LINC00473 as an Immediate Early Gene under the Control of the EGR1 Transcription Factor
Abstract
1. Introduction
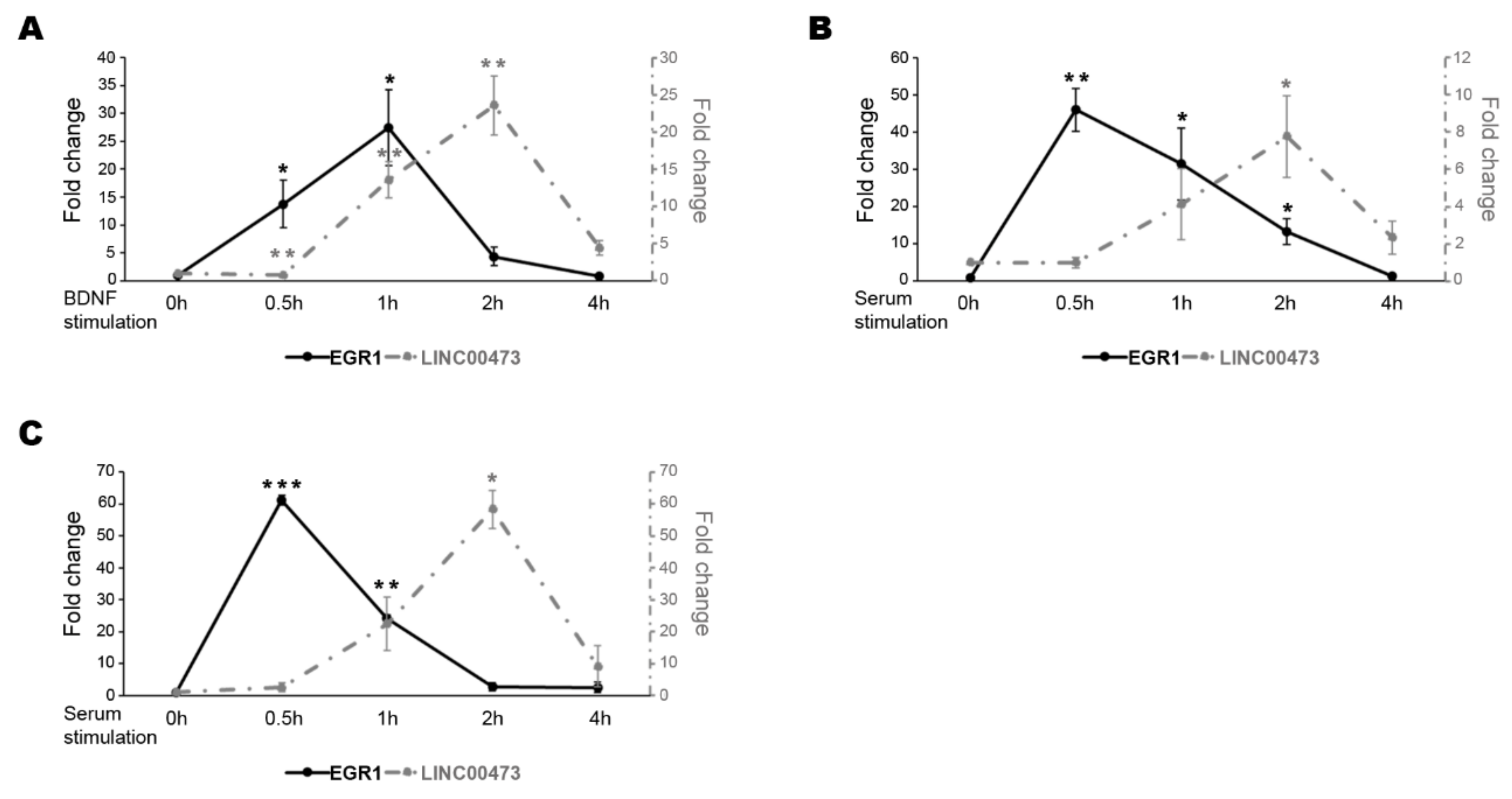
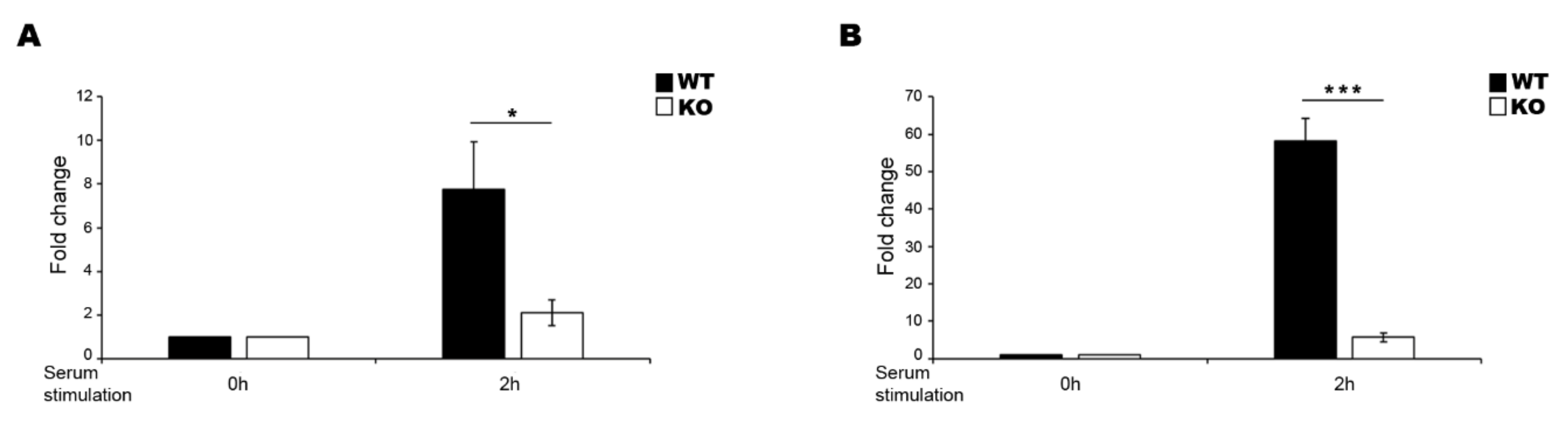
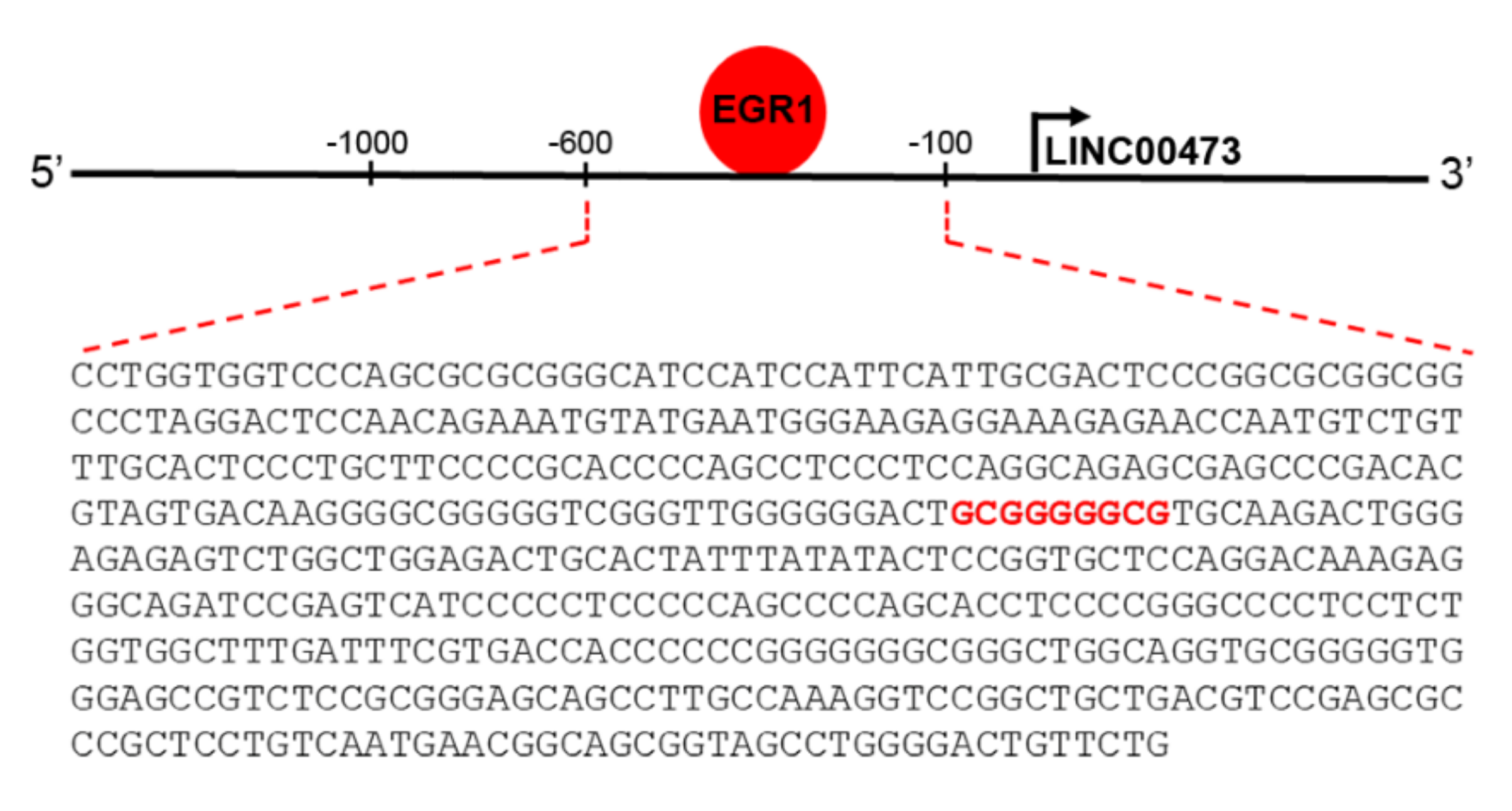
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Cellular Treatments
4.3. RNA Isolation, Retrotranscription, and Quantitative PCR (qPCR) Analysis
4.4. Generation and Validation of EGR1 KO Cell Line
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fowler, T.; Sen, R.; Roy, A.L. Regulation of Primary Response Genes. Mol. Cell 2011, 44, 348–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitken, S.; Magi, S.; Alhendi, A.M.N.; Itoh, M.; Kawaji, H.; Lassmann, T.; Daub, C.O.; Arner, E.; Carninci, P.; Forrest, A.R.R.; et al. Transcriptional Dynamics Reveal Critical Roles for Non-coding RNAs in the Immediate-Early Response. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, A.E.; Greenberg, M.E. Neuronal Activity-Regulated Gene Transcription in Synapse Development and Cognitive Function. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a005744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliperti, V.; Donizetti, A. Long Non-coding RNA in Neurons: New Players in Early Response to BDNF Stimulation. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunch, H.; Choe, H.; Kim, J.; Jo, D.S.; Jeon, S.; Lee, S.; Cho, D.-H.; Kang, K. P-TEFb Regulates Transcriptional Activation in Non-coding RNA Genes. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunch, H.; Lawney, B.P.; Burkholder, A.; Ma, D.; Zheng, X.; Motola, S.; Fargo, D.C.; Levine, S.S.; Wang, Y.E.; Hu, G. RNA polymerase II promoter-proximal pausing in mammalian long non-coding genes. Genomics 2016, 108, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunch, H. Gene regulation of mammalian long non-coding RNA. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2018, 293, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahl, P.B.; Lin, C.Y.; Seila, A.C.; Flynn, R.A.; McCuine, S.; Burge, C.B.; Sharp, P.A.; Young, R.A. c-Myc Regulates Transcriptional Pause Release. Cell 2010, 141, 432–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobeck, K.L.; Buckley, M.S.; Zipfel, W.R.; Lis, J.T. Recruitment Timing and Dynamics of Transcription Factors at the Hsp70 Loci in Living Cells. Mol. Cell 2010, 40, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunch, H. RNA polymerase II pausing and transcriptional regulation of the HSP70 expression. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 96, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Wu, H.-J.; Hsu, J.-M.; Chang, S.-S.; Labaff, A.M.; Li, C.-W.; Wang, Y.; Hsu, J.L.; Hung, M.-C. Long non-coding RNAs: Versatile master regulators of gene expression and crucial players in cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2012, 4, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ulitsky, I.; Bartel, D.P. lincRNAs: Genomics, Evolution, and Mechanisms. Cell 2013, 154, 26–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kung, J.T.Y.; Colognori, D.; Lee, J.T. Long Noncoding RNAs: Past, Present, and Future. Genetics 2013, 193, 651–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, J.J.; Chang, H.Y. Unique features of long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, H.; Fang, S.; Kang, Y.; Wu, W.; Hao, Y.; Li, Z.; Bu, D.; Sun, N.; Zhang, M.Q.; et al. NONCODE 2016: An informative and valuable data source of long non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D203–D208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derrien, T.; Johnson, R.; Bussotti, G.; Tanzer, A.; Djebali, S.; Tilgner, H.; Guernec, G.; Martin, D.; Merkel, A.; Knowles, D.G.; et al. The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: Analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransohoff, J.D.; Wei, Y.; Khavari, P.A. The functions and unique features of long intergenic non-coding RNA. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, G. Integrating the roles of long and small non-coding RNA in brain function and disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St Laurent, G., 3rd; Wahlestedt, C. Noncoding RNAs: Couplers of analog and digital information in nervous system function? Trends Neurosci. 2007, 30, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Pedrosa, E.; Shah, A.; Hrabovsky, A.; Maqbool, S.; Zheng, D.; Lachman, H.M. RNA-Seq of Human Neurons Derived from iPS Cells Reveals Candidate Long Non-Coding RNAs Involved in Neurogenesis and Neuropsychiatric Disorders. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talkowski, M.E.; Maussion, G.; Crapper, L.; Rosenfeld, J.A.; Blumenthal, I.; Hanscom, C.; Chiang, C.; Lindgren, A.; Pereira, S.; Ruderfer, D.M.; et al. Disruption of a Large Intergenic Noncoding RNA in Subjects with Neurodevelopmental Disabilities. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 91, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R. Long non-coding RNAs in Huntington’s disease neurodegeneration. Neurobiol. Dis. 2012, 46, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipovich, L.; Dachet, F.; Cai, J.; Bagla, S.; Balan, K.; Jia, H.; Loeb, J.A. Activity-Dependent Human Brain Coding/Noncoding Gene Regulatory Networks. Genetics 2012, 192, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimoto, Y.; Nakagawa, S.; Hirose, T.; Okano, H.J.; Takao, M.; Shibata, S.; Suyama, S.; Kuwako, K.I.; Imai, T.; Murayama, S.; et al. The Long Non-Coding RNA Nuclear-Enriched Abundant Transcript 1_2 Induces Paraspeckle Formation in the Motor Neuron during the Early Phase of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Mol. Brain 2013, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petazzi, P.; Sandoval, J.; Szczesna, K.; Jorge, O.C.; Roa, L.; Sayols, S.; Gomez, A.; Huertas, D.; Esteller, M. Dysregulation of the long non-coding RNA transcriptome in a Rett syndrome mouse model. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziats, M.N.; Rennert, O.M. Aberrant Expression of Long Noncoding RNAs in Autistic Brain. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2013, 49, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van de Vondervoort, I.G.M.; Gordebeke, P.M.; Ekhoshab, N.; Tiesinga, P.H.; Buitelaar, J.K.; Kozicz, T.; Aschrafi, A.; Glennon, J.C. Long non-coding RNAs in neurodevelopmental disorders. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2013, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Zuo, X.; Deng, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.; Ji, A. Roles of long noncoding RNAs in brain development, functional diversification and neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res. Bull. 2013, 97, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.C.; Morris, K.V.; Woo, M.J.A. The role of long non-coding RNAs in neurodevelopment, brain function and neurological disease. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 369, 20130507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.-W.; Luo, T.; Zou, S.-S.; Wu, A.-S. The Role of Long Noncoding RNAs in Central Nervous System and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, X. Long Non-coding RNA in Neuronal Development and Neurological Disorders. Front. Genet. 2019, 9, 744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmer-Bensch, G. Emerging Roles of Long Non-Coding RNAs as Drivers of Brain Evolution. Cells 2019, 8, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitmair, A.; Sachs, G.; Bin Im, W.; Wheeler, L.; Im, W.B. C6orf176: A novel possible regulator of cAMP-mediated gene expression. Physiol. Genom. 2012, 44, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruunsild, P.; Bengtson, C.P.; Bading, H. Networks of Cultured iPSC-Derived Neurons Reveal the Human Synaptic Activity-Regulated Adaptive Gene Program. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issler, O.; Van Der Zee, Y.Y.; Ramakrishnan, A.; Wang, J.; Tan, C.; Loh, Y.-H.E.; Purushothaman, I.; Walker, D.M.; Lorsch, Z.S.; Hamilton, P.J.; et al. Sex-Specific Role for the Long Non-coding RNA LINC00473 in Depression. Neuron 2020, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, S.; Drabløs, F. Gene regulation in the immediate-early response process. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2016, 62, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schratt, G.; Weinhold, B.; Lundberg, A.S.; Schuck, S.; Berger, J.; Schwarz, H.; Weinberg, R.A.; Rüther, U.; Nordheim, A. Serum Response Factor Is Required for Immediate-Early Gene Activation yet Is Dispensable for Proliferation of Embryonic Stem Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 2933–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-M.; Vasishtha, M.; Prywes, R. Activation and Repression of Cellular Immediate Early Genes by Serum Response Factor Cofactors. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 22036–22049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, F.A.; Hsu, P.D.; Wright, J.; Agarwala, V.; Scott, D.A.; Zhang, F. Genome engineering using the CRISPR-Cas9 system. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 2281–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duclot, F.; Kabbaj, M. The Role of Early Growth Response 1 (EGR1) in Brain Plasticity and Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Wang, Y.; Jia, Z.; Vardar-Sengul, S.; Munawar, A.; Doctor, K.S.; Birrer, M.J.; McClelland, M.; Adamson, E.; Mercola, D. Egr1 regulates the coordinated expression of numerous EGF receptor target genes as identified by ChIP-on-chip. Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, F.T.; Katche, C.; Morici, J.F.; Medina, J.H.; Weisstaub, N.V. Immediate Early Genes, Memory and Psychiatric Disorders: Focus on c-Fos, Egr1 and Arc. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christy, B.; Nathans, D. DNA Binding Site of the Growth Factor-Inducible Protein Zif268. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 8737–8741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavletich, N.P.; O Pabo, C. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: Crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science 1991, 252, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ENCODE Project Consortium. An Integrated Encyclopedia of DNA Elements in the Human Genome. Nature 2012, 489, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ENCODE Project Consortium. A User’s Guide to the Encyclopedia of DNA Elements (ENCODE). PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1001046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farré, D.; Roset, R.; Huerta, M.; Adsuara, J.E.; Roselló, L.; Albà, M.M.; Messeguer, X. Identification of patterns in biological sequences at the ALGGEN server: PROMO and MALGEN. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3651–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabe, N. AliBaba2: Context Specific Identification of Transcription Factor Binding Sites. In Silico Biol. 2002, 2, S1–S15. [Google Scholar]
- Vaudry, D.; Stork, P.J.S.; Lazarovici, P.; Eiden, L.E. Signaling Pathways for PC12 Cell Differentiation: Making the Right Connections. Science 2002, 296, 1648–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, T.; Shimodaira, H.; Ide, K.; Nakakuki, T.; Tani, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Yumoto, N.; Hatakeyama, M. Quantitative Transcriptional Control of ErbB Receptor Signaling Undergoes Graded to Biphasic Response for Cell Differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 282, 4045–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Agostino, S.; Testa, M.; Aliperti, V.; Venditti, M.; Minucci, S.; Aniello, F.; Edonizetti, A. Expression pattern dysregulation of stress- and neuronal activity-related genes in response to prenatal stress paradigm in zebrafish larvae. Cell Stress Chaperons 2019, 24, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tullai, J.W.; Schaffer, M.E.; Mullenbrock, S.; Sholder, G.; Kasif, S.; Cooper, G.M. Immediate-Early and Delayed Primary Response Genes Are Distinct in Function and Genomic Architecture. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 23981–23995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Li, J.-L.; Lin, S.; Cao, C.; Gimbrone, N.T.; Yang, R.; Fu, D.A.; Carper, M.B.; Haura, E.B.; Schabath, M.B.; et al. cAMP/CREB-regulated LINC00473 marks LKB1-inactivated lung cancer and mediates tumor growth. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 2267–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Xia, X.; Li, N.; He, R.; He, H.; Han, C.; Zhao, W. ZBTB7A Enhances Osteosarcoma Chemoresistance by Transcriptionally Repressing lncRNALINC00473-IL24 Activity. Neoplasia 2017, 19, 908–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Yang, Y.; Yu, J.; Meng, F.; Zhang, T.; Gao, Y. The long noncoding RNA LINC00473, a target of microRNA 34a, promotes tumorigenesis by inhibiting ILF2 degradation in cervical cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 2157–2168. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Lin, S.; Li, J.-L.; Ni, W.; Guo, R.; Lu, J.; Kaye, F.J.; Wu, L. CRTC1-MAML2 fusion-induced lncRNA LINC00473 expression maintains the growth and survival of human mucoepidermoid carcinoma cells. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1885–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.-B.; Ji, X.-J.; Zhang, M.; Gao, L.-Y. Upregulation of lncRNA LINC00473 promotes radioresistance of HNSCC cells through activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 7305–7313. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Yang, F.; Li, X.; Gong, Z.-J.; Wang, L.-W. Long noncoding RNA LNC473 inhibits the ubiquitination of survivin via association with USP9X and enhances cell proliferation and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 499, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Song, Y. LINC00473 predicts poor prognosis and regulates cell migration and invasion in gastric cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wang, X. LINC00473 mediates cyclin D1 expression through a balance between activation and repression signals in breast cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2019, 593, 751–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Zhang, M.; Liu, C.; Kang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, X. Long noncoding RNA LINC00473 drives the progression of pancreatic cancer via upregulating programmed death-ligand 1 by sponging microRNA-195-5p. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 23176–23189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Pan, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C. LINC00473/miR-374a-5p regulates esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via targeting SPIN1 to weaken the effect of radiotherapy. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 14562–14572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, G.; Morse, S.; Ararat, M.; Graham, F.L. Preferential transformation of human neuronal cells by human adenoviruses and the origin of HEK 293 cells. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Boone, M.; Meuris, L.; Lemmens, I.; Van Roy, N.; Soete, A.; Reumers, J.; Moisse, M.; Plaisance, S.; Drmanac, R.T.; et al. Genome dynamics of the human embryonic kidney 293 lineage in response to cell biology manipulations. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliperti, V.; Sgueglia, G.; Aniello, F.; Vitale, E.; Fucci, L.; Edonizetti, A. Identification, Characterization, and Regulatory Mechanisms of a Novel EGR1 Splicing Isoform. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caspi, A.; Moffitt, T.E. Gene–environment interactions in psychiatry: Joining forces with neuroscience. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covington, H.E., 3rd; Lobo, M.K.; Maze, I.; Vialou, V.; Hyman, J.M.; Zaman, S.; LaPlant, Q.; Mouzon, E.; Ghose, S.; Tamminga, C.A.; et al. Antidepressant Effect of Optogenetic Stimulation of the Medial Prefrontal Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 16082–16090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stack, A.; Carrier, N.; Dietz, D.; Hollis, F.; Sorenson, J.; Kabbaj, M. Sex Differences in Social Interaction in Rats: Role of the Immediate-Early Gene zif268. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimoto, S.; Bazmi, H.H.; Lewis, D.A. Lower Expression of Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase 67 in the Prefrontal Cortex in Schizophrenia: Contribution of Altered Regulation by Zif268. Am. J. Psychiatry 2014, 171, 969–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aliperti, V.; Vitale, E.; Aniello, F.; Donizetti, A. LINC00473 as an Immediate Early Gene under the Control of the EGR1 Transcription Factor. Non-Coding RNA 2020, 6, 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna6040046
Aliperti V, Vitale E, Aniello F, Donizetti A. LINC00473 as an Immediate Early Gene under the Control of the EGR1 Transcription Factor. Non-Coding RNA. 2020; 6(4):46. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna6040046
Chicago/Turabian StyleAliperti, Vincenza, Emilia Vitale, Francesco Aniello, and Aldo Donizetti. 2020. "LINC00473 as an Immediate Early Gene under the Control of the EGR1 Transcription Factor" Non-Coding RNA 6, no. 4: 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna6040046
APA StyleAliperti, V., Vitale, E., Aniello, F., & Donizetti, A. (2020). LINC00473 as an Immediate Early Gene under the Control of the EGR1 Transcription Factor. Non-Coding RNA, 6(4), 46. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna6040046





