LncRNA-Based Classification of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Revealed Inherent Tumor Heterogeneity and Vulnerabilities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
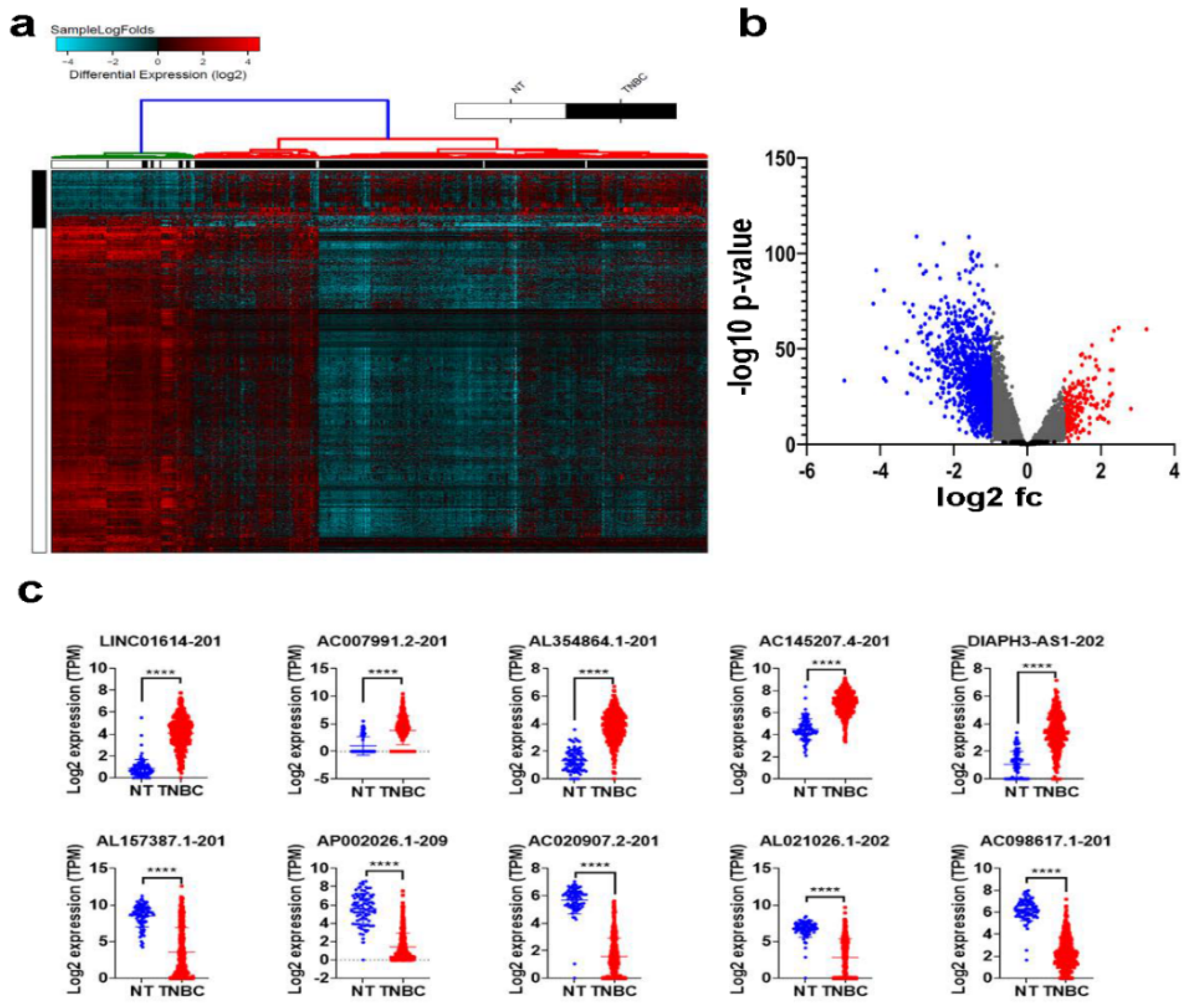
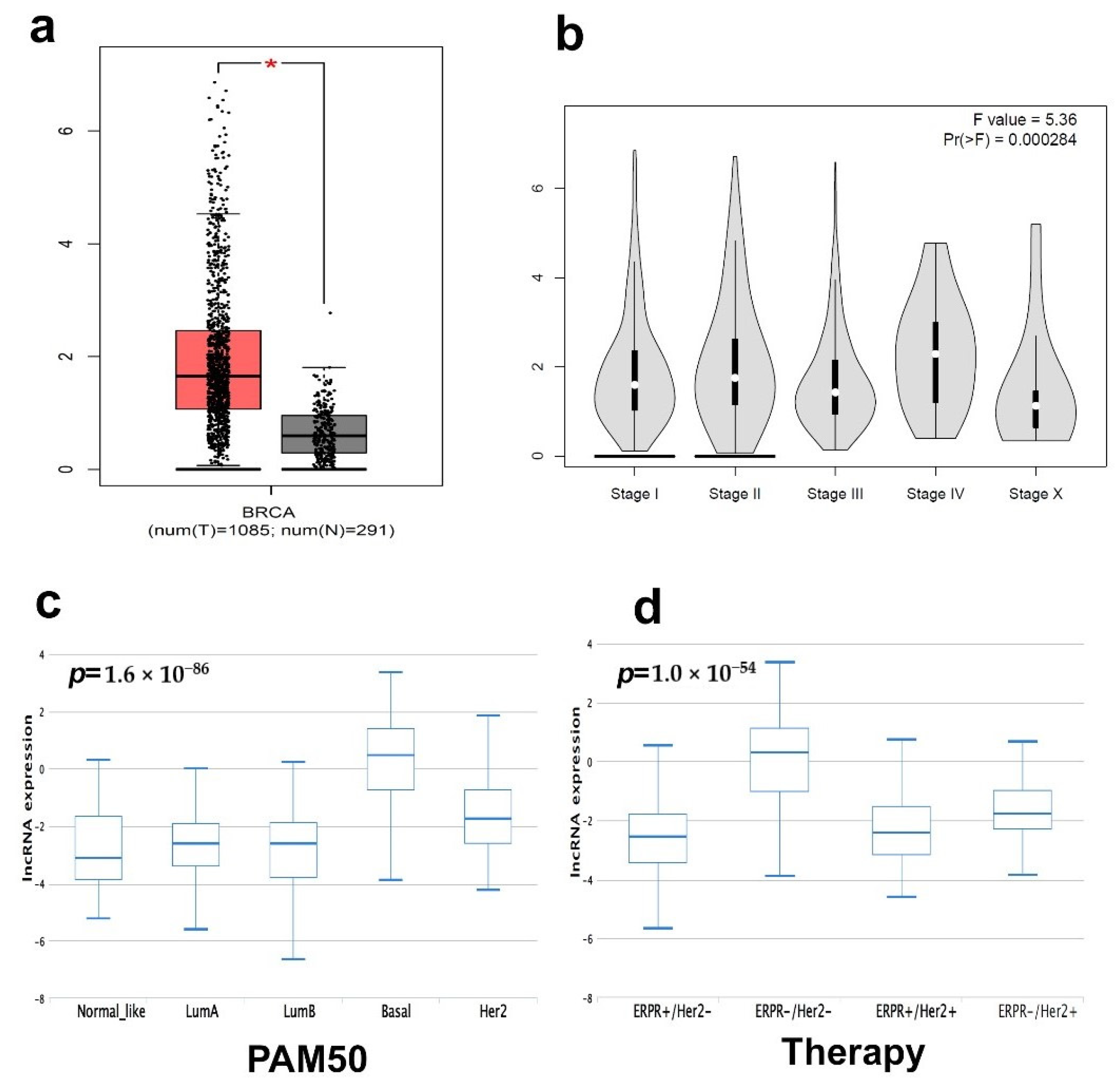
2.1. Differentially Expressed LncRNAs in TNBC Compared to Normal Breast Tissue (NT)
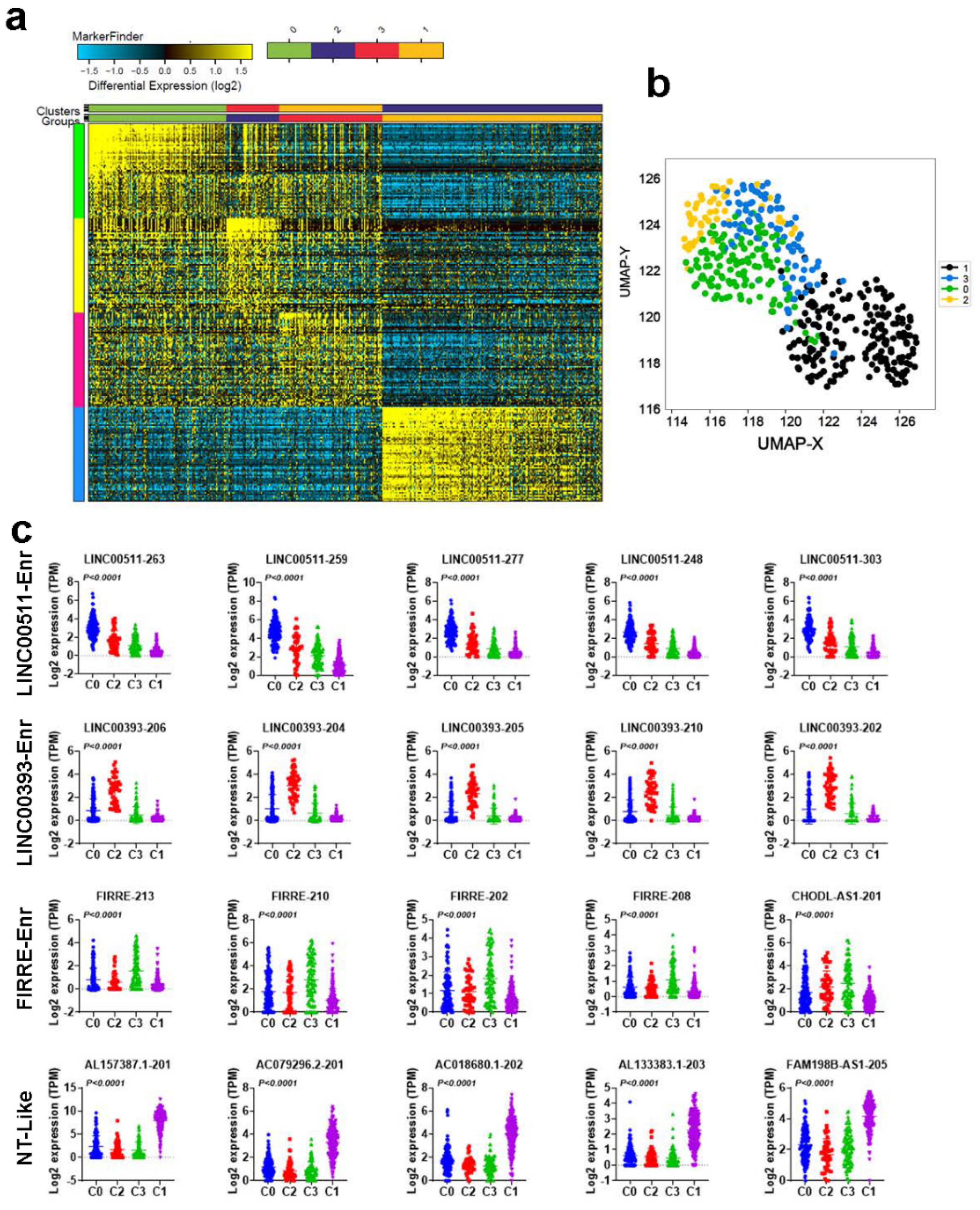
2.2. Molecular Heterogeneity of TNBC Employing the LncRNA Transcriptome
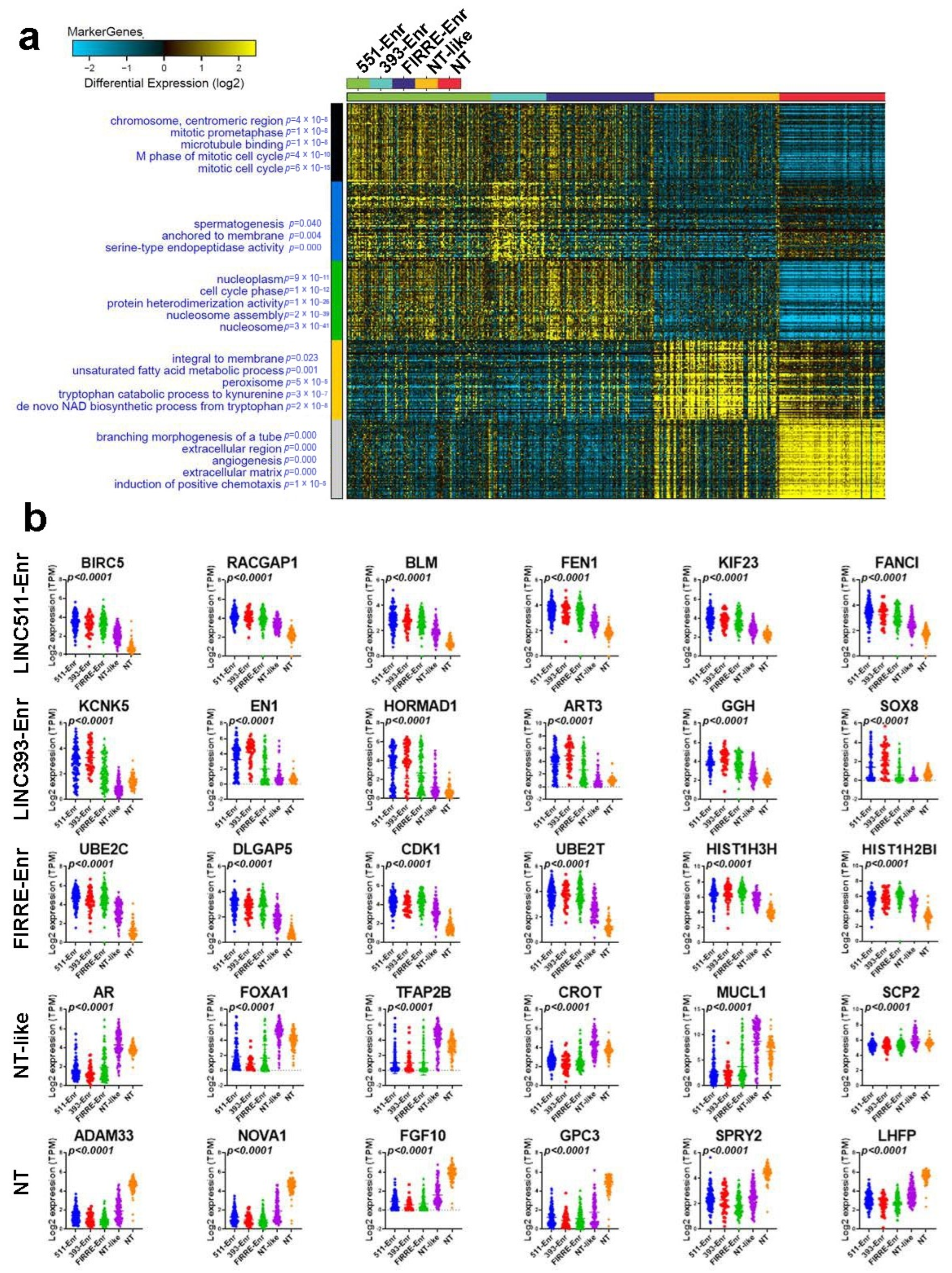
2.3. Functional Heterogeneity of TNBC Employing LncRNA-Based Clustering
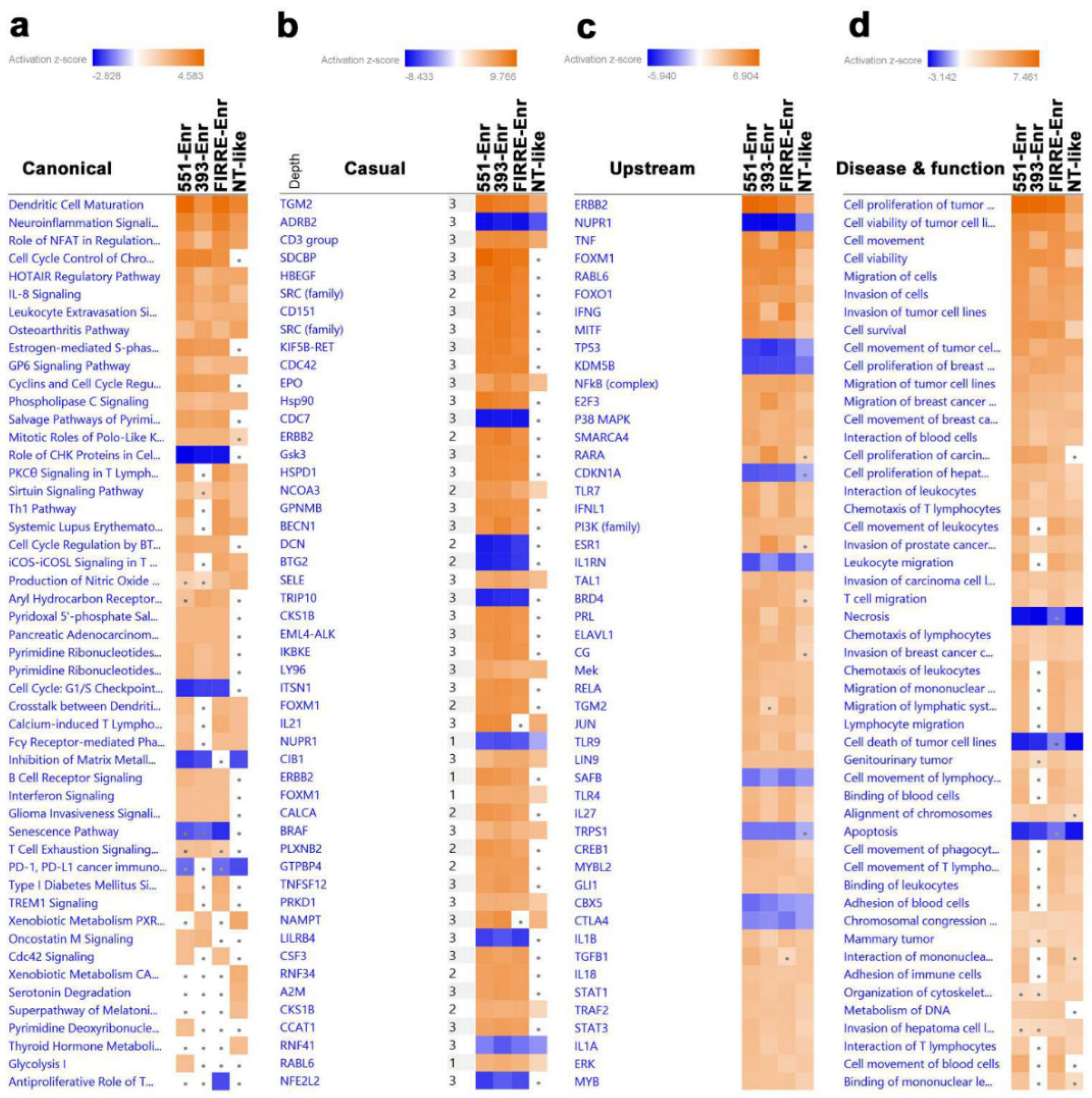
2.4. Upstream Regulator and Functional Annotation Enrichment in LncRNA-Derived TNBC Clusters
2.5. Survival Analysis of TNBC Patients Employing LncRNA-Based Classification
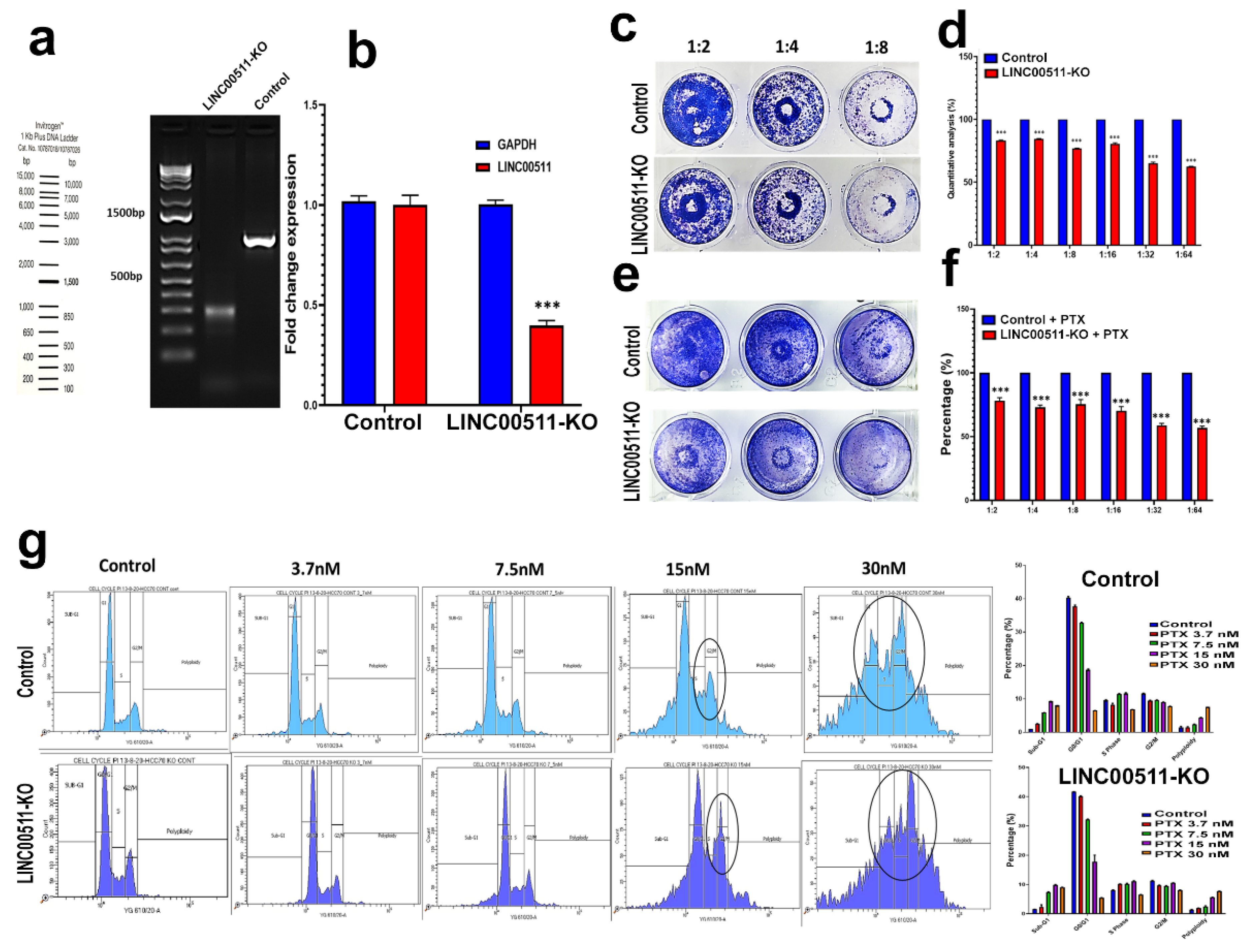
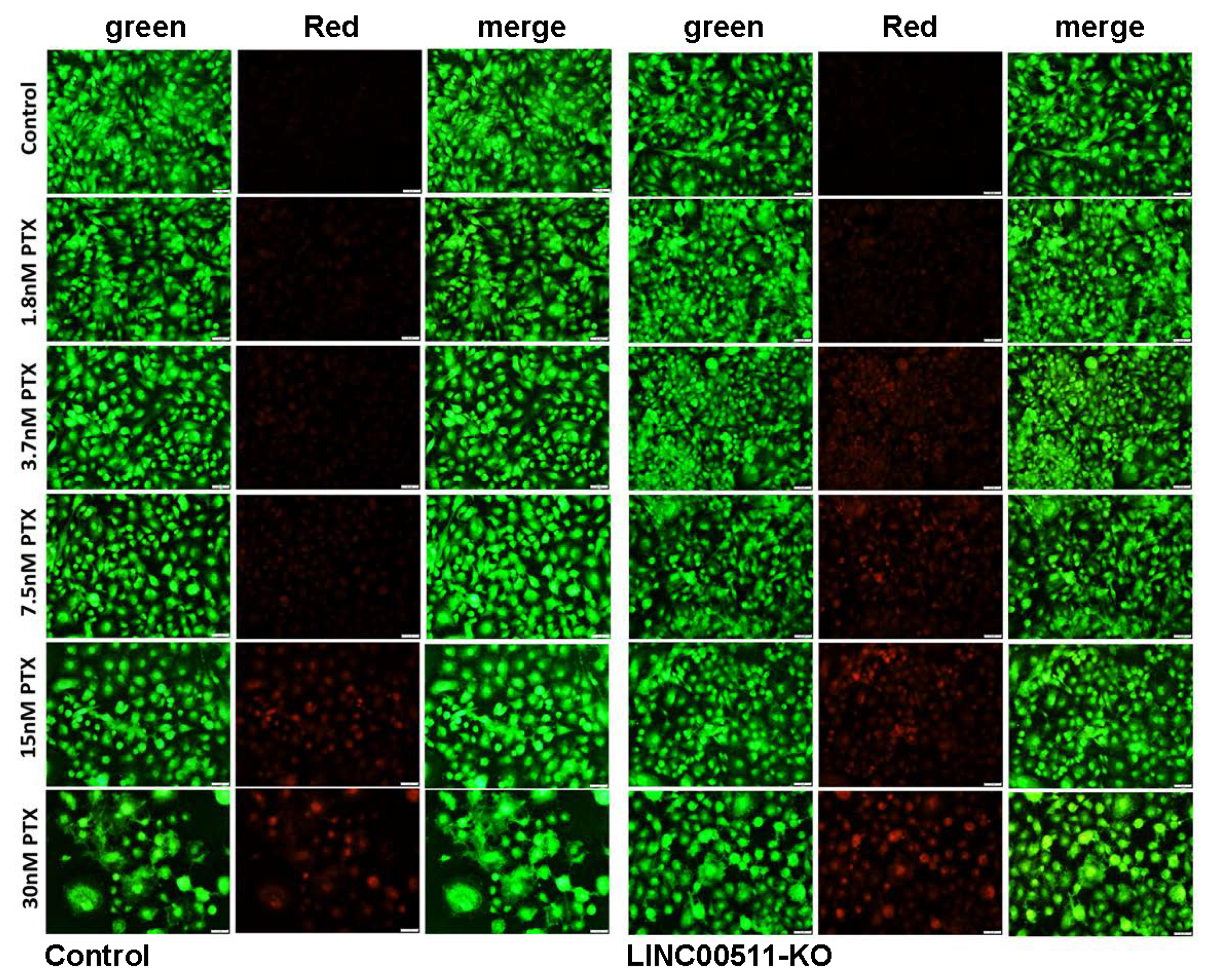
2.6. CRISPR-Cas9-Mediated LINC00511 Suppression Abrogated TNBC CFU Formation and Enhanced Their Sensitivity to Paclitaxel
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Transcriptomic and Bioinformatics Analyses
4.2. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA)
4.3. Protein–Protein Interaction Network Analysis
4.4. Survival Analysis
4.5. Generation of LINC00511 Knockout TNBC Models Using CRISPR-Cas9
4.6. Cas9 RNP Transfection Using Electroporation and PCR-Based Genotyping of LINC00511
4.7. Colony Forming Unit (CFU) Assay and Paclitaxel Sensitivity of LINC00511-KO and Parental TNBC Cells
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weigelt, B.; Reis-Filho, J.S. Histological and molecular types of breast cancer: Is there a unifying taxonomy? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 6, 718–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianchini, G.; Balko, J.M.; Mayer, I.A.; Sanders, M.E.; Gianni, L. Triple-negative breast cancer: Challenges and opportunities of a heterogeneous disease. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 13, 674–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, W.; Zheng, S.; Yang, A.; Zhang, X.; Zou, Y.; Tang, H.; Xie, X. Breast cancer subtypes and the risk of distant metastasis at initial diagnosis: A population-based study. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, 10, 5329–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parker, J.S.; Mullins, M.; Cheang, M.C.; Leung, S.; Voduc, D.; Vickery, T.; Davies, S.; Fauron, C.; He, X.; Hu, Z.; et al. Supervised risk predictor of breast cancer based on intrinsic subtypes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, B.D.; Bauer, J.A.; Chen, X.; Sanders, M.E.; Chakravarthy, A.B.; Shyr, Y.; Pietenpol, J.A. Identification of human triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for selection of targeted therapies. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2750–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koren, S.; Bentires-Alj, M. Breast Tumor Heterogeneity: Source of Fitness, Hurdle for Therapy. Mol. Cell 2015, 60, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elango, R.; Vishnubalaji, R.; Shaath, H.; Alajez, N.M. Molecular subtyping and functional validation of TTK, TPX2, UBE2C, and LRP8 in sensitivity of TNBC to paclitaxel. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2021, 20, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Gao, R.; Sei, E.; Brandt, R.; Hartman, J.; Hatschek, T.; Crosetto, N.; Foukakis, T.; Navin, N.E. Chemoresistance Evolution in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Delineated by Single-Cell Sequencing. Cell 2018, 173, 879–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vishnubalaji, R.; Alajez, N.M. Transcriptional landscape associated with TNBC resistance to neoadjuvant chemotherapy revealed by single-cell RNA-seq. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2021, 23, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoi, L.C.; Iyer, M.K.; Stuart, P.E.; Swindell, W.R.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Tejasvi, T.; Sarkar, M.K.; Li, B.; Ding, J.; Voorhees, J.J.; et al. Analysis of long non-coding RNAs highlights tissue-specific expression patterns and epigenetic profiles in normal and psoriatic skin. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shaath, H.; Elango, R.; Alajez, N.M. Molecular Classification of Breast Cancer Utilizing Long Non-Coding RNA (lncRNA) Transcriptomes Identifies Novel Diagnostic lncRNA Panel for Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaath, H.; Vishnubalaji, R.; Elango, R.; Khattak, S.; Alajez, N.M. Single-cell long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) transcriptome implicates MALAT1 in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) resistance to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasha, N.; Turner, N.C. Understanding and overcoming tumor heterogeneity in metastatic breast cancer treatment. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnubalaji, R.; Shaath, H.; Elkord, E.; Alajez, N.M. Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) transcriptional landscape in breast cancer identifies LINC01614 as non-favorable prognostic biomarker regulated by TGFbeta and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) signaling. Cell Death Discov. 2019, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, A.M.; Chang, H.Y. Long Noncoding RNAs in Cancer Pathways. Cancer Cell 2016, 29, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Brien, C.A.; Pollett, A.; Gallinger, S.; Dick, J.E. A human colon cancer cell capable of initiating tumour growth in immunodeficient mice. Nature 2007, 445, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizrak, D.; Brittan, M.; Alison, M. CD133: Molecule of the moment. J. Pathol. 2008, 214, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Xu, S.; Li, W.; Chen, M.; Jiang, M.; Fan, X. LncRNA FIRRE functions as a tumor promoter by interaction with PTBP1 to stabilize BECN1 mRNA and facilitate autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Cui, Z.; Liu, X.; Wu, S.; Wu, Y.; Fang, F.; Zhao, H. LncRNA FIRRE is activated by MYC and promotes the development of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma via Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 510, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Ding, L.; Mo, H.; Liu, R.; Xu, Q.; Tu, K. Long noncoding RNA FIRRE contributes to the proliferation and glycolysis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by enhancing PFKFB4 expression. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 4099–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, M.; Zang, X.; Wang, J.; Kang, J.; Tan, X.; Fu, B. Comprehensive analysis of differentially expressed long noncoding RNAs, miRNAs and mRNAs in breast cancer brain metastasis. Epigenomics 2021, 13, 1113–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Liu, X.; Yu, L.; Lin, S.; Zhang, C.; Xu, H.; Leng, Z.; Huang, W.; Lei, J.; Li, T.; et al. Comprehensive landscape of epigenetic-dysregulated lncRNAs reveals a profound role of enhancers in carcinogenesis in BC subtypes. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 23, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vishnubalaji, R.; Shaath, H.; Elango, R.; Alajez, N.M. Noncoding RNAs as potential mediators of resistance to cancer immunotherapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 65, 65–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J. The roles of long noncoding RNAs in breast cancer metastasis. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, R.; Bosch, N.; Lanzos, A.; Polidori, T.; Pulido-Quetglas, C.; Johnson, R. Hacking the Cancer Genome: Profiling Therapeutically Actionable Long Non-Coding RNAs Using CRISPR-Cas9 Screening. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 545–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Sui, S.; Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xu, S.; Pang, D. The transcriptional landscape of lncRNAs reveals the oncogenic function of LINC00511 in ER-negative breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, G.; Li, Y.; Ma, Y.; Lu, J.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Qin, Q.; Zhao, L.; Huang, Q.; Luo, Z.; et al. Long noncoding RNA LINC00511 contributes to breast cancer tumourigenesis and stemness by inducing the miR-185-3p/E2F1/Nanog axis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Xie, X.; Bi, R.; Ding, F.; Mei, J. Knockdown of Linc00511 inhibits TGF-beta-induced cell migration and invasion by suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition and down-regulating MMPs expression. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Guo, W.; Geng, H.; Wang, C.; Yang, S.; Xu, X. LINC00511 exacerbated T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia via miR-195-5p/LRRK1 axis. Biosci. Rep. 2020, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, G.; Liu, B. LINC00511 accelerated the process of gastric cancer by targeting miR-625-5p/NFIX axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leinonen, R.; Sugawara, H.; Shumway, M.; International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration. The sequence read archive. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D19–D21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.Z.; Ma, D.; Suo, C.; Shi, J.; Xue, M.; Hu, X.; Xiao, Y.; Yu, K.D.; Liu, Y.R.; Yu, Y.; et al. Genomic and Transcriptomic Landscape of Triple-Negative Breast Cancers: Subtypes and Treatment Strategies. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bray, N.L.; Pimentel, H.; Melsted, P.; Pachter, L. Near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnubalaji, R.; Alajez, N.M. Epigenetic regulation of triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) by TGF-beta signaling. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Kang, B.; Li, C.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Z. GEPIA2: An enhanced web server for large-scale expression profiling and interactive analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W556–W560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Han, L.; Roebuck, P.; Diao, L.; Liu, L.; Yuan, Y.; Weinstein, J.N.; Liang, H. TANRIC: An Interactive Open Platform to Explore the Function of lncRNAs in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 3728–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kramer, A.; Green, J.; Pollard, J., Jr.; Tugendreich, S. Causal analysis approaches in Ingenuity Pathway Analysis. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pulido-Quetglas, C.; Aparicio-Prat, E.; Arnan, C.; Polidori, T.; Hermoso, T.; Palumbo, E.; Ponomarenko, J.; Guigo, R.; Johnson, R. Scalable Design of Paired CRISPR Guide RNAs for Genomic Deletion. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2017, 13, e1005341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vishnubalaji, R.; Elango, R.; Alajez, N.M. LncRNA-Based Classification of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Revealed Inherent Tumor Heterogeneity and Vulnerabilities. Non-Coding RNA 2022, 8, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8040044
Vishnubalaji R, Elango R, Alajez NM. LncRNA-Based Classification of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Revealed Inherent Tumor Heterogeneity and Vulnerabilities. Non-Coding RNA. 2022; 8(4):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8040044
Chicago/Turabian StyleVishnubalaji, Radhakrishnan, Ramesh Elango, and Nehad M. Alajez. 2022. "LncRNA-Based Classification of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Revealed Inherent Tumor Heterogeneity and Vulnerabilities" Non-Coding RNA 8, no. 4: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8040044
APA StyleVishnubalaji, R., Elango, R., & Alajez, N. M. (2022). LncRNA-Based Classification of Triple Negative Breast Cancer Revealed Inherent Tumor Heterogeneity and Vulnerabilities. Non-Coding RNA, 8(4), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna8040044





