Effect of Droplet Viscosity Ratio and Surfactant Adsorption on the Coalescence of Droplets with Interfacial Viscosity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Method of Analysis
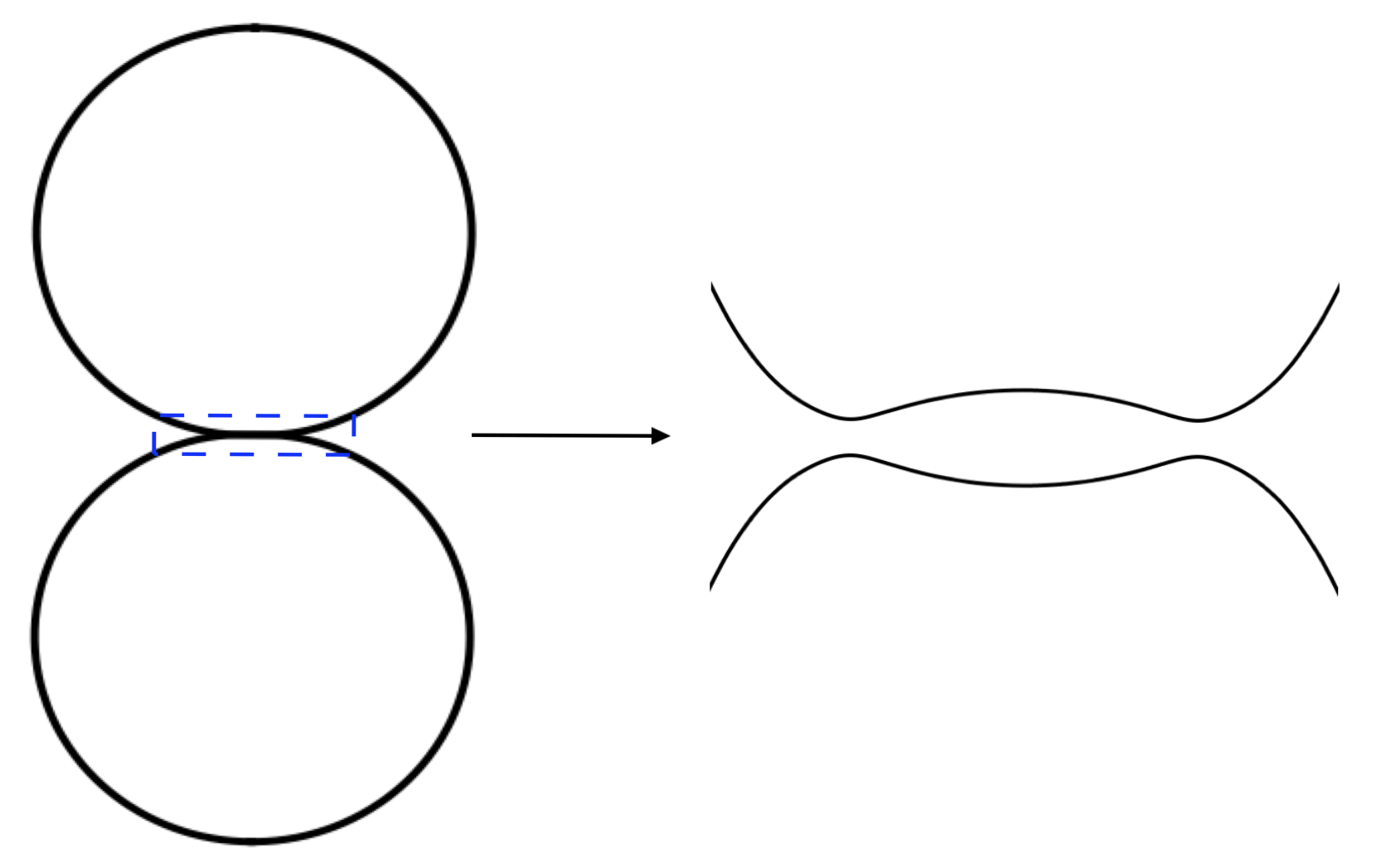
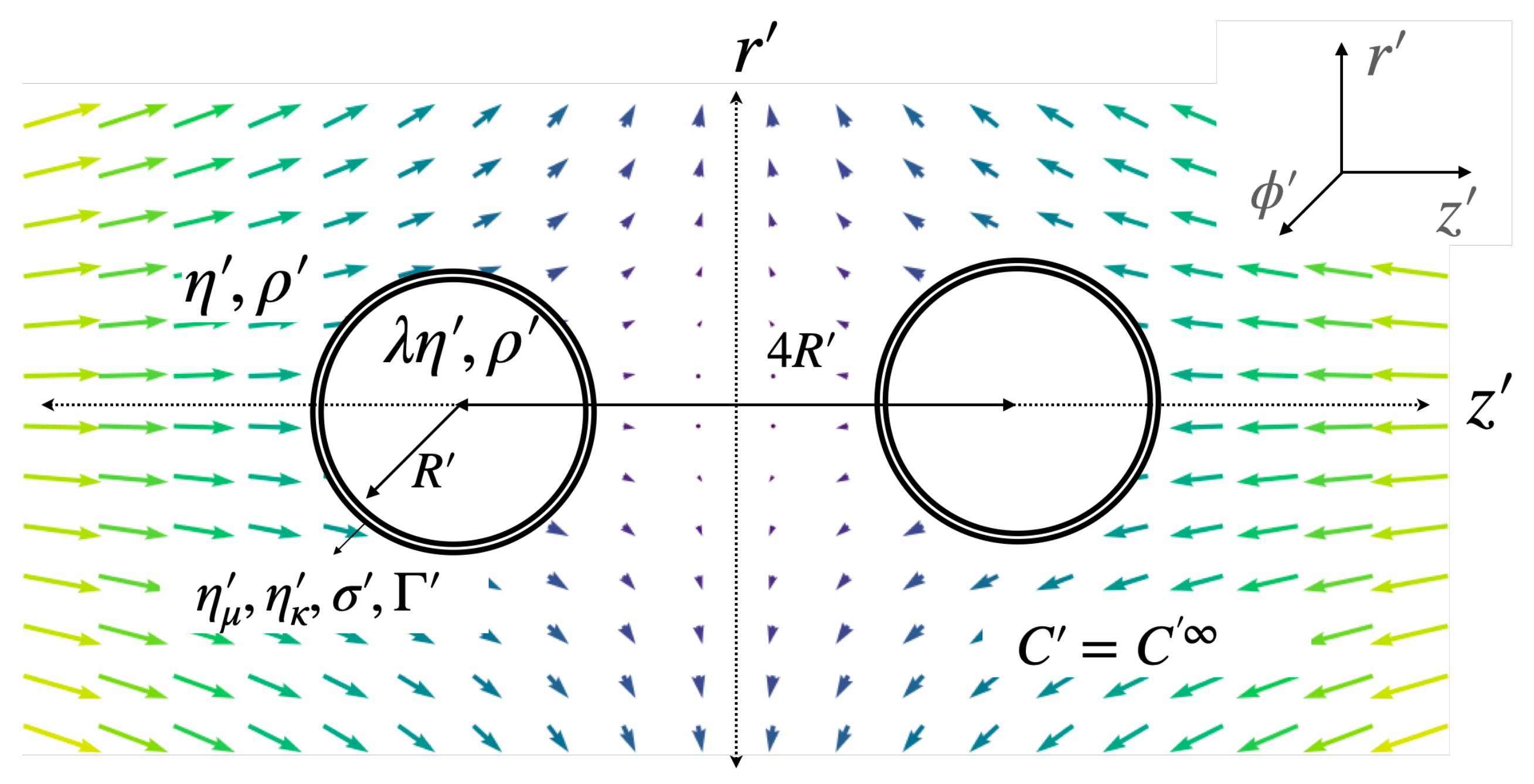
2.1. Problem Overview
2.2. Non-Dimensionalization
2.3. Governing Equations
- Continuity of velocitywhere, is the velocity of the droplet interface.
- Force balance
2.4. Dimensionless Parameters
2.5. Numerical Implementation
- The velocity vector on the droplet’s interface at time t for a given droplet shape and surfactant concentration is evaluated using the boundary integral Equation (10).
- After velocity vector is computed at time t, we use explicit Euler’s method to obtain the updated droplet mesh points at time .
- Re-meshing is performed based on the procedure described in [27] as the mesh points become too close or too separated.
- Using velocity from time t and position vector from time , we solve the surfactant convection-diffusion Equation (6) to obtain the updated surfactant concentration using implicit Euler’s method at time .
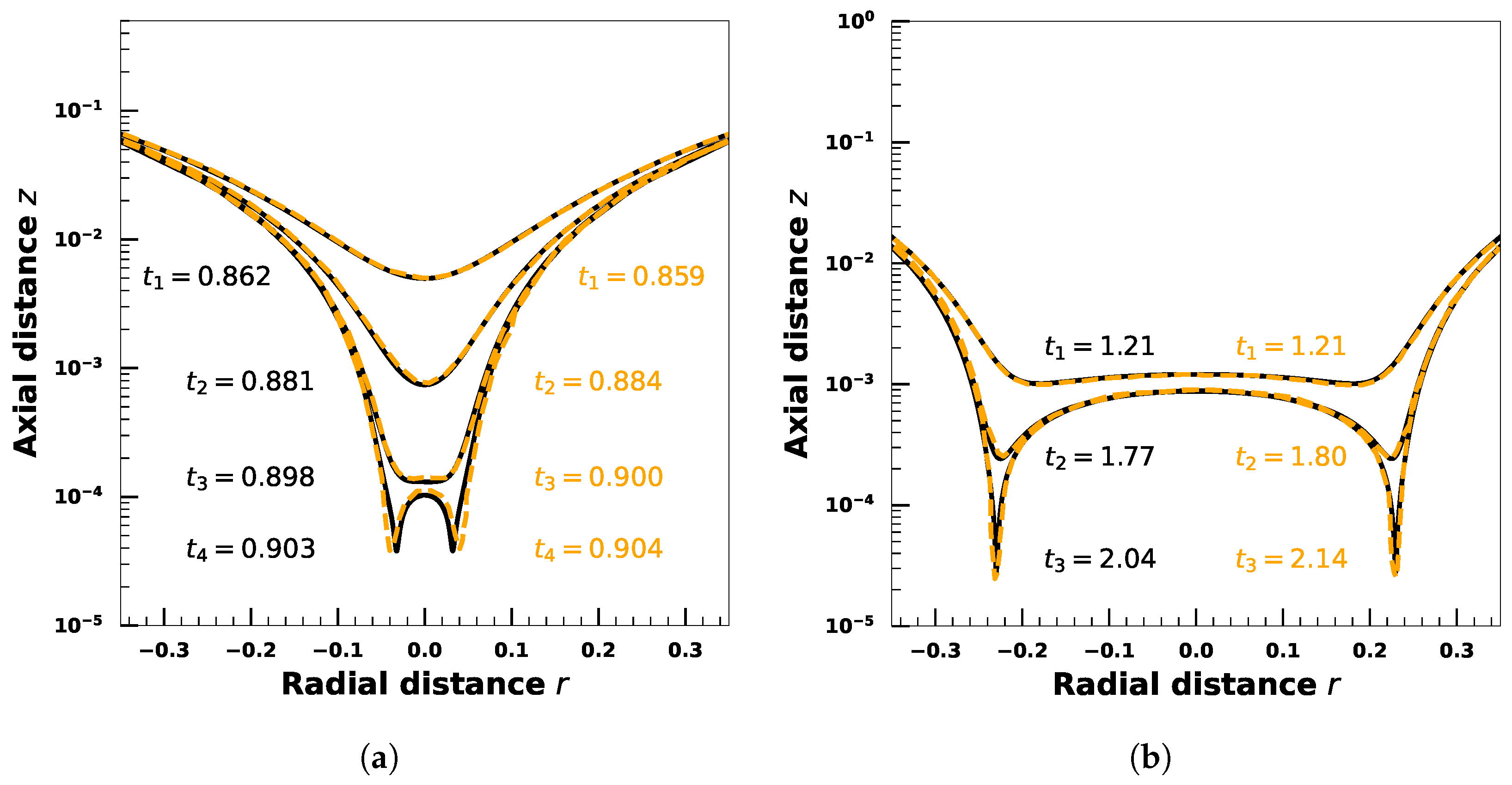
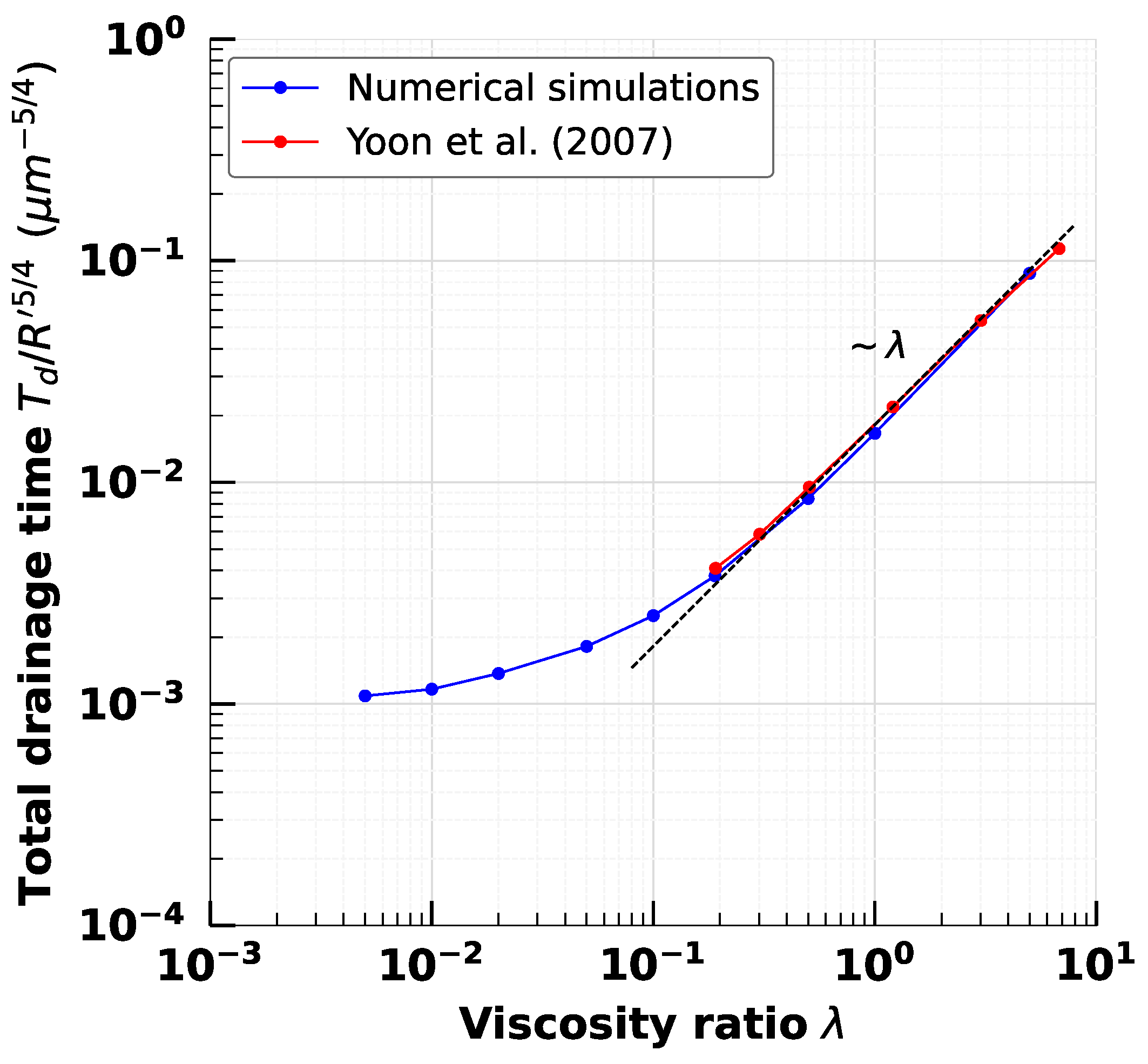
3. Validation: Clean Droplet Coalescence
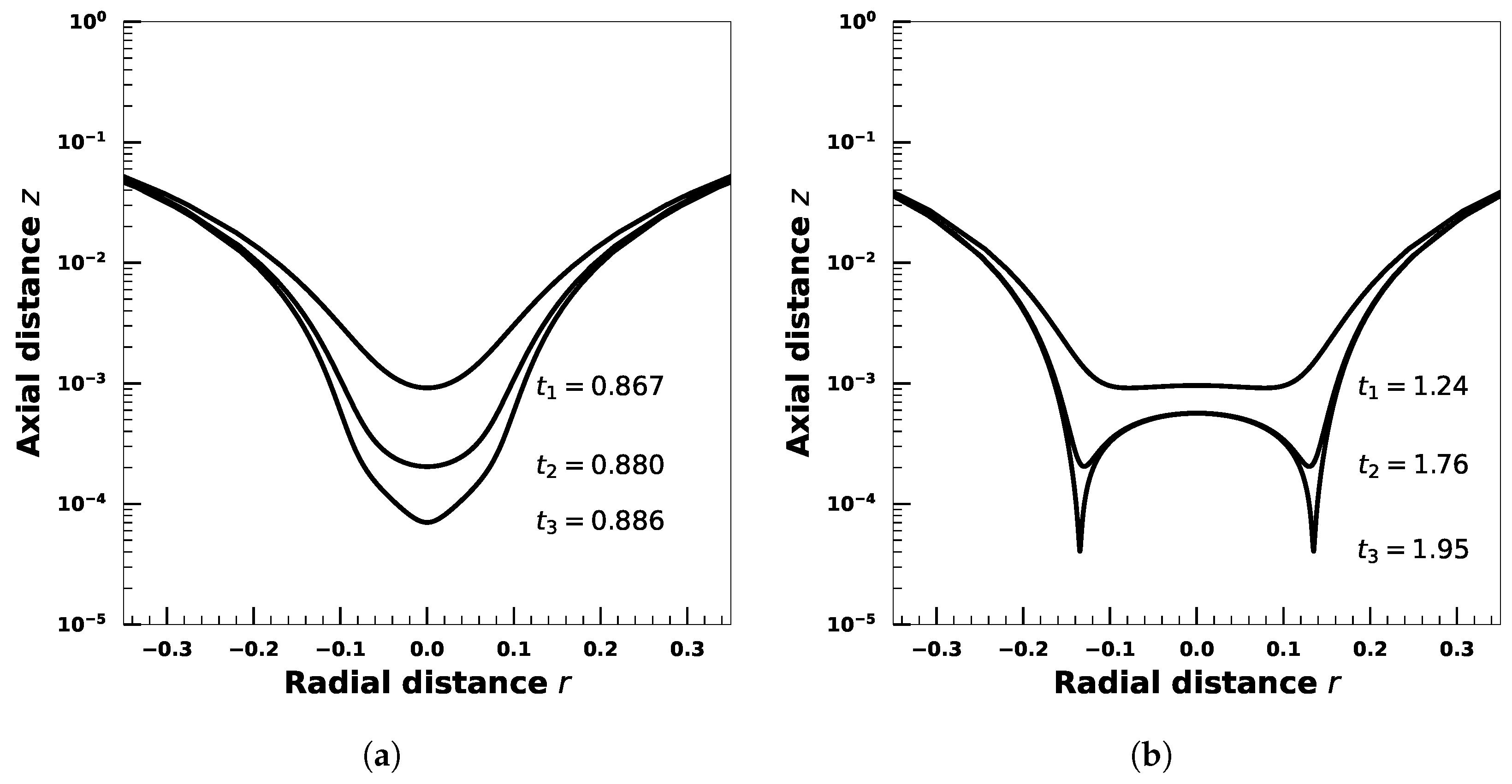
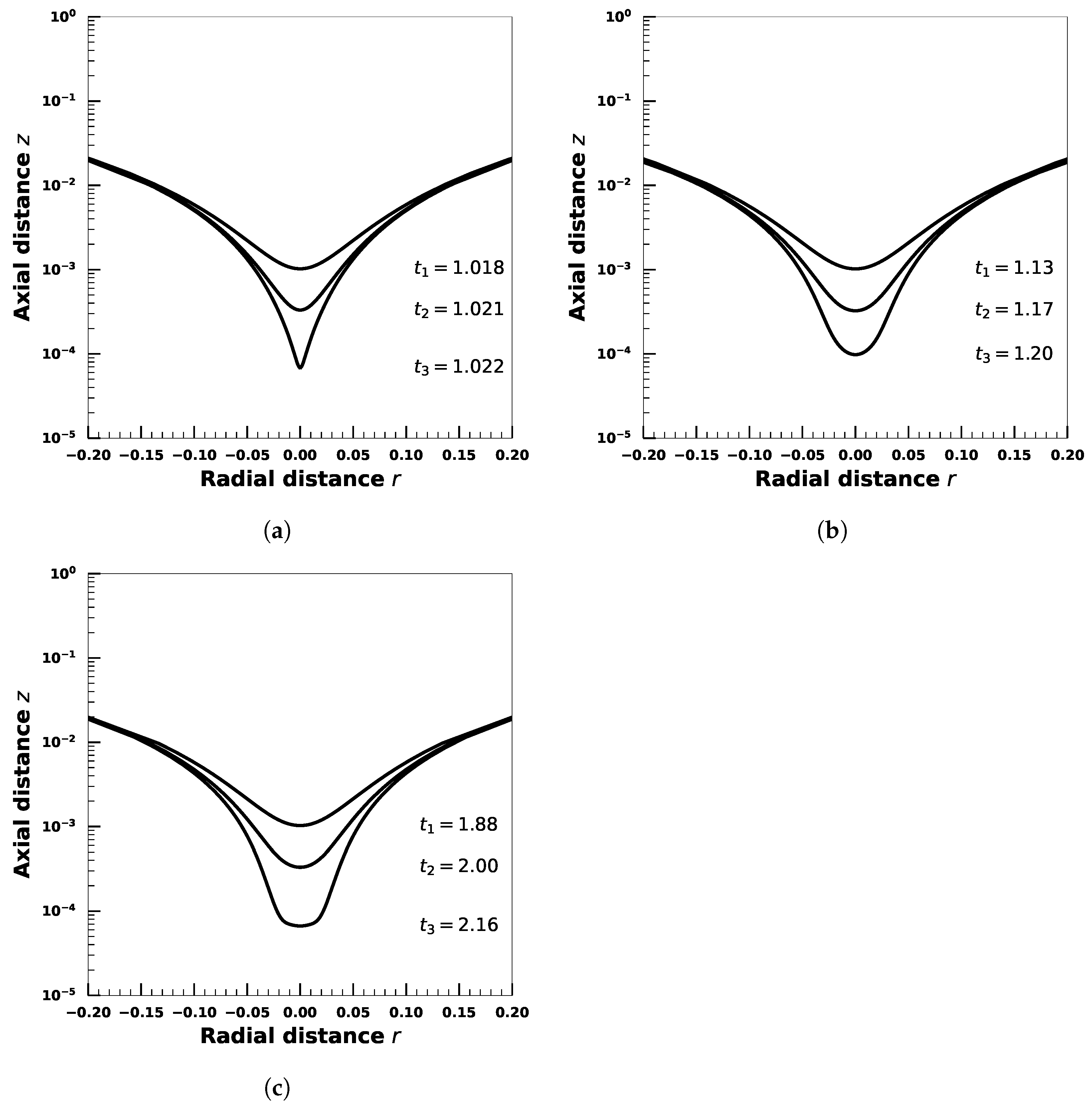
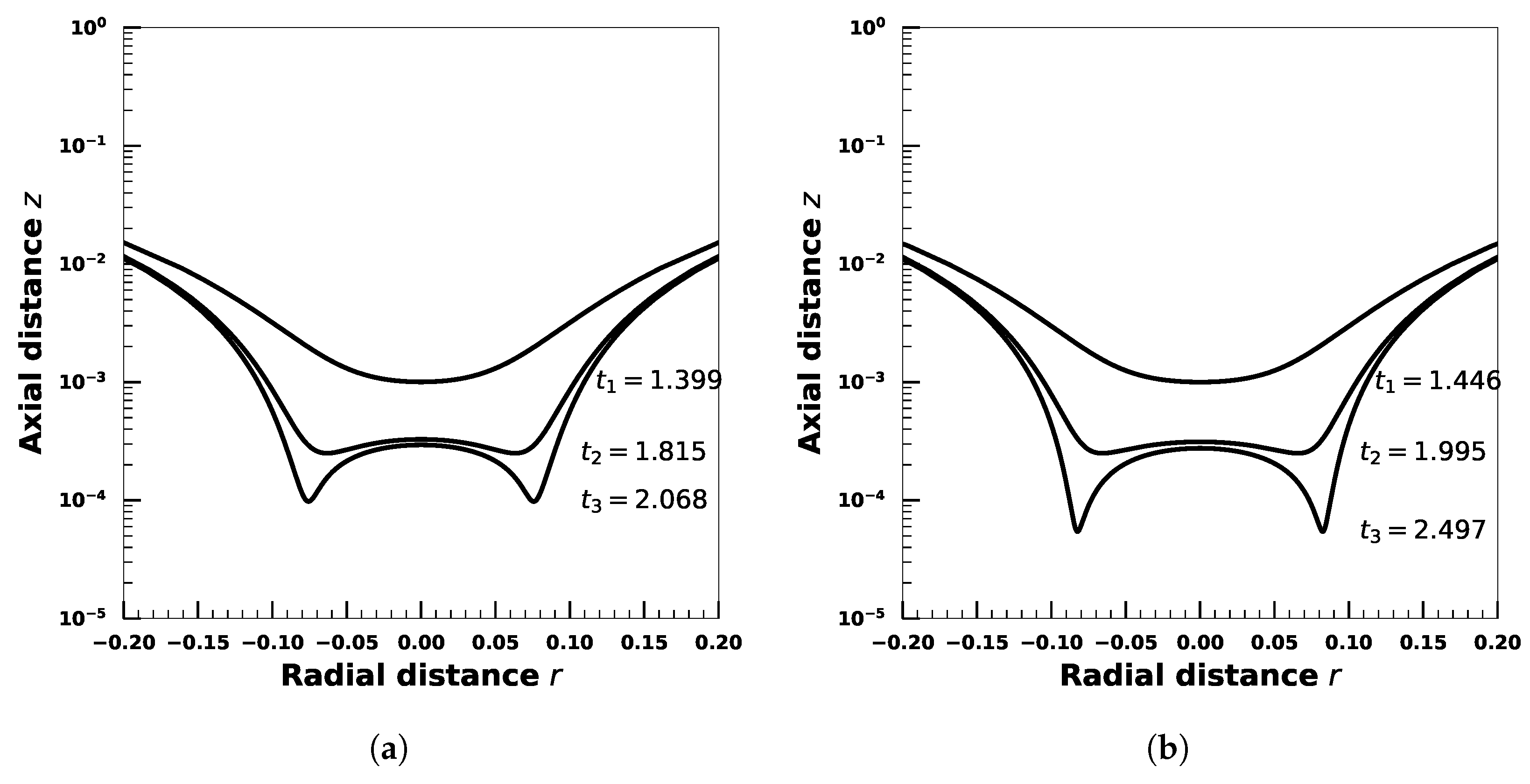
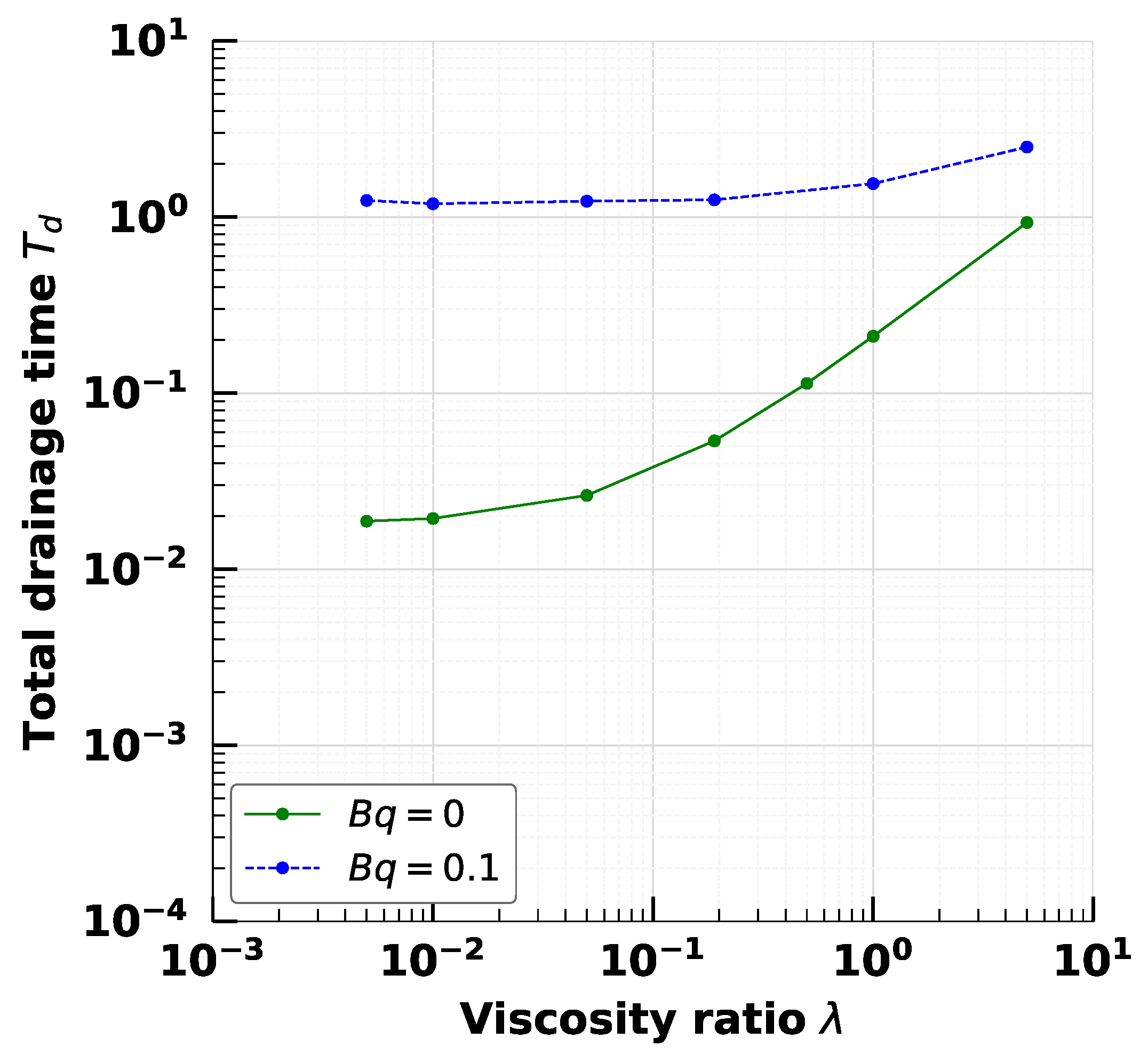
4. Effect of Droplet Viscosity Ratio on Droplets with Interfacial Viscosity
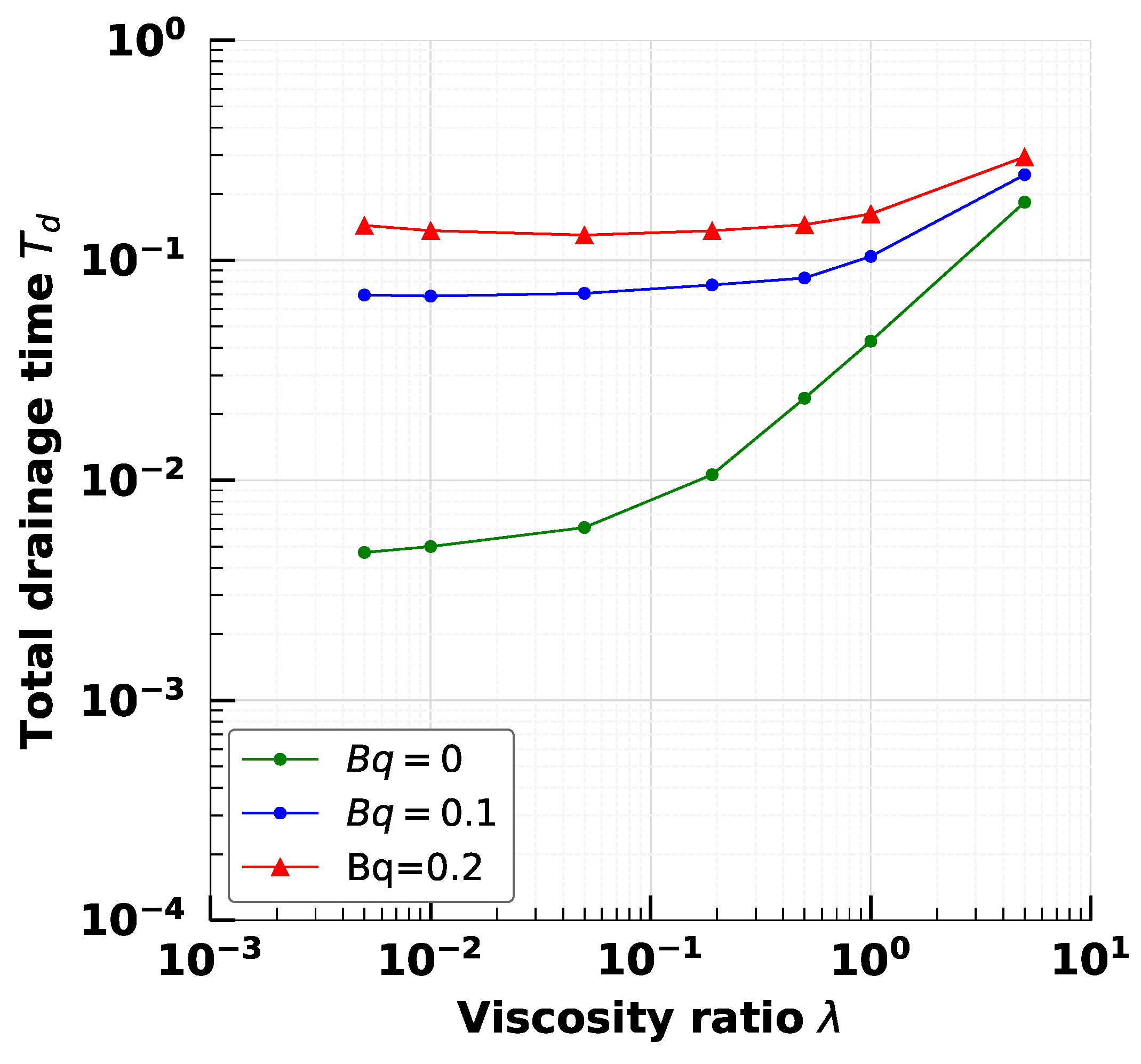
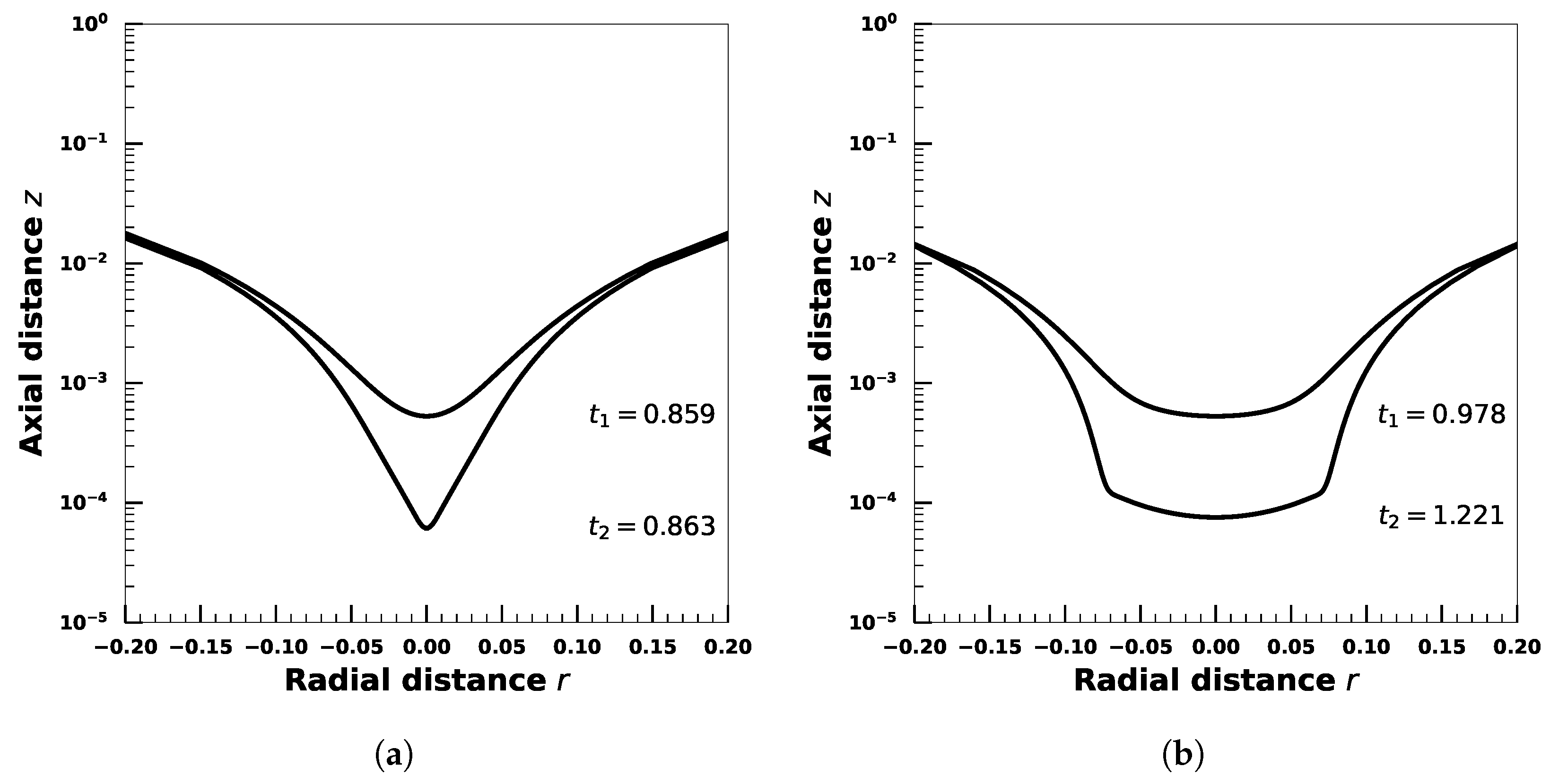
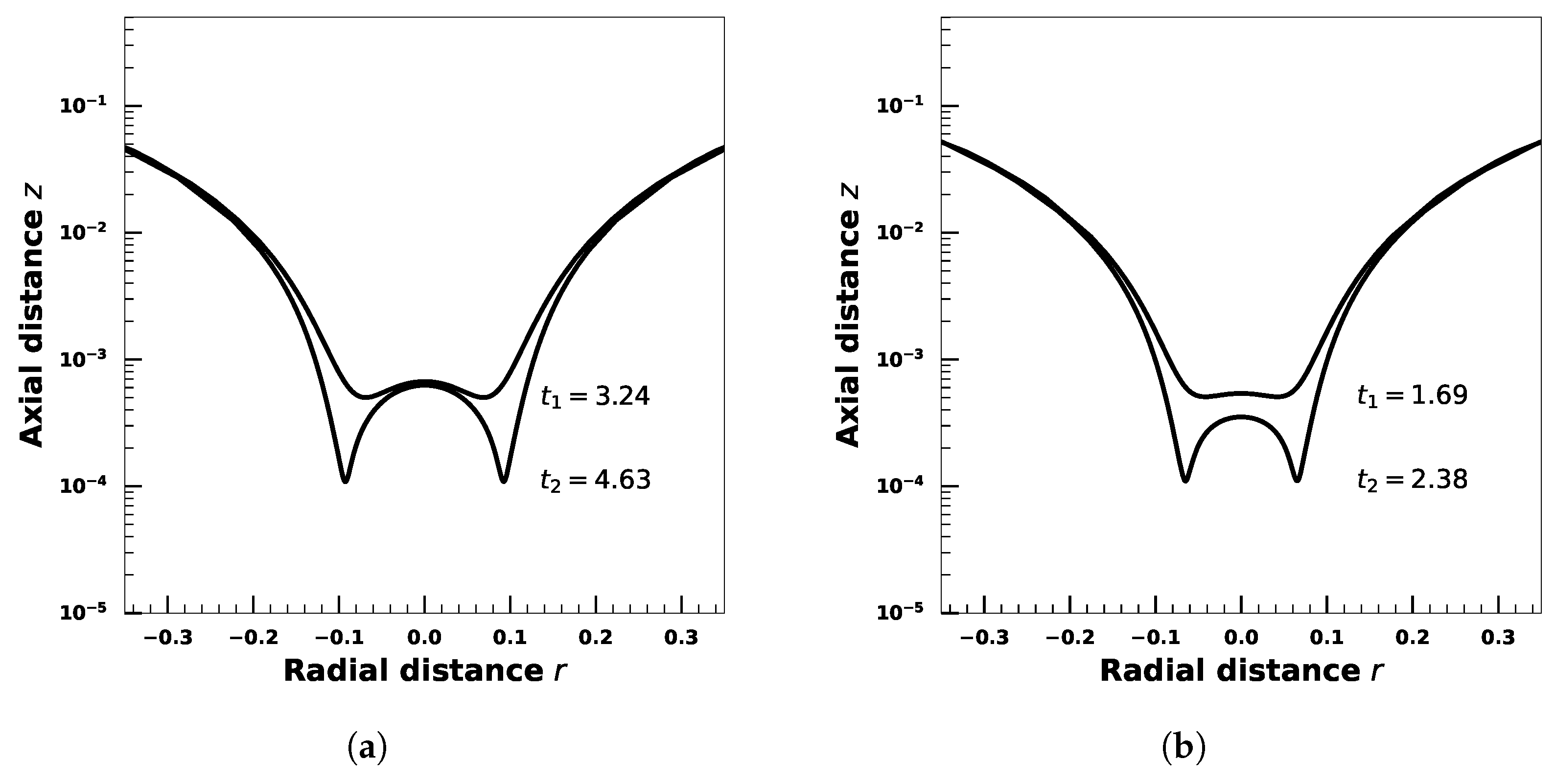
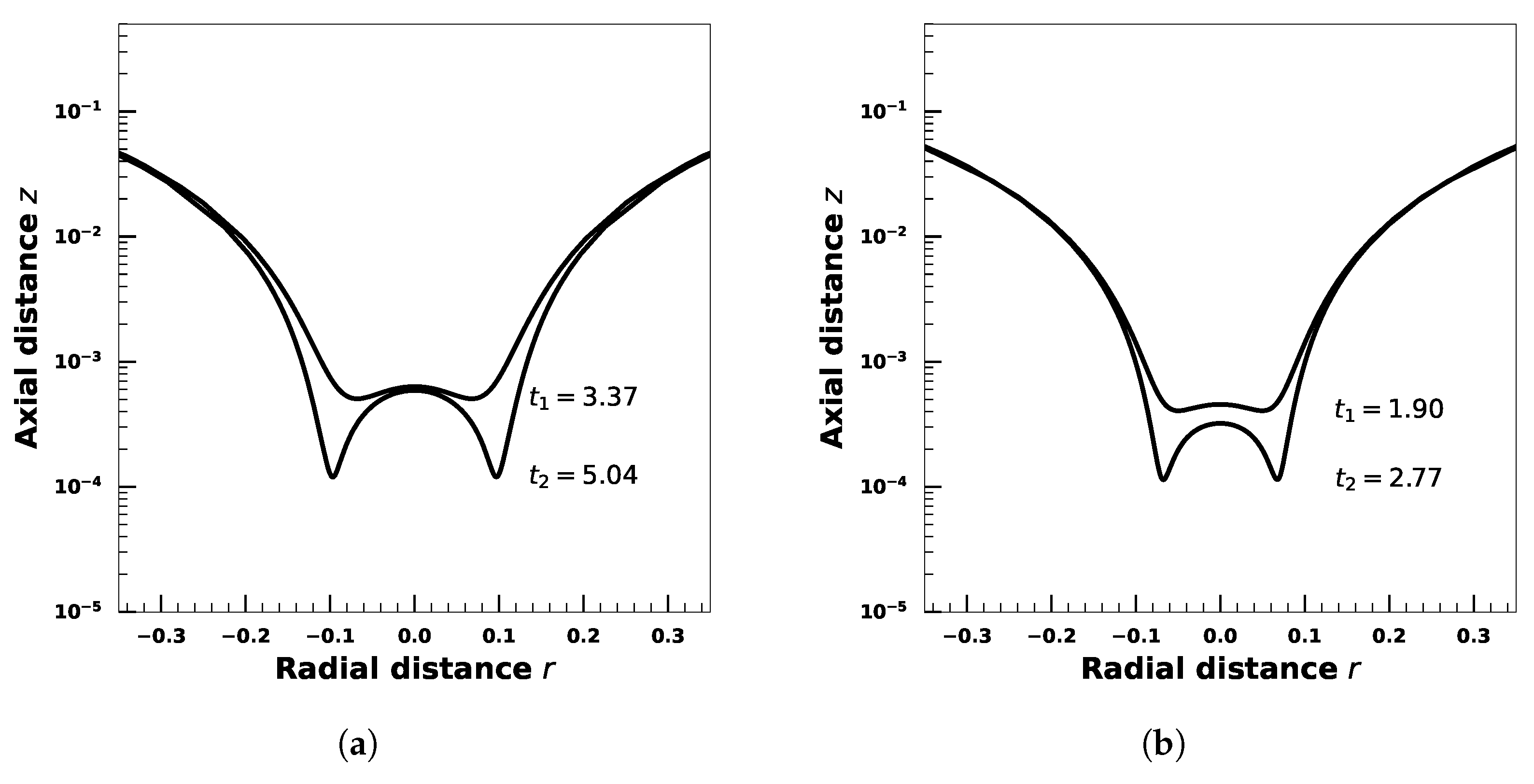
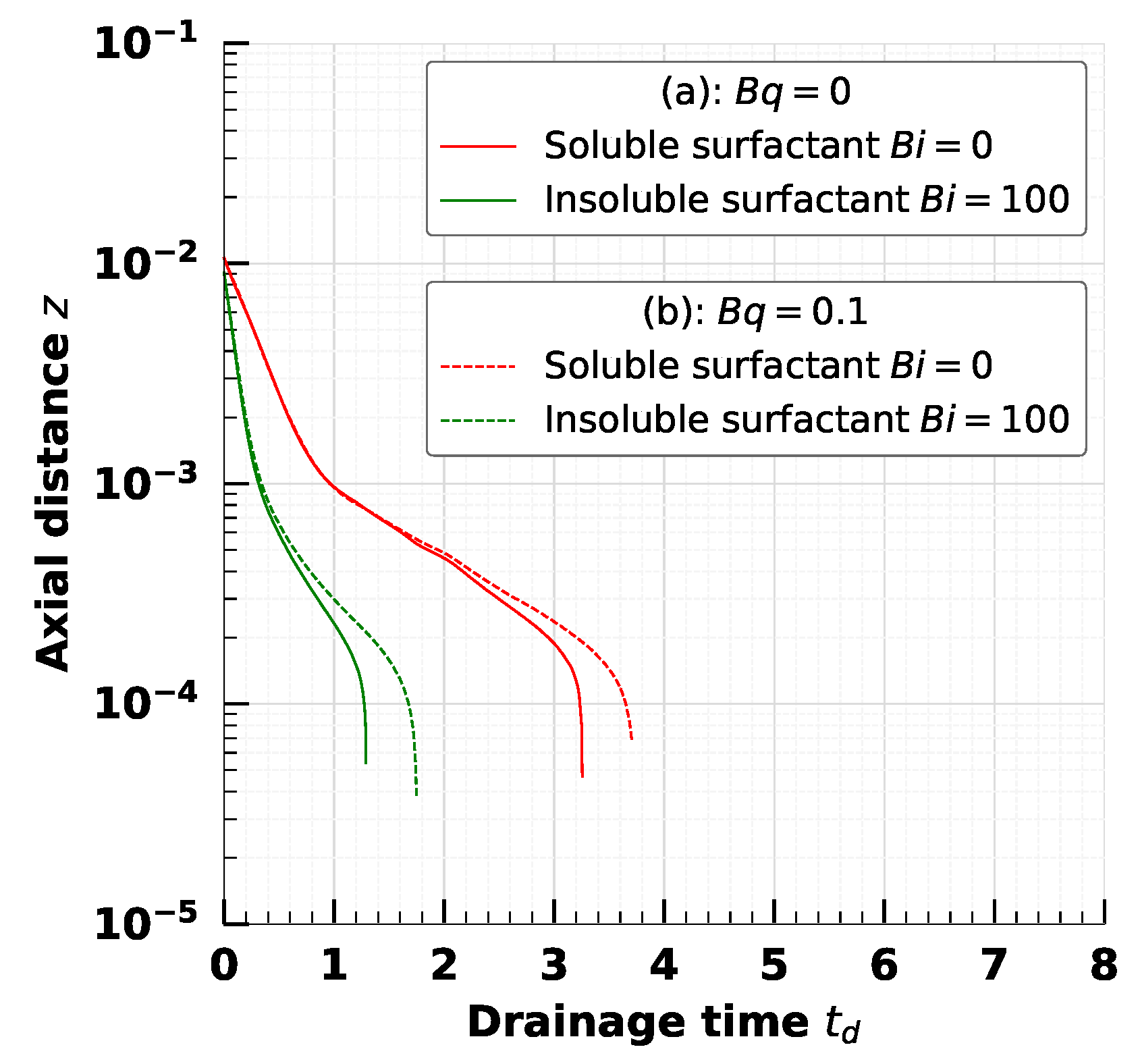
5. Effect of Adsorption-Desorption Controlled Surfactant When Interfacial Viscosity Is Present
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brooks, C.F.; Fuller, G.G.; Frank, C.W.; Robertson, C.R. An interfacial stress rheometer to study rheological transitions in monolayers at the air- water interface. Langmuir 1999, 15, 2450–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwijlen, T.; Moldenaers, P.; Stone, H.A.; Vermant, J. Study of the flow field in the magnetic rod interfacial stress rheometer. Langmuir 2011, 27, 9345–9358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zell, Z.A.; Nowbahar, A.; Mansard, V.; Leal, L.G.; Deshmukh, S.S.; Mecca, J.M.; Tucker, C.J.; Squires, T.M. Surface shear inviscidity of soluble surfactants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3677–3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Steltenkamp, S.; Zasadzinski, J.A.; Squires, T. Active microrheology and simultaneous visualization of sheared phospholipid monolayers. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, V.; da Silva, M.A.; Schmitt, J.; Hossain, K.M.Z.; Scott, J.L.; Edler, K.J. Charge-driven interfacial gelation of cellulose nanofibrils across the water/oil interface. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandebril, S.; Franck, A.; Fuller, G.G.; Moldenaers, P.; Vermant, J. A double wall-ring geometry for interfacial shear rheometry. Rheol. Acta 2010, 49, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noskov, B.; Akentiev, A.; Bilibin, A.Y.; Zorin, I.; Miller, R. Dilational surface viscoelasticity of polymer solutions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 104, 245–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicuta, P. Compression and shear surface rheology in spread layers of β-casein and β-lactoglobulin. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 308, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepicelli, M.; Verwijlen, T.; Tervoort, T.A.; Vermant, J. Characterization and modelling of Langmuir interfaces with finite elasticity. Soft Matter 2017, 13, 5977–5990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kale, S.K.; Cope, A.J.; Goggin, D.M.; Samaniuk, J.R. A miniaturized radial Langmuir trough for simultaneous dilatational deformation and interfacial microscopy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 582, 1085–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.O.; Stebe, K.J. Oscillating bubble tensiometry: A method for measuring the surfactant adsorptive-desorptive kinetics and the surface dilatational viscosity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1994, 168, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, N.J.; Walker, L.M.; Anna, S.L. A microtensiometer to probe the effect of radius of curvature on surfactant transport to a spherical interface. Langmuir 2010, 26, 13310–13319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichert, M.D.; Alvarez, N.J.; Brooks, C.F.; Grillet, A.M.; Mondy, L.A.; Anna, S.L.; Walker, L.M. The importance of experimental design on measurement of dynamic interfacial tension and interfacial rheology in diffusion-limited surfactant systems. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2015, 467, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leser, M.; Acquistapace, S.; Cagna, A.; Makievski, A.; Miller, R. Limits of oscillation frequencies in drop and bubble shape tensiometry. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2005, 261, 25–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liggieri, L.; Attolini, V.; Ferrari, M.; Ravera, F. Measurement of the surface dilational viscoelasticity of adsorbed layers with a capillary pressure tensiometer. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 255, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, R.; Koczo, K.; Erdos, E.; Wasan, D.T. Controlled drop tensiometer for measuring dynamic interfacial and film tension. AIChE J. 1995, 41, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesters, A. Modelling of coalescence processes in fluid-liquid dispersions: A review of current understanding. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 1991, 69, 259–270. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, Y.; Hsu, A.; Leal, L.G. Experimental investigation of the effects of copolymer surfactants on flow-induced coalescence of drops. Phys. Fluids 2007, 19, 023102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, I.B.; Danov, K.D.; Kralchevsky, P.A. Flocculation and coalescence of micron-size emulsion droplets. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1999, 152, 161–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Park, C.C.; Hu, Y.T.; Leal, L.G. The coalescence of two equal-sized drops in a two-dimensional linear flow. Phys. Fluids 2001, 13, 1087–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiantsios, S.G.; Davis, R.H. On the buoyancy-driven motion of a drop towards a rigid surface or a deformable interface. J. Fluid Mech. 1990, 217, 547–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiantsios, S.G.; Davis, R.H. Close approach and deformation of two viscous drops due to gravity and van der Waals forces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1991, 144, 412–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkovska, D.S.; Danov, K.D.; Ivanov, I.B. Effect of surfactants on the stability of films between two colliding small bubbles. Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2000, 175, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, L.Y.; Matar, O.K.; de Ortiz, E.S.P.; Hewitt, G.F. Film drainage between two surfactant-coated drops colliding at constant approach velocity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 257, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Baldessari, F.; Ceniceros, H.D.; Leal, L.G. Coalescence of two equal-sized deformable drops in an axisymmetric flow. Phys. Fluids 2007, 19, 102102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B.; Leal, L.G. The mechanism of surfactant effects on drop coalescence. Phys. Fluids 2008, 20, 040802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Narsimhan, V. Impact of surface rheology on droplet coalescence in uniaxial compressional flow. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2023, 8, 083602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, A.; Leal, G. A scaling theory for the hydrodynamic interaction between a pair of vesicles or capsules. Phys. Fluids 2010, 22, 091702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, R.E.; Lange, A.; Fuller, G.G. Interfacial rheology and structure of straight-chain and branched fatty alcohol mixtures. Langmuir 2006, 22, 5321–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yim, K.S.; Fuller, G.G. Influence of phase transition and photoisomerization on interfacial rheology. Phys. Rev. E 2003, 67, 041601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, G.; López-Montero, I.; Monroy, F.; Langevin, D. Shear rheology of lipid monolayers and insights on membrane fluidity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6008–6013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikantan, H.; Squires, T.M. Pressure-dependent surface viscosity and its surprising consequences in interfacial lubrication flows. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2017, 2, 023301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermans, E.; Vermant, J. Interfacial shear rheology of DPPC under physiologically relevant conditions. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Choi, S.Q.; Zasadzinski, J.A.; Squires, T.M. Interfacial microrheology of DPPC monolayers at the air–water interface. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 7782–7789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaniuk, J.R.; Vermant, J. Micro and macrorheology at fluid–fluid interfaces. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 7023–7033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verwijlen, T.; Moldenaers, P.; Vermant, J. A fixture for interfacial dilatational rheometry using a rotational rheometer. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2013, 222, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krägel, J.; Kretzschmar, G.; Li, J.; Loglio, G.; Miller, R.; Möhwald, H. Surface rheology of monolayers. Thin Solid Films 1996, 284, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erni, P.; Fischer, P.; Windhab, E.J.; Kusnezov, V.; Stettin, H.; Läuger, J. Stress-and strain-controlled measurements of interfacial shear viscosity and viscoelasticity at liquid/liquid and gas/liquid interfaces. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2003, 74, 4916–4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussinesq, M. Sur l’existence d’une viscosité superficielle, dans la mince couche de transition séparant un liquide d’un autre fluide contigu. Ann. Chim. Phys. 1913, 29, 349–357. [Google Scholar]
- Scriven, L. Dynamics of a fluid interface equation of motion for Newtonian surface fluids. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1960, 12, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozrikidis, C. The instability of a moving viscous drop. J. Fluid Mech. 1990, 210, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, H. A simple derivation of the time-dependent convective-diffusion equation for surfactant transport along a deforming interface. Phys. Fluids A Fluid Dyn. 1990, 2, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, H.; Rumschitzki, D.; Maldarelli, C. On the surfactant mass balance at a deforming fluid interface. Phys. Fluids 1996, 8, 3203–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, S.; Metaxas, A.E.; Bachnak, R.; Neumiller, T.; Dutcher, C.S. Zooming in on the role of surfactants in droplet coalescence at the macroscale and microscale. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 50, 101385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, N.J.; Walker, L.M.; Anna, S.L. Diffusion-limited adsorption to a spherical geometry: The impact of curvature and competitive time scales. Phys. Rev. E 2010, 82, 011604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, N.J.; Vogus, D.R.; Walker, L.M.; Anna, S.L. Using bulk convection in a microtensiometer to approach kinetic-limited surfactant dynamics at fluid–fluid interfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 372, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Siegel, M.; Booty, M.R. Numerical simulation of drop and bubble dynamics with soluble surfactant. Phys. Fluids 2014, 26, 052102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggleton, C.D.; Stebe, K.J. An adsorption–desorption-controlled surfactant on a deforming droplet. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 208, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shmyrov, A.; Mizev, A. Surface Diffusion in Gaseous Monolayers of an Insoluble Surfactant. Langmuir 2019, 35, 14180–14187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayan, S.; Makhnenko, I.; Moravec, D.B.; Hauser, B.G.; Dallas, A.J.; Dutcher, C.S. Insights into the microscale coalescence behavior of surfactant-stabilized droplets using a microfluidic hydrodynamic trap. Langmuir 2020, 36, 9827–9842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, P.M.; Wagoner, B.W.; Thete, S.S.; Basaran, O.A. Role of Marangoni stress during breakup of surfactant-covered liquid threads: Reduced rates of thinning and microthread cascades. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2018, 3, 043602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggleton, C.D.; Pawar, Y.P.; Stebe, K.J. Insoluble surfactants on a drop in an extensional flow: A generalization of the stagnated surface limit to deforming interfaces. J. Fluid Mech. 1999, 385, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce-Torres, A.; Rubio, M.; Herrada, M.; Eggers, J.; Montanero, J. Influence of the surface viscous stress on the pinch-off of free surfaces loaded with nearly-inviscid surfactants. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunning, A.P.; Kirby, A.R.; Wilde, P.J.; Penfold, R.; Woodward, N.C.; Morris, V.J. Probing the role of interfacial rheology in the relaxation behaviour between deformable oil droplets using force spectroscopy. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 11473–11479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freer, E.M.; Yim, K.S.; Fuller, G.G.; Radke, C.J. Interfacial rheology of globular and flexible proteins at the hexadecane/water interface: Comparison of shear and dilatation deformation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 3835–3844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hildebrandt, E.; Nirschl, H.; Kok, R.J.; Leneweit, G. Adsorption of phospholipids at oil/water interfaces during emulsification is controlled by stress relaxation and diffusion. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 3730–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozrikidis, C. Boundary Integral and Singularity Methods for Linearized Viscous Flow; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Narsimhan, V. Deformation and burst of a liquid droplet with viscous surface moduli in a linear flow field. Phys. Rev. Fluids 2020, 5, 063601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Narsimhan, V. Numerical investigation of the effect of surface viscosity on droplet breakup and relaxation under axisymmetric extensional flow. J. Fluid Mech. 2022, 946, A24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Narsimhan, V. Impact of surface viscosity on the stability of a droplet translating through a stagnant fluid. J. Fluid Mech. 2021, 927, A44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Viscosity ratio | |||
| Capillary number | |||
| Boussinesq parameter | |||
| Surface Peclet number | |||
| E | Surface elasticity number | ||
| Initial surfactant coverage | |||
| Biot number | |||
| K | Equilibrium partition coefficient |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, N.; Narsimhan, V. Effect of Droplet Viscosity Ratio and Surfactant Adsorption on the Coalescence of Droplets with Interfacial Viscosity. Fluids 2024, 9, 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids9020048
Singh N, Narsimhan V. Effect of Droplet Viscosity Ratio and Surfactant Adsorption on the Coalescence of Droplets with Interfacial Viscosity. Fluids. 2024; 9(2):48. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids9020048
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Natasha, and Vivek Narsimhan. 2024. "Effect of Droplet Viscosity Ratio and Surfactant Adsorption on the Coalescence of Droplets with Interfacial Viscosity" Fluids 9, no. 2: 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids9020048
APA StyleSingh, N., & Narsimhan, V. (2024). Effect of Droplet Viscosity Ratio and Surfactant Adsorption on the Coalescence of Droplets with Interfacial Viscosity. Fluids, 9(2), 48. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids9020048






