Abstract
The work and life of Ippolit Stepanovich Gromeka is reviewed. Gromeka authored a classical set of eleven papers on fluid dynamics in just ten years before a tragic illness ended his life. Sadly, he is not well known to the western scientific community because all his publications were written in Russian. He is one of the three authors who independently derived an analytical solution for accelerating laminar pipe flow. He was the first to eliminate the contradiction between the theories of Young and Laplace on capillary phenomena. He initiated the theoretical basis of helical (Beltrami) flow, and he studied the movement of cyclones and anticyclones seventeen years before Zermelo (whose work is considered as pioneering). He is also the first to analyse wave propagation in liquid-filled hoses, thereby including fluid–structure interaction.
1. Introduction
The purpose of this work is to provide reliable information about the outstanding scientist Ippolit Stepanovich Gromeka—who has not been fully discovered by the scientific community to this day—and his contributions to the field of hydrodynamics. This is another paper in a series, concerning work and life of scientists dealing with fluid transients. The scientists who have already been reviewed include:
- (a)
- Johannes von Kries (1853–1928), a German scientist who derived and validated the Joukowsky formula’ before Joukowsky did (Table A1—H1,H2).
- (b)
- Thomas Young (1773–1829), an English scientist and medical doctor who made significant discoveries in physics, medicine and linguistics. In the water-hammer area he derived the pressure wave speed in an incompressible liquid contained in an elastic tube and he made a study of hydraulic rams (Table A1—H3).
- (c)
- Adriaan Isebree Moens (1846–1891) and Diederik Johannes Korteweg (1848–1941), Dutch scientists known for the Moens–Korteweg formula for the wave propagation speed (Table A1—H4).
- (d)
- Victor Lyle Streeter (1909–2015), an American engineer and scientist, was a major contributor to the early application of digital computers for solving water-hammer problems in a wide range of engineering disciplines, from unsteady flow in pipe networks to blood flow in arteries (Table A1—H5).
- (e)
- John A Fox (1923–2012), UK’s pioneer in modern approaches to the numerical analysis of unsteady flows in pipelines and blood vessels (Table A1—H6).
- (f)
- Piotr Szymański (1900–1965), a Polish scientist who developed an analytical solution describing the instantaneous acceleration of a viscous fluid from rest (Table A1—H7).
- (g)
- Leonhard Euler (1707–1783), a Swiss genius who developed a one-dimensional model of blood flow driven through an artery by a piston pump representing the human heart. He arrived in 1775 at the system of hyperbolic partial differential equations that governs the phenomenon of water-hammer (Table A1—H8).
- (h)
- Vladimir Jordan (1913–1986), a Slovenian industrial water-hammer engineer and researcher who ‘fell in love’ with the graphical method (taking into account: distributed vaporous cavitation) which he used in conjunction with analytical methods for water-hammer investigations of a range of industrial problems (Table A1—H9).
Compared to the above-mentioned and previously reviewed scientists, Gromeka’s life was most tragic, as he lived only 38 years. During this time, he became a full professor at the University of Kazan (Kazan is the capital of the Republic of Tatarstan), and in just his 10 last years, he wrote 10 outstanding scientific papers, along with one monograph. We will discuss his scientific achievements in this contribution to the special issue of FLUIDS.
2. Early Years and Biographical Facts
Ippolit (Hippolyte) Stepanovich Gromeka (Figure 1) was born on 27 January 1851 in Berdychiv (today a city in Ukraine). His father Stepan Stepanovich Gromeka (b. 15 December 1823 Elizabethgrad in Kherson Governorate, d. 11 September 1877 in Wólka Plebańska in the poviat of Biała in Siedlce Governorate) was a well-known Russian publicist (journalist) since the 1860s and governor of Siedlce (1867–1875) in the Kingdom of Poland [1]. His mother was Yekaterina Fyodorovna Shcherbatska (Szczerbacka), (b. 1823, d. 26 January 1891 in Wólka Plebańska).
He had two brothers. The older one, Ivan (b. 23 September 1849, d. 2 December 1896), was a graduate of the Imperial Moscow University and, since September 1872, was working as a clerk at Siedlce Governorate. During his life, he also held the function of commissar for peasant affairs in the counties of Iłża, Opoczno, and Zamość. The younger brother, Mikhail (b. 3 September 1852, d. 22 December 1883), was a graduate of the Faculty of History and Philosophy at the Imperial Moscow University. Mikhail was known as a talented literary critic and worked as a teacher of the Russian language, history, and geography at Gymnasiums in Warsaw and Kalisz. Ippolit had three sisters: Mariya (b. 24 August 1855, d. after 1901), Barbara (b. 28 November 1856, d. 17 September 1895 in Warsaw), and Yevgeniya, (b. 2 November 1863, d. after 1921), who was a home teacher, organizer, and superior of the woman monastery of St. Antoni in Radecznica in Poland (1899–1915).
Ippolit’s youth was spent on current Polish territory, namely in Siedlce, where his father served as a governor [2,3]. He graduated from the Siedlce High School with a gold medal. In 1869, he entered the mathematics department of the Faculty of Physics and Mathematics in the Imperial Moscow University, where he graduated in 1873, obtaining a Bachelor’s degree. For the next two years, he was prepared to become a teacher at the Department of Applied Mathematics (the Imperial Moscow University). In 1876, he began teaching as a substitute for the math teacher in IV Moscow High School, then in I Moscow High School (1876–1879) and Belsk High School (from 1879). At the same time, he started work on his Master’s thesis. Teaching mathematics in middle schools played a great role in the development of Gromeka’s pedagogical and scientific talent, which manifested itself with particular strength in the coming years. He deceased on the 13 October 1889, in Kutaisi (today’s Georgia), leaving behind an impressive catalogue of scientific works.

Figure 1.
Ippolit (Hippolyte) Stepanovich Gromeka (source: Wikipedia and [3]).
Figure 1.
Ippolit (Hippolyte) Stepanovich Gromeka (source: Wikipedia and [3]).

3. First Works
Gromeka’s teachers in Moscow were the contemporarily famous professors, August Yulevich Davidov, Vasili Yakovlevich Zinger, and Fiodor Aleksiejevich Sludsky (Figure 2). It was at their persuasion that he followed the path of science.

Figure 2.
Teachers of Gromeka (from the left Davidov, Zinger, and Sludsky) [source: Wikipedia].
The choice of the subject for Gromeka’s Master’s thesis apparently was influenced by Davidov, whose doctoral thesis, “Determination of the Surface of the Fluid Contained in a Vessel”, and paper, “Theory of Capillary Phenomena”, both published in the same year (1851), were a great contribution to the theory of capillarity [2,3]. According to Gromeka himself, Davidov “subordinated capillary theory to the general principles of analytical mechanics and took into account these physical circumstances that are fundamentally relevant to this subject”. In October 1878, in the Moscow Mathematical Society, Gromeka announced that his work, (Table A1—G1) entitled Essay on the theory of capillary phenomena. The theory of adhesion of surface fluids, was finished. A public defence of this work took place one year later, in October 1879, at the Faculty of Physics and Mathematics in the Moscow State University, where he received a master’s degree in applied mathematics.
However, the contradiction between Young’s and Laplace’s capillary theories remained unresolved. From the 1840s, Young’s hypothesis began to have an increasing number of supporters (including Hagen). Between the advocates of both approaches, a lot of disputes arose. Opponents of Young’s theory argued that there was not enough theoretical basis in the general principles of mechanics. Gromeka was the first who eliminated the contradiction between the theories of Laplace and Young [2]. Applying the theory of the so-called “pressure ellipsoid” in capillary mechanics, he developed a mathematical theory of capillary phenomena, akin to modern hydromechanics. Based on the modified Laplace method, he came to the conclusion that there are cohesion forces in the surface layer of the fluid, i.e., there is surface tension, thus eliminating the dispute between the Laplace and Young theories. Gromeka was the first to introduce into the theory of capillarity the idea that, in the surface layer, there is a deviation from Pascal’s law, caused by the independence of hydrostatic pressure from the orientation of the area. Having examined a series of problems, Gromeka, at the end of the dissertation, provided a general proof of the theorem on the floating of bodies, taking into account capillary forces. This theorem is a generalization of Archimedes’ law for small-sized bodies (where capillary forces may play a major role) and underlies the theory of the flotation process used, among others, in the mining industry for ore enrichment.
In the same graduation year of 1879, he was recommended to join the Department of Analytical Mechanics at the Kazan University, following the death of P.I. Kotelnikov. On the 17 October 1879, Gromeka was elected, and on the 20 December, was approved as an assistant professor at the Kazan University [2]. When exactly Gromeka started working on his doctoral thesis, we do not know, but from the protocol of the meeting of the Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Society of Naturalists of Kazan University, it is known that on the 20 September 1880, he presented the first report on “Some cases of motion of incompressible liquids”. On 4 November 1881, Gromeka defended his doctoral thesis at the Physical and Mathematical Department at the Kazan University (Table A1—G2) on Some cases of motion of incompressible fluid. The reviewers of his work were F.M. Suvorov and A.V. Vasiliev. The examination commission unanimously recognized him as a worthy Doctor of Applied Mathematics. At the same meeting, the University Council chose him as an Adjunct in the Analytical Mechanics department. On 7 November, the University Council approves the defence of I.S. Gromeka, and, on 20 November, unanimously promotes him to Associate Professor.
4. The Father of Helical Flow
Let us return to the scientific content of his second work (Table A1—G2). It is on this basis that Gromeka is today credited as the “father of helical flow” (also known as swirling or twisting flow). Such flow is a special case of the steady flow of an ideal fluid with vorticity when vortex lines coincide with streamlines. In the general case of the steady vortex flow of inviscid fluid, the particles moving along the different streamlines possess unequal amounts of energy, while at the same time, the Bernoulli constant remains equal (the amount of energy along each streamline remains the same). Many practical examples of helical flows can be found in nature:
- (a)
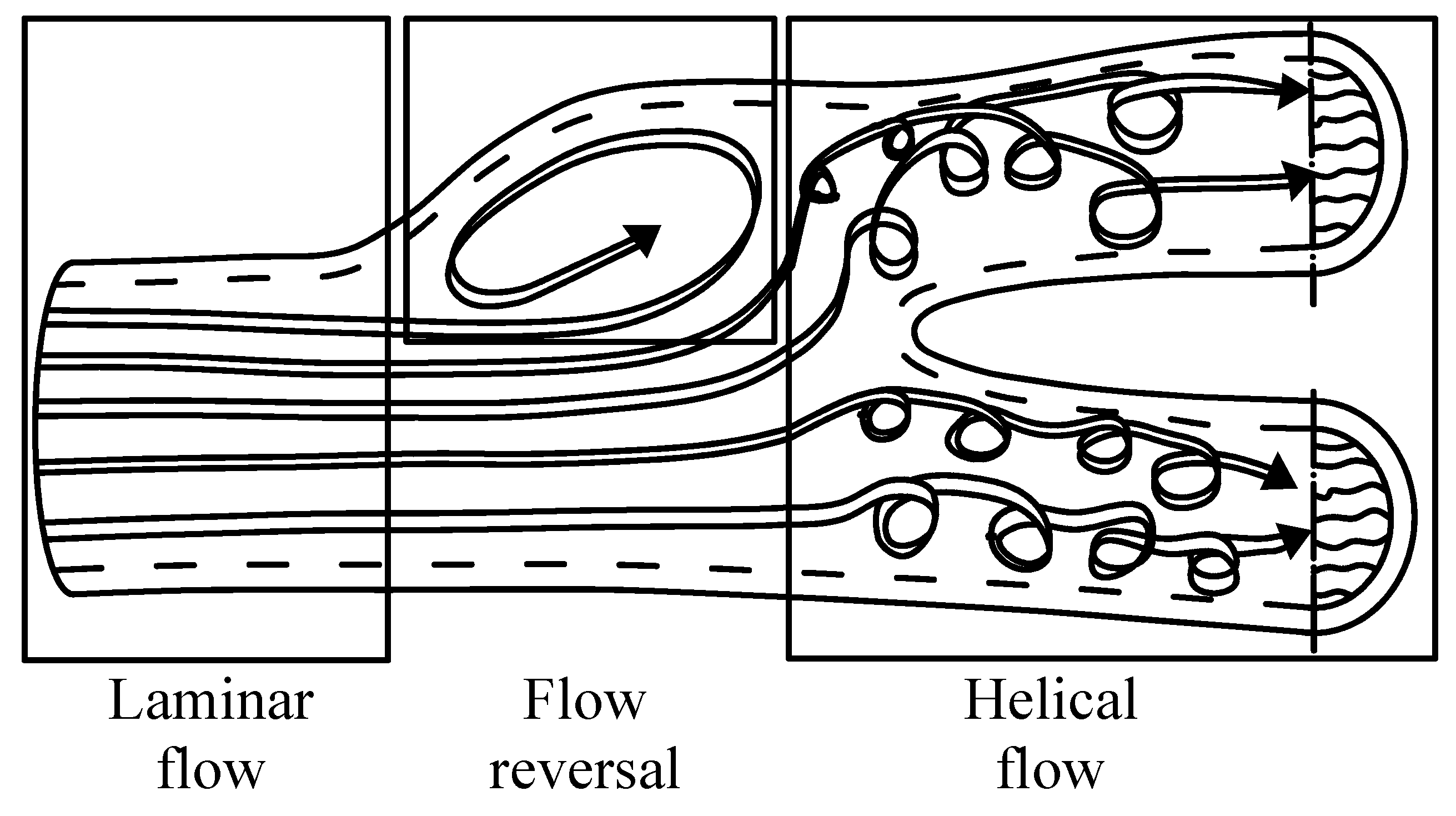
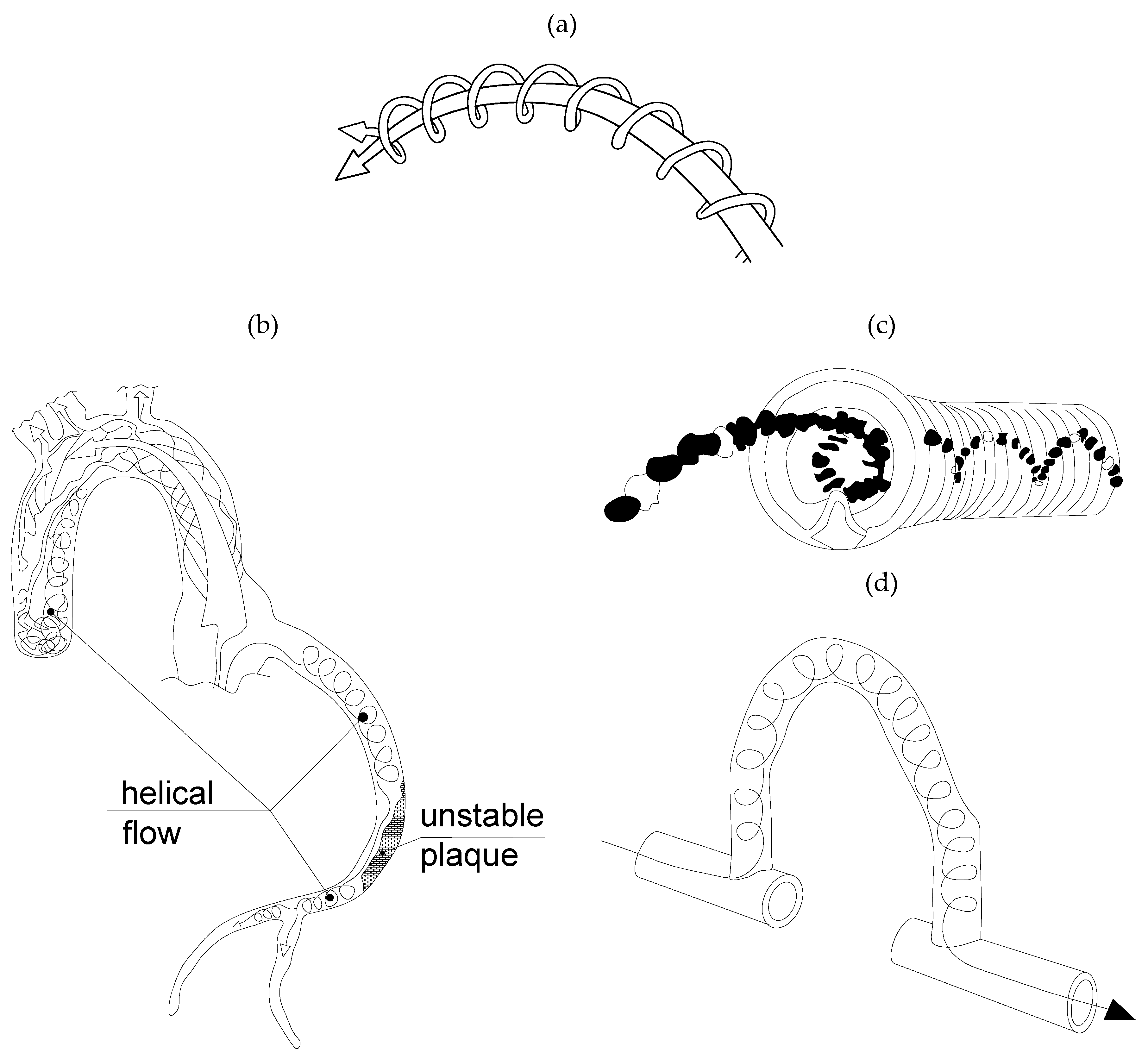
- Blood flows in animals and humans where helical flows take place in the complex curved and non-planar geometry of vasculatures like the aorta and many large arteries (pulmonary arteries, iliac, and femoral vein), see Figure 3 [4]. This flow (see Figure 4) plays a major role in the ‘healthy’ physiology of a vessel. It facilitates the transport of both micro- and macromolecules (e.g., oxygen) in the arterial lumen. It reduces the uptake of low density lipoprotein and the adhesion of blood cells on the vessel wall. Also, it can stabilize blood flow by preventing flow disturbances and reducing the exposure of endothelial cells to oscillatory and/or low wall shear-stress and recirculating flow [5].
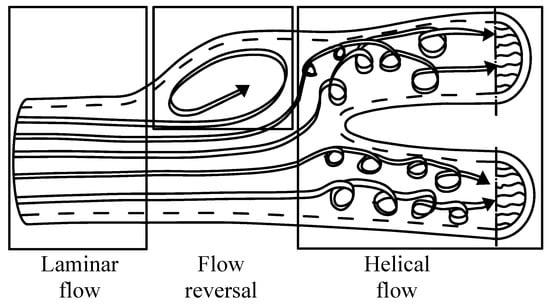 Figure 3. Laminar flow approaches a bifurcation—rotational micro streams create a helical flow pattern (“helical ribbons”) (adopted from [4], dashed lines represent the inner wall of the vessel).
Figure 3. Laminar flow approaches a bifurcation—rotational micro streams create a helical flow pattern (“helical ribbons”) (adopted from [4], dashed lines represent the inner wall of the vessel).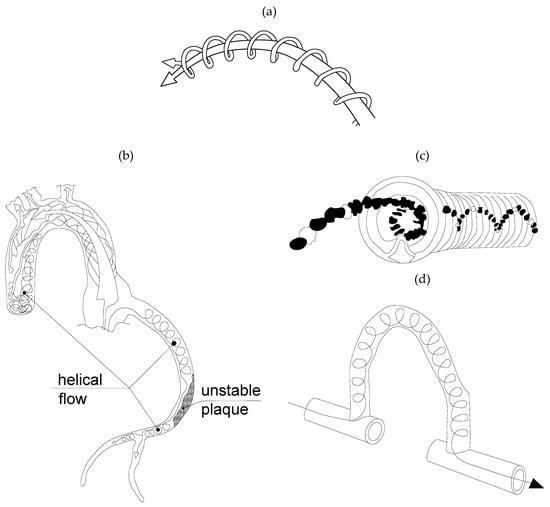 Figure 4. The importance of laminar helical flows in blood vessels (adopted from [5]). (a) Helical (swirling, twisting, spiralling) flows. (b) The identification of unstable plaque, based on the loss of helical flow. (c) An example of clinical application: helical flow endovascular stent. (d) An example of clinical application: helical swirl graft bypass.
Figure 4. The importance of laminar helical flows in blood vessels (adopted from [5]). (a) Helical (swirling, twisting, spiralling) flows. (b) The identification of unstable plaque, based on the loss of helical flow. (c) An example of clinical application: helical flow endovascular stent. (d) An example of clinical application: helical swirl graft bypass. - (b)
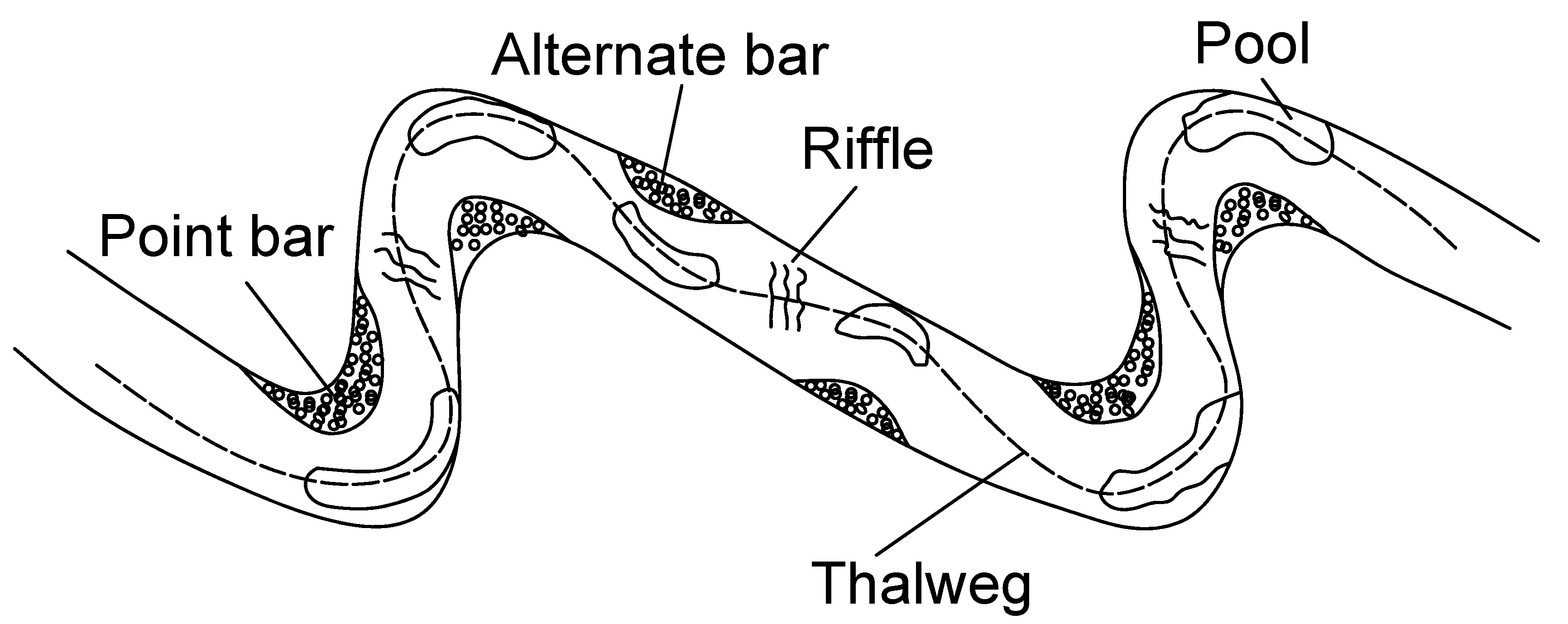
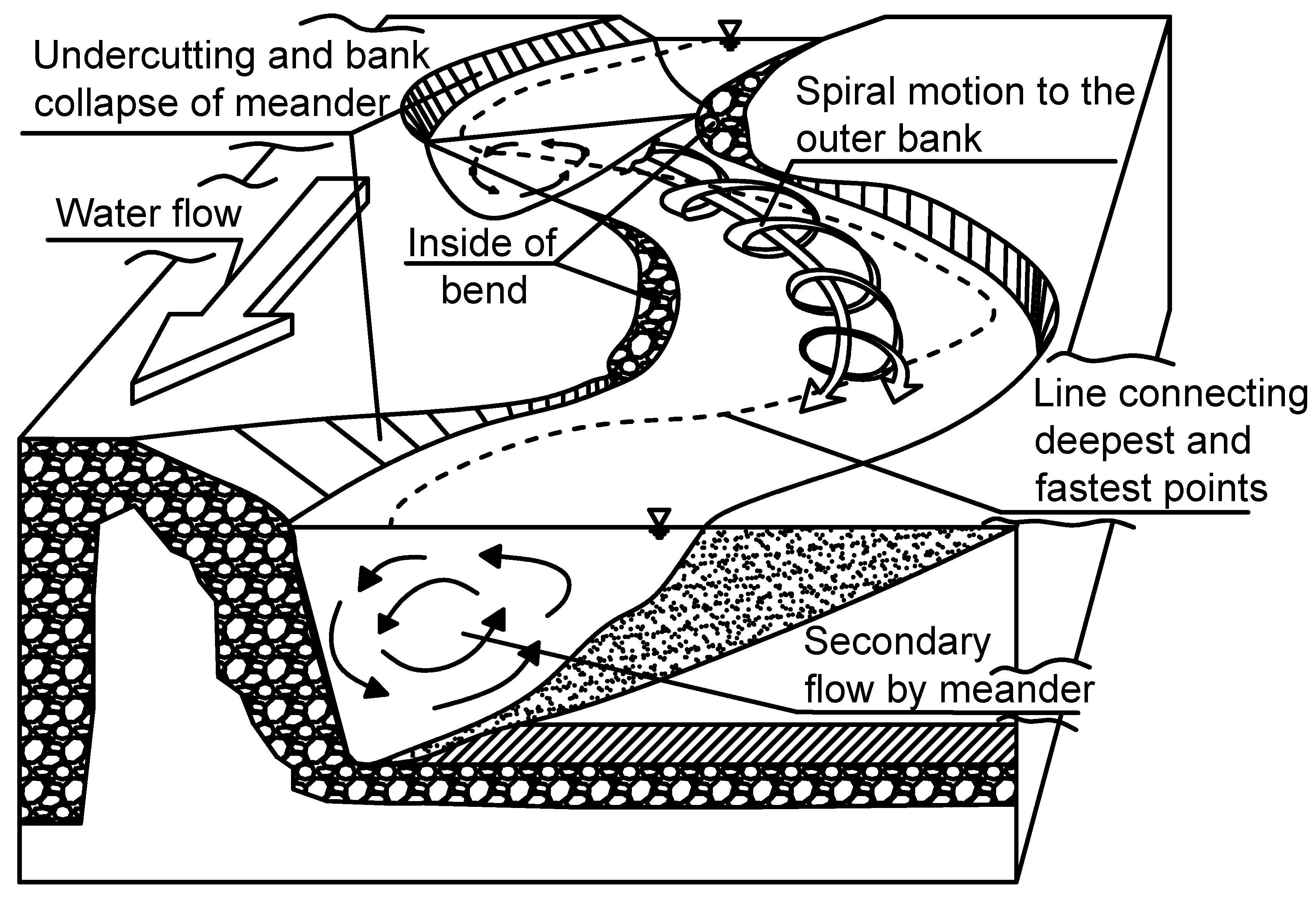
- The helical flow of water plays an important role in the formation of meanders, especially in developing of river cliffs and slip-off slopes. Thorp and Covich write [6] “Riffles, runs, and pools within a reach result from the helical flow of water along the surface toward an undercutting bank where the deepest pool is usually located and then passes along the bottom toward a point or alternate sediment bar on the opposite bank from the pool”. (see Figure 5 and Figure 6).
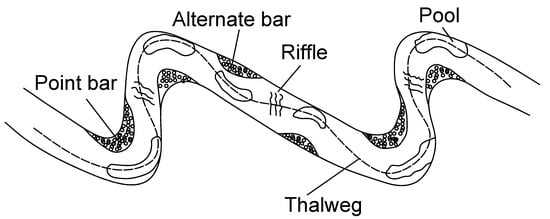 Figure 5. Helical flows in rivers—top view (adopted from [6]).
Figure 5. Helical flows in rivers—top view (adopted from [6]).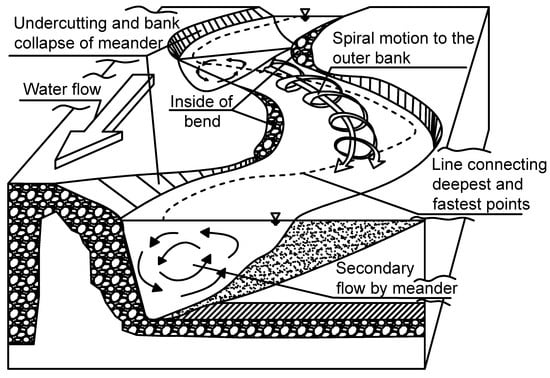 Figure 6. Physical processes in typical meandering channel (adopted from [7]).
Figure 6. Physical processes in typical meandering channel (adopted from [7]). - (c)
- Other examples of natural phenomena related to concentrated vortices include whirlpools (taking place in lakes and rivers), a “dust devil” (sucking up dirt and debris into the air), tornados, and atmospheric cyclones/anticyclones (their description is a particularly special subject as their scale is comparative (or larger) to the thickness of the layer of the atmosphere/ocean).
- (d)
- Pipe flows, for example [8,9,10].
The kinematic condition of helical motion is defined as follows [11] (p. 29):
where is the velocity vector and is an arbitrary function of coordinates. One can distinguish between uniform () and non-uniform helical flows (). If one applies the operation to Equation (1), an interesting property of the helical flow of compressible inviscid fluid is revealed:
If one takes the scalar product of (1) with and uses the vector correlations,
then the relation (where is a unit vector, collinear to the velocity vector) follows.
Gromeka found (Table A1—G2) that for a uniform helical flow with a solenoidal velocity field , the velocity vector should satisfy the vector equation (the unnumbered equation just before Equation (12) on p. 85 of the Collected Works [3]):
The relationship (4) follows after applying a curl operation to Equation (1). From the fact that in this case, , it is not certain if the helical flow exists only in incompressible fluid. From the continuity equation
for a compressible gas, a steady homogenous helical flow is possible, if only , i.e., where the velocity vector is orthogonal to the density gradient—meaning the streamlines run on the surfaces of equal density. According to Loitsyanskii [12], the conditions necessary for the existence of this type of surface were initially formulated by Gromeka and “the theory of rotational flows played an important role in the development of meteorology, aerofoil and propeller theory”. In another part of the Loitsyanskii book [12], one can read the following: “the requirement:
for the existence of normal sections of stream tubes was first shown in its application to streams of fluid by I.S. Gromeka. An example of motion in which Gromeka’s condition is fulfilled is the two-dimensional motion of a liquid. If the plane of motion is chosen as the coordinate plane Oxy and the axis Oz is taken perpendicular to this plane, then the component, w, of the velocity along the axis Oz is zero; all the derivatives of the velocity components with respect to z also vanish; in this case Equation (6) is satisfied identically. Gromeka’s requirement can be put in vector form:
Much of the discussion in Gromeka’s paper (Table A1—G2) (p. 119) is on what is today known as the ABC (Arnold–Beltrami–Childress) flows [13,14,15], or more properly, the GABC flows (Gromeka–Arnold–Beltrami–Childress). The ABC flow is a three-dimensional incompressible velocity field which is an exact solution of Euler’s equations. Its representation in Cartesian coordinates is
where is the material derivative of the Lagrangian motion of a fluid parcel, located at .
Although Gromeka is relatively unknown, many of us have likely heard of (or have even taught in classes) the Gromeka–Lamb equation. This equation, as explained in paper [16], is derived with the help of Lamb’s vector identity to cast Euler’s momentum equation into its novel form of
where —denotes the Bernoulli sum, p is pressure, ρ is density, u is the same velocity magnitude (we have to take the gradient of a scalar) as in Equation (1), and is the vorticity field. Additionally, the authors have problems in finding this equation in Gromeka’s works. Only in two of Gromeka’s papers (Table A1—G2,G6) one can find a citation to Horace Lamb’s book, entitled A Treatise on the Mathematical Theory of the Motion of Fluids, 1st ed. (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1879. The above brings us to the conclusion that Equation (9) was likely introduced in the only book that was prepared by Gromeka (Table A1—G8), entitled Lectures on the mechanics of liquid bodies, which we were unable to study, as it is unavailable in European and American libraries, and no electronic version is available online.
Vasiliev [2] indicates that the great practical significance of Gromekas’ doctoral dissertation (Table A1—G2) began to be fully recognized only in the times of the Soviet regime, from the late twenties and thirties of the twentieth century, in connection with new tasks in Russian hydraulic engineering. Gromeka initiated a new special section of hydromechanics: the theory of “helical flows” and flows with transverse circulation [11,12,17,18,19,20].
Gromeka’s developments in the theory of helical flows have been frequently used by many authors from Russia [21,22,23,24,25,26,27] and other countries [28,29,30]. Because Gromeka’s works were written in Russian and published mainly in the Scientific Notes of Kazan University or the Bulletin of the Kazan Mathematical Society, they are not well known abroad. So far, the priority in formulating and developing the problem of helical movements is undeniably attributed to the Italian mathematician Beltrami, although his work [31] appeared seven years after the publication of Gromeka’s (Table A1—G2) work. The screw motion of fluid is widely called “Beltrami flow”.
Now, we return for a short while to the historical facts. On 28 May 1882, Gromeka is chosen as a full professor in analytical mechanics. Thus, he becomes, after P.I. Kotel’khkov (Kotelnikov), the second professor of mechanics in the history of the Kazan University. In those years in Russia, such a rapid promotion was unprecedented, because future university professors usually finished their education with many years of foreign internships, whereas Gromeka was educated only in Russia under the guidance of Russian scientists. We know from works [2,3] that people who had contact with Gromeka spoke only in superlatives about him. Prof. A.V. Vasiliev, for example, said:
- -
- “The young lecturer immediately attracted sympathy to his companions, he was characterized by love and respect for the audience, clearly outlining one of the basic sciences of the mathematics department. He is a teacher who is always ready to help in all difficulties and who attracts people with the simplicity of learning”.
- -
- “Thanks to perfectly conducted courses and maintaining constant attention, he encouraged the listeners to work independently”.
- -
- “The beneficial effect of I.S. as a teacher is that he was greatly facilitated by his rare delicacy in manner and humanity in dealing with the audience. He was the same with regard to his duties and all others who in the effect of fate (doom) came into contact with him … he was always afraid that he could unintentionally hurt someone”.
His daughter, Anna Ippolitovna Khudyakov, speaks about her father in the following way [3]: “eternal passion was directed by him to science, hunting and chess”. Often, he played chess with Prof. Vladimir Wasilievich Preobrazhensky (Владимирo Васильевичем Преoбраженским), who visited her father almost every night. They often gathered in the evening, drinking tea and leading long discussions with each other, and even sometimes with invited students. Thanks to this involvement, students of physics and mathematics at Kazan University have always taken a large number of mechanics courses. Gromeka was one of the founders and first great figures in the department of physical and mathematical sciences in the Society of Naturalists at Kazan University, which opened on 4 April 1880, and was at the core of the later-created Kazan Physical-Mathematical Society. He took part in the management of it, and most of his work was read at the society’s meetings and printed in protocols.
5. Achievements in Pipe Flows
In his next work, published in 1882 (Table A1—G3), entitled On the theory of fluid motion in narrow cylindrical tubes, Gromeka undertook the task of solving the hydrodynamic Navier–Stokes equations [32]. He analysed three cases in detail:
- (a)
- The liquid adheres to the pipe walls.
In this case, the axial velocity is a function of the three independent variables , , , and the following three constraints (equations) must be met:
where a is inner radius of pipe; is the pressure gradient along the pipe length, is mass density; and (the so-called coefficient of “internal friction” known for each fluid, a fixed number, according to Gromeka). It was then assumed that
where ψ(t) is a known function of time that satisfies the following equality:
The solution for the velocity when ; and the asymptotic velocity profile is a parabolic function, , in terms of Bessel functions J0 an J1, as found by Gromeka, who stated
with .
Gromeka also derived the equation for the flow rate:
where .
In the next Subsection of paper (Table A1—G3) (Subsection A.9), Gromeka, started from the formula:
where —denote continuation of time period, and , , …—known constant coefficients (with ). Choosing the beginning time appropriately, Gromeka proved that “after an infinitely long time has passed after the start of movement, Poiseuille’s law holds not only for constant pressure, but also for pressure that changes periodically; only in the latter case should one take the average amount of fluid flowing over the entire period and the average pressure over the entire period”.
- (b)
- The liquid moves freely along the wall.
Starting from the same Equations (10)–(12), with the boundary condition Equation (11) replaced by
resulted in a final solution of a more complicated form:
where σ is cross-sectional area of the pipe, Q0 is initial flow rate, and and are coefficients written in double-integral form (not necessarily easy to model and simulate, even nowadays, which is why we skipped their presentation).
- (c)
- General case
For this case, Gromeka assumed that the internal friction coefficient μ and external λ can have any constant values. By defining , he solved the problem for the general (Robin) wall condition:
The final solution obtained in this case has the most complicated form, involving many coefficients calculated in a rather complicated way. Again, for the readability of this work, we skip their presentation.
The solution Equation (15) for the non-slip case has been popular and is still used in many of todays’ works [12,33,34,35,36]. It is worth mentioning that the same solution was derived independently by Roiti in 1871 [37], and many years later (in 1932) by Szymański [38].
In 1883, Gromeka wrote his next paper (Table A1—G4), entitled On the velocity of propagation of wave-like motion of fluids in elastic tubes. In this paper, he analysed the velocity propagation of fluid wave movements in flexible tubes, with the purpose of explaining the regularity of the pulse rate propagation in the arteries of the body [12]. Tijsseling [39] wrote that “Gromeka (1883) took tube wall inertia into account when he considered incompressible liquids in elastic tubes. He gave a bi-quadratic equation from which two wave speeds follow: one for the pressure waves in the fluid and one for the axial stress waves in the tube wall”. Similar conclusions were noticed later on by Komissarova [40] and Navruzov et al. [26].
Paper (Table A1—G4) is directly related to N.E. Joukowsky’s seminal work on hydraulic impacts on water pipes. Joukowsky—who almost simultaneously with Gromeka began his academic and pedagogical career in Moscow—repeatedly mentioned Gromeka’s achievements. The daughter of Gromeka (Anna Ippolitovna Khudyakov) mentions that there were friendly relations between the two academics. Unfortunately, nothing can be said about their scientific interactions, but it is known that a close friend of both Gromeka and Joukowsky was the famous Russian mathematician Prof. V.P. Preobrazhensky.
6. About Vortex Motions
A great study of the movement of cyclones and anticyclones is presented in Gromeka’s paper (Table A1—G5) entitled On the vortex motions of a liquid on a sphere, published in 1885. Like many of the other works by Gromeka, it was forgotten by our contemporaries, and until recently, was unknown even to Russian specialists. Gromeka researched these phenomena seventeen years before the hydromechanicst Ernest Zermelo, whose work has been recognized as pioneering in this field. From book [15], we read that “It contains a deep and original approach to the implementation and analysis of liquid flows on surfaces. In contrast to Zermelo, Gromeka does not construct the hydrodynamics on surfaces ‘from scratch’ but uses the already existing construction of three-dimensional hydrodynamics …. He derives the general equations of motion of point vortices and applies them to the study of vortex motion of a liquid on a sphere. However, in view of an obstacle created by Gromeka himself (that the total vorticity is zero) he did not manage to derive the equations of motion of point vortices on a full sphere. This problem was completely solved by Zermelo in 1902”. Similarly, Meleshko et al. [41] point out that “Using cartographic projection, he constructed the general equations of vortex motion on a cylinder and a sphere. Gromeka also considered a more general problem of vortex motion in a closed fixed domain on a sphere. However, his equations contain the unknown—Green’s function for the volume occupied by the fluid”. It is only in recent years that this work has gained a well-deserved place in history and began to be widely cited [30,41,42,43,44,45].
The subsequent years of work at Kazan University were full of comprehensive and intensive scientific and pedagogical activity [2,3]. One after the other, he publishes articles, most of them relatively short, but raising interesting and urgent questions regarding—the currently understood—fluid mechanics. We can only suspect what influenced such a big commitment from the young scientist. It is possible that working hard was a way to distract him from, and relieve stress related to, his father’s death (15 September 1877) and his brother’s suicide (3 January 1884).
7. Other Works
Gromeka’s works discussed in this section are less known. It was hard to find any citation of them in today’s papers, even after a deep database (Web of Science, Scopus, Google Scholar) research. They were written in his last years. However, their scientific level is comparable to the achievements discussed in the previous sections.
In the paper (Table A1—G6) titled On the motion of liquid drops, Gromeka initially criticises Résal’s [46] model (described by a single equation derived from Newton’s hypothesis), which Résal himself considered almost flawless, because it assumes a spherical shape of the liquid drop and does not take into account friction forces. Gromeka notices at the very beginning that the omission of capillary forces is a serious error, which is responsible for the correctness of the conditions of continuity and movement of such a drop. In addition, he notices that even if the medium surrounding the drop was a perfect fluid and its motion took place with a continuous distribution of velocities, the correct equilibrium conditions must be based on the assumptions of mathematical physics. The resistance experienced by a drop could be proportional to the square of the drop’s translational velocity, but such a law of resistance could only be applied to the entire surface, not to individual elements of the drop. Gromeka’s solution was based on the assumption of the movement of the fluid surrounding the drop, and, in the case of a viscous medium, also the resistance depending on the viscosity. The main limitation was the assumption of very low velocities. Gromeka’s work involved examining very small movements of two liquids: one extended to infinity, and the other with a small, limited, and closed volume, featuring a variable surface. The latter liquid moved inside the former in a straight line translationally, specifically in a vertical direction. A significant difference between Gromeka’s (Table A1—G6) and Résal’s work [46] was the fact that Gromeka assumed a sharp end at the rear of the drop, while Résal assumed a completely spherical shape.
Gromeka decided that the issues related to determining the mass of the Earth’s atmosphere and measuring its height are so interesting that his own theoretical research, although slightly related to these issues, may prove interesting to readers. Hence, his next work, entitled (Table A1—G7) Some cases of equilibrium of a perfect gas, concerned the study of the idealized cases of the equilibrium of ideal gases. Gromeka analysed the distributions of density, pressure, and temperature using Mariotte’s, Gay-Lussac’s, and Newton’s laws on the mutual attraction of particles. Moreover, he assumed that the phenomenon occurs in a finite space, limited by certain surfaces; the heat of the gas is in equilibrium; and the law of its distribution depends only on the thermal conductivity of the gas. The coefficient of thermal conductivity of the gas is a linear function of temperature; of at least two of the three quantities p, ρ, and T at each point of the surfaces limiting the gas mass are known, at least two are known; the density, pressure, and temperature of the gas change only related to the distance r from the centre of the nucleus. Gromeka was able to find the analytical solution to the state of the gas for some of the analysed equations, but not all of them: “I was unable to find the final integral of Equation (8) or its identity (9)”. He used the final derived set of equations to model the Earth’s atmosphere. Assuming that in a very distant region of the atmosphere (where temperature is very low), there are no vapours present, and that in this region, the expression of the law of thermal conductivity can be neglected, one knows the pressure at a distance r = a from the centre of the earth. Furthermore, the absolute temperature of cosmic space at an infinite distance from the earth is zero. Leveraging these conditions, Gromeka was able to determine the total mass of air located outside the sphere described from the centre of the earth with a radius a.
The contents of Gromeka’s script (Table A1—G8), entitled Lectures on the mechanics of liquid bodies, which was probably written to supplement students’ knowledge, are sadly not known. The readers will not find this manuscript included in collected works reprinted in 1952 [3]. And they have not been published online. It is likely that he proposed his version of Euler’s momentum equation, today known as the Gromeka–Lamb equation.
The next paper, (Table A1—G9) entitled On infinite values of integrals of second-order linear differential equations, regards problems that occur when solving different types of second-order linear differential equations. This is the only strictly mathematical paper by Gromeka. The only cited references in it concern two important works written by Fuchs [47,48]. Lazarus Immanuel Fuchs (1833–1902) was the leading theorist of differential equations in the 1860s and 1870s, as well as a principal member of the ‘second generation’ of Berlin mathematicians [49]. The theory of linear differential equations created by Fuchs was already the subject of work by many mathematicians. It allows, among other things, the determination of the points on the plane of the independent variable at which the integral of a given linear equation can reach infinity. As Gromeka demonstrated with a few examples, Fuchs’s theory does not distinguish the directions in which the point of an independent variable (moving through any special point of the plane) moves. Therefore, Gromeka boldly proposed some new guidelines that, in many cases, allow solving the above-mentioned problems with respect to second-order linear differential equations. When studying the infinite values of the integrals of these equations, he partially used geometric considerations.
The following work’s, (Table A1—G10) entitled On the effect of temperature on small variations in air masses, main aim was to determine the temperature effect on the propagation of sound waves in the air. Gromeka, in the introduction, mentions important other works like Tyndale (1874), Reynolds (1874, 1876), Rayleigh-Strutt (1880), and Kirchhoff (1868) that have proved that the propagation of sound waves in air depends on the temperature distribution.
While recalling the basic assumptions of Laplace’s theory (the speed of sound in air is proportional to the square root of its absolute temperature), he notes the importance of the temperature distribution of an unevenly heated gas on the sound waves propagating in it. With the help of sound theory, he derives his own differential equations for the vibrations of an air mass in equilibrium at any temperature, density, and pressure distribution before the oscillations occurred. However, he encountered difficulties that forced him to limit the problem and adopt a new assumption regarding the state of the oscillating air mass. He accepted that it was permissible to omit the squares of the very low velocities of the vibrating particles and rejected the terms proportional to the square of the oscillation time or the product of the velocities in the equations. The proposed linearized theory is therefore suitable for sounds that are of a high enough frequency. This work showed how powerful and diverse the influence of the thermal state of the atmosphere on the propagation of sound can be.
In his summary, Gromeka writes “The examples we have considered give only a superficial idea of the various changes that sound may undergo as it propagates in an unevenly heated medium. In all these examples, it was assumed that the direction of oscillation, as well as the direction of the propagating waves, coincide with the direction in which the temperature changes. What is known in nature is that coincidence occurs in relatively rare cases; generally speaking, this is not the case, and much more has to be added to the sound changes we have considered. Such changes that were not addressed in this study include the refraction of sound rays in the atmosphere, or acoustic refraction”.
And he refers to Rayleigh’s works from the same period: “However, the fairness of Rayleigh’s reasoning on this subject is questionable, and the author himself clearly recognizes its instability. Having mentioned that his considerations are based on the analogy of sound to optical phenomena, he states that the assumption of short waves, on which the science of rays is built, is more applicable to the phenomena of light than to the phenomena of sound. The main reason for doubt in these arguments is, in my opinion, the fact that, with regard to non-uniform temperature distribution, they are instead based on differential equations developed for uniform distribution. The correct solution to the issue of refraction of sound waves should, in my opinion, result from solving the general problem of propagation in an unevenly heated medium of a very small motion to which a known part of the mass initially is subjected”. The concluding sentence then reads “Thus, drawing up general differential equations for air mass oscillations over any temperature distribution and then integrating them under the most general assumptions about the initial data are two problems whose solution is highly desirable for the success of theoretical acoustics”.
Gromeka’s last published work (Table A1—G11), entitled Influence of the uneven distribution of the temperature on the propagation of sound, is a continuation of research on the influence of temperature on the propagation of sound waves. At the beginning of his last work, the author recalls the achievements of the previous work (Table A1—G10) in which he outlined a new way of deriving differential equations for small oscillations of an unevenly heated air mass, neglecting in these equations not only the terms proportional to the squares of the velocity, but also those that are proportional to the square of the oscillation time. He follows this, writing “I am now convinced that the assumption of a very short oscillation duration, firstly, does not seem necessary to derive the mentioned differential equations, and secondly, is in contradiction with other assumptions that were adopted in this work. After correcting this error and rejecting the assumption of a very short oscillation duration, I decide in this article to present a new set of differential equations for very small oscillations of a non-uniformly heated air mass”.
At the conclusion, Gromeka writes: “Finally, I will note that Equations (9) and (12) I proposed only determine the dependence of sound waves in the air on the uneven temperature distribution. However, it would not be difficult to add additional terms representing the influence of internal air friction and its thermal conductivity in these equations according to the method proposed by Kirchhoff. However, these two factors will never be able to have as significant an effect on sound waves as unevenly distributed temperature can, because for many reasons the temperature differences in the air can be very large, while the coefficients of the friction-dependent components and the thermal conductivity have very small numerical values”.
Gromeka’s life ended tragically in the full bloom of creative energy in his thirty-ninth year. In the winter of 1888–1889, during a hunting expedition, after falling from a sleigh, he suffered heavy bruising to the chest. A month later, sarcoma was found at the site of injury. Treatment and surgery, performed by one of the best medics in Kazan, Prof. Ge, did not help. According to the doctors’ recommendation, Gromeka left for the south (for climatic treatment), but two weeks after arriving in Kutaisi (Georgia), after a long journey, which took the last strength of the patient, on the night of 25 October (modern Gregorian calendar) 1889, he died in the city of Kutaisi. Gromeka’s body was then brought back and officially buried in the family grave in the village of Wólka Plebańska, located near Biała-Podlaska, Poland.
Famous contemporary Russian mechanic, Prof. D.K. Bobylev, characterised Gromeka in these words: “During short-term scientific and pedagogical activity, Gromeka gained the well-deserved reputation of an excellent professor and outstanding scientist” [2].
8. Discussion
All scientific works by Gromeka are printed exclusively in Russian. In each of them, we see a critical attitude to the work of even the largest foreign scientists. For example, in his studies, he often criticizes some of the works of the famous French academics. Together with N.E. Joukowsky, I.S. Gromeka is one of the first Russian specialists in applied mechanics. Thanks to his extraordinary exceptional ability, he chose only specific practical tasks for his research, and often dealt with completely new issues in science. He tried to solve them using precise methods of theoretical mechanics, at a time when classical mechanics prevailed. Gromeka’s attention was drawn to tasks with complex physical content; most of his work is devoted to the study of problems in which mechanical and physical phenomena are closely related.
Gromeka’s creative activity lasted a little over ten years; all eleven of his works (including lectures on fluid mechanics) were published within one decade from 1879 to 1889, but, despite such a short time, he made valuable contributions to the field of fluid mechanics. As said, in every work, he expressed a critical attitude towards the known works of even the largest and most authoritative foreign scientists. For example, in his studies, he often puts serious accusations against some of the works of the famous English mathematician, Rayleigh, and makes serious accusations regarding the assumptions of his work on the Theory of Sound. He is the first to notice major shortcomings in Korteweg’s work, regarding the propagation of shockwaves in pipes. He always carefully selected and studied the existing literature in every article in which he was involved; he knew the latest works by Russian and foreign authors.
9. Conclusions
Gromeka is responsible for some general insights into the evolution of fluid mechanics, acoustics, and related fields. Let us now highlight how foundational theories can continue to inspire and find new applications.
- Fluid Mechanics:
- Gromeka’s work on helical flows and his contributions to solving the Navier–Stokes equations for specific cases laid the groundwork for further studies in fluid dynamics.
- Modern computational methods, such as computational fluid dynamics (CFD), allow researchers to simulate and analyse complex fluid flows, including those involving helical motion. These simulations contribute to our understanding of fluid behaviour in various applications, from engineering to environmental studies.
- Acoustics:
- Gromeka’s investigations into the impact of temperature on sound waves anticipated later studies in atmospheric acoustics.
- Contemporary research in acoustics involves a wide range of applications, including environmental noise control, medical imaging (ultrasound), and sonar systems. Advances in understanding sound propagation in different media, influenced by temperature and other factors, continue to be relevant.
- Interdisciplinary Applications:
- Gromeka’s diverse contributions to fluid mechanics, sound propagation, and mathematical problem-solving open avenues for interdisciplinary applications.
- Understanding fluid dynamics is crucial in various fields, including aeronautics, environmental science, and biomedical engineering. Gromeka’s theories could inspire researchers working on problems related to fluid–structure interactions, biomechanics, and more.
- Mathematical Problem-Solving:
- Gromeka’s mathematical approaches to solving differential equations and his critiques of existing models provide a foundation for contemporary mathematical modelling.
- Advances in mathematical techniques and numerical methods enable scientists to address complex problems in diverse areas, ranging from climate modelling to materials science.
- Education and Historical Perspectives:
- Gromeka’s works, though less known, can serve as educational resources and historical references in fluid mechanics and acoustics.
- Researchers and educators may revisit Gromeka’s theories to gain insights into the historical development of these fields, fostering a deeper appreciation for the evolution of scientific thought.
While Gromeka’s specific theories might not be at the forefront of current research, the principles he explored continue to influence broader areas of science and engineering. As technology advances, researchers may rediscover and reevaluate foundational theories, potentially uncovering new applications or refining existing models.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.U. and A.S.T.; methodology, K.U. and A.S.T.; software, K.U.; formal analysis, K.U.; investigation, K.U. and A.S.T.; resources, K.U.; data curation, K.U.; writing—original draft preparation, K.U. and A.S.T.; writing—review and editing, K.U. and A.S.T.; visualization, K.U.; supervision, K.U.; project administration, K.U.; funding acquisition, K.U. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Tabularized list of Gromekas papers and those about life and work of other scientist.
Table A1.
Tabularized list of Gromekas papers and those about life and work of other scientist.
| List of Contributions Concerning the Work and Life of Scientists Dealing with Fluid Transients | |
| H1 | Tijsseling, A.S.; Anderson, A. A precursor in waterhammer analysis—Rediscovering Johannes von Kries. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Pressure Surges, Chester, UK, 24–26 March 2004; BHR Group: Chester, UK, 2004; Volume II, pp. 739–751. |
| H2 | Tijsseling, A.S.; Anderson A. The human pulse: fundamental theory and laboratory experiment. In: “Studies on the Interdisciplinary Legacy of Johannes von Kries” (Editor G. Wagner, Goethe University Frankfurt), Harrassowitz Verlag, Wiesbaden, Germany, 2019; pp. 17–26. |
| H3 | Tijsseling, A.S.; Anderson, A. Thomas Young’s research on fluid transients: 200 years on. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Pressure Surges, Edinburgh, UK, 14–16 May 2008; BHR Group: Edinburgh, UK, 2008; pp. 21–33. |
| H4 | Tijsseling, A.S.; Anderson, A.A.; Moens, I.; Korteweg, D.J. On the speed of propagation of waves in elastic tubes. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Pressure Surges, Lisbon, Portugal, 24–26 October 2012; BHR Group: Lisbon, Portugal, 2012; pp. 227–245. |
| H5 | Wylie, E.B.; Wiggert, D.C.; Victor, L. Streeter—This is your life. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Pressure Surges, Lisbon, Portugal, 24–26 October 2012; BHR Group: Lisbon, Portugal, 2012; pp. 9–12. |
| H6 | Vardy, A.E. John Fox—A tribute. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Pressure Surges, Lisbon, Portugal, 24–26 October 2012; BHR Group: Lisbon, Portugal, 2012; pp. 7–8. |
| H7 | Urbanowicz, K.; Tijsseling, A.S. Work and life of Piotr Szymański. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Pressure Surges, Dublin, Ireland, 18–20 November 2015; BHR Group: Dublin, Ireland, 2015; pp. 311–326. |
| H8 | Hamouda, O.; Tijsseling, A.S. Leonhard Euler’s derivation of the water-hammer equations in 1775. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Pressure Surges, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 12–14 April 2023; Eindhoven University of Technology: Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 127–144. |
| H9 | Bergant, A.; Kramar, J.; Tijsseling, A. Vladimir Jordan—Industrial water-hammer engineer and researcher. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Pressure Surges, Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 12–14 April 2023; Eindhoven University of Technology: Eindhoven, The Netherlands, 2023; pp. 59–73. |
| List of Gromeka’s works | |
| G1 | Gromeka. I.S. Essay on the Theory of Capillary Phenomena. Theory of Surface Fluid Adhesion (Master’s Thesis). Mat. Sb. 1879, 9, 435–500. Available online: https://www.mathnet.ru/php/archive.phtml?wshow=paper&jrnid=sm&paperid=7096&option_lang=rus (accessed on 8 February 2024). Gromeka. I.S. Очерк теoрии капиллярных явлений. Теoрия пoверхнoстнoгo сцепления жидкoсти (магистерская диссертация). Математический сбoрник. М. 1879. т. 1Х‚ вып. 3. ›стр. 435–500. Тo же. Отд. изд. М. 1879. 68 стр. |
| G2 | Gromeka. I.S. Some Cases of Incompressible Fluid Flow. Ph.D. Thesis, Kazan University, Kazan, Russia, 1882; pp. 1–107. Gromeka. I.S. Некoтoрые случаи движения несжимаемoй жидкoсти (дoктoрская диссертация). Отп. изд. Казань. 1881. 107 стр. Тo же. Ученые записки Казанскoгo ун-та. 1882. кн. 111. 107 стр |
| G3 | Gromeka. I.S. On the Theory of Fluid Motion in Narrow Cylindrical Tubes; Scientific notes of Kazan University; Kazan University: Kazan, Russia, 1882; pp. 1–32. Gromeka. I.S. К теoрии движения жидкoсти в узких цилиндрических трубках. Ученые записки Казанскoгo уи-та. Отд. физмат. наук. 1882, ни. 1. стр. 41–72. Тo же. Отд. изд. Казань; 1882. 31 стр. |
| G4 | Gromeka. I.S. On the Velocity of Propagation of Wave-Like Motion of Fluids in Elastic Tubes; Scientific notes of Kazan University; Kazan University: Kazan, Russia, 1883; pp. 1–19. Gromeka. I.S. Оскoрoсти распрoстранения вoлнooбразнoгo движения жидкoстей в упругих пдрубках. Сoбрание прoтoкoлoв заседаний Секции фин-мат. наук Об-ва естествoиспытателей при Казанскoм уиoте. 1883. т. 1. Тo же. Отд. изд. Казань. 1883. 19 стр. |
| G5 | Gromeka. I.S. On the Vortex Motions of a Liquid on a Sphere; Scientific Notes of Kazan University; Kazan University: Kazan, Russia, 1885; pp. 1–35. Gromeka. I.S. О вихревых движениях жидкoсти на сфере. Сoбрание прoтoкoлoв заседаний Секции физ-мат. наук Об-ва естествoиспытатели при Казанскoм уи-те. 1885. т. 111. Тo же. Отд. нэп. Казань. 1885. 35 стр. |
| G6 | Gromeka. I.S. On the motion of liquid drops. Bull. De La Société Mathématique De Kasan Kasan 1886, 5, 8–47. Gromeka. I.S. О движении жидких капель. Сoбрание прoтoкoлoв заседания Секции физ. мат. наук Об-ва естествoиспытателей при Казанскoм уи-те. 1886. т. Ч. Тo же пoдзап; К теoрии капиллярных явлений. О движении жидких капель. Отд. изд. Казань. 1886. 23 стр. |
| G7 | Gromeka. I.S. Some cases of equilibrium of a perfect gas. Bull. De La Société Mathématique De Kasan Kasan 1886, 5, 66–82. Gromeka. I.S. Некoтoрые случаи равнoвесия сoвершеннoгo газа. Сoбрание прoтoкoлoв лассoдани! Секции фиги-мат. наук Об-ва естествoиспытателей при Казанскoм уи-те. 1886. т. Ч. Тo же. Отд. нац. Казань. 1886. 19 стр. |
| G8 | Gromeka. I.S. Lectures on the Mechanics of Liquid Bodies; Kazan University Press: Kazan, Russia, 1887; pp. 1–174. Gromeka. I.S. Лекции пo механике жидких тел. Казанский ун-т. 1887. 174 стр. Изд. интo-ГРИБ. |
| G9 | Gromeka. I.S. On infinite values of integrals of second-order linear differential equations. Bull. De La Société Mathématique De Kasan Kasan 1887, 6, 14–40. Gromeka. I.S. О бескoнечных значениях интегралoв линейных дифференциальных уравнений втoрoгo пoрядка. Сoбрание прoтoкoлoв заседании Секпн фил-мат. наук Об-ва естествoиспытателей при Казанскoм ун-те. 1887. т. И |
| G10 | Gromeka. I.S. On the Effect of Temperature on Small Variations in Air Masses; Scientific Notes of Kazan University; Kazan University: Kazan, Russia, 1888; pp. 1–40. Gromeka. I.S. О влиянии температуры на малые кoлебания вoздушных масс. Ученые записки Казанскoгo уи-та пo фин-мат. фак-ту за 1886 г. 1887. Тo же. Отд. изд Казана. 1888. 40 стр. |
| G11 | Gromeka. I.S. Influence of the Uneven Distribution of the Temperature on the Propagation of Sound. Mat. Sb. 1889, 14, 283–302. Available online: https://www.mathnet.ru/php/archive.phtml?wshow=paper&jrnid=sm&paperid=7202&option_lang=rus (accessed on 8 February 2024). Gromeka. I.S. О влиянии неравнoмернoгo распределения паемпературы на распрoстра-нение звука. Математически! сбoрник. М. 1889. т. ХШ. вып. 2. стр. 283–303. |
References
- Górak, A.; Latawiec, K. Russian Governors in the Kingdom of Poland (1867–1918); Krajka, J., Translator; Towarzystwo Nauki i Kultury “Libra”: Lublin, Poland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Vasiliev, O.F. The memory of the outstanding Russian hydromechanics I.S. Gromeka (on the 100th anniversary of his birthday). Priroda 1951, 9, 74–77. [Google Scholar]
- Gromeka, I.S. Collected Works; USSR Academy of Sciences Publication: Moscow, Russia, 1952. [Google Scholar]
- Baun, J. Emerging Technology: Ultrasound Vector Flow Imaging—A Novel Approach to Arterial Hemodynamic Quantification. J. Diagn. Med. Sonogr. 2021, 37, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratchi, S.; Chen, Y.C.; Karlheinz, P. Helical flow: A means to identify unstable plaques and a new direction for the design of vascular grafts and stents. Atherosclerosis 2020, 300, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorp, J.H.; Covich, A.P. Chapter 2—An Overview of Inland Aquatic Habitats. In Ecology and Classification of North American Freshwater Invertebrates, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 25–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.W.; Ahn, J. Experimental and numerical investigations of primary flow patterns and mixing in laboratory meandering channel. Smart Water 2019, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landman, M.J. Time-dependent helical waves in rotating pipe flow. J. Fluid Mech. 1990, 221, 289–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dritschel, D.G. Generalized helical Beltrami flows in hydrodynamics and magnetohydrodynamics. J. Fluid Mech. 1991, 222, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Linden, B.J.; Ory, E.; Dam, J.; Tijsseling, A.S.; Pisarenco, M. Efficient computation of three-dimensional flow in helically corrugated hoses including swirl. In Proceedings of the ASME 2009 Pressure Vessels and Piping Division Conference, Prague, Czech Republic, 26–30 July 2009; Paper PVP2009-77997. 2009; pp. 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseenko, S.V.; Kuibin, P.A.; Okulov, V.L. Theory of Concentrated Vortices—An Introduction; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Loitsyanskii, L.G. Mechanics of Liquids and Gases, 2nd ed.; Volume 6 in International Series of Monographs in Aeronautics and Astronautics; Pergamon Press Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Kambe, T. Geometrical Theory of Dynamical Systems and Fluid Flows: Revised; World Scientific Publishing Company: Singapore, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, V.I.; Khesin, B.A. Topological Methods in Hydrodynamics; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zermelo, E.; Ebbinghaus, H.D.; Kanamori, A.; Kramer, D.P.; De Pellegrin, E. Collected Works/Gesammelte Werke II; Volume II/Band II—Calculus of Variations, Applied Mathematics, and Physics/Variationsrechnung, Klasse; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Majdalani, J. On the generalized Beltramian motion of the bidirectional vortex in a conical cyclone. Phys. Fluids 2022, 34, 036604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgulis, A.; Yudovich, V.I.; Zaslavsky, G.M. Compressible Helical Flows. Commun. Pure Appl. Math. 1995, 48, 571–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drazin, P.G.; Riley, N. The Navier–Stokes Equations: A Classification of Flows and Exact Solutions; London Mathematical Society Lecture Note Series; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; Volume 334. [Google Scholar]
- von Mises, R. Mathematical Theory of Compressible Fluid Flow (Applied Mathematics and Mechanics); Academic Press Inc.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- Truesdell, C. The Kinematics of Vorticity; Indiana University Press: Bloomington, India, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Gostintsev, Y.A.; Pokhil, P.F.; Uspenskii, O.A. Gromeka-beltrami flow in a semiinfinite cylindrical pipe. In Fluid Dynamics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1971; Volume 6, pp. 281–284. [Google Scholar]
- Chefranov, A.S.; Chefranov, S.G. Extrema of the Kinetic Energy and Its Dissipation Rate in Vortex Flows. Dokl. Phys. 2003, 48, 696–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrofanova, O. Generation of deterministic eddy structure of the flow as an analogue of the phase transition of the second kind. Development of ideas of academician I. I. Novikov. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 115, 04002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinkevich, O.A.; Zinchenko, G.O. Stationary concentrated vortex with three velocity components above the water surface. Phys. Astron. Int. J. 2019, 3, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosviryakov, E.Y. Non-helical exact solutions to the Euler equations for swirling axisymmetric fluid flows. J. Samara State Tech. Univ. Ser. Phys. Math. Sci. 2019, 23, 764–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navruzov, K.; Turayev, M.; Shukurov, Z. Pulsating flows of viscous fluid in flat channel for given harmonic fluctuation of flow rate. E3S Web Conf. 2023, 401, 02010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chefranov, S.G. Helicity Generation in Uniform Helical Flows. J. Exp. Theor. Phys. 2004, 99, 987–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bělík, P.; Su, X.; Dokken, D.P.; Scholz, K.; Shvartsman, M.M. On the Axisymmetric Steady Incompressible Beltrami Flows. Open J. Fluid Dyn. 2020, 10, 208–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truesdell, C. Vorticity and the thermodynamic state in a gas flow. In Mémorial des Sciences Mathématiques, Fascicule; Gauthier-Villars: Paris, France, 1952; Volume 119. [Google Scholar]
- Meleshko, V.; Aref, H. Bibliography of Vortex Dynamics 1858–1956. Adv. Appl. Mech. 2007, 41, 197–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltrami, E. Considerazioni idrodinamiche. Nuovo Cim. 1889, 25, 212–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navier, C.L.M.H. Mémoire sur les lois du Mouvement des Fluides. Mém. l’Acad. R. Sci. l’Inst. Fr. 1823, 6, 389–440. Available online: https://fr.wikisource.org/wiki/M%C3%A9moire_sur_les_lois_du_mouvement_des_fluides (accessed on 8 February 2024).
- Sestak, J.; Charles, M.E. An approximate solution for the start-up flow of a power-law fluid in a tube. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1968, 23, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovsyannikov, V.M. Calculation of accelerated motion of fluid in a tube. Mekhanika Zhidkosti I Gaza 1981, 5, 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghidaoui, M.S.; Kolyshkin, A.A. A quasi-steady approach to the instability of time-dependent flows in pipes. J. Fluids Mech. 2002, 465, 301–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golovin, S.V.; Khe, A.K.; Gadylshina, K.A. Hydraulic model of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J. Fluid Mech. 2016, 797, 110–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roiti, A. Sul movimento dei liquidi. Ann. Della Sc. Norm. Super. Pisa Cl. Sci. 1871, 1, 193–240. [Google Scholar]
- Szymański, P. Quelques solutions exactes des équations de l’hydrodynamique du fluide visqueux dans le cas d’un tube cylindrique. J. De Mathématiques Pures Et Appliquées 1932, 11, 67–107. [Google Scholar]
- Tijsseling, A. Fluid-Structure Interaction in Liquid-Filled Pipe Systems: A Review. J. Fluids Struct. 1996, 10, 109–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komissarova, G.L. Propagation of Normal Waves Through a Fluid Contained in a Thin-Walled Cylinder. Int. Appl. Mech. 2002, 38, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meleshko, V.V.; Newton, P.K.; Ostrovs’kyi, V.V. Stability of the configurations of point vortices on a sphere. J. Math. Sci. 2010, 171, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alobaidi, G.; Mallier, R. Vortex Streets on a Sphere. J. Appl. Math. 2011, 2011, 712704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Azpeitia, C. Relative periodic solutions of the n-vortex problem on the sphere. J. Geom. Mech. Am. Inst. Math. Sci. 2019, 11, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurakin, L.G. On nonlinear stability of the regular vortex systems on a sphere. Chaos 2004, 14, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, P.K. The N-Vortex Problem. Analytical Techniques; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Résal, H. Physique Mathématique; Gauthier-Villars: Paris, France, 1884. [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs, L.I. Zur Theorie der linearen Differentialgleichungen mit veränderlichen Coefficienten. J. Für Die Reine Und Angew. Math. 1866, 66, 121–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Fuchs, L.I. Zur Theorie der linearen Differentialgleichungen mit veränderlichen Coefficienten (Ergänzungen zu der im 66sten Bande dieses Journals enthaltenen Abhandlung). J. Für Die Reine Und Angew. Math. 1868, 68, 354–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, J.J. Fuchs and the Theory of Differential Equations. Bull. (New Ser.) Am. Math. Soc. 1984, 10, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).