Binding of the RNA Chaperone Hfq on Target mRNAs Promotes the Small RNA RyhB-Induced Degradation in Escherichia coli
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
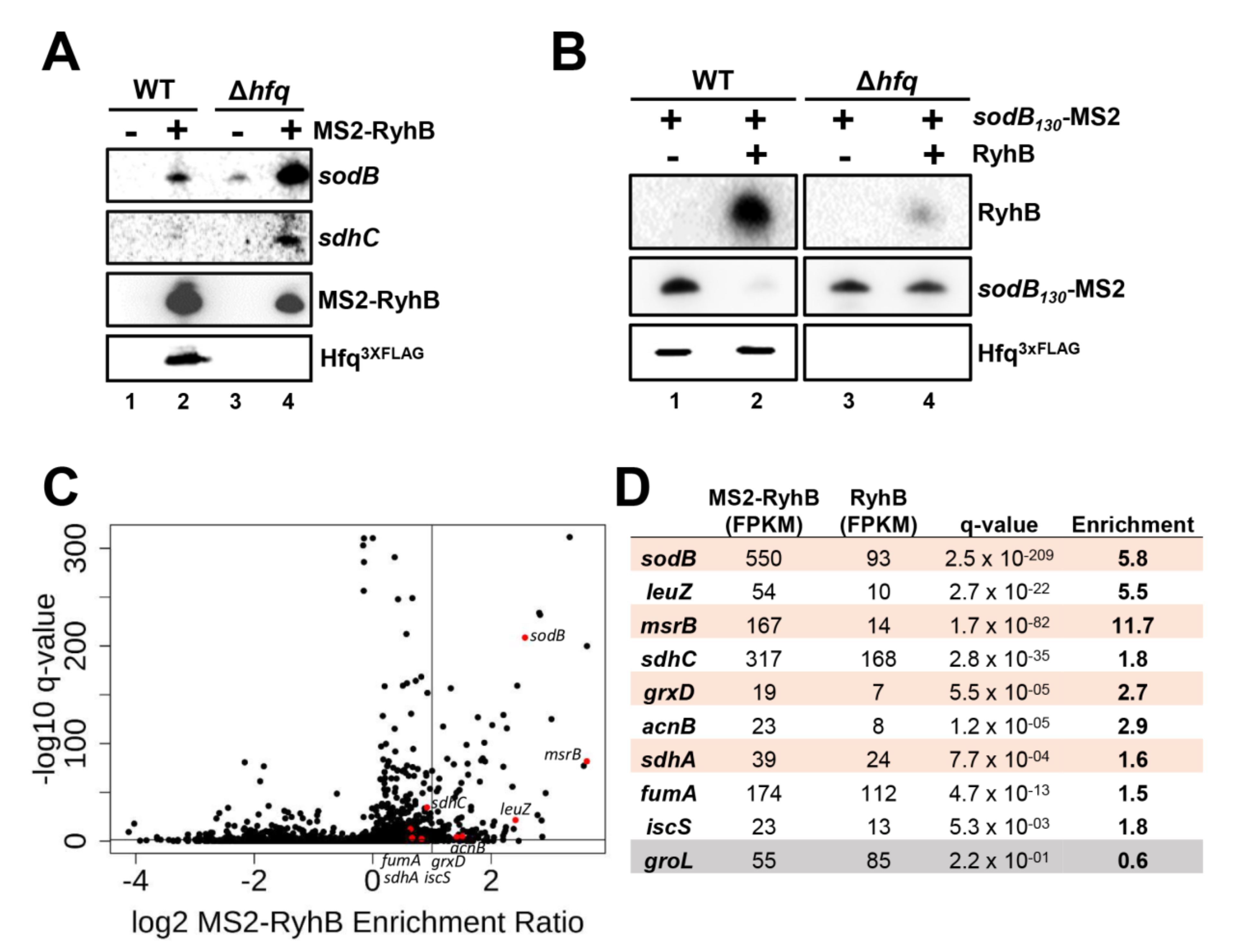
2.1. Absence of Hfq Does Not Prevent MS2-Tagged RyhB Interaction with sodB and sdhC Target mRNAs In Vivo
2.2. Interaction of MS2-RyhB with Some Target mRNAs Is Not Hfq-Dependent In Vivo
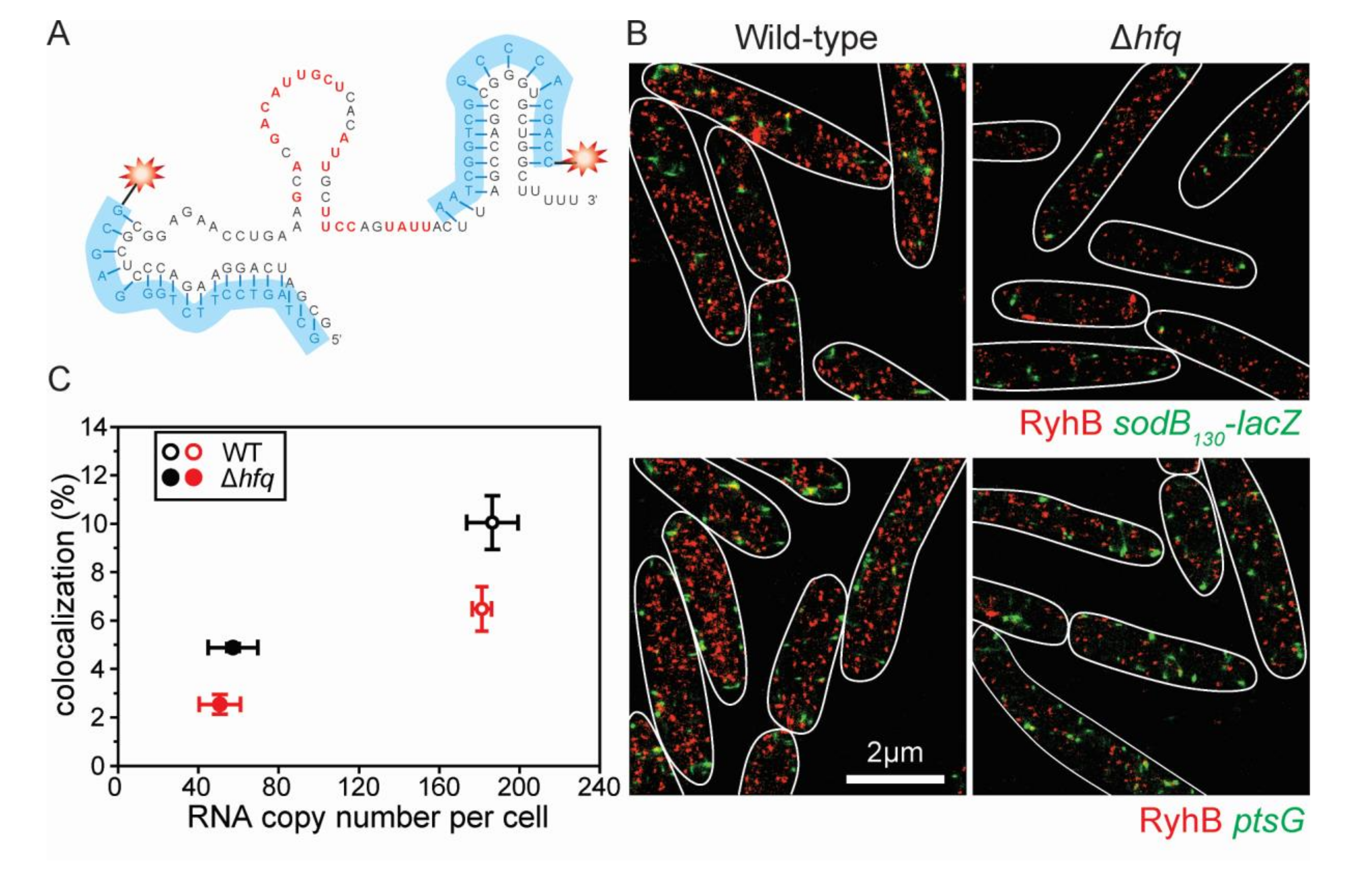
2.3. Formation of RyhB:sodB mRNA Complex in the Absence of Cellular Hfq
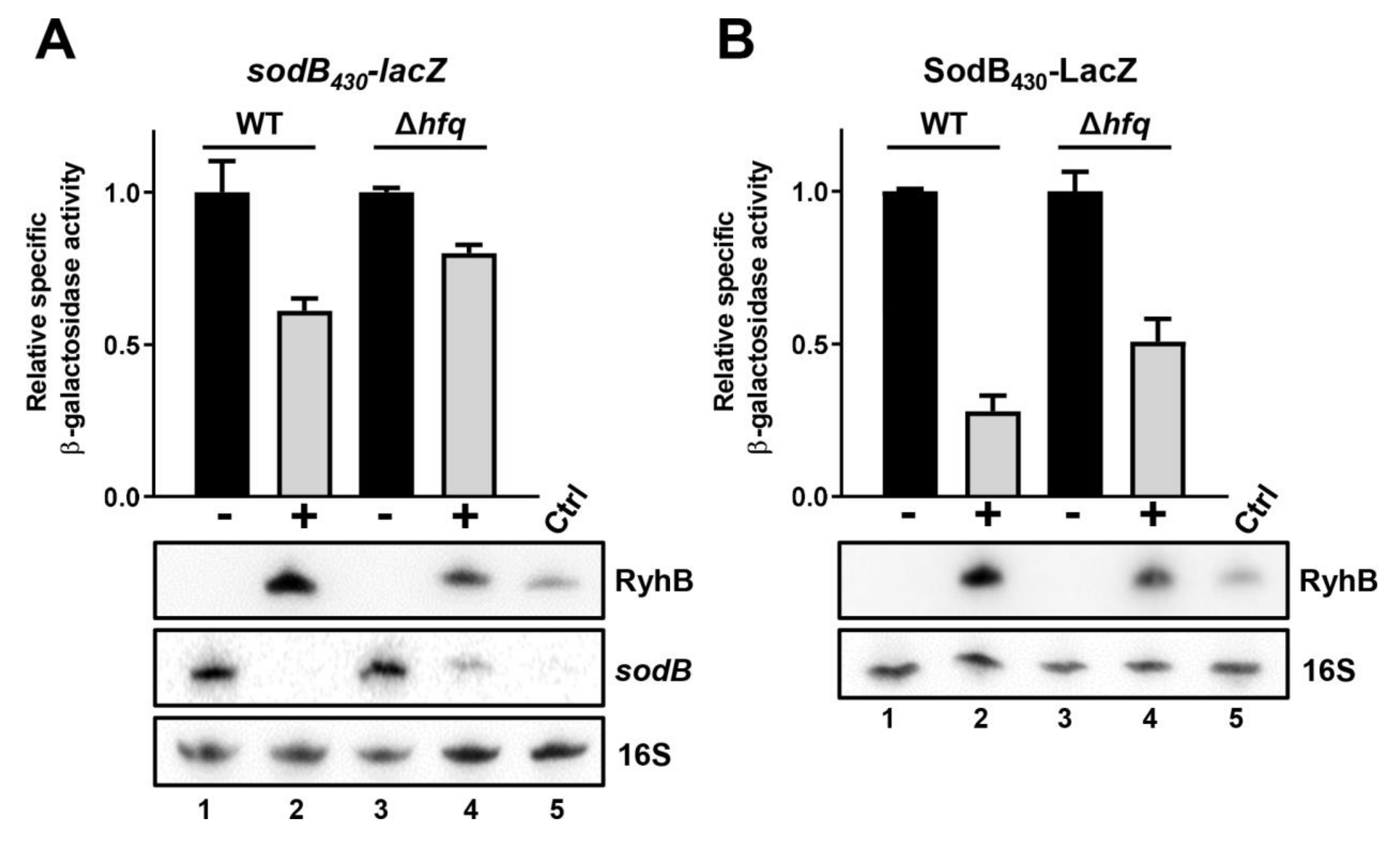
2.4. Efficient RyhB-Induced Degradation of sodB Target mRNA Is Promoted by Hfq
2.5. Absence of Hfq Does Not Prevent RyhB Translation Block of sodB Target mRNA
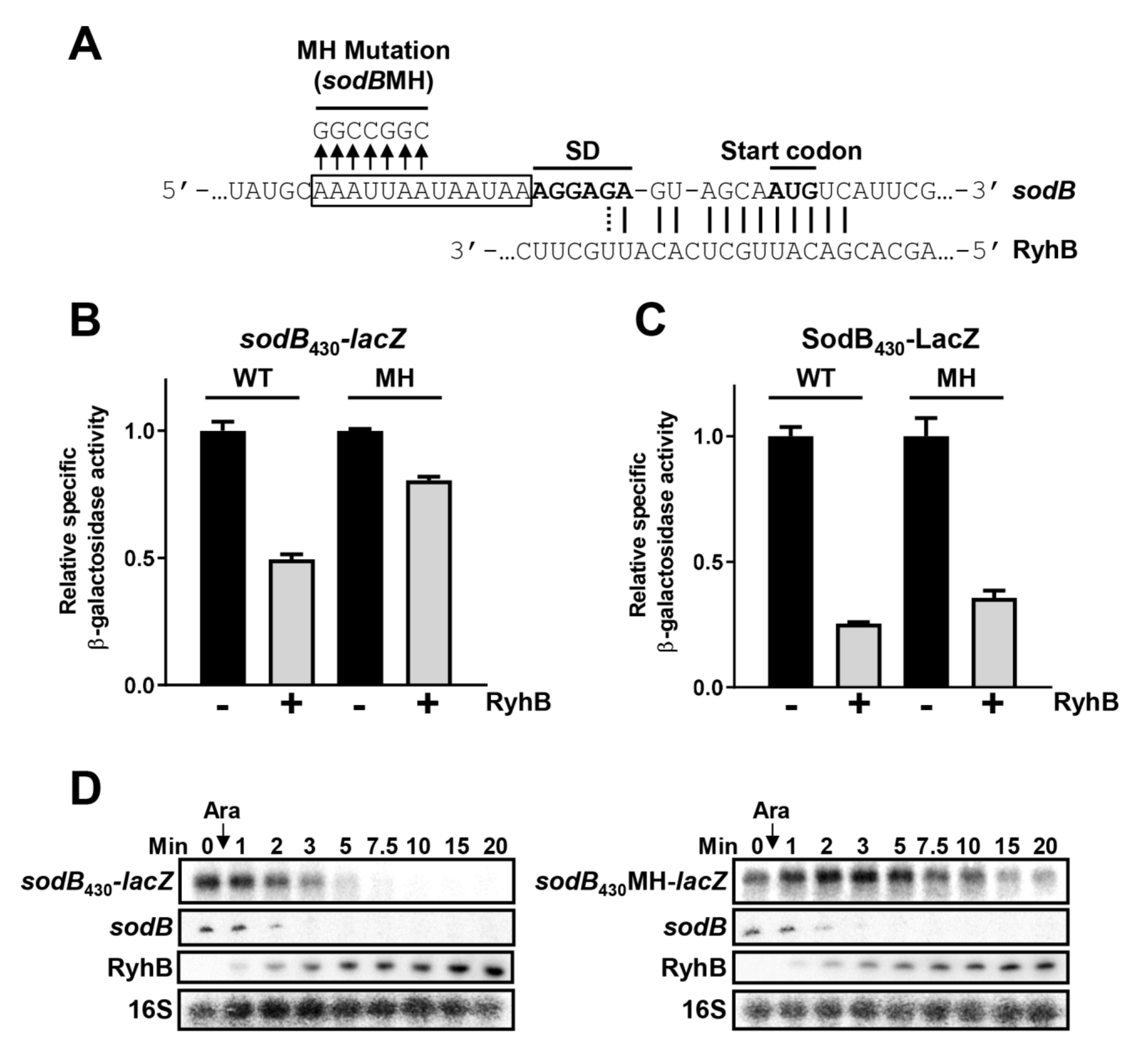
2.6. Hfq Binding Site on Target mRNAs Is Essential for sRNA-Induced Degradation
2.7. Hfq Binding to sodB and sdhC Target mRNAs Is Not Required for RyhB-Induced Translation Block
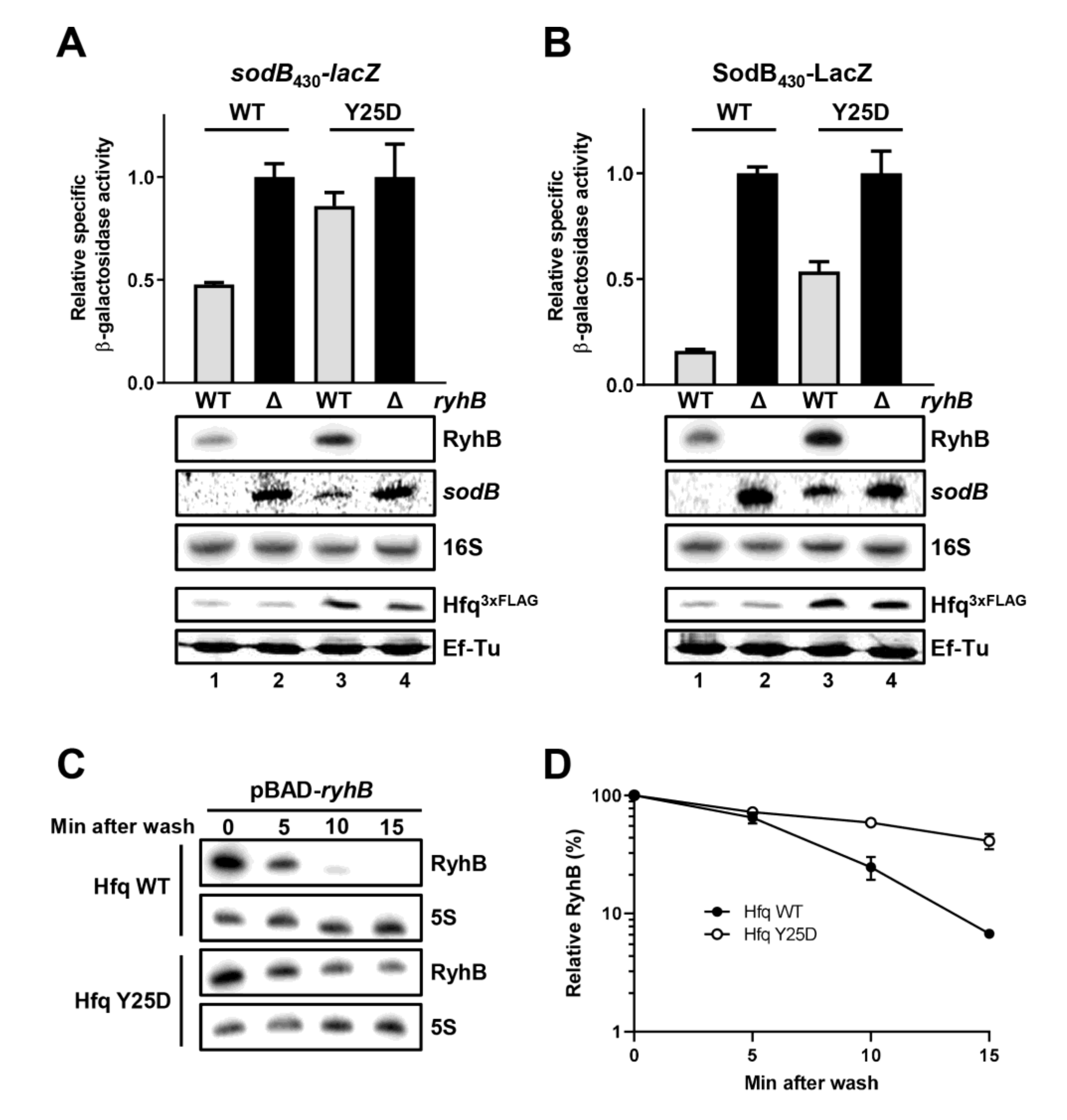
2.8. Hfq Must Bind sodB Target mRNA for Optimal RyhB-Promoted Degradation
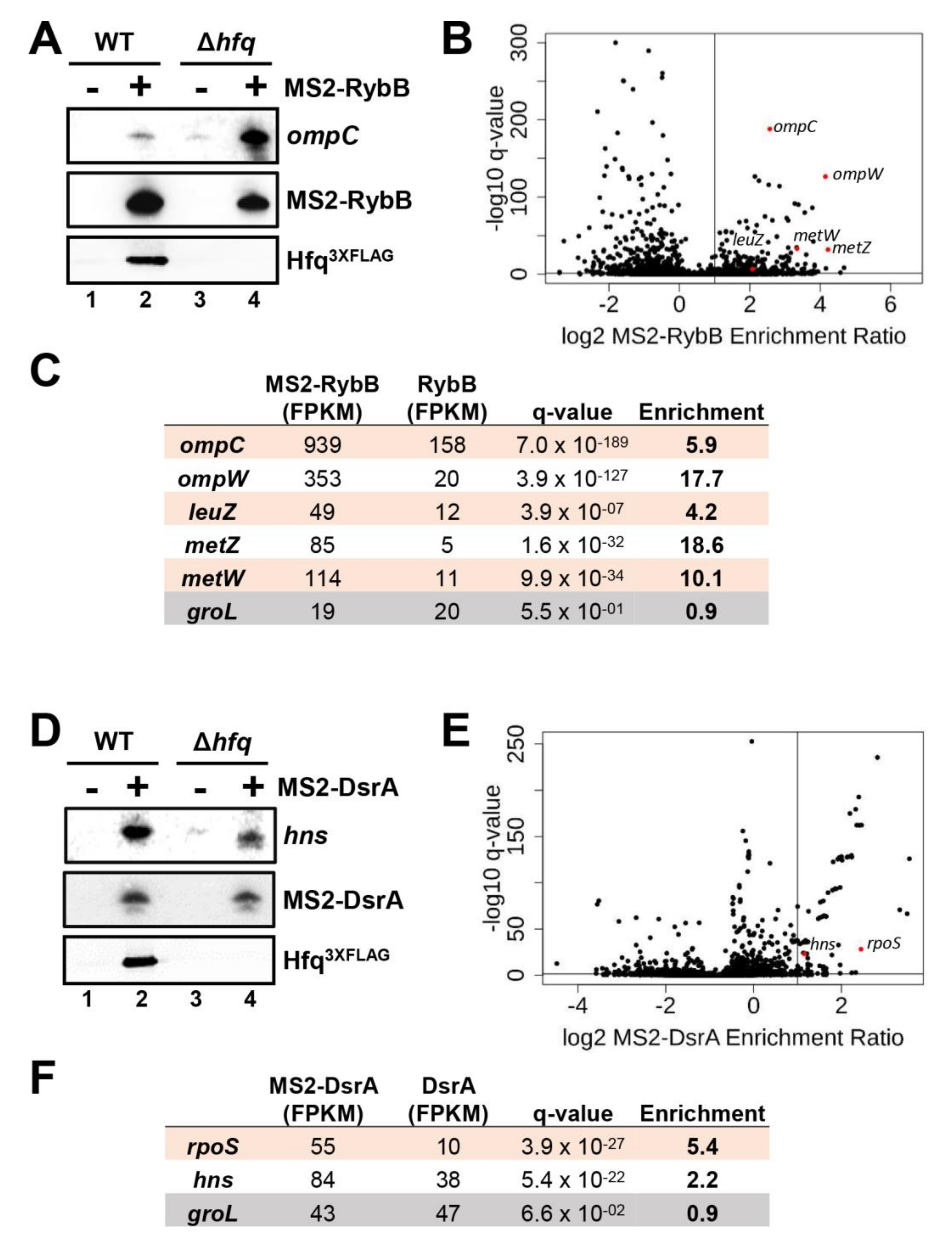
2.9. Effect of Hfq Deletion on the Targetome of RybB and DsrA sRNAs In Vivo
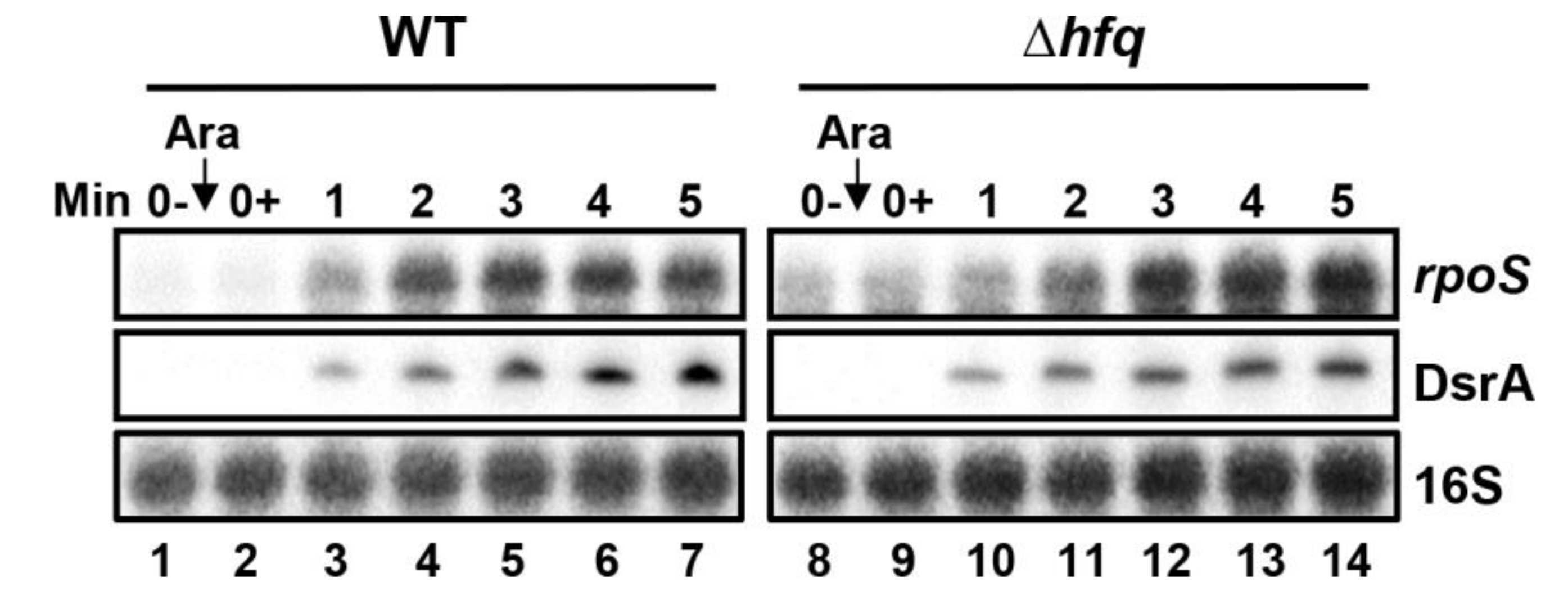
2.10. Effect of Hfq Deletion on rpoS Target mRNA Stabilization by DsrA
3. Discussion
3.1. Hfq Is Not Essential for RyhB, RybB, and DsrA sRNAs Complex Formation with Certain Target mRNAs
3.2. Hfq Binding Sites Are Not Required for sRNA:mRNA Complex Formation
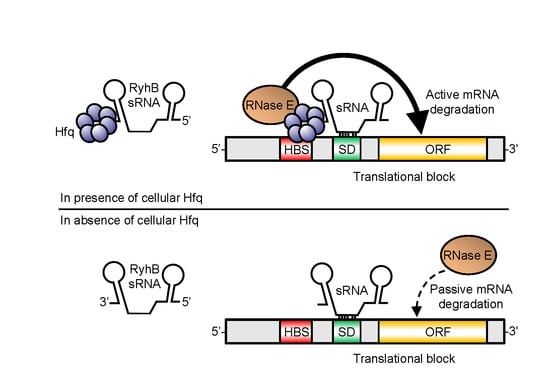
3.3. Hfq Binding to Target mRNA Is Crucial to Induce Rapid sRNA-Dependent Degradation
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Growth Conditions
5.2. RNA Extraction and Northern Blot Analysis
5.3. Proteins Extraction and Western Blot Analysis
5.4. β-Galactosidase Assays
5.5. MS2-Affinity Purification
5.6. MS2-Affinity Purification Coupled with RNA Sequencing
5.7. Super-Resolution Imaging
5.8. Copy Number Calculation and Colocalization Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carrier, M.C.; Lalaouna, D.; Masse, E. Broadening the Definition of Bacterial Small RNAs: Characteristics and Mechanisms of Action. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 72, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, E.G.; Romby, P. Small RNAs in bacteria and archaea: Who they are, what they do, and how they do it. Adv. Genet. 2015, 90, 133–208. [Google Scholar]
- Weiberg, A.; Bellinger, M.; Jin, H. Conversations between kingdoms: Small RNAs. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 32, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmqvist, E.; Wagner, E.G.H. Impact of bacterial sRNAs in stress responses. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2017, 45, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorski, S.A.; Vogel, J.; Doudna, J.A. RNA-based recognition and targeting: Sowing the seeds of specificity. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papenfort, K.; Vanderpool, C.K. Target activation by regulatory RNAs in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 39, 362–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago-Frangos, A.; Woodson, S.A. Hfq chaperone brings speed dating to bacterial sRNA. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2018, 9, e1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodson, S.A.; Panja, S.; Santiago-Frangos, A. Proteins that chaperone RNA regulation. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, J.; Luisi, B.F. Hfq and its constellation of RNA. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franze de Fernandez, M.T.; Eoyang, L.; August, J.T. Factor fraction required for the synthesis of bacteriophage Qbeta-RNA. Nature 1968, 219, 588–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franze de Fernandez, M.T.; Hayward, W.S.; August, J.T. Bacterial proteins required for replication of phage Q ribonucleic acid Pruification and properties of host factor I, a ribonucleic acid-binding protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1972, 247, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Y.; Papenfort, K.; Reinhardt, R.; Sharma, C.M.; Vogel, J. An atlas of Hfq-bound transcripts reveals 3′ UTRs as a genomic reservoir of regulatory small RNAs. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 4005–4019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sittka, A.; Lucchini, S.; Papenfort, K.; Sharma, C.M.; Rolle, K.; Binnewies, T.T.; Hinton, J.C.; Vogel, J. Deep sequencing analysis of small noncoding RNA and mRNA targets of the global post-transcriptional regulator, Hfq. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Wassarman, K.M.; Rosenow, C.; Tjaden, B.C.; Storz, G.; Gottesman, S. Global analysis of small RNA and mRNA targets of Hfq. Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 50, 1111–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, M.A.; Pearson, R.F.; Møller, T.; Valentin-Hansen, P.; Brennan, R.G. Structures of the pleiotropic translational regulator Hfq and an Hfq-RNA complex: A bacterial Sm-like protein. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 3546–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilusic, I.; Popitsch, N.; Rescheneder, P.; Schroeder, R.; Lybecker, M. Revisiting the coding potential of the E. coli genome through Hfq co-immunoprecipitation. RNA Biol. 2014, 11, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Melamed, S.; Adams, P.P.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, H.; Storz, G. RNA-RNA Interactomes of ProQ and Hfq Reveal Overlapping and Competing Roles. Mol. Cell 2020, 77, 411–425.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sittka, A.; Pfeiffer, V.; Tedin, K.; Vogel, J. The RNA chaperone Hfq is essential for the virulence of Salmonella typhimurium. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 63, 193–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissmann, T.A.; Touati, D. Hfq, a new chaperoning role: Binding to messenger RNA determines access for small RNA regulator. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massé, E.; Escorcia, F.E.; Gottesman, S. Coupled degradation of a small regulatory RNA and its mRNA targets in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 2003, 17, 2374–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moll, I.; Leitsch, D.; Steinhauser, T.; Bläsi, U. RNA chaperone activity of the Sm-like Hfq protein. EMBO Rep. 2003, 4, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, T.; Franch, T.; Højrup, P.; Keene, D.R.; Bächinger, H.P.; Brennan, R.G.; Valentin-Hansen, P. Hfq: A Bacterial Sm-like Protein that Mediates RNA-RNA Interaction. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Wassarman, K.M.; Ortega, J.; Steven, A.C.; Storz, G. The Sm-like Hfq protein increases OxyS RNA interaction with target mRNAs. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, R.F.; Arraiano, C.M.; Andrade, J.M. New molecular interactions broaden the functions of the RNA chaperone Hfq. Curr. Genet. 2019, 65, 1313–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamoto, H.; Koide, Y.; Morita, T.; Aiba, H. Base-pairing requirement for RNA silencing by a bacterial small RNA and acceleration of duplex formation by Hfq. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 61, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prévost, K.; Salvail, H.; Desnoyers, G.; Jacques, J.-F.; Phaneuf, É.; Massé, E. The small RNA RyhB activates the translation of shiA mRNA encoding a permease of shikimate, a compound involved in siderophore synthesis. Mol. Microbiol. 2007, 64, 1260–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, E.; Schmidt, S.; Weichenrieder, O. Small RNA binding to the lateral surface of Hfq hexamers and structural rearrangements upon mRNA target recognition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 9396–9401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soper, T.J.; Doxzen, K.; Woodson, S.A. Major role for mRNA binding and restructuring in sRNA recruitment by Hfq. RNA 2011, 17, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavita, K.; de Mets, F.; Gottesman, S. New aspects of RNA-based regulation by Hfq and its partner sRNAs. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2018, 42, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gottesman, S. Hfq links translation repression to stress-induced mutagenesis inE. coli. Genes Dev. 2017, 31, 1382–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Chen, D.; Yan, Y.; Gao, X.; Liu, Z.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, R. Hfq Globally Binds and Destabilizes sRNAs and mRNAs in Yersinia pestis. mSystems 2019, 4, e00245-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmqvist, E.; Wright, P.R.; Li, L.; Bischler, T.; Barquist, L.; Reinhardt, R.; Backofen, R.; Vogel, J. Global RNA recognition patterns of post-transcriptional regulators Hfq and CsrA revealed by UV crosslinking in vivo. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 991–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vytvytska, O.; Moll, I.; Kaberdin, V.R.; von Gabain, A.; Blasi, U. Hfq (HF1) stimulates ompA mRNA decay by interfering with ribosome binding. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Desnoyers, G.; Masse, E. Noncanonical repression of translation initiation through small RNA recruitment of the RNA chaperone Hfq. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 726–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azam, M.S.; Vanderpool, C.K. Translational regulation by bacterial small RNAs via an unusual Hfq-dependent mechanism. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 2585–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandyra, K.J.; Said, N.; Pfeiffer, V.; Gorna, M.W.; Vogel, J.; Luisi, B.F. The seed region of a small RNA drives the controlled destruction of the target mRNA by the endoribonuclease RNase E. Mol. Cell 2012, 47, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, H.; Morita, T.; Shimizu, A.; Inada, T.; Aiba, H. Implication of membrane localization of target mRNA in the action of a small RNA: Mechanism of post-transcriptional regulation of glucose transporter in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, T.; Maki, K.; Aiba, H. RNase E-based ribonucleoprotein complexes: Mechanical basis of mRNA destabilization mediated by bacterial noncoding RNAs. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 2176–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalaouna, D.; Prévost, K.; Eyraud, A.; Massé, E. Identification of unknown RNA partners using MAPS. Methods 2017, 117, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massé, E.; Gottesman, S. A small RNA regulates the expression of genes involved in iron metabolism in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 4620–4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentin-Hansen, P.; Eriksen, M.; Udesen, C. The bacterial Sm-like protein Hfq: A key player in RNA transactions. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 51, 1525–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalaouna, D.; Prévost, K.; Laliberté, G.; Houe, V.; Massé, E. Contrasting silencing mechanisms of the same target mRNA by two regulatory RNAs in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, 2600–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, J.M.; Dos Santos, R.F.; Chelysheva, I.; Ignatova, Z.; Arraiano, C.M. The RNA-binding protein Hfq is important for ribosome biogenesis and affects translation fidelity. EMBO J. 2018, 37, e97631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajnsdorf, E.; Regnier, P. Host factor Hfq of Escherichia coli stimulates elongation of poly(A) tails by poly(A) polymerase I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 1501–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanty, B.K.; Maples, V.F.; Kushner, S.R. The Sm-like protein Hfq regulates polyadenylation dependent mRNA decay in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 54, 905–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Régnier, P.; Hajnsdorf, E. The interplay of Hfq, poly(A) polymerase I and exoribonucleases at the 3′ ends of RNAs resulting from Rho-independent termination. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chareyre, S.; Mandin, P. Bacterial Iron Homeostasis Regulation by sRNAs. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvail, H.; Massé, E. Regulating iron storage and metabolism with RNA: An overview of posttranscriptional controls of intracellular iron homeostasis. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2011, 3, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpousis, A.J.; Van Houwe, G.; Ehretsmann, C.; Krisch, H.M. Copurification of E. coli RNAase E and PNPase: Evidence for a specific association between two enzymes important in RNA processing and degradation. Cell 1994, 76, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prévost, K.; Desnoyers, G.; Jacques, J.-F.; Lavoie, F.; Massé, E. Small RNA-induced mRNA degradation achieved through both translation block and activated cleavage. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalaouna, D.; Carrier, M.C.; Semsey, S.; Brouard, J.S.; Wang, J.; Wade, J.T.; Masse, E. A 3′ external transcribed spacer in a tRNA transcript acts as a sponge for small RNAs to prevent transcriptional noise. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, J.; Singh, D.; Zhang, Q.; Park, S.; Balasubramanian, D.; Golding, I.; Vanderpool, C.K.; Ha, T. RNA biochemistry. Determination of in vivo target search kinetics of regulatory noncoding RNA. Science 2015, 347, 1371–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.; Bogaard, P.V.D.; Rifkin, S.; Van Oudenaarden, A.; Tyagi, S. Imaging individual mRNA molecules using multiple singly labeled probes. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 877–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Jones, S.A.; Brandenburg, B.; Zhuang, X. Whole-cell 3D STORM reveals interactions between cellular structures with nanometer-scale resolution. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Bujnowska, M.; McLean, E.L.; Fei, J. Quantitative Super-Resolution Imaging of Small RNAs in Bacterial Cells. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1737, 199–212. [Google Scholar]
- Schu, D.J.; Zhang, A.; Gottesman, S.; Storz, G. Alternative Hfq- sRNA interaction modes dictate alternative mRNA recognition. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 2557–2573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalaouna, D.; Morissette, A.; Carrier, M.-C.; Massé, E.; And, M.C. DsrA regulatory RNA represses bothhnsandrbsDmRNAs through distinct mechanisms in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 2015, 98, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majdalani, N.; Cunning, C.; Sledjeski, D.; Elliott, T.; Gottesman, S. DsrA RNA regulates translation of RpoS message by an anti-antisense mechanism, independent of its action as an antisilencer of transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 12462–12467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, D.; Shin, D.; Suk, S.; Lee, Y. Mechanisms for Hfq-Independent Activation of rpoS by DsrA, a Small RNA, in Escherichia coli. Mol. Cells 2019, 42, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Soper, T.; Mandin, P.; Majdalani, N.; Gottesman, S.; Woodson, S.A. Positive regulation by small RNAs and the role of Hfq. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9602–9607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, S.A.; McAteer, S.P.; Kudla, G.; Pang, I.; Deshpande, N.P.; Amos, T.G.; Leong, K.W.; Wilkins, M.R.; Strugnell, R.; Gally, D.L.; et al. Small RNA interactome of pathogenic E. coli revealed through crosslinking of RNase E. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melamed, S.; Peer, A.; Faigenbaum-Romm, R.; Gatt, Y.E.; Reiss, N.; Bar, A.; Altuvia, Y.; Argaman, L.; Margalit, H. Global Mapping of Small RNA-Target Interactions in Bacteria. Mol. Cell 2016, 63, 884–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hor, J.; Vogel, J. Global snapshots of bacterial RNA networks. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aiba, H.; Adhya, S.; de Crombrugghe, B. Evidence for two functional gal promoters in intact Escherichia coli cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 11905–11910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afgan, E.; Baker, D.; van den Beek, M.; Blankenberg, D.; Bouvier, D.; Cech, M.; Chilton, J.; Clements, D.; Coraor, N.; Eberhard, C.; et al. The Galaxy platform for accessible, reproducible and collaborative biomedical analyses: 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W3–W10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, K.L. The UCSC Archaeal Genome Browser. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D407–D410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapnell, C.; Williams, B.A.; Pertea, G.; Mortazavi, A.; Kwan, G.; van Baren, M.J.; Salzberg, S.L.; Wold, B.J.; Pachter, L. Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell differentiation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; Smyth, G.K. Small-sample estimation of negative binomial dispersion, with applications to SAGE data. Biostatistics 2007, 9, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daszykowski, M.; Walczak, B.; Massart, D.L. Looking for natural patterns in data: Part 1. Density-based approach. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2001, 56, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, T.; Ara, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Takai, Y.; Okumura, Y.; Baba, M.; A Datsenko, K.; Tomita, M.; Wanner, B.L.; Mori, H. Construction of Escherichia coli K-12 in-frame, single-gene knockout mutants: The Keio collection. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2006, 2, 2006-0008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherepanov, P.P.; Wackernagel, W. Gene disruption in Escherichia coli: TcR and KmR cassettes with the option of Flp-catalyzed excision of the antibiotic-resistance determinant. Gene 1995, 158, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datsenko, K.A.; Wanner, B.L. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2000, 97, 6640–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desnoyers, G.; Morissette, A.; Prévost, K.; Massé, E. Small RNA-induced differential degradation of the polycistronic mRNA iscRSUA. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, B.S.; Court, D.L.; Nakamura, Y.; Rivas, M.P.; Turnbough, C.L. Rapid confirmation of single copy lambda prophage integration by PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 5765–5766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Repoila, F.; Gottesman, S.; Ohkawa, H.; Price, G.D.; Badger, M.R.; Ogawa, T. Signal Transduction Cascade for Regulation of RpoS: Temperature Regulation of DsrA. J. Bacteriol. 2001, 183, 2591–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvail, H.; Caron, M.-P.; Bélanger, J.; Massé, E. Antagonistic functions between the RNA chaperone Hfq and an sRNA regulate sensitivity to the antibiotic colicin. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 2764–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lalaouna, D.; Prévost, K.; Park, S.; Chénard, T.; Bouchard, M.-P.; Caron, M.-P.; Vanderpool, C.K.; Fei, J.; Massé, E. Binding of the RNA Chaperone Hfq on Target mRNAs Promotes the Small RNA RyhB-Induced Degradation in Escherichia coli. Non-Coding RNA 2021, 7, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7040064
Lalaouna D, Prévost K, Park S, Chénard T, Bouchard M-P, Caron M-P, Vanderpool CK, Fei J, Massé E. Binding of the RNA Chaperone Hfq on Target mRNAs Promotes the Small RNA RyhB-Induced Degradation in Escherichia coli. Non-Coding RNA. 2021; 7(4):64. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7040064
Chicago/Turabian StyleLalaouna, David, Karine Prévost, Seongjin Park, Thierry Chénard, Marie-Pier Bouchard, Marie-Pier Caron, Carin K. Vanderpool, Jingyi Fei, and Eric Massé. 2021. "Binding of the RNA Chaperone Hfq on Target mRNAs Promotes the Small RNA RyhB-Induced Degradation in Escherichia coli" Non-Coding RNA 7, no. 4: 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7040064
APA StyleLalaouna, D., Prévost, K., Park, S., Chénard, T., Bouchard, M.-P., Caron, M.-P., Vanderpool, C. K., Fei, J., & Massé, E. (2021). Binding of the RNA Chaperone Hfq on Target mRNAs Promotes the Small RNA RyhB-Induced Degradation in Escherichia coli. Non-Coding RNA, 7(4), 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7040064