Navigating the Multiverse of Antisense RNAs: The Transcription- and RNA-Dependent Dimension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Transcription-Dependent Mechanisms
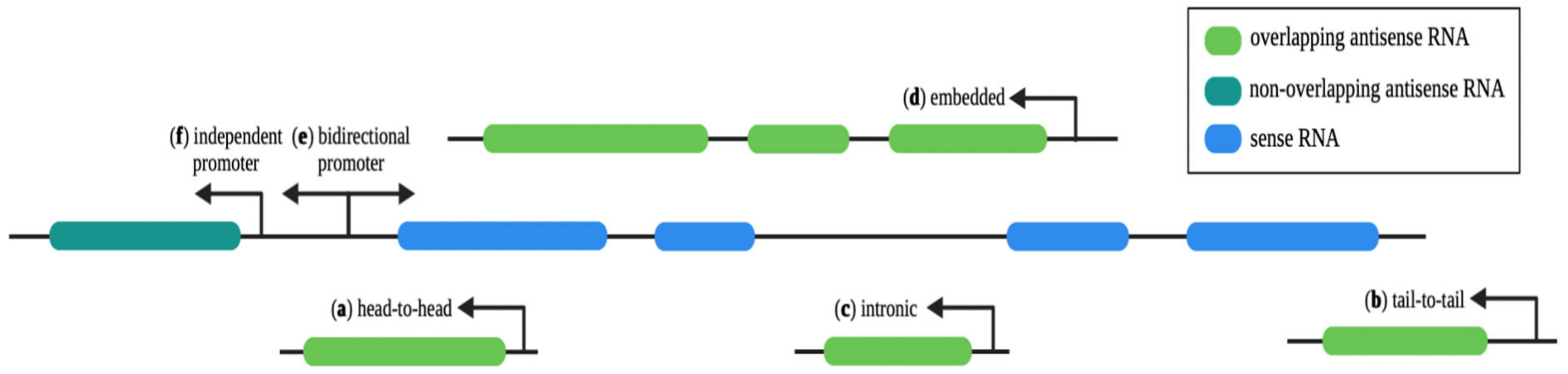
2.1. Antisense Transcription
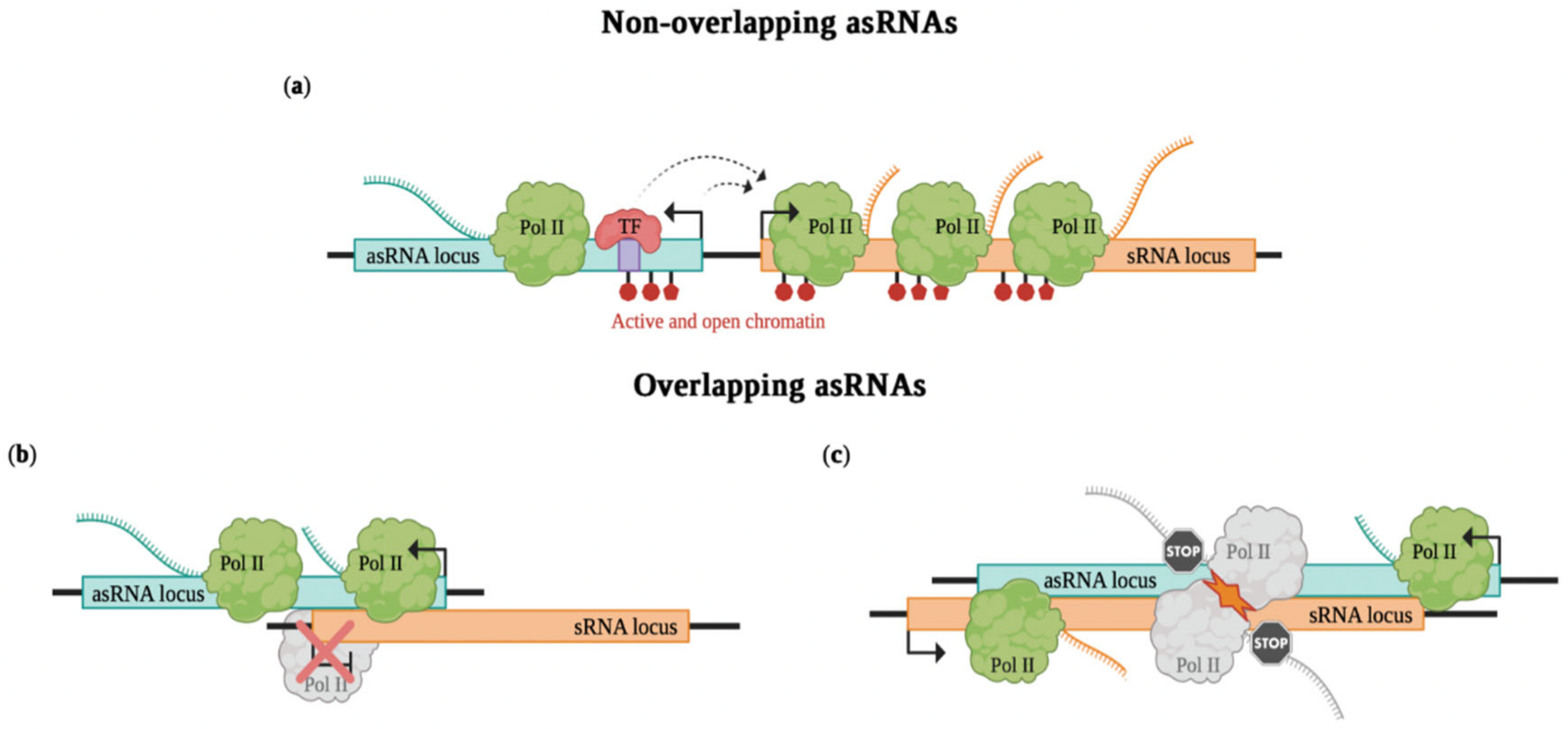
2.2. Non-Overlapping asRNAs
2.3. Overlapping asRNAs
3. RNA-Dependent Mechanisms
3.1. In Cis asRNAs
3.2. In Trans asRNAs
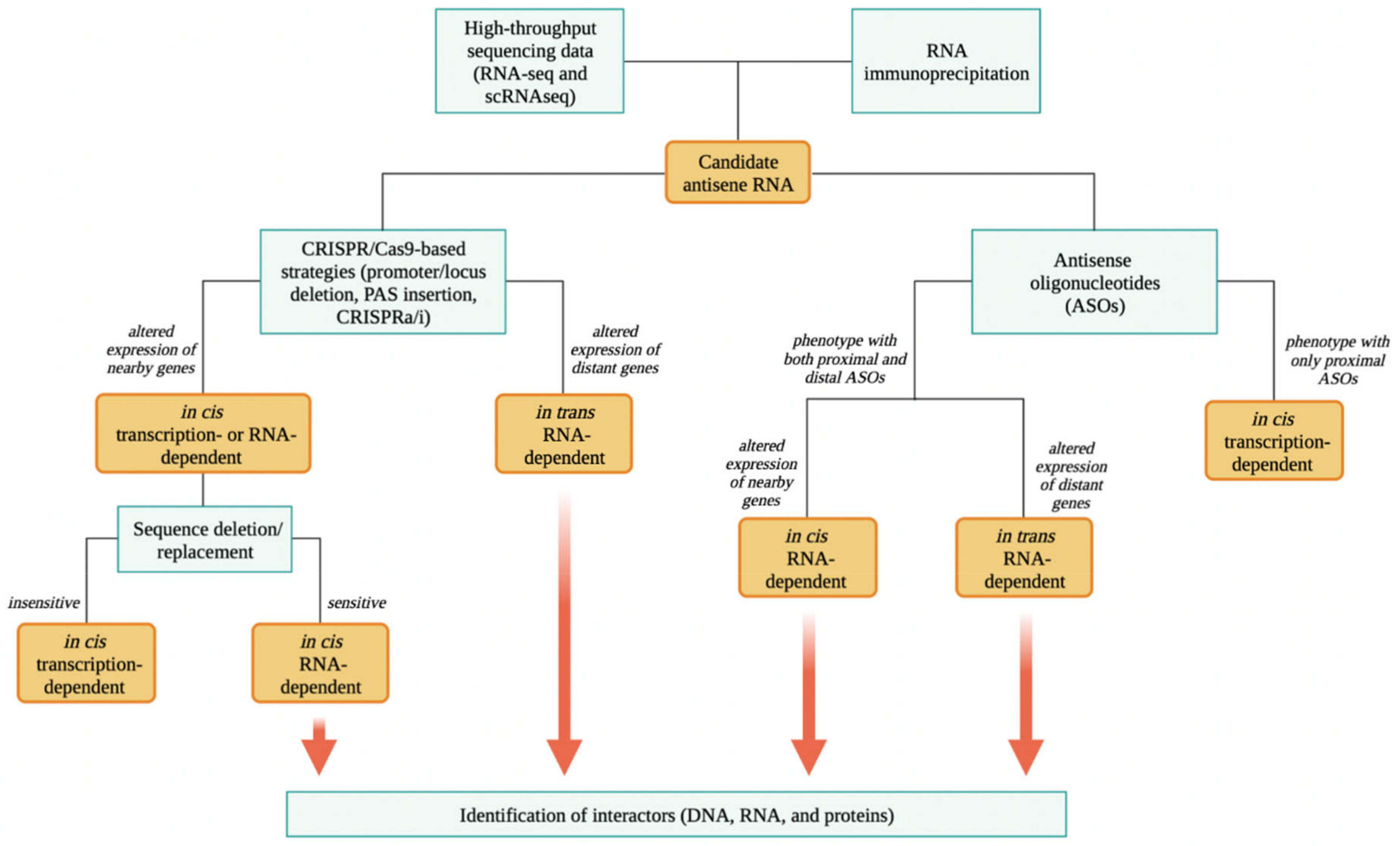
4. Methodologies to Discriminate and Study asRNA Mechanisms of Action
4.1. Identification of asRNAs
4.2. Functional Study of asRNAs
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pelechano, V.; Steinmetz, L.M. Gene regulation by antisense transcription. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 14, 880–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, S.C.; Mellor, J. Using both strands: The fundamental nature of antisense transcription. Bioarchitecture 2016, 6, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Werner, A. Biological functions of natural antisense transcripts. BMC Biol. 2013, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statello, L.; Guo, C.J.; Chen, L.L.; Huarte, M. Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 96–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, E.G.; Simons, R.W. Antisense RNA control in bacteria, phages, and plasmids. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 1994, 48, 713–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozsolak, F.; Kapranov, P.; Foissac, S.; Kim, S.W.; Fishilevich, E.; Monaghan, A.P.; John, B.; Milos, P.M. Comprehensive polyadenylation site maps in yeast and human reveal pervasive alternative polyadenylation. Cell 2010, 143, 1018–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurk, S.; Koren, S.; Rhie, A.; Rautiainen, M.; Bzikadze, A.V.; Mikheenko, A.; Vollger, M.R.; Altemose, N.; Uralsky, L.; Gershman, A.; et al. The complete sequence of a human genome. Science 2022, 376, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujovic, F.; Rezaei-Lotfi, S.; Hunter, N.; Farahani, R.M. The fate of notch-1 transcript is linked to cell cycle dynamics by activity of a natural antisense transcript. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 10419–10430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosig, R.A.; Castaneda, A.N.; Deslauriers, J.C.; Frazier, L.P.; He, K.L.; Maghzian, N.; Pokharel, A.; Schrier, C.T.; Zhu, L.; Koike, N.; et al. Natural antisense transcript of. Genes Dev. 2021, 35, 899–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandini, C.; Garofalo, M.; Rey, F.; Garau, J.; Zucca, S.; Sproviero, D.; Bordoni, M.; Berzero, G.; Davin, A.; Poloni, T.E.; et al. MINCR: A long non-coding RNA shared between cancer and neurodegeneration. Genomics 2021, 113, 4039–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Profumo, V.; Forte, B.; Percio, S.; Rotundo, F.; Doldi, V.; Ferrari, E.; Fenderico, N.; Dugo, M.; Romagnoli, D.; Benelli, M.; et al. LEADeR role of miR-205 host gene as long noncoding RNA in prostate basal cell differentiation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanowska, E.; Kubiak, M.R.; Rosikiewicz, W.; Makałowska, I.; Szcześniak, M.W. Natural antisense transcripts in diseases: From modes of action to targeted therapies. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2018, 9, e1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteller, M. Non-coding RNAs in human disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 12, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, A.M.; Chang, H.Y. Long Noncoding RNAs in Cancer Pathways. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagliardi, S.; Pandini, C.; Garofalo, M.; Bordoni, M.; Pansarasa, O.; Cereda, C. Long non coding RNAs and ALS: Still much to do. Noncoding RNA Res. 2018, 3, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, M.; Pandini, C.; Sproviero, D.; Pansarasa, O.; Cereda, C.; Gagliardi, S. Advances with Long Non-Coding RNAs in Alzheimer’s Disease as Peripheral Biomarker. Genes 2021, 12, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, F.; Pandini, C.; Messa, L.; Launi, R.; Barzaghini, B.; Zangaglia, R.; Raimondi, M.T.; Gagliardi, S.; Cereda, C.; Zuccotti, G.V.; et al. α-Synuclein antisense transcript SNCA-AS1 regulates synapses- and aging-related genes suggesting its implication in Parkinson’s disease. Aging Cell 2021, 20, e13504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, F.; Messa, L.; Pandini, C.; Barzaghini, B.; Micheletto, G.; Raimondi, M.T.; Bertoli, S.; Cereda, C.; Zuccotti, G.V.; Cancello, R.; et al. Transcriptional characterization of subcutaneous adipose tissue in obesity affected women highlights metabolic dysfunction and implications for lncRNAs. Genomics 2021, 113, 3919–3934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halley, P.; Kadakkuzha, B.M.; Faghihi, M.A.; Magistri, M.; Zeier, Z.; Khorkova, O.; Coito, C.; Hsiao, J.; Lawrence, M.; Wahlestedt, C. Regulation of the apolipoprotein gene cluster by a long noncoding RNA. Cell Rep. 2014, 6, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carninci, P.; Kasukawa, T.; Katayama, S.; Gough, J.; Frith, M.C.; Maeda, N.; Oyama, R.; Ravasi, T.; Lenhard, B.; Wells, C.; et al. The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. Science 2005, 309, 1559–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willingham, A.T.; Gingeras, T.R. TUF love for “junk” DNA. Cell 2006, 125, 1215–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Struhl, K. Transcriptional noise and the fidelity of initiation by RNA polymerase II. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007, 14, 103–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hombach, S.; Kretz, M. Non-coding RNAs: Classification, Biology and Functioning. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 937, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, K.V.; Vogt, P.K. Long antisense non-coding RNAs and their role in transcription and oncogenesis. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 2544–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Trinklein, N.D.; Aldred, S.F.; Hartman, S.J.; Schroeder, D.I.; Otillar, R.P.; Myers, R.M. An abundance of bidirectional promoters in the human genome. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigova, A.A.; Mullen, A.C.; Molinie, B.; Gupta, S.; Orlando, D.A.; Guenther, M.G.; Almada, A.E.; Lin, C.; Sharp, P.A.; Giallourakis, C.C.; et al. Divergent transcription of long noncoding RNA/mRNA gene pairs in embryonic stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 2876–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Wu, Z.; Wang, S.; Chen, L. Expression and function of natural antisense transcripts in mouse embryonic stem cells. Sci. China Life Sci. 2014, 57, 1183–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Wei, W.; Gagneur, J.; Clauder-Münster, S.; Smolik, M.; Huber, W.; Steinmetz, L.M. Antisense expression increases gene expression variability and locus interdependency. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, S.C.; Haenni, S.; Howe, F.S.; Fischl, H.; Chocian, K.; Nair, A.; Mellor, J. Sense and antisense transcription are associated with distinct chromatin architectures across genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 7823–7837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.; Howe, F.S.; Murray, S.C.; Wouters, M.; Lorenz, P.; Seward, E.; Rata, S.; Angel, A.; Mellor, J. Antisense transcription-dependent chromatin signature modulates sense transcript dynamics. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2018, 14, e8007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engreitz, J.M.; Haines, J.E.; Perez, E.M.; Munson, G.; Chen, J.; Kane, M.; McDonel, P.E.; Guttman, M.; Lander, E.S. Local regulation of gene expression by lncRNA promoters, transcription and splicing. Nature 2016, 539, 452–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, K.M.; Anderson, D.M.; McAnally, J.R.; Shelton, J.M.; Bassel-Duby, R.; Olson, E.N. Transcription of the non-coding RNA upperhand controls Hand2 expression and heart development. Nature 2016, 539, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Yang, J.; Ishihama, A.; Pittard, A.J. Demonstration that the TyrR protein and RNA polymerase complex formed at the divergent P3 promoter inhibits binding of RNA polymerase to the major promoter, P1, of the aroP gene of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 5466–5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhya, S.; Gottesman, M. Promoter occlusion: Transcription through a promoter may inhibit its activity. Cell 1982, 29, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latos, P.A.; Pauler, F.M.; Koerner, M.V.; Şenergin, H.B.; Hudson, Q.J.; Stocsits, R.R.; Allhoff, W.; Stricker, S.H.; Klement, R.M.; Warczok, K.E.; et al. Airn transcriptional overlap, but not its lncRNA products, induces imprinted Igf2r silencing. Science 2012, 338, 1469–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, E.M.; Proudfoot, N.J. Transcriptional collision between convergent genes in budding yeast. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8796–8801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, A.C.; Ahlgren-Berg, A.; Egan, J.B.; Dodd, I.B.; Shearwin, K.E. Potent transcriptional interference by pausing of RNA polymerases over a downstream promoter. Mol. Cell 2009, 34, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shearwin, K.E.; Callen, B.P.; Egan, J.B. Transcriptional interference--a crash course. Trends Genet. 2005, 21, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epshtein, V.; Toulmé, F.; Rahmouni, A.R.; Borukhov, S.; Nudler, E. Transcription through the roadblocks: The role of RNA polymerase cooperation. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 4719–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongay, C.F.; Grisafi, P.L.; Galitski, T.; Fink, G.R. Antisense transcription controls cell fate in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell 2006, 127, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelfand, B.; Mead, J.; Bruning, A.; Apostolopoulos, N.; Tadigotla, V.; Nagaraj, V.; Sengupta, A.M.; Vershon, A.K. Regulated antisense transcription controls expression of cell-type-specific genes in yeast. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 31, 1701–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tassinari, M.; Richter, S.N.; Gandellini, P. Biological relevance and therapeutic potential of G-quadruplex structures in the human noncoding transcriptome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 3617–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bezzecchi, E.; Pagani, G.; Forte, B.; Percio, S.; Zaffaroni, N.; Dolfini, D.; Gandellini, P. MIR205HG/LEADR Long Noncoding RNA Binds to Primed Proximal Regulatory Regions in Prostate Basal Cells Through a Triplex- and Alu-Mediated Mechanism. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 909097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnsson, P.; Lipovich, L.; Grandér, D.; Morris, K.V. Evolutionary conservation of long non-coding RNAs; sequence, structure, function. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1840, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Washietl, S.; Hofacker, I.L.; Lukasser, M.; Hüttenhofer, A.; Stadler, P.F. Mapping of conserved RNA secondary structures predicts thousands of functional noncoding RNAs in the human genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1383–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhu, H.; Luo, Y. Understanding the Functions of Long Non-Coding RNAs through Their Higher-Order Structures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, S.E.; Mirza, A.H.; Hansen, C.; Bang-Berthelsen, C.H.; Garde, C.; Christensen-Dalsgaard, M.; Torarinsson, E.; Yao, Z.; Workman, C.T.; Pociot, F.; et al. The identification and functional annotation of RNA structures conserved in vertebrates. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 1371–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadaliha, M.; Gholamalamdari, O.; Tang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Petracovici, A.; Hao, Q.; Tariq, A.; Kim, T.G.; Holton, S.E.; Singh, D.K.; et al. A natural antisense lncRNA controls breast cancer progression by promoting tumor suppressor gene mRNA stability. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, K.; Xie, Y. LncRNA FOXC2-AS1 enhances FOXC2 mRNA stability to promote colorectal cancer progression via activation of Ca. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciarlo, E.; Massone, S.; Penna, I.; Nizzari, M.; Gigoni, A.; Dieci, G.; Russo, C.; Florio, T.; Cancedda, R.; Pagano, A. An intronic ncRNA-dependent regulation of SORL1 expression affecting Aβ formation is upregulated in post-mortem Alzheimer’s disease brain samples. Dis. Models Mech. 2013, 6, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, M.; Puig, I.; Peña, C.; García, J.M.; Alvarez, A.B.; Peña, R.; Bonilla, F.; de Herreros, A.G. A natural antisense transcript regulates Zeb2/Sip1 gene expression during Snail1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 756–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Su, Z.; Xu, X.; Liu, G.; Song, X.; Wang, R.; Sui, X.; Liu, T.; Chang, X.; Huang, D. AS1DHRS4, a head-to-head natural antisense transcript, silences the DHRS4 gene cluster in cis and trans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 14110–14115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boque-Sastre, R.; Soler, M.; Oliveira-Mateos, C.; Portela, A.; Moutinho, C.; Sayols, S.; Villanueva, A.; Esteller, M.; Guil, S. Head-to-head antisense transcription and R-loop formation promotes transcriptional activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5785–5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.C.; Hänzelmann, S.; Sentürk Cetin, N.; Frank, S.; Zajzon, B.; Derks, J.P.; Akhade, V.S.; Ahuja, G.; Kanduri, C.; Grummt, I.; et al. Detection of RNA-DNA binding sites in long noncoding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grote, P.; Wittler, L.; Hendrix, D.; Koch, F.; Währisch, S.; Beisaw, A.; Macura, K.; Bläss, G.; Kellis, M.; Werber, M.; et al. The tissue-specific lncRNA Fendrr is an essential regulator of heart and body wall development in the mouse. Dev. Cell 2013, 24, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, K.V.; Santoso, S.; Turner, A.M.; Pastori, C.; Hawkins, P.G. Bidirectional transcription directs both transcriptional gene activation and suppression in human cells. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Gius, D.; Onyango, P.; Muldoon-Jacobs, K.; Karp, J.; Feinberg, A.P.; Cui, H. Epigenetic silencing of tumour suppressor gene p15 by its antisense RNA. Nature 2008, 451, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Myacheva, K.; Groß, M.; Klingenberg, M.; Duran Arqué, B.; Diederichs, S. Challenges of CRISPR/Cas9 applications for long non-coding RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesana, M.; Cacchiarelli, D.; Legnini, I.; Santini, T.; Sthandier, O.; Chinappi, M.; Tramontano, A.; Bozzoni, I. A long noncoding RNA controls muscle differentiation by functioning as a competing endogenous RNA. Cell 2011, 147, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrieri, C.; Forrest, A.R.; Santoro, C.; Persichetti, F.; Carninci, P.; Zucchelli, S.; Gustincich, S. Expression analysis of the long non-coding RNA antisense to Uchl1 (AS Uchl1) during dopaminergic cells’ differentiation in vitro and in neurochemical models of Parkinson’s disease. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2015, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihi, M.A.; Zhang, M.; Huang, J.; Modarresi, F.; Van der Brug, M.P.; Nalls, M.A.; Cookson, M.R.; St-Laurent, G.; Wahlestedt, C. Evidence for natural antisense transcript-mediated inhibition of microRNA function. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapidot, M.; Pilpel, Y. Genome-wide natural antisense transcription: Coupling its regulation to its different regulatory mechanisms. EMBO Rep. 2006, 7, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tay, Y.; Rinn, J.; Pandolfi, P.P. The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature 2014, 505, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, T.B.; Kjems, J.; Damgaard, C.K. Circular RNA and miR-7 in cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 5609–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Jiang, J. The role of lncRNA-mediated ceRNA regulatory networks in pancreatic cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Palo, A.; Siniscalchi, C.; Mosca, N.; Russo, A.; Potenza, N. A Novel ceRNA Regulatory Network Involving the Long Non-Coding Antisense RNA SPACA6P-AS, miR-125a and its mRNA Targets in Hepatocarcinoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinn, J.L.; Kertesz, M.; Wang, J.K.; Squazzo, S.L.; Xu, X.; Brugmann, S.A.; Goodnough, L.H.; Helms, J.A.; Farnham, P.J.; Segal, E.; et al. Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell 2007, 129, 1311–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ohsumi, T.K.; Kung, J.T.; Ogawa, Y.; Grau, D.J.; Sarma, K.; Song, J.J.; Kingston, R.E.; Borowsky, M.; Lee, J.T. Genome-wide identification of polycomb-associated RNAs by RIP-seq. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.C.; Manor, O.; Wan, Y.; Mosammaparast, N.; Wang, J.K.; Lan, F.; Shi, Y.; Segal, E.; Chang, H.Y. Long noncoding RNA as modular scaffold of histone modification complexes. Science 2010, 329, 689–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.J.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Hutchison, E.R.; Mitchell, S.J.; Grammatikakis, I.; Guo, R.; Noh, J.H.; Martindale, J.L.; Yang, X.; Lee, E.K.; et al. HuD regulates coding and noncoding RNA to induce APP→Aβ processing. Cell Rep. 2014, 7, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattick, J.S. Non-coding RNAs: The architects of eukaryotic complexity. EMBO Rep. 2001, 2, 986–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djebali, S.; Davis, C.A.; Merkel, A.; Dobin, A.; Lassmann, T.; Mortazavi, A.; Tanzer, A.; Lagarde, J.; Lin, W.; Schlesinger, F.; et al. Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature 2012, 489, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, R.; Peng, S.; Zhang, G.; Yang, T.; Qian, A. Strategies to identify natural antisense transcripts. Biochimie 2017, 132, 131–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthanari, Y.; Heintzen, C.; Griffiths-Jones, S.; Crosthwaite, S.K. Natural antisense transcripts and long non-coding RNA in Neurospora crassa. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morioka, M.S.; Kawaji, H.; Nishiyori-Sueki, H.; Murata, M.; Kojima-Ishiyama, M.; Carninci, P.; Itoh, M. Cap Analysis of Gene Expression (CAGE): A Quantitative and Genome-Wide Assay of Transcription Start Sites. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2120, 277–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lizio, M.; Harshbarger, J.; Shimoji, H.; Severin, J.; Kasukawa, T.; Sahin, S.; Abugessaisa, I.; Fukuda, S.; Hori, F.; Ishikawa-Kato, S.; et al. Gateways to the FANTOM5 promoter level mammalian expression atlas. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, K.R.; Chanfreau, G.F. Robust mapping of polyadenylated and non-polyadenylated RNA 3’ ends at nucleotide resolution by 3’-end sequencing. Methods 2020, 176, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, C.J.; Schmidt, R.; Kanitz, A.; Artimo, P.; Gruber, A.J.; Zavolan, M. PolyASite 2.0: A consolidated atlas of polyadenylation sites from 3’ end sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D174–D179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.R.; Sambrook, J. Rapid Amplification of Sequences from the 5’ Ends of mRNAs: 5’-RACE. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, M.R.; Sambrook, J. Rapid Amplification of Sequences from the 3’ Ends of mRNAs: 3’-RACE. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ENCODE Project Consortium. An integrated encyclopedia of DNA elements in the human genome. Nature 2012, 489, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurman, R.E.; Rynes, E.; Humbert, R.; Vierstra, J.; Maurano, M.T.; Haugen, E.; Sheffield, N.C.; Stergachis, A.B.; Wang, H.; Vernot, B.; et al. The accessible chromatin landscape of the human genome. Nature 2012, 489, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, H. Histone modifications for human epigenome analysis. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 58, 439–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, F.; Mendell, J.T. Functional Classification and Experimental Dissection of Long Noncoding RNAs. Cell 2018, 172, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallunki, T.; Barisic, M.; Jäättelä, M.; Liu, B. How to Choose the Right Inducible Gene Expression System for Mammalian Studies? Cells 2019, 8, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, Y.A.; Yang, B.; Chen, W.; Hung, T.; Kuchel, R.P.; Zammit, N.W.; Grey, S.T.; Goldys, E.M.; Deng, W. Spatial and Temporal Control of CRISPR-Cas9-Mediated Gene Editing Delivered via a Light-Triggered Liposome System. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 52433–52444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senturk, S.; Shirole, N.H.; Nowak, D.G.; Corbo, V.; Pal, D.; Vaughan, A.; Tuveson, D.A.; Trotman, L.C.; Kinney, J.B.; Sordella, R. Rapid and tunable method to temporally control gene editing based on conditional Cas9 stabilization. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbashir, S.M.; Harborth, J.; Lendeckel, W.; Yalcin, A.; Weber, K.; Tuschl, T. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature 2001, 411, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crooke, S.T.; Baker, B.F.; Crooke, R.M.; Liang, X.H. Antisense technology: An overview and prospectus. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 427–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Mendell, J.T. Antisense-Mediated Transcript Knockdown Triggers Premature Transcription Termination. Mol. Cell 2020, 77, 1044–1054.e1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazal, G.; Gagnon, J.; Jacques, P.E.; Landry, J.R.; Robert, F.; Elela, S.A. Yeast RNase III triggers polyadenylation-independent transcription termination. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, T.; Subhash, S.; Kanduri, C. Chromatin RNA Immunoprecipitation (ChRIP). Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1689, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engreitz, J.M.; Sirokman, K.; McDonel, P.; Shishkin, A.A.; Surka, C.; Russell, P.; Grossman, S.R.; Chow, A.Y.; Guttman, M.; Lander, E.S. RNA-RNA interactions enable specific targeting of noncoding RNAs to nascent Pre-mRNAs and chromatin sites. Cell 2014, 159, 188–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marín-Béjar, O.; Huarte, M. RNA pulldown protocol for in vitro detection and identification of RNA-associated proteins. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1206, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagliardi, M.; Matarazzo, M.R. RIP: RNA Immunoprecipitation. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1480, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stork, C.; Zheng, S. Genome-Wide Profiling of RNA-Protein Interactions Using CLIP-Seq. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016, 1421, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.A.; Shah, N.; Wang, K.C.; Kim, J.; Horlings, H.M.; Wong, D.J.; Tsai, M.C.; Hung, T.; Argani, P.; Rinn, J.L.; et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature 2010, 464, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Liao, Y.T.; He, J.C.; Xie, C.L.; Chen, S.Y.; Fan, H.H.; Su, Z.P.; Wang, Z. Plasma long non-coding RNA BACE1 as a novel biomarker for diagnosis of Alzheimer disease. BMC Neurol. 2018, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.C.; Langer, R.; Wood, M.J.A. Advances in oligonucleotide drug delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2020, 19, 673–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pagani, G.; Pandini, C.; Gandellini, P. Navigating the Multiverse of Antisense RNAs: The Transcription- and RNA-Dependent Dimension. Non-Coding RNA 2022, 8, 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8060074
Pagani G, Pandini C, Gandellini P. Navigating the Multiverse of Antisense RNAs: The Transcription- and RNA-Dependent Dimension. Non-Coding RNA. 2022; 8(6):74. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8060074
Chicago/Turabian StylePagani, Giulia, Cecilia Pandini, and Paolo Gandellini. 2022. "Navigating the Multiverse of Antisense RNAs: The Transcription- and RNA-Dependent Dimension" Non-Coding RNA 8, no. 6: 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8060074
APA StylePagani, G., Pandini, C., & Gandellini, P. (2022). Navigating the Multiverse of Antisense RNAs: The Transcription- and RNA-Dependent Dimension. Non-Coding RNA, 8(6), 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8060074







