Abstract
As an essential part of central dogma, RNA delivers genetic and regulatory information and reflects cellular states. Based on high-throughput sequencing technologies, cumulating data show that various RNA molecules are able to serve as biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of various diseases, for instance, cancer. In particular, detectable in various bio-fluids, such as serum, saliva and urine, extracellular RNAs (exRNAs) are emerging as non-invasive biomarkers for earlier cancer diagnosis, tumor progression monitor, and prediction of therapy response. In this review, we summarize the latest studies on various types of RNA biomarkers, especially extracellular RNAs, in cancer diagnosis and prognosis, and illustrate several well-known RNA biomarkers of clinical utility. In addition, we describe and discuss general procedures and issues in investigating exRNA biomarkers, and perspectives on utility of exRNAs in precision medicine.
1. Introduction
Biomarkers are defined as measurable alterations in biological substance that associate with normal or abnormal conditions [1]. In the past decades, various types of biomarkers have assisted diagnosis and prognosis of diseases in clinical trials [2,3].
In the field of oncology, biomarkers generally possess three types of clinical relevance: diagnostic values, prognostic values, and predictive values. The diagnostic values include early detection of diseases, determination of tumor origins, and classification of cancer subtypes. The prognostic values include prediction of disease outcomes and risk assessment independent of treatments. The predictive values contain the prediction of responses to treatments, etc. [4,5]. Sensitive and specific biomarkers in many clinical trials are essential to precision medicine in that they enable the determination of clinical outcomes in a relatively earlier stage. Biomarkers also serve as potential targets for drug design. Moreover, integration of biomarker data using bioinformatics methods would enhance our understanding of biological pathways and regulatory mechanisms associated with diseases [6]. In this review, we will summarize latest studies on various of RNA biomarkers, especially extracellular RNA (exRNA) biomarkers, in cancer. In addition, we will describe biogenesis and clinical relevance of exRNA, and related bioinformatics methods and databases.
2. Comparison of Different Types of Biomarkers
RNAs serve not only as transmitters of genetic information, but also subjects of transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation [7,8]. Although RNAs are unstable in alkaline conditions, they are easy to detect and quantify at very low abundance (Table 1) [9]. Compared with protein biomarkers, RNA biomarkers have more sensitivity and specificity. PCR enables traces of RNA sequences to be amplified and thus captured specifically with high sensitivity. Moreover, the cost of RNA biomarker is much lower than protein biomarker because detecting each protein requires a specific antibody. Compared with DNA biomarkers, RNA biomarkers have the advantage of providing dynamic insights into cellular states and regulatory processes than DNA biomarkers. Besides, RNA has multiple copies in a cell, which delivers more information than DNA. Moreover, some RNAs with specific structures, such as circular RNA, have the potential to exist stably in plasma and/or serum [10,11].

Table 1.
Comparison of macromolecular biomarkers.
Recently, next-generation sequencing technology facilitates the quantified measurements of RNA expression levels at whole genome level. Increasing depth of RNA sequencing also enables the detection of novel transcripts, such as lowly expressed noncoding RNAs, and subtle variations in expression with greater accuracy [17,18]. In summary, large scale expression profiles of RNAs provide both genetic and dynamic regulatory information, and thus can work as accurate and direct markers of cellular state [19].
3. Different Types of RNA Biomarkers in Cancer
The high-throughput sequencing technologies have enabled the detection of protein–coding RNAs (i.e., mRNAs) and different types of non-coding RNAs (e.g., small nuclear RNA, micro RNA, small nucleolar RNA, etc.) in human at transcriptome level. Of particular note is that there are lots of novel non-coding RNAs discovered recently. With many international collaborated projects conducted (e.g., The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), International Cancer Genome Consortium (ICGC)) and vast data in cancer accumulated, the number of studies on cancer associated RNA biomarkers has been increasing quickly (Figure 1A). Various types of RNAs were typically used as biomarkers in cancer (Figure 1B).
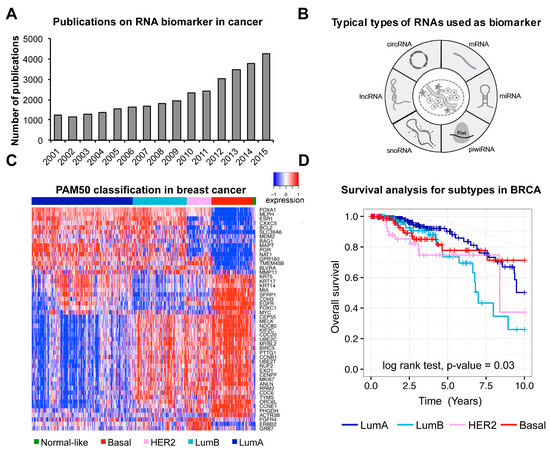
Figure 1.
Studies and examples of RNA biomarkers in cancer. (A) Numbers of publications on RNA biomarker in cancer (The data were collected using keywords of “RNA biomarker” and “cancer” browsed in NCBI PubMed); (B) Typical types of RNAs used as biomarkers in cancer; (C) Gene expression pattern of PAM50 genes, calculated from published TCGA breast cancer data (BRCA). The patients were classified into five subtypes (Basal, HER2, LumB, LumA and Normal-like) based on PAM50 genes’ expression profile; (D) Kaplan-Meier analysis for different subtypes in the TCGA BRCA cohort. Subtypes were classified using the PAM50 panel. p-value was determined based on log-rank test.
The first well-studied type of RNA as biomarker is mRNA. Differential expression of specific genes would positively or negatively correlate with disease pathology. So far, multi-gene expression profiles have been used as biomarker for clinical outcome in many cancer studies [20]. For instance, PAM50, a 50-gene panel, has been successfully applied to the classification of breast cancer [2]. Here, we have used the PAM50 panel to reanalyze TCGA breast cancer data [21] to show its power of classification and prognosis in breast cancer (Figure 1C,D). Similarly, another expression panel of 31 mRNAs related to cell cycle progression was used as prognosis marker to predict metastasis, recurrence and risk of prostate cancer [22].
In addition to mRNAs, lots of functionally important RNAs that do not encode proteins have been discovered recently. Many of them can also be used as biomarkers. For instance, microRNAs (miRNAs) are small and evolutionary conserved non-coding RNAs that usually involve in RNA silencing and other types of post-transcriptional regulations. Some miRNAs play pivotal roles in cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis, and thus function as oncogenes or tumor suppressors [23]. Expression profile of miRNAs has been reported to successfully classify poorly differentiated tumor types [24]. In addition, low expression of miR-21 was shown to indicate low hazard rate for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients after adjuvant therapy. Moreover, miR-21 was reported as a potential therapy target (Table 2) [25].

Table 2.
Tissue-based RNA biomarkers for cancer.
Piwi-interacting RNA (piRNA) is a novel type of small non-coding RNA that interacts with Piwi subclass Argonaute proteins, which participate in transposon silencing via DNA methylation. PiRNAs have been shown related to cell proliferation and invasion [31]. Low expression of a piRNA, piR-651, was found to be associated with short survival time for lymphoma patients, which could serve as an prognostic marker (Table 2) [28].
Small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA discovered in nucleolar and regulate ribosome maturation and function [32]. Studies also show that some snoRNAs are involved in alternative splicing and gene silencing [33,34]. Furthermore, expression profile of a snoRNA panel can be used to detect early non-small-cell lung cancer (Table 2) [29].
In addition to small RNAs, long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) could also serve as biomarkers. Accumulating evidence has emerged to show their presence and function, although the classification and characterization of lncRNAs is still rather premature. For instance, a well-known lncRNA, HOTAIR, was reported to be correlated with tumorigenesis, tumor progression, metastasis and patient survival. Therefore, HOTAIR has a potential to be a promising biomarker (Table 2) [27,35,36].
In addition to linear RNA molecules described above, a specific type of non-coding RNA, circular RNA (circRNA), is generated from pre-mRNA with a back splice mechanism, which connects the 3’ end and 5’ end of a transcript’s precursor to form a circle [10]. The circular structure makes circRNA more resistant to exonucleases than other types of RNA molecules [10,11]. Its hypothetical function involves downregulation of miRNAs by sequestering complementary miRNAs like a sponge [37]. As an example related to cancer, Hsa_circ_002059 is significantly downregulated in gastric tumor tissues compared to normal tissues, and correlated with tumor metastasis (Table 2) [30].
Furthermore, regulatory alterations such as alternative splicing can be revealed by RNA-seq using specific bioinformatics analyses [38]. Distorted alternative splicing produces dysfunctional isoforms that may have detrimental consequences. Isoform ratios for alternatively-spliced genes can be estimated from RNA-seq results. Aberrant splicing events have been reported to be associated with survival of cancer patients [39]. Another important event that assist clinical trials is gene fusion. Fusion genes result from chromosomal aberrations and are usually absent in normal tissues. Presence and abundance of chimeric RNA transcripts generated from fusion genes in tumor samples can effectively classify cancer subtypes and identify unstable chromosome regions [40]. For instance, gene fusion of TMPRSS2 to ERG leads to lower survival rate, making it a potential marker for prognosis and stratification of cancer [41].
4. Category of Extracellular RNAs
In addition to the RNAs inside tumor cells, recent studies have shown the existence of different types of exRNAs. ExRNAs include almost all known types of RNAs, for instance, miRNA, piRNA, siRNA, snoRNA, circRNA, tRNA and lncRNA (Figure 2). They have been found in various kinds of bio-fluids, including plasma, serum, breast milk, saliva, cerebrospinal fluid, bile, urine, etc. [16,42,43].
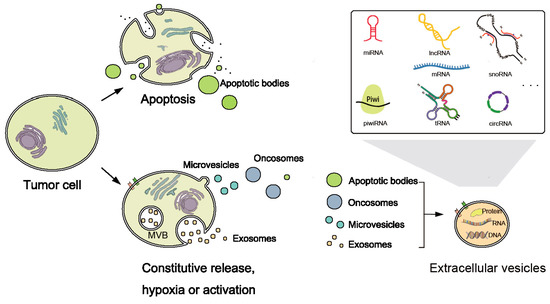
Figure 2.
Biogenesis and categories of extracellular RNAs (exRNAs). Biogenesis of Extracellular vesicles (EVs) released by tumor cells. EVs include exosomes, micro-vesicles, oncosomes, and apoptotic bodies. Apoptotic tumor cells release apoptotic bodies, while normal or active tumor cells release exosomes, micro-vesicles, and oncosomes. Exosomes are endocytic membrane-derived vesicles released by the fusion of the multivesicular bodies (MVBs) with the cell membrane. However, the cell membrane directly outwards buds to the extracellular milieu and forms the micro-vesicle. Besides, oncosomes are large EVs formed through the budding of the tumor cell membrane. EVs deliver a variety of DNA, protein, and RNA species including miRNA, piwiRNA, lncRNA, mRNA, tRNA, snoRNA, circRNA, etc.
Studies on exRNA have a long history, although major progresses were made in the last decade. In 1971, exRNA was found in bio-fluids, which laid the basis for the hypothesis that exRNA could play important role in cell-cell communication [44]. ExRNAs as signaling molecules in the regulatory circuitry have been detected in both plants and animals [45]. Surprisingly, exRNAs detected in plasma has unexpected abundance (Table 1) despite of the relative high level of RNase in blood [46].
Later, studies on exRNA profiles have extended the knowledgebase of exRNA types. In 2016, Freedman et al. first performed RNA sequencing using ion proton system for plasma of 40 individuals. They identified several classes of the 1192 exRNAs including miRNA, piwiRNA and snRNA. They then performed RT-qPCR on additional two thousand individuals for the top 500 expressed exRNAs. This study is so far the largest profiling of plasma extracellular miRNA species and other small RNAs from a large population [47]. While there are many different types of RNAs, miRNA is the most abundant type of exRNAs. The abundance of miRNA in recipient cells can be altered by miRNAs transferred from vesicles, which will lead to the downregulation of several mRNAs inside the cells [48].
5. Biogenesis of exRNAs
To survive degradation, exRNAs are hypothesized to be stabilized by protein or lipid complexes, such as proteolipid, lipoprotein or other RNA-binding proteins, and packed in vesicle structures [43,49]. They may be released as a result of cell death, and packed into apoptotic bodies [50] or as communicators (Figure 2). Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are nanomeric cell-released vesicles carrying DNAs, RNAs, and proteins which function in intercellular communication [51]. EVs have been divided into several classes including exosomes, oncosomes, micro-vesicles, and apoptotic bodies, according to size, morphology and origin [52,53]. They can travel to nearby or distant tissues, captured by target cells and transmit genetic and regulatory information from their origins to targets. Analyses of EVs and their RNA contents will be useful since the concentration and characteristics of RNAs reflects their cellular origins and diffusing conditions [54].
There are several different mechanisms in the process of transferring content into the recipient cells from vesicles. For instance, exosomal membrane proteins could associate with and activate receptors of recipient cell [55]. In some situations, these proteins are cleaved by proteases before targeting. Then the membranes of vesicles fuse with the recipient cells. They can also transmit their cargo to targets via endocytosis [55]. Many studies focus on the influence of exRNAs on the recipient cells. Studies have shown that exosomal shuttle RNAs in the EVs can be delivered into the recipient cells, and translated into proteins [49]. Vesicles transmitted among normal cells are the basis for many important biological events and communications between cells, which may shed light on clinical treatments.
ExRNAs provide the great promise in molecular diagnostics, but at present the understandings of their regulatory mechanisms are still limited. The mechanisms of exRNA release, uptake, regulation and function on recipient cells need further investigation.
6. Clinical Relevance of exRNAs in Cancer
At present, exRNAs found in the blood of cancer patients has encouraged more and more studies [56]. Actually, both normal cells and tumor cells can secrete vesicles. Using deep sequencing methods, altered expression of exRNAs has been found in different cancers which can be of potential clinical relevance [57].
More vesicles are secreted from tumor cells than from normal cells and work as helpers for cancer progression. ExRNAs in the vesicles play key roles in the intercellular communication and influence the phenotype of the recipient cells by targeting specific genes. For example, hepatocellular carcinoma cells (HCC) can secret miRNAs and lncRNAs via EVs to adjacent cells that alter local environment, which potentially enhance the local spread and multifocal growth of tumor [58,59]. Tumor cells can also release exosomes that assist organ-specific metastasis by transforming the distant tissues into ideal microenvironments for the early survival of disseminating tumor cells called pre-metastatic niche [60]. For instance, U1 snRNAs in exosomes may serve as possible ligands of Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3), which further trigger the formation of pre-metastatic niche [61]. It has also been shown that tumor exosomes, which contain a variety of proteins, RNAs, and DNAs, could decrease the immune ability of T cells in preparation for metastasis [62].
ExRNAs’ potential to be therapeutic targets for cancer therapy has become a hot research topic of exRNA studies [63]. It was proved that short interfering RNAs (siRNAs) can downregulate the EVs release in tumor microenvironment, and thus enhance the tumor suppression [64]. SiRNA delivery system has been performed in phase 1 clinical trial. For example, Khvalevsky et al. succeeded in delivering siRNA to mutated KRAS oncogene and found that this local prolonged siRNA delivery system suppressed the growth of human pancreatic tumor cells [65]. Ozpolat et al. reported the feasibility and stability of liposomal nanoparticles as means for the siRNAs’ transporting to tumor cells [66]. Therefore, EVs containing siRNAs may become therapeutic tools targeting tumor cells in the future. Moreover, extracellular miRNAs in EVs may also be used in therapy, considering their inhibiting or suppressing properties in cancer growth. For example, Nishimura et al. proved that the EphA2-targeting siRNA and the tumor suppressor miR-520d-3p could target oncogenic pathways and repress ovarian cancer growth [67].
7. Extracellular RNA Biomarkers
ExRNAs have promising potential as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers, because exRNAs are easy to detect and provide non-invasive molecular diagnosis techniques. Samples acquired from blood, saliva and other cell-free fluids do not require direct operations on tissues. Currently, blood is the most widely used bio-fluids in exRNA biomarker development. So far, a large amount of experimental data and potential biomarkers have been accumulated and reported [68,69]. Previous studies have verified the potential of exRNAs as biomarkers in certain diseases, especially in several types of cancer. For instance, exRNAs can aid the diagnosis and classification of cancer patients when the solid tumor tissue is not available [70].
Prostate cancer is a common type of cancer in the male reproductive system. Some tumor-derived exRNAs are present in the blood of prostate cancer patients with remarkable stability. For instance, upregulated telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) mRNA have been discovered with similar expression behaviors in peripheral blood and tumor tissues in prostate cancer patients, and is associated with tumor size and malignancy (Table 3) [71]. In addition, miR-141 was found to be expressed in various epithelial cancers, showing strong differential expression between serum of prostate cancer patients and healthy controls [72]. Biomarkers for cancers in reproductive systems can also be found in urine. For instance, PCA3, a lncRNA exclusively expressed in prostate, can be detected with significant abundance in prostate cancer patients’ urine (Table 3) [73,74].

Table 3.
Cancer extracellular RNA (exRNA) biomarkers.
Cancers that occur in the digestive system include liver, gastric, pancreatic and esophageal cancers, etc. A study of serum exosomal RNAs in liver cancer showed that several miRNAs are differentially expressed between hepatocellular carcinoma and chronic hepatitis [75]. Examples of piRNA in peripheral blood of gastric cancer patients are associated with occurrence, sub-type and metastasis status of tumor (Table 3) [76]. In addition, for these types of cancer, saliva is also shown to be a promising source of biomarker discovery [77]. Saliva RNAs have been found to associate with parotid gland, esophageal, pancreatic and oral squamous cell cancer [78,79,80,81]. Jae Hoon Bahn et al. described the landscape of several types of exRNAs in human saliva, including miRNA, piRNA and circular RNA, providing a comprehensive extracellular non-coding RNA database in human saliva for further biomarker discovery [82].
Glioblastoma is a common and highly aggressive cancer in the nervous system [83]. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) circulates in the ventricular system of human brain. It is a promising source to study brain’s RNA expression profile [75]. A couple of miRNAs, such as miR-10b and miR-21, have been found to be enriched in CSF for glioblastoma patients and patients having brain metastasis from breast and lung cancer (Table 3) [84]. For instance, Akers et al. used the RT-PCR to quantitatively assess the miRNAs in the EVs of the glioblastoma and non-oncologic patients’ cerebrospinal fluid [85]. They found that the miR-21 was significantly increased in gliblastoma patients. Furthermore, they have discriminated glioblastoma patients from the non-oncologic patients using miR-21’s expression level, based on a relatively small patient cohort (twenty-nine).
8. Identification of Novel Extracellular RNA Biomarkers
Many more exRNAs continue to be found as potential biomarkers. For instance, as important components of splicing machinery, U2 snRNAs’ fragments were found in blood, showing altered abundance in mice when implanted with several human cancer types [88,89]. Circular RNAs (CircRNAs) were found to be stably existed in exosomes and differentially expressed between cancer and normal serum, making a potential source of biomarkers as well [90]. Discovery of novel RNA biomarkers in cell-free fluids requires preparation of RNA samples and libraries, data generation with quantified methods, and correlation with diagnostic or prognostic properties using bioinformatics analysis (Figure 3).
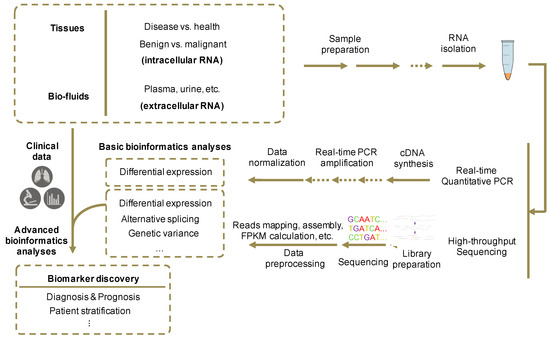
Figure 3.
Experimental and analytical procedures for the identification of novel RNA biomarkers. First, tissues and/or bio-fluids are collected from both patients and health individuals. Then RT-qPCR, small RNA-seq or other RNA sequencing methods are performed on isolated and purified RNA samples. RT-qPCR procedure includes cDNA synthesis by reverse transcription from total RNAs and qPCR reactions with the synthesized cDNA templates. RNA-seq procedure includes library preparation, in which RNA transcripts are fragmentized and transcribed into cDNAs, and high-throughput sequencing. Then, RNA-seq data are processed with a pipeline that includes mapping of reads to the reference genome, assembly of transcriptome from mapped reads, calculating each transcript’s expression abundance (i.e., FPKM, fragments per kilobase of transcript, per million fragments sequenced), and differential expression analysis. Differential expression of selected RNA biomarkers can then be validated by RT-qPCR results in different sample groups. Finally, advanced bioinformatics and statistical analyses will integrate clinical data with expression profiles to obtain the biomarkers’ correlations with diagnostic or prognostic properties.
In contrast to tissue collection, most body fluid samples can be collected less invasively, without direct operation on tissues. For example, plasma and serum of both healthy controls and cancer individuals could be collected though venipuncture and separator tubes [68,91]. Then RNAs can be isolated using certain RNA isolation kits that best meet the experimental requirements [92]. Meanwhile, flow cytometry and dynamic light scattering could be used for the assessment of RNA quantity [93,94].
After the isolation of RNA samples, several methods can be used to obtain quantified expression profile data. RT-qRCR procedure includes cDNA synthesis by reverse transcription from total RNAs and qPCR reactions with the synthesized cDNA templates [95]. High throughput sequencing such as RNA-seq is performed on the purified RNA samples after library preparation. In preparation of RNA-seq libraries, RNA transcripts are fragmentized and reverse transcribed into cDNAs [96].
The collected quantification data would then go through bioinformatics and statistical analysis. RNA-seq data are processed with a pipeline that includes mapping of reads to the reference genome, assembly of transcriptome from mapped reads and differential expression analysis [97]. Using regression algorithms, features in the expression profile data across samples could be selected and correlated with clinical features such as existence and subtype of diseases, tumor recurrence, normal and tumor tissues, usage of treatments, and patient survival, varying with the purpose of the study. Since experiment process has significant influence on the results, it is necessary to ensure the consistency of the experimental and analytical procedures in the different sample types [91]. In addition, considering the fluctuation of RNA abundance in bio-fluids and difference of total reads generated between experiments, data normalization is an essential part for the following advanced analyses [98]. Furthermore, differential expression of selected RNA biomarkers should be validated by RT-qPCR.
9. Published Databases of RNA Biomarkers
With the accumulation of the nucleic acid biomarker studies, several integrative databases have been developed (Table 4).

Table 4.
Available database for RNA biomarkers for cancer.
Many of the biomarker databases are disease-centered (Table 4). For instance, the Human MicroRNA Disease Database (HMDD) is an experiment-supported database of human miRNA-disease associations with experimental evidences from genetics, epigenetics, circulating miRNAs and miRNA-target interactions. Osteosarcoma Database contains osteosarcoma-associated protein-coding genes and miRNAs by literature search and manual annotation, providing a platform for evaluating potential miRNAs as osteosarcoma biomarkers [99]. Colon Rectal Cancer Gene (CoReCG) is a resource for factual colon-rectal carcinoma related genes and relating mechanisms, as well as information about differentially expressed, mutated, and polymorphic genes involved in distinct cancer stages [100]. Bladder Cancer Biomarker Evaluation Tool (BC-BET) provides an online platform for evaluating diagnostic and prognostic gene expression biomarkers integrating curated gene expression data from publicly available patient cohorts. It enables users to estimate the association between gene expression and the presence, grade, stage and predicted outcome of tumor [101]. A database of disease-related biomarkers uses a dictionary-based Named Entity Recognition system to curate a dataset of biomarkers with minimized false positive ratio [102].
Some other biomarker databases are more comprehensive than the above disease-centered databases (Table 4). For instance, MIRUMIR includes publicly available miRNA datasets annotated with patients’ survival information. It can be used to predict whether a given miRNA is a potential robust biomarker for survival of cancer patients [103]. Biomarker Database (BMDB) is a database constructed by the United States National Cancer Institute’s (NCI) Early Detection Research Network (EDRN). Based on the curation of the currently available biomarker data and raw results, EDRN team developed a common information model for cancer biomarker research, normalized and screened the data before combined into an integrated knowledge system including gene, protein, genetic, genomic, epigenetic and proteomic biomarkers classified by organs (Table 4) [104].
In addition, several databases specifically designed for exosomal and extracellular biomarkers have been developed (Table 4). For instance, exRNA Atlas collects the latest information on various exRNA studies, including exRNA profiling data derived from small RNA sequencing and RT-qPCR, standardized exRNA protocols, and many other useful tools and technologies [105]. A miRNA database, miRandola, is an extracellular circulating miRNA database, which is useful for studying biological function of the predicted extracellular miRNA biomarkers [106]. ExoCarta stores various published and unpublished information of exosomal studies about exosomal proteins, RNAs and lipids [107,108].
10. Future Perspectives and Challenges
Since the identification of exRNAs in various human bio-fluids, an increasing number of studies have positioned exRNA as a new type of non-invasive biomarker with numerous clinical potential. Due to the important roles of exRNAs in biological processes and promising potentials in molecular diagnosis, a number of exRNA projects have been funded by National Institutes of Health to advance the technologies of exRNA identification from different types of bio-fluid. The Extracellular RNA Communication Consortium (ERCC) [109] was organized in 2012 and supported by the American National Institutes of Health (NIH) Common Fund. ERCC aims to investigate the mechanism of exRNA biogenesis, delivery and function; to define a reference catalogue of exRNA in normal individual body fluids; to develop the clinical utility of exRNA as biomarkers of disease or therapeutic molecules [105]. Compared to previous researches on the discovery and feasibility of exRNA before 2015 revealing the potential use of exRNA, recent studies focus more on exploring the usage of extracellular RNAs as biomarkers.
In the future, systematic identification of novel exRNA biomarkers will need to be further explored, although a few exRNA biomarkers have been discovered individually. Considering the variety of exRNA species, though most studies focused on profiling miRNA outside cells, other exRNA species such as piwiRNA, circRNA and lncRNA may also serve as alternatives in clinical utility. Currently, there are only limited mature exRNA biomarkers that could guide clinical decision making. Large cohorts with matched clinical information, including survival time, disease recurrence, response for drug usage or other information are urgently needed in the identification of novel exRNA biomarkers. Sufficient clinical cohorts are also required to validate the performance of biomarkers for early-diagnosis, prognosis and drug usage.
Moreover, the mechanisms of exRNA biogenesis and regulation are still unclear. A better understanding of pathways, interactomes and regulatory networks of exRNAs would serve as guidance for biomarker screening and drug design. With the advancements in researches on relating mechanisms, more biomarkers with greater predictive and explanatory power could be identified for different types of cancer from various sources, which will in return facilitate the understanding of mechanisms.
It is also possible to target exRNAs as cancer therapeutic methods. The secretion and circulation of extracellular vesicle that contain regulatory RNAs can be blocked to prevent cancer from progressing and metastasis. In addition, extracellular vesicles could be used as a transmitter of specific regulatory elements into target cells, inhibiting the development of tumor. Some regulatory RNAs that play roles in pivotal processes in tumor development could be repressed or sequestered to lower their abundance and inhibit their functions. Further applications require more comprehensive understanding of the biogenesis of exRNA and extracellular vesicles, as well as regulatory roles of different types of non-coding RNAs.
Many challenges exist in the studies of exRNAs. For instance, exRNAs’ abundance in different human body fluids is distinct. For instance, using high-throughput RT-PCR, Shah R. et al. illustrated that miRNAs isolated from simultaneous whole blood and plasma in 2391 individuals had different expression levels [110]. The divergent miRNA levels indicate that exRNAs obtained from consistent human sources are required when designing the experimental procedure for biomarker investigation in future.
Because RNA is easy to be degraded by RNAase and the abundance of exRNA is relatively low, the extraction, purification and protection of exRNAs from body fluids are essential for further high-throughput sequencing and bioinformatics analyses. RNA isolation kits, RNA-seq library preparation, PCR methodology and even the gel size selection would affect the results of the RNA quantitative measurement and the RNA species detection. Another issue is that data normalization in the exRNA quantification may also introduce technical bias. Therefore, standardized methods may lead to reasonable comparison between different studies. Furthermore, due to the relative low exRNA abundance and noisy background, retrieving useful information from the fragmented raw reads being sequenced is a challenging problem for both experiment and bioinformatics. Large scale sample size, sequencing technology with substantial depth, improved data mining method (e.g., machine learning method), standard bioinformatics tools and pipelines are the potential key points to provide solutions. In summary, a fine-tuned and standardized pipeline, starting from exRNA isolation procedures, low abundance RNA amplification and sequencing to the advanced bioinformatics analysis methods with high efficiency, sensitivity and specificity, would play an essential role in the exRNA biomarker development.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Plan of China [2016YFA0500803], National Natural Science Foundation of China [31522030] and Tsinghua University Initiative Scientific Research Program [2014z21045]. This work was also supported by the Computing Platform of National Protein Facilities (Tsinghua University).
Author Contributions
Z.J.L. conceived the project, X. Xi., T. Li., Y.Y. and Z.J.L. wrote the paper. Y.H., J. Sun. and Y. Zhu provided part of supporting data.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Strimbu, K.; Tavel, J.A. What are biomarkers? Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2010, 5, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, J.S.; Mullins, M.; Cheang, M.C.U.; Leung, S.; Voduc, D.; Vickery, T.; Davies, S.; Fauron, C.; He, X.; Hu, Z.; et al. Supervised risk predictor of breast cancer based on intrinsic subtypes. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrini, K.L.; Sanda, M.G.; Moreno, C.S. RNA biomarkers to facilitate the identification of aggressive prostate cancer. Mol. Asp. Med. 2015, 45, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayeux, R. Biomarkers: Potential uses and limitations. NeuroRx 2004, 1, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, S.; Shelling, A.; Muthukaruppan, A.; Lasham, A.; Blenkiron, C.; Laking, G. Predictive and prognostic molecular markers for cancer medicine. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2010, 2, 125–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Mariani, T.J. Array of hope: Expression profiling identifies disease biomarkers and mechanism. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2009, 37, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yang, Y.-C.T.; Di, C.; Hu, B.; Zhou, M.; Liu, Y.; Song, N.; Li, Y.; Umetsu, J.; Lu, Z.J. CLIPdb: A CLIP-seq database for protein-RNA interactions. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Yang, Y.-C.T.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, Z.J. POSTAR: A platform for exploring post-transcriptional regulation coordinated by RNA-binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D104–D114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, J.P.; Cruceanu, C.; Fiori, L.M.; Laboissiere, S.; Guillet, I.; Fontaine, J.; Ragoussis, J.; Benes, V.; Turecki, G.; Ernst, C. Biomarker discovery: Quantification of microRNAs and other small non-coding RNAs using next generation sequencing. BMC Med. Genom. 2015, 8, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-L. The biogenesis and emerging roles of circular RNAs. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memczak, S.; Jens, M.; Elefsinioti, A.; Torti, F.; Krueger, J.; Rybak, A.; Maier, L.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Gregersen, L.H.; Munschauer, M. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013, 495, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, J.; Russo, I.H. Techniques and Methodological Approaches in Breast Cancer Research; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Finka, A.; Goloubinoff, P. Proteomic data from human cell cultures refine mechanisms of chaperone-mediated protein homeostasis. Cell Stress Chaperones 2013, 18, 591–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzenbach, H.; Hoon, D.S.; Pantel, K. Cell-free nucleic acids as biomarkers in cancer patients. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleischhacker, M.; Schmidt, B. Circulating nucleic acids (CNAs) and cancer—A survey. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2007, 1775, 181–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caby, M.-P.; Lankar, D.; Vincendeau-Scherrer, C.; Raposo, G.; Bonnerot, C. Exosomal-like vesicles are present in human blood plasma. Int. Immunol. 2005, 17, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Di, C.; Kai, M.; Yang, Y.-C.T.; Li, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Hu, X.; Yip, K.Y.; Zhang, M.Q.; Lu, Z.J. A common set of distinct features that characterize noncoding RNAs across multiple species. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.; Xu, Z.; Hu, B.; Lu, Z.J. COME: A robust coding potential calculation tool for lncRNA identification and characterization based on multiple features. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, Y.-C.T.; Yuan, J.; Lu, Z.J.; Li, J.J. Large-scale mapping of mammalian transcriptomes identifies conserved genes associated with different cell states. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 1657–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Ledesma, E.; Verhaak, R.G.; Treviño, V. Identification of a multi-cancer gene expression biomarker for cancer clinical outcomes using a network-based algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 2012, 490, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Cuzick, J.; Swanson, G.P.; Fisher, G.; Brothman, A.R.; Berney, D.M.; Reid, J.E.; Mesher, D.; Speights, V.; Stankiewicz, E.; Foster, C.S. Prognostic value of an RNA expression signature derived from cell cycle proliferation genes in patients with prostate cancer: A retrospective study. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glavac, D.; Hrasovec, S. MicroRNAs as novel biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 180. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Getz, G.; Miska, E.A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Lamb, J.; Peck, D.; Sweet-Cordero, A.; Ebert, B.L.; Mak, R.H.; Ferrando, A.A. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005, 435, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, J.-H.; Voortman, J.; Giovannetti, E.; Steinberg, S.M.; Leon, L.G.; Kim, Y.-T.; Funel, N.; Park, J.K.; Kim, M.A.; Kang, G.H. Identification of microRNA-21 as a biomarker for chemoresistance and clinical outcome following adjuvant therapy in resectable pancreatic cancer. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, W.; Gao, W.; Feng, J. Long noncoding RNA HULC is a novel biomarker of poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajjari, M.; Salavaty, A. HOTAIR: An oncogenic long non-coding RNA in different cancers. Cancer Biol. Med. 2015, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cordeiro, A.; Navarro, A.; Gaya, A.; Díaz-Beyá, M.; Gonzalez-Farré, B.; Castellano, J.J.; Fuster, D.; Martínez, C.; Martínez, A.; Monzó, M. PiwiRNA-651 as marker of treatment response and survival in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 46002–46013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Yu, L.; Mei, Y.; Guarnera, M.; Shen, J.; Li, R.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, F. Small nucleolar RNA signatures as biomarkers for non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Chen, S.; Chen, H.; Mo, X.; Li, T.; Shao, Y.; Xiao, B.; Guo, J. Using circular RNA as a novel type of biomarker in the screening of gastric cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 444, 132–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Y.; Clark, D.; Mao, L. Novel dimensions of piRNAs in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013, 336, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepanov, G.A.; Filippova, J.A.; Komissarov, A.B.; Kuligina, E.V.; Richter, V.A.; Semenov, D.V. Regulatory role of small nucleolar RNAs in human diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 206849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishore, S.; Stamm, S. The snoRNA HBII-52 regulates alternative splicing of the serotonin receptor 2C. Science 2006, 311, 230–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ender, C.; Krek, A.; Friedländer, M.R.; Beitzinger, M.; Weinmann, L.; Chen, W.; Pfeffer, S.; Rajewsky, N.; Meister, G. A human snoRNA with microRNA-like functions. Mol. Cell 2008, 32, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, Y.; Liu, X.; Qu, S.; Song, E.; Zou, H.; Gong, C. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is an independent prognostic marker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression and survival. Cancer Sci. 2013, 104, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.A.; Shah, N.; Wang, K.C.; Kim, J.; Horlings, H.M.; Wong, D.J.; Tsai, M.-C.; Hung, T.; Argani, P.; Rinn, J.L. Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature 2010, 464, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, T.B.; Jensen, T.I.; Clausen, B.H.; Bramsen, J.B.; Finsen, B.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 2013, 495, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Ying, D.; Lau, Y.-L. In-depth cDNA library sequencing provides quantitative gene expression profiling in cancer biomarker discovery. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2009, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Wu, Y.N.; Xing, Y. SURVIV for survival analysis of mRNA isoform variation. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asmann, Y.W.; Necela, B.M.; Kalari, K.R.; Hossain, A.; Baker, T.R.; Carr, J.M.; Davis, C.; Getz, J.E.; Hostetter, G.; Li, X. Detection of redundant fusion transcripts as biomarkers or disease-specific therapeutic targets in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 1921–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attard, G.; Clark, J.; Ambroisine, L.; Fisher, G.; Kovacs, G.; Flohr, P.; Berney, D.; Foster, C.; Fletcher, A.; Gerald, W. Duplication of the fusion of TMPRSS2 to ERG sequences identifies fatal human prostate cancer. Oncogene 2008, 27, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, T.C.; Chang, T.T.; Young, K.C.; Lin, X.Z.; Lin, C.Y.; Wu, H.L. Detection of HCV RNA in saliva, urine, seminal fluid, and ascites. J. Med. Virol. 1992, 37, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wieczorek, A.J.; Rhyner, C.; Block, L.H. Isolation and characterization of an RNA-proteolipid complex associated with the malignant state in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 3455–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolodny, G. Evidence for transfer of macromolecular RNA between mammalian cells in culture. Exp. Cell Res. 1971, 65, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinger, M.E.; Mercer, T.R.; Mattick, J.S. RNAs as extracellular signaling molecules. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 40, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, N.B.; Ng, E.K.; Lo, Y.D. Stability of endogenous and added RNA in blood specimens, serum, and plasma. Clin. Chem. 2002, 48, 1647–1653. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Freedman, J.E.; Gerstein, M.; Mick, E.; Rozowsky, J.; Levy, D.; Kitchen, R.; Das, S.; Shah, R.; Danielson, K.; Beaulieu, L. Diverse human extracellular RNAs are widely detected in human plasma. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittelbrunn, M.; Gutiérrez-Vázquez, C.; Villarroya-Beltri, C.; González, S.; Sánchez-Cabo, F.; González, M.Á.; Bernad, A.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. Unidirectional transfer of microRNA-loaded exosomes from T cells to antigen-presenting cells. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halicka, H.D.; Bedner, E.; Darzynkiewicz, Z. Segregation of RNA and separate packaging of DNA and RNA in apoptotic bodies during apoptosis. Exp. Cell Res. 2000, 260, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaj, L.; Lessard, R.; Dai, L.; Cho, Y.-J.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Breakefield, X.O.; Skog, J. Tumour microvesicles contain retrotransposon elements and amplified oncogene sequences. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, S.J.; Raposo, G. As we wait: Coping with an imperfect nomenclature for extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2, 20389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaborowski, M.P.; Balaj, L.; Breakefield, X.O.; Lai, C.P. Extracellular vesicles: Composition, biological relevance, and methods of study. BioScience 2015, 65, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullock, M.D.; Silva, A.M.; Kanlikilicer-Unaldi, P.; Filant, J.; Rashed, M.H.; Sood, A.K.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Calin, G.A. Exosomal non-coding RNAs: Diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic applications in cancer. Non-Coding RNA 2015, 1, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathivanan, S.; Ji, H.; Simpson, R.J. Exosomes: Extracellular organelles important in intercellular communication. J. Proteom. 2010, 73, 1907–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzenbach, H.; Nishida, N.; Calin, G.A.; Pantel, K. Clinical relevance of circulating cell-free microRNAs in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 11, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, J.; Skog, J.; Nordstrand, A.; Baranov, V.; Mincheva-Nilsson, L.; Breakefield, X.; Widmark, A. Prostate cancer-derived urine exosomes: A novel approach to biomarkers for prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 1603–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogure, T.; Yan, I.K.; Lin, W.-L.; Patel, T. Extracellular Vesicle–Mediated Transfer of a Novel Long Noncoding RNA TUC339: A Mechanism of Intercellular Signaling in Human Hepatocellular Cancer. Genes Cancer 2013, 4, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogure, T.; Lin, W.L.; Yan, I.K.; Braconi, C.; Patel, T. Intercellular nanovesicle-mediated microRNA transfer: A mechanism of environmental modulation of hepatocellular cancer cell growth. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1237–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psaila, B.; Lyden, D. The metastatic niche: Adapting the foreign soil. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Huang, B.; Xu, X.; Zheng, J.; Cao, X. Tumor exosomal RNAs promote lung pre-metastatic niche formation by activating alveolar epithelial TLR3 to recruit neutrophils. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipazzi, P.; Bürdek, M.; Villa, A.; Rivoltini, L.; Huber, V. Recent advances on the role of tumor exosomes in immunosuppression and disease progression. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2012, 22, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quesenberry, P.J.; Aliotta, J.; Camussi, G.; Abdel-Mageed, A.B.; Wen, S.; Goldberg, L.; Zhang, H.-G.; Tetta, C.; Franklin, J.; Coffey, R.J. Potential functional applications of extracellular vesicles: A report by the NIH Common Fund Extracellular RNA Communication Consortium. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redzic, J.S.; Balaj, L.; van der Vos, K.E.; Breakefield, X.O. Extracellular RNA mediates and marks cancer progression. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2014, 28, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khvalevsky, E.Z.; Gabai, R.; Rachmut, I.H.; Horwitz, E.; Brunschwig, Z.; Orbach, A.; Shemi, A.; Golan, T.; Domb, A.J.; Yavin, E. Mutant KRAS is a druggable target for pancreatic cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20723–20728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozpolat, B.; Sood, A.K.; Lopez-Berestein, G. Liposomal siRNA nanocarriers for cancer therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2014, 66, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, M.; Jung, E.-J.; Shah, M.Y.; Lu, C.; Spizzo, R.; Shimizu, M.; Han, H.D.; Ivan, C.; Rossi, S.; Zhang, X. Therapeutic synergy between microRNA and siRNA in ovarian cancer treatment. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 1302–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, T.; Huang, X.; Woodcock, M.; Du, M.; Dittmar, R.; Wang, Y.; Tsai, S.; Kohli, M.; Boardman, L.; Patel, T. Plasma extracellular RNA profiles in healthy and cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinn, J.F.; Patel, T.; Wong, D.; Das, S.; Freedman, J.E.; Laurent, L.C.; Carter, B.S.; Hochberg, F.; Van Keuren-Jensen, K.; Huentelman, M. Extracellular RNAs: Development as biomarkers of human disease. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopreski, M.S.; Benko, F.A.; Gocke, C.D. Circulating RNA as a Tumor Marker. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 945, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- March-Villalba, J.A.; Martínez-Jabaloyas, J.M.; Herrero, M.J.; Santamaria, J.; Alino, S.F.; Dasí, F. Cell-free circulating plasma hTERT mRNA is a useful marker for prostate cancer diagnosis and is associated with poor prognosis tumor characteristics. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, P.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; O'Briant, K.C.; Allen, A. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussemakers, M.J.; van Bokhoven, A.; Verhaegh, G.W.; Smit, F.P.; Karthaus, H.F.; Schalken, J.A.; Debruyne, F.M.; Ru, N.; Isaacs, W.B. DD3: A New Prostate-specific Gene, Highly Overexpressed in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 5975–5979. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hessels, D.; Gunnewiek, J.M.K.; van Oort, I.; Karthaus, H.F.; van Leenders, G.J.; van Balken, B.; Kiemeney, L.A.; Witjes, J.A.; Schalken, J.A. DD3 PCA3-based molecular urine analysis for the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Eur. Urol. 2003, 44, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgos, K.L.; Javaherian, A.; Bomprezzi, R.; Ghaffari, L.; Rhodes, S.; Courtright, A.; Tembe, W.; Kim, S.; Metpally, R.; Van Keuren-Jensen, K. Identification of extracellular miRNA in human cerebrospinal fluid by next-generation sequencing. RNA 2013, 19, 712–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, H.; Deng, H.; Song, H.; Yu, X.; Xiao, B.; Wang, W.; Guo, J. Detection of circulating tumor cells in peripheral blood from patients with gastric cancer using piRNAs as markers. Clin. Biochem. 2011, 44, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; John, M.A.S.; Zhou, X.; Kim, Y.; Sinha, U.; Jordan, R.C.; Eisele, D.; Abemayor, E.; Elashoff, D.; Park, N.-H. Salivary transcriptome diagnostics for oral cancer detection. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 8442–8450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matse, J.H.; Yoshizawa, J.; Wang, X.; Elashoff, D.; Bolscher, J.G.; Veerman, E.C.; Bloemena, E.; Wong, D.T. Discovery and prevalidation of salivary extracellular microRNA biomarkers panel for the noninvasive detection of benign and malignant parotid gland tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 3032–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Huang, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, P.; Qin, Y.; Duan, Y.; Gong, B. Salivary microRNAs as promising biomarkers for detection of esophageal cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Yin, X.; Gong, B.; Nie, W.; Wu, B.; Zhang, X.; Huang, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Z. Salivary microRNAs show potential as a noninvasive biomarker for detecting resectable pancreatic cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2015, 8, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Park, J.W.; Guo, M.; Lin, G.; Crandall, L.; Compton, T.; Wang, X.; Li, X.J.; Chen, F.P.; Xu, R.H. Lack of ABCG2 expression and side population properties in human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 2435–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahn, J.H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, F.; Chan, T.-M.; Lin, X.; Kim, Y.; Wong, D.T.; Xiao, X. The landscape of microRNA, Piwi-interacting RNA, and circular RNA in human saliva. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleeker, F.E.; Molenaar, R.J.; Leenstra, S. Recent advances in the molecular understanding of glioblastoma. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2012, 108, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teplyuk, N.M.; Mollenhauer, B.; Gabriely, G.; Giese, A.; Kim, E.; Smolsky, M.; Kim, R.Y.; Saria, M.G.; Pastorino, S.; Kesari, S. MicroRNAs in cerebrospinal fluid identify glioblastoma and metastatic brain cancers and reflect disease activity. Neuro-Oncology 2012, 14, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akers, J.C.; Ramakrishnan, V.; Kim, R.; Skog, J.; Nakano, I.; Pingle, S.; Kalinina, J.; Hua, W.; Kesari, S.; Mao, Y. MiR-21 in the extracellular vesicles (EVs) of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): A platform for glioblastoma biomarker development. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadal, E.; Truini, A.; Nakata, A.; Lin, J.; Reddy, R.M.; Chang, A.C.; Ramnath, N.; Gotoh, N.; Beer, D.G.; Chen, G. A novel serum 4-microRNA signature for lung cancer detection. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, W.; Kim, J.; Kang, S.H.; Yang, S.R.; Cho, J.-Y.; Cho, H.C.; Shim, S.G.; Paik, Y.-H. Serum exosomal microRNAs as novel biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47, e184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baraniskin, A.; Nöpel-Dünnebacke, S.; Ahrens, M.; Jensen, S.G.; Zöllner, H.; Maghnouj, A.; Wos, A.; Mayerle, J.; Munding, J.; Kost, D. Circulating U2 small nuclear RNA fragments as a novel diagnostic biomarker for pancreatic and colorectal adenocarcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, E48–E57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhlmann, J.D.; Wimberger, P.; Wilsch, K.; Fluck, M.; Suter, L.; Brunner, G. Increased level of circulating U2 small nuclear RNA fragments indicates metastasis in melanoma patients. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2015, 53, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Bao, C.; Li, S.; Guo, W.; Zhao, J.; Chen, D.; Gu, J.; He, X.; Huang, S. Circular RNA is enriched and stable in exosomes: A promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witwer, K.W.; Buzas, E.I.; Bemis, L.T.; Bora, A.; Lässer, C.; Lötvall, J.; Nolte, E.N.; Piper, M.G.; Sivaraman, S.; Skog, J. Standardization of sample collection, isolation and analysis methods in extracellular vesicle research. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seashols-Williams, S.; Lewis, C.; Calloway, C.; Peace, N.; Harrison, A.; Hayes-Nash, C.; Fleming, S.; Wu, Q.; Zehner, Z.E. High-throughput miRNA sequencing and identification of biomarkers for forensically relevant biological fluids. Electrophoresis 2016, 37, 2780–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunwald, D. Flow cytometry and RNA studies. Biol. Cell 1993, 78, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, B. Dynamic Light Scattering, in Soft Matter Characterization; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 335–372. [Google Scholar]
- Jönsson, U.; Fägerstam, L.; Löfas, S.; Stenberg, E.; Karlsson, R.; Frostell, A.; Markey, F.; Schindler, F. Introducing a biosensor based technology for real-time biospecific interaction analysis. Ann. Biol. Clin. 1992, 51, 19–26. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Gerstein, M.; Snyder, M. RNA-Seq: A revolutionary tool for transcriptomics. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapnell, C.; Roberts, A.; Goff, L.; Pertea, G.; Kim, D.; Kelley, D.R.; Pimentel, H.; Salzberg, S.L.; Rinn, J.L.; Pachter, L. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 562–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Witten, D.M.; Johnstone, I.M.; Tibshirani, R. Normalization, testing, and false discovery rate estimation for RNA-sequencing data. Biostatistics 2012, 13, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poos, K.; Smida, J.; Nathrath, M.; Maugg, D.; Baumhoer, D.; Neumann, A.; Korsching, E. Structuring osteosarcoma knowledge: An osteosarcoma-gene association database based on literature mining and manual annotation. Database 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, R.; Kumar, B.; Jayadev, M.; Raghav, D.; Singh, A. CoReCG: A comprehensive database of genes associated with colon-rectal cancer. Database 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dancik, G.M. An online tool for evaluating diagnostic and prognostic gene expression biomarkers in bladder cancer. BMC Urol. 2015, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, À.; Cases, M.; Queralt-Rosinach, N.; Sanz, F.; Furlong, L.I. A knowledge-driven approach to extract disease-related biomarkers from the literature. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 253128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonov, A.; Knight, R.; Melino, G.; Barlev, N.; Tsvetkov, P. MIRUMIR: An online tool to test microRNAs as biomarkers to predict survival in cancer using multiple clinical data sets. Cell Death Differ. 2013, 20, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hart, A.F.; Tran, J.J.; Crichton, D.J.; Anton, K.; Kincaid, H.; Kelly, S.C.; Hughes, J.S.; Mattmann, C. An Extensible Biomarker Curation Approach and Software Infrastructure for the Early Detection of Cancer. HEALTHINF 2009, 387–392. [Google Scholar]
- Ainsztein, A.M.; Brooks, P.J.; Dugan, V.G.; Ganguly, A.; Guo, M.; Howcroft, T.K.; Kelley, C.A.; Kuo, L.S.; Labosky, P.A.; Lenzi, R. The NIH Extracellular RNA Communication Consortium. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, F.; Di Bella, S.; Nigita, G.; Macca, V.; Lagana, A.; Giugno, R.; Pulvirenti, A.; Ferro, A. miRandola: Extracellular circulating microRNAs database. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Li, J.; Huang, B.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, X.-M.; Xu, Y.-M.; Huang, L.-F.; Wang, X.-Z. Exosomes: Novel biomarkers for clinical diagnosis. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 657086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathivanan, S.; Fahner, C.J.; Reid, G.E.; Simpson, R.J. ExoCarta 2012: Database of exosomal proteins, RNA and lipids. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1241–D1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institutes of Health. Available online: http://commonfund.nih.gov/Exrna (accessed on 17 February 2017).
- Shah, R.; Tanriverdi, K.; Levy, D.; Larson, M.; Gerstein, M.; Mick, E.; Rozowsky, J.; Kitchen, R.; Murthy, V.; Mikalev, E. Discordant Expression of Circulating microRNA from Cellular and Extracellular Sources. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).