Abstract
For several decades, magnetic nano- and microparticles have been used in various applications, as they can be attracted and controlled using external magnetic fields. Recently, carbonyl iron microparticles were used in a feasibility study of a new cardiac pacing application. The particles were inserted into a heart, attracted to its sidewall using a pulsating magnetic field, and applied pulsating pressure on its sidewall. The magnitude of the sidewall pressure is a critical parameter for the success and safety of the application, and it was evaluated analytically using a simplified model. In the present study, the behaviour of carbonyl iron microparticles in a water chamber was studied experimentally. Several masses of these particles were attracted to the sidewall of the chamber using an external pulsating magnetic field; the behaviours of the masses of particles, the particle–particle interaction, and the influence of fluid dynamics on them were examined during different periods of pulses. The sidewall pressure during their attraction was measured using an in-house piezoelectric polyvinylidene fluoride sensor. The relations between the measured sidewall pressure and the mass of the particles, their sizes, and the magnetic field exposure time were investigated. The obtained results suggest an asymptotic sidewall pressure value for the specified magnetic field. The measurements of the sidewall pressure are compared with evaluated results from the analytical model, showing that the model over-predicts the sidewall pressure.
1. Introduction
Suspensions of ferromagnetic particles have been used in research and applications, as they can be attracted and controlled by external magnetic fields. Two primary medical applications being investigated currently are the elimination of tumours with local hyperthermia and drug delivery [1]. Ferromagnetic particles are also used in mechanical applications such as dumpers and film bearings [2,3], as well as in magnetic field sensors [4]. Another mechanical use of suspended magnetic particles is as a heat transfer medium [5,6].
Recently, the feasibility study of a new medical application was presented: leadless cardiac pacing [7]. In this application, ferromagnetic particles are injected into the vascular system and maintained in the right ventricle using an external direct current (DC) electromagnetic field. Subsequently, electromagnetic pulses are applied to the heart to attract the particles to the sidewall of the heart and to release them. During their attraction, the particles apply pressure on the sidewall, thus stimulating the heart muscle and provoking pacing. The above study focuses on the functioning of the heart when the pulses are applied, while the behaviour of the particles is outside the scope of the study. The pressure that the particles apply on the sidewall, a critical parameter for the success and safety of the above application, was not measured.
In order to successfully provoke cardio pacing, a local pressure as low as is required. However, controlling the pressure is crucial, since impacts that exceed can cause tissue damage [7,8]. The sidewall pressure in Reference [7] was evaluated to be for a given magnetic field and gradient of and . This pressure was evaluated using a simplified model, which relied on two main assumptions. The first is that the magnetization of the particles is at saturation, which for the specified magnetic field is in line with results from Reference [9]. The second assumption is that the aggregation of particles may be modelled as a solid body, a sphere with radius and a uniform magnetization.
Two parameters discussed in Reference [7], which may influence the sidewall pressure, are the diameter of the particles and the duty cycle of the electromagnetic pulse. However, the influence of these parameters on the aggregation of particles and thereby on the sidewall pressure has not been discussed. In the current work, the influence of these two parameters on the sidewall pressure is investigated.
In several studies, a magnetic field was used to attract suspended particles. In Reference [10], a planar coil was used to accumulate suspended ferromagnetic particles on a microelectromechanical systems (MEMS) sensor, as a device to detect the appearance of ferromagnetic particles in liquid. In Reference [11], a high-gradient magnetic separation technique was used to capture weakly magnetic mineral particles. In three studies [12,13,14], the percentage of attracted particles was measured in order to rate the success of the attraction. However, the behaviour of the particles during the attraction was not investigated in the studies presented above. The behaviour of particles in a colloidal suspension called ferrofluid was investigated in References [15,16]. The ferrofluid was injected into a horizontal cell filled with colloidal silica and subsequently attracted to a sidewall using a magnetic field. In these studies, the particles did not settle because of the design of the experimental setup. In addition, an experimental method for measuring the pressure that ferrofluids apply on the sidewall was presented. The disadvantage of this method is that it is designed for static measurements of pressure and may not be suitable for dynamic measurements.
The response of ferrofluid flow to various configurations of a steady magnetic field is discussed in Reference [17]. The accumulation of ferrofluids, after it was attracted to the sidewall of a horizontal pipeline, is presented in References [18,19,20]; a similar accumulation of larger particles in a vertical pipeline is presented in Reference [21]. The pressure that the particles apply on the sidewall was not measured in those works, and the magnetic field was constant during the experiments.
In addition to the experimental investigations above, several numerical models were used to compute the attraction of particles in fluids [15,18,19,22,23,24]. These models did not include particle-particle interaction, and they were validated qualitatively, or not at all. A model that included particle-particle interaction is presented in Reference [21], but the in-phase magnetic interaction was not included.
Experimental and numerical studies described earlier did not report the measurement of pressure that magnetic particles apply on a sidewall, under the effect of a magnetic field. In addition, the behaviour of the particles near the sidewall in a pulsating magnetic field was not investigated. Therefore, those two subjects are investigated in the current study. To study the behaviour of the particles in a pulsating field an experiment was performed, and the pressure the particles applied on the sidewall during the experiment was measured. This study is intended to explain the dependence of the sidewall pressure on three primary parameters: the amount of the particles involved, their sizes, and the duty cycle of the pulsating magnetic field, at a given frequency in the study. The particles used for this study are the same particles as in Reference [7] (US5004, US Research Nanomaterials, Inc., Houston, TX, USA), and evaluated results from a simplified model are compared with recent experimental results.
2. Experimental
To focus on the behaviour of the particles in a pulsating electromagnetic field, the experiment was performed in a neutral system: a system that eliminates factors that could affect the particles, such as moving walls and induced flow. In the experiment, suspended particles were attracted to a sidewall using a pulsating magnetic field. The behaviour of the particles was qualitatively analysed using video records of (CamRecord 1000, Optronis, Kehl, Germany). In addition, the pressure that the particles applied on the sidewall during their attraction was measured, using an in-house piezoelectric pressure sensor.
2.1. Experimental Setup
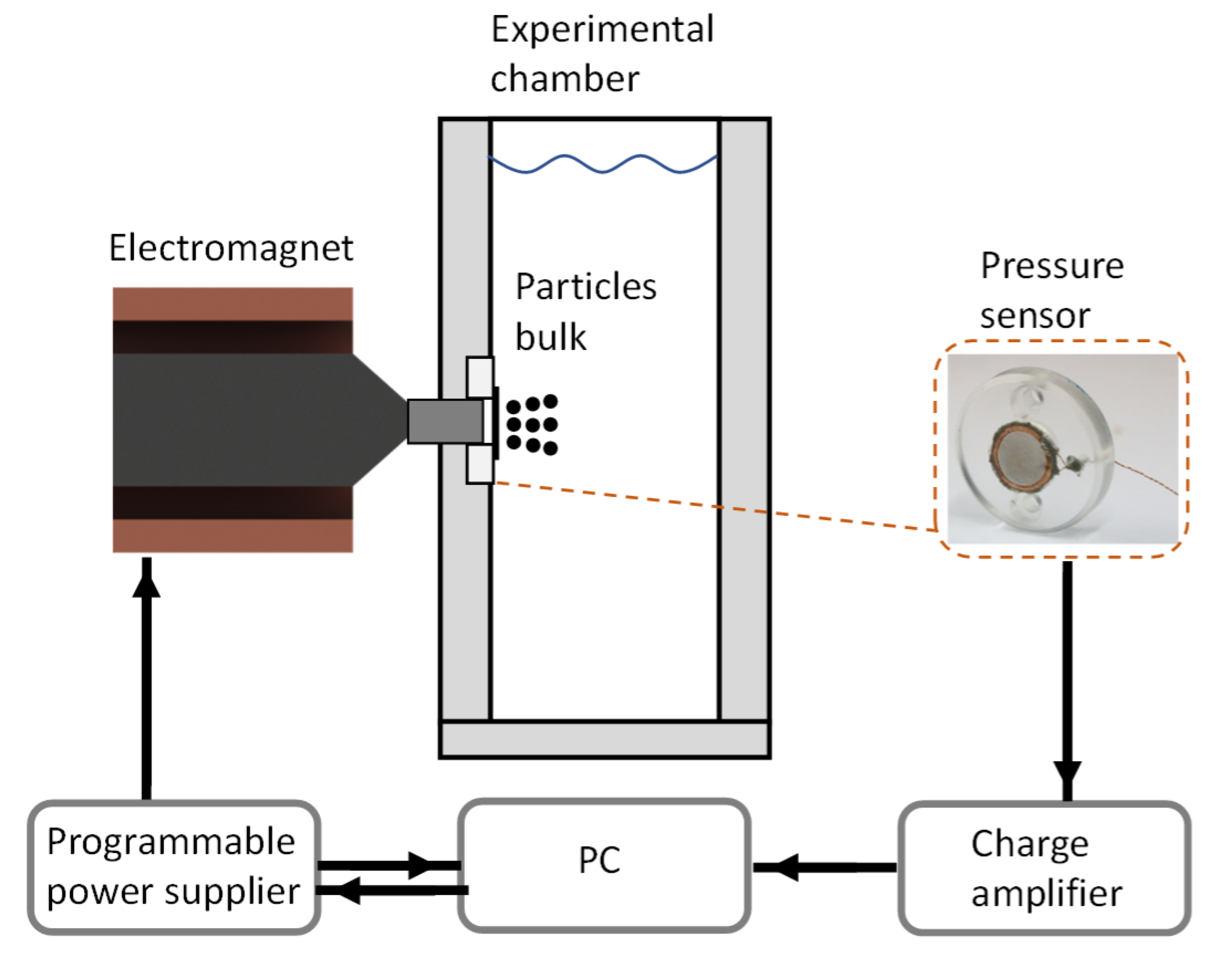
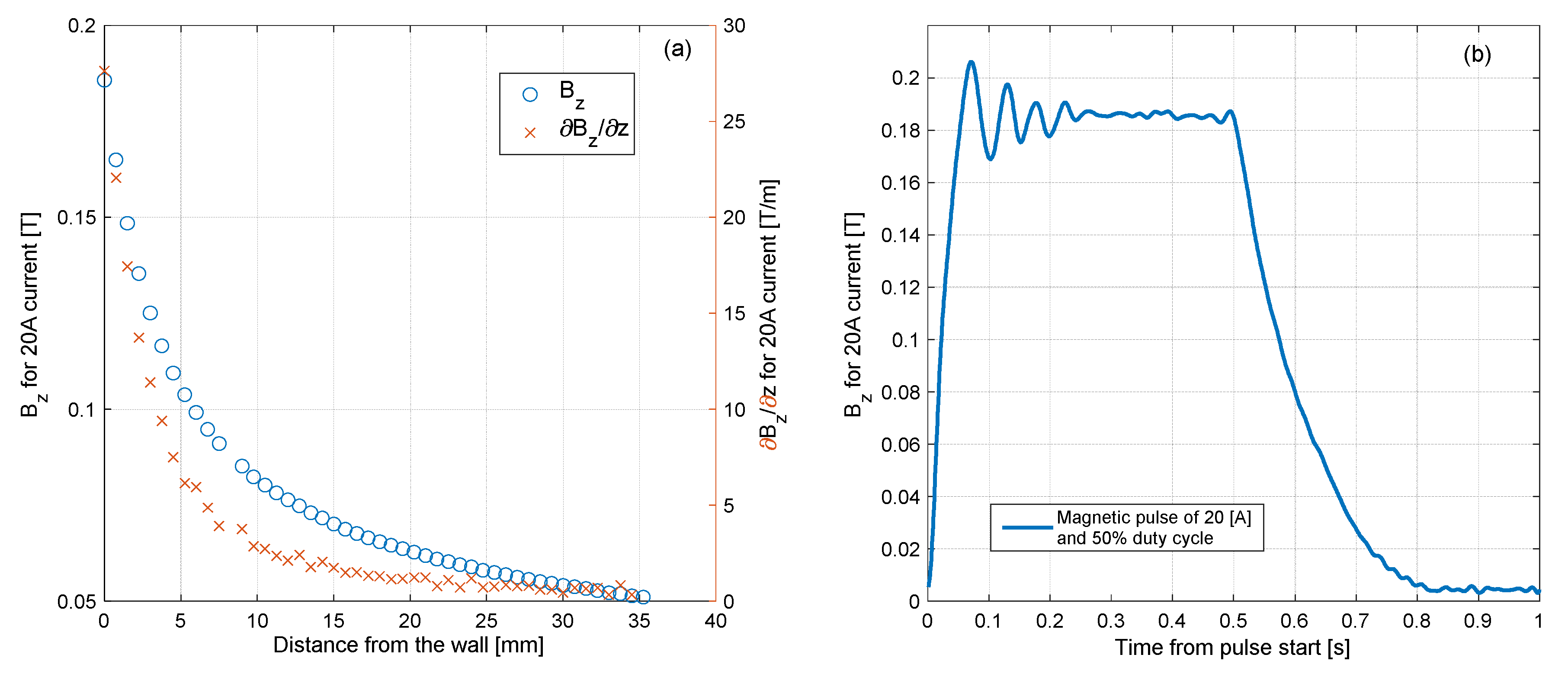
An illustration of the experimental system is presented in Figure 1. The primary part of the system is the experimental chamber, of internal dimensions . It contains acrylic glass windows from all sides to enable a clear video recording of the experiment. In one of the windows, a pressure sensor was inserted, from the bottom of the chamber. An electromagnet was positioned behind the sensor from outside of the chamber to attract the particles in the chamber toward the sensor. The electromagnet was contributed to this research after it was used in another work, of which its details are presented in Reference [7]. Briefly, it contains 900 windings on a permendur core of diameter, and the core ends with a tip of diameter, to increase the magnetic field and its gradient [25]. An iron cylindrical bar was inserted in the window, between the electromagnet and the sensor. The bar touches the tip from one side, and ends from the inner sidewall on the other side. This arrangement increases the magnetic field near the sidewall, especially where the sensor is located. The magnetic field in the experimental system, induced with current of , is presented in Figure 2; the magnetic field as a function of the distance from the sensor is presented in Figure 2a, and the time-varying magnetic field during a pulse is presented in Figure 2b. The time-varying magnetic field, as well as time-varying sidewall pressure presented in the following section, was processed with a low-pass filter with a cutoff frequency of (the frequency of the power grid).
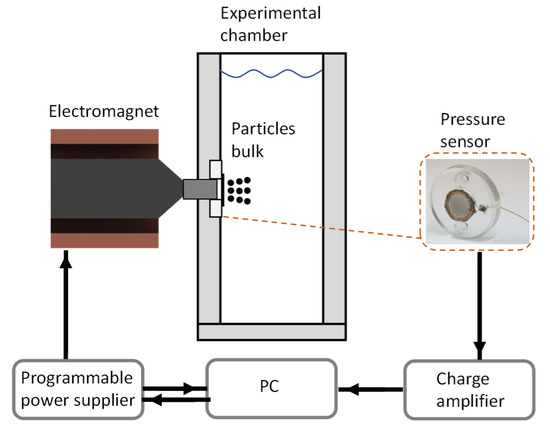
Figure 1.
Illustration of experimental system.
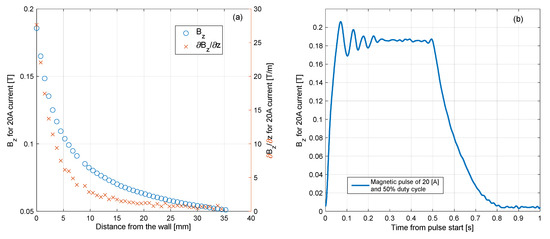
Figure 2.
Characterization of the electromagnetic field. (a)—Electromagnetic field and its gradient, against distance from the inner wall. (b)—The pulse of the electromagnetic field varies in time.
2.2. Electrical Instrumentation
The magnetic field in the current study was induced by an electromagnet, connected to a programmable DC power supply (Gen 60-25, TDK-Lambda, Karmiel, Israel) in the ‘current mode’, in which a voltage signal provided to the power supply controls the current. The provided signal was in the shape of pulses of a positive step function. The pulses were characterised by three parameters: the magnitude of the current, frequency, and duty cycle of the pulses. The duty cycle is the percentage of time in which the step function is positive and not zero. Those three parameters were controlled with a PC using a LabVIEW (National Instruments, Austin, TX, USA) application that was written for this purpose. The current in the electromagnet was indicated by the power supply and was read in the application.
To transform the electric charge from the piezoelectric sensor to a readable voltage signal, a charge amplifier (504D, Kistler, Winterthur, Switzerland) was used. It was operated in the ‘long’ mode, in which the charge amplifier performed as an integrator. The time constant of the amplifier in this mode was found to be sufficiently long for the quasi-static measurements in the study. The signal from the charge amplifier was also read in the LabVIEW application, which used a total amount of three channels. The data acquisition was performed with a rate of , using a PCI device (NI PCI-6035E, National Instruments, Austin, TX, USA).
2.3. The In-House Pressure Sensor
The pressure that the particles apply on a surface can be measured with a pressure sensor [26,27]. However, studies in which sidewall pressure was measured in a time-varying magnetic field were not found. A solution to eliminate the influence of the magnetic field on the measurement is presented in Reference [15], but it may not be suitable for the dynamic measurements of pressure. In addition to the magnetic field restriction, a geometrical restriction exists as well: the thickness of the pressure sensor must not exceed a few millimetres. Otherwise, the distance between the electromagnet and the particles would be large, and the magnetic field would not be sufficiently strong near the wall. Because of those considerations, an in-house pressure sensor was developed; it is thin, and not significantly affected by the magnetic field, as discussed below in Section 2.4.
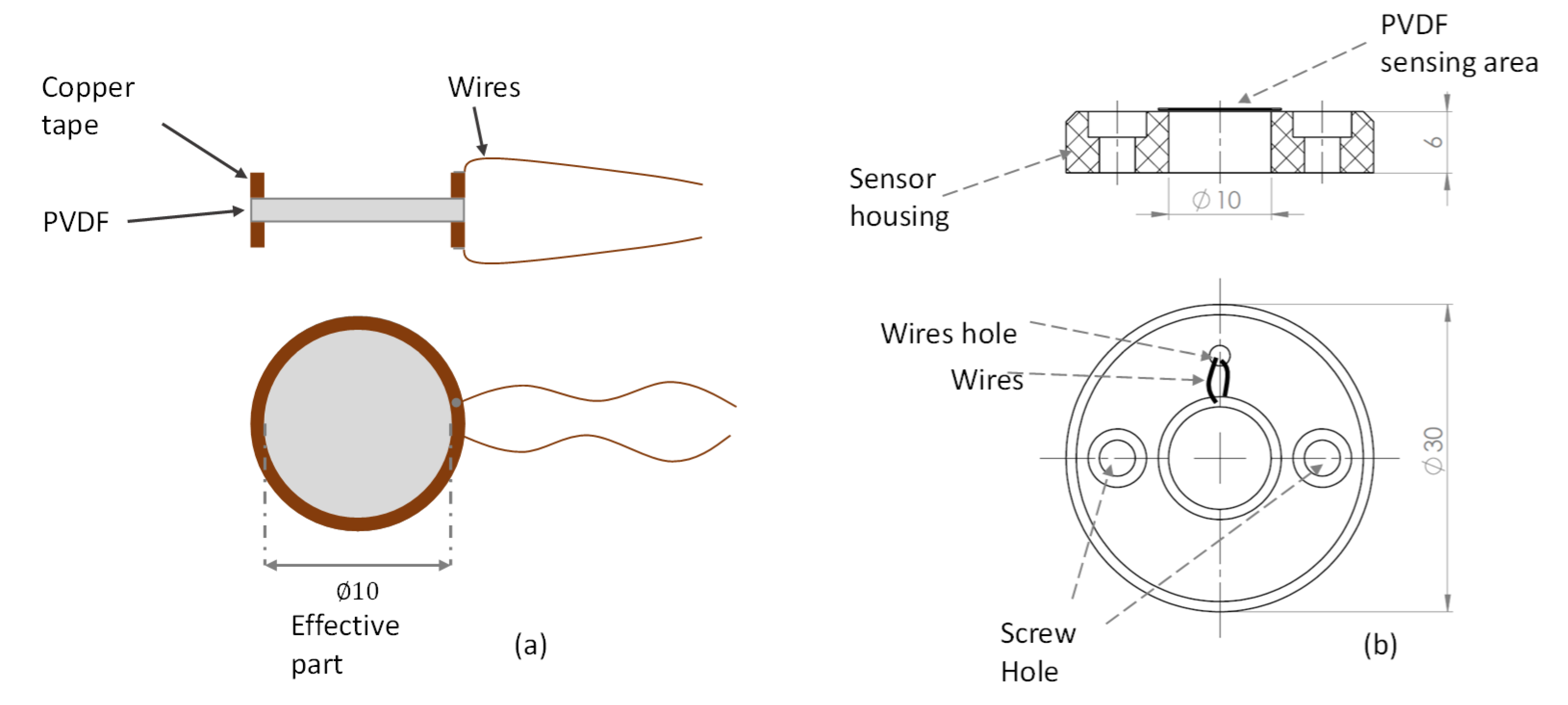
The active part of the sensor is a diaphragm that stretched when a relative pressure is applied to it; the diaphragm made from piezoelectric polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) film of (1-1003702-7, Measurement Specialties Inc., Berwyn, PA, USA). Wired ringed-shape copper tape was glued on each side of the PVDF using a conductive adhesive (see Figure 3a). It is noteworthy that the thickness shown in the figure is out of proportion, so it can be noticed easily in the scheme. The wired PVDF unit was glued with epoxy to a solid back, which was the sensor housing. A hole of diameter was made in the middle of the housing such that the PVDF could be deformed when pressure was applied. The sensor had to be protected completely from water leaks. Therefore, the window where the sensor was inserted was covered with nylon. Prior to that, silicone grease was smeared on the PVDF to prevent an air gap between the PVDF and nylon.
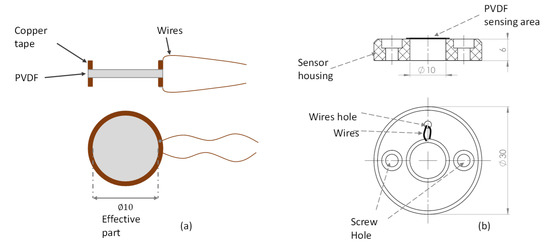
Figure 3.
The in-house pressure sensor. (a) Illustration of the wired polyvinylidene fluoride PVDF unit; (b) drawing of the sensor and the housing.
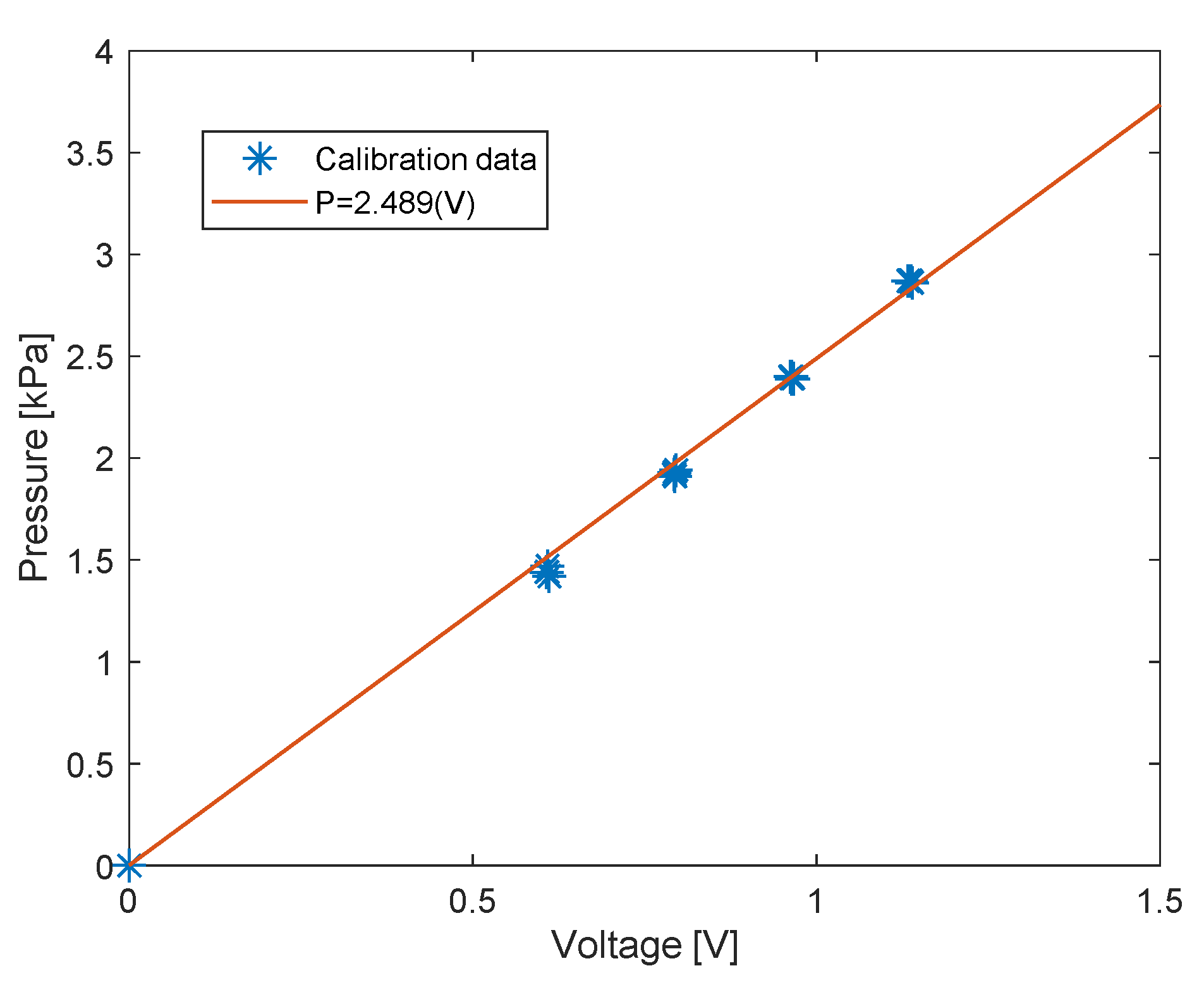
The sensor was calibrated in the experimental chamber using increasing hydrostatic pressure. Initially, the chamber was filled with water to the same height as in the experiment. Subsequently, the pressure in the chamber was increased to a desired level, each time from the same initial pressure. The duration until the pressure reached the desired level was approximately . The pressure increase was measured with a pressure calibrator (Presscal Pressure Calibrator PC105, Beamex, Pietarsaari, Finland), and compared with the signal difference from the charge amplifier. The calibration was performed after every replacement of the nylon cover. A typical calibration curve is presented in Figure 4.
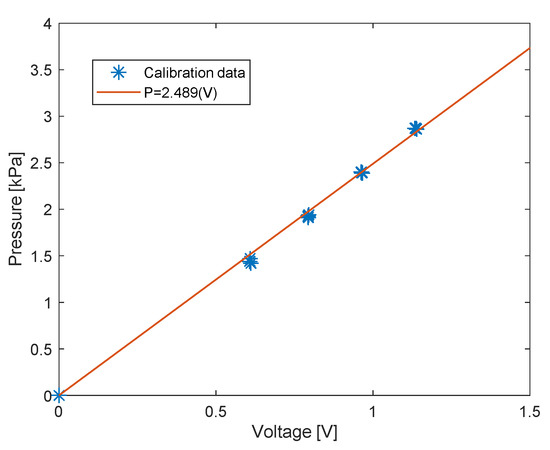
Figure 4.
Calibration results with linear fitting.
2.4. Measurement Errors
The sensor exhibits three types of measurement errors. The significant one is the calibration error, defined as a linearity-repeatability error. It is the maximum absolute error between the calibration measurements and the linear curve. The largest calibration error is , which is of the full-scale output. The second error is the influence of the magnetic field. To evaluate this error, a magnetic pulse was applied on the sensor while the hydrostatic pressure was maintained constant. The largest influence of the magnetic field on the sensor was equivalent to a pressure of . The third error is drifting, meaning that the measured signal from the charge amplifier was drifting slowly to saturation, even when the pressure was constant. The drifting was measured over a long duration while no additional pressure was applied on the sensor, and it was linear in general. The error was calculated as the drift per measurement time in the experiment, and the largest value was equivalent to a pressure of .
2.5. Preparation of Particle Suspension
The particles used in the current experiment were iron carbonyl powder, of diameters and (US5004, US Research Nanomaterials, Inc.), as in Reference [7]. The particles were weighted to the desired amount in test tubes. Each test tube with particles was filled with of phosphate-buffered saline solution and subsequently mixed to create a suspension. The suspension was drawn with a syringe, and was subsequently ready to be injected into the experimental chamber. The syringes used were ones, with a needle.
2.6. Experimental Method
The experiment was performed with different amounts of suspended particles (. The experimental procedure was as follows: the suspensions were injected into the experimental chamber from a distance of 1–2 cm from the centre of the pressure sensor; during the injection, the electromagnetic field was maintained steady using a current to attract the particles in the required location. Subsequently, pulses were applied using a positive step function of ; The first pulses were with duty cycle, and then the duty cycle was gradually reduced by every pulses. Before every injection, the experimental chamber was cleaned to remove the old particles.
During the preparation of the particles to injection, some particles were not drawn or stuck in the syringe, and therefore were lost and not injected. For consistency, all the results of the experiment were referred to by the initial amount of particles that were weighted instead of the injected amount of the particles.
3. Results and Discussions
The general behaviour of the particles was investigated using video records of the experiment, which is separated into three stages. The first stage is when the particles are in the presence of a steady magnetic field. The behaviour of the particles in this stage is compared with particles from previous works. The second and third stages are when the field is turned off and on, similar to a pulsating field.
Along with the qualitative investigation, the pressure that the particles apply on the sidewall was measured during the pulses. The measurements were used to investigate the influence of three parameters on the sidewall pressure: the amount of the particles, duty cycle, and size of the particles.
3.1. Behaviour of Particles in Steady Magnetic Field
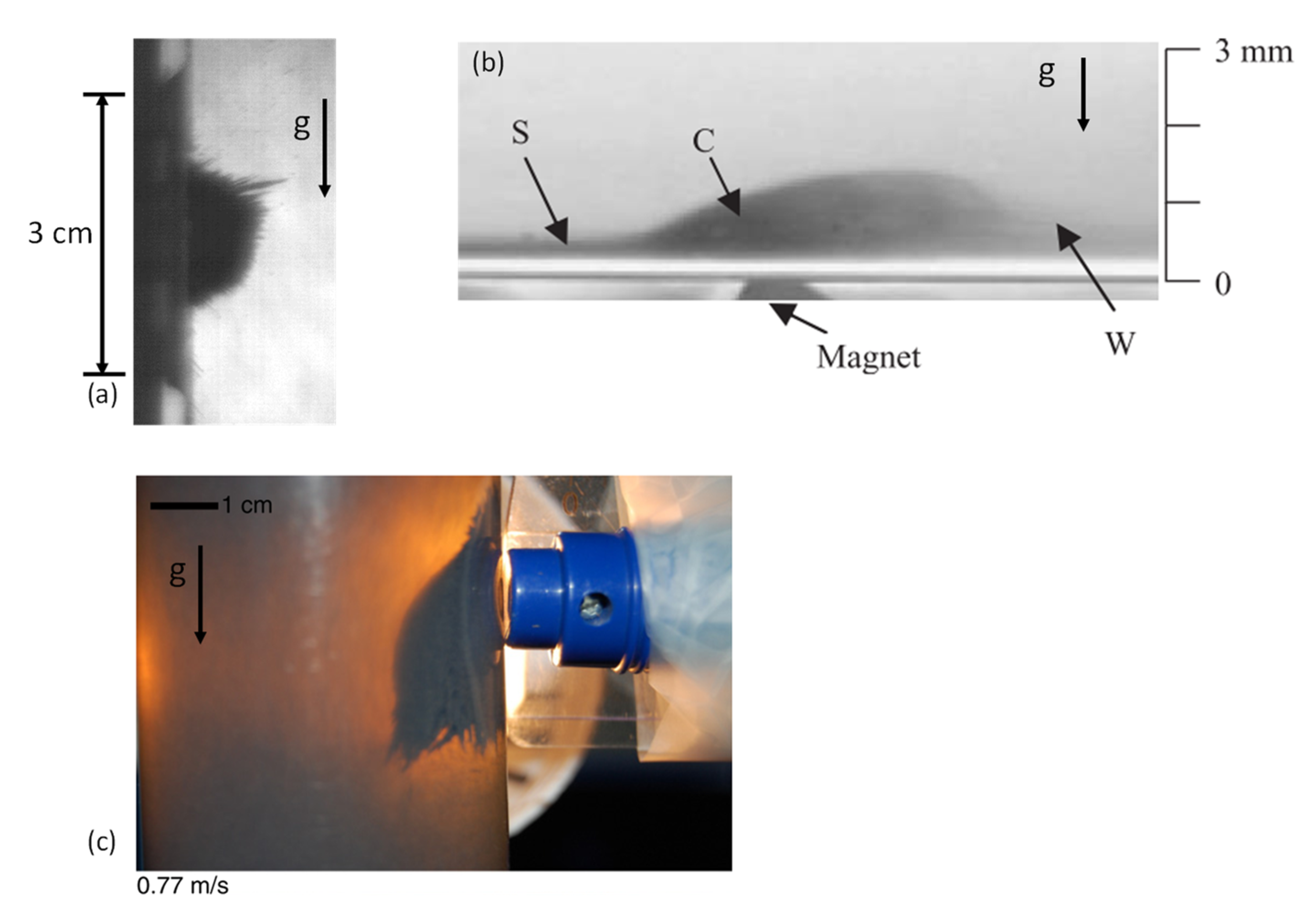
When the particles in the experiment were subjected to a magnetic field, they no longer behaved as a suspension of powder. Instead, the particles created long structures, which will be referred to as chains (see Figure 5a). This behaviour is unlike to that reported by Ganguly [18,19,20], in which chains were not created in the core region (marked as C in Figure 5c). The absence of the chains in References [18,19,20] is due to the small size of the coated particles used (). The chain structures were observed in the results of Balakin [21] for particles with an average size of (see Figure 5b). The chains that occur are due to the dominant particle–particle interaction. This interaction is both magnetic and mechanical: the particles are attracted to each other owing to magnetic force; in addition, the particles induce mechanical friction when they are in contact with other particles. The friction could explain how the chains are held horizontally, despite the gravity/buoyancy force. The chains in the current study do not break because the shear stress is not sufficiently strong, owing to the absence of flow [28,29]. The relation between the particle–particle attraction and the friction force can be explained by the static friction model, based on Amontons–Coulomb friction low:
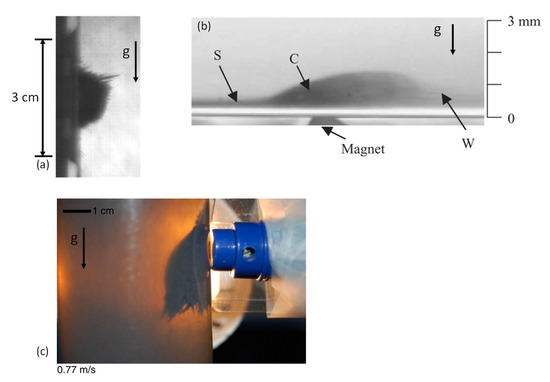
Figure 5.
Observation of bulk of particles. (a)—Particles in the present work. (b)—Experiment from Reference [18]. (c)—Experiment from Reference [21].
Here, is the friction coefficient for the particles, and is the normal force between the particles. The normal force depends on the magnetic attraction of the particles, and it is stronger when closer to the sidewall.
3.2. Behaviour of Particles in a Pulsating Electromagnetic Field
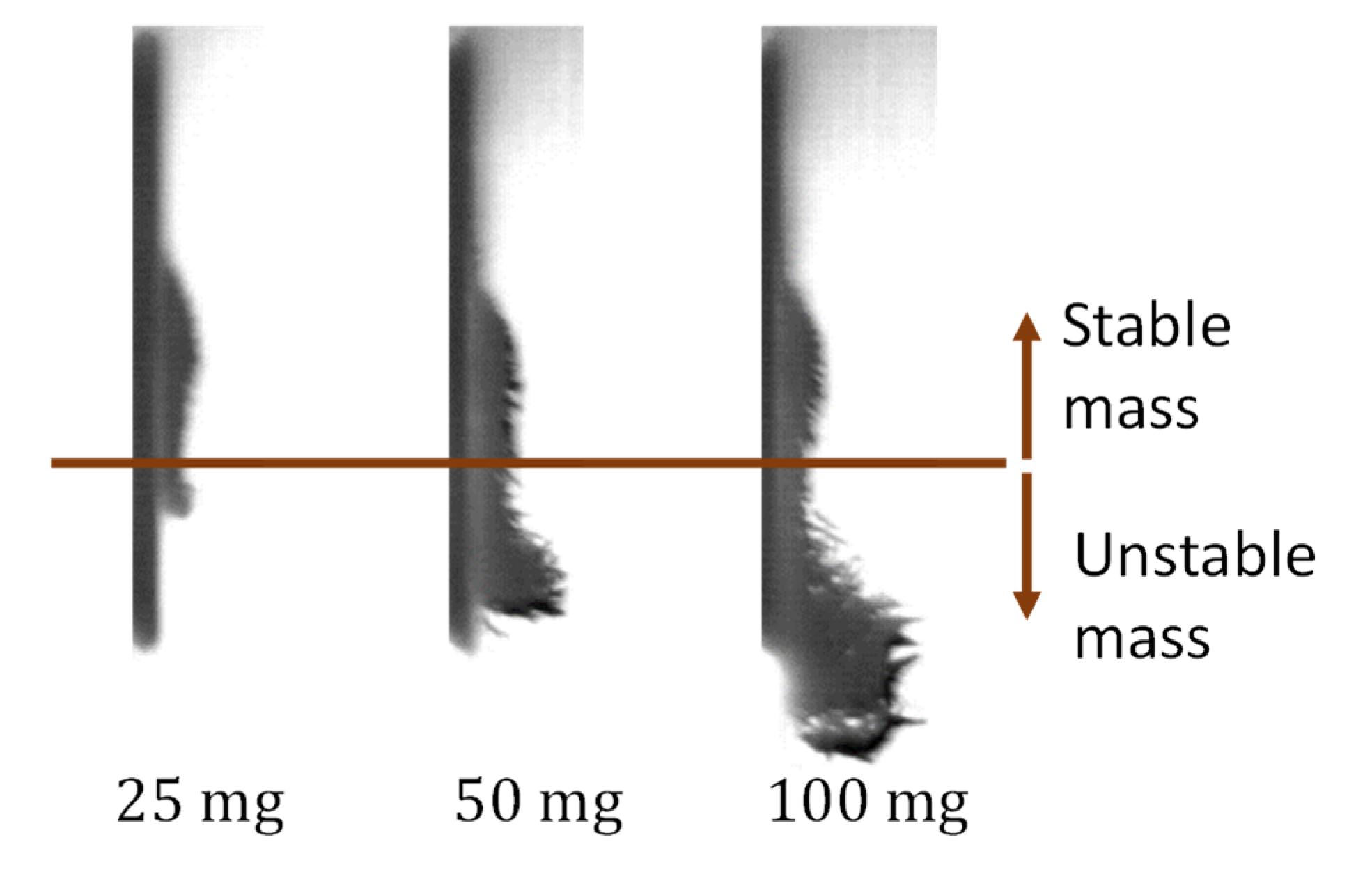
The part in which the magnetic field was turned off was not included in previous studies; in the current study, it occurs between pulses. In the absence of a magnetic field, the particles are expected to detach from the wall and settle. The final position of three settled bulks of particles with different amounts is presented in Figure 6, after the field was turned off, immediately before it was turned on again. It appears that part of each bulk did not settle and remained attached to the wall. The part that did not settle is referred to as “stable mass,” and the part that settled as “unstable mass.”
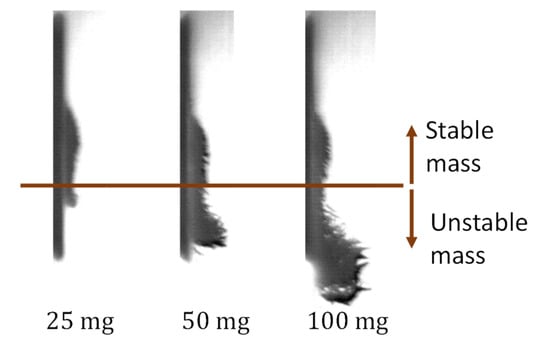
Figure 6.
Bulk of particles of three amounts, after the field is turned off for 0.5 s.
The stable mass did not settle because it was held by the residual magnetic field of both the core of the electromagnet and the particles; measurements of the magnetic field, presented in Figure 2b, shows that the electromagnet has remanence of ; as can be seen in Figure 6, settling particles were maintained in structures even when they were far from the electromagnet due to their own hysteresis. Because of the hysteresis, the particles in the stable mass were still attracted to the core of the electromagnet and to each other, even while the current was turned off. The size of the stable mass depends on the location where the magnetic force is too weak and the friction could not hold any more particles. Because the stable mass depends completely on the hysteresis, it does not depend on the initial amount of the particles. Hence, the stable mass should be the same for all the amounts, as long as the initial injected amount is greater than that of the stable mass. This statement was tested in the experiment when the duty cycle of the electromagnetic field was gradually reduced from to . The results are discussed in detail hereinafter.
Figure 6 shows that the greater the amount of the particles, the farther that the unstable mass settles; this observation is attributable to the cluster behaviour of the unstable mass in a viscous medium. The normalised gravity/buoyancy force, per amount of particles, is equal for all the amounts. However, the larger amounts create larger clusters, on which the normalised drag force is weaker. Therefore, in the balance between the gravity/buoyancy force and drag force, the drag force becomes less dominant in larger clusters. Hence, the larger unstable mass settles faster.
When the electromagnetic field was turned on again, the unstable mass was attracted to the electromagnet. The bulks of and , after they were collected again, are presented in Figure 7. The shape of the bulk after the attraction was not symmetrical, and the particles tended to aggregate below the stable mass. This is reasonable because at a lower position the magnetic force comprises a larger vertical component. When the amount of the particles was higher, more particles aggregated at the lower position, and therefore did not apply pressure on the required location. Hence, the sidewall pressure is assumed to have an asymptote, limiting the possible pressure for the given electromagnetic field. That assumption was tested with results from subsequent experiments.

Figure 7.
Shapes of two bulks after they were attracted again.
3.3. Pressure Measurements
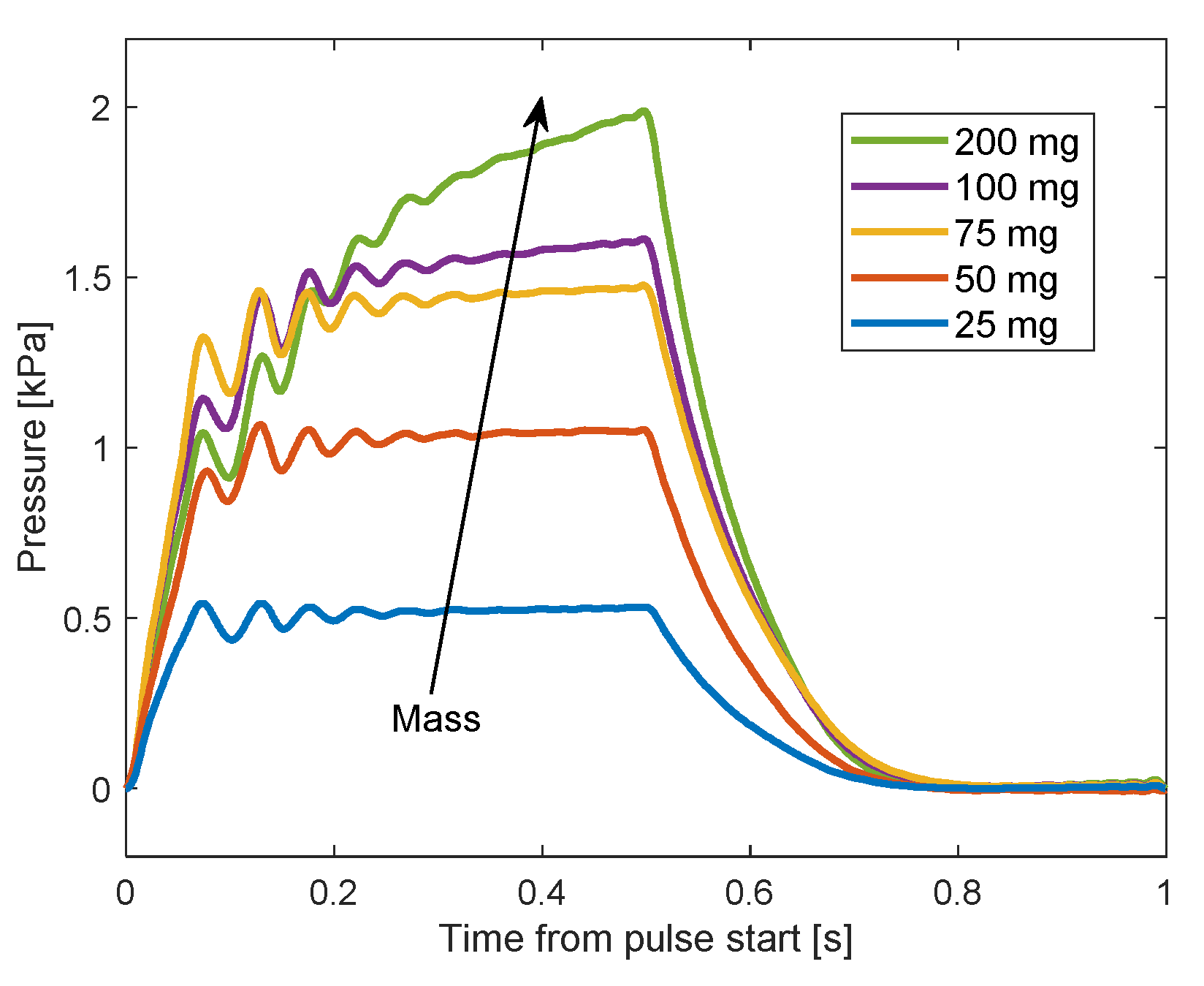
The sidewall pressure applied by the particles was measured during the experiment. Five different amounts of particles were used to investigate the influence of the amount on the sidewall pressure, during pulses of duty cycle. The influence of the duty cycle was investigated with a series of pulses with reduced duty. Finally, the influence of the particle size on the sidewall pressure was investigated by comparing the results of the particles with similar results of particles. The typical measured sidewall pressure during one pulse of duty cycle is presented in Figure 8 for five amounts of particles. Each value of the sidewall pressure is relative to the value at the beginning of the pulse. For all the amounts, but mostly in and cases, the sidewall pressure when the electromagnetic field is turned on can exhibit a response to a step function rather than an impulse function. Hence, it can be concluded that the effect of the particles’ impact is neglected compared to the magnetic force. One reason for the weak impact effect is that the particles were not attracted as a bulk, i.e., as one unit, with one large mass. Instead, they were attracted as groups that contain a small amount of particles. That is because particles closer to the core experienced a stronger magnetic field and therefore attracted faster than farther particles. In addition, the particles were affected by the drag force from the interaction with the fluid, reducing their speed the therefore their impact.
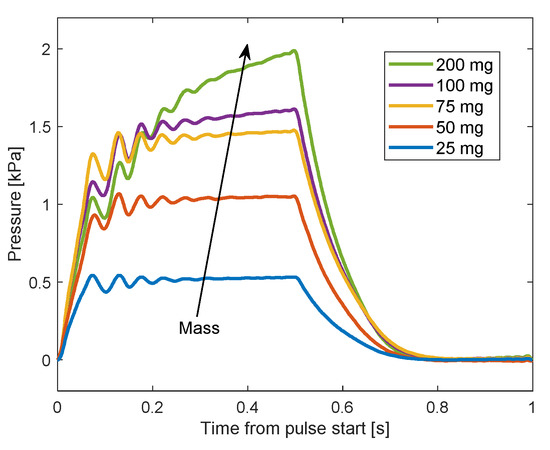
Figure 8.
Pressure results during one pulse for different amounts.
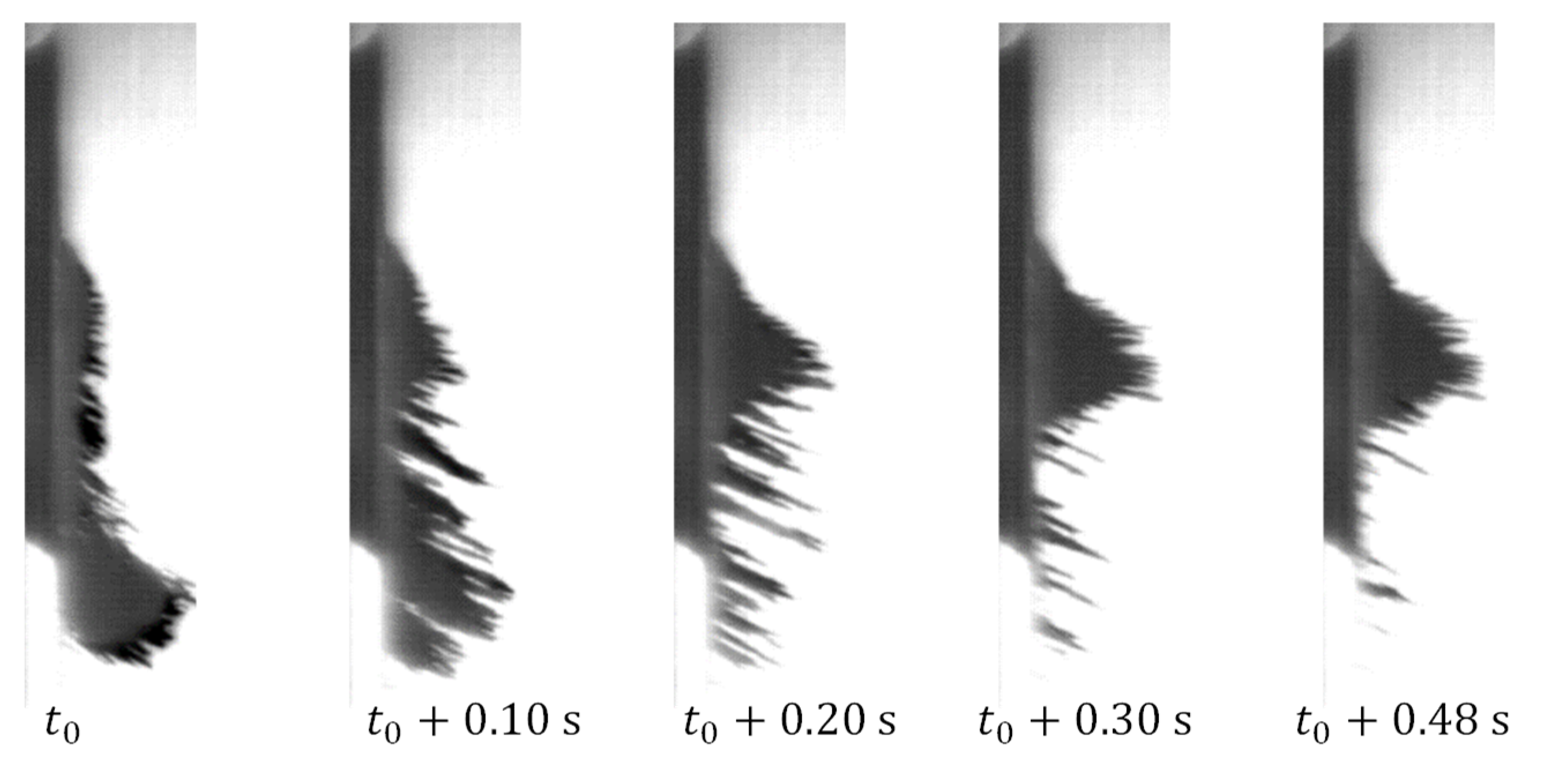
It also appears in Figure 8 that the maximal pressure in , and cases was achieved after , which is also the peak time of the electromagnetic field (the time between the beginning and the first peak). In these cases, all or most of the particles were collected near the transducer before the peak time of the electromagnetic field. In the cases of and , the sidewall pressure continued to increase after the rise of until the electromagnetic field was turned off. The reason for that can be seen in Figure 9 for the case. A significant amount of particles were still collected to the transducer after , while some of the particles were not collected during the whole magnetic pulse. These measurements of the pressure during one pulse support a previous analysis in that larger amounts of particles settle farther away.
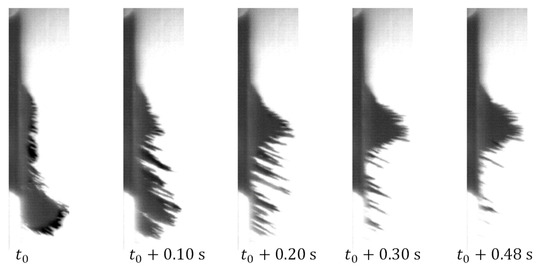
Figure 9.
The evolution of a bulk of during pulse of duty cycle.
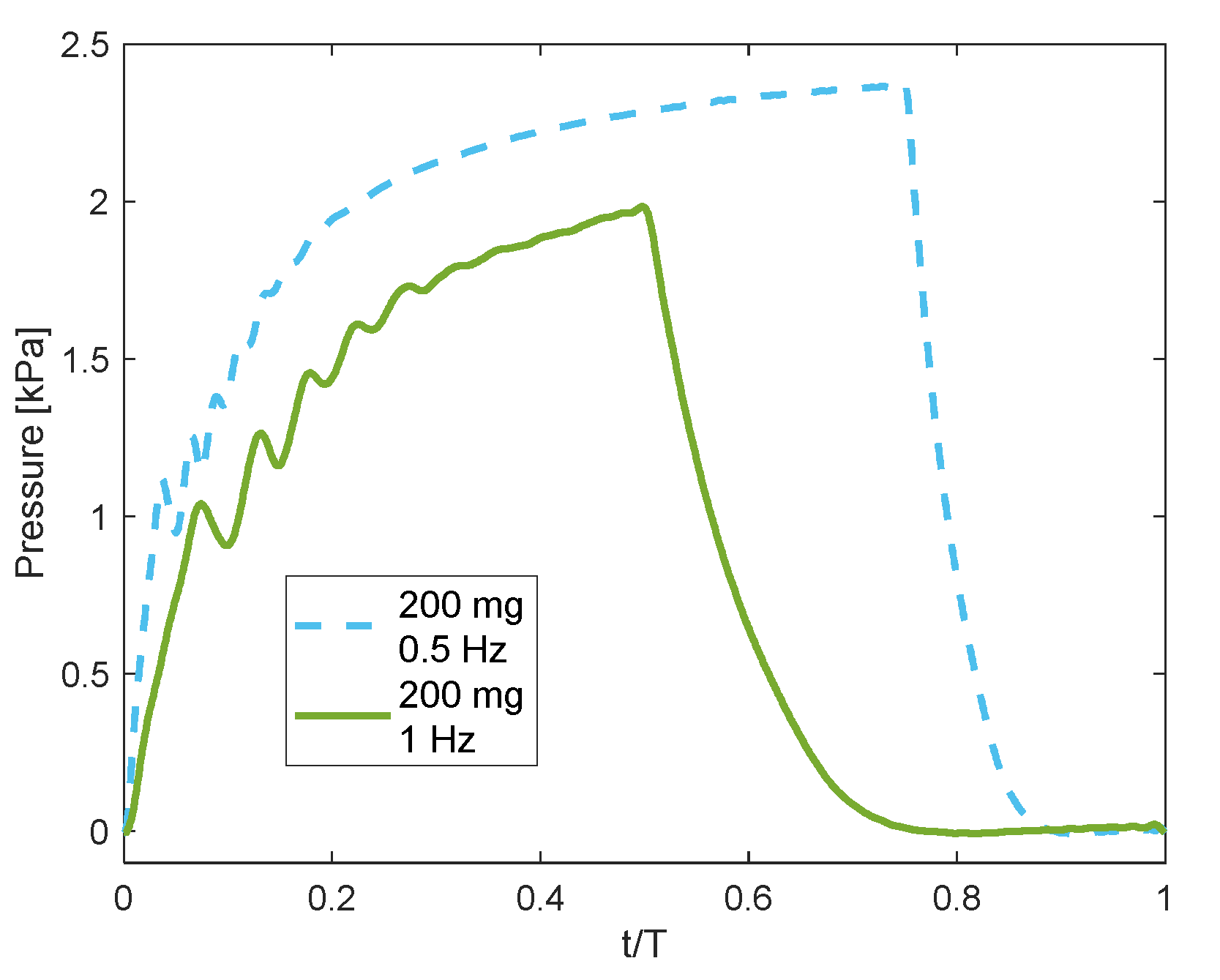
For the amounts of and , a longer time in which the electromagnetic field is turned on is required to collect more particles and achieve steady pressure. Figure 10 shows the recorded pressures for two pulses; the first is pulse with duty cycle, and the second is with duty cycle; hence, for the two cases the electromagnetic turn-off time was the same. In this figure, the time, the horizontal axis, is normalised by the time period of the pulse. It appears that the pressure resulted from the pulse increased until , and reached a maximum value higher by about than that resulted from the pulse. The reason for that is the attraction of more particles when the 0 pulse was used. The pressure did not reach a constant value since not all the available particles were collected until .
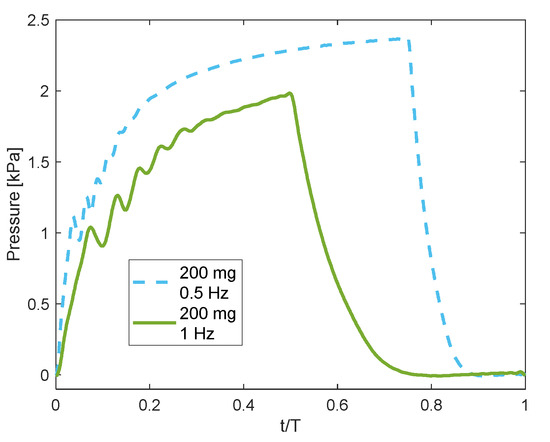
Figure 10.
Pressure results during two shapes of pulses for the amount of 200 mg of particles.
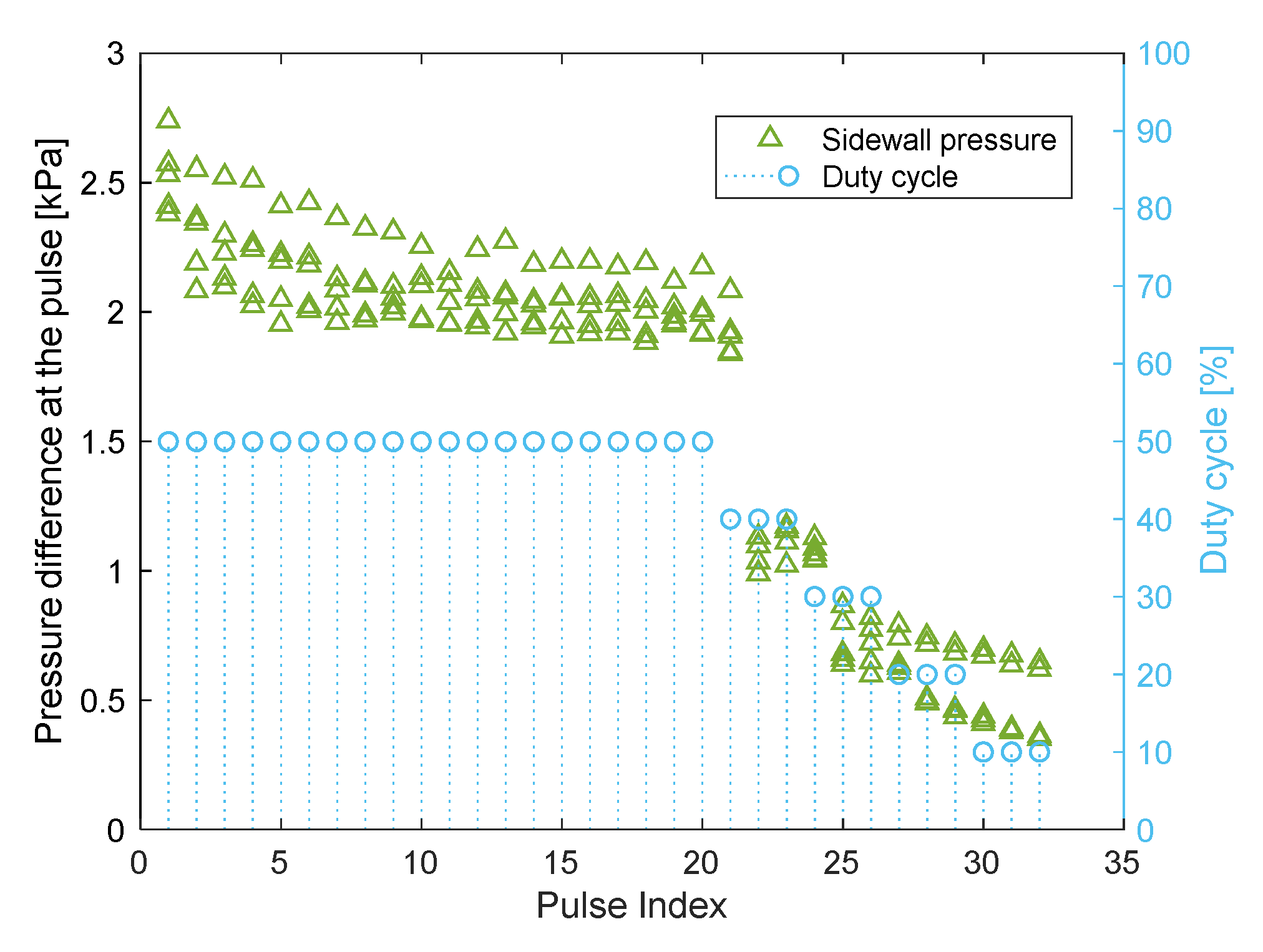
To enable a comparison between the sidewall pressure measurements of different amounts, the results in this section are referred to the maximum pressure difference at the pulses. It is the difference between the maximum pressure at the pulse, and the pressure at the beginning of the pulse. Typical results of the sidewall pressure are presented in Figure 11, for five measurements of . The horizontal axis is the chronological number of the pulse, the left axis is the maximum pressure difference in each pulse, and the right axis is the duty in the pulse. Between the first and the twentieth pulses, which is the last pulse of the duty, the sidewall pressure converges. That is because at the first pulses the bulk is dependent on the position and rate of the injection. Subsequently, when the pulses were continued, the particles arranged themselves in a repeatable form. The forms are referred to as “undeveloped forms” and “developed forms,” analogous to undeveloped and developed flow in piping. Additionally, dispersion occurred between the pressures, even in the pulses of developed forms. It is assumed to have occurred because of the actual amount of the particles that was successfully injected, which was slightly different at each time.
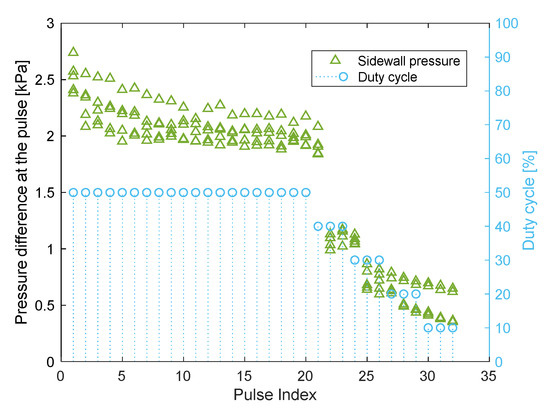
Figure 11.
Maximum pressure difference at each pulse, for five measurements of
.
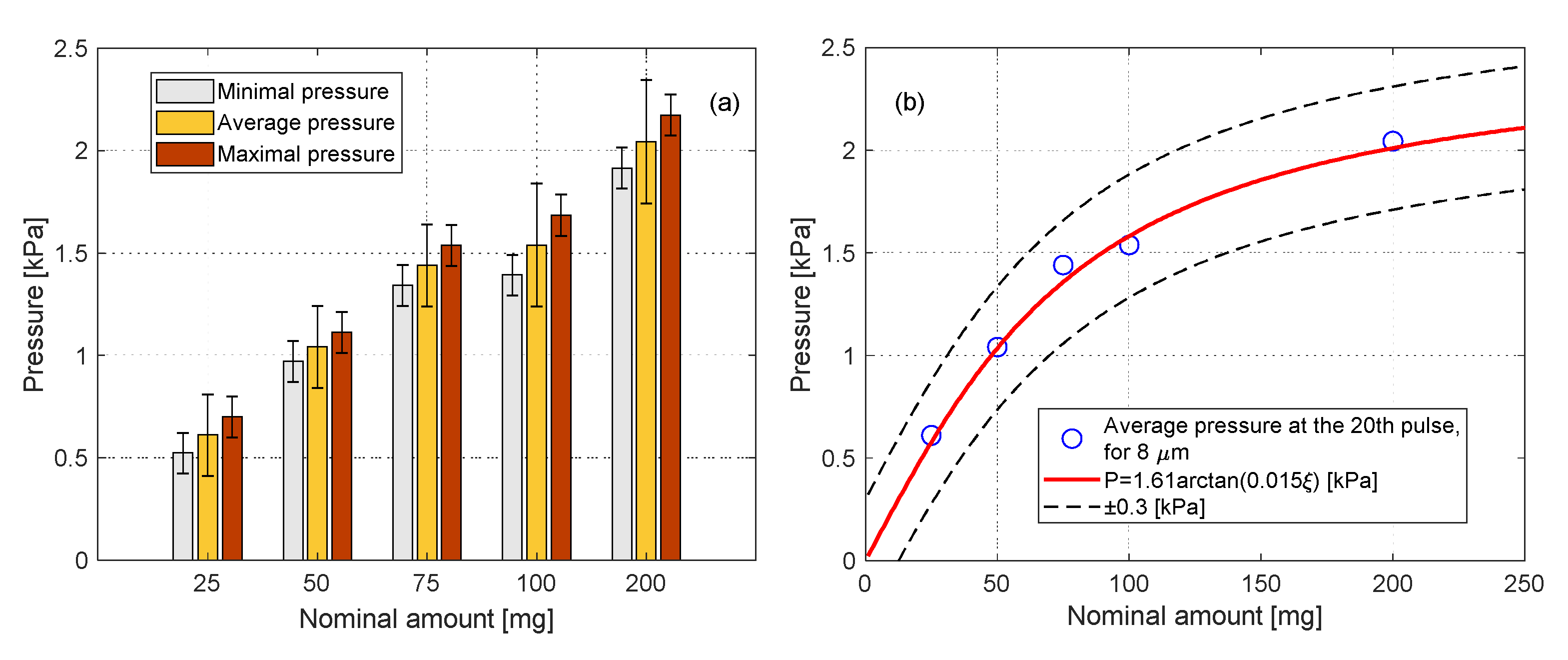
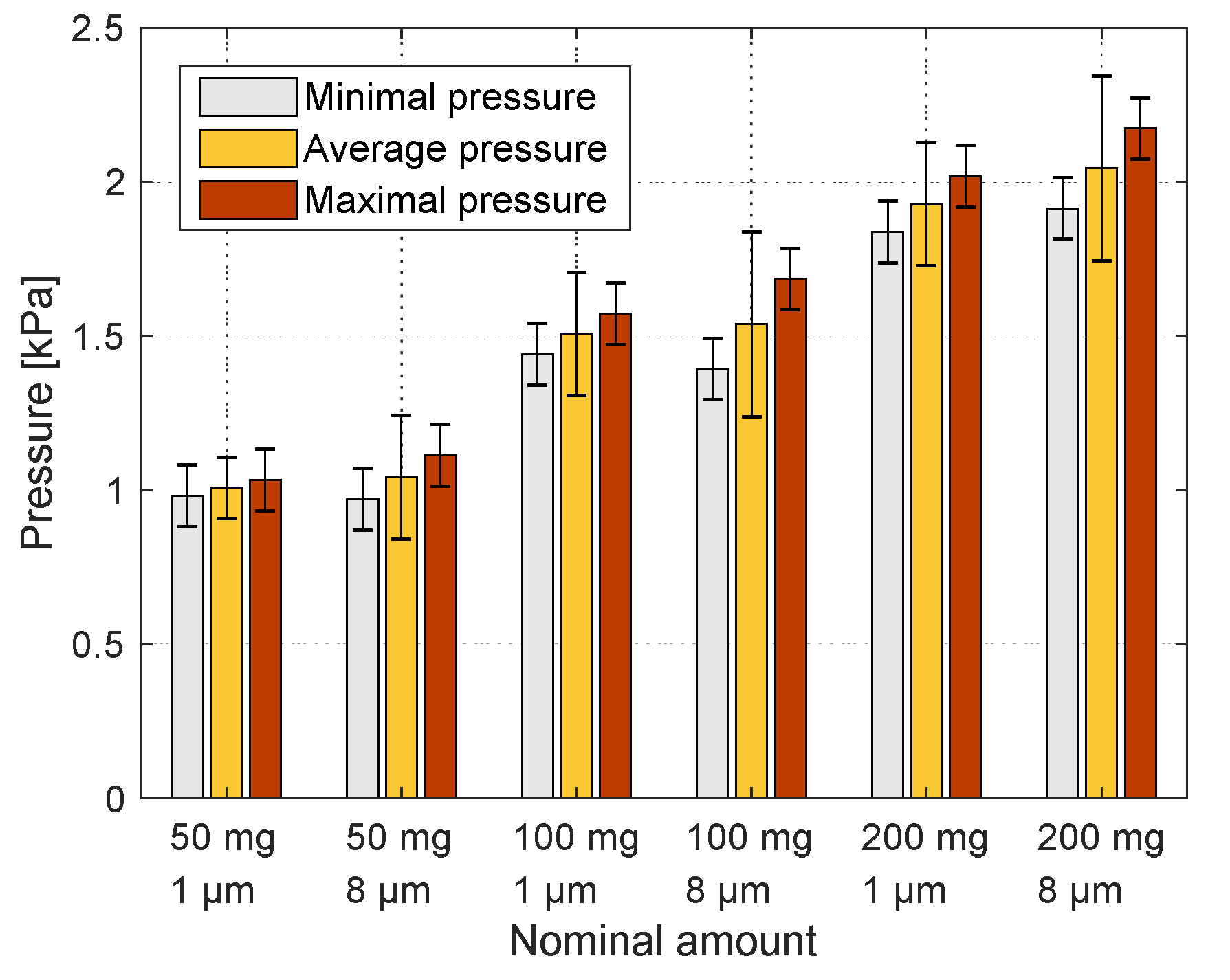
Because of the development of the forms during the pulses, the sidewall pressure at the 20th pulse is considered as the most accurate sidewall pressure that the injected amount of particles applies. The results of the sidewall pressure at the 20th pulse are summarized in Figure 12a, for all five amounts of . The results include the minimum, maximum, and average pressure at the pulse, for each amount. A correlation was fitted with the average sidewall pressures:
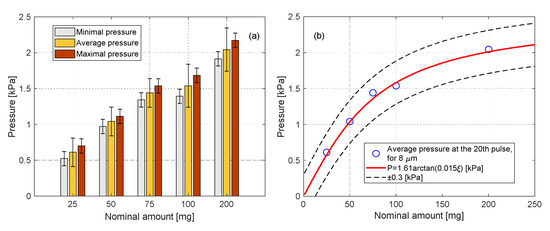
Figure 12.
Results of the maximum pressure difference at the 20th pulse, for different amounts. (a)—Min, Average and Max of each set of measurements. (b)—The average of each set of measurements, with a correlation.
Here, is the amount of the particles, and it varies in the range 25–200 mg. The agreement of the correlation to the results is presented in Figure 12b. The horizontal axis is the nominal amount of the particles, and the vertical axis is the average sidewall pressure at the 20th pulse for a given amount. The fitting suggests that asymptotic sidewall pressure exists, although that pressure was not achieved experimentally. By the correlation, the maximum sidewall pressure is .
The experimental results of the sidewall pressure are compared with a simplified model, which was also used in Reference [7]:
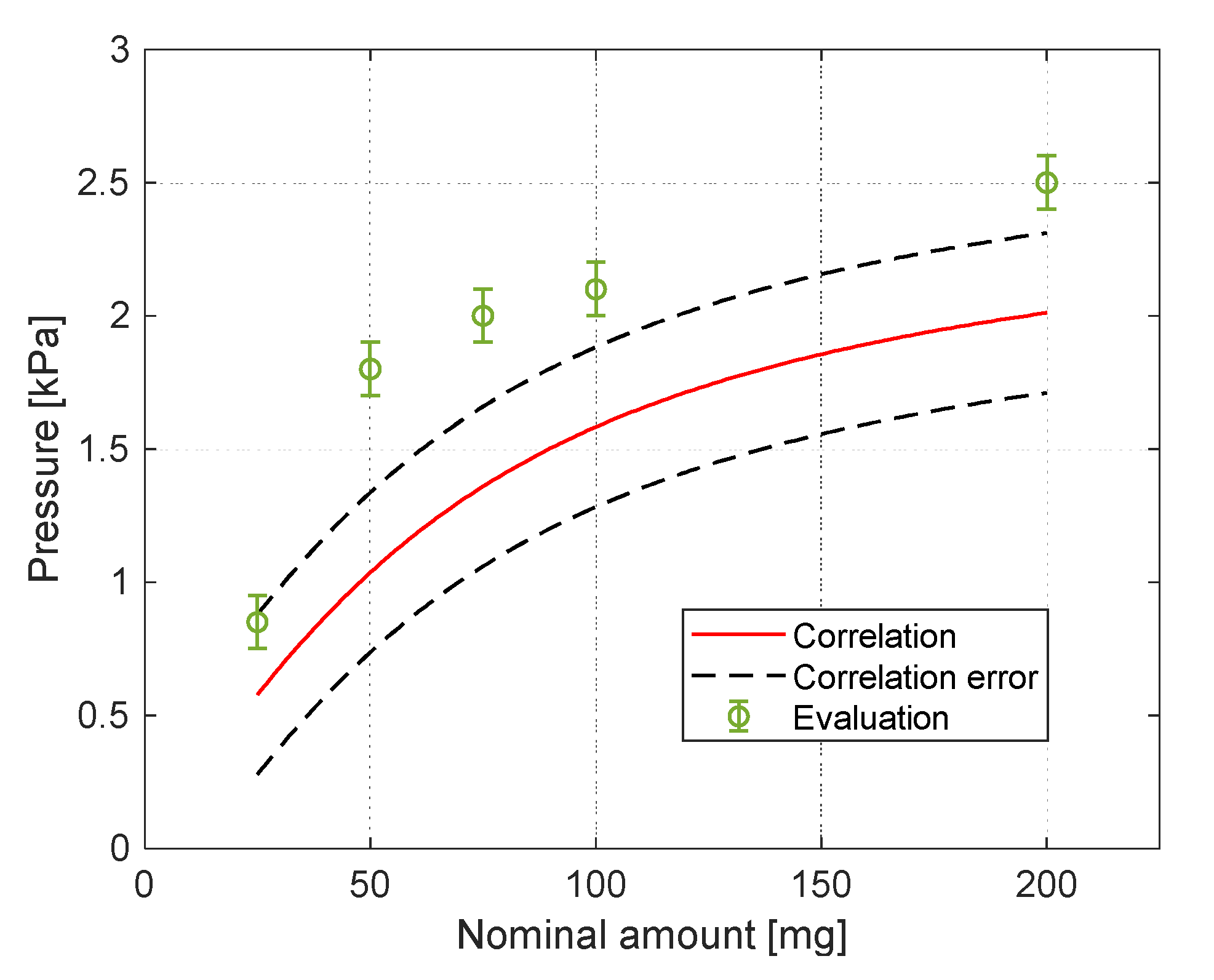
Here, is the magnetic force on the aggregation, perpendicular to the sidewall, is the volume of the spherical aggregation, is the apparent density, and is the magnetization of the aggregation. In the current study, the values of the above parameters are , , and . As can be seen in Figure 7, the aggregation cannot be described as a sphere, as assumed in Reference [7]. Considering an area of a spherical aggregation would yield errors of more than an order. Instead, the area of the aggregations was evaluated using photo analysis under an assumption of a hemispherical aggregation. The values for the amounts of and were interpolated/extrapolated. A comparison between the estimated (Equations (3) and (4)) and the experimental sidewall pressure is presented in Figure 13 and shows good enough agreement between them. A reason for the difference between the measured and evaluated sidewall pressure is the behaviour of the particles [15]. Due to the formation of long and dispersed chains of particles under the influence of the magnetic field and drag force, not all the particles experience the same magnetic field and its gradient.
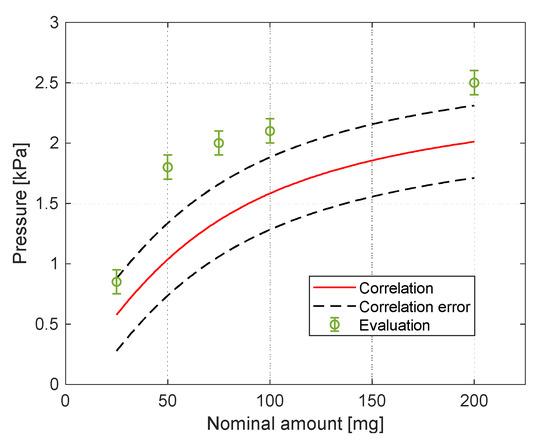
Figure 13.
Comparison between the modelled and experimental pressure.
To investigate the influence of the duty cycle on the sidewall pressure, the duty cycle was reduced gradually from to during the pulses 20–32. The reduced duty cycle implies the increased duration of the field being turned off. As the duty cycle was reduced, the unstable masses settled lower and could not be collected again when the field was turned on. As a consequence of the loss of the particles, the measured sidewall pressure was reduced. The results of the sidewall pressure measurements during the reduction in the duty cycle are presented in Figure 14 for the 5 amounts of particles. The horizontal axis is the chronological number of the pulse (as in Figure 11), and the vertical axis is the maximum pressure difference in the pulse; the beginning is with the 19th pulse to focus on the pulses in which the duty cycle was reduced; each black marker refers to another amount of particles and includes the multiple repetitions for the amount. The colored and marked trend lines show how the average sidewall pressure of each amount changes with the reduction of the duty cycle. It appears that three pulses for each duty cycle may be insufficient to achieve the developed form and repeatable sidewall pressure; therefore, the discussed results are only of duty cycle reduction from (the developed form) to . A significant decrease in the measured pressure occurred only at the 22nd pulse, instead of at the 21st pulse. The reason is that the 22nd pulse is the first one that occurs after the field was turned off; therefore, before that pulse, a critical mass settled far away. The decrease in the sidewall pressure during the 22nd pulse was higher for larger initial amounts of particles, supporting the previous discussion in that larger unstable masses settle faster. It was also discussed that the stable mass should be the same regardless of the initial amount of the particles. While the duty cycle was reduced to , most of the particles were settled and not attracted again. Hence, the particles at the final pulse can be regarded as the “stable mass.” It appears that the final sidewall pressure at the 32nd pulse is almost the same for all the amounts of particles. Hence, it can be concluded that the stable mass is indeed not dependent on the initial amount of the particles.
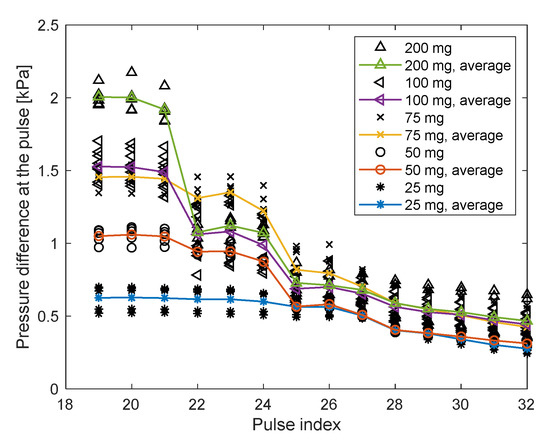
Figure 14.
Maximum pressure at the pulses while reducing the duty cycle.
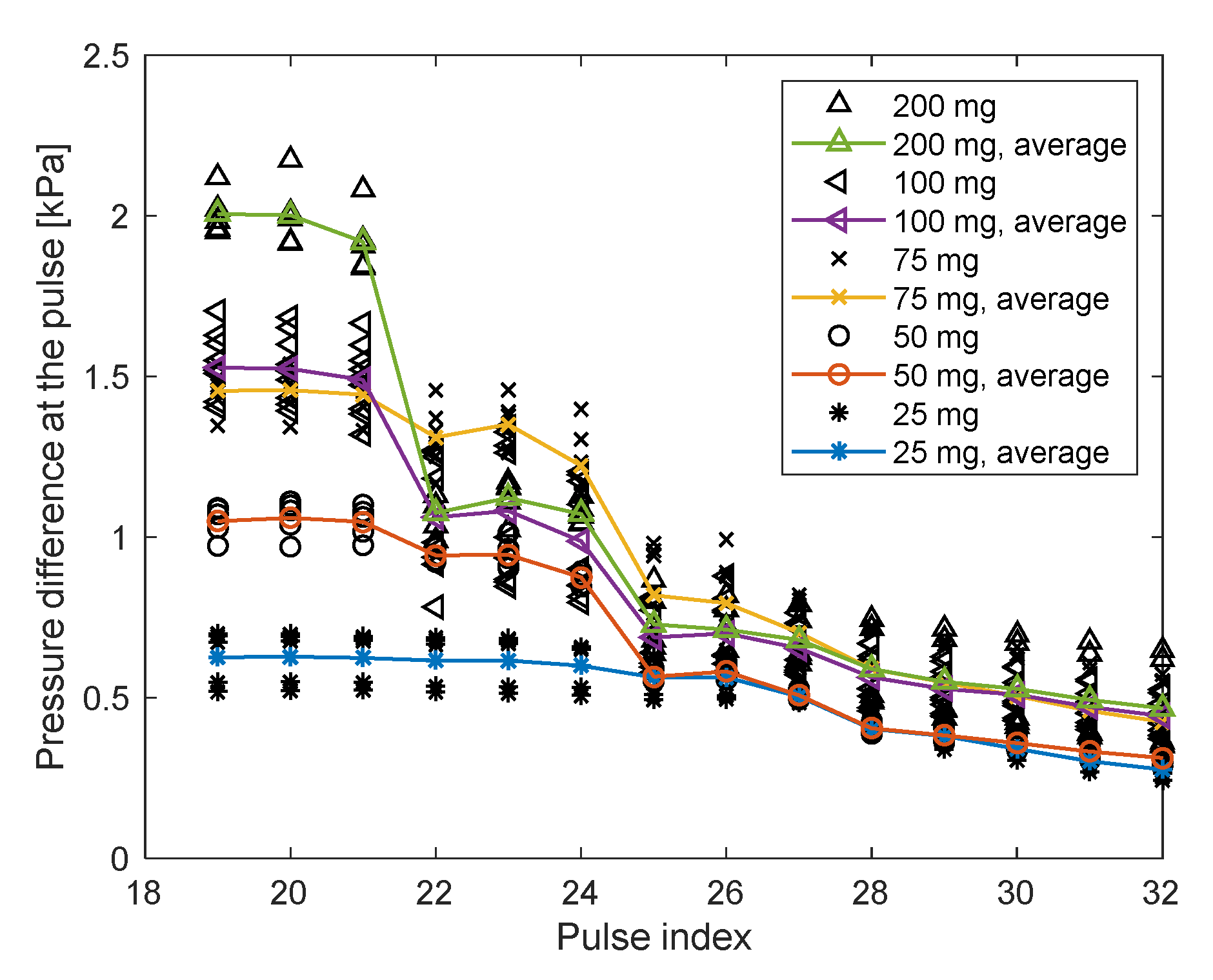
For different applications, smaller particles might be required. Cardiac pacing, for example, requires particles smaller than , instead of as were used for the feasibility of the application [7]. The sidewall pressure applied by three amounts of particles was measured in a similar procedure as that of the particles. The results of the sidewall pressure of the and particles during the 20th pulse are compared in Figure 15. The sidewall pressure that the particles applied was lower than that of the particles, but with a difference of less than , for the three amounts. It is possible that such difference is only attributable to the fine-tuning of the different parts of the system. Therefore, the influence of particle size on pressure is not clear for the particles studied. Further research with smaller particles is required to determine the influence of particle size on the sidewall pressure.
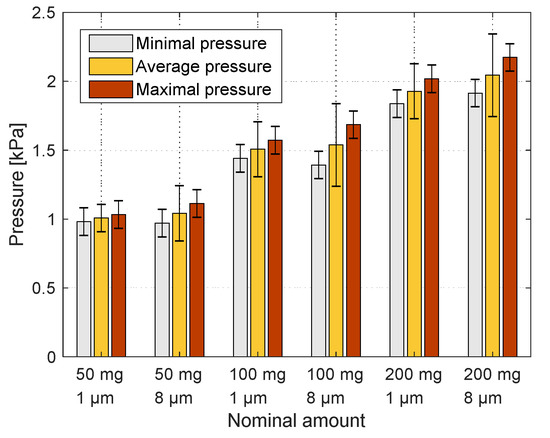
Figure 15.
Comparison between the pressure results of 1 and 8 μm particles.
4. Conclusions
In this work, a pulsating magnetic field was used to attract ferromagnetic particles toward the sidewall of a water chamber. The behaviour of the particles was investigated, and the pressure they apply on the wall was measured.
When the magnetic field was turned off, a certain part of the particles (the stable mass) remained attached to the chamber sidewall due to magnetic hysteresis. The stable mass was significant to the immediate sidewall pressure that was applied when the field was turned on at each pulse, and to the sidewall pressure at pulses with low duty cycle. The results of the experiments confirmed that for the specified configuration, the size of the stable mass did not depend on the initial amount of the particles.
The remaining particles that detached from the sidewall (the unstable mass) settled toward the bottom of the chamber. Larger unstable masses settled faster and farther away from the stable mass, because of the cluster behaviour of the bulk of the particles. When the duty cycle of the magnetic pulses was reduced, some particles migrated far away and could not be attracted again when the magnetic field was turned on. As a result, the sidewall pressure during the following pulses was decreased.
The relation between the amount of the particles and the sidewall pressure was investigated experimentally with measurements of the pressure. According to the measurement results, an approximate asymptotic dependence between the sidewall pressure and the mass of the particles was proposed for the specified particles and magnetic pulses. The proposed experimental correlation allows for an effective evaluation of the sidewall pressure values in similar experiments.
The experimental results were compared with simplified estimations. The comparison shows their satisfactory agreement for the assessment of maximum allowable sidewall pressure in similar experiments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A. and A.L.; methodology, A.A. and O.W.; software, O.W.; validation, O.W., A.L. and B.M.; formal analysis, O.W.; investigation, O.W.; resources, A.L. and A.A; data curation, O.W.; writing—original draft preparation, O.W.; writing—review and editing, O.W., A.L., B.M. and A.A.; visualization, O.W.; supervision, A.L., B.M. and A.A.; project administration, A.L.; funding acquisition, A.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Yoram Etzion from Ben-Gurion University of the Negev for the contribution of the electromagnet and particles and to Rafi Shikler from Ben-Gurion University of the Negev for the contribution of the PVDF film and the help for the sensor development.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Connolly, J.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, M.R.; Bender, J.W.; Carlson, J.D. Properties and applications of commercial magnetorheological fluids. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 1999, 10, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, K.; Moskowitz, R. Commercial applications of ferrofluids. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1990, 85, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberto, N.; Domingues, M.F.; Marques, C.; André, P.; Antunes, P. Optical fiber magnetic field sensors based on magnetic fluid: A review. Sensors 2018, 18, 4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkurikiyimfura, I.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Z. Heat transfer enhancement by magnetic nanofluids—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 21, 548–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goharkhah, M.; Salarian, A.; Ashjaee, M.; Shahabadi, M. Convective heat transfer characteristics of magnetite nanofluid under the influence of constant and alternating magnetic field. Powder Technol. 2015, 274, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotenberg, M.Y.; Gabay, H.; Etzion, Y.; Cohen, S. Feasibility of leadless cardiac pacing using injectable magnetic microparticles. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, P.J.; Epstein, A.; MacLeod, I.A.; Schaaf, S.T.M.; Sheldon, J.; Boulin, C.; Kohl, P. Soft tissue impact characterisation kit (STICK) for ex situ investigation of heart rhythm responses to acute mechanical stimulation. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2006, 90, 444–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bombard, A.J.F.; Joekes, I.; Alcântara, M.R.; Knobel, M. Magnetic susceptibility and saturation magnetization of some carbonyl iron powders used in magnetorheological fluids. Mater. Sci. Forum 2003, 416–418, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patocka, F.; Schlögl, M.; Schneider, M.; Schmid, U. Novel MEMS sensor for detecting magnetic particles in liquids. Proceedings 2018, 2, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Han, Y.; Xu, R.; Gong, E. A preliminary investigation into separating performance and magnetic field characteristic analysis based on a novel matrix. Minerals 2018, 8, 94. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, Y.Y.; Maldonado-Camargo, L.; Patel, N.S.; Biedrzycki, A.H.; Yarmola, E.G.; Dobson, J.; Rinaldi, C.; Allen, K.D. Magnetic particle translation as a surrogate measure for synovial fluid mechanics. J. Biomech. 2017, 60, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, F.; Takeda, S.; Izumi, Y.; Nishijima, S. Development of magnetic field control for magnetically targeted drug delivery system using a superconducting magnet. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2007, 17, 2303–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilés, M.O.; Ebner, A.D.; Ritter, J.A. In vitro study of magnetic particle seeding for implant-assisted-magnetic drug targeting: Seed and magnetic drug carrier particle capture. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 1586–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldenburg, C.; Borglin, S.; Moridis, G. Numerical simulation of ferrofluid flow for subsurface environmental engineering applications. Transp. Porous Media 2000, 319–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moridis, G.J.; Borgh, S.E.; Oldenburg, C.M.; Becker, A. Theoretical and Experimental Investigations of Ferrofluids for Guiding aid Detecting Liquids in the Subsurface; Lawrence Berkeley National Lab., Earth Sciences Div.: Berkeley, CA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; He, Y. Magnetically induced flow focusing of non- magnetic microparticles in ferrofluids under inclined magnetic fields. Micromachines 2019, 10, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, R.; Gaind, A.P.; Sen, S.; Puri, I.K. Analyzing ferrofluid transport for magnetic drug targeting. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2005, 289, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, R.; Gaind, A.P.; Puri, I.K. A strategy for the assembly of three-dimensional mesoscopic structures using a ferrofluid. Phys. Fluids 2005, 17, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganguly, R.; Zellmer, B.; Puri, I.K. Field-induced self-assembled ferrofluid aggregation in pulsatile flow. Phys. Fluids 2005, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakin, B.V.; Notøy, I.; Hoffmann, A.C.; Kosinski, P. The formation of deposit in a magnetic fluid: Numerical and experimental study. Powder Technol. 2012, 228, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminfar, H.; Mohammadpourfard, M.; Mohseni, F. Two-phase mixture model simulation of the hydro-thermal behavior of an electrical conductive ferrofluid in the presence of magnetic fields. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 324, 830–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminfar, H.; Mohammadpourfard, M.; Zonouzi, S.A. Numerical study of the ferrofluid flow and heat transfer through a rectangular duct in the presence of a non-uniform transverse magnetic field. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 327, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminfar, H.; Mohammadpourfard, M.; Kahnamouei, Y.N. A 3D numerical simulation of mixed convection of a magnetic nanofluid in the presence of non-uniform magnetic field in a vertical tube using two phase mixture model. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 1963–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexiou, C.; Diehl, D.; Henninger, P.; Iro, H.; Röckelein, R.; Schmidt, W.; Weber, H. A high field gradient magnet for magnetic drug targeting. IEEE Trans. Appl. Supercond. 2006, 16, 1527–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horabik, J.; Beczek, M.; Mazur, R.; Parafiniuk, P.; Ryżak, M.; Molenda, M. Determination of the restitution coefficient of seeds and coefficients of visco-elastic Hertz contact models for DEM simulations. Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 161, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Castillejos, R.; Plaza, J.A.; Esteve, J.; Losantos, P.; Acero, M.C.; Cané, C.; Serra-Mestres, F. Use of ferrofluids in micromechanics. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2000, 84, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubarev, A.Y.; Odenbach, S.; Fleischer, J. Rheological properties of dense ferrofluids. Effect of chain-like aggregates. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 252, 241–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubarev, A.Y.; Fleischer, J.; Odenbach, S. Towards a theory of dynamical properties of polydisperse magnetic fluids: Effect of chain-like aggregates. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 2005, 358, 475–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).