Interrupter Technique Revisited: Building an Experimental Mechanical Ventilator to Assess Respiratory Mechanics in Large Animals
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Techniques for Assessment of Respiratory Mechanics in Large Animals
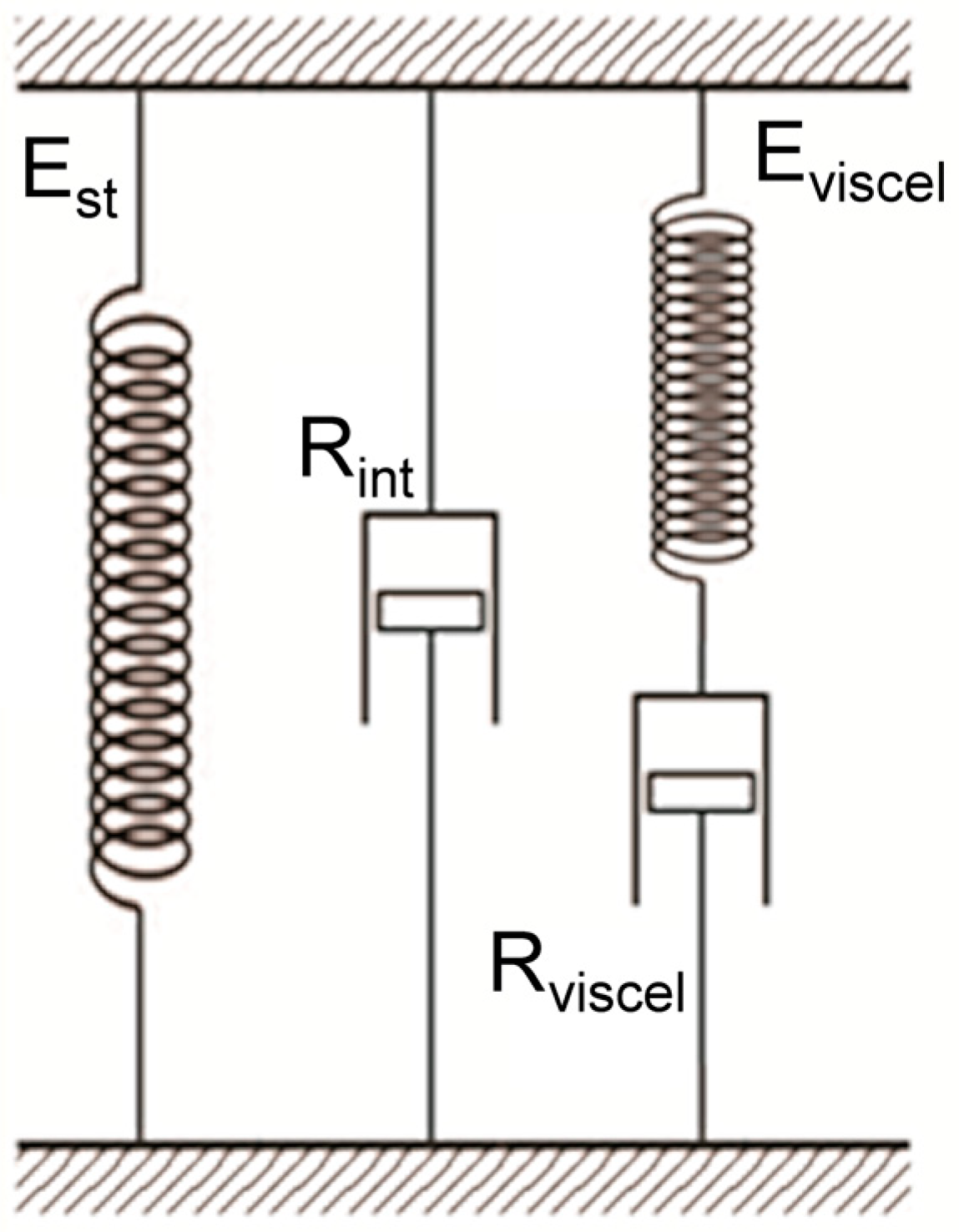
1.2. Measurements Implementation in the Laboratory Setting
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Ventilator
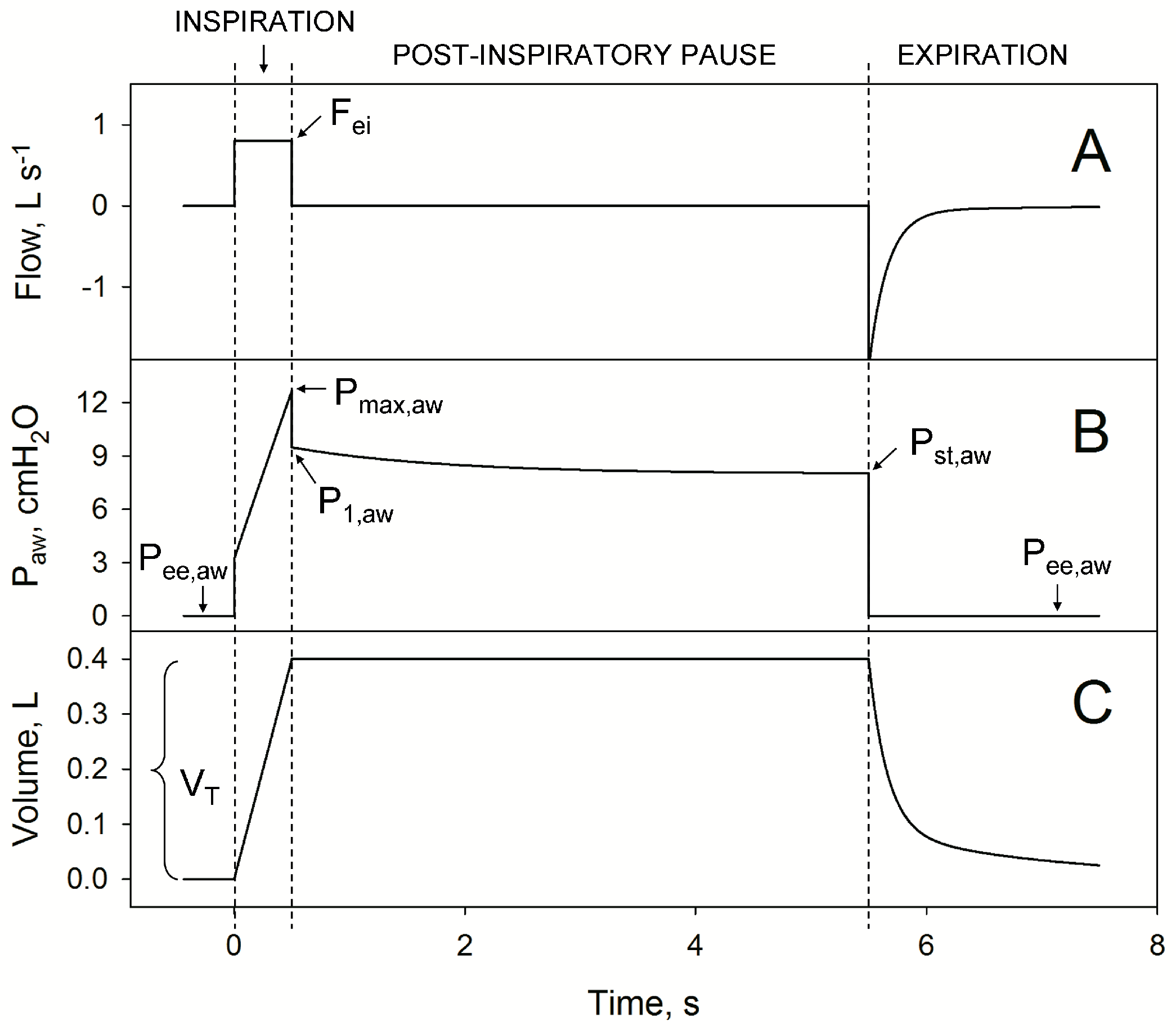
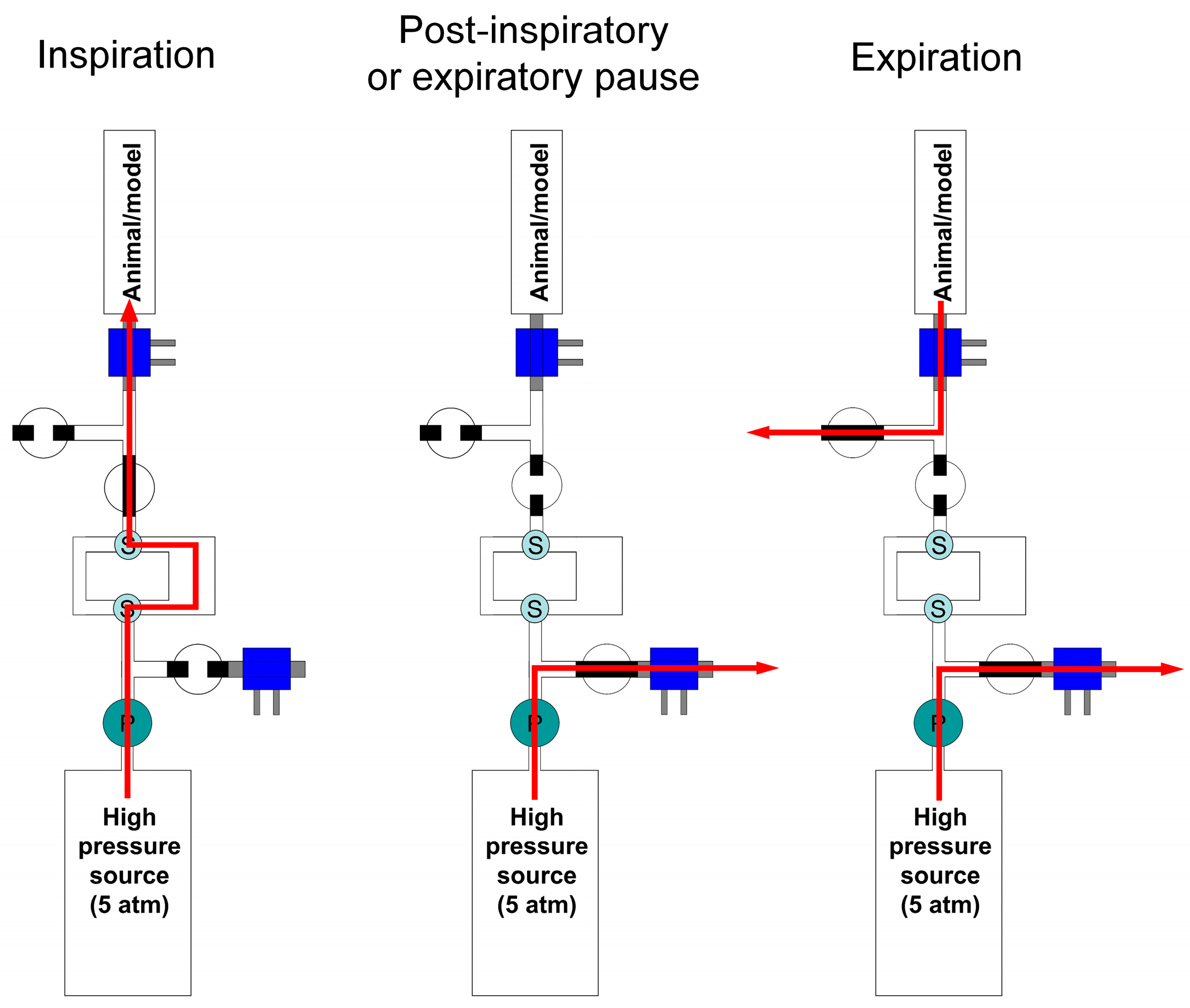
2.1.1. Principle of Operation
2.1.2. Hardware
2.1.3. Production of the Breathing Pattern
2.1.4. Software
2.2. Data Acquisition
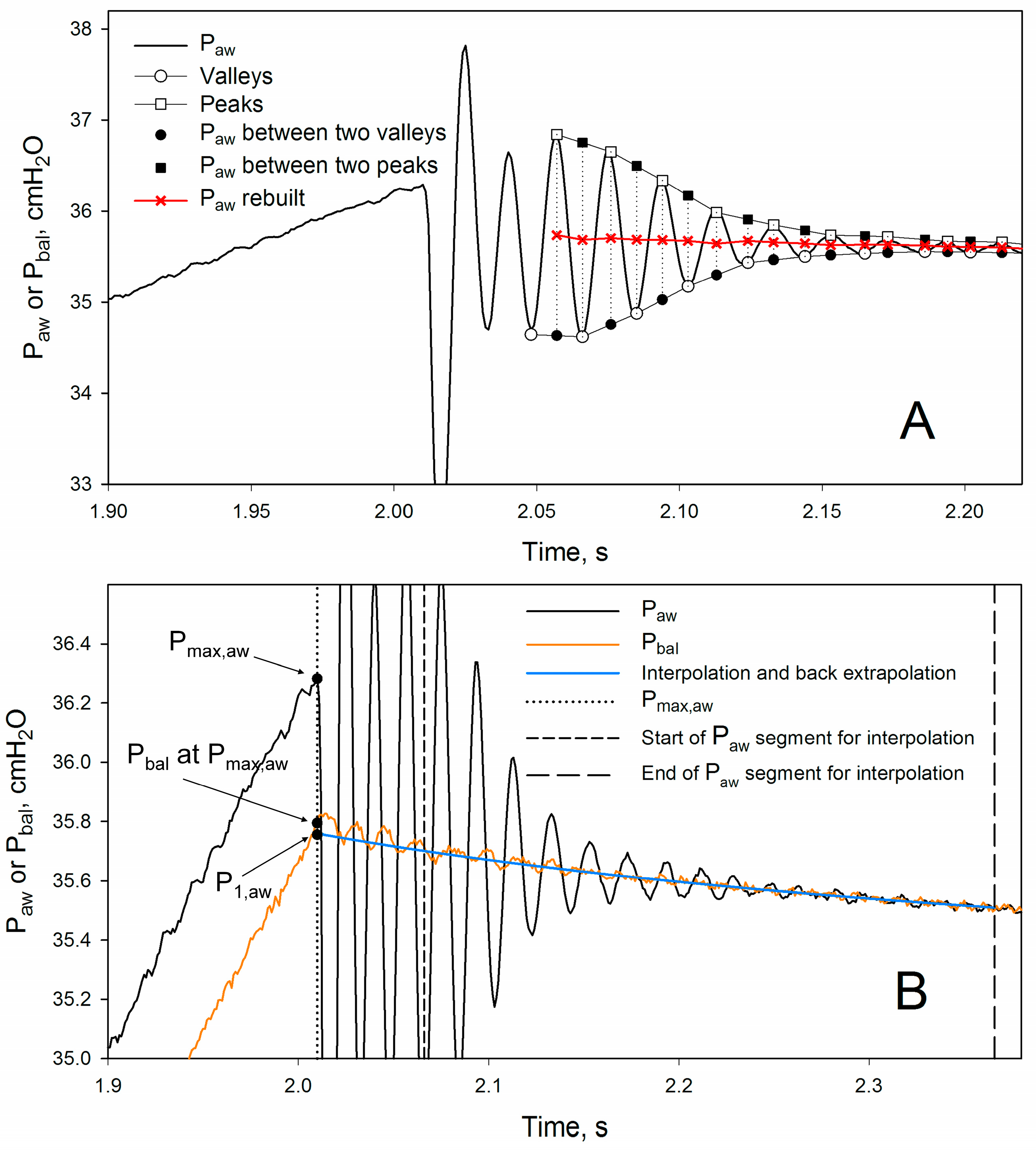
2.3. Validation Procedure
2.4. Statistical Methods
3. Results
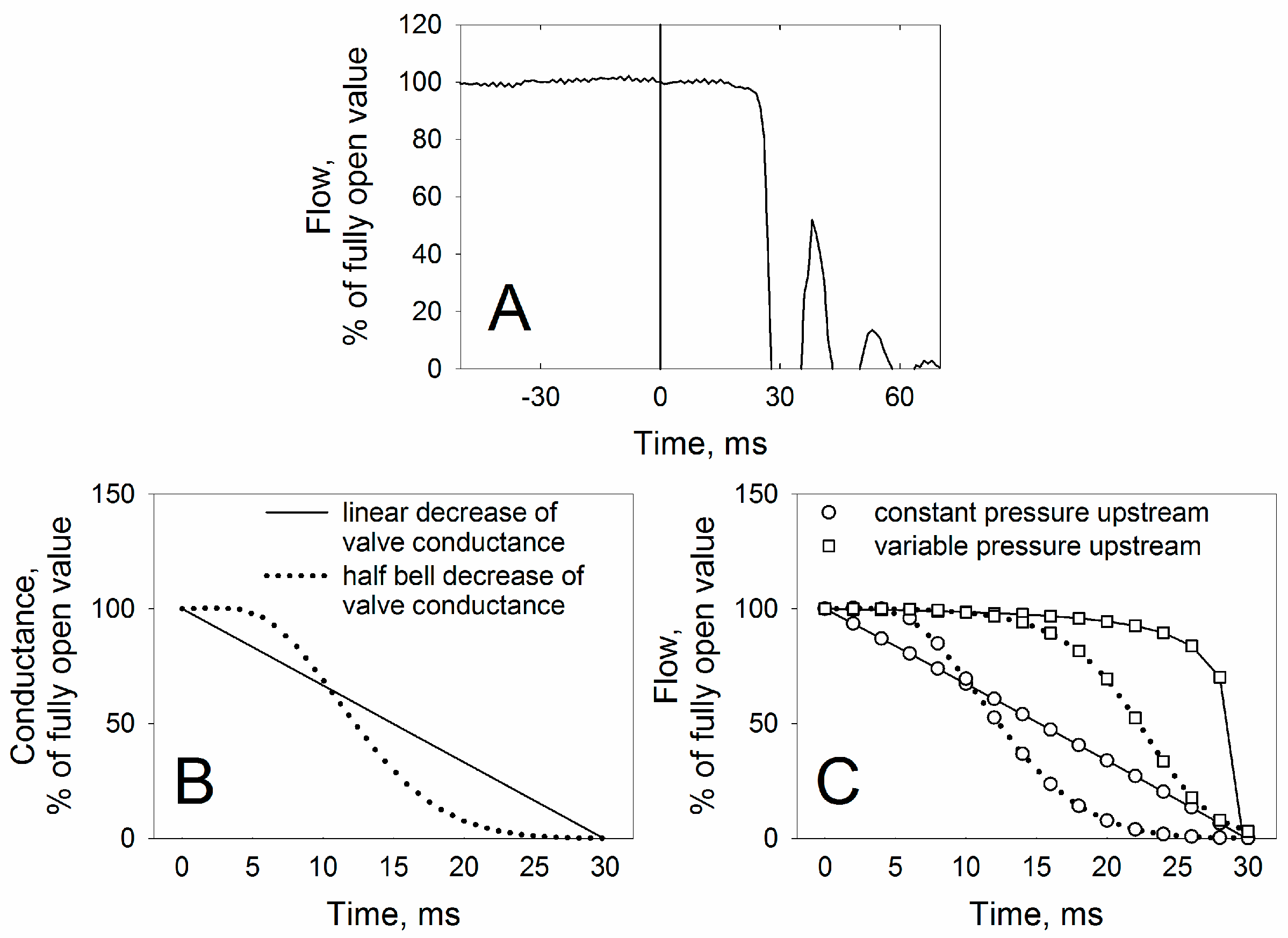
3.1. Technical Characteristics
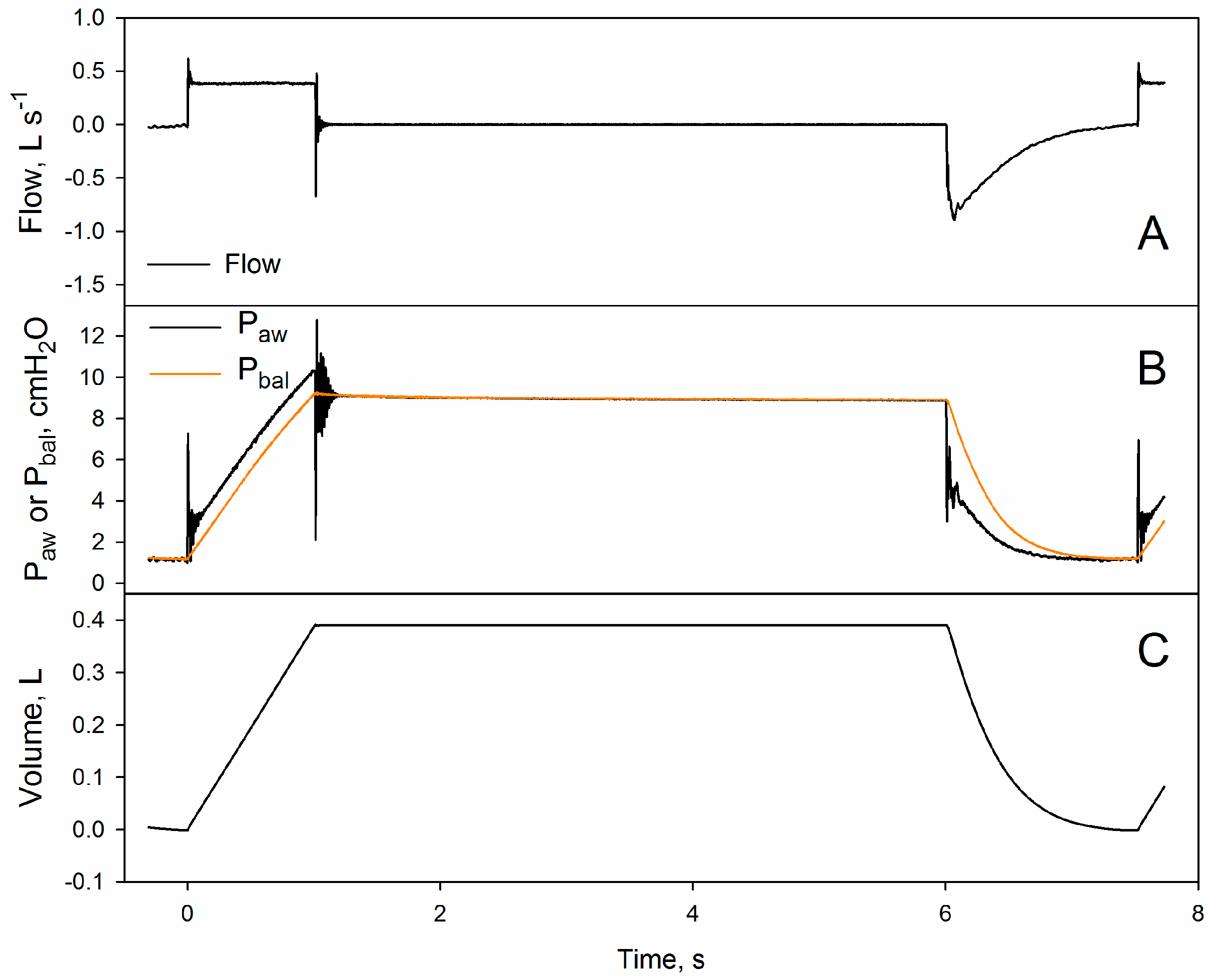
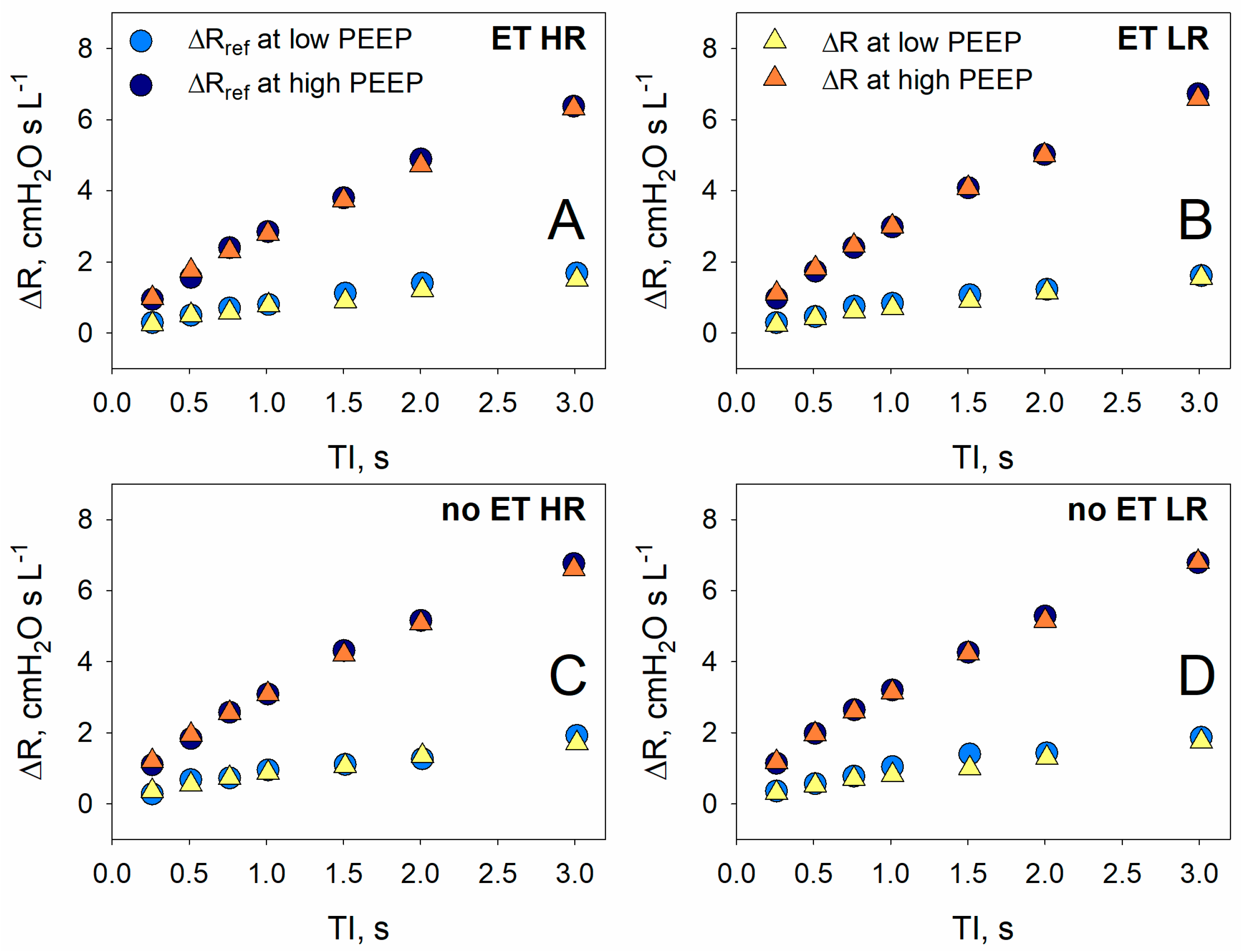
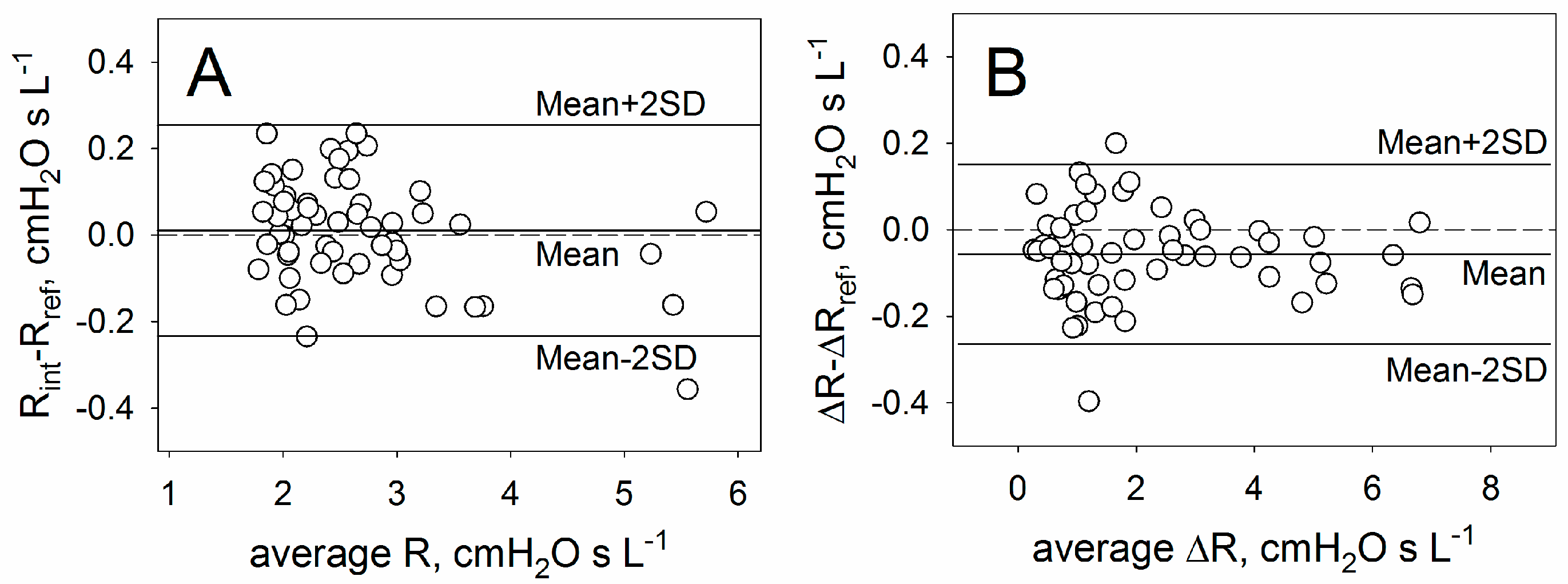
3.2. Validation
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Meeusen, E.N.; Snibson, K.J.; Hirst, S.J.; Bischof, R.J. Sheep as a Model Species for the Study and Treatment of Human Asthma and Other Respiratory Diseases. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Model. 2009, 6, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyfuss, D.; Saumon, G. Ventilator-Induced Lung Injury. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1998, 157, 294–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snider, G.L.; Lucey, E.C.; Stone, P.J. Animal Models of Emphysema 1–3. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1986, 133, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wald, A.; Jason, D.; Murphy, T.W.; Mazzia, V.D.B. A Computers System for Respiratory Parameters. Comput. Biomed. Res. 1969, 2, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhl, R.R.; Lewis, F.J. Digital Computer Calculation of Human Pulmonary Mechanics Using a Least Squares Fit Technique. Comput. Biomed. Res. 1974, 7, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegmaier, P.A.; Zollinger, A.; Brunner, J.X.; Pasch, T. Assessment of Pulmonary Mechanics in Mechanical Ventilation: Effects of Imprecise Breath Detection, Phase Shift and Noise. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 1998, 14, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, J.H.T.; Irvin, C.G.; Farré, R.; Hantos, Z. Oscillation Mechanics of the Respiratory System. Compr. Physiol. 2011, 1233–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuessler, T.F.; Bates, J.H.T. A Computer-Controlled Research Ventilator for Small Animals: Design and Evaluation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1995, 42, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, R.S. Pressure-Volume Curves of the Respiratory System. Respir. Care 2005, 50, 78–98; discussion 98–99. [Google Scholar]
- Milic-Emili, J.; Robatto, F.M.; Bates, J.H.T. Respiratory Mechanics in Anaesthesia. Br. J. Anaesth. 1990, 65, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, J.H.; Ludwig, M.S.; Sly, P.D.; Brown, K.; Martin, J.G.; Fredberg, J.J. Interrupter Resistance Elucidated by Alveolar Pressure Measurement in Open-Chest Normal Dogs. J. Appl. Physiol. 1988, 65, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, E.; Prandi, E.; Tavola, M.; Calderini, E.; Milic-Emili, J. Chest Wall Interrupter Resistance in Anesthetized Paralyzed Humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 1994, 77, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnas, G.M.; Yoshino, K.; Loring, S.H.; Mead, J. Impedance and Relative Displacements of Relaxed Chest Wall up to 4 Hz. J. Appl. Physiol. 1987, 62, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otis, A.B.; McKerrow, C.B.; Bartlett, R.A.; Mead, J.; McIlroy, M.B.; Selverstone, N.J.; Radford, E.P. Mechanical Factors in Distribution of Pulmonary Ventilation. J. Appl. Physiol. 1956, 8, 427–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecchiari, M.; Radovanovic, D.; Zilianti, C.; Saderi, L.; Sotgiu, G.; D’Angelo, E.; Santus, P. Tidal Expiratory Flow Limitation Induces Expiratory Looping of the Alveolar Pressure-Flow Relation in COPD Patients. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 129, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilianti, C.; Santus, P.; Pecchiari, M.; D’Angelo, E.; Radovanovic, D. Diagnostic Insights from Plethysmographic Alveolar Pressure Assessed during Spontaneous Breathing in COPD Patients. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutsoukou, A.; Bekos, B.; Sotiropoulou, C.; Koulouris, N.G.; Roussos, C.; Milic-Emili, J. Effects of Positive End-Expiratory Pressure on Gas Exchange and Expiratory Flow Limitation in Adult Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 30, 1941–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armaganidis, A.; Stavrakaki-Kallergi, K.; Koutsoukou, A.; Lymberis, A.; Milic-Emili, J.; Roussos, C. Intrinsic Positive End-Expiratory Pressure in Mechanically Ventilated Patients with and without Tidal Expiratory Flow Limitation. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 28, 3837–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laghi, F.; Goyal, A. Auto-PEEP in Respiratory Failure. Minerva Anestesiol. 2012, 78, 201–221. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, A.; Gottfried, S.B.; Zocchi, L.; Higgs, B.D.; Lennox, S.; Calverley, P.M.; Begin, P.; Grassino, A.; Milic-Emili, J. Measurement of Static Compliance of the Total Respiratory System in Patients with Acute Respiratory Failure during Mechanical Ventilation. The Effect of Intrinsic Positive End-Expiratory Pressure. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1985, 131, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briscoe, W.A.; Dubois, A.B. The Relationship Between Airway Resistance, Airway Conductance and Lung Volume in Subjects of Different Age and Body Size. J. Clin. Investig. 1958, 37, 1279–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mount, L.E. The Ventilation Flow-Resistance and Compliance of Rat Lungs. J. Physiol. 1955, 127, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanborn, W.G. Monitoring Respiratory Mechanics during Mechanical Ventilation: Where Do the Signals Come From? Respir. Care 2005, 50, 28–52; discussion 52–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- D’Angelo, E.; Robatto, F.M.; Calderini, E.; Tavola, M.; Bono, D.; Torri, G.; Milic-Emili, J. Pulmonary and Chest Wall Mechanics in Anesthetized Paralyzed Humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 1991, 70, 2602–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D′Angelo, E.; Calderini, E.; Tavola, M.; Bono, D.; Milic-Emili, J. Effect of PEEP on Respiratory Mechanics in Anesthetized Paralyzed Humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 1992, 73, 1736–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D′Angelo, E.; Tavola, M.; Milic-Emili, J. Volume and Time Dependence of Respiratory System Mechanics in Normal Anaesthetized Paralysed Humans. Eur. Respir. J. 2000, 16, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, J.R.; Hoorn, E.; Van Goudoever, J.; Versprille, A. A Computerized Respiratory System Including Test Functions of Lung and Circulation. J. Appl. Physiol. 1989, 67, 1687–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, M.; Slama, H. A Versatile Hydraulically Operated Respiratory Servo System for Ventilation and Lung Function Testing. J. Appl. Physiol. 1983, 55, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, V.; Mols, G.; Bernhard, H.; Haberthür, C.; Guttmann, J. Interrupter Airway and Tissue Resistance: Errors Caused by Valve Properties and Respiratory System Compliance. J. Appl. Physiol. 1999, 87, 1546–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, E.; Koutsoukou, A.; Della Valle, P.; Gentile, G.; Pecchiari, M. The Development of Various Forms of Lung Injury with Increasing Tidal Volume in Normal Rats. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2020, 274, 103369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecchiari, M.; Monaco, A.; Koutsoukou, A.; Valle, P.D.; Gentile, G.; D’Angelo, E. Effects of Various Modes of Mechanical Ventilation in Normal Rats. Anesthesiology 2014, 120, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Angelo, E.; Koulouris, N.G.N.G.; Della Valle, P.; Gentile, G.; Pecchiari, M. The Fall in Exhaled Nitric Oxide with Ventilation at Low Lung Volumes in Rabbits: An Index of Small Airway Injury. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2008, 160, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujino, Y.; Goddon, S.; Dolhnikoff, M.; Hess, D.; Amato, M.B.P.; Kacmarek, R.M. Repetitive High-Pressure Recruitment Maneuvers Required to Maximally Recruit Lung in a Sheep Model of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 29, 1579–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarrete-Calvo, R.; Parra, P.; Rodríguez-Gómez, I.M.; Morgaz, J.; Domínguez, J.M.; Gómez-Villamandos, R.J.; Quirós-Carmona, S.; Pineda, C.; del Mar Granados, M. Comparison of the Efficacy of Two Alveolar Recruitment Manoeuvres in Improving the Lung Mechanics and the Degree of Atelectasis in Anaesthetized Healthy Sheep. Res. Vet. Sci. 2022, 150, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zheng, R.; Zhuang, Z. Effect of Transpulmonary Pressure-Guided Positive End-Expiratory Pressure Titration on Lung Injury in Pigs with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2020, 34, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, F.; Pan, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Liu, S.; Guo, F.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y. Physiological Effects of Different Recruitment Maneuvers in a Pig Model of ARDS. BMC Anesthesiol. 2020, 20, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calzia, E.; Stahl, W.; Handschuh, T.; Marx, T.; Fröba, G.; Bäder, S.; Georgieff, M.; Radermacher, P. Respiratory Mechanics during Xenon Anesthesia in Pigs. Anesthesiology 1999, 91, 1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaño, J.; Giraldo, M.A.; Montoya, Y.; Montagut, Y.J.; Palacio, A.F.; Jiménez, L.D. Electropneumatic System for the Simulation of the Pulmonary Viscoelastic Effect in a Mechanical Ventilation Scenario. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, J.H.T.; Hunter, I.W.; Sly, P.D.; Okubo, S.; Filiatrault, S.; Milic-Emili, J. Effect of Valve Closure Time on the Determination of Respiratory Resistance by Flow Interruption. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 1987, 25, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, P.V.; Sato, J.; Shardonofsky, F.; Bates, J.H. High-Frequency Characteristics of Respiratory Mechanics Determined by Flow Interruption. J. Appl. Physiol. 1990, 69, 1682–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochi, T.; Okubo, S.; Zin, W.A.; Milic-Emili, J. Flow and Volume Dependence of Pulmonary Mechanics in Anesthetized Cats. J. Appl. Physiol. 1988, 64, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zilianti, C.; Bashar, E.; Kyriakoudi, A.; Pecchiari, M. Interrupter Technique Revisited: Building an Experimental Mechanical Ventilator to Assess Respiratory Mechanics in Large Animals. Fluids 2024, 9, 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids9060142
Zilianti C, Bashar E, Kyriakoudi A, Pecchiari M. Interrupter Technique Revisited: Building an Experimental Mechanical Ventilator to Assess Respiratory Mechanics in Large Animals. Fluids. 2024; 9(6):142. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids9060142
Chicago/Turabian StyleZilianti, Camilla, Erfan Bashar, Anna Kyriakoudi, and Matteo Pecchiari. 2024. "Interrupter Technique Revisited: Building an Experimental Mechanical Ventilator to Assess Respiratory Mechanics in Large Animals" Fluids 9, no. 6: 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids9060142
APA StyleZilianti, C., Bashar, E., Kyriakoudi, A., & Pecchiari, M. (2024). Interrupter Technique Revisited: Building an Experimental Mechanical Ventilator to Assess Respiratory Mechanics in Large Animals. Fluids, 9(6), 142. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids9060142




