Extracellular Vesicles as Conduits of Non-Coding RNA Emission and Intercellular Transfer in Brain Tumors
Abstract
:1. Pathways of Intercellular Communication in Brain Tumors
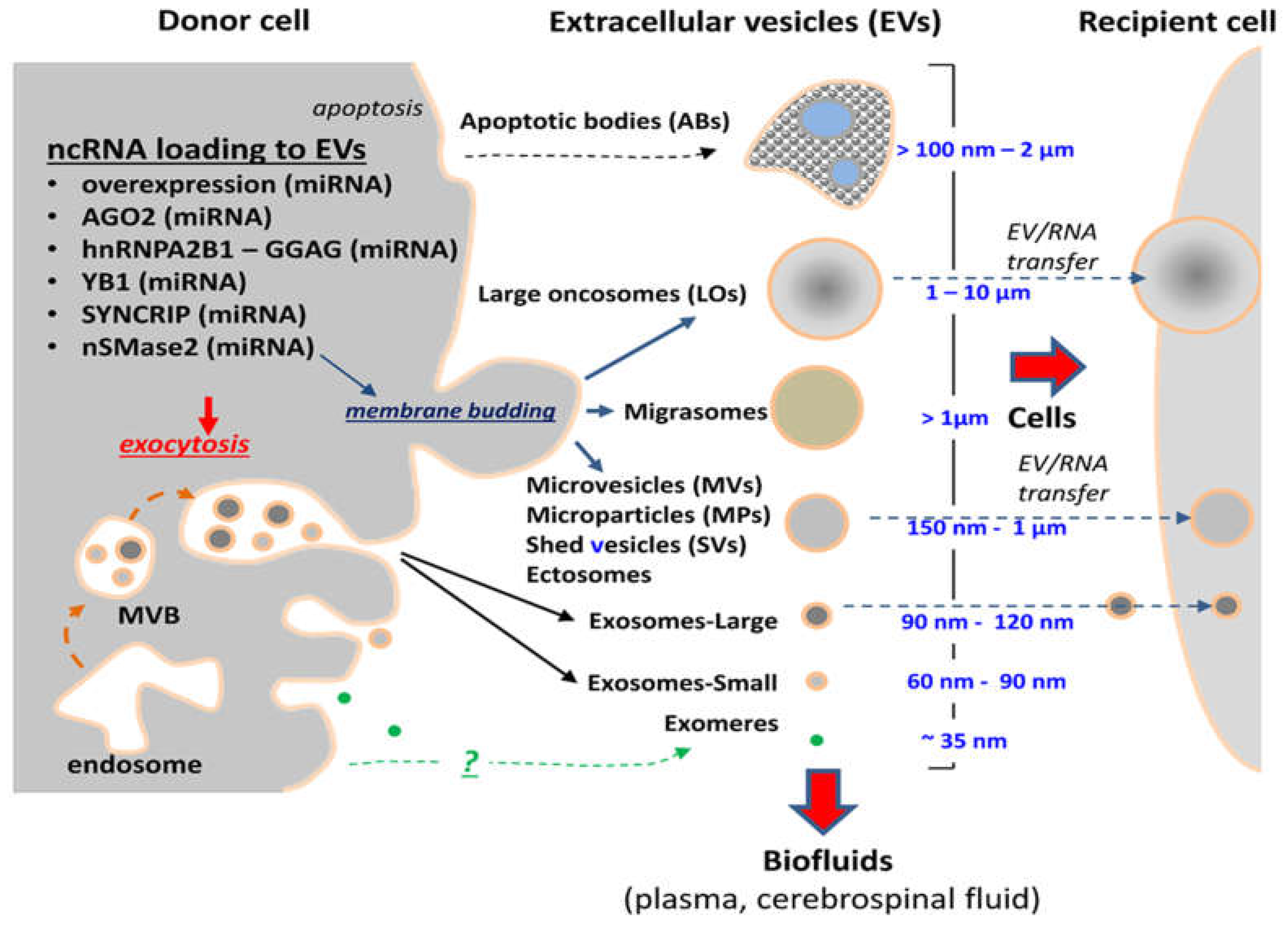
2. Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) as Molecular Information Carriers
3. The Emerging Role of Extracellular Vesicles as Biological Regulators in Brain Tumor Progression
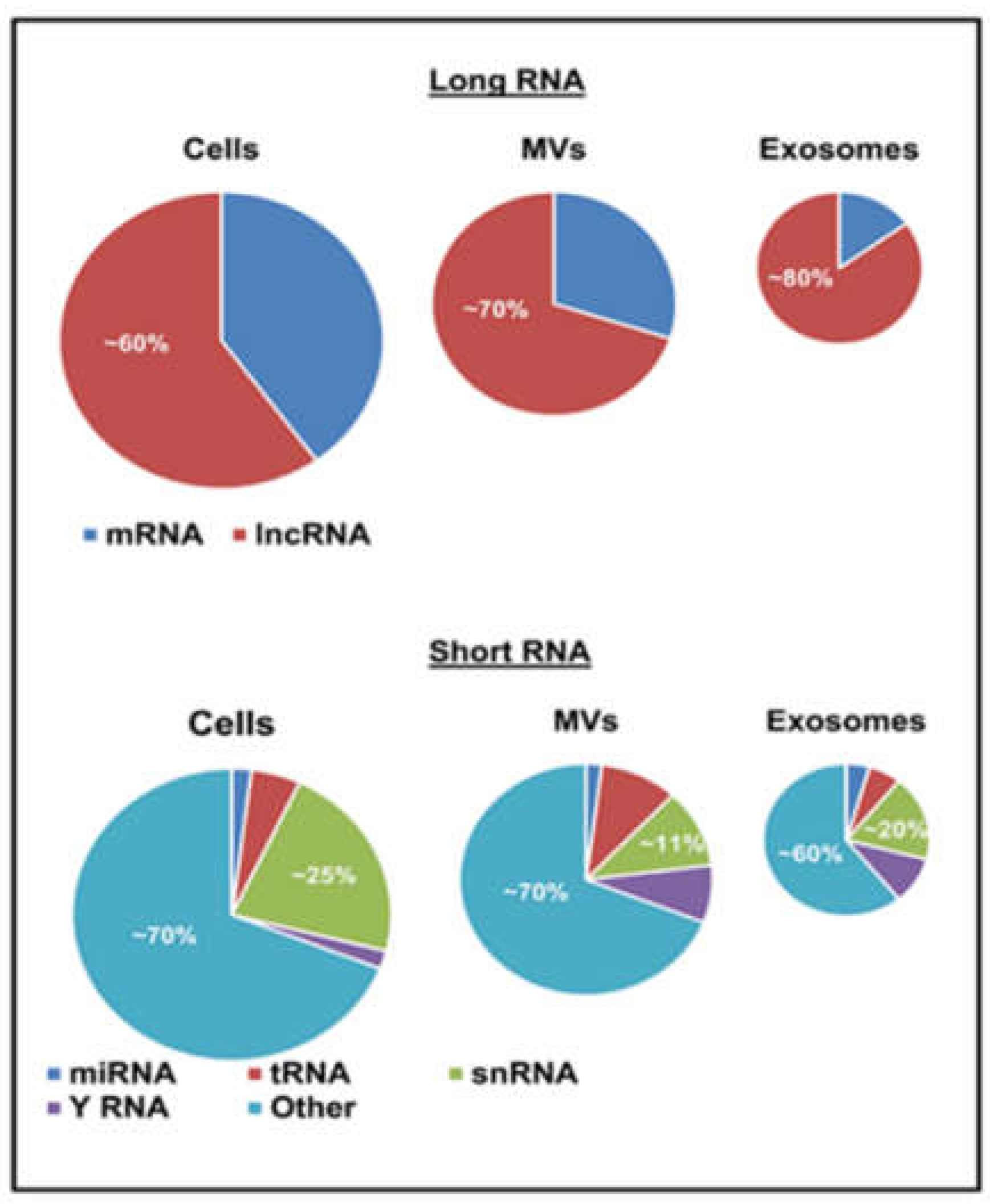
4. EV-Associated RNA Biotypes
5. Evidence for the Functional Role of EV-Associated RNA in Cancer
6. EV-Associated Non-Coding RNAs as Biological Mediators in Primary Brain Tumors
7. EV-Associated Non-Coding RNA in Metastatic Brain Tumors
8. EV-Associated Non-Coding RNA as Emerging Biomarker Platform in Brain Malignancies
9. EVs as Carriers of Therapeutic Non-Coding RNA
10. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reifenberger, G.; Wirsching, H.G.; Knobbe-Thomsen, C.B.; Weller, M. Advances in the molecular genetics of gliomas–implications for classification and therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 434–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnier, D.; Magnus, N.; Meehan, B.; Kislinger, T.; Rak, J. Qualitative changes in the proteome of extracellular vesicles accompanying cancer cell transition to mesenchymal state. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 2747–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steeg, P.S.; Camphausen, K.A.; Smith, Q.R. Brain metastases as preventive and therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kieran, M.W.; Walker, D.; Frappaz, D.; Prados, M. Brain tumors: From childhood through adolescence into adulthood. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 4783–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Northcott, P.A.; Korshunov, A.; Pfister, S.M.; Taylor, M.D. The clinical implications of medulloblastoma subgroups. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2012, 8, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grobner, S.N.; Worst, B.C.; Weischenfeldt, J.; Buchhalter, I.; Kleinheinz, K.; Rudneva, V.A.; Johann, P.D.; Balasubramanian, G.P.; Segura-Wang, M.; Brabetz, S.; et al. The landscape of genomic alterations across childhood cancers. Nature 2018, 555, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winkler, F.; Wick, W. Harmful networks in the brain and beyond. Science (New York NY) 2018, 359, 1100–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier, D.; Meehan, B.; Kislinger, T.; Daniel, P.; Sinha, A.; Abdulkarim, B.; Nakano, I.; Rak, J. Divergent evolution of temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma stem cells is reflected in extracellular vesicles and coupled with radiosensitization. Neuro-oncology 2018, 20, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.K.; Hawkins, C.; Clarke, I.D.; Squire, J.A.; Bayani, J.; Hide, T.; Henkelman, R.M.; Cusimano, M.D.; Dirks, P.B. Identification of human brain tumor initiating cells. Nature 2004, 432, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, I.; Garnier, D.; Minata, M.; Rak, J. Extracellular vesicles in the biology of brain tumor stem cells–Implications for inter-cellular communication, therapy and biomarker development. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 40, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quail, D.F.; Joyce, J.A. The Microenvironmental Landscape of Brain Tumors. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 326–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abels, E.R.; Breakefield, X.O. Introduction to Extracellular Vesicles: Biogenesis, RNA Cargo Selection, Content, Release, and Uptake. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Godlewski, J.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Johnson, M.D.; Chiocca, E.A.; Bronisz, A. Belonging to a network--microRNAs, extracellular vesicles, and the glioblastoma microenvironment. Neuro-oncology 2015, 17, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronisz, A.; Godlewski, J.; Chiocca, E.A. Extracellular Vesicles and MicroRNAs: Their Role in Tumorigenicity and Therapy for Brain Tumors. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rak, J. Extracellular vesicles–biomarkers and effectors of the cellular interactome in cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2013, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Smithson, L.J.; Ma, Y.; Hambardzumyan, D.; Gutmann, D.H. Ccl5 establishes an autocrine high-grade glioma growth regulatory circuit critical for mesenchymal glioblastoma survival. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 32977–32989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagci, T.; Wu, J.K.; Pfannl, R.; Ilag, L.L.; Jay, D.G. Autocrine semaphorin 3A signaling promotes glioblastoma dispersal. Oncogene 2009, 28, 3537–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jain, R.K.; Di, T.E.; Duda, D.G.; Loeffler, J.S.; Sorensen, A.G.; Batchelor, T.T. Angiogenesis in brain tumors. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 610–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inda, M.M.; Bonavia, R.; Mukasa, A.; Narita, Y.; Sah, D.W.; Vandenberg, S.; Brennan, C.; Johns, T.G.; Bachoo, R.; Hadwiger, P.; et al. Tumor heterogeneity is an active process maintained by a mutant EGFR-induced cytokine circuit in glioblastoma. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 1731–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Prager, B.C.; Wu, Q.; Kim, L.J.Y.; Gimple, R.C.; Shi, Y.; Yang, K.; Morton, A.R.; Zhou, W.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Reciprocal Signaling between Glioblastoma Stem Cells and Differentiated Tumor Cells Promotes Malignant Progression. Cell Stem Cell 2018, 22, 514–528.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naus, C.C.; Aftab, Q.; Sin, W.C. Common mechanisms linking connexin43 to neural progenitor cell migration and glioma invasion. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 50, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Tunneling nanotubes between rat primary astrocytes and C6 glioma cells alter proliferation potential of glioma cells. Neurosci. Bull. 2015, 31, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Osswald, M.; Jung, E.; Sahm, F.; Solecki, G.; Venkataramani, V.; Blaes, J.; Weil, S.; Horstmann, H.; Wiestler, B.; Syed, M.; et al. Brain tumor cells interconnect to a functional and resistant network. Nature 2015, 528, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Herst, P.M.; Dawson, R.H.; Berridge, M.V. Intercellular Communication in Tumor Biology: A Role for Mitochondrial Transfer. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zijlstra, A.; Di Vizio, D. Size matters in nanoscale communication. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 228–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Thery, C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunavat, T.R.; Cheng, L.; Einarsdottir, B.O.; Olofsson Bagge, R.; Veppil Muralidharan, S.; Sharples, R.A.; Lasser, C.; Gho, Y.S.; Hill, A.F.; Nilsson, J.A.; et al. BRAF(V600) inhibition alters the microRNA cargo in the vesicular secretome of malignant melanoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E5930–E5939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowal, J.; Arras, G.; Colombo, M.; Jouve, M.; Morath, J.P.; Primdal-Bengtson, B.; Dingli, F.; Loew, D.; Tkach, M.; Thery, C. Proteomic comparison defines novel markers to characterize heterogeneous populations of extracellular vesicle subtypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E968–E977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thery, C.; Clayton, A.; Amigorena, S.; Raposo, G. Isolation and characterization of exosomes from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids. In Current Protocols in Cell Biology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Freitas, D.; Kim, H.S.; Fabijanic, K.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; Martin, A.B.; Bojmar, L.; et al. Identification of distinct nanoparticles and subsets of extracellular vesicles by asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montermini, L.; Meehan, B.; Garnier, D.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, T.H.; Guha, A.; Al-Nedawi, K.; Rak, J. Inhibition of oncogenic epidermal growth factor receptor kinase triggers release of exosome-like extracellular vesicles and impacts their phosphoprotein and DNA content. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 24534–24546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muralidharan-Chari, V.; Clancy, J.; Plou, C.; Romao, M.; Chavrier, P.; Raposo, G.; Souza-Schorey, C. ARF6-regulated shedding of tumor cell-derived plasma membrane microvesicles. Curr Biol. 2009, 19, 1875–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, F.; Perrotta, C.; Novellino, L.; Francolini, M.; Riganti, L.; Menna, E.; Saglietti, L.; Schuchman, E.H.; Furlan, R.; Clementi, E.; et al. Acid sphingomyelinase activity triggers microparticle release from glial cells. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fujii, T.; Sakata, A.; Nishimura, S.; Eto, K.; Nagata, S. TMEM16F is required for phosphatidylserine exposure and microparticle release in activated mouse platelets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 12800–12805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piccin, A.; Murphy, W.G.; Smith, O.P. Circulating microparticles: Pathophysiology and clinical implications. Blood Rev. 2007, 21, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Antonyak, M.A.; Zhang, J.; Cerione, R.A. RhoA triggers a specific signaling pathway that generates transforming microvesicles in cancer cells. Oncogene 2012, 10, 4740–4749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Gilkes, D.M.; Takano, N.; Xiang, L.; Luo, W.; Bishop, C.J.; Chaturvedi, P.; Green, J.J.; Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-inducible factors and RAB22A mediate formation of microvesicles that stimulate breast cancer invasion and metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E3234–E3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nabhan, J.F.; Hu, R.; Oh, R.S.; Cohen, S.N.; Lu, Q. Formation and release of arrestin domain-containing protein 1-mediated microvesicles (ARMMs) at plasma membrane by recruitment of TSG101 protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 4146–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Y.; Wu, N.; Gan, X.; Yan, W.; Morrell, J.C.; Gould, S.J. Higher-order oligomerization targets plasma membrane proteins and HIV gag to exosomes. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, F.J.; Bebelman, M.P.; Jimenez, C.R.; Garcia-Vallejo, J.J.; Janssen, H.; Neefjes, J.; Knol, J.C.; de Goeij-de Haas, R.; Piersma, S.R.; Baglio, S.R.; et al. Quantifying exosome secretion from single cells reveals a modulatory role for GPCR signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 1129–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murrow, L.; Malhotra, R.; Debnath, J. ATG12-ATG3 interacts with Alix to promote basal autophagic flux and late endosome function. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, J.P. Flow Cytometry of Extracellular Vesicles: Potential, Pitfalls, and Prospects. Curr. Protoc. Cytom. 2015, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Montermini, L.; Kim, D.K.; Meehan, B.; Roth, F.P.; Rak, J. The Impact of Oncogenic EGFRvIII on the Proteome of Extracellular Vesicles Released from Glioblastoma Cells. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2018, 17, 1948–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.; Lee, T.H.; Spinelli, C.; Chennakrishnaiah, S.; D’Asti, E.; Rak, J. Extracellular vesicle communication pathways as regulatory targets of oncogenic transformation. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 67, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathivanan, S.; Fahner, C.J.; Reid, G.E.; Simpson, R.J. ExoCarta 2012: Database of exosomal proteins, RNA and lipids. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1241–D1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.R.; Choi, D.S.; Yoon, Y.J.; Kim, J.H.; Go, G.; Nhung, D.; Hong, K.; Jang, S.C.; et al. EVpedia: A community web portal for extracellular vesicles research. Bioinformatics (Oxf. Engl.) 2015, 31, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, H.; Simpson, R.J.; Ji, H.; Aikawa, E.; Altevogt, P.; Askenase, P.; Bond, V.C.; Borras, F.E.; Breakefield, X.; Budnik, V.; et al. Vesiclepedia: A compendium for extracellular vesicles with continuous community annotation. PLoS Biol. 2012, 10, e1001450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratajczak, J.; Miekus, K.; Kucia, M.; Zhang, J.; Reca, R.; Dvorak, P.; Ratajczak, M.Z. Embryonic stem cell-derived microvesicles reprogram hematopoietic progenitors: Evidence for horizontal transfer of mRNA and protein delivery. Leukemia 2006, 20, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjostrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lotvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skog, J.; Wurdinger, T.; van Rijin, S.; Meijer, D.H.; Gainche, L.; Curry, W.T., Jr.; Carter, B.S.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Breakefield, X.O. Glioblastoma microvesicles transport RNA and proteins that promote tumor growth and provide diagnostic biomarkers. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 1470–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevillet, J.R.; Kang, Q.; Ruf, I.K.; Briggs, H.A.; Vojtech, L.N.; Hughes, S.M.; Cheng, H.H.; Arroyo, J.D.; Meredith, E.K.; Gallichotte, E.N.; et al. Quantitative and stoichiometric analysis of the microRNA content of exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14888–14893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, B.T.; Johnstone, R.M. Fate of the transferrin receptor during maturation of sheep reticulocytes in vitro: Selective externalization of the receptor. Cell 1983, 33, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chairoungdua, A.; Smith, D.L.; Pochard, P.; Hull, M.; Caplan, M.J. Exosome release of beta-catenin: A novel mechanism that antagonizes Wnt signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 20, 1079–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verweij, F.J.; van Eijndhoven, M.A.; Hopmans, E.S.; Vendrig, T.; Wurdinger, T.; Cahir-McFarland, E.; Kieff, E.; Geerts, D.; van der Kant, R.; Neefjes, J.; et al. LMP1 association with CD63 in endosomes and secretion via exosomes limits constitutive NF-kappaB activation. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 2115–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostenfeld, M.S.; Jeppesen, D.K.; Laurberg, J.R.; Boysen, A.T.; Bramsen, J.B.; Primdal-Bengtson, B.; Hendrix, A.; Lamy, P.; Gnaes-Hansen, F.; Rasmussen, M.H.; et al. Cellular Disposal of miR23b by RAB27-Dependent Exosome Release Is Linked to Acquisition of Metastatic Properties. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5758–5771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peinado, H.; Zhang, H.; Matei, I.R.; Costa-Silva, B.; Hoshino, A.; Rodrigues, G.; Psaila, B.; Kaplan, R.N.; Bromberg, J.F.; Kang, Y.; et al. Pre-metastatic niches: Organ-specific homes for metastases. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 302–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzner, D.; Schnaars, M.; van Rossum, D.; Krishnamoorthy, G.; Dibaj, P.; Bakhti, M.; Regen, T.; Hanisch, U.K.; Simons, M. Selective transfer of exosomes from oligodendrocytes to microglia by macropinocytosis. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- French, K.C.; Antonyak, M.A.; Cerione, R.A. Extracellular vesicle docking at the cellular port: Extracellular vesicle binding and uptake. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 67, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldon, H.; Heikamp, E.; Turley, H.; Dragovic, R.; Thomas, P.; Oon, C.E.; Leek, R.; Edelmann, M.; Kessler, B.; Sainson, R.C.; et al. New mechanism for Notch signaling to endothelium at a distance by Delta-like 4 incorporation into exosomes. Blood 2010, 116, 2385–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garnier, D.; Magnus, N.; Lee, T.H.; Bentley, V.; Meehan, B.; Milsom, C.; Montermini, L.; Kislinger, T.; Rak, J. Cancer Cells Induced to Express Mesenchymal Phenotype Release Exosome-like Extracellular Vesicles Carrying Tissue Factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 43565–43572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sung, B.H.; Ketova, T.; Hoshino, D.; Zijlstra, A.; Weaver, A.M. Directional cell movement through tissues is controlled by exosome secretion. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Xu, Y.; Ding, T.; Zu, Y.; Yang, C.; Yu, L. Pairing of integrins with ECM proteins determines migrasome formation. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 1397–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mulcahy, L.A.; Pink, R.C.; Carter, D.R. Routes and mechanisms of extracellular vesicle uptake. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.H.; Chennakrishnaiah, S.; Meehan, B.; Montermini, L.; Garnier, D.; D’Asti, E.; Hou, W.; Magnus, N.; Gayden, T.; Jabado, N.; et al. Barriers to horizontal cell transformation by extracellular vesicles containing oncogenic H-ras. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 51991–52002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakase, I.; Kobayashi, N.B.; Takatani-Nakase, T.; Yoshida, T. Active macropinocytosis induction by stimulation of epidermal growth factor receptor and oncogenic Ras expression potentiates cellular uptake efficacy of exosomes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Nedawi, K.; Meehan, B.; Micallef, J.; Lhotak, V.; May, L.; Guha, A.; Rak, J. Intercellular transfer of the oncogenic receptor EGFRvIII by microvesicles derived from tumor cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, C.; Montermini, L.; Meehan, B.; Brisson, A.R.; Tan, S.; Choi, D.; Nakano, I.; Rak, J. Molecular subtypes and differentiation programmes of glioma stem cells as determinants of extracellular vesicle profiles and endothelial cell-stimulating activities. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1490144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharzewska, P.; Christianson, H.C.; Welch, J.E.; Svensson, K.J.; Fredlund, E.; Ringner, M.; Morgelin, M.; Bourseau-Guilmain, E.; Bengzon, J.; Belting, M. Exosomes reflect the hypoxic status of glioma cells and mediate hypoxia-dependent activation of vascular cells during tumor development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7312–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoshino, A.; Costa-Silva, B.; Shen, T.L.; Rodrigues, G.; Hashimoto, A.; Tesic, M.M.; Molina, H.; Kohsaka, S.; Di, G.A.; Ceder, S.; et al. Tumor exosome integrins determine organotropic metastasis. Nature 2015, 527, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, N.; Kosaka, N.; Ono, M.; Katsuda, T.; Yoshioka, Y.; Tamura, K.; Lotvall, J.; Nakagama, H.; Ochiya, T. Brain metastatic cancer cells release microRNA-181c-containing extracellular vesicles capable of destructing blood-brain barrier. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Yao, J.; Lowery, F.J.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, W.C.; Li, P.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C.; et al. Microenvironment-induced PTEN loss by exosomal microRNA primes brain metastasis outgrowth. Nature 2015, 527, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ricklefs, F.; Mineo, M.; Rooj, A.K.; Nakano, I.; Charest, A.; Weissleder, R.; Breakefield, X.O.; Chiocca, E.A.; Godlewski, J.; Bronisz, A. Extracellular Vesicles from High-Grade Glioma Exchange Diverse Pro-oncogenic Signals That Maintain Intratumoral Heterogeneity. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2876–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bronisz, A.; Wang, Y.; Nowicki, M.O.; Peruzzi, P.; Ansari, K.I.; Ogawa, D.; Balaj, L.; De, R.G.; Mineo, M.; Nakano, I.; et al. Extracellular vesicles modulate the glioblastoma microenvironment via a tumor suppression signaling network directed by miR-1. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 738–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Vos, K.E.; Abels, E.R.; Zhang, X.; Lai, C.; Carrizosa, E.; Oakley, D.; Prabhakar, S.; Mardini, O.; Crommentuijn, M.H.; Skog, J.; et al. Directly visualized glioblastoma-derived extracellular vesicles transfer RNA to microglia/macrophages in the brain. Neuro-oncology 2016, 18, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricklefs, F.L.; Alayo, Q.; Krenzlin, H.; Mahmoud, A.B.; Speranza, M.C.; Nakashima, H.; Hayes, J.L.; Lee, K.; Balaj, L.; Passaro, C.; et al. Immune evasion mediated by PD-L1 on glioblastoma-derived extracellular vesicles. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graner, M.W.; Alzate, O.; Dechkovskaia, A.M.; Keene, J.D.; Sampson, J.H.; Mitchell, D.A.; Bigner, D.D. Proteomic and immunologic analyses of brain tumor exosomes. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 1541–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Figueroa, J.M.; Skog, J.; Akers, J.; Li, H.; Komotar, R.; Jensen, R.; Ringel, F.; Yang, I.; Kalkanis, S.; Thompson, R.; et al. Detection of wild-type EGFR amplification and EGFRvIII mutation in CSF-derived extracellular vesicles of glioblastoma patients. Neuro-oncology 2017, 19, 1494–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Romero, N.; Carrion-Navarro, J.; Esteban-Rubio, S.; Lazaro-Ibanez, E.; Peris-Celda, M.; Alonso, M.M.; Guzman-De-Villoria, J.; Fernandez-Carballal, C.; de Mendivil, A.O.; Garcia-Duque, S.; et al. DNA sequences within glioma-derived extracellular vesicles can cross the intact blood-brain barrier and be detected in peripheral blood of patients. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 1416–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Chung, J.; Balaj, L.; Charest, A.; Bigner, D.D.; Carter, B.S.; Hochberg, F.H.; Breakefield, X.O.; Weissleder, R.; Lee, H. Protein typing of circulating microvesicles allows real-time monitoring of glioblastoma therapy. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putz, U.; Howitt, J.; Doan, A.; Goh, C.P.; Low, L.H.; Silke, J.; Tan, S.S. The tumor suppressor PTEN is exported in exosomes and has phosphatase activity in recipient cells. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5, ra70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.W.; Balaj, L.; Liau, L.M.; Samuels, M.L.; Kotsopoulos, S.K.; Maguire, C.A.; Loguidice, L.; Soto, H.; Garrett, M.; Zhu, L.D.; et al. BEAMing and Droplet Digital PCR Analysis of Mutant IDH1 mRNA in Glioma Patient Serum and Cerebrospinal Fluid Extracellular Vesicles. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids. 2013, 2, e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaj, L.; Lessard, R.; Dai, L.; Cho, Y.J.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Breakefield, X.O.; Skog, J. Tumor microvesicles contain retrotransposon elements and amplified oncogene sequences. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Nedawi, K.; Meehan, B.; Kerbel, R.S.; Allison, A.C.; Rak, J. Endothelial expression of autocrine VEGF upon the uptake of tumor-derived microvesicles containing oncogenic EGFR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3794–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nilsson, R.J.; Balaj, L.; Hulleman, E.; van Rijn, S.; Pegtel, D.M.; Walraven, M.; Widmark, A.; Gerritsen, W.R.; Verheul, H.M.; Vandertop, W.P.; et al. Blood platelets contain tumor-derived RNA biomarkers. Blood 2011, 118, 3680–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chennakrishnaiah, S.; Meehan, B.; D’Asti, E.; Montermini, L.; Lee, T.H.; Karatzas, N.; Buchanan, M.; Tawil, N.; Choi, D.; Divangahi, M.; et al. Leukocytes as a reservoir of circulating oncogenic DNA and regulatory targets of tumor-derived extracellular vesicles. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH. 2018, 16, 1800–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, G.M.; Balaj, L.; Stott, S.L.; Nahed, B.; Carter, B.S. Liquid biopsy for brain tumors. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2017, 17, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anfossi, S.; Babayan, A.; Pantel, K.; Calin, G.A. Clinical utility of circulating non-coding RNAs - an update. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 541–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolodny, G.M. Evidence for transfer of macromolecular RNA between mammalian cells in culture. Exp. Cell Res. 1971, 65, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ba, Y.; Ma, L.; Cai, X.; Yin, Y.; Wang, K.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Guo, X.; et al. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: A novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, A.; Bajracharya, S.D.; Yuen, P.S.; Zhou, H.; Star, R.A.; Illei, G.G.; Alevizos, I. Exosomes from human saliva as a source of microRNA biomarkers. Oral Dis. 2010, 16, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Ochiya, T. Circulating microRNA in body fluid: A new potential biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Cancer Sci. 2010, 101, 2087–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menke, T.B.; Warnecke, J.M. Improved conditions for isolation and quantification of RNA in urine specimens. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1022, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, H.; Kosaka, N.; Ochiya, T. Secretory microRNAs as a versatile communication tool. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2010, 3, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rennert, R.C.; Hochberg, F.H.; Carter, B.S. ExRNA in Biofluids as Biomarkers for Brain Tumors. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsatsaronis, J.A.; Franch-Arroyo, S.; Resch, U.; Charpentier, E. Extracellular Vesicle RNA: A Universal Mediator of Microbial Communication? Trends microbiol. 2018, 26, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte-’t Hoen, E.N.; Buermans, H.P.; Waasdorp, M.; Stoorvogel, W.; Wauben, M.H.; Hoen, P.A. Deep sequencing of RNA from immune cell-derived vesicles uncovers the selective incorporation of small non-coding RNA biotypes with potential regulatory functions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, 9272–9285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Batagov, A.O.; Kurochkin, I.V. Exosomes secreted by human cells transport largely mRNA fragments that are enriched in the 3’-untranslated regions. Biol. Direct. 2013, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, F.A.; Benoit Bouvrette, L.P.; Perras, L.; Blanchet-Cohen, A.; Garnier, D.; Rak, J.; Lecuyer, E. Comparative transcriptomic analysis of human and Drosophila extracellular vesicles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, Z.; Batagov, A.O.; Schinelli, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; El Fatimy, R.; Rabinovsky, R.; Balaj, L.; Chen, C.C.; Hochberg, F.; et al. Coding and noncoding landscape of extracellular RNA released by human glioma stem cells. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolukbasi, M.F.; Mizrak, A.; Ozdener, G.B.; Madlener, S.; Strobel, T.; Erkan, E.P.; Fan, J.-B.; Breakefield, X.O.; Saydam, O. miR-1289 and “zipcode”-like sequence enrich mRNA in microvesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2012, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, D.J.; Franklin, J.L.; Dou, Y.; Liu, Q.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Demory Beckler, M.; Weaver, A.M.; Vickers, K.; Prasad, N.; Levy, S.; et al. KRAS-dependent sorting of miRNA to exosomes. eLife 2015, 4, e07197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, S.A.; Sugimoto, H.; O’Connell, J.T.; Kato, N.; Villanueva, A.; Vidal, A.; Qiu, L.; Vitkin, E.; Perelman, L.T.; Melo, C.A.; et al. Cancer Exosomes Perform Cell-Independent MicroRNA Biogenesis and Promote Tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 707–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gibbings, D.J.; Ciaudo, C.; Erhardt, M.; Voinnet, O. Multivesicular bodies associate with components of miRNA effector complexes and modulate miRNA activity. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 1143–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroya-Beltri, C.; Gutierrez-Vazquez, C.; Sanchez-Cabo, F.; Perez-Hernandez, D.; Vazquez, J.; Martin-Cofreces, N.; Martinez-Herrera, D.J.; Pascual-Montano, A.; Mittelbrunn, M.; Sanchez-Madrid, F. Sumoylated hnRNPA2B1 controls the sorting of miRNAs into exosomes through binding to specific motifs. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shurtleff, M.J.; Temoche-Diaz, M.M.; Karfilis, K.V.; Ri, S.; Schekman, R. Y-box protein 1 is required to sort microRNAs into exosomes in cells and in a cell-free reaction. eLife 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faury, D.; Nantel, A.; Dunn, S.E.; Guiot, M.C.; Haque, T.; Hauser, P.; Garami, M.; Bognar, L.; Hanzely, Z.; Liberski, P.P.; et al. Molecular profiling identifies prognostic subgroups of pediatric glioblastoma and shows increased YB-1 expression in tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 1196–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartzentruber, J.; Korshunov, A.; Liu, X.Y.; Jones, D.T.; Pfaff, E.; Jacob, K.; Sturm, D.; Fontebasso, A.M.; Quang, D.A.; Tonjes, M.; et al. Driver mutations in histone H3.3 and chromatin remodelling genes in paediatric glioblastoma. Nature 2012, 482, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santangelo, L.; Giurato, G.; Cicchini, C.; Montaldo, C.; Mancone, C.; Tarallo, R.; Battistelli, C.; Alonzi, T.; Weisz, A.; Tripodi, M. The RNA-Binding Protein SYNCRIP Is a Component of the Hepatocyte Exosomal Machinery Controlling MicroRNA Sorting. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppers-Lalic, D.; Hackenberg, M.; Bijnsdorp, I.V.; van Eijndhoven, M.A.J.; Sadek, P.; Sie, D.; Zini, N.; Middeldorp, J.M.; Ylstra, B.; de Menezes, R.X.; et al. Nontemplated nucleotide additions distinguish the small RNA composition in cells from exosomes. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 1649–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, N.; Iguchi, H.; Yoshioka, Y.; Takeshita, F.; Matsuki, Y.; Ochiya, T. Secretory mechanisms and intercellular transfer of microRNAs in living cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 17442–17452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trajkovic, K.; Hsu, C.; Chiantia, S.; Rajendran, L.; Wenzel, D.; Wieland, F.; Schwille, P.; Brugger, B.; Simons, M. Ceramide triggers budding of exosome vesicles into multivesicular endosomes. Science (New York NY). 2008, 319, 1244–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Garnier, D.; Lee, T.H.; D’Asti, E.; Montermini, L.; Meehan, B.; Rak, J. PML-RARa modulates the vascular signature of extracellular vesicles released by acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Angiogenesis 2016, 19, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldh, M.; Ekstrom, K.; Valadi, H.; Sjostrand, M.; Olsson, B.; Jernas, M.; Lotvall, J. Exosomes communicate protective messages during oxidative stress; possible role of exosomal shuttle RNA. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, M.; Silva, J.; Herrera, A.; Herrera, M.; Pena, C.; Martin, P.; Gil-Calderon, B.; Larriba, M.J.; Coronado, M.J.; Soldevilla, B.; et al. Exosomes enriched in stemness/metastatic-related mRNAS promote oncogenic potential in breast cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 40575–40587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robbins, P.D.; Morelli, A.E. Regulation of immune responses by extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, M.F.; Zhu, H.; Millard, R.W.; Fan, G.C. Exosomes Function in Pro- and Anti-Angiogenesis. Curr. Angiogenes. 2013, 2, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.P.; Kim, E.Y.; Badr, C.E.; Weissleder, R.; Mempel, T.R.; Tannous, B.A.; Breakefield, X.O. Visualization and tracking of tumor extracellular vesicle delivery and RNA translation using multiplexed reporters. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridder, K.; Sevko, A.; Heide, J.; Dams, M.; Rupp, A.K.; Macas, J.; Starmann, J.; Tjwa, M.; Plate, K.H.; Sultmann, H.; et al. Extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer of functional RNA in the tumor microenvironment. Oncoimmunology 2015, 19, E1008371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.S.; Cho, J.H.; Kim, H.; Choi, E.J.; Rho, S.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, D.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Hwang, D.; et al. Colorectal cancer cell-derived microvesicles are enriched in cell cycle-related mRNAs that promote proliferation of endothelial cells. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drusco, A.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNAs and Cancer: A Long Story for Short RNAs. Adv. Cancer Res. 2017, 135, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosaka, N.; Yoshioka, Y.; Hagiwara, K.; Tominaga, N.; Katsuda, T.; Ochiya, T. Trash or Treasure: Extracellular microRNAs and cell-to-cell communication. Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baccarini, A.; Chauhan, H.; Gardner, T.J.; Jayaprakash, A.D.; Sachidanandam, R.; Brown, B.D. Kinetic analysis reveals the fate of a microRNA following target regulation in mammalian cells. Curr. Biol. CB. 2011, 21, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dews, M.; Homayouni, A.; Yu, D.; Murphy, D.; Sevignani, C.; Wentzel, E.; Furth, E.E.; Lee, W.M.; Enders, G.H.; Mendell, J.T.; et al. Augmentation of tumor angiogenesis by a Myc-activated microRNA cluster. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y. Tumor exosomal RNAs promote lung pre-metastatic niche formation by activating alveolar epithelial TLR3 to recruit neutrophils. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umezu, T.; Ohyashiki, K.; Kuroda, M.; Ohyashiki, J.H. Leukemia cell to endothelial cell communication via exosomal miRNAs. Oncogene 2013, 32, 2747–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, G.; Liu, Y.; Fang, X.; Liu, Y.; Fang, L.; Lin, L.; Liu, X.; Wang, N. Tumor-derived microRNA-494 promotes angiogenesis in non-small cell lung cancer. Angiogenesis 2015, 18, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.K.; Park, S.R.; Jung, B.K.; Jeon, Y.K.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, M.K.; Kim, Y.G.; Jang, J.Y.; Kim, C.W. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells suppress angiogenesis by down-regulating VEGF expression in breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Fong, M.Y.; Min, Y.; Somlo, G.; Liu, L.; Palomares, M.R.; Yu, Y.; Chow, A.; O’Connor, S.T.; Chin, A.R.; et al. Cancer-secreted miR-105 destroys vascular endothelial barriers to promote metastasis. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 501–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.T.; Hamar, P.; Guo, C.; Basar, E.; Perdigao-Henriques, R.; Balaj, L.; Lieberman, J. miR-200-containing extracellular vesicles promote breast cancer cell metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 5109–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Teruya-Feldstein, J.; Weinberg, R.A. Tumor invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature 2007, 449, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Chen, J.; Zhou, L.; Chen, W.; Ding, G.; Cao, L. Pancreatic cancer derived exosomes regulate the expression of TLR4 in dendritic cells via miR-203. Cell. Immunol. 2014, 292, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berchem, G.; Noman, M.Z.; Bosseler, M.; Paggetti, J.; Baconnais, S.; Le Cam, E.; Nanbakhsh, A.; Moussay, E.; Mami-Chouaib, F.; Janji, B.; et al. Hypoxic tumor-derived microvesicles negatively regulate NK cell function by a mechanism involving TGF-beta and miR23a transfer. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1062968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, S.; Elkahloun, A.G.; Arakelyan, A.; Young, L.; Myers, T.G.; Otaizo-Carrasquero, F.; Wu, W.; Margolis, L.; Roberts, D.D. CD63, MHC class 1, and CD47 identify subsets of extracellular vesicles containing distinct populations of noncoding RNAs. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.H.; Chennakrishnaiah, S.; Audemard, E.; Montermini, L.; Meehan, B.; Rak, J. Oncogenic ras-driven cancer cell vesiculation leads to emission of double-stranded DNA capable of interacting with target cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 451, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Derrien, T.; Johnson, R.; Bussotti, G.; Tanzer, A.; Djebali, S.; Tilgner, H.; Guernec, G.; Martin, D.; Merkel, A.; Knowles, D.G.; et al. The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: Analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Zhou, H.; Lu, K.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Feng, T. Exosome-mediated delivery of MALAT1 induces cell proliferation in breast cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2018, 11, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iempridee, T. Long non-coding RNA H19 enhances cell proliferation and anchorage-independent growth of cervical cancer cell lines. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood NJ) 2017, 242, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gezer, U.; Ozgur, E.; Cetinkaya, M.; Isin, M.; Dalay, N. Long non-coding RNAs with low expression levels in cells are enriched in secreted exosomes. Cell Biol. Int. 2014, 38, 1076–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Deng, Z.; Dahmane, N.; Tsai, K.; Wang, P.; Williams, D.R.; Kossenkov, A.V.; Showe, L.C.; Zhang, R.; Huang, Q.; et al. Telomeric repeat-containing RNA (TERRA) constitutes a nucleoprotein component of extracellular inflammatory exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E6293–E6300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redzic, J.S.; Ung, T.H.; Graner, M.W. Glioblastoma extracellular vesicles: Reservoirs of potential biomarkers. Pharmgenom. Pers. Med. 2014, 7, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Chung, J.; Lee, K.; Balaj, L.; Min, C.; Carter, B.S.; Hochberg, F.H.; Breakefield, X.O.; Lee, H.; Weissleder, R. Chip-based analysis of exosomal mRNA mediating drug resistance in glioblastoma. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Figueroa, J.M.; Carter, B.S. Detection of glioblastoma in biofluids. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.Y.; Kesari, S. Malignant gliomas in adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 492–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaak, R.G.; Hoadley, K.A.; Purdom, E.; Wang, V.; Qi, Y.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Miller, C.R.; Ding, L.; Golub, T.; Mesirov, J.P.; et al. Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sottoriva, A.; Spiteri, I.; Piccirillo, S.G.; Touloumis, A.; Collins, V.P.; Marioni, J.C.; Curtis, C.; Watts, C.; Tavare, S. Intratumor heterogeneity in human glioblastoma reflects cancer evolutionary dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4009–4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Cazzato, E.; Ladewig, E.; Frattini, V.; Rosenbloom, D.I.; Zairis, S.; Abate, F.; Liu, Z.; Elliott, O.; Shin, Y.J.; et al. Clonal evolution of glioblastoma under therapy. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Broekman, M.L.; Maas, S.L.N.; Abels, E.R.; Mempel, T.R.; Krichevsky, A.M.; Breakefield, X.O. Multidimensional communication in the microenvirons of glioblastoma. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 482–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.C.; Eaton, S.A.; Young, P.E.; Lee, M.; Shuttleworth, R.; Humphreys, D.T.; Grau, G.E.; Combes, V.; Bebawy, M.; Gong, J.; et al. Glioma microvesicles carry selectively packaged coding and non-coding RNAs which alter gene expression in recipient cells. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kefas, B.; Godlewski, J.; Comeau, L.; Li, Y.; Abounader, R.; Hawkinson, M.; Lee, J.; Fine, H.; Chiocca, E.A.; Lawler, S.; et al. microRNA-7 inhibits the epidermal growth factor receptor and the Akt pathway and is down-regulated in glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 3566–3572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannakopoulos, T.; Friedmann-Morvinski, D.; Neveu, P.; Dugas, J.C.; Gill, R.M.; Huillard, E.; Liu, C.; Zong, H.; Rowitch, D.H.; Barres, B.A.; et al. Pro-neural miR-128 is a glioma tumor suppressor that targets mitogenic kinases. Oncogene 2012, 31, 1884–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yelamanchili, S.V.; Morsey, B.; Harrison, E.B.; Rennard, D.A.; Emanuel, K.; Thapa, I.; Bastola, D.R.; Fox, H.S. The evolutionary young miR-1290 favors mitotic exit and differentiation of human neural progenitors through altering the cell cycle proteins. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuzesi, A.; Kling, T.; Wenger, A.; Lunavat, T.R.; Jang, S.C.; Rydenhag, B.; Lotvall, J.; Pollard, S.M.; Danielsson, A.; Caren, H. Pediatric brain tumor cells release exosomes with a miRNA repertoire that differs from exosomes secreted by normal cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 90164–90175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peruzzi, P.; Bronisz, A.; Nowicki, M.O.; Wang, Y.; Ogawa, D.; Price, R.; Nakano, I.; Kwon, C.H.; Hayes, J.; Lawler, S.E.; et al. MicroRNA-128 coordinately targets Polycomb Repressor Complexes in glioma stem cells. Neuro-Oncology 2013, 15, 1212–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lopez-Bertoni, H.; Lal, B.; Li, A.; Caplan, M.; Guerrero-Cazares, H.; Eberhart, C.G.; Quinones-Hinojosa, A.; Glas, M.; Scheffler, B.; Laterra, J.; et al. DNMT-dependent suppression of microRNA regulates the induction of GBM tumor-propagating phenotype by Oct4 and Sox2. Oncogene 2015, 34, 3994–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.; Zhu, A.; Gong, L. Exosomes of glioma cells deliver miR-148a to promote proliferation and metastasis of glioblastoma via targeting CADM1. Bull. Cancer 2018, 105, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, J.; Phillips, L.M.; Shahar, T.; Hossain, A.; Gumin, J.; Kim, H.; Bean, A.J.; Calin, G.A.; Fueyo, J.; Walters, E.T.; et al. Exosomes from Glioma-Associated Mesenchymal Stem Cells Increase the Tumorigenicity of Glioma Stem-like Cells via Transfer of miR-1587. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5808–5819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, J.L.; Bliss, S.A.; Greco, S.J.; Ramkissoon, S.H.; Ligon, K.L.; Rameshwar, P. Delivery of Functional Anti-miR-9 by Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Exosomes to Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells Conferred Chemosensitivity. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2013, 2, e126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katakowski, M.; Buller, B.; Zheng, X.; Lu, Y.; Rogers, T.; Osobamiro, O.; Shu, W.; Jiang, F.; Chopp, M. Exosomes from marrow stromal cells expressing miR-146b inhibit glioma growth. Cancer Lett. 2013, 335, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ivanov, P.; Emara, M.M.; Villen, J.; Gygi, S.P.; Anderson, P. Angiogenin-induced tRNA fragments inhibit translation initiation. Mol. Cell 2011, 43, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, H.L.; Hu, G.W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tu, W.; Lu, Y.M.; Wu, L.; Xu, G.H. Glioma cells promote angiogenesis through the release of exosomes containing long non-coding RNA POU3F3. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 959–972. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, R.; Vallee, B.L. Human placental ribonuclease inhibitor abolishes both angiogenic and ribonucleolytic activities of angiogenin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 2238–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strydom, D.J.; Fett, J.W.; Riordan, J.F. The odyssey of angiogenin: A protein that induces blood vessel growth. Anal. Chem. 1989, 61, 1173a–1179a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, H.L.; Hu, G.W.; Zhang, B.; Kuang, W.; Chen, Y.; Wu, L.; Xu, G.H. Glioma cells enhance angiogenesis and inhibit endothelial cell apoptosis through the release of exosomes that contain long non-coding RNA CCAT2. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 785–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Li, Z.; Li, T.; Zhu, L.; Li, Z.; Tian, N. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR enhances angiogenesis by induction of VEGFA expression in glioma cells and transmission to endothelial cells via glioma cell derived-extracellular vesicles. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 5012–5021. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heyn, C.; Ronald, J.A.; Ramadan, S.S.; Snir, J.A.; Barry, A.M.; MacKenzie, L.T.; Mikulis, D.J.; Palmieri, D.; Bronder, J.L.; Steeg, P.S.; et al. In vivo MRI of cancer cell fate at the single-cell level in a mouse model of breast cancer metastasis to the brain. Magn. Reson. Med. 2006, 56, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eichler, A.F.; Chung, E.; Kodack, D.P.; Loeffler, J.S.; Fukumura, D.; Jain, R.K. The biology of brain metastases-translation to new therapies. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 8, 344–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priego, N.; Zhu, L.; Monteiro, C.; Mulders, M.; Wasilewski, D.; Bindeman, W.; Doglio, L.; Martinez, L.; Martinez-Saez, E.; Cajal, S.R.Y.; et al. STAT3 labels a subpopulation of reactive astrocytes required for brain metastasis. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1024–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peinado, H.; Aleckovic, M.; Lavotshkin, S.; Matei, I.; Costa-Silva, B.; Moreno-Bueno, G.; Hergueta-Redondo, M.; Williams, C.; Garcia-Santos, G.; Ghajar, C.M.; et al. Melanoma exosomes educate bone marrow progenitor cells toward a pro-metastatic phenotype through MET. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 833–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Erviti, L.; Seow, Y.; Yin, H.; Betts, C.; Lakhal, S.; Wood, M.J. Delivery of siRNA to the mouse brain by systemic injection of targeted exosomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 341–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geddings, J.E.; Mackman, N. Tumor-derived tissue factor-positive microparticles and venous thrombosis in cancer patients. Blood 2013, 122, 1873–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fong, M.Y.; Zhou, W.; Liu, L.; Alontaga, A.Y.; Chandra, M.; Ashby, J.; Chow, A.; O’Connor, S.T.; Li, S.; Chin, A.R.; et al. Breast-cancer-secreted miR-122 reprograms glucose metabolism in premetastatic niche to promote metastasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siravegna, G.; Marsoni, S.; Siena, S.; Bardelli, A. Integrating liquid biopsies into the management of cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 531–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochberg, F.H.; Atai, N.A.; Gonda, D.; Hughes, M.S.; Mawejje, B.; Balaj, L.; Carter, R.S. Glioma diagnostics and biomarkers: An ongoing challenge in the field of medicine and science. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2014, 14, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, J.P.; Nahed, B.V.; Madden, M.W.; Oliveira, S.M.; Springer, S.; Bhere, D.; Chi, A.S.; Wakimoto, H.; Rothenberg, S.M.; Sequist, L.V.; et al. Brain tumor cells in circulation are enriched for mesenchymal gene expression. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1299–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garzia, L.; Kijima, N.; Morrissy, A.S.; De Antonellis, P.; Guerreiro-Stucklin, A.; Holgado, B.L.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Parsons, M.; Zayne, K.; et al. A Hematogenous Route for Medulloblastoma Leptomeningeal Metastases. Cell 2018, 173, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Asti, E.; Chennakrishnaiah, S.; Lee, T.H.; Rak, J. Extracellular Vesicles in Brain Tumor Progression. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 383–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.S.; Lee, J.; Go, G.; Kim, Y.K.; Gho, Y.S. Circulating extracellular vesicles in cancer diagnosis and monitoring: An appraisal of clinical potential. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2013, 17, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabili, M.N.; Trapnell, C.; Goff, L.; Koziol, M.; Tazon-Vega, B.; Regev, A.; Rinn, J.L. Integrative annotation of human large intergenic noncoding RNAs reveals global properties and specific subclasses. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 1915–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Papagiannakopoulos, T.; Shapiro, A.; Kosik, K.S. MicroRNA-21 targets a network of key tumor-suppressive pathways in glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 8164–8172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriely, G.; Wurdinger, T.; Kesari, S.; Esau, C.C.; Burchard, J.; Linsley, P.S.; Krichevsky, A.M. MicroRNA 21 promotes glioma invasion by targeting matrix metalloproteinase regulators. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 5369–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.M.; Hwang, S.J.; Masuda, K.; Choi, K.M.; Jeong, M.R.; Nam, D.H.; Gorospe, M.; Kim, H.H. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein C1/C2 controls the metastatic potential of glioblastoma by regulating PDCD4. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 4237–4244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akers, J.C.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Kim, R.; Skog, J.; Nakano, I.; Pingle, S.; Kalinina, J.; Hua, W.; Kesari, S.; Mao, Y.; et al. MiR-21 in the extracellular vesicles (EVs) of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): A platform for glioblastoma biomarker development. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.; Wang, P.Y.; Li, X.Y.; Chen, J.X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zhang, C.G.; Jiang, T.; Li, W.B.; Ding, W.; et al. Exosomal levels of miRNA-21 from cerebrospinal fluids associated with poor prognosis and tumor recurrence of glioma patients. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 26971–26981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santangelo, A.; Imbruce, P.; Gardenghi, B.; Belli, L.; Agushi, R.; Tamanini, A.; Munari, S.; Bossi, A.M.; Scambi, I.; Benati, D.; et al. A microRNA signature from serum exosomes of patients with glioma as complementary diagnostic biomarker. J. Neuro-oncol. 2018, 136, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.K.; Yang, J.P.; Tong, J.; Jing, S.Y.; Fan, B.; Wang, F.; Sun, G.Z.; Jiao, B.H. Exosomal miR-221 targets DNM3 to induce tumor progression and temozolomide resistance in glioma. J. Neuro-oncol. 2017, 131, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, F.; Qing, Q.; Pan, Q.; Hu, M.; Yu, H.; Yue, X. Serum exosomal miR-301a as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for human glioma. Cell. Oncol. (Dordrecht) 2018, 41, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manterola, L.; Guruceaga, E.; Gallego Perez-Larraya, J.; Gonzalez-Huarriz, M.; Jauregui, P.; Tejada, S.; Diez-Valle, R.; Segura, V.; Sampron, N.; Barrena, C.; et al. A small noncoding RNA signature found in exosomes of GBM patient serum as a diagnostic tool. Neuro-oncology 2014, 16, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Camacho, L.; Guerrero, P.; Marchetti, D. MicroRNA and protein profiling of brain metastasis competent cell-derived exosomes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.K.; Pastori, C.; Penas, C.; Komotar, R.J.; Ivan, M.E.; Wahlestedt, C.; Ayad, N.G. Serum long noncoding RNA HOTAIR as a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in glioblastoma multiforme. Mol. Cancer. 2018, 17, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teplyuk, N.M.; Mollenhauer, B.; Gabriely, G.; Giese, A.; Kim, E.; Smolsky, M.; Kim, R.Y.; Saria, M.G.; Pastorino, S.; Kesari, S.; et al. MicroRNAs in cerebrospinal fluid identify glioblastoma and metastatic brain cancers and reflect disease activity. Neuro-oncology 2012, 14, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, A.; Wei, Z.; Yan, W.; Yin, J.; Huang, X.; Zhou, X.; Li, R.; Shen, F.; Wu, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Exosomal transfer of miR-151a enhances chemosensitivity to temozolomide in drug-resistant glioblastoma. Cancer Lett. 2018, 436, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rooj, A.K.; Mineo, M.; Godlewski, J. MicroRNA and extracellular vesicles in glioblastoma: Small but powerful. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2016, 33, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, D.; Yang, N.; Nadithe, V. Exosomes as therapeutic drug carriers and delivery vehicles across biological membranes: Current perspectives and future challenges. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2016, 6, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Dommelen, S.M.; Vader, P.; Lakhal, S.; Kooijmans, S.A.; van Solinge, W.W.; Wood, M.J.; Schiffelers, R. Microvesicles and exosomes: Opportunities for cell-derived membrane vesicles in drug delivery. J. Control Release 2012, 161, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozpolat, B.; Sood, A.K.; Lopez-Berestein, G. Liposomal siRNA nanocarriers for cancer therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 66, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chowdhury, N.; Vhora, I.; Patel, K.; Doddapaneni, R.; Mondal, A.; Singh, M. Liposomes co-Loaded with 6-Phosphofructo-2-Kinase/Fructose-2, 6-Biphosphatase 3 (PFKFB3) shRNA Plasmid and Docetaxel for the Treatment of non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 34–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunavat, T.R.; Jang, S.C.; Nilsson, L.; Park, H.T.; Repiska, G.; Lasser, C.; Nilsson, J.A.; Gho, Y.S.; Lotvall, J. RNAi delivery by exosome-mimetic nanovesicles - Implications for targeting c-Myc in cancer. Biomaterials 2016, 102, 231–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamerkar, S.; LeBleu, V.S.; Sugimoto, H.; Yang, S.; Ruivo, C.F.; Melo, S.A.; Lee, J.J.; Kalluri, R. Exosomes facilitate therapeutic targeting of oncogenic KRAS in pancreatic cancer. Nature 2017, 546, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahlgren, J.; De, L.; Karlson, T.; Brisslert, M.; Vaziri Sani, F.; Telemo, E.; Sunnerhagen, P.; Valadi, H. Plasma exosomes can deliver exogenous short interfering RNA to monocytes and lymphocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooijmans, S.A.A.; Stremersch, S.; Braeckmans, K.; de Smedt, S.C.; Hendrix, A.; Wood, M.J.A.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Raemdonck, K.; Vader, P. Electroporation-induced siRNA precipitation obscures the efficiency of siRNA loading into extracellular vesicles. J. Control Release 2013, 172, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vader, P.; Mager, I.; Lee, Y.; Nordin, J.Z.; Andaloussi, S.E.; Wood, M.J. Preparation and Isolation of siRNA-Loaded Extracellular Vesicles. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1545, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Q.; Ramakrishnaiah, V.; Henry, S.; Fouraschen, S.; de Ruiter, P.E.; Kwekkeboom, J.; Tilanus, H.W.; Janssen, H.L.; van der Laan, L.J. Hepatic cell-to-cell transmission of small silencing RNA can extend the therapeutic reach of RNA interference (RNAi). Gut 2012, 61, 1330–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shtam, T.A.; Kovalev, R.A.; Varfolomeeva, E.Y.; Makarov, E.M.; Kil, Y.V.; Filatov, M.V. Exosomes are natural carriers of exogenous siRNA to human cells in vitro. Cell Commun. Signal. 2013, 11, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haraszti, R.A.; Miller, R.; Didiot, M.C.; Biscans, A.; Alterman, J.F.; Hassler, M.R.; Roux, L.; Echeverri, D.; Sapp, E.; DiFiglia, M.; et al. Optimized Cholesterol-siRNA Chemistry Improves Productive Loading onto Extracellular Vesicles. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 1973–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Charrier, A.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, R.; Yu, B.; Agarwal, K.; Tsukamoto, H.; Lee, L.J.; Paulaitis, M.E.; Brigstock, D.R. Epigenetic regulation of connective tissue growth factor by MicroRNA-214 delivery in exosomes from mouse or human hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology 2014, 59, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lou, G.; Song, X.; Yang, F.; Wu, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, Y. Exosomes derived from miR-122-modified adipose tissue-derived MSCs increase chemosensitivity of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luther, K.M.; Haar, L.; McGuinness, M.; Wang, Y.; Lynch Iv, T.L.; Phan, A.; Song, Y.; Shen, Z.; Gardner, G.; Kuffel, G.; et al. Exosomal miR-21a-5p mediates cardioprotection by mesenchymal stem cells. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2018, 119, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragomir, M.; Chen, B.; Calin, G.A. Exosomal lncRNAs as new players in cell-to-cell communication. Transl. Cancer Res. 2018, 7, S243–S252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Asti, E.; Huang, A.; Kool, M.; Meehan, B.; Chan, J.A.; Jabado, N.; Korshunov, A.; Pfister, S.M.; Rak, J. Tissue Factor Regulation by miR-520g in Primitive Neuronal Brain Tumor Cells: A Possible Link between Oncomirs and the Vascular Tumor Microenvironment. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, C. Exosome cancer diagnostic reaches market. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 359–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witwer, K.W.; Buzas, E.I.; Bemis, L.T.; Bora, A.; Lasser, C.; Lotvall, J.; Nolte-’t Hoen, E.N.; Piper, M.G.; Sivaraman, S.; Skog, J.; et al. Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotvall, J.; Hill, A.F.; Hochberg, F.; Buzas, E.I.; Di, V.D.; Gardiner, C.; Gho, Y.S.; Kurochkin, I.V.; Mathivanan, S.; Quesenberry, P.; et al. Minimal experimental requirements for definition of extracellular vesicles and their functions: A position statement from the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 26913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Deun, J.; Mestdagh, P.; Agostinis, P.; Akay, O.; Anand, S.; Anckaert, J.; Martinez, Z.A.; Baetens, T.; Beghein, E.; Bertier, L.; et al. EV-TRACK: Transparent reporting and centralizing knowledge in extracellular vesicle research. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Name | Source | Detection Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| miRNAs | |||
| miR-1290, miR-1246 | Pediatric glioma stem cells | Microarray and qRT-PCR | [154] |
| miR-21 | Serum | qRT-PCR | [52] |
| miR-21 | Cerebrospinal fluid | qRT-PCR | [184,185] |
| miR-21, miR-222, miR-124-3p | Serum (World Health Organization (WHO) Grade I–IV GBM, post-surgical resection) | qRT-PCR | [186] |
| miR-210 | Metastatic (brain-tropic 70W, MDA-MB-231BR, and CTC1BMSM variants), Non-metastatic (non-BM MeWo, MDA-MB-231P and CTC1P) | MicroRNA PCR array | [190] |
| miR-221 | Serum (WHO Grade I–IV GBM) and cells (SHG-44, U251, U87MG) | qRT-PCR | [187] |
| miR-301a | Serum (WHO Grade I–IV GBM, post-surgical resection, recurrence) | qRT-PCR | [188] |
| miR-320, miR-574-3p | Serum | qRT-PCR | [189] |
| Other ncRNAs | |||
| HOTAIR | Serum | qRT-PCR | [191] |
| linc-CCAT2 | Cells (U87MG) | qRT-PCR | [165] |
| linc-POU3F3 | Cells (A172) | qRT-PCR | [162] |
| RNU6-1 | Serum | qRT-PCR | [189] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spinelli, C.; Adnani, L.; Choi, D.; Rak, J. Extracellular Vesicles as Conduits of Non-Coding RNA Emission and Intercellular Transfer in Brain Tumors. Non-Coding RNA 2019, 5, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna5010001
Spinelli C, Adnani L, Choi D, Rak J. Extracellular Vesicles as Conduits of Non-Coding RNA Emission and Intercellular Transfer in Brain Tumors. Non-Coding RNA. 2019; 5(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna5010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpinelli, Cristiana, Lata Adnani, Dongsic Choi, and Janusz Rak. 2019. "Extracellular Vesicles as Conduits of Non-Coding RNA Emission and Intercellular Transfer in Brain Tumors" Non-Coding RNA 5, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna5010001
APA StyleSpinelli, C., Adnani, L., Choi, D., & Rak, J. (2019). Extracellular Vesicles as Conduits of Non-Coding RNA Emission and Intercellular Transfer in Brain Tumors. Non-Coding RNA, 5(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna5010001





