-3p as a potential prognostic biomarker in melanoma. Hum. Cell 2021, 34, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, J.M.; Elahi, A.; Clark, C.W.; Wang, J.; Humphries, L.A.; Centeno, B.; Bloom, G.; Fuchs, B.C.; Yeatman, T.; Shibata, D. miR-675 mediates downregulation of Twist1 and Rb in AFP-secreting hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20 (Suppl. S3), S625–S635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Lou, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Huang, W. miR-675 promotes colorectal cancer cell growth dependent on tumor suppressor DMTF1. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Q.; Chen, T.; Wu, Y.; Wu, W.; Xu, Y.; Gong, Z.; Chen, S. MicroRNA-675-3p promotes esophageal squamous cell cancer cell migration and invasion. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 3631–3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, B.K.; Pfeifer, K.; Dutta, A. The H19 long noncoding RNA gives rise to microRNAs miR-675-3p and miR-675-5p to promote skeletal muscle differentiation and regeneration. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 491–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Shao, W.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Du, D. Diagnostic and Prognostic Significance of miR-675-3p in Patients With Atherosclerosis. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2021, 27, 10760296211024754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funahashi, Y.; Yoshino, Y.; Iga, J.I.; Ueno, S.I. Impact of clozapine on the expression of miR-675-3p in plasma exosomes derived from patients with schizophrenia. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2023, 24, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freed, W.J.; Chen, J.; Bäckman, C.M.; Schwartz, C.M.; Vazin, T.; Cai, J.; Spivak, C.E.; Lupica, C.R.; Rao, M.S.; Zeng, X. Gene expression profile of neuronal progenitor cells derived from hESCs: Activation of chromosome 11p15.5 and comparison to human dopaminergic neurons. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Bao, H.-L.; Dong, L.-X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.-W.; An, F.-M. Silenced lncRNA H19 and up-regulated microRNA-129 accelerates viability and restrains apoptosis of PC12 cells induced by Aβ. Cell Cycle 2021, 20, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, V.; Oliveira-Ferrer, L.; Steinbach, B.; Pantel, K.; Schwarzenbach, H. Interplay of lncRNA H19/miR-675 and lncRNA NEAT1/miR-204 in breast cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saieva, L.; Barreca, M.M.; Zichittella, C.; Prado, M.G.; Tripodi, M.; Alessandro, R.; Conigliaro, A. Hypoxia-Induced miR-675-5p Supports β-Catenin Nuclear Localization by Regulating GSK3-β Activity in Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vennin, C.; Spruyt, N.; Dahmani, F.; Julien, S.; Bertucci, F.; Finetti, P.; Chassat, T.; Bourette, R.P.; Le Bourhis, X.; Adriaenssens, E. H19 non coding RNA-derived miR-675 enhances tumorigenesis and metastasis of breast cancer cells by downregulating c-Cbl and Cbl-b. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 29209–29223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harari-Steinfeld, R.; Gefen, M.; Simerzin, A.; Zorde-Khvalevsky, E.; Rivkin, M.; Ella, E.; Friehmann, T.; Gerlic, M.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Caruso, S.; et al. The lncRNA H19-Derived MicroRNA-675 Promotes Liver Necroptosis by Targeting FADD. Cancers 2021, 13, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Qiu, G.-R.; Zhou, F.; Gong, L.-Y.; Gao, F.; Sun, K.-L. Overexpression of DICER1 induced by the upregulation of GATA1 contributes to the proliferation and apoptosis of leukemia cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 42, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, N.; Ojima, H.; Shirakihara, T.; Shimizu, H.; Kokubu, A.; Urushidate, T.; Totoki, Y.; Kosuge, T.; Miyagawa, S.; Shibata, T. Downregulation of the microRNA biogenesis components and its association with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galgano, A.; Forrer, M.; Jaskiewicz, L.; Kanitz, A.; Zavolan, M.; Gerber, A.P. Comparative analysis of mRNA targets for human PUF-family proteins suggests extensive interaction with the miRNA regulatory system. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, W.O.; Tschöp, K.; Herr, A.; Ji, J.Y.; Dyson, N.J. Pumilio facilitates miRNA regulation of the E2F3 oncogene. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedde, M.; Van Kouwenhove, M.; Zwart, W.; Oude Vrielink, J.A.F.; Elkon, R.; Agami, R. A Pumilio-induced RNA structure switch in p27-3’ UTR controls miR-221 and miR-222 accessibility. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 1014–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Jia, S.; Wu, M.; An, J.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, W.; Lu, D. miR675 upregulates long noncoding RNA H19 through activating EGR1 in human liver cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 31958–31984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlick, T.; Zhu, Q.; Dey, A.; Jain, S.; Yan, S.; Laederach, A. To Knot or Not to Knot: Multiple Conformations of the SARS-CoV-2 Frameshifting RNA Element. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 11404–11422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathews, D.H. Using an RNA secondary structure partition function to determine confidence in base pairs predicted by free energy minimization. RNA 2004, 10, 1178–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciafrè, S.A.; Galardi, S. microRNAs and RNA-binding proteins: A complex network of interactions and reciprocal regulations in cancer. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Kim, S.; Chang, H.R.; Kim, D.; Park, J.; Son, N.; Park, J.; Yoon, M.; Chae, G.; Kim, Y.-K.; et al. The regulatory impact of RNA-binding proteins on microRNA targeting. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wu, Y.-C.; Mullane, P.; Ji, Y.J.; Liu, H.; He, L.; Arora, A.; Hwang, H.-Y.; Alessi, A.F.; Niaki, A.G.; et al. FUS Regulates Activity of MicroRNA-Mediated Gene Silencing. Mol. Cell 2018, 69, 787–801.e788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Shen, P.; Chen, Q.; Wu, P.; Yuan, H.; Ge, W.; Meng, L.; Huang, X.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; et al. FUS-induced circRHOBTB3 facilitates cell proliferation via miR-600/NACC1 mediated autophagy response in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.F.; Xu, X.; Gin, A.; Nshimiyimana, J.D.; Mooers, B.H.M.; Caputi, M.; Hannafon, B.N.; Ding, W.-Q. SRSF1 regulates exosome microRNA enrichment in human cancer cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Martin, R.; Wang, G.; Brandão, B.B.; Zanotto, T.M.; Shah, S.; Patel, S.K.; Schilling, B.; Kahn, C.R. MicroRNA sequence codes for small extracellular vesicle release and cellular retention. Nature 2022, 601, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Bao, Q.; Hu, C.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, L.; Tong, L.; Zhang, W.; Shen, Y. Exosomal miR-675 from metastatic osteosarcoma promotes cell migration and invasion by targeting CALN1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 500, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; He, J.; Feng, C.; Tu, C. Exosomal MiRNAs in Osteosarcoma: Biogenesis and Biological Functions. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 902049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galardi, A.; Colletti, M.; Di Paolo, V.; Vitullo, P.; Antonetti, L.; Russo, I.; Di Giannatale, A. Exosomal MiRNAs in Pediatric Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Shen, J.; Peng, D.; He, X.; Xu, C.; Chen, X.; Tanyi, J.L.; Montone, K.; Fan, Y.; Huang, Q.; et al. RNA-binding protein LIN28B inhibits apoptosis through regulation of the AKT2/FOXO3A/BIM axis in ovarian cancer cells. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2018, 3, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Bi, C.; Ching, Y.Q.; Chooi, J.-Y.; Lu, X.; Quah, J.Y.; Toh, S.H.-M.; Chan, Z.-L.; Tan, T.Z.; Chong, P.S.; et al. Inhibition of LIN28B impairs leukemia cell growth and metabolism in acute myeloid leukemia. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redmon, I.C.; Ardizzone, M.; Hekimoğlu, H.; Hatfield, B.M.; Waldern, J.M.; Dey, A.; A Montgomery, S.; Laederach, A.; Ramos, S.B.V. Sequence and tissue targeting specificity of ZFP36L2 reveals Elavl2 as a novel target with co-regulation potential. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2022, 50, 4068–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.Y.; Hur, J.; Jeong, S. Emerging roles of RNA and RNA-binding protein network in cancer cells. BMB Rep. 2009, 42, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Habermacher, R.; Martine, U.; Closs, E.I.; Filipowicz, W. Relief of microRNA-mediated translational repression in human cells subjected to stress. Cell 2006, 125, 1111–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epis, M.R.; Barker, A.; Giles, K.M.; Beveridge, D.J.; Leedman, P.J. The RNA-binding protein HuR opposes the repression of ERBB-2 gene expression by microRNA miR-331-3p in prostate cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 41442–41454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helsmoortel, H.H.; De Moerloose, B.; Pieters, T.; Ghazavi, F.; Bresolin, S.; Cavé, H.; de Vries, A.; de Haas, V.; Flotho, C.; Labarque, V.; et al. LIN28B is over-expressed in specific subtypes of pediatric leukemia and regulates lncRNA H19. Haematologica 2016, 101, e240–e244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keniry, A.; Oxley, D.; Monnier, P.; Kyba, M.; Dandolo, L.; Smits, G.; Reik, W. The H19 lincRNA is a developmental reservoir of miR-675 that suppresses growth and Igf1r. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, B.-C.; Yu, S.-L.; Chen, J.J.; Chang, S.-Y.; Yan, B.-S.; Hong, Q.-S.; Singh, S.; Kao, C.-L.; Chen, H.-Y.; Su, K.-Y.; et al. Enterovirus-induced miR-141 contributes to shutoff of host protein translation by targeting the translation initiation factor eIF4E. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 9, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tian, Y. miRNA for diagnosis and clinical implications of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- László, B.; Antal, L.; Gyöngyösi, E.; Szalmás, A.; Póliska, S.; Veress, G.; Kónya, J. Coordinated action of human papillomavirus type 16 E6 and E7 oncoproteins on competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network members in primary human keratinocytes. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Li, A.; Yu, B.; Li, S. Interplay between miRNAs and lncRNAs: Mode of action and biological roles in plant development and stress adaptation. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 2567–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matouk, I.J.; Halle, D.; Gilon, M.; Hochberg, A. The non-coding RNAs of the H19-IGF2 imprinted loci: A focus on biological roles and therapeutic potential in Lung Cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Tian, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Z.; Du, C.; Wang, F.; Xie, X.; Gao, H.; Zhuang, Y.; Kornmann, M.; et al. Long noncoding RNA H19 derived miR-675 regulates cell proliferation by down-regulating E2F-1 in human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J. Cancer 2018, 9, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Yan, X.; Liu, K.; Wu, M.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhong, X.; Qin, L.; Huang, C.; Wei, X. lncRNA H19 acts as a ceRNA to regulate the expression of CTGF by targeting miR-19b in polycystic ovary syndrome. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2020, 53, e9266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.; Fang, Z.; Ling, Y.; Luo, W. LncRNA-H19 acts as a ceRNA to regulate HE4 expression by sponging miR-140 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells under hyperglycemia with or without α-Mangostin. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 118, 109256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busscher, D.; Boon, R.A.; Juni, R.P. The multifaceted actions of the lncRNA H19 in cardiovascular biology and diseases. Clin. Sci. 2022, 136, 1157–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, K.A.; Merino, E.J.; Weeks, K.M. Selective 2’-hydroxyl acylation analyzed by primer extension (SHAPE): Quantitative RNA structure analysis at single nucleotide resolution. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1610–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MSmola, J.; Rice, G.M.; Busan, S.; Siegfried, N.A.; Weeks, K.M. Selective 2’-hydroxyl acylation analyzed by primer extension and mutational profiling (SHAPE-MaP) for direct, versatile and accurate RNA structure analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 1643–1669. [Google Scholar]
- Busan, S.; Weeks, K.M. Accurate detection of chemical modifications in RNA by mutational profiling (MaP) with ShapeMapper 2. RNA 2018, 24, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegfried, N.A.; Busan, S.; Rice, G.M.; Nelson, J.A.; Weeks, K.M. RNA motif discovery by SHAPE and mutational profiling (SHAPE-MaP). Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darty, K.; Denise, A.; Ponty, Y. VARNA: Interactive drawing and editing of the RNA secondary structure. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1974–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irving, P.S.; Weeks, K.M. RNAvigate: Efficient exploration of RNA chemical probing datasets. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Fang, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Shen, H.B. RBPsuite: RNA-protein binding sites prediction suite based on deep learning. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, A.R.; Lorenz, R.; Bernhart, S.H.; Neuböck, R.; Hofacker, I.L. The Vienna RNA websuite. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2008, 36, W70–W74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhart, S.H.; Tafer, H.; Mückstein, U.; Flamm, C.; Stadler, P.F.; Hofacker, I.L. Partition function and base pairing probabilities of RNA heterodimers. Algorithms Mol. Biol. 2006, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dey, A. Structural Modifications and Novel Protein-Binding Sites in Pre-miR-675—Explaining Its Regulatory Mechanism in Carcinogenesis. Non-Coding RNA 2023, 9, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9040045
Dey A. Structural Modifications and Novel Protein-Binding Sites in Pre-miR-675—Explaining Its Regulatory Mechanism in Carcinogenesis. Non-Coding RNA. 2023; 9(4):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9040045
Chicago/Turabian StyleDey, Abhishek. 2023. "Structural Modifications and Novel Protein-Binding Sites in Pre-miR-675—Explaining Its Regulatory Mechanism in Carcinogenesis" Non-Coding RNA 9, no. 4: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9040045
APA StyleDey, A. (2023). Structural Modifications and Novel Protein-Binding Sites in Pre-miR-675—Explaining Its Regulatory Mechanism in Carcinogenesis. Non-Coding RNA, 9(4), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna9040045