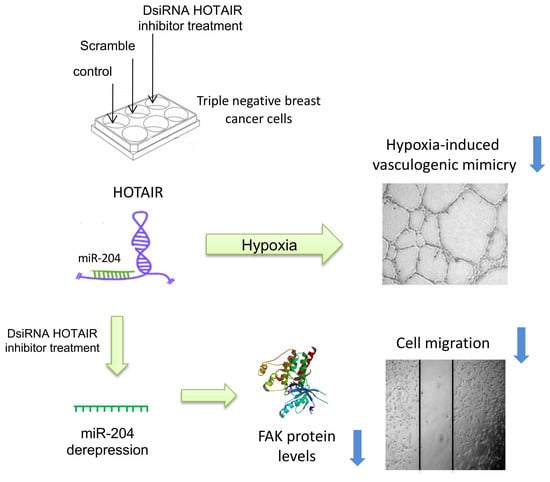
HOX Transcript Antisense RNA HOTAIR Abrogates Vasculogenic Mimicry by Targeting the AngiomiR-204/FAK Axis in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
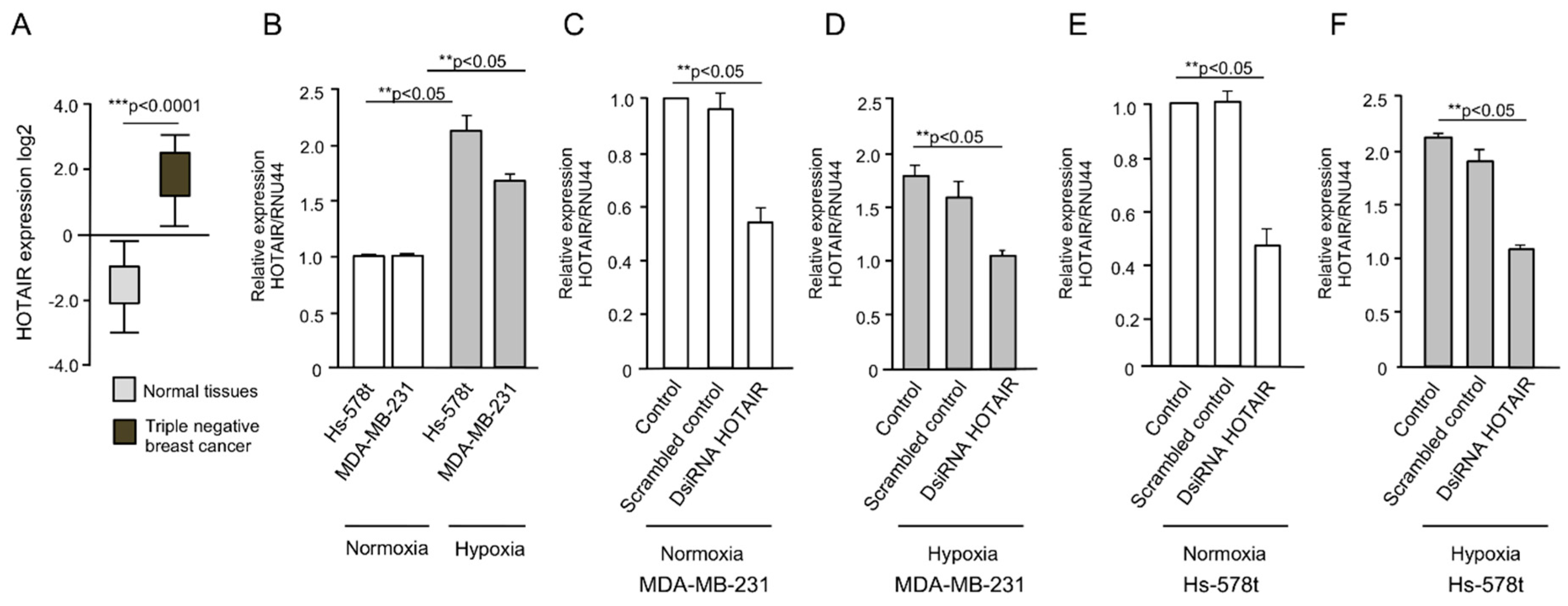
2.1. HOTAIR Expression Is Increased Under Hypoxia in Breast Cancer Cells
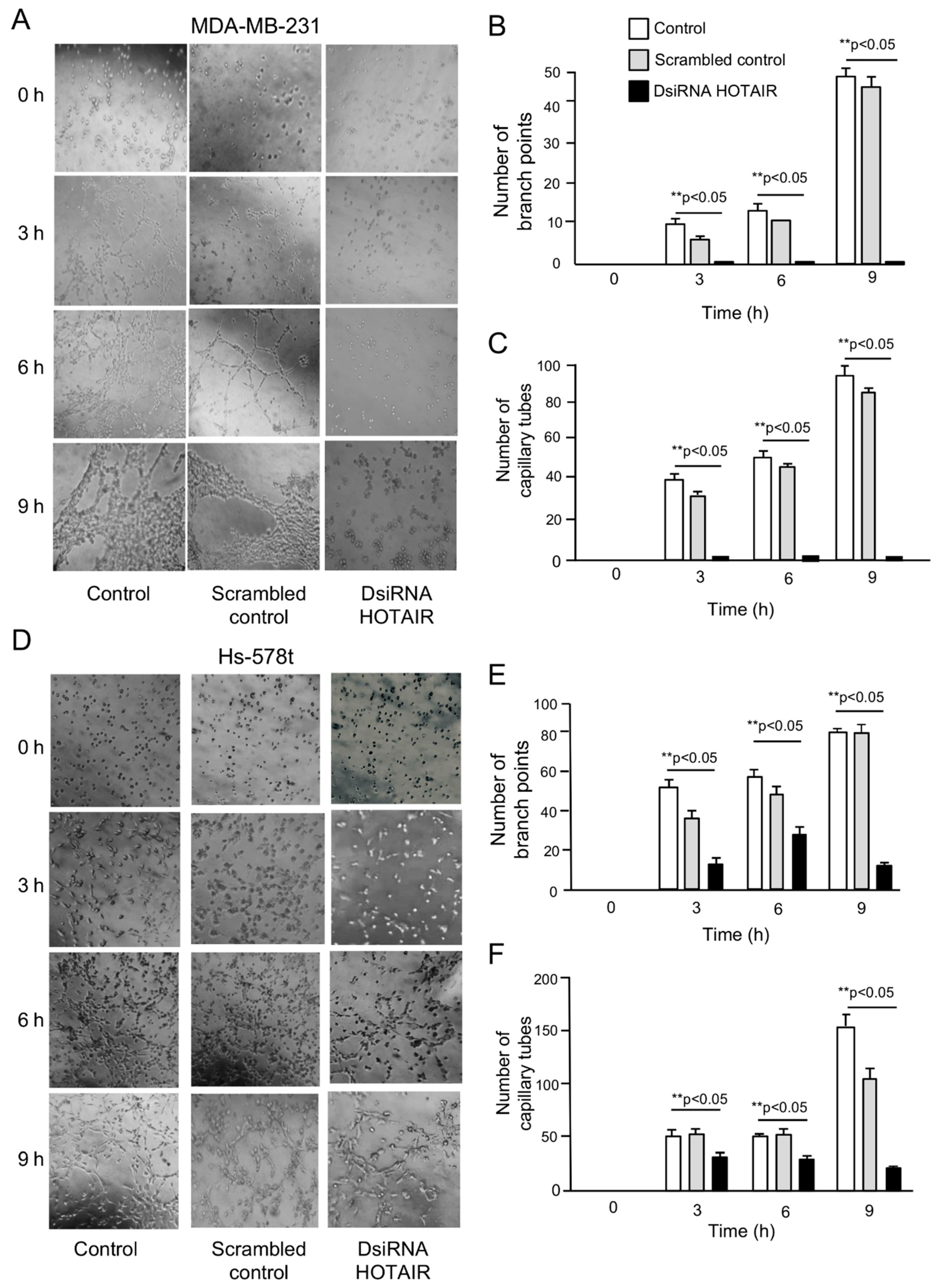
2.2. Inhibition of HOTAIR Impairs Hypoxia-Induced Vasculogenic Mimicry in Breast Cancer Cells
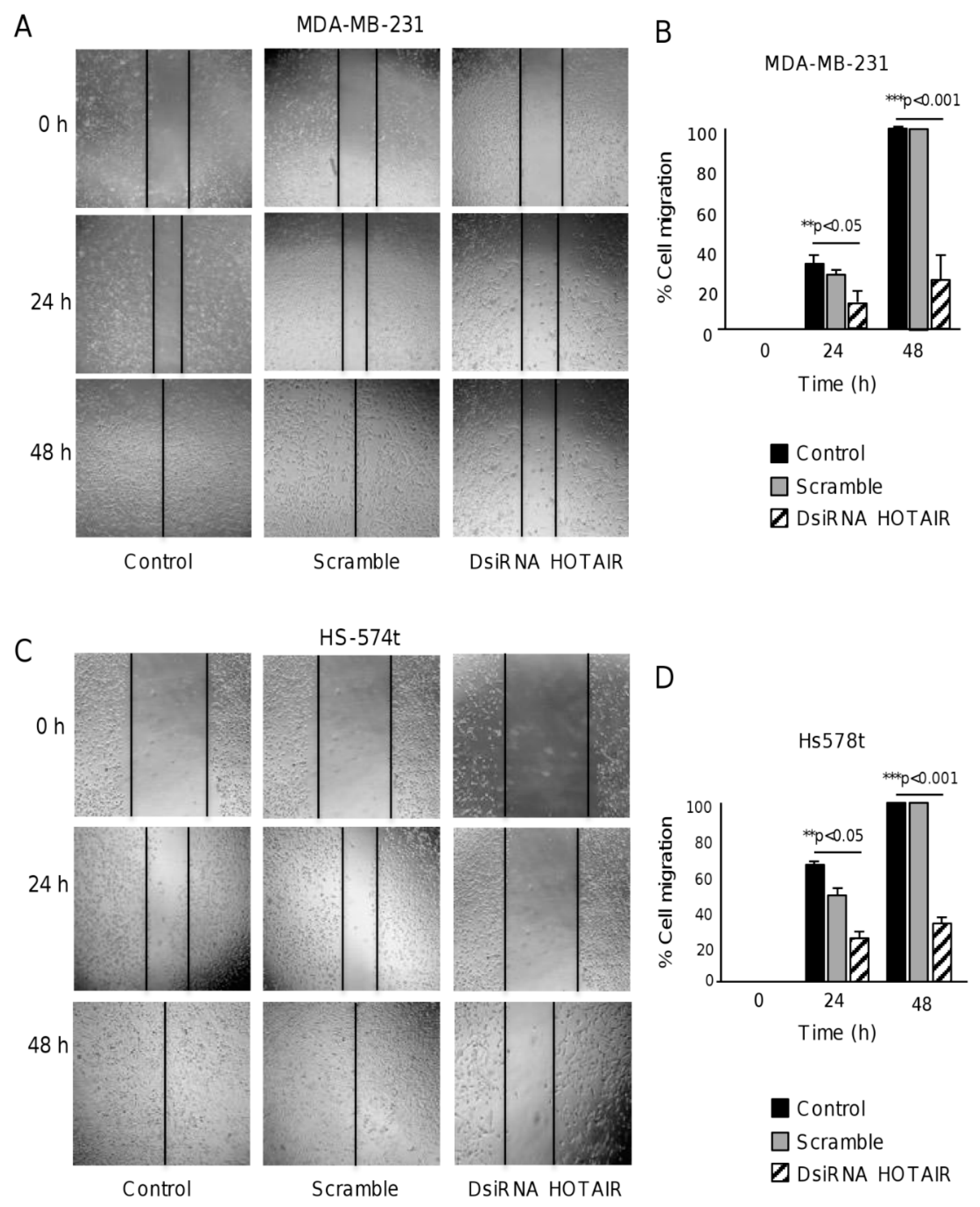
2.3. HOTAIR Regulates Cell Migration in Breast Cancer Cells
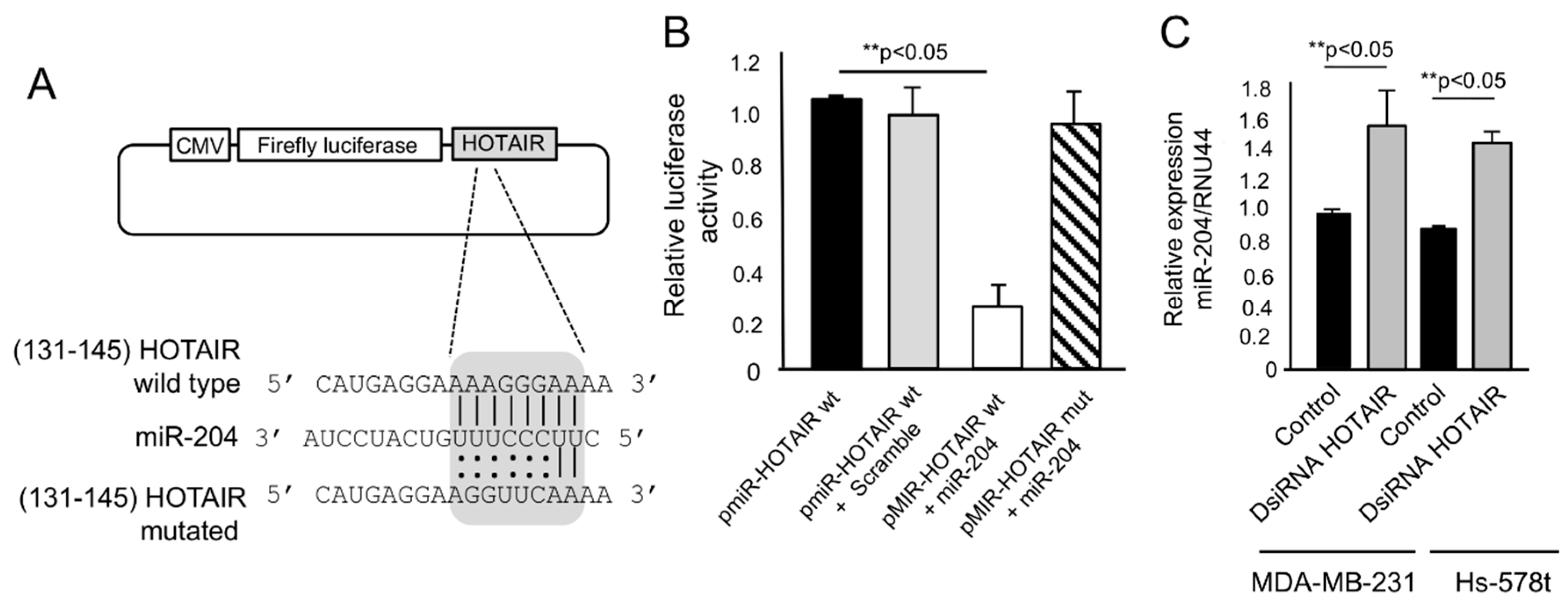
2.4. HOTAIR Sponges the Tumor Suppressor miR-204
2.5. FAK Is a Novel Target of miR-204 in Breast Cancer Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines
4.2. Transfection of DsiRNA HOTAIR Inhibitor and Precursor miR-204
4.3. Vasculogenic Mimicry Inhibition Assays
4.4. RNA Isolation
4.5. Bioinformatics Analysis
4.6. Western Blot Assays
4.7. Luciferase Gene Reporter Assays
4.8. Immunofluorescence Analysis
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, X.; Li, Z. Lon non-coding RNA HOTAIR: A novel oncogene (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 5611–5618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, B.; Song, X.Q.; Cai, J.; Zhang, S. HOTAIR: A cancer-related long non-coding RNA. Neoplasma 2014, 61, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Shah, N.; Wang, K.; Kim, J.; Horlings, H.M.; Wong, D.; Tsai, M.; Hung, T.; Argani, P.; Rinn, J.; et al. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature 2010, 464, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, L. Large intervening non-coding RNA HOTAIR is an indicator of poor prognosis and a therapeutic target in human cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 18985–18999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Qin, Y.; Zhen, Z.; Shen, H.; Cong, T.; Schiferle, E.; Xiao, S. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR/microRNA-206 sponge regulates STC2 and further influences cell biological functions in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Prolif. 2019, 52, 12651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Jia, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Fan, R. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes cervical cancer progression through regulating BCL2 via targeting miR-143-3p. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2018, 4, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Jiang, C.; Wu, Q.; Liu, L.; Yan, X.; Shi, R. A Feed-Forward Regulatory Loop between HuR and the Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR Promotes Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression and Metastasis. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 40, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Li, Y.; Lu, H.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Wu, K.; Li, Z.; Han, X. Long Noncoding RNA HOTAIR Controls Cell Cycle by Functioning as a Competing Endogenous RNA in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Transl. Oncol. 2016, 9, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, E.; Ma, C.; He, X.; Wang, C.; Zong, G.; Wang, H.; Zhao, B. Epigenetic modification of miR-141 regulates SKA2 by an endogenous ‘sponge’ HOTAIR in glioma. Oncotarget 2016, 24, 30610–30625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrix, M.; Seftor, E.; Hess, A.; Seftor, R. Vasculogenic mimicry and tumour-cell plasticity: Lessons from melanoma. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirakawa, K.; Kobayashi, H.; Heike, Y.; Kawamoto, S.; Brechbiel, M.; Kasumi, F.; Iwanaga, T.; Konishi, F.; Terada, M.; Wakasugi, H. Hemodynamics in vasculogenic mimicry and angiogenesis of inflammatory breast cancer xenograft. Cancer Res. 2002, 15, 560–566. [Google Scholar]
- Racordon, D.; Valdivia, A.; Mingo, G.; Erices, R.; Aravena, R.; Santoro, F.; Bravo, M.; Ramirez, C.; Gonzalez, P.; Sandoval, A.; et al. Structural and functional identification of vasculogenic mimicry in vitro. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6985–6997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Duda, D.; Willett, C.; Sahani, D.; Zhu, A.; Loeffler, J.; Batchelor, T.; Sorensen, A. Biomarkers of response and resistance to antiangiogenic therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 6, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Quan, J.; Wang, M.; Li, S.; Yang, J.; Lv, M.; Yang, J. Tumor vasculogenic mimicry formation as an unfavorable prognostic indicator in patients with breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 56408–56416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, D.; Du, J.; Guo, H.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, W.; Hao, X. Vasculogenic mimicry is associated with high tumor grade, invasion and metastasis, and short survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2006, 16, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velez, D.; Tsui, B.; Goshia, T.; Chute, C.; Han, A.; Carter, H.; Fraley, S. 3D collagen architecture induces a conserved migratory and transcriptional response linked to vasculogenic mimicry. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1651–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, A.; López, E.; Orozco, L.; López, C.; Meza, T.; Figueroa, G.; Bustamante, L.; Pérez, C. Long Non-Coding RNAs as New Master Regulators of Resistance to Systemic Treatments in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salinas, Y.; Marchat, L.; Garcia, R.; González, C.H.; Castañeda, E.; Tito, N.; Flores, C.; Pérez, C.; Cruz, J.; Carlos, A.; et al. Cooperative multi-targeting of signaling networks by angiomiR-204 inhibits vasculogenic mimicry in breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2018, 432, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, A.; Marchat, L.; Rodríguez, S.; Bautista, V.; Hidalgo, A.; Ocampo, E.; Martínez, M.; Palma, C.; Fonseca, M.; Astudillo, H.; et al. Dual targeting of ANGPT1 and TGFBR2 genes by miR-204 controls angiogenesis in breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34504–34522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Ni, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, C.; Chang, Q.; Li, Y.; Gao, Z.; Wu, S.; Shi, X.; Song, J.; et al. Expression profiling of long noncoding RNAs associated with vasculogenic mimicry in osteosarcoma. J. Cell Biochem. 2019, 8, 12473–12488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Wu, F.; Mu, S.; Hu, B.; Zhong, B.; Gao, F.; Qing, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, Z. LncRNA AFAP1-AS1 promotes tumorigenesis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of osteosarcoma through RhoC/ROCK1/p38MAPK/Twist1 signaling pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 375–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xue, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, J.; Shen, S.; Yang, C.; Chen, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, L.; Ma, J.; et al. ZRANB2/SNHG20/FOXK1 Axis regulates Vasculogenic mimicry formation in glioma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 68–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yuan, J.; Sun, L.; Lin, L.; Huang, N.; Bin, J.; Liao, Y.; Liao, W. Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 promotes gastric cancer tumorigenicity and metastasis by regulating vasculogenic mimicry and angiogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2017, 395, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Wang, J.; Shan, B.; Li, B.; Peng, W.; Dong, Y.; Shi, W.; Zhao, W.; He, D.; Duan, M.; et al. The long noncoding RNA LINC00312 induces lung adenocarcinoma migration and vasculogenic mimicry through directly binding YBX1. Mol Cancer. 2018, 17, 167–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Ding, J.; He, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, R.; Han, Z.; Xing, E.; Zhang, C.; Yeh, S. Estrogen receptor β promotes the vasculogenic mimicry (VM) and cell invasion via altering the lncRNA-MALAT1/miR-145-5p/NEDD9 signals in lung cancer. Oncogene 2019, 38, 1225–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, W.; Sun, W.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, J. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA TP73-AS1 suppresses triple negative breast cancer cell vasculogenic mimicry by targeting miR-490-3p/TWIST1 axis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 504, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Sun, B.; Liu, T.; Shao, B.; Sun, R.; Zhu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, Q.; Dong, X.; Liu, F.; et al. Long noncoding RNA n339260 promotes vasculogenic mimicry and cancer stem cell development in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 3197–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Yu, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, J.; Ma, J.; Gong, W.; Chen, J.; Zhao, L.; Tian, Y.; et al. Long Non-Coding RNA HOXA-AS2 Regulates Malignant Glioma Behaviors and Vasculogenic Mimicry Formation via the MiR-373/EGFR Axis. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Ye, L.; Jiang, C.; Bai, J.; Chi, Y.; Zhang, H. Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR, a hypoxia-inducible factor-1α activated driver of malignancy, enhances hypoxic cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour. Biol. 2015, 36, 9179–9188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golubovskaya, V.M.; Ylagan, L.; Miller, A.; Hughes, M.; Wilson, J.; Wang, D.; Brese, E.; Bshara, W.; Edge, S.; Morrison, C.; et al. High focal adhesion kinase expression in breast carcinoma is associated with lymphovascular invasion and triple-negativephenotype. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, M.S.; Harb, O.A.; Nawar, N.; Taha, H.F.; Amer, S.A.; Eltokhy, E.A.; Gertallah, L.M.; Mawla, W.A.; Abdelmonem, D.M. The Value of FAK and SLUG Expression in Patients with Breast Carcinoma and Relation of Their Expression to Clinicopathological and Prognostic Parameters. J. Clin. Exp. Oncol. 2018, 7, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökmen-Polar, Y.; Vladislav, I.T.; Neelamraju, Y.; Janga, S.C.; Badve, S. Prognostic impact of HOTAIR expression is restricted to ER-negative breast cancers. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, K.P.; Thomassen, M.; Tan, Q.; Bak, M.; Cold, S.; Burton, M.; Larsen, M.J.; Kruse, T.A. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is an independent prognostic marker of metastasis in estrogen receptor-positive primary breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 142, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lozano-Romero, A.; Astudillo-de la Vega, H.; Terrones-Gurrola, M.C.d.R.; Marchat, L.A.; Hernández-Sotelo, D.; Salinas-Vera, Y.M.; Ramos-Payan, R.; Silva-Cázares, M.B.; Nuñez-Olvera, S.I.; Hernández-de la Cruz, O.N.; et al. HOX Transcript Antisense RNA HOTAIR Abrogates Vasculogenic Mimicry by Targeting the AngiomiR-204/FAK Axis in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Non-Coding RNA 2020, 6, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna6020019
Lozano-Romero A, Astudillo-de la Vega H, Terrones-Gurrola MCdR, Marchat LA, Hernández-Sotelo D, Salinas-Vera YM, Ramos-Payan R, Silva-Cázares MB, Nuñez-Olvera SI, Hernández-de la Cruz ON, et al. HOX Transcript Antisense RNA HOTAIR Abrogates Vasculogenic Mimicry by Targeting the AngiomiR-204/FAK Axis in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Non-Coding RNA. 2020; 6(2):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna6020019
Chicago/Turabian StyleLozano-Romero, Allan, Horacio Astudillo-de la Vega, María Cruz del Rocío Terrones-Gurrola, Laurence A. Marchat, Daniel Hernández-Sotelo, Yarely M. Salinas-Vera, Rosalío Ramos-Payan, Macrina B. Silva-Cázares, Stephanie I. Nuñez-Olvera, Olga N. Hernández-de la Cruz, and et al. 2020. "HOX Transcript Antisense RNA HOTAIR Abrogates Vasculogenic Mimicry by Targeting the AngiomiR-204/FAK Axis in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells" Non-Coding RNA 6, no. 2: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna6020019
APA StyleLozano-Romero, A., Astudillo-de la Vega, H., Terrones-Gurrola, M. C. d. R., Marchat, L. A., Hernández-Sotelo, D., Salinas-Vera, Y. M., Ramos-Payan, R., Silva-Cázares, M. B., Nuñez-Olvera, S. I., Hernández-de la Cruz, O. N., & López-Camarillo, C. (2020). HOX Transcript Antisense RNA HOTAIR Abrogates Vasculogenic Mimicry by Targeting the AngiomiR-204/FAK Axis in Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells. Non-Coding RNA, 6(2), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna6020019