Circular RNAs: Potential Applications as Therapeutic Targets and Biomarkers in Breast Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Biogenesis, Discovery, and Biological Functions of CircRNAs
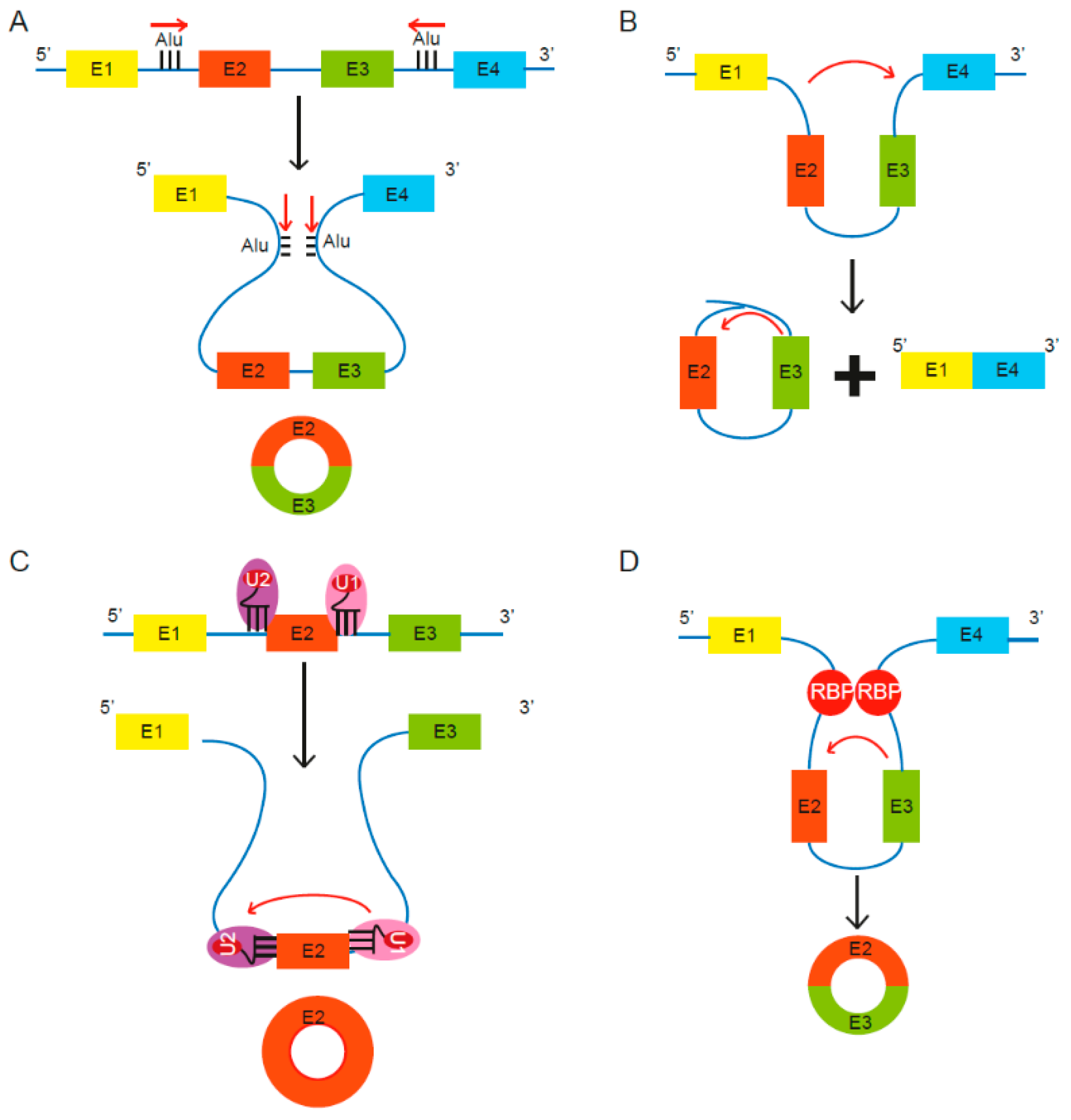
2.1. Biogenesis of CircRNAs
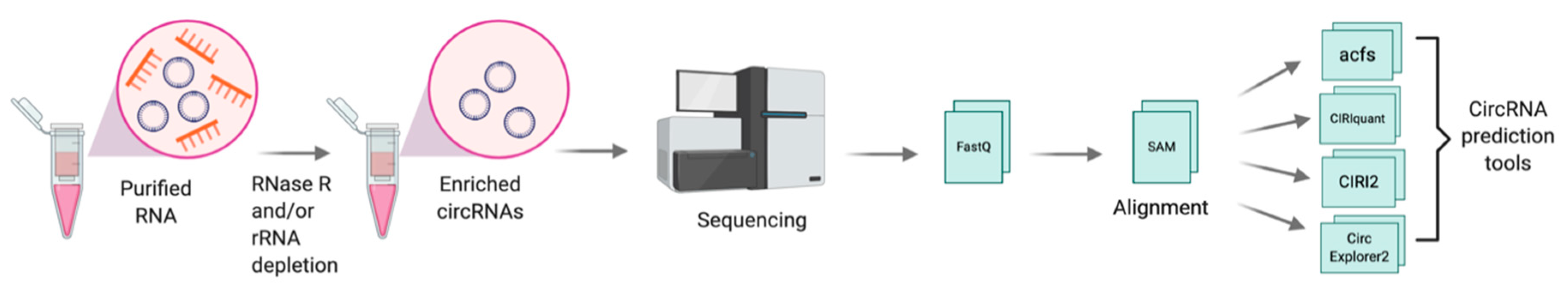
2.2. Discovery and Detection of CircRNAs
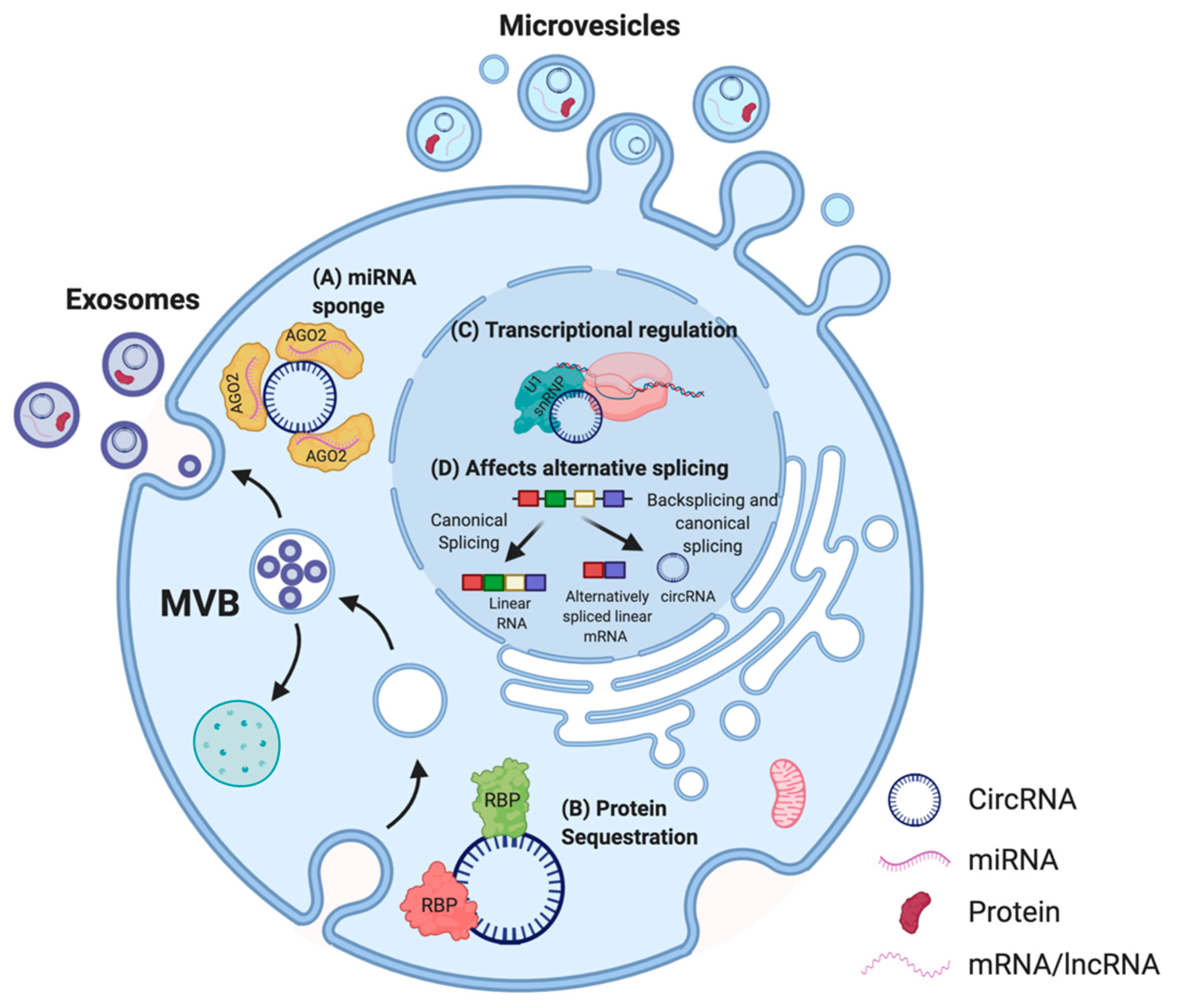
2.3. Mechanism of Action of CircRNAs
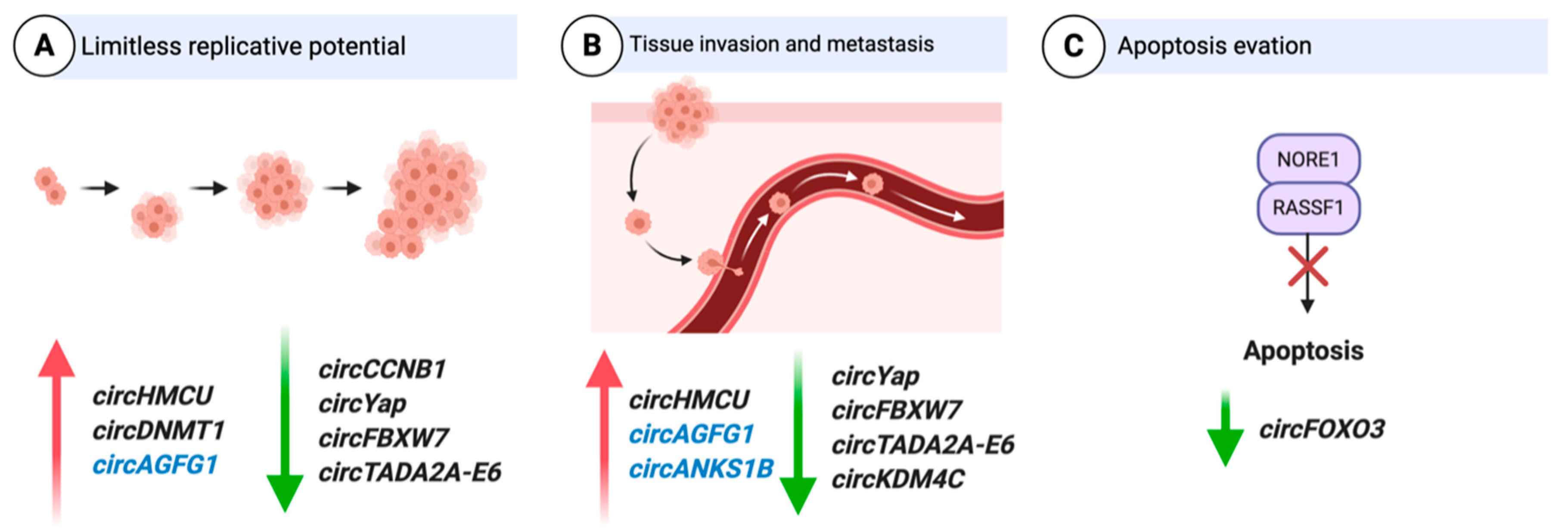
3. Function of CircRNAs in Breast Cancer
3.1. CircRNAs as Oncogenes
3.1.1. Cell Cycle
3.1.2. Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT)
3.1.3. Hypoxia
3.1.4. Autophagy
3.1.5. Invasion
3.2. CircRNAs as Tumor Suppressors
3.2.1. Cell Cycle
3.2.2. EMT
3.2.3. Invasion
3.2.4. Apoptosis
3.2.5. Immune Evasion
4. Clinical Relevance of circRNAs in BC
4.1. CircRNAs as Diagnostic/Prognostic Markers
4.2. CircRNAs as Markers of Drug Resistance
4.3. CircRNAs as Therapies and Therapeutic Targets in BC
5. Limitations and Challenges in the Field of CircRNAs in BC
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heer, E.; Harper, A.; Escandor, N.; Sung, H.; McCormack, V.; Fidler-Benaoudia, M.M. Global burden and trends in premenopausal and postmenopausal breast cancer: A population-based study. Lancet Glob. Health 2020, 8, e1027–e1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragomeni, S.M.; Sciallis, A.; Jeruss, J.S. Molecular Subtypes and Local-Regional Control of Breast Cancer. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 27, 95–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Duan, J.-J.; Bian, X.-W.; Yu, S.-C. Triple-negative breast cancer molecular subtyping and treatment progress. Breast Cancer Res. BCR 2020, 22, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignatiadis, M.; Sotiriou, C. Luminal breast cancer: From biology to treatment. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 10, 494–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuello, M.; Ettenberg, S.A.; Clark, A.S.; Keane, M.M.; Posner, R.H.; Nau, M.M.; Dennis, P.A.; Lipkowitz, S. Down-regulation of the erbB-2 receptor by trastuzumab (herceptin) enhances tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated apoptosis in breast and ovarian cancer cell lines that overexpress erbB-2. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 4892–4900. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchini, G.; Balko, J.M.; Mayer, I.A.; Sanders, M.E.; Gianni, L. Triple-negative breast cancer: Challenges and opportunities of a heterogeneous disease. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 13, 674–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanya, E.K.; Sara, M.T. Role of Immunotherapy in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2020, 18, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diana, A.; Carlino, F.; Franzese, E.; Oikonomidou, O.; Criscitiello, C.; De Vita, F.; Ciardiello, F.; Orditura, M. Early Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Conventional Treatment and Emerging Therapeutic Landscapes. Cancers 2020, 12, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, A.; Viale, G.; Curigliano, G. Recent advances in triple negative breast cancer: The immunotherapy era. BMC Med. 2019, 17, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelio, I.; Bernassola, F.; Candi, E. Emerging roles of long non-coding RNAs in breast cancer biology and management. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanger, H.L.; Klotz, G.; Riesner, D.; Gross, H.J.; Kleinschmidt, A.K. Viroids are single-stranded covalently closed circular RNA molecules existing as highly base-paired rod-like structures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 3852–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Wang, K.; Slevin, M.K.; Burd, C.E.; Liu, J.; Marzluff, W.F.; Sharpless, N.E. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA 2013, 19, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sharpless, N.E. Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs. Nat. Biotech. 2014, 32, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memczak, S.; Jens, M.; Elefsinioti, A.; Torti, F.; Krueger, J.; Rybak, A.; Maier, L.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Gregersen, L.H.; Munschauer, M.; et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013, 495, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.L. The expanding regulatory mechanisms and cellular functions of circular RNAs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 475–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.U.; Agarwal, V.; Guo, H.; Bartel, D.P. Expanded identification and characterization of mammalian circular RNAs. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.; He, A. Circles reshaping the RNA world: From waste to treasure. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.J.; Shen, J. Circular RNA participates in the carcinogenesis and the malignant behavior of cancer. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Wilusz, J.E. Short intronic repeat sequences facilitate circular RNA production. Genes Dev. 2014, 28, 2233–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starke, S.; Jost, I.; Rossbach, O.; Schneider, T.; Schreiner, S.; Hung, L.H.; Bindereif, A. Exon circularization requires canonical splice signals. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzman, J.; Chen, R.E.; Olsen, M.N.; Wang, P.L.; Brown, P.O. Cell-type specific features of circular RNA expression. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak-Wolf, A.; Stottmeister, C.; Glažar, P.; Jens, M.; Pino, N.; Giusti, S.; Hanan, M.; Behm, M.; Bartok, O.; Ashwal-Fluss, R.; et al. Circular RNAs in the Mammalian Brain Are Highly Abundant, Conserved, and Dynamically Expressed. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 870–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, J.; Tang, Y.; Tian, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, Z.; Yang, D.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Circular RNAs in Cancer: Emerging functions in hallmarks, stemness, resistance and roles as potential biomarkers. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardini, B.; Sabo, A.A.; Birolo, G.; Calin, G.A. Noncoding RNAs in Extracellular Fluids as Cancer Biomarkers: The New Frontier of Liquid Biopsies. Cancers 2019, 11, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasda, E.; Parker, R. Circular RNAs Co-Precipitate with Extracellular Vesicles: A Possible Mechanism for circRNA Clearance. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.; Greenman, C.; Cook, P.R.; Papantonis, A. Exon Skipping Is Correlated with Exon Circularization. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 2414–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Tatomer, D.C.; Luo, Z.; Wu, H.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.-L.; Cherry, S.; Wilusz, J.E. The Output of Protein-Coding Genes Shifts to Circular RNAs When the Pre-mRNA Processing Machinery Is Limiting. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 940–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Meyer, M.; Pamudurti, N.R.; Ivanov, A.; Bartok, O.; Hanan, M.; Evantal, N.; Memczak, S.; Rajewsky, N.; Kadener, S. circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conn, S.J.; Pillman, K.A.; Toubia, J.; Conn, V.M.; Salmanidis, M.; Phillips, C.A.; Roslan, S.; Schreiber, A.W.; Gregory, P.A.; Goodall, G.J. The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of circRNAs. Cell 2015, 160, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaphiropoulos, P.G. Circular RNAs from transcripts of the rat cytochrome P450 2C24 gene: Correlation with exon skipping. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 6536–6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, S.; Geiger, P.; Cuyugan, L.; Boyle, A.; Serrano, G.; Beach, T.G.; Liang, W.S. Identification of Circular RNAs using RNA Sequencing. J. Vis. Exp. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Conrad, T.O. Acfs: Accurate circRNA identification and quantification from RNA-Seq data. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Yang, J.; Zhao, F. Accurate quantification of circular RNAs identifies extensive circular isoform switching events. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, F. Circular RNA identification based on multiple seed matching. Brief. Bioinform. 2017, 19, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-O.; Dong, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.-L.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.-L.; Yang, L. Diverse alternative back-splicing and alternative splicing landscape of circular RNAs. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdt, L.M.; Kohlmaier, A.; Teupser, D. Molecular roles and function of circular RNAs in eukaryotic cells. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 1071–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukiw, W.J. Circular RNA (circRNA) in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.Y. Roles of the circular RNA circ-Foxo3 in breast cancer progression. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 589–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perriman, R.; Ares, M., Jr. Circular mRNA can direct translation of extremely long repeating-sequence proteins in vivo. RNA 1998, 4, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.O.; Chen, T.; Xiang, J.F.; Yin, Q.F.; Xing, Y.H.; Zhu, S.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. Circular intronic long noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell 2013, 51, 792–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wang, B.; Feng, X.; Xu, Y.; Lu, K.; Sun, M. circRNAs and Exosomes: A Mysterious Frontier for Human Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 19, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Abraham, J.M.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Ashktorab, H.; Smoot, D.T.; Cole, R.N.; Boronina, T.N.; et al. Synthetic Circular RNA Functions as a miR-21 Sponge to Suppress Gastric Carcinoma Cell Proliferation. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 13, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, L.; Bai, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Deng, T.; Yang, H.; Sun, W.; Wang, X.; Zhu, K.; et al. Exosomal circRNA derived from gastric tumor promotes white adipose browning by targeting the miR-133/PRDM16 pathway. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 2501–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.B.; Jensen, T.I.; Clausen, B.H.; Bramsen, J.B.; Finsen, B.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 2013, 495, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.B.; Kjems, J.; Damgaard, C.K. Circular RNA and miR-7 in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 5609–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piwecka, M.; Glažar, P.; Hernandez-Miranda, L.R.; Memczak, S.; Wolf, S.A.; Rybak-Wolf, A.; Filipchyk, A.; Klironomos, F.; Cerda Jara, C.A.; Fenske, P.; et al. Loss of a mammalian circular RNA locus causes miRNA deregulation and affects brain function. Science 2017, 357, eaam8526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Dai, L.; Fu, X.; Zhang, J.; Ao, Y. Circular RNA Related to the Chondrocyte ECM Regulates MMP13 Expression by Functioning as a MiR-136 ‘Sponge’ in Human Cartilage Degradation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Guo, S.; Li, W.; Yu, P. The circular RNA Cdr1as, via miR-7 and its targets, regulates insulin transcription and secretion in islet cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhuo, H.; Xu, M.; Wang, L.; Xu, H.; Peng, J.; Hou, J.; Lin, L.; Cai, J. Regulatory network of circRNA–miRNA–mRNA contributes to the histological classification and disease progression in gastric cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, K.-Y.; Lin, Y.-C.; Gupta, S.K.; Chang, N.; Yen, L.; Sun, H.S.; Tsai, S.-J. Noncoding Effects of Circular RNA CCDC66 Promote Colon Cancer Growth and Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2339–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Liang, Y.; Sang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, B.; Du, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, W.; et al. circHMCU Promotes Proliferation and Metastasis of Breast Cancer by Sponging the let-7 Family. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 20, 518–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.-d.; Dang, Y.-w.; Lin, P.; Wen, D.-y.; He, R.-q.; Luo, D.-z.; Feng, Z.-b.; Chen, G. A circRNA–miRNA–mRNA network identification for exploring underlying pathogenesis and therapy strategy of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.-M.; Wen, X.; Han, X.-R.; Wang, S.; Wang, Y.-J.; Shen, M.; Fan, S.-H.; Zhang, Z.-F.; Shan, Q.; Li, M.-Q.; et al. Role of Circular RNA DLEU2 in Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 38, e00259-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Ma, W.; Ke, Z.; Xie, F. CircRNA hsa_circ_100395 regulates miR-1228/TCF21 pathway to inhibit lung cancer progression. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 2080–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdt, L.; Stahringer, A.; Sass, K.; Pichler, G.; Kulak, N.; Wilfert, W.; Kohlmaier, A.; Herbst, A.; Northoff, B.; Nicolaou, A. Circular non-coding RNA ANRIL modulates ribosomal RNA maturation and atherosclerosis in humans. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Du, W.W.; Fang, L.; Yang, W.; Wu, N.; Awan, F.M.; Yang, Z.; Yang, B.B. Induction of tumor apoptosis through a circular RNA enhancing Foxo3 activity. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 357–370. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Bao, C.; Chen, L.; Lin, M.; Wang, X.; Zhong, G.; Yu, B.; Hu, W.; Dai, L.; et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, J.; Deng, H.; Ma, R.; Liao, J.-Y.; Liang, H.; Hu, J.; Li, J.; Guo, Z.; Cai, J.; et al. Targeting Mitochondria-Located circRNA SCAR Alleviates NASH via Reducing mROS Output. Cell 2020, 183, 76–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposo, G.; Stahl, P.D. Extracellular vesicles: A new communication paradigm? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 509–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhu, X.; Huang, S. Extracellular vesicle long non-coding RNAs and circular RNAs: Biology, functions and applications in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2020, 489, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Ling, Y.; Mehrpour, M.; Saw, P.E.; Liu, Z.; Tan, W.; Tian, Z.; Zhong, W.; Lin, W.; Luo, Q.; et al. Autophagy-associated circRNA circCDYL augments autophagy and promotes breast cancer progression. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, C.; Hu, Q.; Fu, Z.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Li, A.; Marks, J.R.; et al. CircIRAK3 sponges miR-3607 to facilitate breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2018, 430, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Song, X.; Li, Y.; Su, P.; Han, D.; Ma, T.; Guo, R.; Chen, B.; Zhao, W.; Sang, Y.; et al. circKDM4C suppresses tumor progression and attenuates doxorubicin resistance by regulating miR-548p/PBLD axis in breast cancer. Oncogene 2019, 38, 6850–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; He, B.; Yang, B.B.; Xu, T.; Chen, X.; Xu, M.; Liu, X.; Sun, H.; Pan, Y.; Wang, S. The pro-metastasis effect of circANKS1B in breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, A.M.; Chalbatani, G.M.; Berland, L.; Cruz De los Santos, M.; Raj, P.; Jalali, S.A.; Gharagouzloo, E.; Ivan, C.; Dragomir, M.P.; Calin, G.A. A New World of Biomarkers and Therapeutics for Female Reproductive System and Breast Cancers: Circular RNAs. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Xing, L.; Zheng, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, J. The circRNA circAGFG1 acts as a sponge of miR-195-5p to promote triple-negative breast cancer progression through regulating CCNE1 expression. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, P.; Xiang, R.; Ren, G.; Yang, S. ZEB1 confers chemotherapeutic resistance to breast cancer by activating ATM. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Liu, S.; Liu, F.; Sang, M.; Ju, Y.; Fan, X.; Gu, L.; Li, Z.; Geng, C.; Sang, M. ZEB1-Mediated Transcriptional Upregulation of circWWC3 Promotes Breast Cancer Progression through Activating Ras Signaling Pathway. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 22, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, M.; Yao, Y.; Cai, Z. WWC3 Inhibits Glioma Cell Proliferation Through Suppressing the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. DNA Cell Biol. 2018, 37, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Liu, Z.; Tan, L.; Su, A.N.; Jiang, W.G.; Gong, C. HIF1α-associated circDENND4C Promotes Proliferation of Breast Cancer Cells in Hypoxic Environment. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 4337–4343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, B.; Johnson, R.S.; Simon, M.C. HIF1α and HIF2α: Sibling rivalry in hypoxic tumour growth and progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 12, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Liu, J.; Feng, Y.; Li, Z.; He, L.; Li, L.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Knockdown of circDENND4C inhibits glycolysis, migration and invasion by up-regulating miR-200b/c in breast cancer under hypoxia. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Wang, M.; Dong, Y.; Xu, B.; Chen, J.; Ding, Y.; Qiu, S.; Li, L.; Karamfilova Zaharieva, E.; Zhou, X.; et al. Circular RNA circRNF20 promotes breast cancer tumorigenesis and Warburg effect through miR-487a/HIF-1α/HK2. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.W.; Yang, W.; Li, X.; Awan, F.M.; Yang, Z.; Fang, L.; Lyu, J.; Li, F.; Peng, C.; Krylov, S.N.; et al. A circular RNA circ-DNMT1 enhances breast cancer progression by activating autophagy. Oncogene 2018, 37, 5829–5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.W.; Yang, W.; Li, X.; Fang, L.; Wu, N.; Li, F.; Chen, Y.; He, Q.; Liu, E.; Yang, Z.; et al. The Circular RNA circSKA3 Binds Integrin β1 to Induce Invadopodium Formation Enhancing Breast Cancer Invasion. Mol. Ther. 2020, 28, 1287–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blouw, B.; Patel, M.; Iizuka, S.; Abdullah, C.; You, W.K.; Huang, X.; Li, J.-L.; Diaz, B.; Stallcup, W.B.; Courtneidge, S.A. The Invadopodia Scaffold Protein Tks5 Is Required for the Growth of Human Breast Cancer Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Liu, M.; Yang, L.; Tu, G.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, M.; Cheng, H.; Luo, H.; Fu, W.; Li, Z.; et al. Acquisition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype in the tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cell: A new role for G protein-coupled estrogen receptor in mediating tamoxifen resistance through cancer-associated fibroblast-derived fibronectin and β1-integrin signaling pathway in tumor cells. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Du, W.W.; Lyu, J.; Dong, J.; Zhang, C.; Yang, W.; He, A.; Kwok, Y.S.S.; Ma, J.; Wu, N.; et al. Enhanced breast cancer progression by mutant p53 is inhibited by the circular RNA circ-Ccnb1. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 2195–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.; Du, W.W.; Awan, F.M.; Dong, J.; Yang, B.B. The circular RNA circ-Ccnb1 dissociates Ccnb1/Cdk1 complex suppressing cell invasion and tumorigenesis. Cancer Lett. 2019, 459, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Gao, G.; Zou, Y.; Zheng, S.; Zhang, L.; Ou, X.; Xie, X.; Tang, H. circFBXW7 Inhibits Malignant Progression by Sponging miR-197-3p and Encoding a 185-aa Protein in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 18, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Yuan, Z.; Du, K.Y.; Fang, L.; Lyu, J.; Zhang, C.; He, A.; Eshaghi, E.; Zeng, K.; Ma, J.; et al. Translation of yes-associated protein (YAP) was antagonized by its circular RNA via suppressing the assembly of the translation initiation machinery. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 2758–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.Z.; Shao, C.C.; Wang, X.J.; Zhao, X.; Chen, J.Q.; Ouyang, Y.X.; Feng, J.; Zhang, F.; Huang, W.H.; Ying, Q.; et al. circTADA2As suppress breast cancer progression and metastasis via targeting miR-203a-3p/SOCS3 axis. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 10, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.Y.; Yu, Y.B.; Gunawardena, H.P.; Xie, L.; Chen, X. BCLAF1 is a radiation-induced H2AX-interacting partner involved in γH2AX-mediated regulation of apoptosis and DNA repair. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, D.; Alfonso-Pérez, T.; Cundell, M.J.; Hopkins, M.; Holder, J.; Bancroft, J.; Hutter, L.H.; Novak, B.; Barr, F.A.; Gruneberg, U. CDK1-CCNB1 creates a spindle checkpoint–permissive state by enabling MPS1 kinetochore localization. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 218, 1182–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, S.; Nikkhoo, A.; Hojjat-Farsangi, M.; Namdar, A.; Azizi, G.; Mohammadi, H.; Yousefi, M.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F. CDK1 in Breast Cancer: Implications for Theranostic Potential. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androic, I.; Krämer, A.; Yan, R.; Rödel, F.; Gätje, R.; Kaufmann, M.; Strebhardt, K.; Yuan, J. Targeting cyclin B1 inhibits proliferation and sensitizes breast cancer cells to taxol. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailo, B.L.; Banik, K.; Girisa, S.; Bordoloi, D.; Fan, L.; Halim, C.E.; Wang, H.; Kumar, A.P.; Zheng, D.; Mao, X.; et al. FBXW7 in Cancer: What Has Been Unraveled Thus Far? Cancers 2019, 11, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, X.; Zhang, M.; Yan, S.; Sun, C.; Xiao, F.; Huang, N.; Yang, X.; Zhao, K.; Zhou, H.; et al. Novel Role of FBXW7 Circular RNA in Repressing Glioma Tumorigenesis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 110, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Yan, Q.; Zhao, X.; Zhong, J.; Yang, H.; Feng, Z.; Du, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; et al. Decreased expression of PBLD correlates with poor prognosis and functions as a tumor suppressor in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 524–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, F.X.; Guan, K.L. The Hippo pathway: Regulators and regulations. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barclay, J.L.; Anderson, S.T.; Waters, M.J.; Curlewis, J.D. SOCS3 as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer cells, and its regulation by PRL. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 1756–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Gan, T.-Y.; Li, N.; Liu, C.-Y.; Zhou, L.-Y.; Gao, J.-N.; Chen, C.; Yan, K.-W.; Ponnusamy, M.; Zhang, Y.-H.; et al. Circular RNA mediates cardiomyocyte death via miRNA-dependent upregulation of MTP18 expression. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutebi, M.; Anderson, B.O.; Duggan, C.; Adebamowo, C.; Agarwal, G.; Ali, Z.; Bird, P.; Bourque, J.-M.; DeBoer, R.; Gebrim, L.H.; et al. Breast cancer treatment: A phased approach to implementation. Cancer 2020, 126, 2365–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wu, Q.; Yan, Z.; Zheng, H.; Chen, C.-J.; Liu, Y.; Qi, Z.; Calandrelli, R.; Chen, Z.; Chien, S.; et al. Extracellular RNA in a single droplet of human serum reflects physiologic and disease states. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 19200–19208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitzer, E.; Haque, I.S.; Roberts, C.E.S.; Speicher, M.R. Current and future perspectives of liquid biopsies in genomics-driven oncology. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everaert, C.; Helsmoortel, H.; Decock, A.; Hulstaert, E.; Van Paemel, R.; Verniers, K.; Nuytens, J.; Anckaert, J.; Nijs, N.; Tulkens, J.; et al. Performance assessment of total RNA sequencing of human biofluids and extracellular vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.-B.; Yan, M.-G.; Fang, X.; Guo, J.-J.; Xiong, W.; Zhang, R.-P. Circulating circular RNA hsa_circ_0001785 acts as a diagnostic biomarker for breast cancer detection. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 487, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Kong, S.; Wang, F.; Ju, S. CircRNAs: Biogenesis, functions, and role in drug-resistant Tumours. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Lu, Y.; Tian, H.; Meng, X.; Wei, M.; Cho, W.C. Chemoresistance mechanisms of breast cancer and their countermeasures. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 114, 108800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yan, J.; Lang, X.; Zhuang, Y. Expression of circ_001569 is upregulated in osteosarcoma and promotes cell proliferation and cisplatin resistance by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 5856–5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wan, Z.; Tang, M.; Lin, Z.; Jiang, S.; Ji, L.; Gorshkov, K.; Mao, Q.; Xia, S.; Cen, D.; et al. N6-methyladenosine-modified CircRNA-SORE sustains sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating β-catenin signaling. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Cheng, J.; Quan, C.; Wen, H.; Feng, Z.; Hu, Q.; Zhu, J.; Huang, Y.; Wu, X. circCELSR1 (hsa_circ_0063809) Contributes to Paclitaxel Resistance of Ovarian Cancer Cells by Regulating FOXR2 Expression via miR-1252. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 19, 718–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, B.; Tian, Z.; Fan, W.; Ni, B. Circular RNA: A novel biomarker and therapeutic target for human cancers. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 16, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, F.C.; Lim, J.K.; Zhu, H.; Hin, L.C.; Wang, S. Using artificial microRNA sponges to achieve microRNA loss-of-function in cancer cells. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 81, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomir, M.; Calin, G.A. Circular RNAs in Cancer—Lessons Learned From microRNAs. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meganck, R.M.; Borchardt, E.K.; Rivera, R.M.C.; Scalabrino, M.L.; Wilusz, J.E.; Marzluff, W.F.; Asokan, A. Tissue-dependent expression and translation of circular RNAs with recombinant AAV vectors in vivo. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2018, 13, 89–98. [Google Scholar]
- Cortés-López, M.; Miura, P. Emerging Functions of Circular RNAs. Yale J. Biol. Med. 2016, 89, 527–537. [Google Scholar]
- Santer, L.; Bär, C.; Thum, T. Circular RNAs: A Novel Class of Functional RNA Molecules with a Therapeutic Perspective. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 1350–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, X.; Xue, W.; Zhang, L.; Cao, S.-M.; Lei, Y.-N.; Yang, L.-Z.; Guo, S.-K.; Zhang, J.-L.; Gao, X.; et al. Screening for functional circular RNAs using the CRISPR-Cas13 system. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Nguyen, T.M.; Zhang, X.-O.; Phan, T.; Clohessy, J.G.; Pandolfi, P.P. Optimized RNA-targeting CRISPR/Cas13d technology outperforms shRNA in identifying essential circRNAs. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konermann, S.; Lotfy, P.; Brideau, N.J.; Oki, J.; Shokhirev, M.N.; Hsu, P.D. Transcriptome Engineering with RNA-Targeting Type VI-D CRISPR Effectors. Cell 2018, 173, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research, N.; Weinstein, J.N.; Collisson, E.A.; Mills, G.B.; Shaw, K.R.M.; Ozenberger, B.A.; Ellrott, K.; Shmulevich, I.; Sander, C.; Stuart, J.M. The Cancer Genome Atlas Pan-Cancer analysis project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, L.S.; Hansen, T.B.; Venø, M.T.; Kjems, J. Circular RNAs in cancer: Opportunities and challenges in the field. Oncogene 2018, 37, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.-L. The Biogenesis, Functions, and Challenges of Circular RNAs. Mol. Cell 2018, 71, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Zheng, S.; Xiao, W.; Xie, X.; Yang, A.; Gao, G.; Xiong, Z.; Xue, Z.; Tang, H.; Xie, X. circRAD18 sponges miR-208a/3164 to promote triple-negative breast cancer progression through regulating IGF1 and FGF2 expression. Carcinogenesis 2019, 40, 1469–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chen, S.; Chen, H.; Mo, X.; Li, T.; Shao, Y.; Xiao, B.; Guo, J. Using circular RNA as a novel type of biomarker in the screening of gastric cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 444, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memczak, S.; Papavasileiou, P.; Peters, O.; Rajewsky, N. Identification and Characterization of Circular RNAs as a New Class of Putative Biomarkers in Human Blood. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royal Surrey County Hospital NHS Foundation Trust, CIRcular and Non-Coding RNAs as Clinically USeful Biomarkers in Pancreaticobiliary Cancers. Available online: https://ClinicalTrials.gov/show/NCT04584996:2020 (accessed on 5 January 2021).
| CircRNA | Expression in BC | Function in BC | Mechanism of Action | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CircHMCU | Upregulated | Promotes proliferation and metastasis | Modulates MYC, HMGA2, and CCND1 expression by acting as a miRNA sponge of let-7 | [52] |
| CircAGFG1 | Upregulated | Promotes proliferation, invasion, and metastasis | Regulates CCNE1 expression by acting as a sponge for miR-195-5p | [67] |
| CircWWC3 | Upregulated | Promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) | Acts as a sponge for miR-26b-3p and miR-660-3p and upregulates expression of EGFR, GRB2, PAK4, MAPK1, and AKT1 (Ras signaling pathway) | [69] |
| CircANKS1B | Upregulated | Induces EMT | Sponges miR-148-3p and miR-152-3p and increases expression of USF1. USF1 upregulates TGF-β1 | [65] |
| CircDENND4C | Upregulated | Regulates proliferation under hypoxic condition | Acts as a sponge for miR-200b and miR-200c under hypoxia | [71,73] |
| CircRNF20 | Upregulated | Increases glucose uptake and lactate production | Sponges miR-487a, which targets 3′ UTR of HIF1 α | [74] |
| CircDNMT1 | Upregulated | Stimulates cellular autophagy | Interacts with p53 and AUF1 and promotes their nuclear translocation, which induces autophagy and reduces DNMT1 mRNA stability | [75] |
| CircCDYL | Upregulated | Promotes proliferation via autophagy | Acts as a miR-1275 decoy, which targets ULK1 and ATG7 mRNAs associated with autophagy and autophagosome | [62] |
| CircSKA3 | Upregulated | Induces invapodium formation and cell invasion | Interacts with Tks5 and ITGB1 CircSKA3-Tks5-ITGB1 complex promotes cell invasion | [76] |
| CircCCNB1 | Downregulated | Decreases cell proliferation and survival, increases apoptosis | In mutant p53 cells, BCLAF1 interacts with H2AX and circCCNB1 to induce apoptosis Forms a complex with CCNB1 and CDK1 and prevents nuclear translocation, thereby suppressing cell proliferation and survival | [79,80] |
| CircFBXW7 | Downregulated | Suppresses cell proliferation and migration | Upregulates FBWX7 expression by sponging miR-197-3p | [81] |
| circKDM4C | Downregulated | Suppresses proliferation, metastasis, and doxorubicin resistance | Sponges miR-548p, which targets a tumor-suppressor PBLD | [64] |
| CircYAP | Downregulated | Supresses proliferation and migration | Inhibits YAP translation initiation by interacting with eIF4G and PABP | [82] |
| CircFOXO3 | Downregulated | Decreases cell viability and increases apoptosis | Facilitates p53 ubiquitination and degration by binding to p53 and MDM2. Leads to increased stability of FOXO3 which promotes PUMA expression and cell apoptosis | [57] |
| CircTADA2A | Downregulated | Suppresses proliferation, migration, invasion, and clonogenicity | Sponges miR-203a-3p, which leads to increased expression of SOCS3, regulator of cytokine signaling | [83] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarkar, D.; Diermeier, S.D. Circular RNAs: Potential Applications as Therapeutic Targets and Biomarkers in Breast Cancer. Non-Coding RNA 2021, 7, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7010002
Sarkar D, Diermeier SD. Circular RNAs: Potential Applications as Therapeutic Targets and Biomarkers in Breast Cancer. Non-Coding RNA. 2021; 7(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarkar, Debina, and Sarah D. Diermeier. 2021. "Circular RNAs: Potential Applications as Therapeutic Targets and Biomarkers in Breast Cancer" Non-Coding RNA 7, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7010002
APA StyleSarkar, D., & Diermeier, S. D. (2021). Circular RNAs: Potential Applications as Therapeutic Targets and Biomarkers in Breast Cancer. Non-Coding RNA, 7(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7010002






