Non-Coding RNAs as Prognostic Biomarkers: A miRNA Signature Specific for Aggressive Early-Stage Lung Adenocarcinomas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
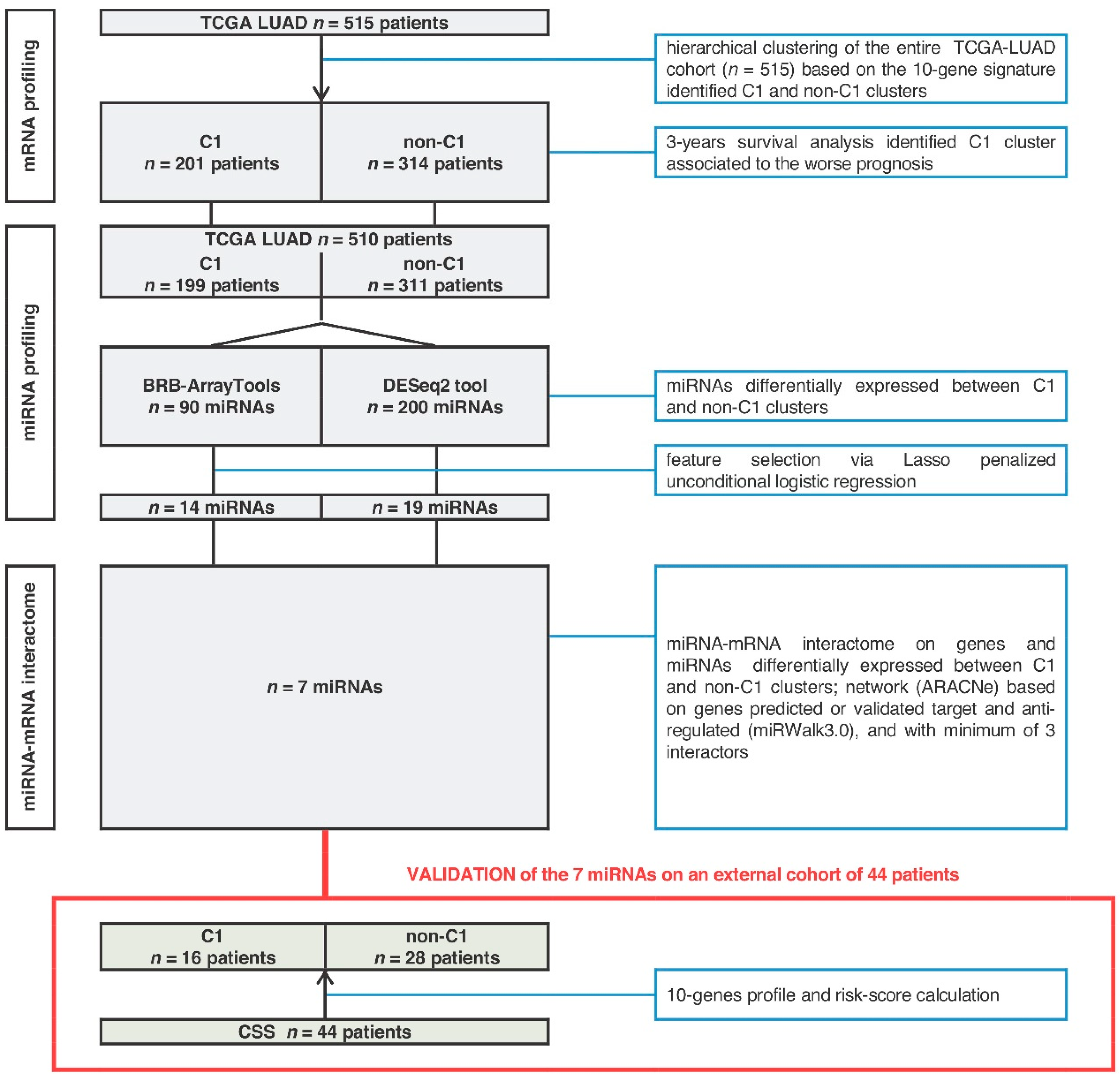
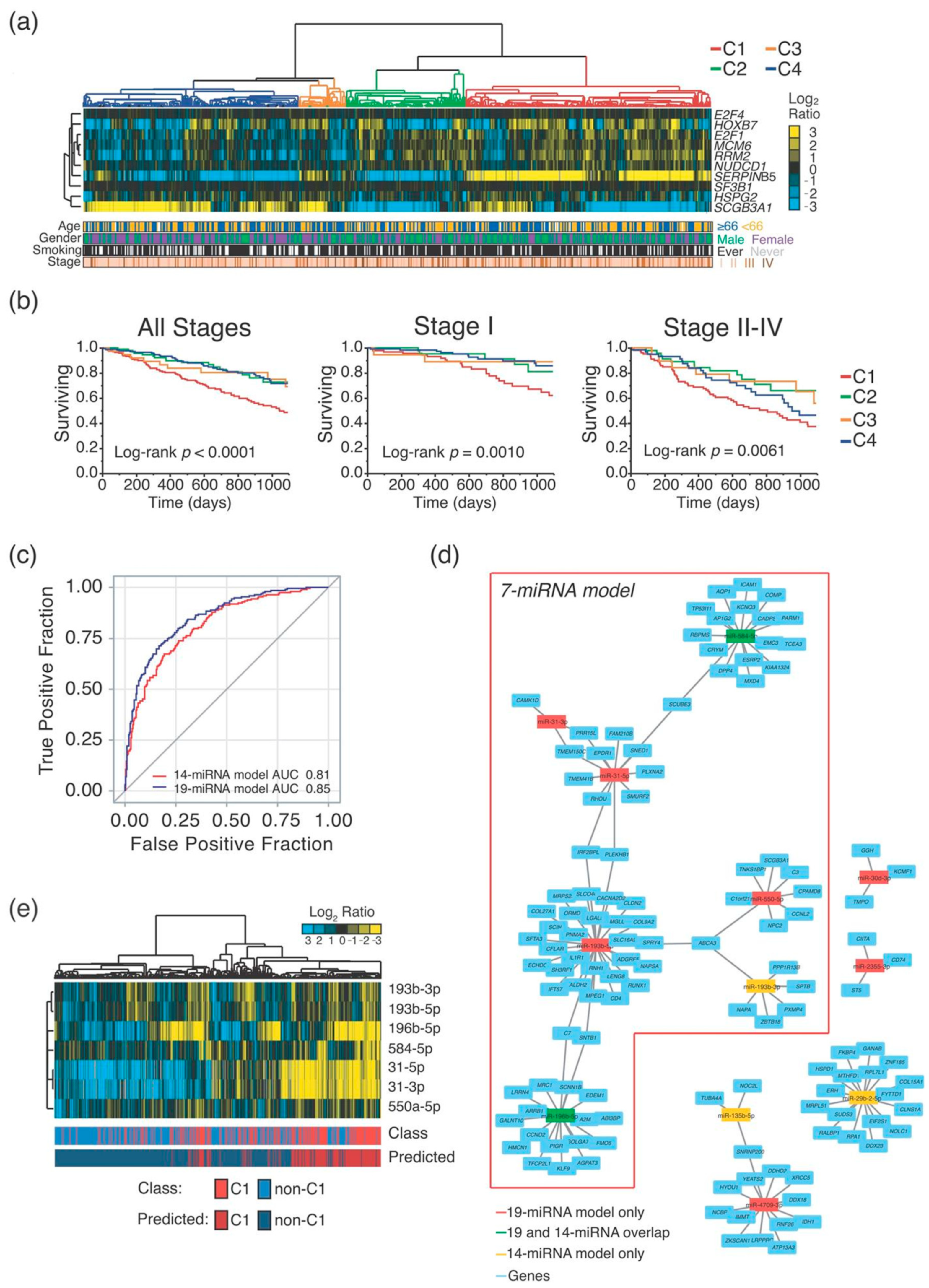
2.1. MiRNA-Signature Identification
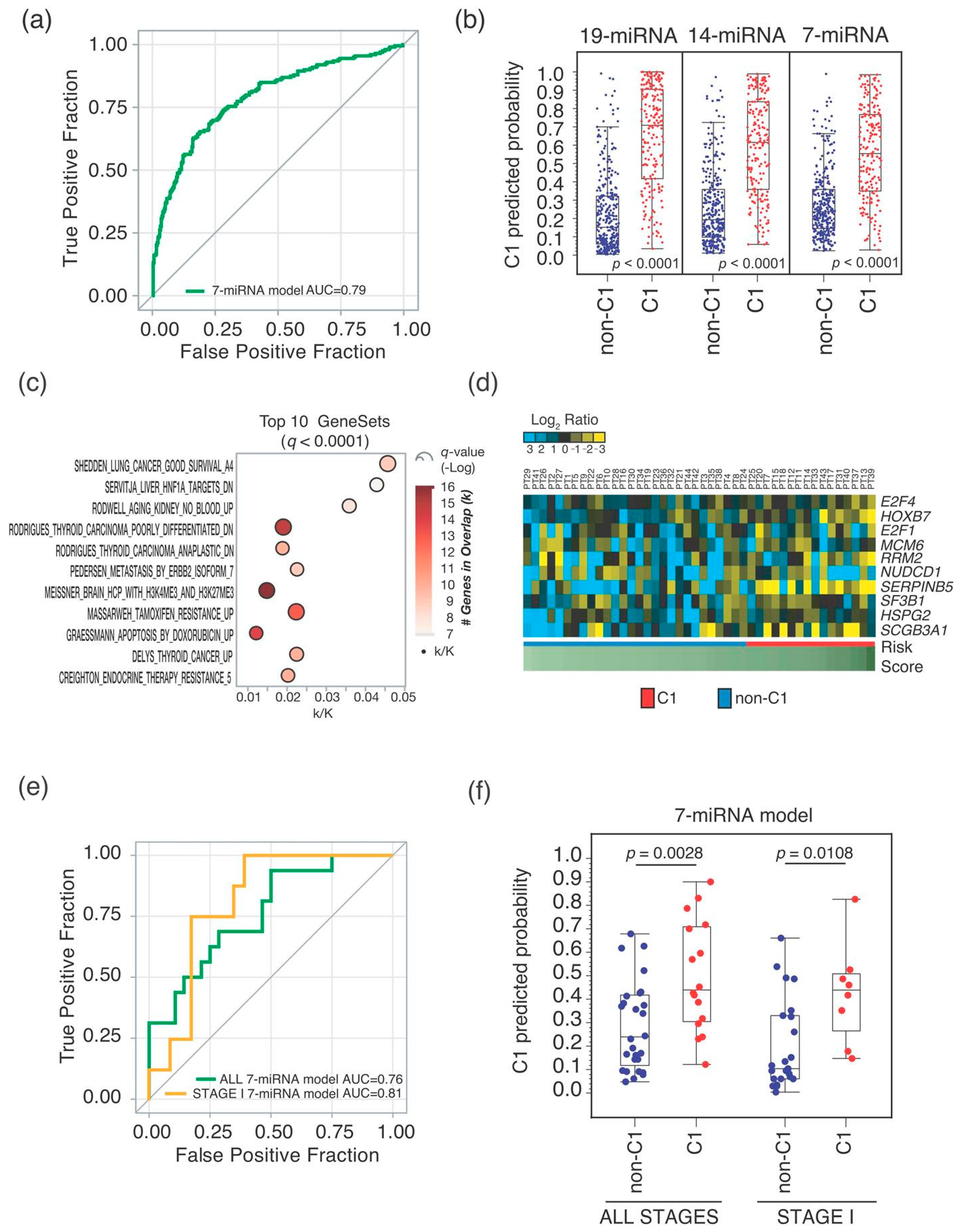
2.2. Seven-miRNA-Signature Validation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. TCGA-LUAD Cohort
4.2. The CSS Cohort
4.3. Gene Expression Analysis of the TCGA-LUAD Cohort
4.4. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR Analysis and Data Interpretation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; Colby, T.V.; Corrin, B.; Shimosato, Y.; Brambilla, E. Histological Typing of Lung and Pleural Tumours, 3rd ed.; WHO. World Health Organization. International Histological Classification of Tumours; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; ISBN 978-3-540-65219-9. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, G.S.; Baldwin, D.R. Recent advances in the management of lung cancer. Clin. Med. 2018, 18, s41–s46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falzone, L.; Salomone, S.; Libra, M. Evolution of Cancer Pharmacological Treatments at the Turn of the Third Millennium. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoach, C.E. A Cautionary Analysis of Immunotherapy Prior to Targeted Therapy. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barta, J.A.; Powell, C.A.; Wisnivesky, J.P. Global Epidemiology of Lung Cancer. Ann. Glob. Health 2019, 85, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The National Lung Screening Trial Research Team. Reduced Lung-Cancer Mortality with Low-Dose Computed Tomographic Screening. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 395–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Koning, H.J.; van der Aalst, C.M.; de Jong, P.A.; Scholten, E.T.; Nackaerts, K.; Heuvelmans, M.A.; Lammers, J.-W.J.; Weenink, C.; Yousaf-Khan, U.; Horeweg, N.; et al. Reduced Lung-Cancer Mortality with Volume CT Screening in a Randomized Trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchi, F.; Nuciforo, P.; Vecchi, M.; Bernard, L.; Tizzoni, L.; Marchetti, A.; Buttitta, F.; Felicioni, L.; Nicassio, F.; Fiore, P.P.D. Survival prediction of stage I lung adenocarcinomas by expression of 10 genes. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 3436–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dama, E.; Melocchi, V.; Dezi, F.; Pirroni, S.; Carletti, R.M.; Brambilla, D.; Bertalot, G.; Casiraghi, M.; Maisonneuve, P.; Barberis, M.; et al. An Aggressive Subtype of Stage I Lung Adenocarcinoma with Molecular and Prognostic Characteristics Typical of Advanced Lung Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Smyth, P.; Flavin, R.; Cahill, S.; Denning, K.; Aherne, S.; Guenther, S.M.; O’Leary, J.J.; Sheils, O. Comparison of miRNA expression patterns using total RNA extracted from matched samples of formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) cells and snap frozen cells. BMC Biotechnol. 2007, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, J.S.; Taylor, J.; Valentine, H.R.; Irlam, J.J.; Eustace, A.; Hoskin, P.J.; Miller, C.J.; West, C.M.L. Enhanced stability of microRNA expression facilitates classification of FFPE tumour samples exhibiting near total mRNA degradation. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 684–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dijkstra, K.K.; Voabil, P.; Schumacher, T.N.; Voest, E.E. Genomics- and Transcriptomics-Based Patient Selection for Cancer Treatment with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Review. JAMA Oncol. 2016, 2, 1490–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beane, J.; Campbell, J.D.; Lel, J.; Vick, J.; Spira, A. Genomic approaches to accelerate cancer interception. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, e494–e502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dama, E.; Melocchi, V.; Colangelo, T.; Cuttano, R.; Bianchi, F. Deciphering the Molecular Profile of Lung Cancer: New Strategies for the Early Detection and Prognostic Stratification. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.; Schaefer, A.; Steiner, I.; Kempkensteffen, C.; Stephan, C.; Erbersdobler, A.; Jung, K. Robust MicroRNA Stability in Degraded RNA Preparations from Human Tissue and Cell Samples. Clin. Chem. 2010, 56, 998–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creighton, C.J.; Fountain, M.D.; Yu, Z.; Nagaraja, A.K.; Zhu, H.; Khan, M.; Olokpa, E.; Zariff, A.; Gunaratne, P.H.; Matzuk, M.M.; et al. Molecular Profiling Uncovers a p53-Associated Role for MicroRNA-31 in Inhibiting the Proliferation of Serous Ovarian Carcinomas and Other Cancers. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manceau, G.; Imbeaud, S.; Thiébaut, R.; Liébaert, F.; Fontaine, K.; Rousseau, F.; Génin, B.; Corre, D.L.; Didelot, A.; Vincent, M.; et al. Hsa-miR-31-3p Expression Is Linked to Progression-free Survival in Patients with KRAS Wild-type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Treated with Anti-EGFR Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 3338–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Yu, F.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, R.; Chen, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J. MicroRNA-31 Activates the RAS Pathway and Functions as an Oncogenic MicroRNA in Human Colorectal Cancer by Repressing RAS p21 GTPase Activating Protein 1 (RASA1). J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 9508–9518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angius, A.; Pira, G.; Scanu, A.M.; Uva, P.; Sotgiu, G.; Saderi, L.; Manca, A.; Serra, C.; Uleri, E.; Piu, C.; et al. MicroRNA-425-5p Expression Affects BRAF/RAS/MAPK Pathways In Colorectal Cancers. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 16, 1480–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sempere, L.F.; Ouyang, H.; Memoli, V.A.; Andrew, A.S.; Luo, Y.; Demidenko, E.; Korc, M.; Shi, W.; Preis, M.; et al. MicroRNA-31 functions as an oncogenic microRNA in mouse and human lung cancer cells by repressing specific tumor suppressors. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 1298–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmonds, M.D.; Boyd, K.L.; Moyo, T.; Mitra, R.; Duszynski, R.; Arrate, M.P.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Z.; Blackwell, T.S.; Andl, T.; et al. MicroRNA-31 initiates lung tumorigenesis and promotes mutant KRAS-driven lung cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, W.; Ye, Z.; Cui, R.; Perry, J.; Dedousi-Huebner, V.; Huebner, A.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Volinia, S.; Nakanishi, H.; et al. MicroRNA-31 Predicts the Presence of Lymph Node Metastases and Survival in Patients with Lung Adenocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5423–5433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Liu, S.; Fu, H.; Li, S.; Tie, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xing, R.; Jin, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zheng, X. MicroRNA-193b regulates proliferation, migration and invasion in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 2828–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Luo, Y.; Mu, Y.-F.; Qin, S.-L.; Qi, Y.; Qiu, Y.-E.; Zhong, M. miR-193b directly targets STMN1 and inhibits the malignant phenotype in colorectal cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 2463–2475. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mazzu, Y.Z.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Nandakumar, S.; Chakraborty, G.; Armenia, J.; Jehane, L.E.; Lee, G.-S.M.; Kantoff, P.W. Methylation-associated miR-193b silencing activates master drivers of aggressive prostate cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 1944–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, G.; Meng, W.; Huang, X.; Zhu, W.; Yin, C.; Wang, C.; Fassan, M.; Yu, Y.; Kudo, M.; Xiao, S.; et al. miR-196b-5p–mediated downregulation of TSPAN12 and GATA6 promotes tumor progression in non-small cell lung cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 4347–4357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stiegelbauer, V.; Vychytilova-Faltejskova, P.; Karbiener, M.; Pehserl, A.-M.; Reicher, A.; Resel, M.; Heitzer, E.; Ivan, C.; Bullock, M.; Ling, H.; et al. miR-196b-5p Regulates Colorectal Cancer Cell Migration and Metastases through Interaction with HOXB7 and GALNT5. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 5255–5266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monterisi, S.; Lo Riso, P.; Russo, K.; Bertalot, G.; Vecchi, M.; Testa, G.; Di Fiore, P.P.; Bianchi, F. HOXB7 overexpression in lung cancer is a hallmark of acquired stem-like phenotype. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3575–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Lv, Y.; Liang, R.; Yuan, C.; Zhang, J.; He, D.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, J. Four-miRNA signature as a prognostic tool for lung adenocarcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Wei, S.; Wang, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Chen, L.; Li, B.; Sun, G.; Xu, J.; et al. Overexpression of miR-584-5p inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis by targeting WW domain-containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 in gastric cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Wang, J.; Xu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhuo, C.; Tan, C.; Tang, Q.; Pu, J. miR-584-5p regulates hepatocellular carcinoma cell migration and invasion through targeting KCNE2. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2019, 7, e702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, R.; Lam, A.; Li, M.-C.; Ngan, M.; Menenzes, S.; Zhao, Y. Analysis of Gene Expression Data Using BRB-Array Tools. Cancer Inform. 2007, 3, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachmann, A.; Giorgi, F.M.; Lopez, G.; Califano, A. ARACNe-AP: Gene network reverse engineering through adaptive partitioning inference of mutual information. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2233–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sticht, C.; Torre, C.D.L.; Parveen, A.; Gretz, N. miRWalk: An online resource for prediction of microRNA binding sites. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montani, F.; Marzi, M.J.; Dezi, F.; Dama, E.; Carletti, R.M.; Bonizzi, G.; Bertolotti, R.; Bellomi, M.; Rampinelli, C.; Maisonneuve, P.; et al. miR-Test: A Blood Test for Lung Cancer Early Detection. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, djv063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| TCGA-LUAD Cohort n = 515 | CSS Cohort n = 44 | |
|---|---|---|
| Age [years] | ||
| Median (Q1; Q3) | 66 (59;73) 1 | 73 (67;77) |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 238 (46.2%) | 27 (61.4%) |
| Female | 277 (53.8%) | 17 (38.6%) |
| Smoking status | ||
| Current/former smoker | 367 (71.3%) | 20 (45.5%) |
| Never smoker | 63 (12.2%) | 11 (25.0%) |
| Missing smoking status | 85 (16.5%) | 13 (29.5%) |
| Stage | ||
| Stage I | 279 (54.2%) | 31 (70.5%) 2 |
| Stage II | 124 (24.1%) | 6 (13.6%) |
| Stage III | 84 (16.3%) | 6 (13.6%) |
| Stage IV | 27 (5.2%) | 1 (2.3%) |
| Missing stage | 1 (0.2) | - |
| Follow-up 3 | ||
| Survivors length of follow-up | ||
| <1 year | 52 (10.3%) | 13 (31.7%) |
| 1–2 years | 128 (25.3%) | 11 (26.8%) |
| 2–3 years | 56 (11.1%) | 10 (24.4%) |
| >3 years | 133 (26.3%) | 5 (12.2%) |
| Deaths within 3 years | 137 (27.1%) | 2 (4.9%) 4 |
| miRNA | Accession | Signature | TCGA-LUAD Cohort— C1 vs. non-C1 Cluster | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FC | p-value 1 | C1 Trend | |||
| hsa-miR-193b-5p | MIMAT0004767 | 19- and 7-miRNA | 1.5 | 3.3 × 10−7 | ↑ |
| hsa-miR-31-3p | MIMAT0004504 | 19- and 7-miRNA | 3.2 | 1.9 × 10−20 | ↑ |
| hsa-miR-31-5p | MIMAT0000089 | 19- and 7-miRNA | 3.1 | 1.7 × 10−18 | ↑ |
| hsa-miR-550a-5p | MIMAT0004800 | 19- and 7-miRNA | 1.5 | 6.0 × 10−9 | ↑ |
| hsa-miR-196b-5p | MIMAT0001080 | 19-, 14-miRNA and 7-miRNA | 3.2 | 9.8 × 10−21 | ↑ |
| hsa-miR-584-5p | MIMAT0003249 | 19-, 14-miRNA and 7-miRNA | 2.8 | 1.2 × 10−40 | ↑ |
| hsa-miR-30d-5p | MIMAT0000245 | 19- and 14-miRNA | 0.6 | 4.8 × 10−16 | ↓ |
| hsa-miR-582-3p | MIMAT0004797 | 19- and 14-miRNA | 2.2 | 2.5 × 10−18 | ↑ |
| hsa-miR-9-5p | MIMAT0000441 | 19 and 14-miRNA | 1.8 | 1.7 × 10−6 | ↑ |
| hsa-let-7c-3p | MIMAT0026472 | 19-miRNA | 0.8 | 1.9 × 10−2 | ↓ |
| hsa-miR-138-5p | MIMAT0000430 | 19-miRNA | 1.9 | 1.2 × 10−10 | ↑ |
| hsa-miR-196a-5p | MIMAT0000226 | 19-miRNA | 1.4 | 2.7 × 10−2 | ↑ |
| hsa-miR-203a-3p | MIMAT0000264 | 19-miRNA | 1.4 | 3.1 × 10−4 | ↑ |
| hsa-miR-215-5p | MIMAT0000272 | 19-miRNA | 5.0 | 1.2 × 10−37 | ↑ |
| hsa-miR-2355-3p | MIMAT0017950 | 19-miRNA | 1.3 | 5.4 × 10−5 | ↑ |
| hsa-miR-30d-3p | MIMAT0004551 | 19-miRNA | 0.6 | 2.5 × 10−15 | ↓ |
| hsa-miR-4709-3p | MIMAT0019812 | 19-miRNA | 0.5 | 1.3 × 10−19 | ↓ |
| hsa-miR-548b-3p | MIMAT0003254 | 19-miRNA | 0.6 | 7.2 × 10−10 | ↓ |
| hsa-miR-675-3p | MIMAT0006790 | 19-miRNA | 2.1 | 1.5 × 10−8 | ↑ |
| hsa-miR-193b-3p | MIMAT0002819 | 14- and 7-miRNA | 1.4 | 8.6 × 10−6 | ↑ |
| hsa-miR-135b-5p | MIMAT0000758 | 14-miRNA | 0.7 | 3.7 × 10−6 | ↓ |
| hsa-miR-187-3p | MIMAT0000262 | 14-miRNA | 0.6 | 2.3 × 10−4 | ↓ |
| hsa-miR-192-5p | MIMAT0000222 | 14-miRNA | 3.1 | 9.8 × 10−21 | ↑ |
| hsa-miR-210-3p | MIMAT0000267 | 14-miRNA | 1.2 | 6.4 × 10−2 | ↑ |
| hsa-miR-29b-2-5p | MIMAT0004515 | 14-miRNA | 0.7 | 1.2 × 10−7 | ↓ |
| hsa-miR-3065-3p | MIMAT0015378 | 14-miRNA | 0.7 | 4.2 × 10−5 | ↓ |
| hsa-miR-375-3p | MIMAT0000728 | 14-miRNA | 1.2 | 1.7 × 10−1 | ↑ |
| hsa-miR-708-5p | MIMAT0004926 | 14-miRNA | 1.3 | 2.7 × 10−3 | ↑ |
| Univariate Analysis | Multivariable Analysis 1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (n Deaths) | HR (95% CI) | Wald Test p-value | HR (95% CI) | Wald Test p-value | |
| ALL STAGES | 501 (135) 2 | ||||
| 10-gene | 194 (75) | 2.21 (1.57–3.10) | <0.0001 | 2.03 (1.43–2.87) | <0.0001 |
| 19-miRNA | 169 (66) | 2.13 (1.52–2.99) | <0.0001 | 1.85 (1.31–2.61) | 0.0005 |
| 14-miRNA | 165 (67) | 2.17 (1.55–3.04) | <0.0001 | 2.06 (1.46–2.91) | <0.0001 |
| 7-miRNA | 146 (67) | 2.90 (2.07–4.06) | <0.0001 | 2.69 (1.91–3.78) | <0.0001 |
| STAGE I | 274 (40) | ||||
| 10-gene | 92 (23) | 2.86 (1.53–5.36) | 0.0010 | 2.96 (1.55–5.65) | 0.0010 |
| 19-miRNA | 73 (11) | 1.07 (0.54–2.15) | 0.8462 | 1.12 (0.55–2.26) | 0.7529 |
| 14-miRNA | 79 (17) | 1.90 (1.01–3.56) | 0.0451 | 1.99 (1.05–3.79) | 0.0359 |
| 7-miRNA | 65 (15) | 2.11 (1.11–4.00) | 0.0223 | 2.14 (1.11–4.12) | 0.0235 |
| STAGE II-IV | 226 (95) | ||||
| 10-gene | 101 (52) | 1.69 (1.13–2.54) | 0.0108 | 1.64 (1.08–2.49) | 0.0207 |
| 19-miRNA | 95 (55) | 2.27 (1.51–3.41) | <0.0001 | 2.18 (1.43–3.31) | 0.0003 |
| 14-miRNA | 86 (50) | 2.00 (1.34–3.00) | 0.0007 | 2.04 (1.35–3.08) | 0.0007 |
| 7-miRNA | 80 (52) | 2.89 (1.93–4.33) | <0.0001 | 2.91 (1.93–4.39) | <0.0001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dama, E.; Melocchi, V.; Mazzarelli, F.; Colangelo, T.; Cuttano, R.; Di Candia, L.; Ferretti, G.M.; Taurchini, M.; Graziano, P.; Bianchi, F. Non-Coding RNAs as Prognostic Biomarkers: A miRNA Signature Specific for Aggressive Early-Stage Lung Adenocarcinomas. Non-Coding RNA 2020, 6, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna6040048
Dama E, Melocchi V, Mazzarelli F, Colangelo T, Cuttano R, Di Candia L, Ferretti GM, Taurchini M, Graziano P, Bianchi F. Non-Coding RNAs as Prognostic Biomarkers: A miRNA Signature Specific for Aggressive Early-Stage Lung Adenocarcinomas. Non-Coding RNA. 2020; 6(4):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna6040048
Chicago/Turabian StyleDama, Elisa, Valentina Melocchi, Francesco Mazzarelli, Tommaso Colangelo, Roberto Cuttano, Leonarda Di Candia, Gian Maria Ferretti, Marco Taurchini, Paolo Graziano, and Fabrizio Bianchi. 2020. "Non-Coding RNAs as Prognostic Biomarkers: A miRNA Signature Specific for Aggressive Early-Stage Lung Adenocarcinomas" Non-Coding RNA 6, no. 4: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna6040048
APA StyleDama, E., Melocchi, V., Mazzarelli, F., Colangelo, T., Cuttano, R., Di Candia, L., Ferretti, G. M., Taurchini, M., Graziano, P., & Bianchi, F. (2020). Non-Coding RNAs as Prognostic Biomarkers: A miRNA Signature Specific for Aggressive Early-Stage Lung Adenocarcinomas. Non-Coding RNA, 6(4), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna6040048







