1. Introduction
A reduced-order model (ROM) provides a practical solution for computationally challenging problems. ROM is typically seen as representing a physical phenomenon with a small number of equations or mathematically reducing the infinite or large dimensions of the problem through projection onto a low-dimensional subspace. Many ROM methods in fluid mechanics are derived from the proper orthogonal decomposition (POD)-Galerkin projection approach and are often employed for control purposes [
1,
2]. The POD provides a tool to formulate an optimal, solution-adapted basis with minimum degrees of freedom (often termed as modes) required to represent the solution to a dynamical system.
Building systems are complex systems that involve multi-scales in time and space with uncertainties due to disturbances present in the system. Therefore, the simulation of these buildings is a grand challenge. Modern mathematical and engineering methods have only recently begun to be applied to the design of energy-efficient buildings. Building management systems can be made efficient using integrated design principles that could achieve 30% reduction of building energy usage. Instead, buildings need to be viewed as a system and its subsystems must be functionally integrated during both design and operation to make optimal use of ambient sources and sinks for heating, cooling, ventilation, lighting, and energy storage, and must be robustly coordinated and controlled. Low-energy building designs for both new construction and for retrofits involve new highly efficient components and highly coupled active and passive subsystems. Existing building control systems are not capable of dealing with the uncertainties in complex multi-scale dynamics. What is needed is an aggressive research effort to overcome these challenges. By itself, whole-building simulation is a significant computational challenge. However, when addressing additional performance requirements that center on design, optimization, and control of whole buildings, it becomes a scientific challenge to develop the new numerical algorithms and computational tools that are scalable and widely applicable to current and future building stock. This challenge must be addressed through a holistic approach that takes advantage of High-Performance and High-Productivity Computing (HP2C). The use of HP2C tools in an online fashion is not feasible especially for design, control, and optimization purposes. Thus, a natural approach is to use HP2C tools to build ROM for efficient design and control.
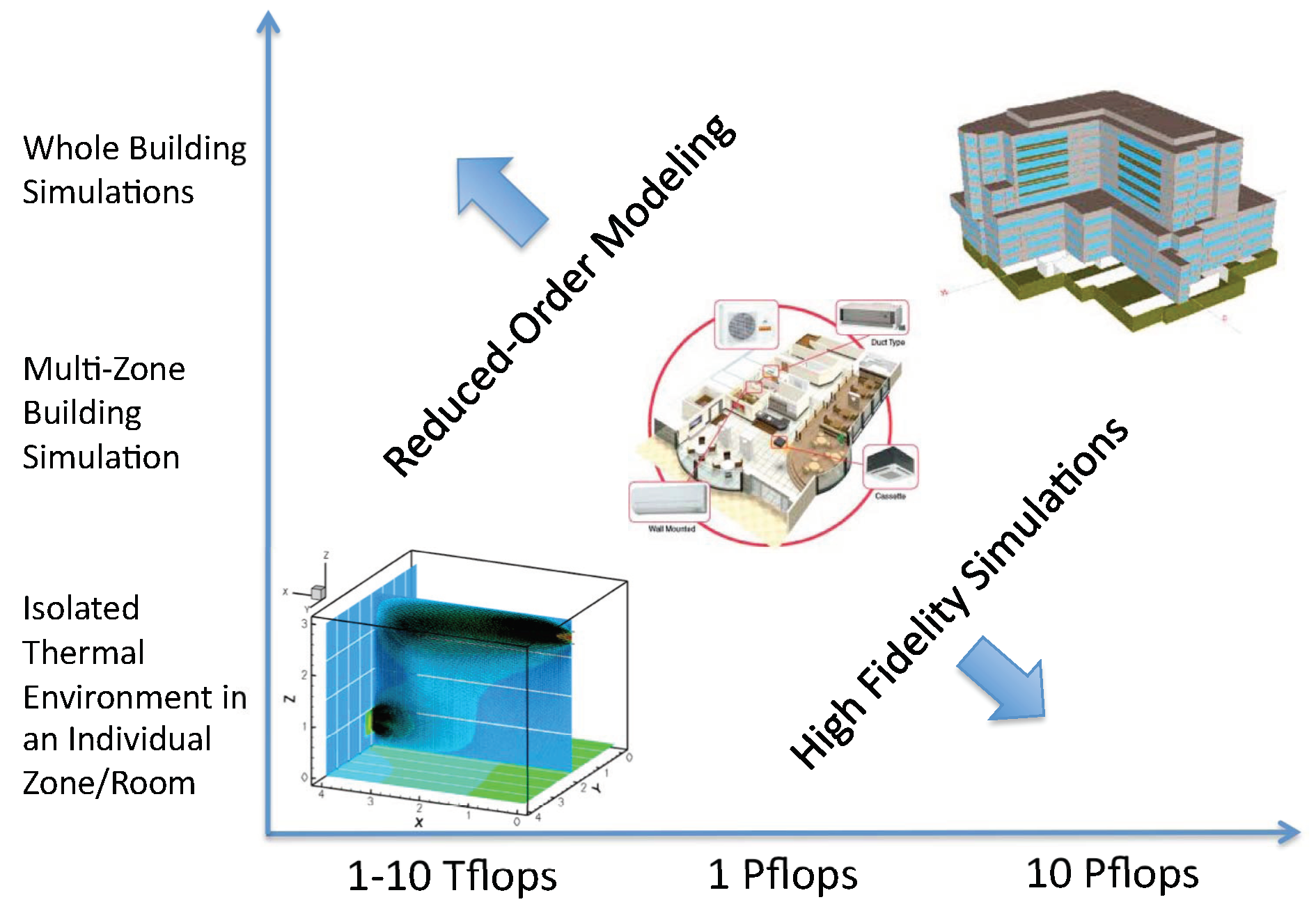
This point is emphasized in
Figure 1 displaying the computational performance required to conduct high-fidelity simulations for designing the turnaround time of order of minutes and how this scales from understanding airflow and thermal properties of small zones to the coupling and control of whole-building situations. Research efforts in model reduction are required to reduce the computational cost. Moreover, analysis methods are needed to understand the underlying structure involving multi-scale issues and uncertainty that can enable novel design tools to deliver energy-efficient buildings management systems.
The approach we propose is to first develop projection-based computational methods-based model reduction as a direct approach to whole-building modeling, simulation, and sensitivity analysis. We review extensions of POD and Principal Interval Decomposition (PID) algorithms to HP2C generated snapshots. Borggaard et al. [
4] considered estimation and control for a distributed parameter model of a multi-room building. They demonstrated that distributed parameter control theory, coupled with high-performance computing, could provide insight and computational algorithms for the optimal placement of sensors and actuators to maximize observability and controllability
If advanced control algorithms and optimal design tools are to lead the way in producing zero-energy buildings, then modern model reduction methods for the reduce-then-control approach must be used [
5]. Furthermore, these ROMs allow sophisticated control and optimization strategies to be used, which would not be available using full-order simulations alone [
6].
POD-based low-dimensional models have been successfully implemented for various control strategies. Bergmann and Cordier [
7] used optimal control theory to minimize the mean drag for a circular cylinder with amplitude and frequency as the control parameters using cylinder rotation. They employed a trust-region POD model for the wake and the optimization of the control parameters converged to the minimum predicted by an open-loop control and lead to a relative mean drag reduction of 30%. Akhtar and Nayfeh [
8] and [
9] designed a full-state feedback controller and a linear quadratic regulator (LQR), respectively, based on a low-dimensional model to suppress the vortex shedding past a circular cylinder. Akhtar et al. [
10] computed and analyzed the functional gains for the flow in the latter case to provide effective sensor placement to control vortex shedding. They demonstrated, using a numerical approach, that functional gains provide a better indication of sensor placement than using the dominant POD mode.
In this study, we compute and discuss the functional gains of the temperature field for the flow in a
model room simulated using a parallel CFD solver. The functional gains identify preferred location of the sensors for developing an effective control strategy. The manuscript is organized as follows. In
Section 2, we present the governing equations for the problem followed by a brief methodology on the POD modes in
Section 3. We then present optimal control theory in
Section 4 employed for control purposes. In
Section 5, we analyze the numerical results and the POD modes for the velocity and temperature fields.
Section 6 presents the functional gains for the given problem for different inlet temperature fields.
2. Computational Methodology
A parallel CFD solver [
11,
12,
13] is used to simulate the incompressible flow field in a room along with its temperature distribution. The governing equations are the Continuity, Momentum, and Energy equations written in a nondimensional form as:
where
,
p, and
T are the velocity, pressure, and temperature fields, respectively.
is the Reynolds number,
is the Grashof number, and
is the Prandtl number in the governing equations. The control term is given by
where
is a given distribution and
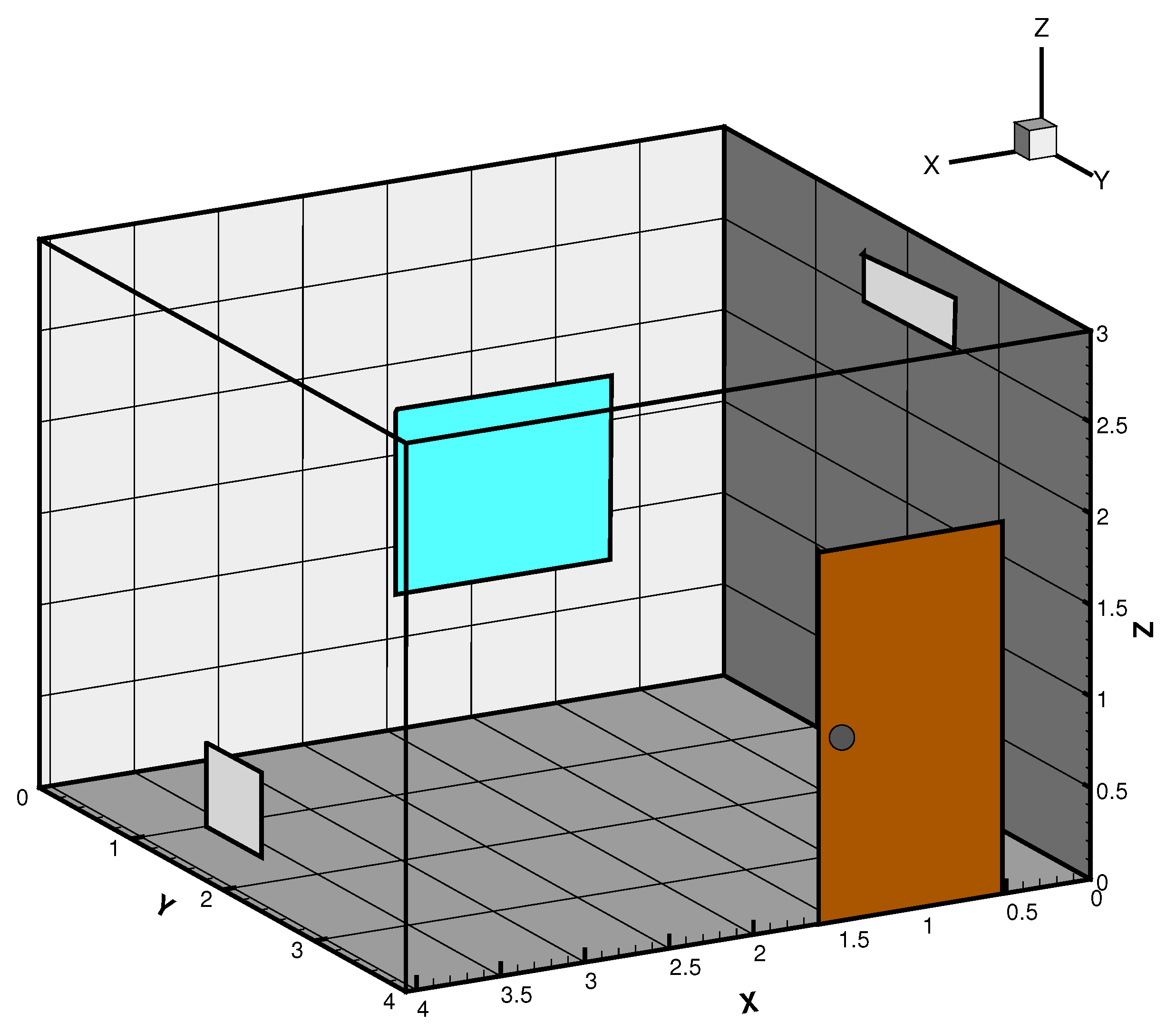
is a thermal control input. The domain models a room
as shown in
Figure 2. The inlet and the outlet vent is modeled on the opposite walls.
is the velocity input term while and
affects the temperature at the inlet. The input velocity field has a parabolic profile with uniform temperature at the inlet. Walls of the room are modeled with no slip boundary conditions while homogeneous Neumann (insulated) conditions are assumed for the remaining boundary conditions on temperature.
3. Proper Orthogonal Decomposition Modes
The POD provides a tool to formulate an optimal basis functions (or modes) required to represent a dynamical system [
14,
15,
16,
17]. POD has been widely used to identify the coherent structures in the flow field. Some of the classical applications include examination of stability [
18], pressure field [
12], and flow control [
5,
8].
Initial step requires availability of flow field data (
) obtained, in this case, from numerical simulations. The data set is recorded in a matrix
through a collection of
snapshots as follows:
where
S is the total number of snapshots for
N grid points in the domain. Similarly, temperature field is also recorded.
We compute the POD modes (
) by maximizing the following:
where
is the time averaging. Using the
method of snapshots [
19], the constrained optimization problem is equivalent to a Fredholm integral eigenvalue problem that can be written as follows
where
are the temporal eigenfunctions and
is the temporal correlation tensor defined as
We calculate each POD mode as
A physical interpretation of the is that it depicts energy of the corresponding POD mode
4. Optimal Control
We develop a flow control strategy for the flow field with certain assumptions. The main assumption is that we ignore the buoyancy term that decouples Equations (
1) and (
2) from Equation (
3). If we assume that the fan is always on, then the distributed parameter control problem can be built from Equation (
3) with
computed by solving the steady-state Navier-Stokes equations. The treatment of temperature is similar, so we only consider the control problem for the temperature.
Using LQR control, system (
2) takes the form of a differential equation on a Hilbert space
Z,
where
. The objective is to find the control that minimizes
subject to (
9), where
Q corresponds to a characteristic function in a workspace (see
Figure 2). Under reasonable conditions, see [
20], an optimal control exists and has the form
where
is a bounded linear “gain” operator. In addition,
where
is a bounded linear operator,
and
P satisfies the Riccati equation
With the control being applied only on the temperature field, the Riesz Representation Theorem implies that there exists a function
such that
The kernel
is called a functional gain. The functional gains define the optimal LQR controller and can be used to place sensors and design low order controllers (see [
21,
22]).
5. Numerical Solution
We perform the numerical simulation of the flow field in a
size room with a
nonuniform grid with finer mesh close to the walls.
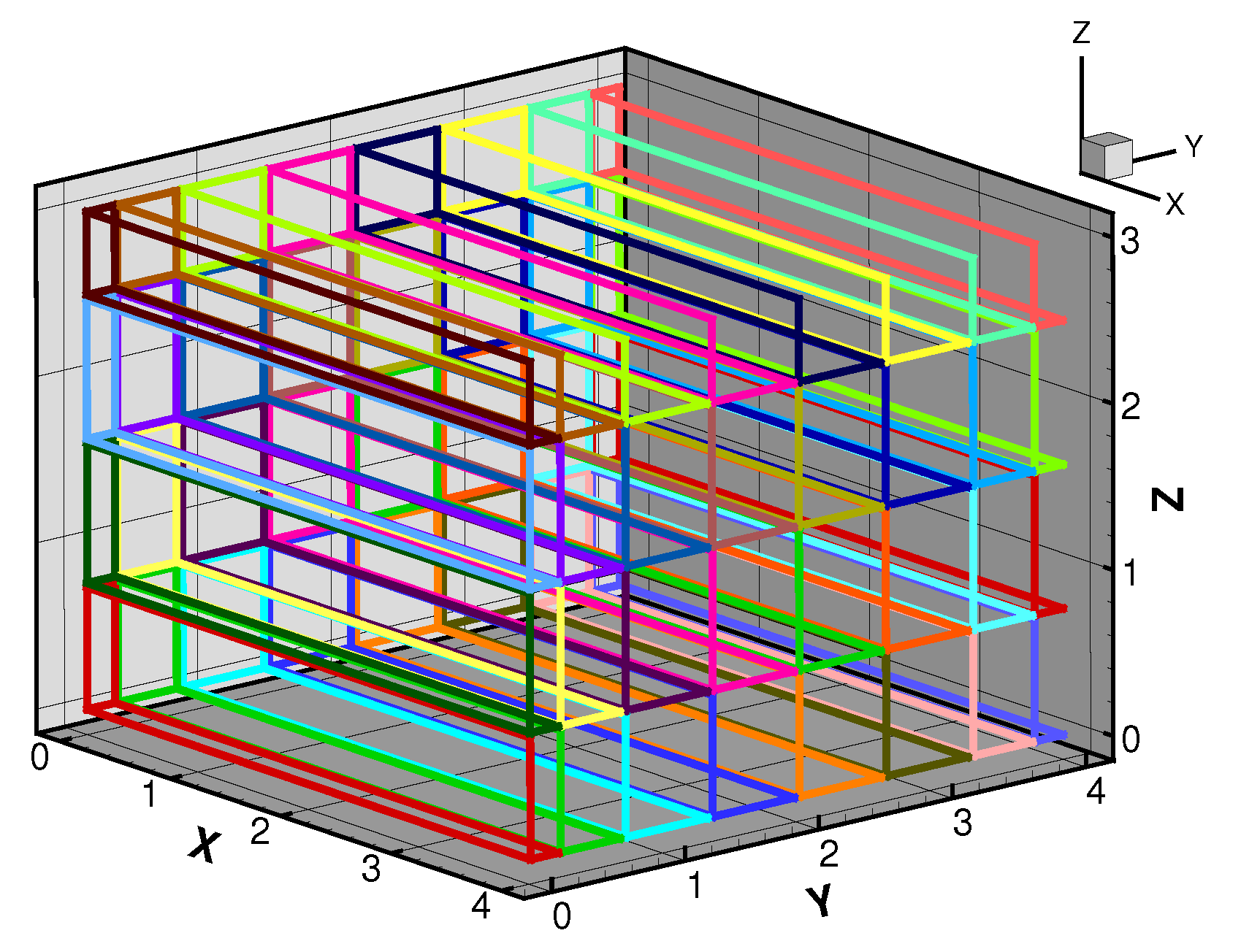
Figure 2 illustrates a domain depicting a typical office room serving as a unit in a building. It also shows a rectangular inlet at X = 0 and a square outlet (return) at X = 4 on the YZ-plane representing a heating, ventilation, and air-conditioning (HVAC) system. With the given grid size, the domain is equally partitioned into 32 processors using a two-dimensional domain decomposition topology of
in the Y- and Z-directions, respectively, as shown in
Figure 3 [
3,
23]. Thus, the grid distribution becomes
per processor.
The choice of 32 processors ensures that the latency factor between computation and communication gives close to ideal speed-up and is scalable.
We simulate the flow with the inflow and outflow vent locations tabulated in
Table 1.
Based on the average velocity of the parabolic inflow and inlet width, the Reynolds number and Prandtl number is chosen as 100 and 0.71, respectively. The inlet and ambient temperatures are taken as °C and °C, respectively.
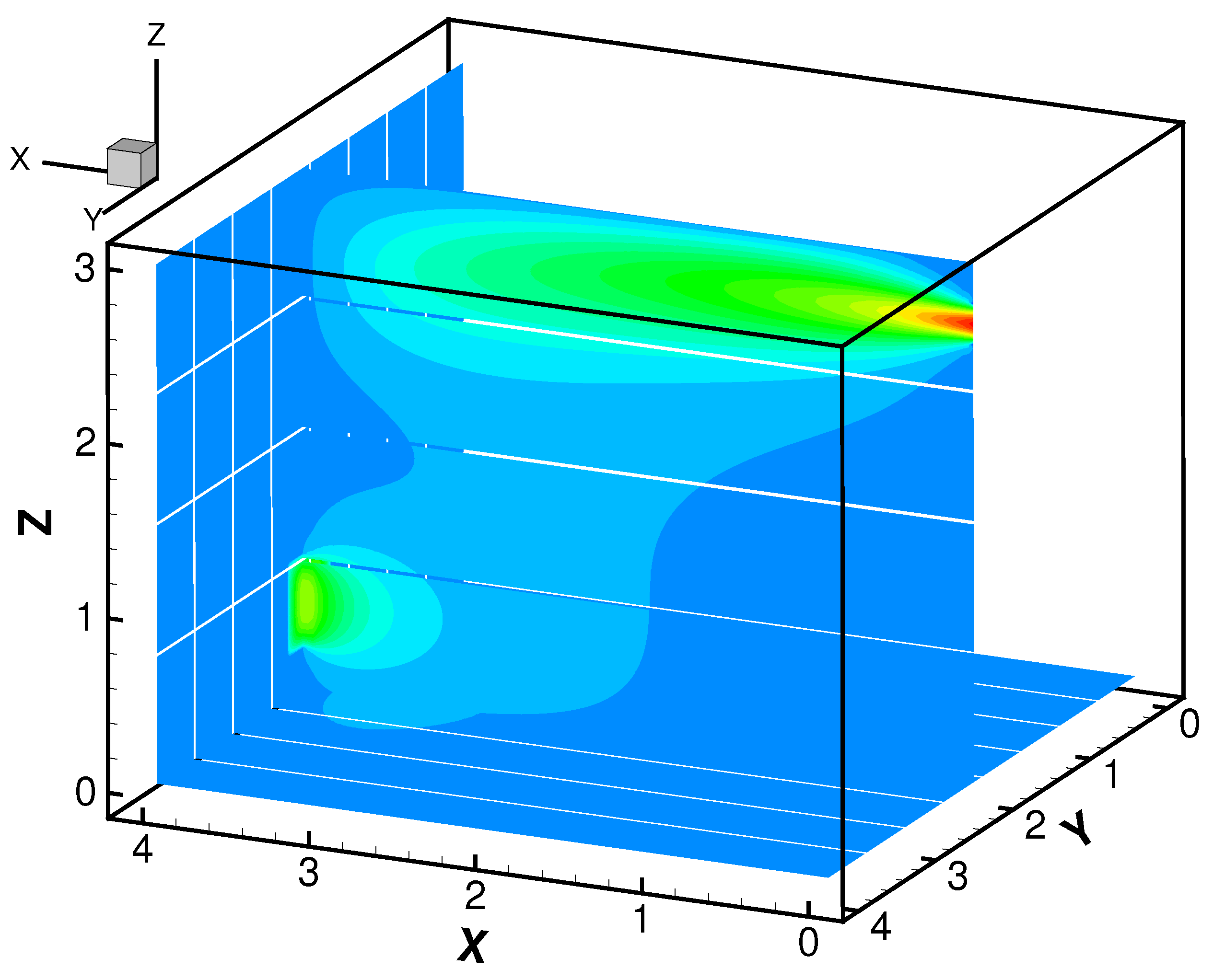
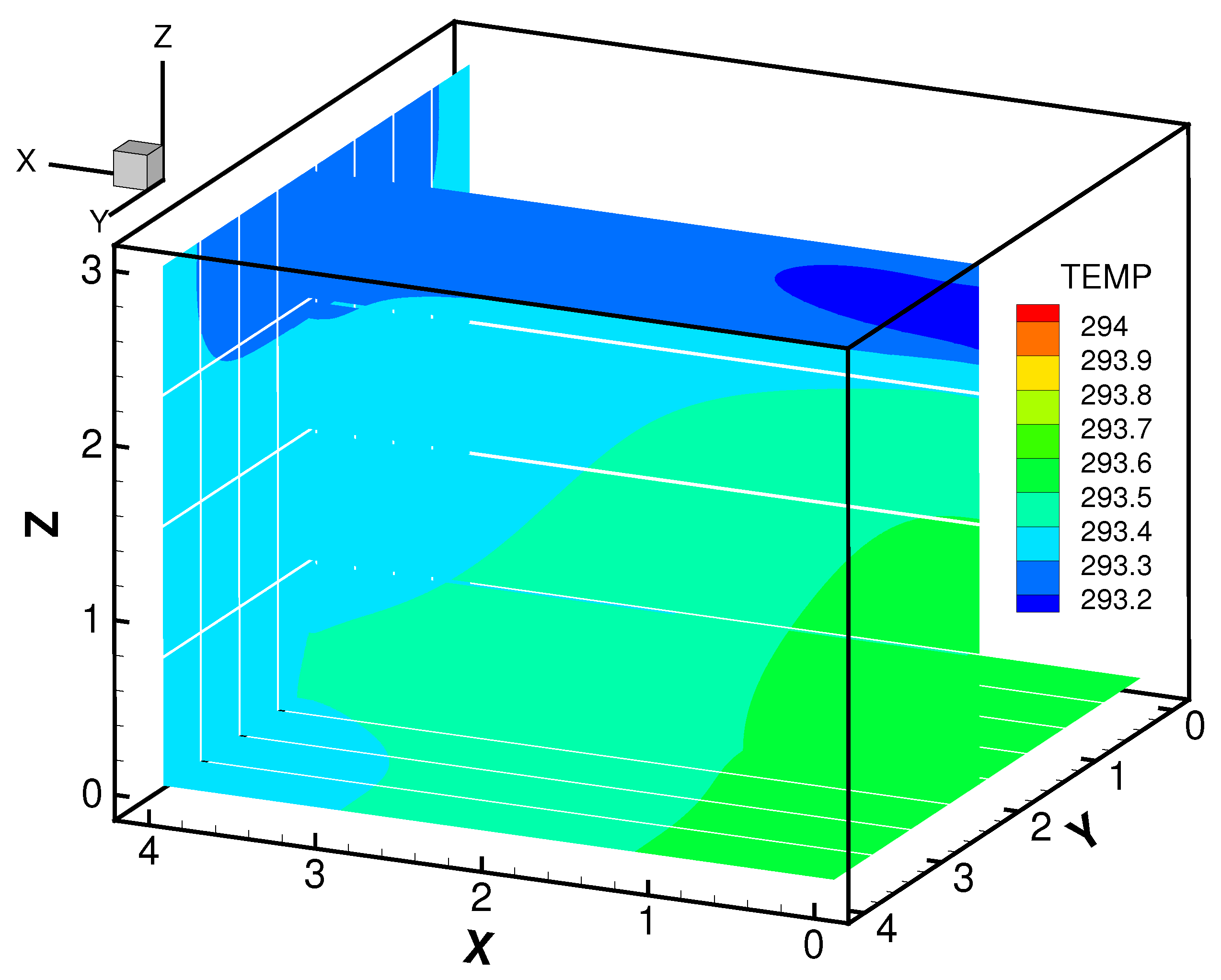
We simulate the flow field with these conditions and plot the snapshots of
and
T in
Figure 4 and
Figure 5, respectively, at nondimensional time of
.
The equispaced temporal data comprising 200 snapshots of the velocity and temperature fields is recorded and ensembled in a matrix form as Equation (
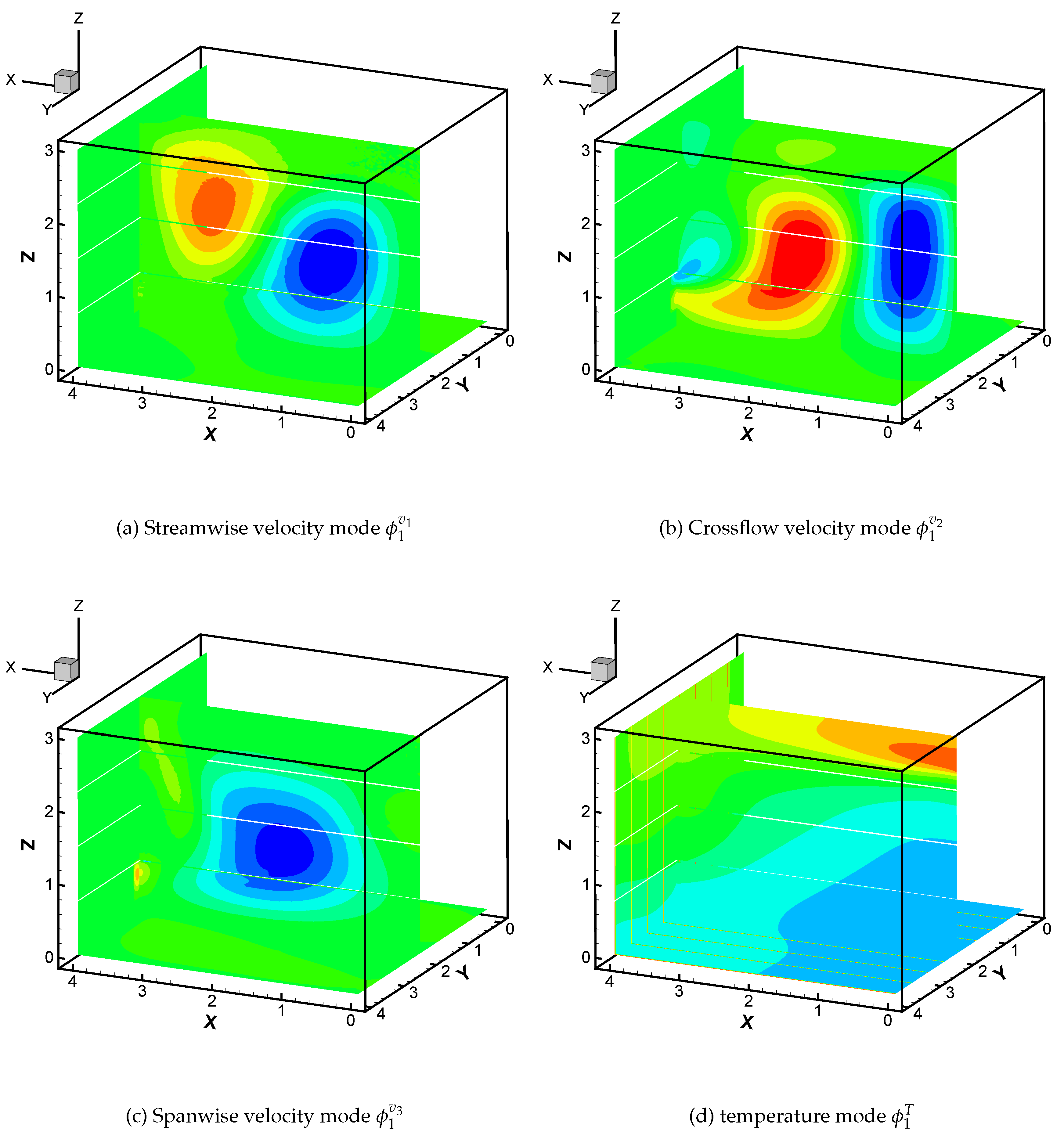
4). The POD modes are computed using the method of snapshots the first modes of velocity and temperature fields are plotted in
Figure 6, we plot the first POD mode of the velocity and temperature fields representing 98.47% and 99.88% of the total contribution, These figures clearly demonstrate the dominant features of the flow field is captured by the first modes.
It is important to note that simulation and post-processing of this large data was possible due to parallel computing. Despite high-performance computing tools, significance of ROM cannot be overemphasized due to its application in design, control, and optimization process. The ROM can be developed by projecting the governing equations onto the dominant modes and can be employed to design optimal control of temperature of an HVAC system in a building to make it energy efficient.
6. Functional Gains for Sensor Placement
In the current study, we use inlet temperature of the HVAC unit as the control input. Thus, the following equation is used for the input as a function of time:
where
is the functional gain. For a real-time problem, it is not practical to compute
directly for a thermal flow control system. In a recent study, Akhtar et al. [
10] employed functional gains to locate sensors effectively in the wake of a circular cylinder to suppress vortex shedding. They demonstrated that functional gains provide effective sensor placement than the POD basis. This directly relates to the efficiency of the feedback controller.
The main limitation is the availability of temperature field at each point in the domain required in the integration process of Equation (
14). Thus, we need to estimate the state. Here, the functional gains provide insight to the temperature distribution and are approximated using POD basis functions. The algorithm for computing functional gains is explained is the
Appendix A. In other words, functional gains contain the contribution of each state to the control The distribution of functional gains signifies the regions where the magnitude of
is large with major contribution in the integral and the estimation needs to be accurate. On the other hand, the regions where
magnitude is small, the contribution is negligible. The integral equation in fact becomes a weighted quadrature problem if point measurements of perturbed velocity (
) and temperature are sensed to compute the control, then these points are the effective location.
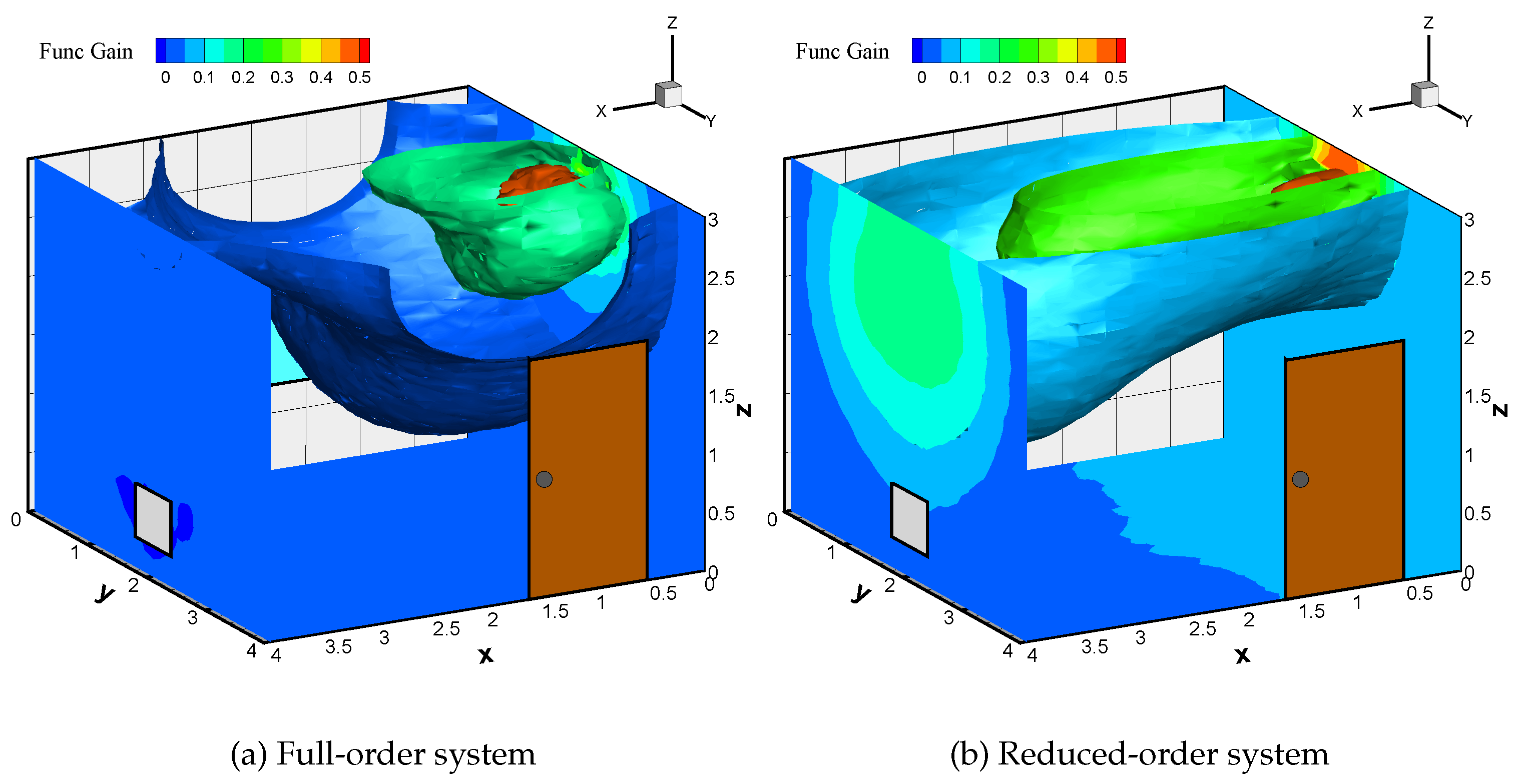
Here, with the velocity field as stationary and using Equation (
3), full-order gain is computed. We also approximate
using the mean temperature mode and the
(
) with zero reference temperature and unit temperature input. In
Figure 7, we provide the functional gain approximations for the full-order and reduced-order systems. This work demonstrates how the snapshot data of the flow field can be used to compute the POD modes and subsequently the functional gains. Thus, a framework can be developed for the control design of HVAC systems in energy-efficient buildings since computation of full-order gains is complex.