Pulsation-Enhanced Transport in Pseudo-Periodic Porous Channels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
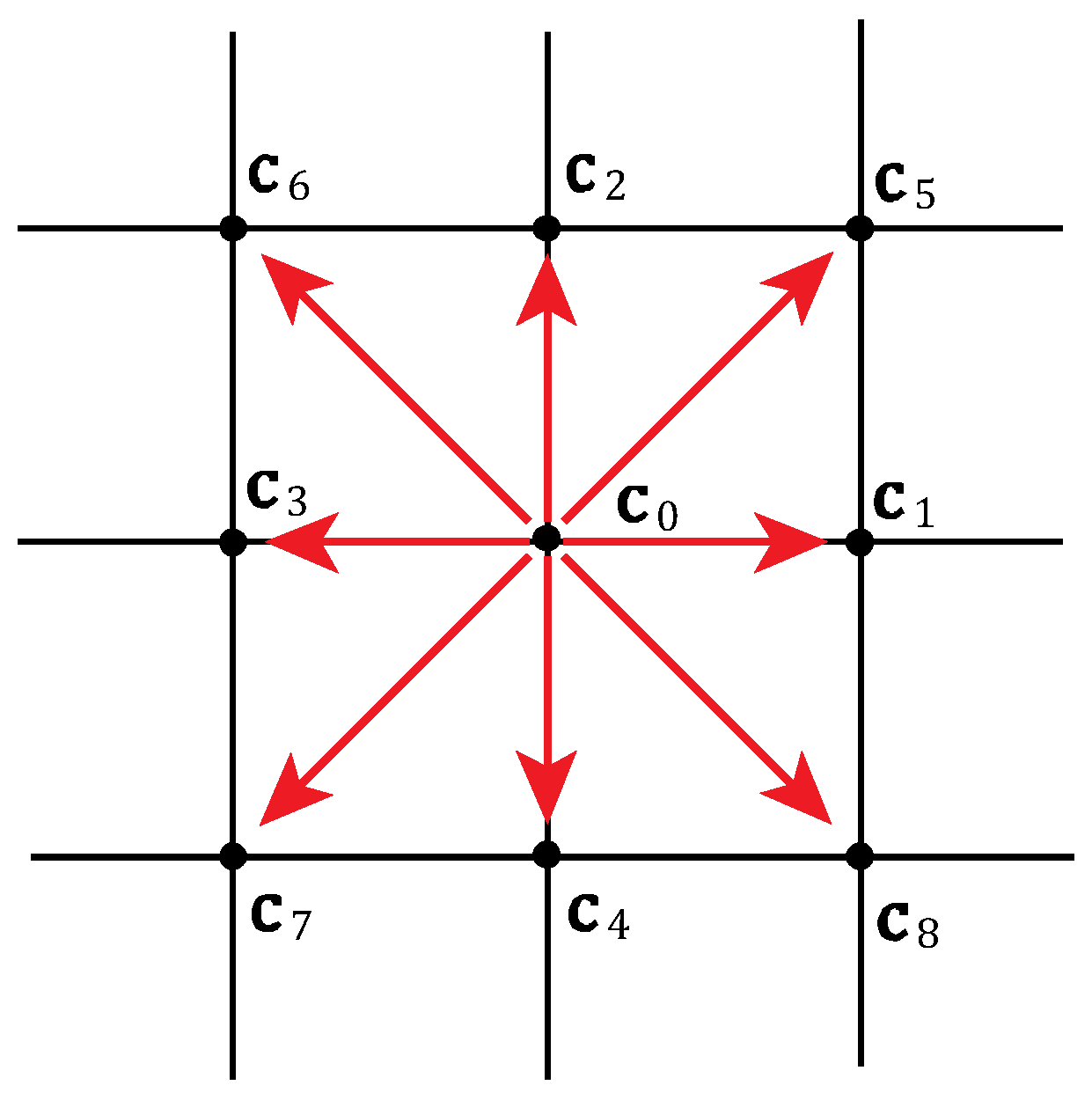
2.1. Lattice Boltzmann Model
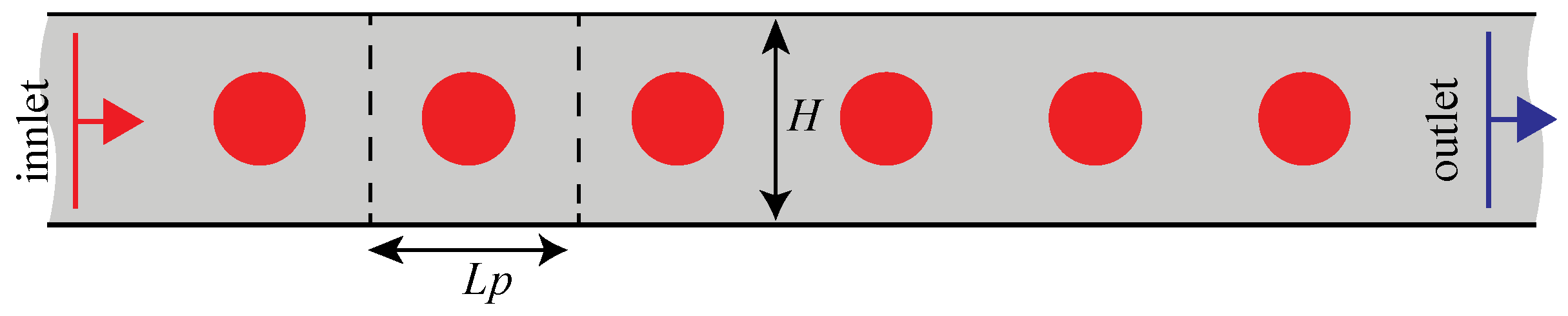
2.2. Geometry
2.3. Boundary Conditions
2.4. Dimensionless Parameters
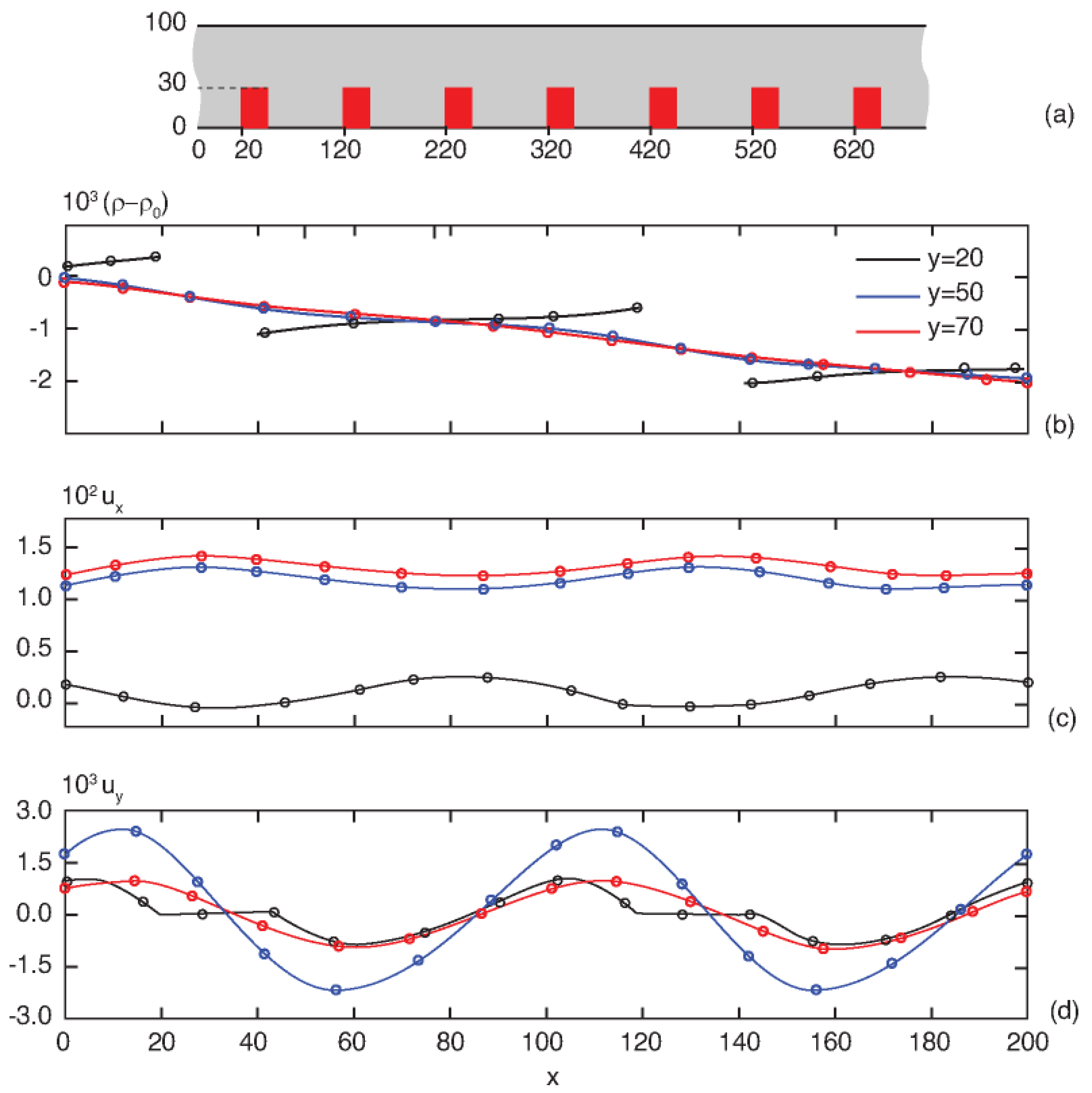
2.5. Verification and Validation
2.6. Grid and Time-Step
3. Results
3.1. Definition of Quantitative Metrics
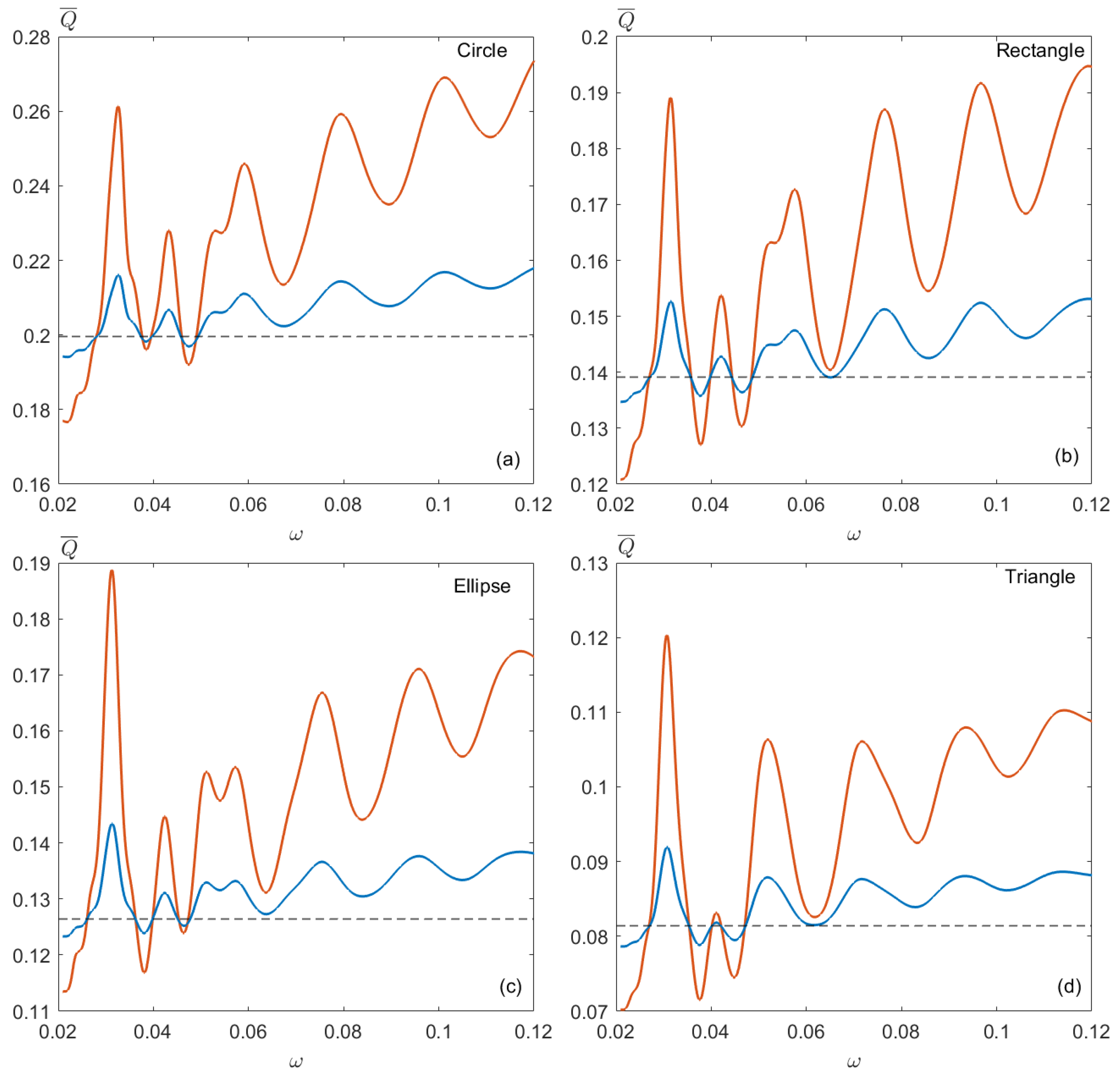
3.2. Frequency Dependence of Flow Rate
3.3. Effect of Porosity
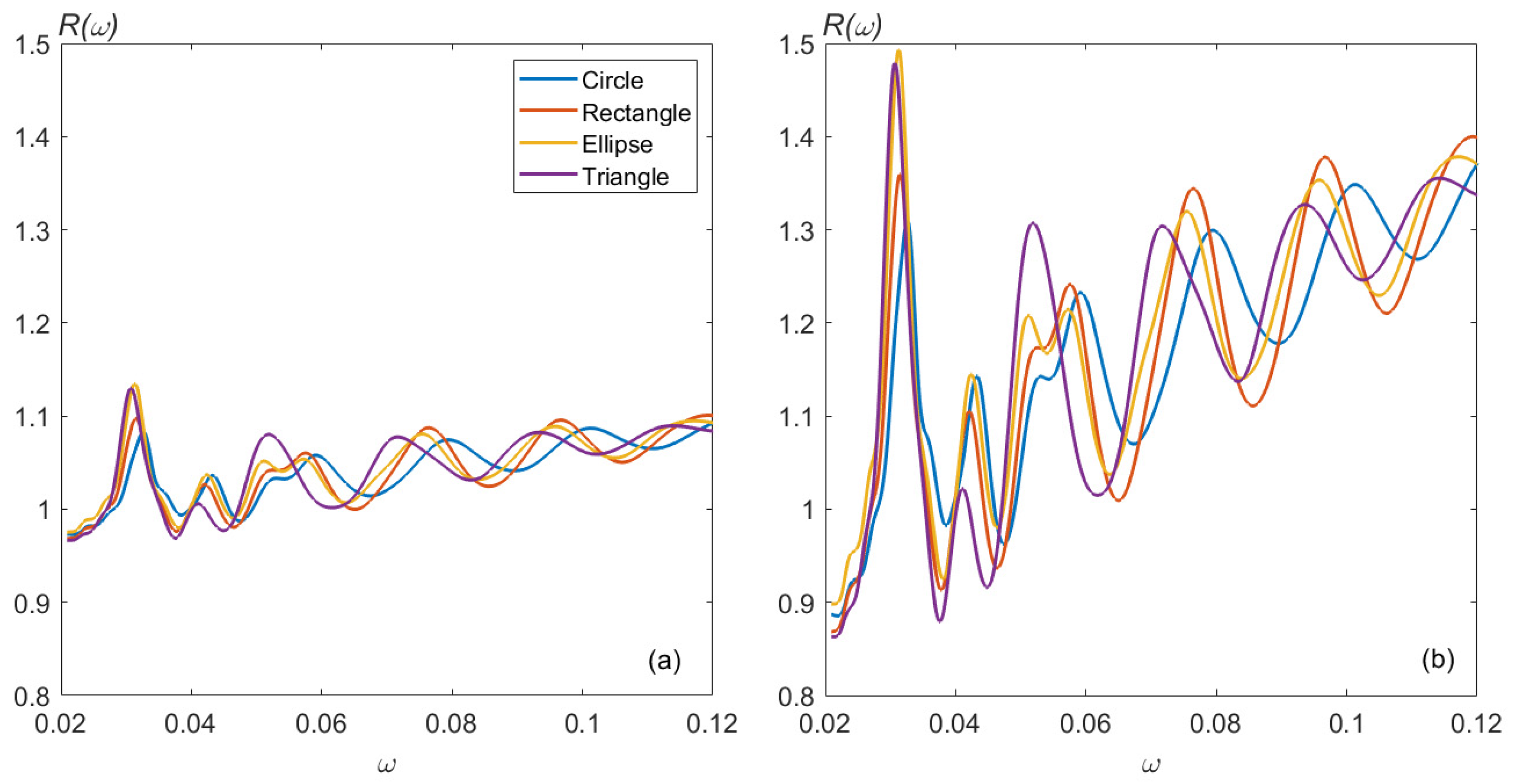
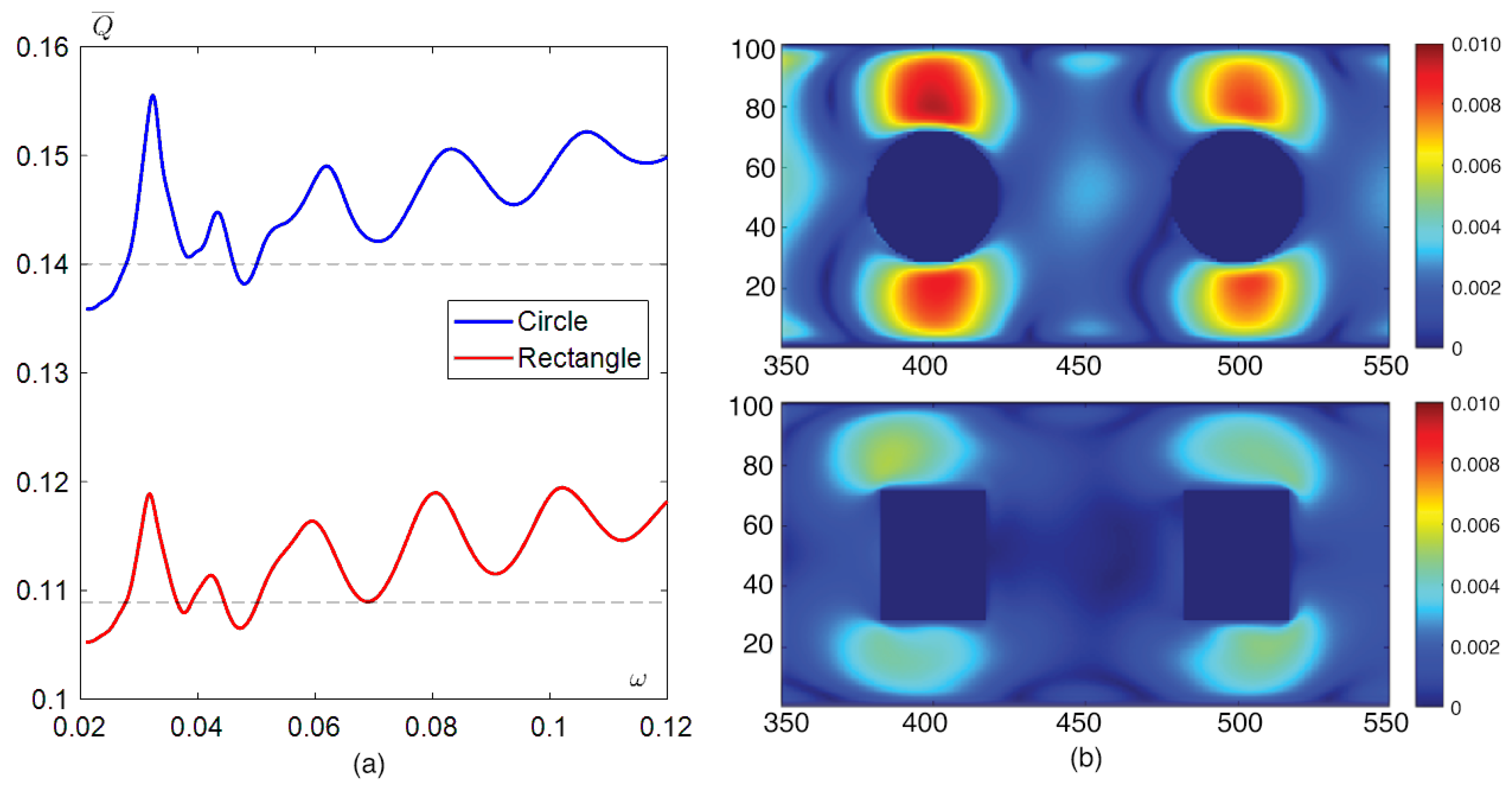
3.4. Influence of Obstacle Geometry
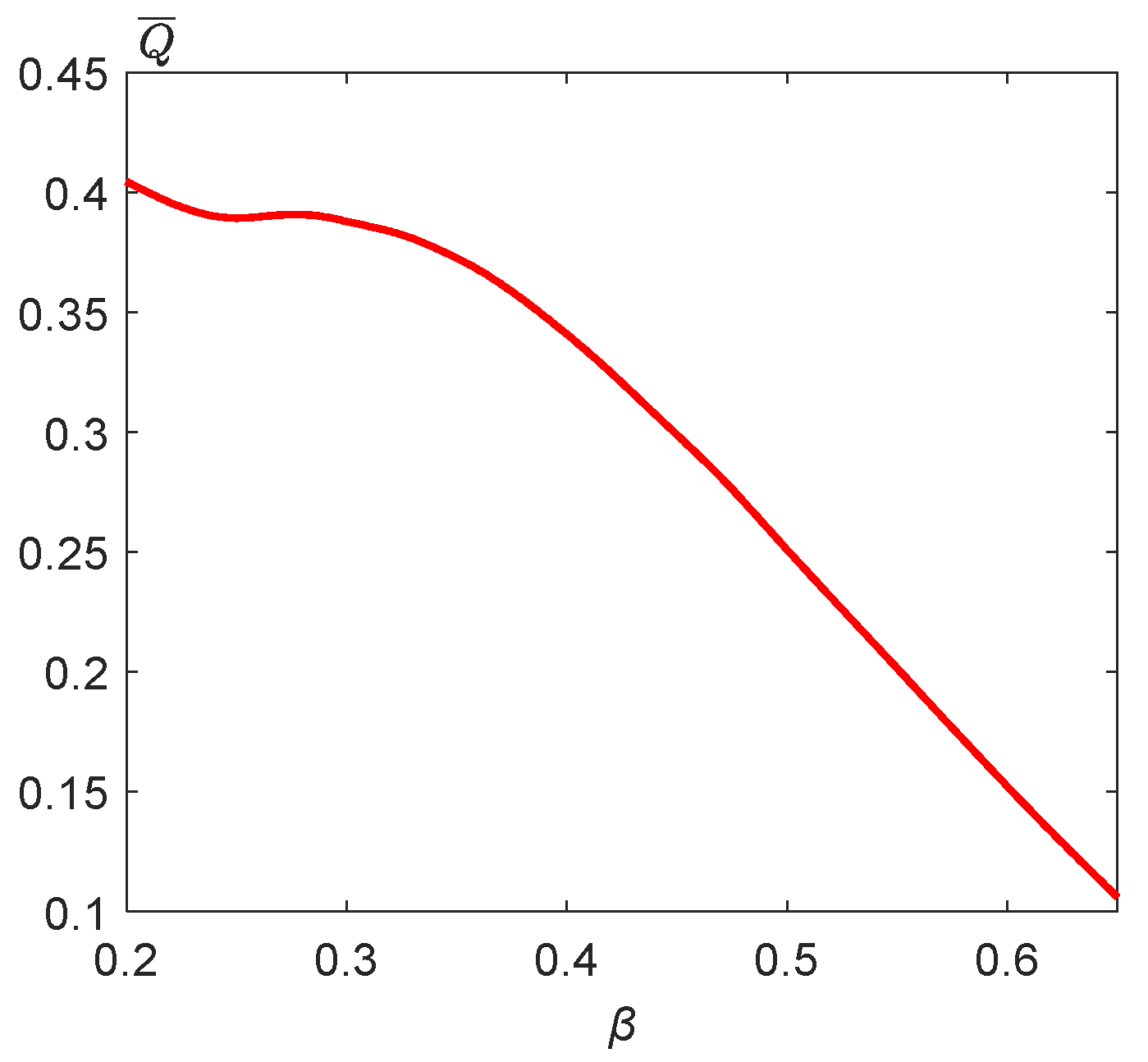
3.5. Effect of Blockage Ratio and Obstacle Position
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blunt, M.J. Multiphase Flow in Permeable Media: A Pore-Scale Perspective; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Das, M.K.; Mukherjee, P.P.; Muralidhar, K. Modeling Transport Phenomena in Porous Media with Applications; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nield, D.A.; Bejan, A. Mechanics of Fluid Flow Through a Porous Medium; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secomb, T.W. Blood Flow in the Microcirculation. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2017, 49, 443–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pries, A.R.; Secomb, T.W. Making Microvascular Networks Work: Angiogenesis, Remodeling, and Flow Control. Nat. Rev. Physiol. 2022, 1, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lao, J.; Tong, D.; Song, H. Numerical Investigation on EOR in Porous Media by Cyclic Water Injection with Vibration Frequency. Water 2022, 14, 3961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Wang, S.; Le-Clech, P.; Shen, Y. LBM-DEM simulation of particle deposition and resuspension of pre-deposited dynamic membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 295, 121222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Orazio, A.; Karimipour, A.; Ranjbarzadeh, R. Lattice Boltzmann Modelling of Fluid Flow through Porous Media: A Comparison between Pore-Structure and Representative Elementary Volume Methods. Energies 2023, 16, 5354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, D.; Shu, S.; Niu, X. Finite-volume method with lattice Boltzmann flux scheme for incompressible porous media flow at the representative-elementary-volume scale. Phys. Rev. E 2016, 93, 023308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Succi, S. The Lattice Boltzmann Equation: For Complex States of Flowing Matter; Oxford Academic: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, Y.-F.; Gong, B.; Yu, J.-P.; Cui, S.-T. From molecular dynamics to lattice Boltzmann: A new approach for pore-scale modeling of multi-phase flow. Pet. Sci. 2015, 12, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, T.; Kusumaatmaja, H.; Kuzmin, A.; Shardt, O.; Silva, G.; Viggen, E.M. The Lattice Boltzmann Method: Principles and Practice; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Womersley, J.R. Method for the calculation of velocity, rate of flow and viscous drag in arteries when the pressure gradient is known. J. Physiol. 1955, 127, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biot, M.A. Theory of propagation of elastic waves in a fluid-saturated porous solid. I. Low frequency range. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1956, 28, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biot, M.A. Theory of propagation of elastic waves in a fluid-saturated porous solid. II. Higher frequency range. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1956, 28, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.L.; Koplik, J.; Dashen, R. Theory of dynamic permeability and tortuosity in fluid-saturated porous media. J. Fluid Mech. 1987, 176, 379–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortis, A.; Smeulders, D.M.; Guermond, J.L.; Lafarge, D. Influence of pore roughness on high-frequency permeability. Phys. Fluids 2003, 15, 1766–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlois, V. High-frequency permeability of porous media with thin constrictions. I. Wedge-shaped porous media. Phys. Fluids 2022, 34, 077119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Champoux, Y.; Allard, J.F. Dynamic tortuosity and bulk modulus in air-saturated porous media. J. Appl. Phys. 1991, 70, 1975–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, A.M.; Higdon, J.J.L. Oscillatory Stokes flow in periodic porous media. Phys. Fluids 1992, 4, 2099–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.M.; Hong, B.S.; Shyu, S.H. A Numerical Investigation of Sinusoidal Flow in Porous Media with a Simple Cubic Beam Structure at 1 Hz and 100 Hz Under Different Porosity Conditions. Fluids 2025, 10, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berselli, L.C.; Miloro, P.; Menciassi, A.; Sinibaldi, E. Exact solution to the inverse Womersley problem for pulsatile flows in cylindrical vessels, with application to magnetic particle targeting. Appl. Math. Comp. 2013, 219, 5717–5729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manopoulos, C.; Raptis, A.; Tsangaris, S. Analytical Solution of Oscillatory Stokes Flow in a Porous Pipe with Spatiotemporally Periodic Suction/Injection. Appl. Mech. 2022, 3, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobhnamayan, F.; Sarhaddi, F.; Behzadmehr, A. Analytical solution of pulsating flow and forced convection heat transfer in a pipe filled with porous medium. J. Comp. Appl. Mech. 2021, 52, 570–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatnagar, P.L.; Gross, E.P.; Krook, M. A model for collision processes in gases. I. Small amplitude processes in charged and neutral one-component systems. Phys. Rev. 1954, 94, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.H.; d’Humières, D.; Lallemand, P. Lattice BGK models for Navier–Stokes equation. Europhys. Lett. 1992, 17, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Q.; He, X. On pressure and velocity boundary conditions for the lattice Boltzmann BGK model. Phys. Fluids 1997, 9, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Kwok, D.Y. Pressure boundary condition of the lattice Boltzmann method for fully developed periodic flows. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 73, 047702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parameter | Symbol | Tested Values/Settings | Description/Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Channel height (lattice nodes) | 80, 100, 120 | Defines grid resolution in the transverse direction | |
| Channel length (lattice nodes) | — | 1000 | Ensures pseudo-periodicity and developed resonance response |
| Length of obstacle unit cell | 100 | ||
| Lattice spacing | 1 (lattice unit) | Spatial discretization step | |
| Time step | 1 (lattice unit) | Temporal discretization step | |
| Relaxation time | 1 | Adjusted to preserve kinematic viscosity | |
| Kinematic viscosity | Maintained constant across tests | ||
| Porosity (reference case) | ϕ | 0.85, 0.9 | Representative test configuration |
| Oscillation amplitude | 0.05, 0.1 | Dimensionless inlet density amplitude | |
| Number of pulsation periods for averaging | 3 | Ensures stable averaged value of flow rate | |
| Maximum Mach number | — | <0.05 | Ensures weakly compressible, laminar regime |
| Obstacle Shape | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Circular | 1.11 | 1.43 | 1.08 | 1.31 |
| Rectangular | 1.13 | 1.48 | 1.09 | 1.36 |
| Elliptical | 1.19 | 1.69 | 1.14 | 1.49 |
| Triangular | 1.16 | 1.56 | 1.13 | 1.48 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Noselidze, I.; Tavzarashvili, K. Pulsation-Enhanced Transport in Pseudo-Periodic Porous Channels. Fluids 2025, 10, 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids10110299
Noselidze I, Tavzarashvili K. Pulsation-Enhanced Transport in Pseudo-Periodic Porous Channels. Fluids. 2025; 10(11):299. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids10110299
Chicago/Turabian StyleNoselidze, Irakli, and Kakhaber Tavzarashvili. 2025. "Pulsation-Enhanced Transport in Pseudo-Periodic Porous Channels" Fluids 10, no. 11: 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids10110299
APA StyleNoselidze, I., & Tavzarashvili, K. (2025). Pulsation-Enhanced Transport in Pseudo-Periodic Porous Channels. Fluids, 10(11), 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/fluids10110299




