Abstract
The phenomenon known as non-wetting phase (nwp) entrapment, and the multiphase fluid flow within porous media that gives rise to it, is important in several areas such as contaminant transport and subsequent remediation, subsurface energy storage, oil recovery, carbon dioxide sequestration, and pore structural characterisation. The aim of this review was to survey the various different modelling and simulation approaches used to predict the pore-scale processes involved in the entrapment of nwp in disordered porous media, and the impact of pore structural features on the level of entrapment. The various modelling and simulation approaches considered included empirical models, pore network models (PNMs), percolation models, models derived directly from imaging data, and thermodynamic and statistical mechanical techniques. Dynamic flow simulations within models derived from images have validated the quasi-static idealisation for low capillary number, often used with PNMs. Modelling using this approximation has demonstrated the importance of pore connectivity and macroscopic heterogeneities in the spatial distribution of pore sizes in determining entrapment. Dynamic simulations in image-derived models have also shown the need for proper representation of menisci configurations in the complex void spaces of mixed-wetting systems in order to accurately predict entrapment, something that is not always currently possible.
1. Introduction
The entrapment of a non-wetting phase (nwp) is the residual saturation left behind following its displacement by the flooding of the containing void space by a wetting phase (wp), in a process known as imbibition. This phenomenon, and the multiphase fluid flow within porous media that gives rise to it, is important in several areas such as contaminant transport and subsequent remediation [1,2], subsurface energy storage [3], oil recovery [4], carbon dioxide sequestration [5], and pore structural characterisation [6]. In reservoir applications, field-scale models require constitutive data such as capillary pressure and relative permeability pressure curves [7]. Many of these applications arise in natural materials so the porous media involved are typically disordered and complex. Relevant data are hard to measure, so pore-scale modelling is used to predict the constitutive properties needed for field-scale models. The entrapment phenomenon can, itself, also be actively utilised in pore structural characterisation [6]. Pore-scale modelling is also necessary to correctly and accurately interpret indirect pore structural characterisation data, such as mercury porosimetry. As will be seen below, the entrapment of mercury during mercury extrusion can be used to infer information on the pore connectivity and spatial distribution of macroscopic heterogeneities in pore sizes.
It is the aim of this review to survey the various different modelling and simulation approaches used to predict the pore-scale processes involved in the entrapment of nwp in disordered porous media, since, to the author’s knowledge, no comprehensive and thorough review article on this specific topic has been published to date. This review thus focuses upon the retraction of the nwp, known as imbibition, and only refers to intrusion (drainage) as appropriate. A particular consideration of this review is the impact of the various structural features of disordered porous media, such as connectivity and pore geometry, on the levels of entrapment under different flow conditions. While this work will briefly mention phenomenological, data-modelling-type (empirical) approaches, the focus of this review will be those approaches that offer insight into the mechanisms of the nwp entrapment process.
First, this review will define the key physical parameters that impact the processes of interest, and then discuss some fundamental constraints on what is possible with mathematical models and computer simulations. Second, it will consider the various possible approaches in detail. The approaches considered include empirical models (briefly), pore network models, percolation models, models derived directly from imaging data, and thermodynamic and statistical mechanical techniques. It will be seen that, even within a given overall classification, a number of different variant approaches are feasible and each has its own set of advantages and limitations. Third, some overall conclusions will be drawn, the remaining issues highlighted, and some speculations made concerning how the approaches described may develop in the future to finally address and solve the remaining problems.
2. Impact of the System Parameters and Physical Constraints
Wettability is a key factor affecting the degree of entrapment and is the ability of one immiscible fluid to wet a solid surface in the presence of another immiscible fluid [8]. It is characterised by the contact angle. Different wettability conditions lead to different fluid configurations within the void space at equilibrium [9]. Wettability is a continuous variable ranging from fully wetting to fully non-wetting. In the case of fully wetting, the fluid in question wets the entire solid surface and leaves the other fluid in the core of the pores. In the case of fully non-wetting, the fluid is in the pore core and the other fluid forms the surface layers. More complex wettability conditions arise at intermediate wetting, where both fluids have an equal affinity for the solid surface, and mixed wettability where both fully wetting and non-wetting conditions can be found in different locations within the same overall void space. Wettability can be changed by varying the physical properties of the fluids, as occurs in low-salinity water-flooding following high-salinity water-flooding [9].
The key forces that control the pore-scale processes occurring during imbibition are capillary, viscous, and, sometimes, buoyancy (gravity) forces. The balance between capillary forces and viscous forces in the control of fluid–fluid displacement within porous media is captured by the capillary number, denoted Ca, given by the following [10]:
where μ is the dynamic viscosity of the displacing phase, q is the total Darcy velocity (volume flowing per unit area per unit time), and σ is the interfacial tension between the two fluid phases. For typical oil–water flows in reservoirs, Ca ≈ 2 × 10−7. Viscous forces only become significant at the pore scale when Ca > ~10−4 to 10−3. Mercury porosimetry experiments also correspond to the capillary-control regime. The viscous forces become important in systems with relatively high viscosity, such as polymer flooding enhanced oil recovery (EOR) processes, or when the surface tension is low, as with surfactant EOR methods [4,10].
The physical process of the imbibition of the wetting phase, and retraction of the non-wetting phase, can be simplified to a varying degree depending upon the relevant physical parameters of the system. Quasi-static retraction of the non-wetting phase is when the process happens very slowly (when q is small), such that the flow dynamics of the nwp are not important [11].
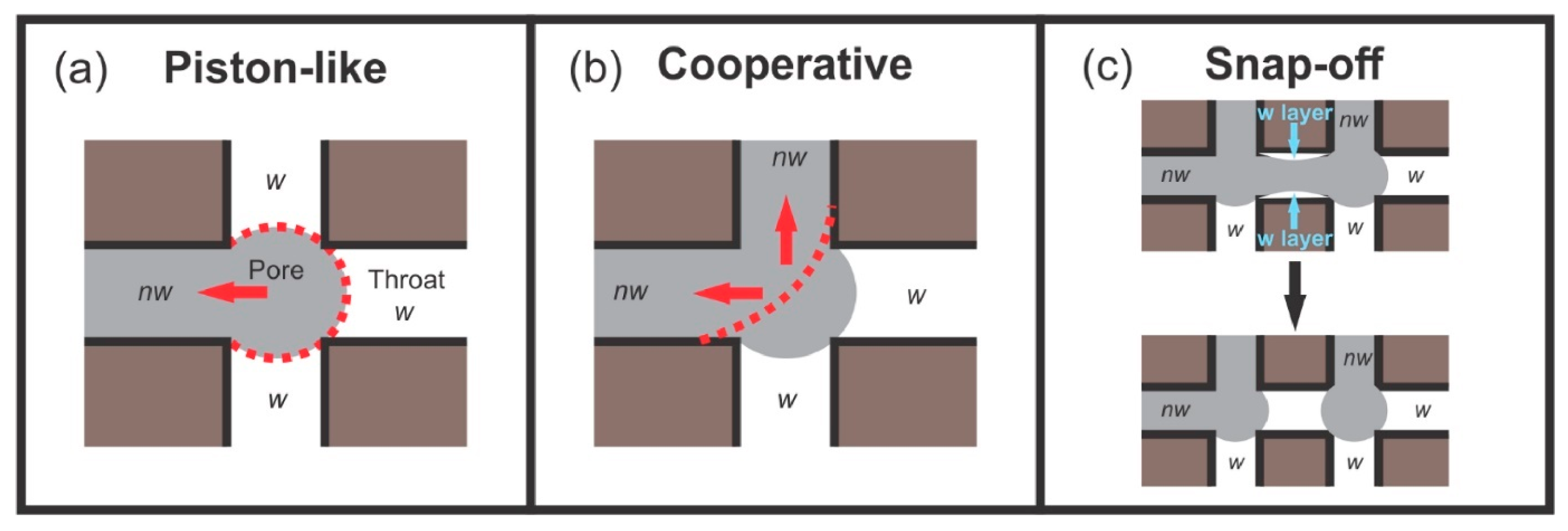
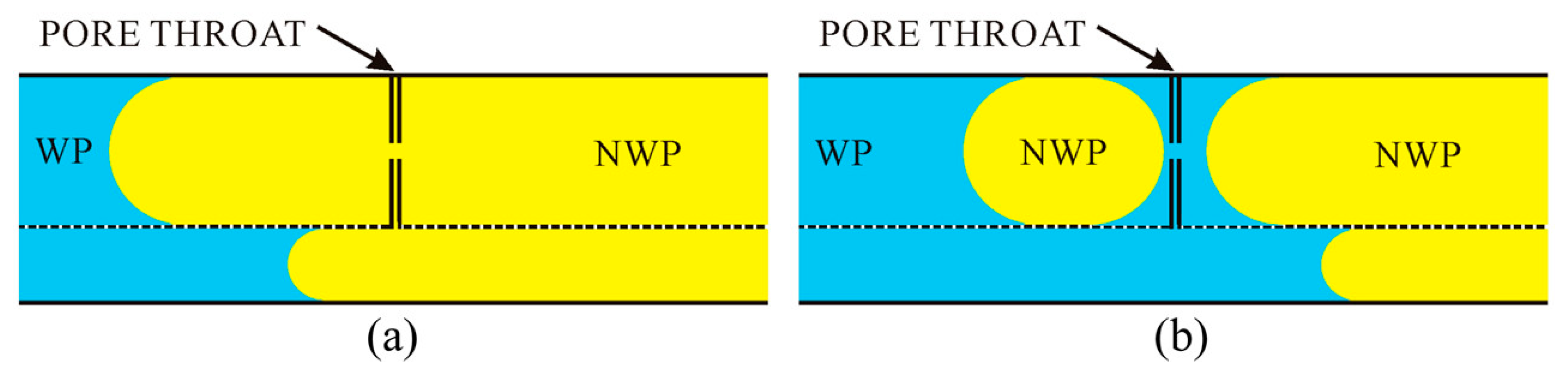
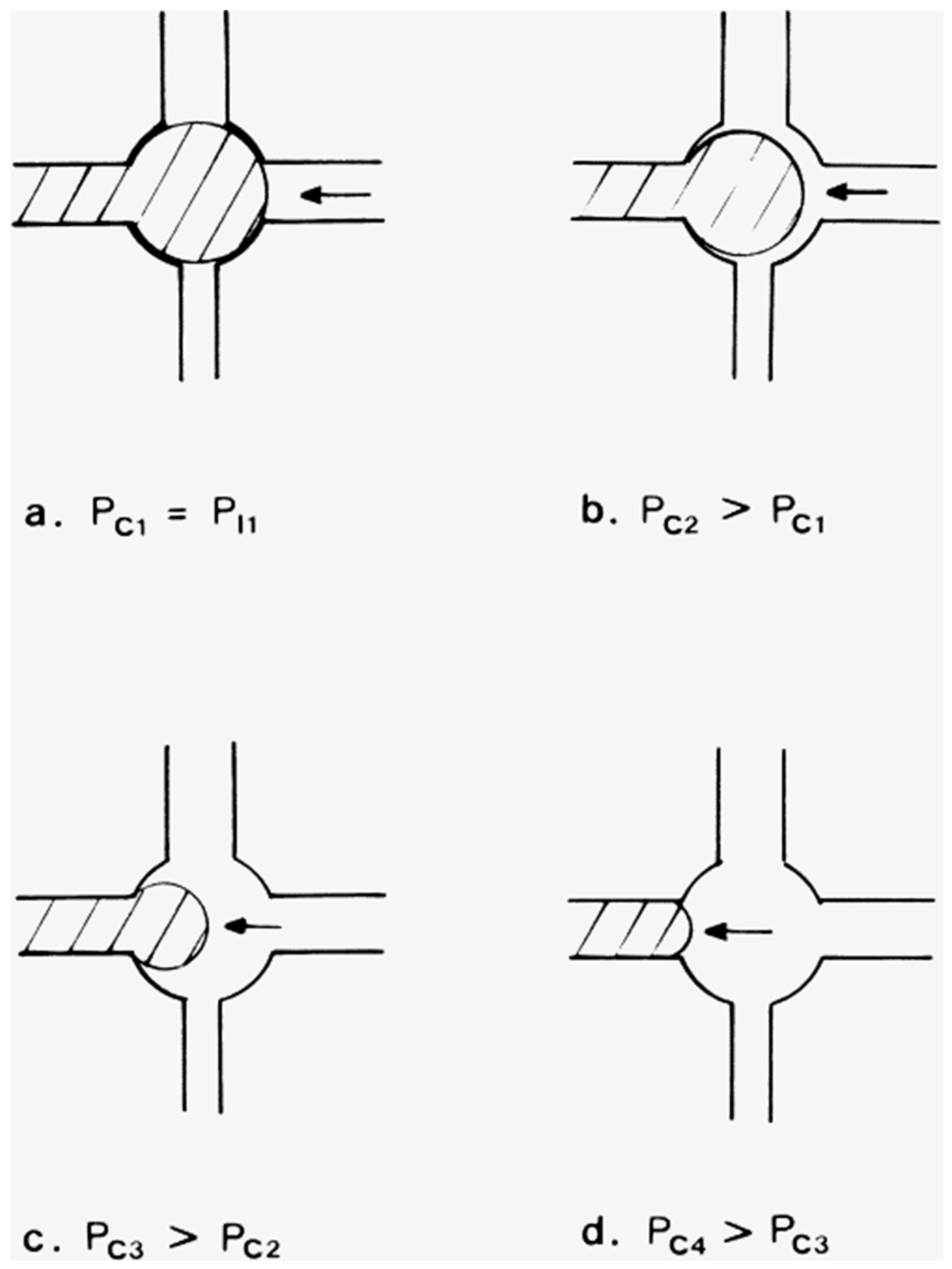
Furthermore, when the imbibing wetting phase is a vacuum (low-pressure air), and the retracting phase is highly non-wetting mercury, then the system is more straightforward than for less distinctly non-wetting systems such as oil–water. This is because, since the invading phase is a vacuum, it is not possible to apply a positive pressure (a negative capillary pressure), and, thus, the initiation of pore filling by a so-called I2 or I3 process, as defined below, is unlikely [8]. In a pore body–throat network, where n throats are attached to each pore body, the interface between nwp and wp can adopt a number of different configurations depending upon the number of pore throats initially filled with nwp together with the pore body. The initial configurations are denoted Ii where the upper case I stands for the interface and the subscript i is an integer that represents the number of pore throats initially filled with nwp. Hence, I2 or I3 correspond to two or three throats initially filled with nwp. The number of filled throats affects the process of retraction of the interface, and thus the particular type of fluid displacement obtained. The types of displacement are typically classified into three general categories, namely piston-like, co-operative, and snap-off, as shown schematically in Figure 1 [7,8]. In addition, the displacement of mercury must stop at a positive capillary pressure equal to atmospheric pressure, as a vacuum cannot be imposed within the mercury itself. Therefore, displacement of mercury is entirely controlled by snap-off. This snap-off does not require consideration of the layer flow of the wetting phase (at the solid boundary) as that wetting phase is the vacuum.
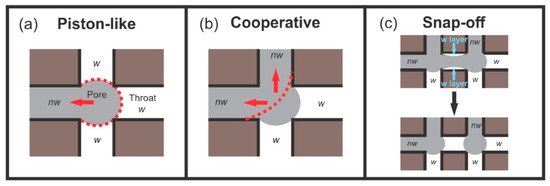
Figure 1.
The dashed red line represents the position of the meniscus immediately prior to displacement (a) and immediately after displacement (b). (a) Piston-like displacement; (b) cooperative pore-filling, specifically an I2 displacement as two throats are filled with non-wetting fluid as the displacement occurs; (c) snap-off. “w“ represents the wetting fluid and “nw” represents the non-wetting fluid. The red arrows indicate direction of flow. The blue arrows indicate the direction of movement of the meniscus. Reprinted from [7]. Copyright (2024), with permission from Elsevier.
Further, the statistical mechanical modelling of porosimetry suggests that mercury retraction involves two different dynamical regimes [11]. The first regime, known as the transport regime, is associated with the mass transfer (displacement) of mercury to the external surface, while the second regime, known as the quasi-equilibrium regime, corresponds to re-distribution of the fluid inside the material once entrapment has occurred. The time-scale of the equilibration period, following a pressure decrement change during a porosimetry experiment, is usually chosen to try to exceed the time-scale of the transport regime. In general, the total porosimetry experimental time-scale does not necessarily exceed the typical time-scale of the quasi-equilibrium regime. As will be seen, in statistical mechanical simulations, the mass transport, even in the transport regime, is considered to be diffusional relaxation.
A key issue with predicting entrapment is the boundary condition (BC) for the imbibition process [12]. This is because it affects the number of potential accessible routes for the different phases to the free surface. The first BC often used is pure linear 1D countercurrent imbibition where the model is considered sealed on all sides except one. The second BC is where two opposite ends of the model are considered open, typically with one end in contact with wp and one in contact with nwp. Sometimes a pressure gradient is applied between the two open ends. In many circumstances, such as simulations of mercury porosimetry experiments, the All Faces Open BC is the most commonly used BC, but it is also the most difficult to model using differential equations for two-phase flow [12].
Since heterogeneous, disordered porous materials are necessarily highly complex, the full representation of the geometry and topology of the void space, together with the multiphase flow therein, for a length-scale statistically representative of the real system is often a problem beyond what is feasible with current computing power. Hence, some sort of so-called Galilean idealisation, whereby the system is simplified to the point that it becomes computationally and/or mathematically tractable with current techniques, is required [13,14,15]. As will be seen below, a commonly adopted simplification is the extraction of a pore network model (PNM) from imaging data of the full void space. While some essential elements of this procedure will be discussed where relevant below, a more detailed review of PNM extraction algorithms has been made elsewhere [14,15]. For Galilean idealisations, it is not possible to know in advance if a particular level of simplification will maintain empirical adequacy. However, an alternate strategy to Galilean idealisation is to construct minimalist-type models, which, specifically, only contain the minimum necessary features of the system that are predictive of the entrapment of the nwp [13,14,15]. The key step in this approach is identifying these key features based upon theoretical ideas or empirical studies. Examples of both types of modelling strategy will be considered in this work.
3. Empirical Models
The simplest models for the prediction of entrapment are empirical models where a function has been fitted to experimental data [8]. In the past, extensive experimental studies have been conducted in order to generate empirical curves that quantify the residual (en)trapped saturation of the nwp as a function of its initial saturation for a variety of porous media. These studies have also already been extensively surveyed in the past [16,17,18,19], and, thus, only a few key studies will be mentioned briefly here.
The most often applied model is that of Land [20], which was originally developed to describe the entrapment of gas during the ingress of water, such that the residual saturation (entrapment fraction) Snwr of the non-wetting phase is given by
where Snwi is the initial saturation of non-wetting phase, Swc is the connate water saturation (water trapped at the point of formation), and C is a fitting parameter called the Land constant.
A further purely empirical model was developed based upon network modelling, where the residual saturation of non-wetting phase is given as follows [8]:
where the two fitting parameters α and β are obtained from matching Equation (3) to experimental data.
Salmas and Androutsopoulos [21] provided a correlation of mercury entrapment with the tortuosity factor for their corrugated pore structure model (CPSM), which consisted of a sequence of Ns cylindrical pore segments of constant length but distributed diameter within a particular range. These parameters for the model can, in turn, be obtained from nitrogen sorption experiments. Overall, the amount of mercury entrapment increased with the CPSM tortuosity factor, as might be plausibly expected as a large part of the latter was a result of the amount of variation in pore cross-section along its length.
As with all empirical modelling, the usefulness of the empirical formulae beyond the particular systems, or types of systems, used to construct them depends upon how remote the new system to which they are applied is in terms of the nature of the fluids, flow parameters, and porous materials involved. Further, empirical models do not tend to improve the understanding of the underlying physical causes, or provide full mechanistic explanations, for varying levels of entrapment under different sets of conditions. The model types discussed below also, often, have these aims.
4. Pore Network Models
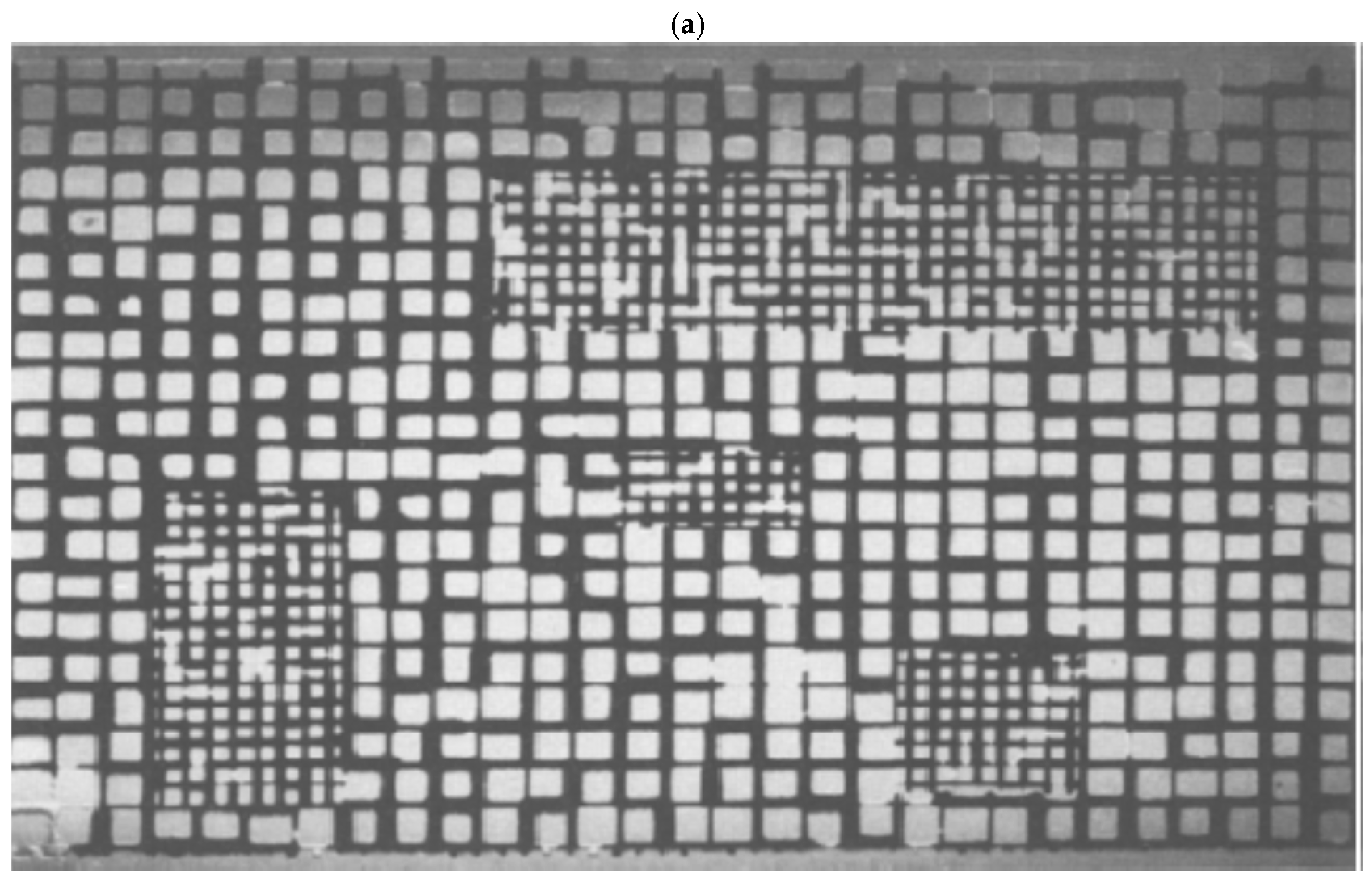
PNMs come in a variety of forms including pore bond networks and pore body–pore throat networks [6]. Examples of such models are shown in Figure 2.
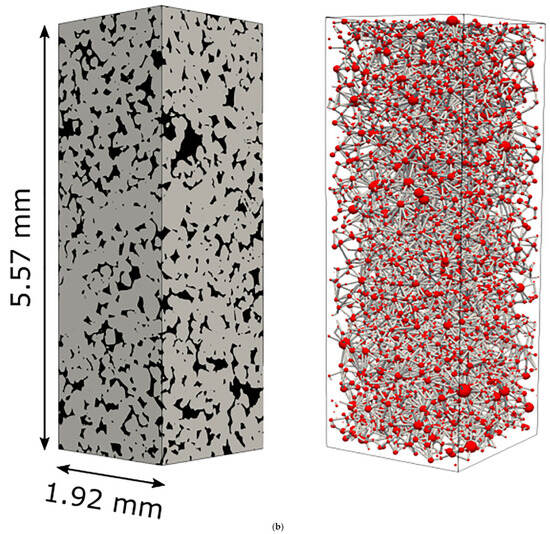
Figure 2.
Examples of (a) a random pore bond network (reprinted from [22], Copyright (2017), with permission from Elsevier) and (b) a pore body–throat network extracted from a CXT image [23] (reproduced under Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 licence).
4.1. Simple Pore Networks
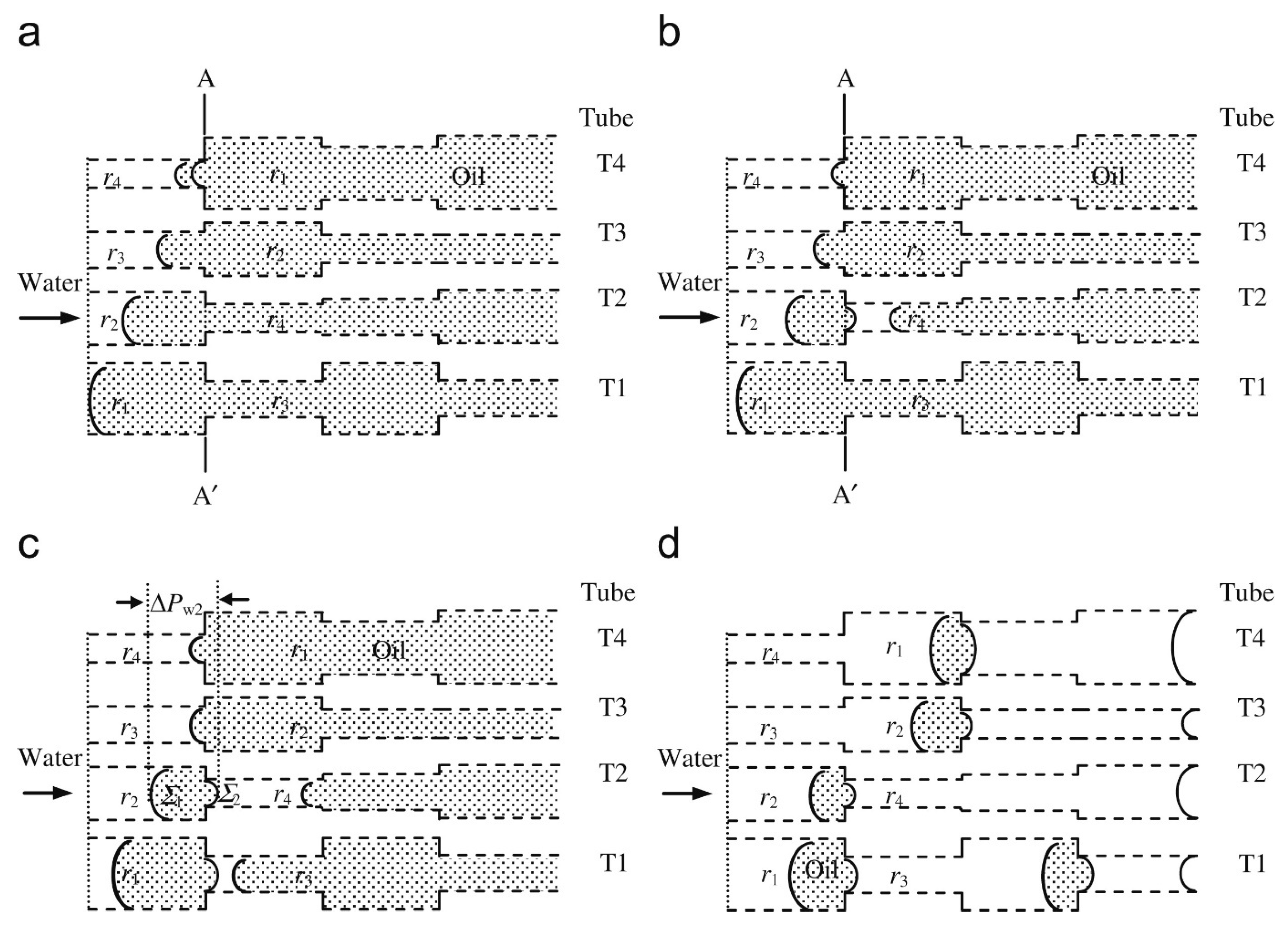
Many simulators of the entrapment of nwp employ quasi-static displacements in pore network models (PNMs) [8]. It will be seen that the simulations of retraction of nwp differ in their level of sophistication in describing the behaviour of individual menisci in pore elements. The threshold capillary pressure for pore filling with wp is highly sensitive to the geometry of the pore, which throats are filled with wp, and how they are arranged [8]. As will be seen, in PNMs only rather simplified, sometimes empirical, expressions have been proposed to quantify the threshold pressures. Even in the simplified geometries of PNMs it is hard to find the largest radius of curvature, leading to the use of even more simplified geometries or rules for determining the movement of interfaces.
In the simplest PNMs—such as that of Mann and co-workers [24,25] and that of Dias and co-workers [26,27], which employ a pore bond network consisting of smooth, straight cylinders meeting at volume-less nodes—a small set of rules is used to describe the retraction. Since nwp is assumed to end the invasion process with a pair of free (uncoalesced) menisci within the smallest pore of the network, retraction is initiated from there. Retraction generally occurs only when a pore bond has a free meniscus at one end, when that pore bond maintains a continuous connection to the exterior only via pore bonds filled with nwp, and when the applied pressure also drops below the critical value (as from the standard Washburn equation [24,25,26,27]). In the models of Mann and co-workers [24,25] and of Dias and co-workers [26,27], when the meniscus reaches a new node all pore bonds attached to that node are considered to have a free meniscus. Hence, the initial retraction from the uncoalesced menisci would create six new free menisci at the entrances to the six adjacent pores in a square grid network of connectivity equal to four. In such a system, entrapment arises from the situation when a pore bond ends up with a free meniscus at both ends. Similarly, a cluster of pores all filled with nwp can become disconnected if all the bonds on the periphery of the cluster have free menisci. In a macroscopically homogeneous system (where the overall sample size exceeds the correlation length for average pore size), with an underlying random distribution of pore sizes across the network, mercury entrapment arises across the whole network. The amount of entrapment increases as the overall size of the network increases, and as the coefficient of variation in the pore size distribution increases. In tests of the model of Androutsopoulos and Mann against experimental data, the level of mercury entrapment was not predicted accurately; however, this may be due to the restriction of the model to a two-dimensional (2D) square grid with fixed connectivity [24].
Simulations of mercury retraction have also been carried out on more complex pore bond networks (PBNs) and using mechanisms of mercury retraction validated against experimental data. Portsmouth and Gladden [28,29] constructed a PBN by scattering nodes at random in space and then connecting each node to a number Z, the connectivity, of its nearest neighbours with bonds. It was assumed that there was no correlation between pore bond diameter and length.
Three different mechanisms of mercury retraction were tested by comparing the resultant mercury entrapment for a 2D square lattice with experimental data obtained for a glass micro-model with a similar network geometry [30]. In general, for all mechanisms, mercury retraction was allowed from a given pore bond if the applied capillary pressure was below the critical pressure from the Washburn equation, if a percolation path existed from that pore via only pores still filled with mercury to the periphery of the network, and if a free meniscus existed at one end of the pore or could be generated. More specifically, for the process denoted Mechanism 1, the smallest pores to fill last (during intrusion/drainage) in each local cluster of pores were identified and these were taken as “seed” sites from which mercury retraction was commenced. The retraction from such seed pore bonds was considered to generate free menisci for all adjoining pore bonds connected to the same two nodes. In Mechanism 2, when the mercury meniscus first reached a node it was not emptied but only when (Z-1) of the pore bonds attached to it were empty. Mechanism 3 was similar to Mechanism 1 except that any pore bond with a critical retraction pressure higher than the current applied capillary pressure could act as a seed site through snap-off of the meniscus within that pore. Simulations of mercury retraction were conducted on square grids of 31 × 31 nodes, with uniform pore bond sizes and a pore connectivity of four, according to each of the three aforementioned mechanisms [28,29]. This model was considered to represent a lattice similar to the glass micro-model studied by Wardlaw and McKellar [30]. Since the pore bonds were considered to all be of the same size, the seed site for retraction was considered to be the last pore bond to fill during a simulation of intrusion. In the experiments, it was observed that such a grid had no mercury entrapment following retraction back to atmospheric pressure. In the simulations, it was found that only Mechanism 2 led to this result, with Mechanisms 1 and 3 both leading to some residual entrapment. Hence, it was concluded that Mechanism 2 was more in line with the empirical findings. Portsmouth and Gladden [28,29] observed that the high entrapment associated with Mechanisms 1 and 3 was caused by the large-scale disintegration and disconnection of the mercury ganglia, resulting from the high incidence of snap-off, which did not occur for Mechanism 2.
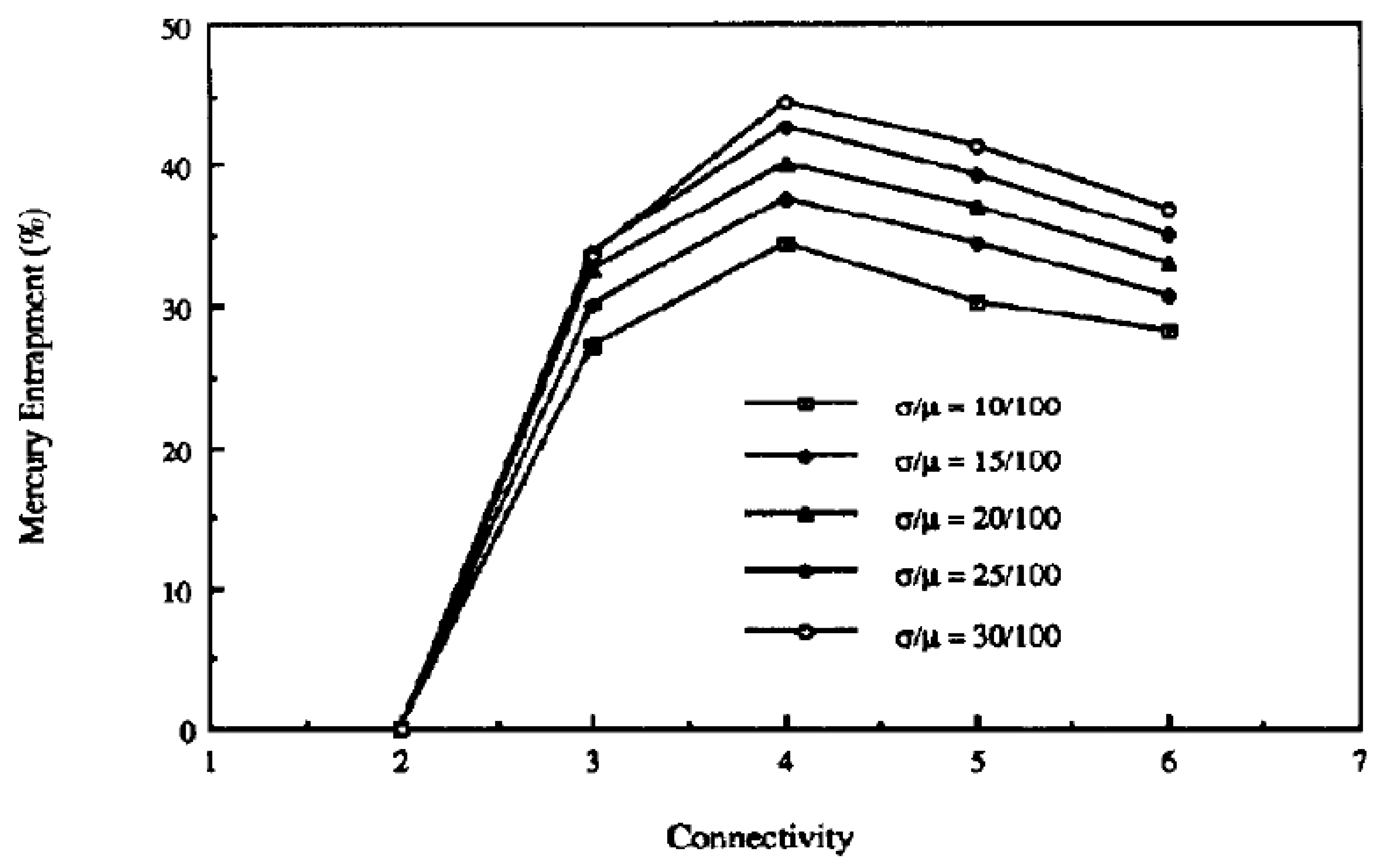
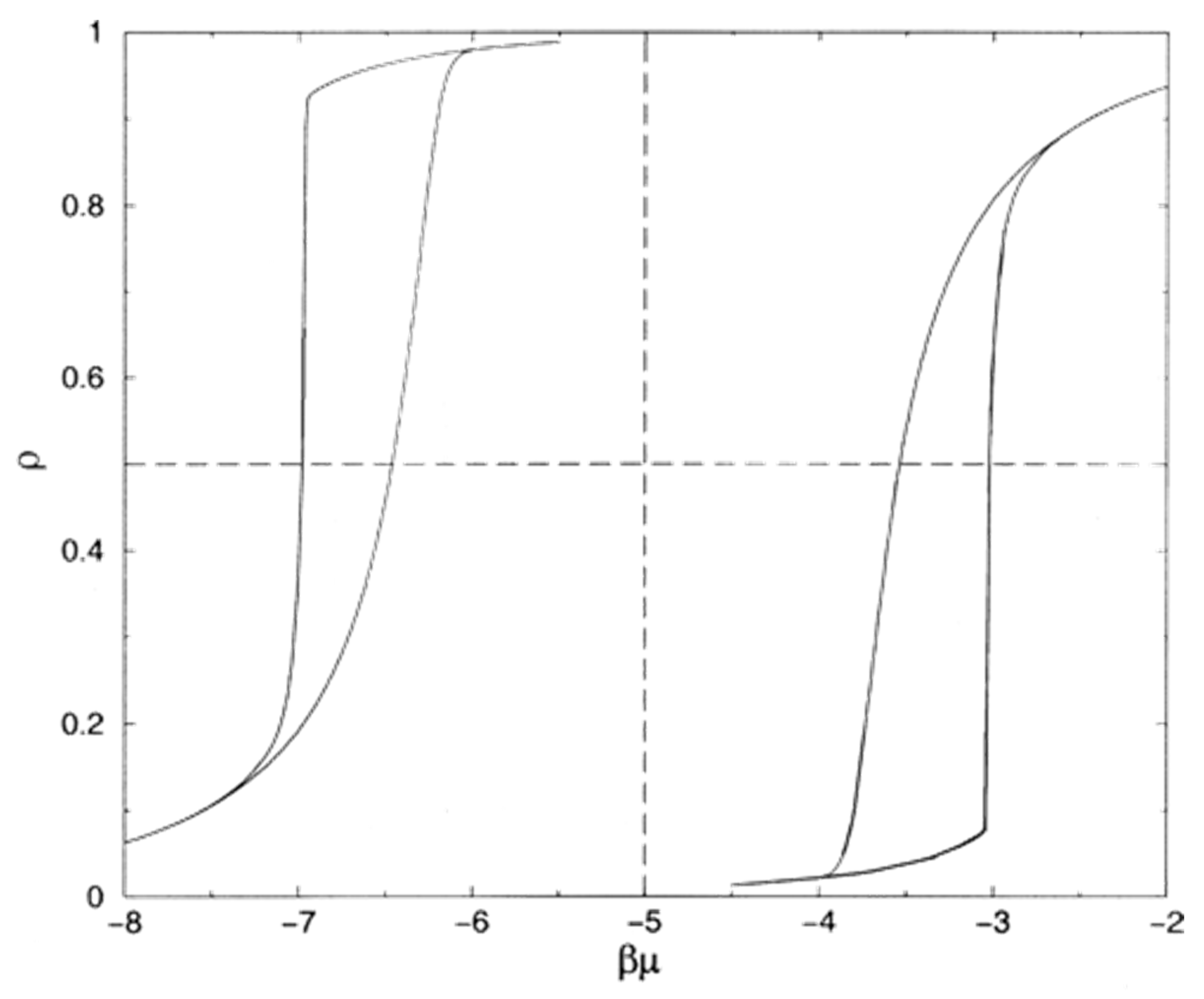
For simulations of mercury retraction on random PBNs with different pore connectivities and coefficients of variation for the PSD, it was found that the level of mercury entrapment depended upon the values of both of these parameters as shown in Figure 3 [28,29]. From Figure 3, it can be seen that the level of entrapment reaches a maximum at intermediate values of connectivity. For extremely low and extremely high values of connectivity, the chances of entrapment are lowered. This is because, without snap-off, mercury can retract from all pores when the connectivity is two, and a high connectivity provides many different potential routes for the mercury to exit—thereby meaning it is unlikely to become disconnected before being able to retreat. An increased width (spread) of the PSD means that a large pore is more likely to be surrounded by smaller pores from which the mercury retreats before the mercury can retreat from the larger pore.
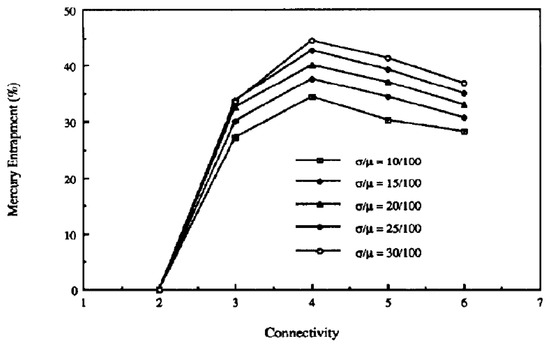
Figure 3.
Variation of entrapment as a function of the width of the PSD (coefficient of variation σ/μ) and pore connectivity for the random pore bond network model of Portsmouth and Gladden [28]. Reprinted from [28]. Copyright (1991), with permission from Elsevier.
Entrapment levels can be actively manipulated using mercury porosimetry scanning curves and loops [6,28,29,30]. In this way, the particular entrapment arising in specific void space features or pore size ranges can be determined and utilised to deliver information on these particular pore network elements.
Simple straight pore models can also be used to consider dynamic effects. A relatively simple interacting capillary bundle developed by Dong and co-workers [31,32] has been used to explain the large difference in the levels of entrapment of nwp during co-current spontaneous imbibition of packed beds of glass beads or quartz sand [33]. The key difference in the void space of the two packed beds was the pore size distribution (PSD). While the PSD for the glass beads was narrow, that for the sand was much wider. The original interacting capillary bundle model consisted of a bundle of parallel tubes of different diameters where communication and pressure equilibration between tubes is possible at every position along the long axis of the tubes. However, Meng et al. [33] made a further modification of the basic interacting capillary bundle model to include a very narrow pore throat within a larger tube, as shown in Figure 4. In general, the theory predicts that for porous media with a wide PSD, during immiscible displacement, the meniscus boundary between nwp and wp advances faster in smaller pores than larger pores. Hence, for the capillary bundle with the throat added, when the meniscus in the smaller pore reaches the equivalent position of the pore throat in the larger pore, the pore throat will rapidly fill with wetting phase from the smaller pore because the curvature of the pore throat is large and its volume is relatively small. This will result in snap-off of the nwp in the larger pore, as seen in Figure 4b. Hence, nwp may become entrapped in the larger pore if there are no further interconnections with other tubes into which the nwp could escape. For void spaces with narrower PSDs, such as glass bead packing, the advancement rate of menisci in different pores is virtually the same, such that the imbibition front is almost flat, and the situation in Figure 4 rarely arises. This model can also explain why the level of entrapment is often observed to increase with nwp viscosity. This is because the difference in the advancement rate of the menisci in the smaller and larger pores increases with increased nwp viscosity. Hence, it means the situation seen in Figure 4b may arise more frequently and, thus, more entrapment results. These findings suggest that a relatively simple capillary model can explain many of the dynamic features of entrapment in fairly complex void spaces.
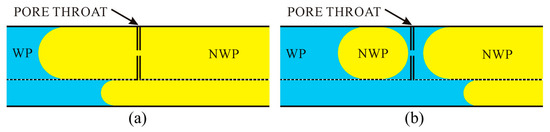
Figure 4.
Schematic of (a) before and (b) after snap-off of the non-wetting phase (NWP, yellow) in the interacting tube model. The wetting phase (WP) is in blue. Reprinted from [33]. Copyright (2015), with permission from Elsevier.
The shape of the tubes in the interacting capillary bundle model was subsequently modified, by Wang and Dong, from circular to triangular to permit the formation of films of wetting phase in the corners and, thereby, continuous flow of wp throughout the entire model [34]. In such a model, trapping of nwp happens when the wp pressure drop across an upstream nwp slug is smaller than that of the capillary pressure difference between the front and rear menisci. In a simulation with a constant rate of injection, the water pressure drop keeps decreasing with increasing water saturation, as more oil gets trapped. The process by which the trapping of oil occurs in an interacting-serial type triangular tube bundle model with varying pore segment cross-sections is shown schematically in Figure 5. The model showed that a relatively smaller tube size results in higher residual oil saturation at the same capillary number, but more uniformity in tube sizes gives a much lower oil saturation as might be anticipated from the trapping events in Figure 5 occurring where the tube size goes from larger to smaller. The interacting capillary bundle model allows the mechanisms of trapping to be studied in detail.
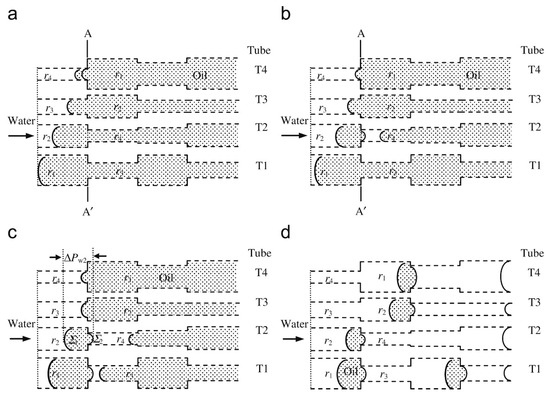
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of the stages (a–d) of the trapping of oil occurring in an interacting-serial-type triangular tube bundle model. Reprinted from [34]. Copyright (2011), with permission from Elsevier.
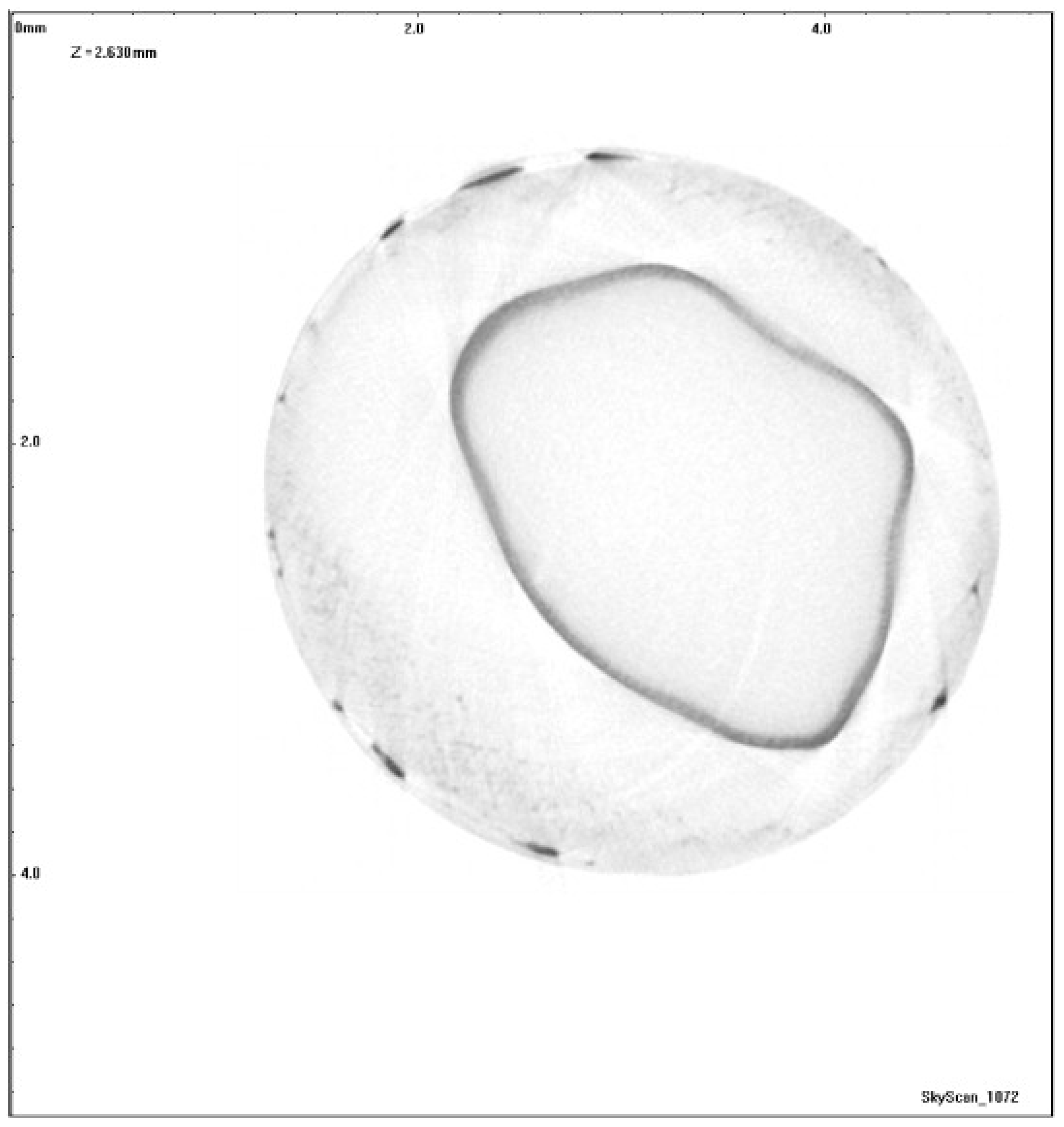
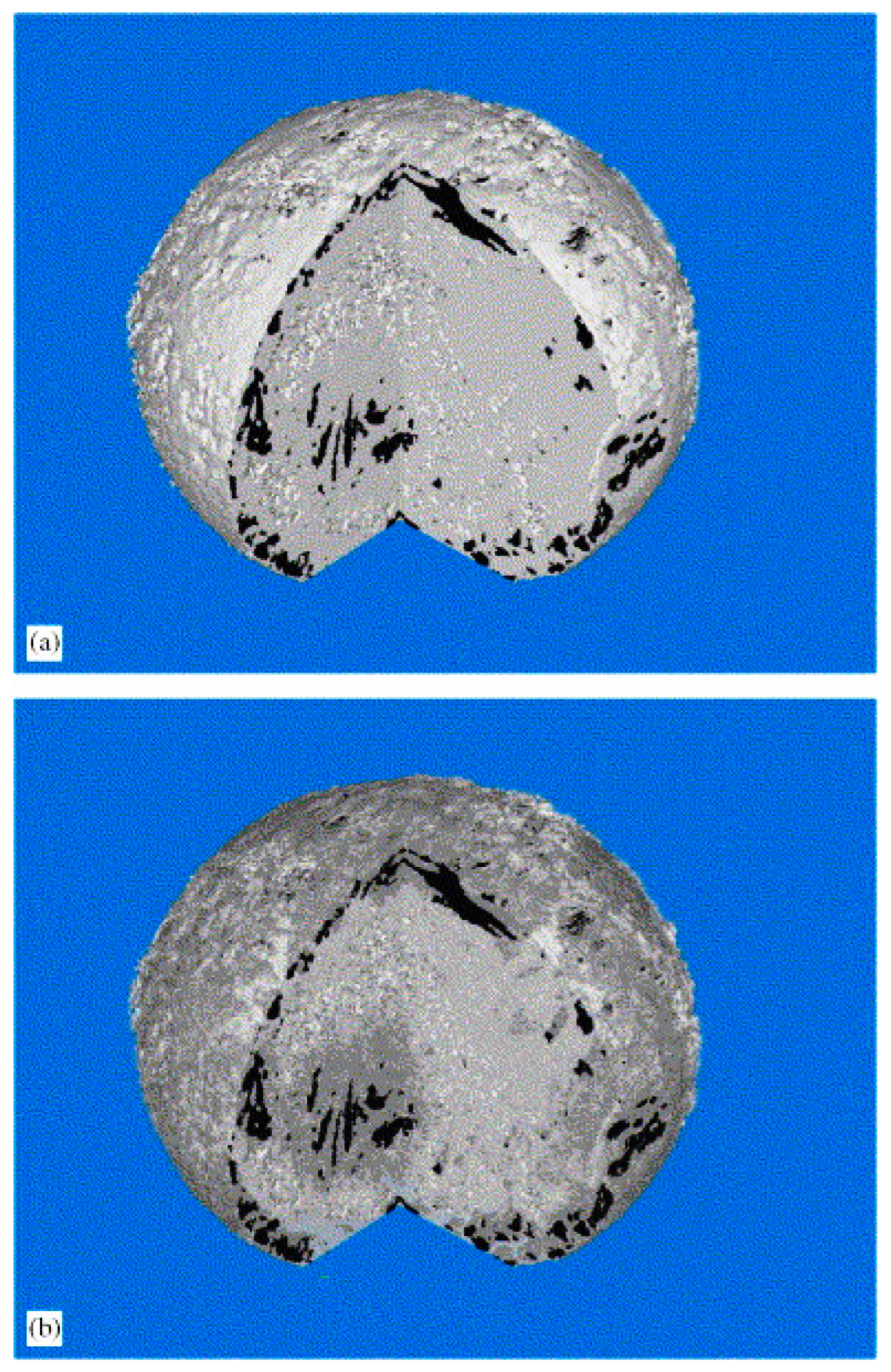
The type of entrapment shown for the interacting capillary model in Figure 5d, where the nwp occurs as a short band at the narrowing of the pores, may be what is occurring during mercury retraction from a sol–gel silica pellet—where computerised X-ray tomography (CXT) has shown a shell of mercury (appearing as a ring in the 2D cross-section in Figure 6), probably where the seed particle forming the core of the pellet bounds the mantle of new silica added in the so-called “oil-drop” synthesis method typically used for forming such materials [11]. The sol–gel silica has a disordered, interconnected, mesoporous network. However, the whole spherical shell-like boundary seen in the CXT image may be associated with a particular narrowing of the pore size, due to the blinding-off of pores on the exterior of the core region during precipitation of further silica in the mantle. This is supported by the fact that the entrapment disappears entirely when the pellet is fragmented to a powder with particle sizes smaller than the core region, since the pore-shielding from the narrowed pores, giving rise to the entrapment, is then removed. However, an alternative hypothesis is that the entrapment arises within a band of larger pores sandwiched between core and mantle regions both composed of smaller pore sizes.
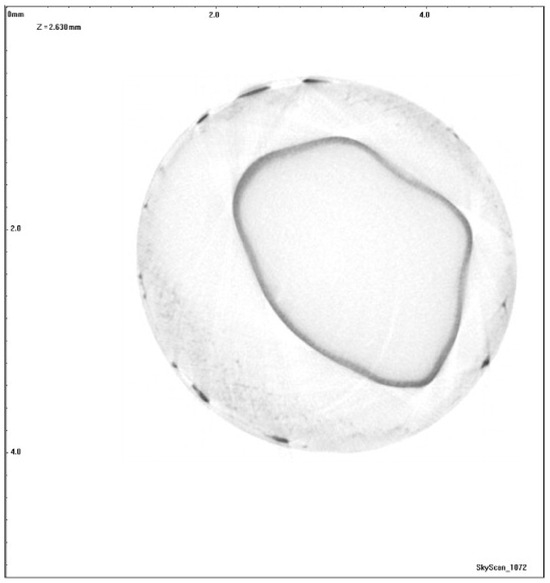
Figure 6.
Two-dimensional X-ray micro-CT image of a cross-section through a spherical pellet of sol–gel silica following porosimetry. The porosimetry equilibration time was 15 s. Black corresponds to entrapped mercury and grey corresponds to silica matrix. Reprinted from [11]. Copyright (2008), with permission from Elsevier.
Other types of pore networks have also been used to study entrapment. Felipe et al. [35] conducted simulations of mercury retraction from models consisting of networks of spherical sites connected by cylindrical bonds using a mercury retraction algorithm that consisted of relatively simple rules. It was proposed that the mercury ganglion (thread) within pore bonds smaller than a critical limiting size could undergo snap-off if the capillary pressure was lower than the critical pressure needed to exit the pore bond and both exits from the bond had percolating paths via bonds still occupied by mercury all the way to the periphery of the network. More generally, a pore bond would empty by a piston-like mechanism if one end had a free meniscus and the other two criteria above were also met. A pore body would empty of mercury if the capillary pressure was below the critical value for the body size, one of the neighbouring bonds was empty of mercury, and a percolation path to the network periphery existed via one of the other neighbouring filled bonds. Mercury entrapment generally arose due to the creation of isolated “islands” of filled bonds and sites. The amount of entrapment increased with the frequency of snap-off (increased by increasing the critical snap-off size) and for low-connectivity networks and networks with a low pore size spatial correlation.
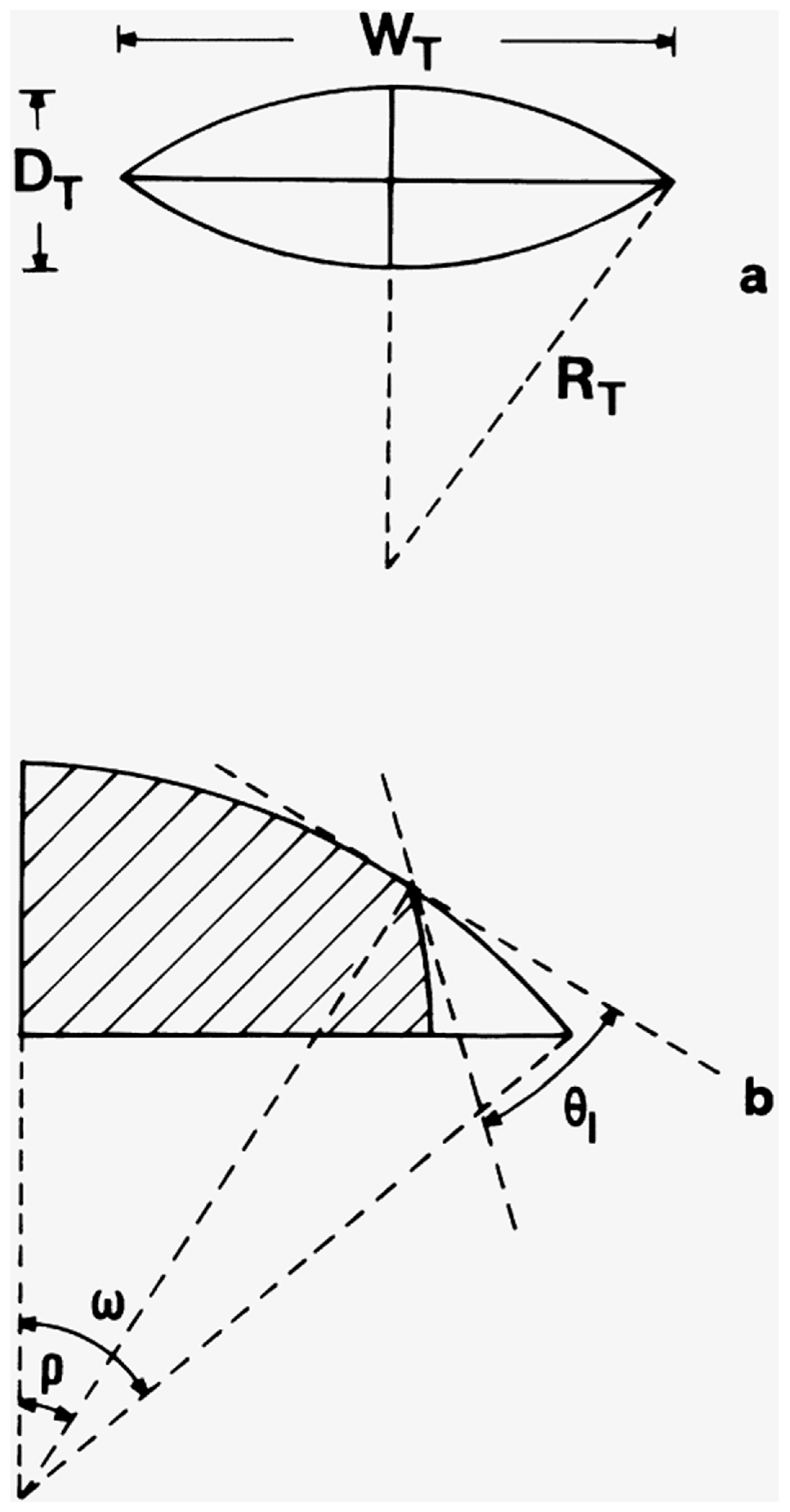
In most natural and industrial porous materials, the pore cross-section is irregular such that the pores have corners [36,37]. The existence of corners also occurs for the lenticular pores formed by acid-etching of glass to make micro-models, as shown schematically in Figure 7 [37]. The geometry of the corner can be described by a corner half-angle β. In such materials, the wp is usually retained throughout the network in the deepest recesses of the corners even at the highest capillary pressure because the radius of curvature is too high for the nwp to fill the corner completely.
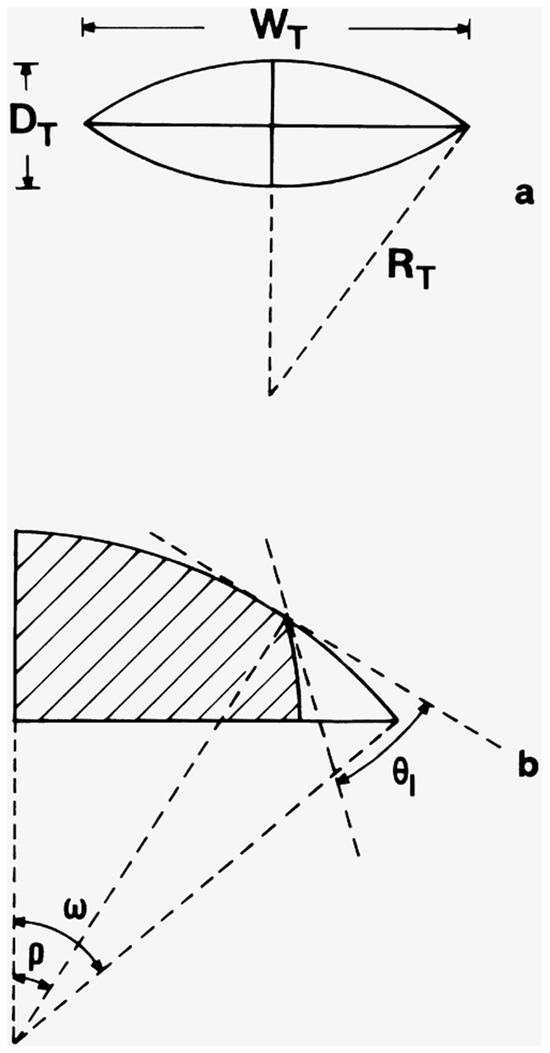
Figure 7.
(a) Cross-section of a lenticular throat of the mathematical model. (b) Cross-section of a meniscus in a lenticular throat. The shaded region represents nwp and the corner is occupied with wp. The symbols denote various dimensions and parameters of the throat and meniscus. Reprinted from [37]. Copyright (1998), with permission from Elsevier.
In more sophisticated treatments of the mechanism of mercury retraction from pore bond–throat (neck) networks than already discussed, the amount of entrapment of nwp is controlled by the competition, occurring within throats, between piston-like filling with wp and the snap-off of nwp [8]. The piston-like filling with wp is what would occur for the throat in Figure 8d indicated by the arrow, as the nwp retreats in the direction of the arrow. If there is no contact angle hysteresis (so that the advancing (ΘA) and retreating angles are equal), the threshold capillary pressure for piston-like filling Pc is given by
where σ is the surface tension, rt is the throat radius, and C1t is a geometrical factor which is approximately two for circular pores and unity for slit-shaped pores.
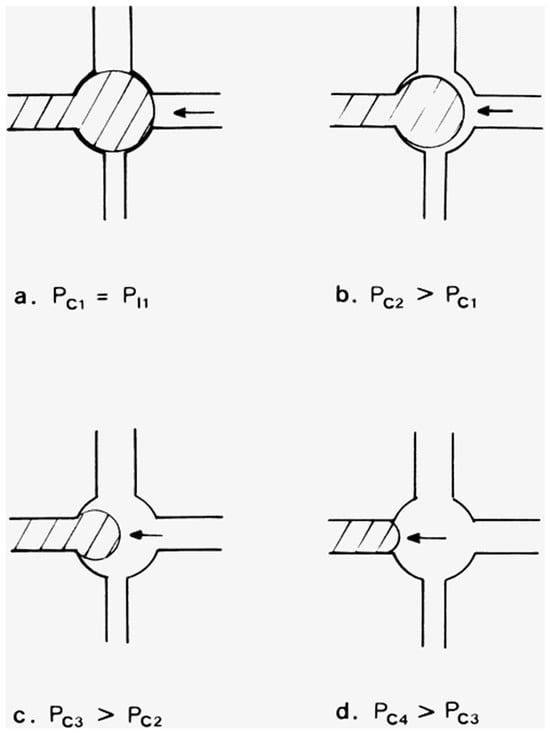
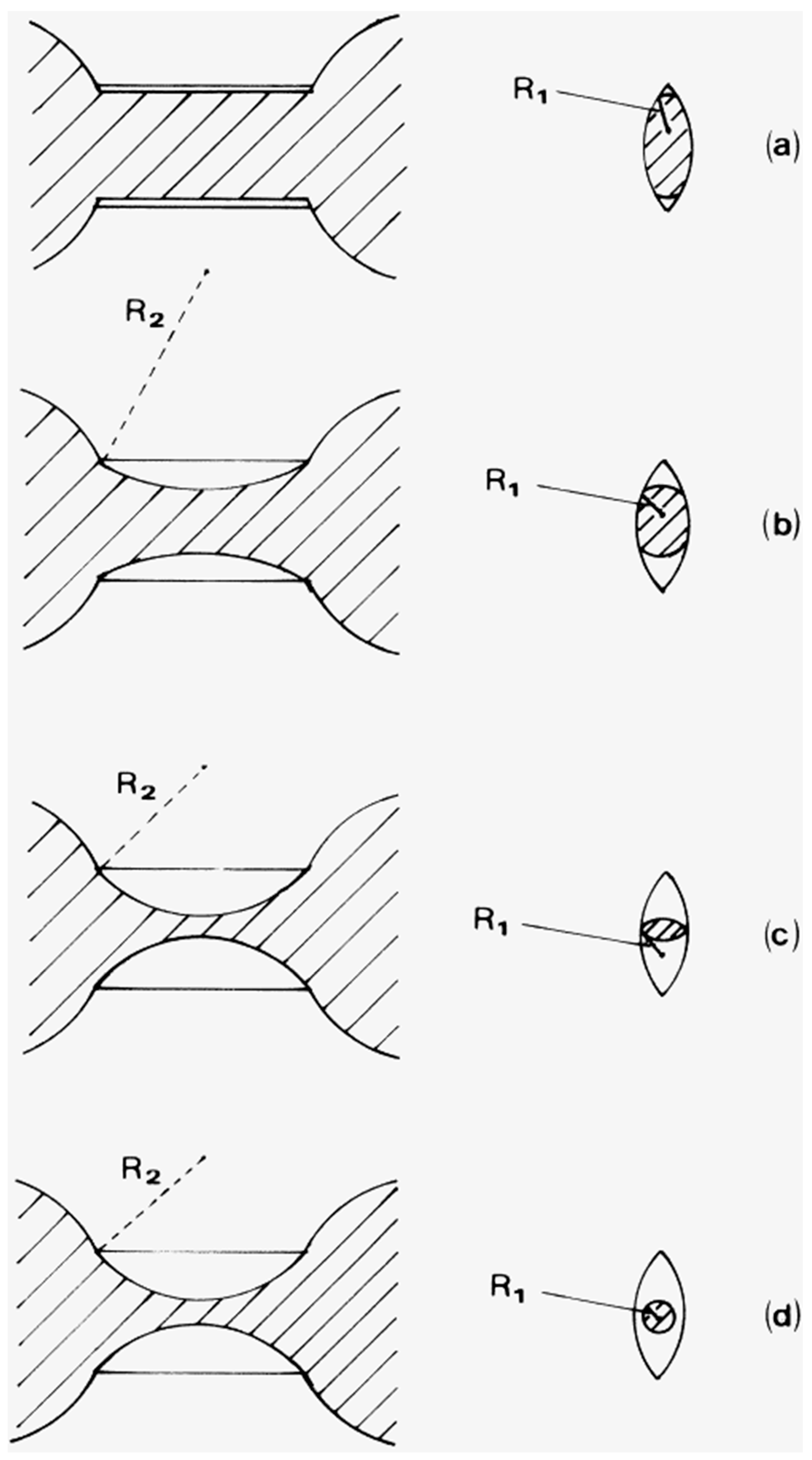
Figure 8.
Consecutive stages (a–d) of the retraction of an I1-type interface where, initially (a), only one throat adjacent to a pore body is filled with nwp. The shaded region represents nwp. Reprinted from [37]. Copyright (1998), with permission from Elsevier.
Snap-off in a throat is the process whereby the ganglion of nwp thins out, as shown schematically in Figure 9, until it finally disconnects. The ratio of the threshold capillary pressures for snap-off Pcsnap to that for piston-like filling Pcpiston is given as follows [8]:
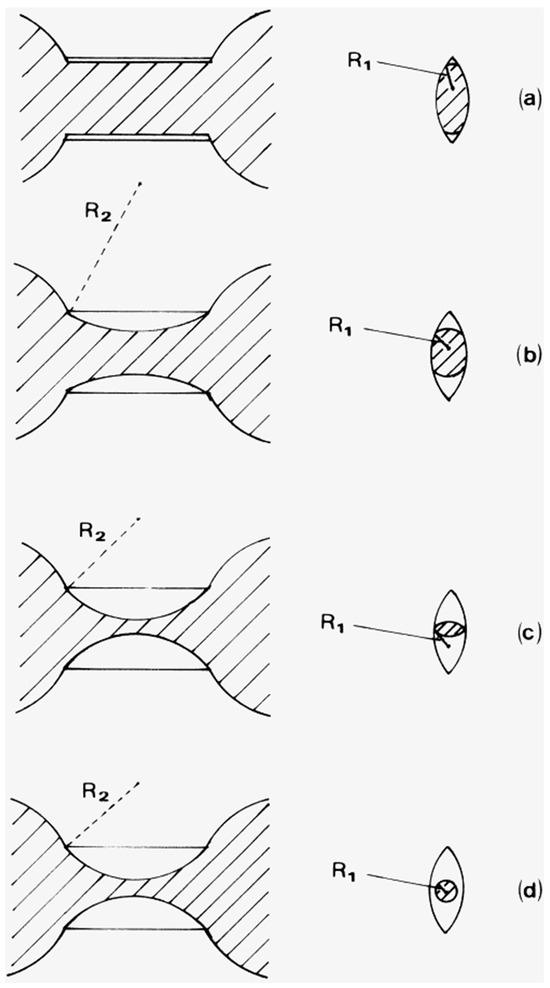
Figure 9.
Consecutive stages (a–d) of snap-off in a lenticular throat connected with two chambers. The shaded region represents nwp. Reprinted from [37]. Copyright (1998), with permission from Elsevier.
Since C1t ≥ 1, piston-like advance is typically favoured over snap-off. Further, a similar ratio denoted PIcR can also be constructed for the ratio of the threshold pressure for snap-off (of nwp) in a throat to that for the most favoured pore body-filling (with wp) mechanism, denoted I1 (as shown in Figure 8), and it is given by
where rp is the radius of the pore body, and CIp is a geometry factor for the pore body. For the filling mechanism I1, this geometry factor is equal to 2 for a circular pore. To favour snap-off, the throat radius has to be less than half the pore body radius. In irregular pore throats, snap-off is also favoured by the presence of sharp corners (i.e., when tan β is small) since this increases the likelihood of the presence of residual wp present at the end of nwp intrusion. In addition, snap-off is favoured for more highly non-wetting nwps (i.e., when θA (if defined as being within the densest phase for oil–water) is small).
Particular expressions, similar in form to Equation (4), can be derived for specific pore geometries, such as the lenticular pore bonds/throats (pores with lens-shaped cross-sections) obtained in acid-etched glass micro-models [37], and different interface configurations therein. In real glass micro-models, the pore throat (bond) length is always finite, and, thus, requires an approximate method of analysis in order to calculate the pressure for snap-off within them. In such glass micro-models, the pore bodies are typically drum-shaped. The full pore size distribution (PSD) of glass micro-models can be determined by impregnating the model with epoxy resin and then measuring the pore sizes from random slices sectioned from the impregnated model [37]. These measurements included the width and depth of each pore throat and pore body. This PSD can be used to construct a computer model of the real network with which to simulate mercury intrusion and retraction using the expressions derived for the change in interface position depending upon its particular initial configuration. The sizes from the experimentally derived PSD were allocated to the computer model at random. The glass micro-model used by Tsakiroglou and Payatakes [37] was a square lattice with a fixed pore throat connectivity of 4. Obviously, as the pore throat connectivity increases, then the number of potential interface configurations also increases, but experiments have shown that most of the additional types of interfaces thereby obtained are just variations on those observed in square lattices and do not change the main features of the overall process. The mercury retraction from the glass micro-model was simulated, using a combination of the aforementioned expressions, for processes arising for particular mercury ganglia and interface configurations, and a set of rules as follows:
- A throat initially filled with mercury that is also connected to two pore bodies still filled with mercury is emptied via snap-off and the creation of two menisci at the mouths of the throat at each pore body if the critical pressure for snap-off is larger than the applied capillary pressure.
- A throat initially filled with mercury and connected to just one pore body still filled with mercury is emptied through piston-like retraction to the mouth of the throat at that chamber if the applied capillary pressure is lower than the critical pressure for this process.
- For each pore body filled with mercury that is connected to at least one empty throat, mercury will retract from the pore body if the capillary pressure is lower than the critical pressure for retraction from a meniscus of configuration Ii.
At low values of network connectivity, the role of fluid topology in determining retraction is amplified. In the initial stages of retraction, I3-type configurations in pore bodies will predominate, as they are formed by snap-off in neighbouring throats. Since the retractions of mercury from interface configurations of value i less than 3 have higher critical pressures than for I3, any formed by retraction from an I3 meniscus will simultaneously retract at the same time. As the typical number of pore throats adjoining a pore body increases, the differences in the critical pressures for retraction of interfaces with different configurations Ii diminishes, and thus mercury retraction will become only weakly dependent on network topology. Further, as the pore body depth of a drum-shaped pore body increases, the ratio of the width-to-depth decreases, and the differences between the critical pressures for the retraction of the various types of interface configuration increase, thereby enhancing the role of the fluid topology, such that the relative frequency of disconnections via I2 configurations increases versus those of other events. This, in turn, leads to a narrowing of the pressure range over which emptying of the network occurs, ultimately leading to lower mercury entrapment. In addition, as might be expected, as the pore body-to-throat ratio increased the frequency of snap-off events increased, and more mercury entrapment occurred. Overall, in the computer simulations of mercury retraction from glass pore body–throat square-lattice network micro-models of sizes 80 × 40 and 65 × 35, the predicted intrusion and extrusion curves matched the experimental ones well.
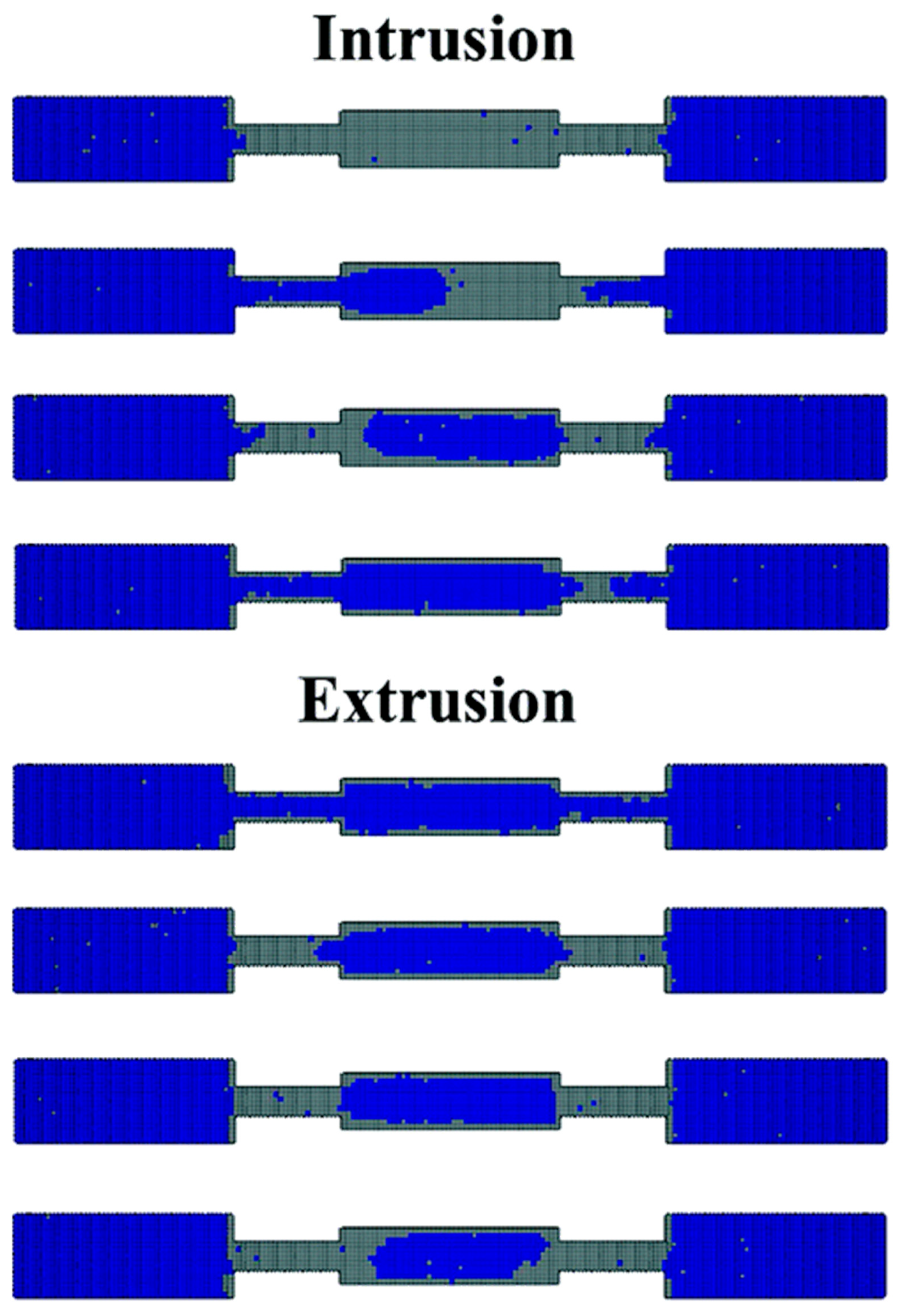
Tian et al. [38] compared the predictions of lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) simulations (see also Section 6) of the displacement of oil from glass micro-models via the injection of water at different flowrates, and thus different capillary numbers, with experiments. The glass micro-models consisted of two-dimensional, regular square lattices of pore bonds, as well as similar model grids but with fracture-like features consisting of wider channels cutting diagonally across the square lattice at an angle relative to the pore bonds therein. At a low capillary number, it was found that these fractures behaved somewhat like the vugs in the micro-models studied previously by Wardlaw and McKellar [30] in that residual oil was entrapped in these features. The LBM simulation predicted the final spatial distribution of oil well, but the geometry of the system was relatively simple. At a higher capillary number, the stronger viscous force led to less residual oil being left in the fracture-like features.
4.2. Networks with Wettability Effects
Mixed-wettability systems are especially common in geological applications, such as carbon dioxide sequestration, due to differences in contact angles for different mineral grains within reservoir rocks. Pavuluri et al. [39] studied capillary trapping in a mixed-wetting structural model for fluid flows with a capillary number of around 10−3 and, thus, viscous force dominated. The structural model consisted of non-overlapping circular grains distributed randomly within a rectangular region, where different contact angles were allocated at random to individual rectangular cells comprising a regular grid dividing up the overall simulation region such that each grain within a given cell had the same wettability but it differed between cells. The incompressible fluid flow dynamics for the injection of one fluid into the model already occupied by another, with differing viscosity but the same density, were governed by the Navier–Stokes equations which were solved using a volume-of-fluid–continuum-surface-force (VOF-CSF) method. It was found that the trapping of the defending phase was dominated by flow-bypassing events and arose in those void spaces that were wetting to the defending phase.
The impact of different wettability (in terms of a varied single oil contact angle) on residual fluid saturation in regular (homogeneous) and heterogeneous two-dimensional, pore body–throat networks has also been studied using LBM [40]. The structural model consisted of a 2D lattice of square pore bodies and cuboid throats. In order to introduce structural heterogeneity, the initially regular lattice could have the position of each solid grain displaced randomly. For models with varying heterogeneity, oil contact angle, and capillary number, the residual oil saturation following simulated displacement by water decreased with increased oil contact angle. Higher values of structural heterogeneity and capillary number resulted in a decrease in residual oil. However, it is noted that the models studied in this work were largely two-dimensional and of relatively small size.
The influence of complex mixed wettability at the single pore- [41] and core-scale [42] has been studied. Complex wettability is when different pore walls have different wetting properties characterised by variation in contact angles. Liu et al. [42] constructed two-dimensional (2D) heterogeneous matrix models consisting of either Y-shaped or S-shaped fractures within a porous matrix consisting of a network of pores. The model assigned one of three different (30°, 60°, or 90°) contact angles to pore walls in the matrix. Imbibition within these mixed-wettability models was compared with similar models but with a constant contact angle. It was found that while the imbibition recovery rates were 38.23% and 27.85% for the Y-shaped and S-shaped fracture mixed-wettability systems, respectively, the imbibition recovery rates for the uniform (macro-wettability) models (with contact angle 30°) were 50.49% and 39.38%, respectively. This marked difference was attributed to the lack of imbibition of partial non-wetting (to wp) pores. This study showed that mixed wettability can have a dramatic effect on the level of residual entrapment of nwp, though it was only seen for 2D pore models.
The impact of changes in wettability occurring due to the fluid displacement process can be studied using PNMs. In the field, wettability alteration can be achieved by low-salinity water-flooding following high-salinity water-flooding of oil-saturated reservoir rocks [9]. This process has been simulated in PNMs with the same pore connectivity but either low (0.273) or high (0.753) coefficients of variation in pore sizes, denoted as homogeneous and heterogeneous systems, respectively. The wettability, characterised by the contact angle, was changed as a function of the salinity of the water phase. The simulations were performed with the volume of fluid (VoF) method under conditions corresponding to a capillary number of ~10−4. While the capillary number was fairly high, it was noted that flow dynamics were still capillary-dominated. The flow dynamics simulated in both PNMs were either (i) high-salinity water-flooding under initial oil-wet conditions or (ii) low-salinity, tertiary water-flooding with wettability alteration. In the former, for the heterogeneous model, clear preferential water flow pathways were observed due to the wider pore size distribution (PSD), resulting in the bypassing of oil and a larger residual oil saturation compared with the homogeneous PNM. The pore size distribution also affected the effectiveness of tertiary, low-salinity water-flooding through two effects, described below. At the end of secondary high-salinity water-flooding, the water phase is left in either flowing regions or stagnant regions. Hence, when the low-salinity water is injected, the wettability change resulting from the mixing with high-salinity pore water occurs at different rates in the two different types of regions within the PNM. The local heterogeneous wettability alteration leads to a fluid flow mechanism denoted as the “push-pull” effect [9]. The change to wettability at capillary interfaces destabilises the particular saturation distribution established following high-salinity water-flooding. As low-salinity water permeates to them, the capillary pressure at the oil–water menisci changes toward more water-wet conditions which assists the water to invade new regions. However, since the stagnant regions remain oil-wetting, water will pull out of them and then push the oil out of the now more water-wetting flowing region, causing an ultimate coalescence of oil ganglia. The second effect of the width of the PSD arises because, after wettability alteration, a higher variation in pore sizes leads to a larger pressure gradient in the oil ganglia, which helps remobilisation. Hence, overall, the results of Aziz et al. [9] suggest that, for tertiary low-salinity water-flooding, a wide PSD leads to a greater recovery of oil. However, this is the opposite to the previous findings of Watson et al. [43] regarding the impact of the width of the PSD on oil recovery This discrepancy between the two studies may arise from an unconsidered, but potentially confounding, variable, such as model lattice size, and Aziz et al. [9] state that they did not study the impact of larger structural model lattices on their findings.
Simulations have been conducted in PNMs where the wettability of the surface altered following contact with the nwp (oil) during primary drainage [44]. After drainage, the oil–water contact angle in the drained network element could increase due to wettability alteration. The pore body–throat network had straight throats with idealised cross-sectional shapes, namely triangles, squares or circles. The fluids were considered Newtonian, incompressible and immiscible, and the fluid–fluid displacements were in the quasi-static regime, with a capillary number less than 10−6. The simulations showed that, as the wettability of the system changed from strongly water-wet to strongly oil-wet, the trapped oil saturation decreased significantly. It was also found that trapped oil saturation and the number of trapped oil clusters depended upon the number of oil layers formed and their stability, with more formed by main water flood than scanning processes. In a strongly oil-wetting system, the advancing oil–water contact angle is very high, and the majority of corners satisfy the relation for oil layer formation. These oil layers then maintain oil-phase connectivity, leading to lower residual oil trapping. These studies of PNMs allow scenarios of wettability change to be studied in detail.
4.3. Dynamic Models
PNMs have also been used for dynamic simulation of drainage and imbibition processes for wps and nwps. Al-Gharbi and Blunt [10] constructed a PNM consisting of a square lattice of pore throats connecting pore bodies, where the cross-section of both was a scalene triangle with randomised internal angles and the inscribed radius of each varied sinusoidally. Further, the length of pore bodies and throats was allowed to vary, such that the network lattice was distorted from a regular shape. The simulations of fluid movements were dynamic but restricted snap-off to throats alone. An equivalent resistor network for the PNM was used to simplify the calculation of fluid pressures at pore body and throat centres. Simulations were conducted of multiphase flow with varying capillary number by varying the injected fluid flow rate. Overall, the simulations confirmed the general pattern that, at high capillary numbers, the nwp filled all of the pore elements regardless of size and moved toward the outlet in a piston-like fashion, whereas, at low capillary numbers, the nwp preferentially flowed through the largest pore bodies and throats with the lowest capillary pressure, leading to a ramified invasion percolation-like displacement, as found with quasi-static models. Indeed, for Ca values lower than ~10−5, the pore scale fluid distribution and fractional flows (of each phase) were similar to those obtained via a quasi-static model. However, more isolated ganglia of nwp were formed by snap-off as Ca increased, and, at the highest values of Ca studied of 0.33, the disconnected ganglia of nwp also moved indiscriminately through pore bodies and necks of any size. Hence, overall, these fuller, more complex dynamic simulations suggested the validity of the more minimalist idealisation quasi-static models for low values of Ca.
5. Percolation Models
Percolation theory [45,46] can be used to predict the distribution of ganglia (clusters of nwp) and the overall saturation of entrapped nwp [8]. Percolation theory is an approach that seems particularly pertinent for application to the problem of entrapment of nwp since its main concern is the requirement for the interconnectivity of networks [45]. Percolation theory is concerned with predicting whether the clusters of pores filled with nwp at a given saturation of nwp remain connected, such that there is at least one pathway from any pore filled with nwp, only passing through other pores filled with nwp, to the surface of the porous solid. The key parameter in percolation theory is the fraction of sites, or bonds, in a given pore network lattice occupied by the phase in question (in this case nwp). As saturation of the phase under consideration increases, there will be a certain saturation where the fraction of pores filled with nwp becomes such that the nwp is first connected up (or where it becomes disconnected if the saturation of nwp is being reduced), which is known as the percolation threshold. For the simplest systems, consisting of large samples of relatively homogeneous media with similar pore sizes, the residual saturation (entrapment) when the nwp becomes disconnected is equal to the percolation threshold [47].
The entrapment of nwp becomes amenable to analysis via percolation theory when the retraction occurs very slowly (under quasi-static) conditions and the problem becomes one of simply determining the cross-over between stable and unstable interface configurations. Ioannidis and Chatzis [48] performed similar calculations to those of Tsakiroglou and Payatakes [37] of the critical pressures for piston-like retraction and snap-off in a network model consisting of a cubic lattice-based network of cube-shaped pore bodies (sites) fully connected by cuboid throats (bonds) with a constant ratio of width to breadth. The required overall porosity (voidage fraction) for the model was used to fix the throat lengths. In the expressions used by Ioannidis and Chatzis [48], the critical pressure for snap-off in a throat depended upon both its width and length, since it was assumed that snap-off occurred when two saddle-shaped interfaces, anchored at the junctions with the adjoining pore bodies, met on the throat centre-line. This contrasted with the corresponding expression obtained previously by Lenormand et al. [49], who assumed that snap-off in a cuboid throat occurred when the nwp first lost contact with the wall.
Ioannidis and Chatzis [48] used their model to develop a mixed-percolation-based approach to entrapment in mercury porosimetry. The mixed percolation consisted of site-withdrawal (retraction from pore bodies) and bond-withdrawal (snap-off in pore throats) processes and arose when the critical pressures for each type of process occurred within a similar pressure range, with the degree of competition between the two dependent upon the degree of overlap of these pressure ranges. Under the conditions mentioned above, the retraction process becomes amenable to a percolation-type algorithm where all the potential snap-off and piston-type retraction events are placed in a ranked list in terms of decreasing critical capillary pressure. The retraction process is initiated by declaring the first ranked bonds now “open”, which physically corresponds to initial snap-off events. The subsequent retraction process then reduces to simply proceeding down the ranked list progressively declaring the relevant bonds “open” if they are still part of a percolating cluster and have not become disconnected from the periphery of the model using a path taken only via “closed” sites. Pore bodies (or sites) may be declared “open” if they meet the above condition and also possess a neighbouring bond that is already “open”. The list of open bonds and sites can be converted into a point on the mercury retraction curve by calculating the relevant pore volumes and summing them. In mixed percolation, the entrapment occurs via two mechanisms, namely snap-off of all surrounding pore throats or bypassing due to piston-type retraction from pore bodies. If the underlying pore throat size distribution was shifted towards larger sizes for a fixed body size distribution, then mercury entrapment volume decreased since the overlap between critical pressures for snap-off and piston-type retraction processes increased. This is also equivalent to the aforementioned result from other workers that snap-off tended to increase as the pore body-to-throat size ratio increased. Ioannidis and Chatzis [48] found that the overall size of entrapped mercury ganglia (clusters of filled sites and bonds) formed increased as the network was emptied due to the declining connectivity of remaining nwp, and they were generally formed by the bypassing mechanism. Conversely, long-range spatial correlation in pore body sizes tended to reduce entrapment as it led to a reduction in bypassing [50].
A similar quasi-static, invasion percolation simulation of imbibition, with potential trapping of an incompressible nwp, was performed on a simple cubic lattice of cuboid pore throats and cubic pore bodies by Mahmud and Nguyen [51]. They found that decreased residual nwp saturation occurred with increased contact angle, decreased pore body–throat aspect ratio, and the presence of long-range correlations in pore size. This third finding was similar to that obtained by Ioannidis and Chatzis [50].
The inception of 3D imaging methods has expanded the application of percolation theory to the characterisation of the spatial distribution of nwp. The snap-off process tends to lead to the loss of percolation of the clusters of pores filled with nwp. In a percolating system of nwp, the connected cluster of pores containing nwp will have particular pores (usually throats) for which filling with wp will disconnect the remaining nwp from the periphery of the sample. These pores are called “red bonds” [8]. In random systems, the number of these so-called red bonds nred scales with the overall size of the cluster according to
where ξ is the correlation length of the cluster, l is the typical size of a pore, and Dred = 1/ν, where ν is the universal scaling exponent with a value of 0.88 [52]. Further, in a percolation-controlled system, the size of the clusters (ganglia) of entrapped nwp tends to follow a power law where the number of clusters containing s pores, n(s), is given by
where τ is the Fisher exponent which takes a value of 2.189 ± 0.002 in 3D [8]. This prediction is easily tested using 3D imaging data from the likes of CXT.
6. Models and Simulations Based upon Imaging Data for the Void Space
6.1. Imaging Modalities and Flow Simulation Techniques
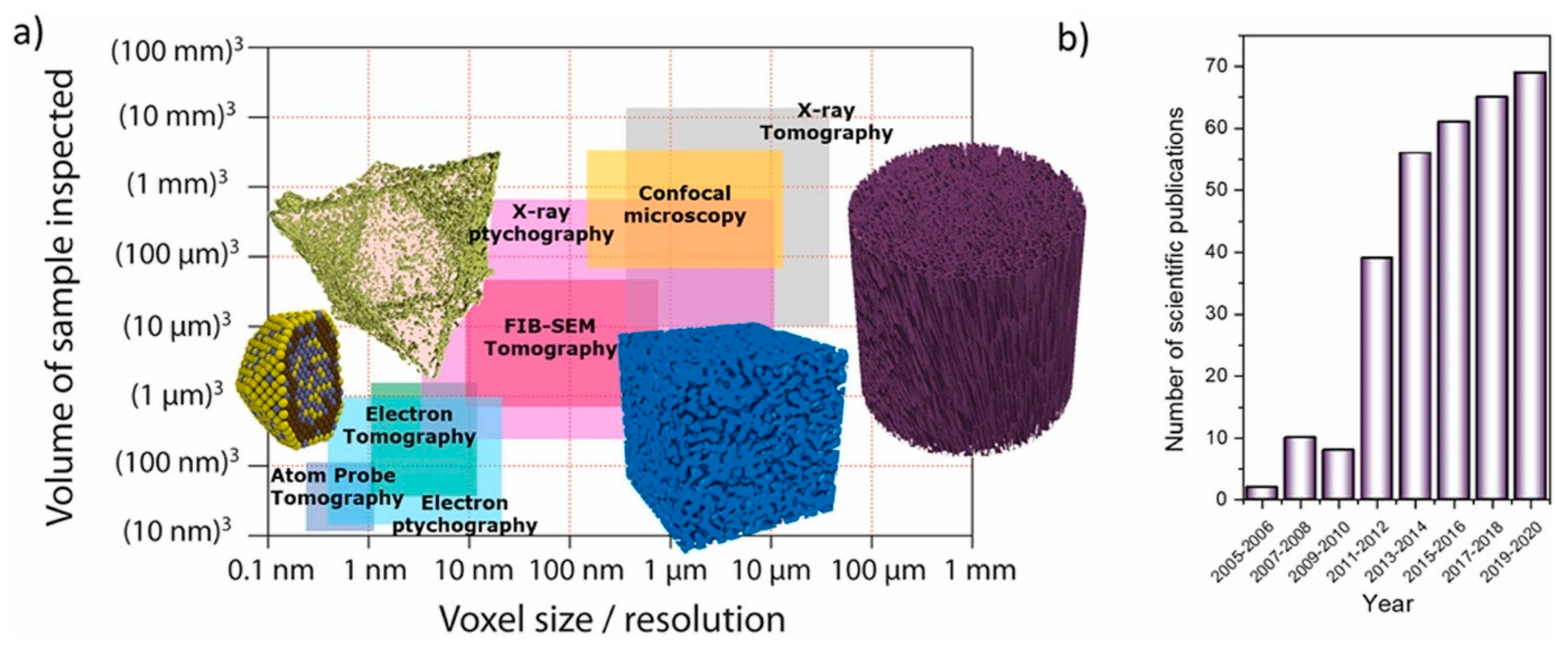
The development of high-resolution imaging modalities has allowed the void space of heterogeneous porous media to be visualised directly. The ranges of spatial resolution, and the capacity for volumetric sampling, of various imaging techniques is shown in Figure 10 [53]. However, since many porous materials, such as carbonate rocks, possess void space features over the wide length-scale range from nanometres to millimetres, even within core samples, it is often not possible to fully characterise a single core sample with just one imaging modality.
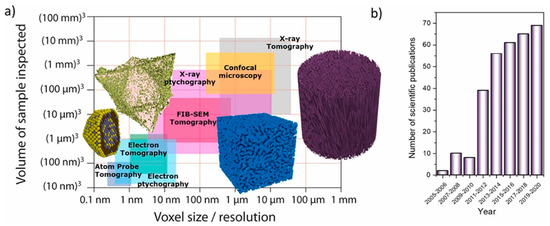
Figure 10.
(a) Classification of various tomographic imaging methods of significance for research in porous media, according to their spatial resolution and their volumetric sampling capacity. (b) Evolution of the number of scientific publications applying FIB-SEM tomography for investigations in the area of (electro)catalysis. Reprinted from Catalysis Today, Vol. 405–406, Rodenas, T. & Prieto, G., FIB-SEM tomography in catalysis and electrochemistry, p.2 [53], Copyright (2022), with permission from Elsevier.
The capabilities of computerised X-ray tomography (CXT) as depicted in Figure 10 are pertinent for lab-based equipment, but synchrotron X-ray tomography can reach resolutions below 50 nm [54], though this is still larger than most mesopores, and the beam energy required may damage the sample. Further, X-ray microscopes equipped with Fresnel zone plate (FZP) optics can reach approximately 10 nm, which is close to the theoretical limit, but with a limited field of view [54]. The types of imaging data shown in Figure 10 can be used as the basis for the fabrication of structural models on which to conduct direct numerical simulations (DNS) of multiphase flows. These simulations provide the opportunity to control parameters such as the wettability and injection rate of fluids, which is not always possible with experiments.
Cai et al. [55] listed the commonly used DNS techniques as the volume of fluid (VOF) [56], phase field (PF) [57], and lattice Boltzmann (LB) [58] methods. They suggested that both VOF and PF methods can obtain clear fluid–fluid interfaces through specified interface capture algorithms. Further, the LB method for multiphase flows includes the colour gradient [59], pseudo-potential [60], and free-energy models (see below Section 7). The VOF model can solve the Stokes equations directly on lattices formed from imaging data, and simulation results have been validated against microfluidic experiments on invasion patterns, nwp ganglia distribution, trapping mechanisms and other relevant characteristics [61]. The VOF method does not require a complex phase interface tracking algorithm, which makes it more amenable to complex geometric shapes as found in disordered porous media. Since the VOF method employs the Navier–Stokes equations, it permits the use of physical properties, such as contact angle, interfacial tension, and viscosity, which cannot be easily achieved in other approaches like lattice Boltzmann and smoothed particle hydrodynamics [9]. However, it can be seen as an advantage of the LB method that no explicit interface tracking or contact angle method is required [62].
6.2. Use of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) in Combination with CXT
As is clear from Figure 10, for macroscopically (>10 μm) heterogeneous, disordered, mesoporous materials (with pore sizes less than 50 nm), it is difficult to obtain by methods like synchrotron CXT [63], FIB-SEM [64], or even electron tomography (3D-TEM) [65] full, direct image data of the void space with sufficient resolution for regions of the void space large enough to achieve a (statistically) representative elemental volume, since, in some materials, the correlation length may even exceed the sample size (~mm) [66].
However, relaxation time-weighted magnetic resonance images, such as those in Figure 11, can be used to construct empirically adequate PNMs able to predict the macroscopic distribution of entrapped nwp. Some types of porous catalyst support pellets possess long-range correlations in local (meso)pore size such that the size of regions of similar pore size exceeds the typical spatial resolution (>~40 μm) possible with relaxation time-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) so that MRI can map variations in local average pore size [67,68]. The NMR relaxation time of an imbibed fluid (such as water) is a measure of the local average pore size [67,68]. The MR imaging procedure also delivers a map of the local average porosity in the form of a spin density map.
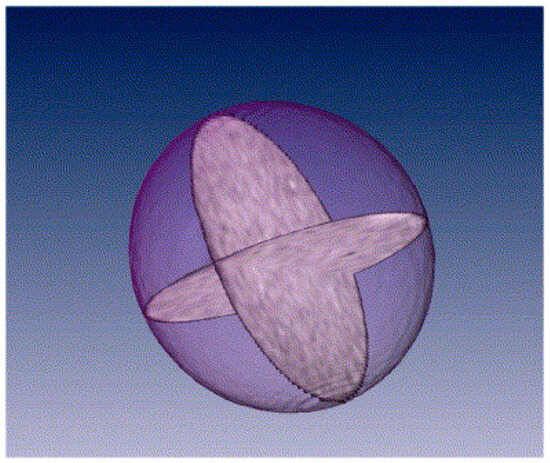
Figure 11.
Magnetic resonance spin-spin relaxation time images of perpendicular 2D slices through the centre of a pellet from sol–gel silica batch G2. The pixel resolution is 40 μm and the slice thickness is 250 μm. Reprinted from [68]. Copyright (2006), with permission from Elsevier.
For such materials, it is possible to use the MRI data to construct a PNM consisting of a 2D or 3D grid of sites where each site consists of a pore bond network with pores of a size corresponding to that obtained from the NMR relaxation time for an individual voxel of the MR image itself. Hence, the MRI-derived computer model constructed had some similarity in form to the square grid glass micro-models constructed by Wardlaw and McKellar [30] where rectangular regions of network consisting entirely of larger pores were located within a wider network of smaller pores, as shown in Figure 12.
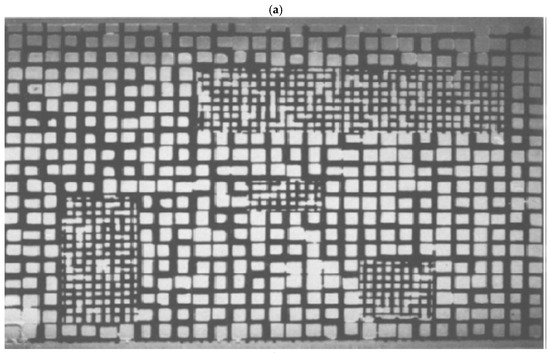
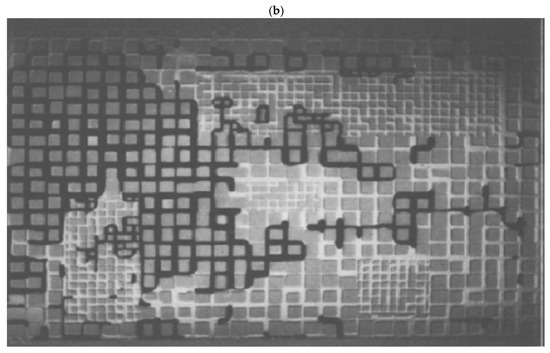
Figure 12.
Glass micro-model with non-random heterogeneity (a) filled with mercury and (b) following mercury retraction. Reprinted from Powder Technology, 29, Wardlaw NC, McKellar M, Mercury porosimetry and the interpretation of pore geometry in sedimentary rocks and artificial models, 17, Copyright (1981), with permission from Elsevier [30].
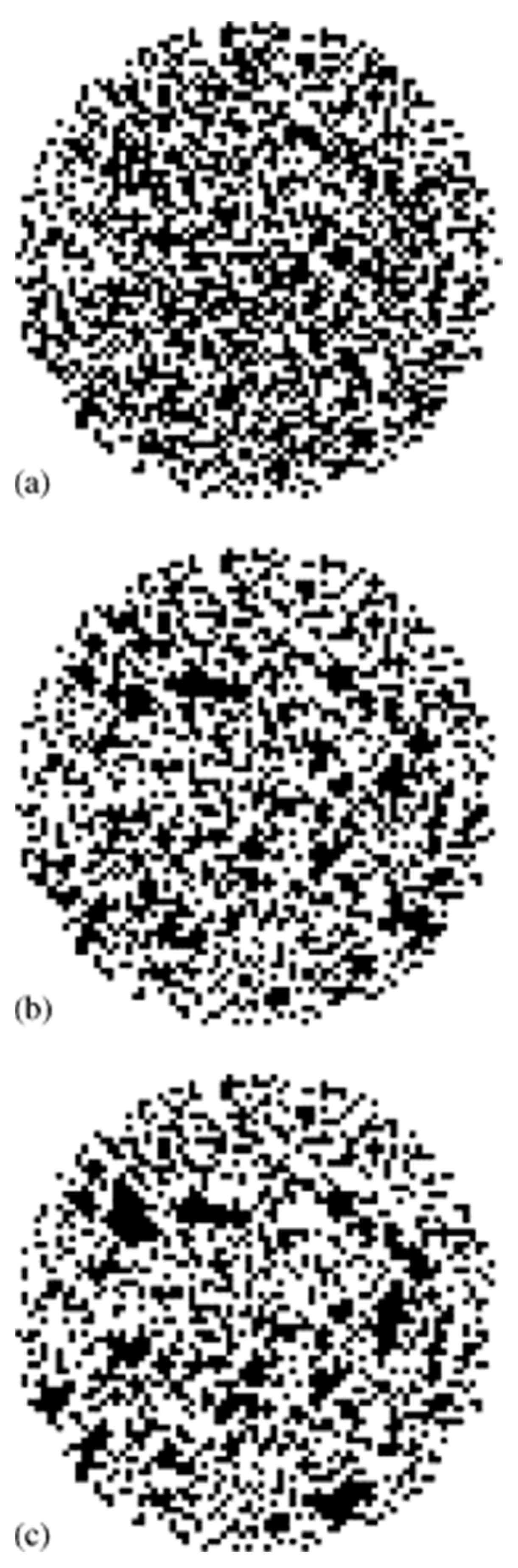
Once the model had been constructed, mercury intrusion and retraction could be simulated upon it based upon site percolation. Mercury was allowed to enter a site (and thus the bonds in the network within) if the applied capillary pressure exceeded the critical pressure from the Washburn equation corresponding to the pore size allocated to that site. As with the aforementioned PBNs, some rule must be adopted to control mercury snap-off, and, thus, retraction from the network. The experimental observations of Wardlaw and McKellar [30] as shown in Figure 12 were used as the basis of the development of the mercury displacement rules. In previous work, it was assumed that there was a “snap-off ratio” (SOR) that determined the ratio of pore sizes allocated to two neighbouring sites to enable snap-off to spontaneously occur at the boundary between them during retraction once the imposed capillary pressure dropped below the critical retraction pressure for one of those sites [69]. In later work [68], SORs in the range 1+ to 2 were considered. Simulations were performed of mercury retraction in MR image-derived models for different types of catalyst support pellets to predict the final level of mercury entrapment and the spatial distribution of that entrapment, as shown in Figure 13.
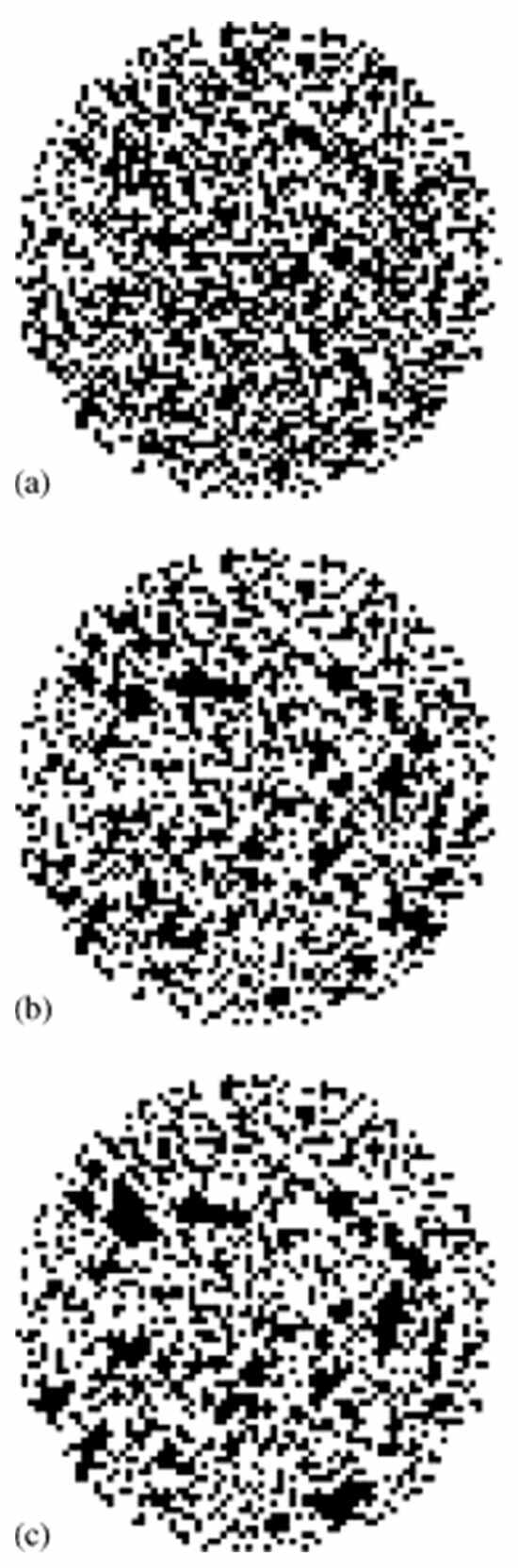

Figure 13.
The variation in the spatial arrangement of entrapped mercury (black pixels) with SOR ((a) SOR = 1, (b) SOR = 1.5, and (c) SOR = 2) for simulations of mercury porosimetry on models constructed from NMR images of an “equatorial” slice from a typical pellet taken from batch G2. The pellet diameter is ~3 mm and the pixel resolution is 40 μm. Reprinted from [68]. Copyright (2006), with permission from Elsevier.
The latter was achieved because MRI could be combined with CXT to map the spatial arrangement of mercury entrapment following porosimetry. For sol–gel silica spheres, it was found that a SOR of 2 in the simulations on the MRI-derived models (see Figure 13c) gave rise to the same overall levels of mercury entrapment and patterns of the spatial distribution of mercury entrapment, as characterised by the correlation length, as measured in experiments (from images as shown in Figure 14). It is noted that this SOR of 2 corresponds to that suggested by Blunt [8] mentioned above. Overall, it was found that the higher the degree of spatial correlation of NMR relaxation times (and thus pore sizes), the lower the mercury entrapment. This finding is similar to that found for the percolation models of Ioannidis and Chatzis [48,50] and Mahmud and Nguyen [51]. The lower entrapment was because more spatial correlation in pore sizes meant less frequent snap-off of the mercury meniscus (because ratios of neighbouring pore sizes in MRI voxels did not exceed the SOR), and thus the continuity of the mercury ganglia was retained to a greater extent before retraction. This work [68] clearly demonstrated the links between the macroscopic structure of a porous material and the microscopic pore-level fluid processes.
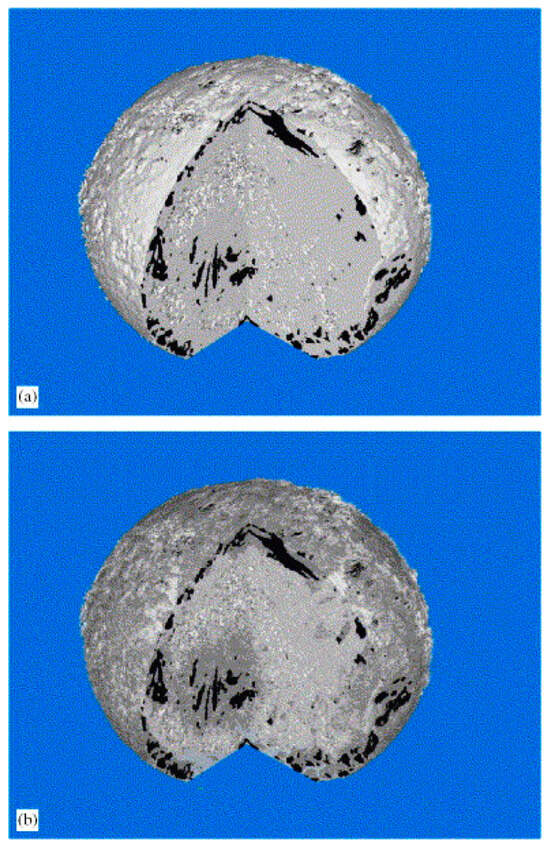
Figure 14.
(a) Three-dimensional micro-computed X-ray tomography (μ-CXT) image of a typical sol–gel silica pellet taken from batch G2 following mercury intrusion to 414 MPa and retraction back to ambient. A segment of the pellet image has been excised by computer to display the interior of the sample. The black areas on the excision planes correspond to regions containing entrapped mercury. The overall pellet diameter at its equator is ~3 mm; (b) the same 3D X-ray image as in (a) but where the main matrix (silica) has been changed, by computer software, to a 50% transparent material allowing more mercury entrapment features deeper within the pellet structure to become visible. Reprinted from [68]. Copyright (2006), with permission from Elsevier.
The wider impact of macroscopic (>10 μm) structural heterogeneities in the spatial distribution of local (average) meso- and smaller macro-pore size on mercury entrapment has been studied using more generalised abstract models analogous to those derived from MR images. It was found that just four statistical parameters (the degree of correlation, the correlation length, a fractal dimension, and the percolation threshold) characterising the spatial arrangement were needed to be able to correlate the level of mercury entrapment and any general spatial disposition of local pore sizes using an artificial intelligence (AI) model, consisting of an artificial neural network (ANN) [70].
6.3. Model Construction Using CXT and EM Imaging Data
The imbibition process within a disordered porous solid is controlled by the geometry and topology of the void space. As mentioned above, various imaging modalities, such as computerised X-ray tomography and focused ion beam scanning electron microscopy (FIB SEM), can used to create reconstructions of the void space on which fluid displacement processes can be simulated directly [15]. In principle, it is possible to calculate, for each voxel in the image, the radii of curvature of an interface between two fluids that passes through the voxel obeying the Young equation at the surface [8]. The capillary pressure can then be calculated from this using the Young–Laplace equation. Within the void space, the pore throats are the regions with the smallest radii of curvature and, thus, correspond to a surface of voxels where capillary pressure is a local maximum. In principle, it would be possible to perform a calculation using the watershed segmentation algorithm similar to that used to gate images between solid and void but based upon the capillary pressure rather than voxel intensity [15]. This would divide the void space into regions where the capillary pressure continually decreases to a minimum value (the pore centre) bounded by surfaces of local maxima (throats). This would then permit the calculation of fluid displacements and interface geometries without the need for any simplified structural model [8].
However, until recently (see below), this type of calculation has not been performed except in the simple case when the contact angle is zero, and it is equivalent to the maximal ball approach [8]. This is because, while the aforementioned imaging techniques can readily supply pore structural information, they are much less able to supply spatially resolved information on wetting properties. In heterogeneous systems, like rocks with many different types of mineral grains, it is not possible to perform precise calculations of displacement processes unless the solid–fluid interaction (often expressed as the contact angle) is also described in detail [8]. Further, even the more simplified pore structures of network models will not permit a priori calculation of the fluid displacement since an independent assessment of the contact angles is required [8].
Imaging data for disordered materials can be used to predict the entrapment of nwp within them via two strategies. The main limitation on this approach is the limit of resolution of the images. For example, CXT is typically performed with a resolution limit of a few microns [12]. Mason and Morrow [12] highlighted that the typical resolution limit often exceeds the microporosity where residual wp can be found, which impacts the potential to simulate the two-phase flow fully. The residual nwp saturation (entrapment) may not have a well-defined value in mixed-wettability systems, as these lie “beyond the rules for definitive trapping” [12]. A further issue arising from resolution will be discussed in more detail below. The imaging data must be segmented to produce a complex disordered model on which simulations are conducted directly using numerical techniques, such as computerised fluid dynamics or lattice Boltzmann methods. However, the image segmentation needed to convert the raw image data into a form suitable for conducting fluid flow simulations has many issues, which have been discussed in detail elsewhere [14,15]. Further, if the imaging is also used to study two-phase fluid behaviour within the porous medium, it is often difficult to segment the image between the two fluids, especially if they have similar electron density (for CXT) [12].
Alternatively, the raw image data can be converted to a pore network model (PNM), and the fluid behaviour simulated on the latter, potentially using much simpler, less computationally intensive algorithms for describing the fluid behaviour. The issue with the PNM-based approach is that it often does not properly capture the pore size distribution and/or connectivity of the original void space imaged. This issue has been reviewed extensively elsewhere, and the reader is referred to these publications for more information [14,15]. Other issues include that the size of the network must be large enough that the capillary pressure curve is reproduced with sufficient accuracy [12]. Further, even simulations of imbibition in the more regular, well-defined geometries of PNMs suffer from a lack of proper mathematical descriptions of the behaviour of interfaces in many types of connected pore spaces [12].
6.4. Image-Derived Models
Sok et al. [71] compared the residual saturation of nwp, following quasi-static displacement with wp, in a PNM constructed directly from CXT images with another PNM with preserved topological parameters but with randomly rearranged pore throats; they found relatively little change in the residual saturation of nwp, probably due to only small spatial correlation between pore throat sizes. However, when they compared the rearranged networks with fully stochastic networks, but which preserved the pore co-ordination number distribution, the residual saturation was smaller for the stochastic network than the rearranged network. Sok et al. [71] thus suggested that even matching the full co-ordination number distribution does not give enough information to accurately predict residual saturation. Sok et al. [71] also found that finite size effects were important for the image-derived models because the resultant lattice size was quite small. This is a general issue for image-derived models where the field-of-view possible with a given resolution determines the maximum size possible for the resultant model (see Figure 10). More recently, attempts have been made to resolve this issue by using ANN methods to construct artificial model lattices to expand the model size [72,73]. However, this relies upon a sufficiently large training set of real samples being available to train the ANN and requires that these exceed the statistically representative volume in size.
Aghaei and Piri [74] conducted dynamic simulations on extensive PNMs derived from CXT images and compared the findings with water-flooding experiments. Their simulations included capillary, viscous and gravitational forces, and wp corner flows. They found that residual nwp saturation decreased as the flow pattern became more viscous-dominated.
Rough surfaces of fractures enable the formation of wp layers that enable the maintenance of the connectivity of wp, similar to those found in the corners of angular pores mentioned above. Gong and Piri [19] constructed a network model of a rough-walled fracture in strongly water-wet Berea sandstone using CXT data to provide spatial mapping of the aperture thickness. They conducted dynamic simulations of fluid drainage and imbibition including gravity and viscous forces as well as capillary forces. The parameters of the simulations, such as the fluid volumetric injection rate, were chosen to match those in oil–water experiments conducted on the fracture, and the findings were validated against CXT images of the experimental fluid distributions. While it was found that the simulations gave rise to good predictions of the initial oil saturation following drainage (prediction of 0.67 versus measured value of 0.65), and residual oil saturation following imbibition (prediction of 0.38 versus measured value of 0.37), the predictions of the final morphologies and locations of oil clusters were less so. In particular, the simulation did not entirely establish many of the trapped oil clusters close to the boundary regions of the fracture. This was attributed to the model over-estimation of the threshold capillary pressure for piston-like displacements near the side or inlet boundaries.
Hyväluoma et al. [75] compared the predictions of intrusion of a nwp (mercury) into paper using an invasion percolation-based algorithm with those from the lattice Boltzmann method for a structural model obtained from a CXT image. They suggested that the relative agreement between both methods with the experimental intrusion data indicated that the intrusion process can indeed be well described by invasion percolation (IP). They then used a percolation-based approach to simulate extrusion such that the pore body sizes from the CXT data determined the maximum sizes of pores that could be evacuated at a given capillary pressure and whether a continuous liquid phase reached the sample surface from the pore bodies in question. They found that the percolation method gave consistent results for the residual saturation of the sample after extrusion of the nwp.
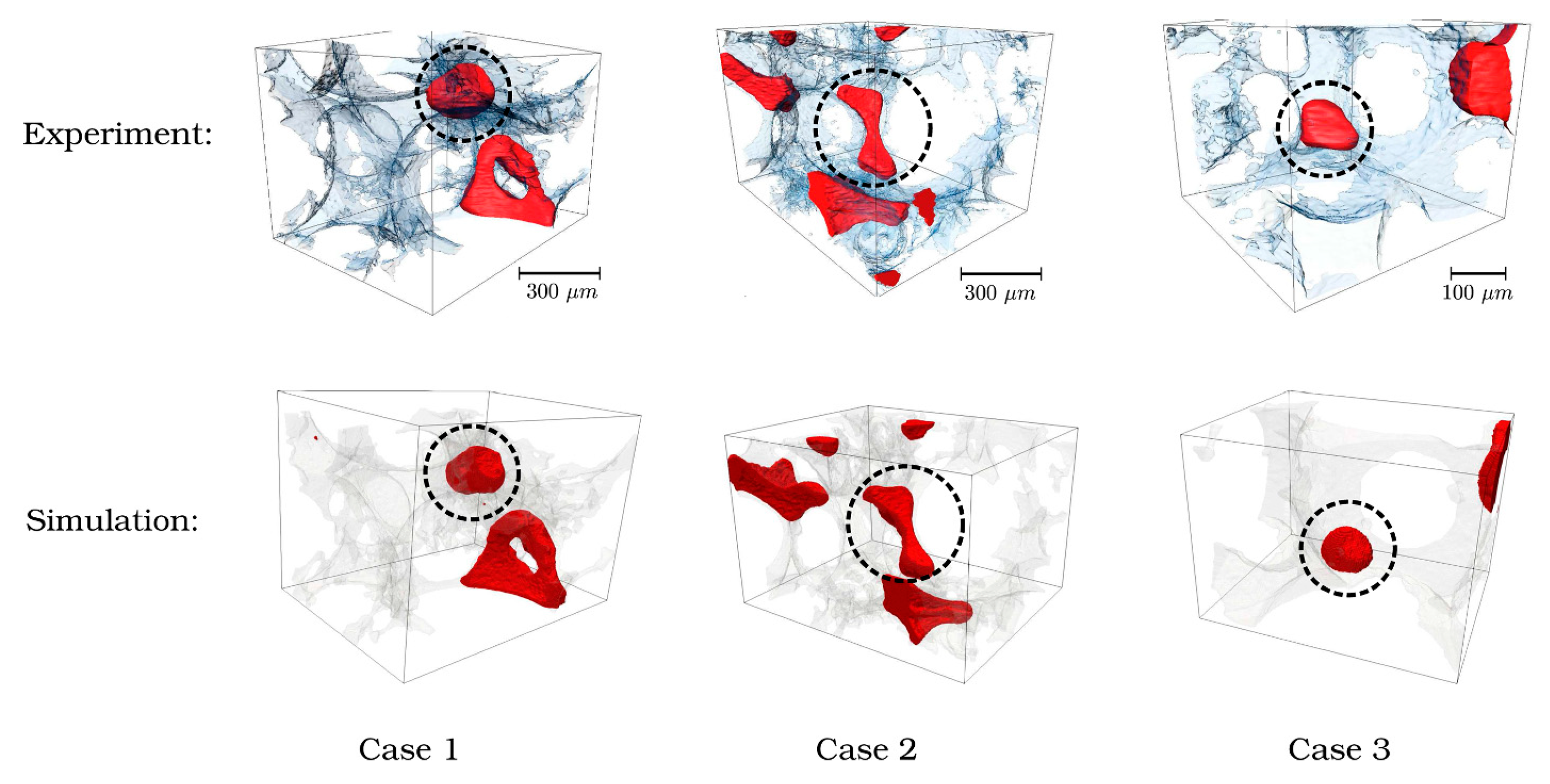
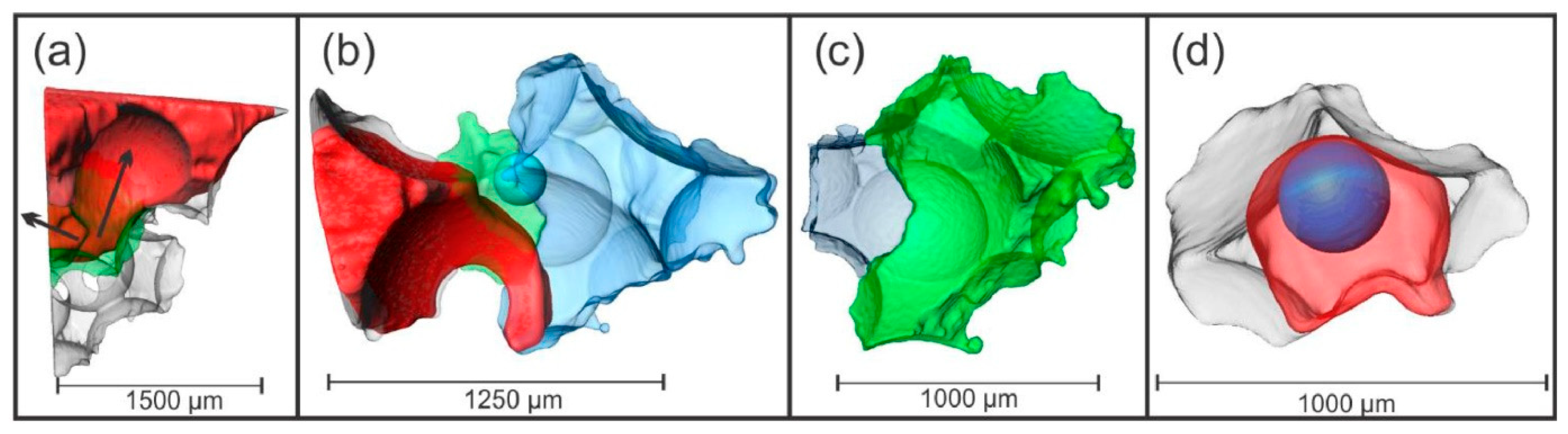
The entrapment of the non-wetting phase in a limestone rock can be predicted using a pore structural model based upon synchrotron X-ray images of resolution 3.28 μm [76]. The fluid behaviour within the model was simulated by computational fluid dynamics where the two fluids were treated as one single-fluid continuum, but the fluid–fluid interface was captured using an indicator function which represented the volume fraction of one of the two fluids and the interface corresponded to a value of this function of 0.5. However, limitations on the feasible computation time meant that only a few seconds of the dynamic physical process could be simulated. To overcome this issue, the wetting phase was injected two-to-four orders of magnitude faster than was the case in the experiment. Hence, the capillary number in the simulations was ~10−5 to 10−6 rather than the value of 10−9 in the experiments. However, it was suggested that, as the capillary number in the simulations was very low, the flow regime was still capillary-dominated; thus, the physical process would still match that in the experiment. The simulations were conducted on a cropped sample of the structural model, such that the lattice size of the simulated volume was up to 300 × 300 × 300 voxels3, corresponding to a side-length of ~984 mm and 6,575,974 simulation cells. The boundary conditions of the simulated volume were adapted to account for it being only a small fraction of the whole material volume. Six case studies of individual snap-off events seen in the CXT experimental data were simulated. Three of the snap-off events were such that they were consistent with the idea that a particular ratio of pore body-to-neck ratio gives rise to snap-off, as shown in Figure 15. However, the error in the prediction of the absolute volume of nwp entrapped by the snap-off event was in the range of 8–14%. This error in the observed volume was a composite of errors arising from the gating of the experimental images into different phases and from the CFD simulation. Further, the simulations could not predict the time-scale of the fluid dynamics. In contrast, in three other case studies, the conventional snap-off ratio idea was found to be inconsistent with the experimental results. For one case, it was found that, while the pore-throat aspect ratios for two throats adjoining a pore body were ~4.4 and 3.3, and, thus snap-off might be expected, it did not arise, and the nwp emptied through the throats in a piston-like manner before the throats themselves emptied. From an analysis of the results, it was found that the flow pattern depended upon the interface curvature, which, in turn, depended upon dynamic and geometric factors. In a further two cases, entrapment of nwp occurred in the experiments even though this was not predicted by the simulations. It was found that this discrepancy could be removed only by the use of a phenomenological model. This post hoc adaptation of the simulations assumed that there was a patch, on the wall of the pore body, with undetectable surface roughness, being of a characteristic size below the imaging resolution, which led to a difference in contact angle that, in turn, led to the pinning of the nwp such that snap-off of a residual ganglion occurred. Hence, it was seen that, while some snap-off events could be predicted based upon the information available within the CXT images, they did not contain sufficient information to be fully predictive of all snap-off events that were observed in the sample studied. A further issue raised by Mason and Morrow [12] is how well the relatively small pore spaces used in simulations such as the above can be scaled to behaviour in larger pore spaces, for which continuum models will probably be needed.
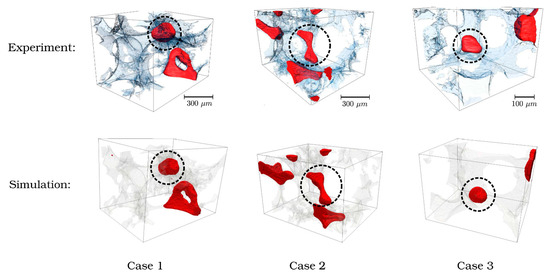
Figure 15.
Visualisations of the non-wetting phase distribution after snap-off occurred for both experimental and simulation results for three validation cases in a study by Shams et al. [76]. The wetting phase and solid are transparent with light shading of the pore space. This figure was reproduced from [64] under the terms of the Creative Commons CC BY licence.
Simulations in models created from images allow direct correlation of flow events with particular aspects of the void space, quantified by descriptors such as co-ordination number. Zhang et al. [77] simulated two-phase oil–water flow in a 1.59 × 0.795 × 0.795 mm3 model constructed from a CXT image of a volume of sandstone rock with a porosity of 0.166. In particular, the volume-of-fluid method was used to track the location of the fluid interface and the sharp surface model (SSF) was used for the calculation of the curvature. Overall, the wp fluid invasion process of pores initially filled with nwp occurred as a combination of piston-like displacements, co-operative pore fillings of pore bodies (with interface configurations according to the Ii designation mentioned above), and snap-off events. Zhang et al. [77] correlated various pore structure characterisation parameters with pore sweep efficiency and nwp displacement efficiency. They found that unswept pores had the lowest average co-ordination number, indicating that poor connectivity severely restricted the development of a flow path through pores. These workers found that, at low values of capillary number, a large amount of oil was bypassed in large pores with low connectivity and residual oil clusters were formed due to snap-off in pore body–throat pairs with an aspect ratio of 2.02, as might be expected from the above discussion. However, as the capillary number increased, the oil phase tended to keep connected—leading to more piston-like displacement.
Cai et al. [55] simulated dynamic forced imbibition of water into six different types of oil-filled sandstone rocks using structural models of size 1503 voxels derived from CXT images with a resolution of 2.25 μm and employing the VOF DNS method. The capillary number varied between 8.2 × 10−3 and 8.2 × 10−4, in the range where viscous forces are starting to become important [10]. The results showed that, at low capillary numbers, corner flow “promoted to dominance” a co-operative pore-filling process [55]. This was found to lead to unstable inlet pressure, mass flow, and interface curvature, which corresponded to complicated interface dynamics and led to high residual nwp saturation. Cai et al. [55] highlighted that the irregular form of the void space in heterogeneous materials means the curvature of the interface is constantly varying, causing the capillary pressure on either side to vary naturally. Hence, the interface may expand or contract—leaving the cross-sectional curvature in an unbalanced transient state. A steady-state forced imbibition was also simulated by setting specific time-scale control parameters. Higher water saturation occurred at higher capillary numbers, but more residual oil ganglia formed in the core regions of pores and in dead-end pores at lower capillary numbers. The increase in viscous forces led to increased mobility of oil ganglia. In order to more easily extract void space structural characterisation descriptors, the image-derived models were converted into PNMs. These descriptors included a tortuosity defined as the ratio of the actual flow length to the apparent length of the porous medium, and obtained from the ratio of the total velocity to the velocity component in the flow direction derived from single-phase flow simulations. It was found that porosity, pore throat radius, and pore throat co-ordination number were negatively correlated with residual oil saturation, but the aforementioned tortuosity showed a positive correlation. However, there was an exception of one rock type that had a low tortuosity but a high residual oil saturation. Cai et al. [55] attributed this discrepancy to water flowing along a dominant channel but leaving oil trapped in other poorly connected pores. This result demonstrated that overall average parameters may not be predictive of aggregated local fluid behaviour.
Yang et al. [62] developed a Galilean idealisation of a carbonate rock by simplifying down CXT image data (with voxel resolution of 21.1361 μm) to a single-connected pore space (of overall size 200 × 300 × 165 voxels) in which they simulated the dynamics of water-flooding using the VOF method employing the filtered surface force interface model. In particular, these workers considered recirculation inside oil clusters/ganglia and noted two main patterns, namely lid–cavity driven flow and co-current driven flow, with the particular one that arose depending upon wettability. Lid–cavity-driven flow occurs when the displacement is limited in the corners of porous media and when the contact area between the two fluids is less than that between the fluid and solid. Viscous shear forces at the boundary of the two fluids cause internal recirculation of the oil phase, and the direction of the recirculation and displacement is in the opposite direction to the fluid flow. In contrast, with co-current-driven flow, all displacement of the oil is consistent with the fluid flow direction. Overall, the lid-driven flow pattern tended to result in an increase in the remaining oil saturation and lowering of oil mobility.
CXT image data of the packing of glass beads has been used to validate models involving quasi-static displacements in PNMs [7]. This work was motivated by discrepancies in the fluid distributions predicted by PNMs in previous work by the same authors [78,79]. In addition, direct measurements of the local contact angle using CXT were used to overcome the aforementioned issue of the spatial heterogeneity in wettability present in real samples, even in such relatively simple ones as glass bead packs. Further, PNMs have previously typically been validated to only a limited extent by comparing the macroscopic capillary pressure for the whole real sample with the overall curve predicted by the model, using an assumed contact angle distribution as an adjustable model parameter.
In contrast, Ellman et al. [7] validated quasi-static invasion percolation models for artificial pore networks on an individual displacement-by-displacement basis using high-spatial- and temporal-resolution CXT data. The CXT data was used to identify and classify individual fluid displacements and to measure local meniscus curvature and local contact angles at the particular sites of the fluid displacements. Displacement identification was achieved by superposing the PNM back on the image data and determining which pore bodies and necks were filled with either wp or nwp before and after a particular time step. Three types of displacement were considered, namely piston-like, co-operative, and snap-off (see Figure 1). The PNM was tested by comparing the capillary pressures predicted by the PNM, using the local contact angle measurement as an input for the identified displacements, with those obtained using the meniscus curvature measurement from the image data together with the Young–Laplace equation, as well as with the macroscopic experimental pressure transducer reading. A number of discrepancies were observed between the PNM predictions and the image data and pressure transducer readings. It was found that some of the discrepancies arose from the PNM extraction algorithm due to mis-identification of individual pores and the characterisation of pore body sizes by the minimum inscribed sphere, as shown schematically in Figure 16. These problems with extraction algorithms have been discussed in more detail elsewhere [14,15]. The simplification of the void space geometry meant that the true complexity of the meniscus geometry at a particular location was not properly captured by the model, so the type of displacement occurring at that location was not accurately predicted by the model. The predicted pressure was also discrepant because the model pore sizes did not correspond to the required characteristic dimensions needed for the correct meniscus curvature at that site either. Despite the use of a low flow rate in order to achieve a low capillary number in the experiments, Ellman et al. [7] speculated that the discrepancies in predicted capillary pressure for displacements at a given location may also have arisen from dynamic effects due to the local flow rate through a given void space region being higher than the overall rate, thereby leading to viscous forces becoming important, though neglected by the model. However, Ellman et al. [7] also accepted that, despite being much better than had been achieved in the past, limitations of the spatial and temporal resolution possible in their new CXT data itself may still have given rise to some of the discrepancies observed between the PNM predictions and the image-derived and experimental capillary pressures.
Figure 16.
This figure illustrates some sources of mismatch between predicted invasion-capillary pressure and local image-based capillary pressure. (a) The oil in the green (middle) pore can escape in the direction of the left arrow or the right arrow. The right arrow’s path is captured by the maximum inscribed sphere of the throat between the green pore and its neighbour, but there is no throat assigned at the location of the left arrow since it leads to outside the field of view. Thus, no conclusions can be drawn from this displacement. (b) The throat between the green pore (left) and the blue pore (right) is represented by the blue ball at their boundaries. The filling state of that ball determines whether the throat is classified as containing oil or brine. Since the ball is devoid of oil, this throat was classified as brine-filled, whereas there is oil in the lower part of the throat. (c) An over-separated pore. The pore network extraction results in what should be one pore being split into the green (right) and blue (left) pores. (d) The radius of curvature of the inscribed sphere (blue) is smaller than the radius of curvature of the oil protrusion (transparent red) within the pore (grey). The pore body is constrained by the pore walls in the axis running into and out of the page, which are not shown. Reprinted from [7]. Copyright (2024), with permission from Elsevier.
7. Thermodynamic and Statistical Mechanical Approaches
The introduction of the concept of “pore potential” has enabled a qualitative explanation of some experimentally observed effects of the presence of heavy metal salts, on the internal surface of pores of oxide materials (silica/alumina), on levels of nwp (mercury) entrapment [80]. In this theory, when a pore is filled with mercury at the (critical) breakthrough pressure, the stored free surface energy exceeds the pore potential—denoted by U. Upon lowering of the applied capillary pressure, the nwp moves out of the pore until the free energy equals the pore potential. Hence, flow out of the pore and reduction in the contact angle are spontaneous processes resulting in lower free energy. The pore potential is the sum of the work required to lower the contact angle and the stored surface energy of the residual, entrapped mercury. It was found that the pore potential for mercury can be increased or decreased by prior impregnation of the porous solid with polar (e.g., heavy metal salts) or non-polar (e.g., dichlorodimethylsilane) materials, respectively. Hence, the retraction contact angle decreased more, and the level of mercury entrapment increased, with increased doping of copper or cobalt salts due to increased work to change the contact angle and increased work of entrapment. However, without prior knowledge of the explicit quantitative effect of the changing surface properties on the work terms, it is not possible to predict a priori the level of entrapment, and the former is difficult to obtain.
Monson and co-workers have proposed a statistical mechanical model for mercury porosimetry of porous solids [81,82,83]. They first constructed a mean-field density functional theory (MF-DFT) lattice-based model [81]. For this lattice model, they noted a symmetry in the Hamiltonian between mercury intrusion and extrusion, and gas desorption and adsorption, respectively. In the non-wetting mercury system Hamiltonian, the solid–fluid interaction parameter was repulsive, but it was attractive for gas sorption, which meant that fluid density increases occurred only above the saturation chemical potential for the former but could occur below for the latter. The MF-DFT model gave rise to mercury intrusion and extrusion curves which were symmetric about the saturation conditions with desorption and adsorption curves, as seen in Figure 17. However, this symmetry meant that the MF-DFT extrusion curve did not show any feature that corresponded to the entrapment phenomenon observed in experiments on return to low imposed pressure. Monson and co-workers [81] suggested that entrapment could not be predicted by their MF-DFT model because the thermodynamic states obtained by solving the DFT represent at least a local minimum of the grand potential function for the system and complete extrusion must occur at the limit of low pressure. This finding suggested that mercury entrapment had a dynamic origin as this aspect was missing from the MF-DFT model.
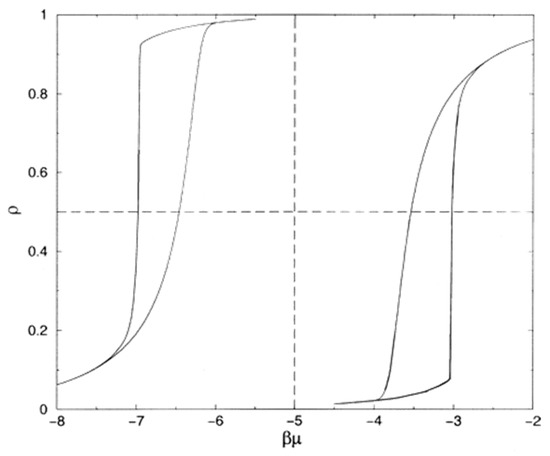
Figure 17.
Adsorption/desorption curves of a wetting fluid (α = ratio of the wall–fluid interaction strength to the fluid–fluid interaction strength = 1.0, left part) and intrusion/extrusion curves of a non-wetting fluid (α = 0.0, right part) in Vycor porous glass. MF-DFT, T/Tc = 0.4, βμ0 = −5. The curves are symmetric (with regard to chemical potential μ = μ0 and density ρ = 1/2). Reprinted with permission from [81]. Copyright 2004 American Chemical Society.
Monson and co-workers also conducted Monte-Carlo simulations of the intrusion and extrusion of nwp (mercury) using Glauber and/or Kawasaki dynamics [82,83]. These workers suggested that “the straightforward implementation of the Metropolis algorithm in the Grand Canonical ensemble for the lattice model generated Glauber dynamics, where the creation and destruction of particles are possible throughout the system regardless of the relative position to the bulk interface”. They highlighted that this method ignores that density fluctuations inside the material can only occur via diffusion or flow. Therefore, for the fluid within the porous solid part of their structural model (as opposed to the bulk phase) they instituted Kawasaki dynamics instead. Kawasaki dynamics models a diffusive process wherein an occupied (by fluid) lattice site can swap its occupancy with a neighbouring unoccupied site. Hence, this model does not account for hydrodynamics. While, in simulations of mercury intrusion and extrusion from dead-end, regular, slit-shaped pores, the mercury intrusion and extrusion seen in snapshots was piston-like within the bulk of the slit-shaped pores, for through-ink-bottle pores, differences were observed compared with percolation models. For relatively narrow, slit-shaped pores, the pore body filled during intrusion while the necks were left empty. Snapshots of the stages of the simulation, as seen in Figure 18, showed that during intrusion of a through-ink-bottle system the meniscus penetrated the neck as far as the body, and then, after penetrating the body for part of its length, it snapped off and retracted from the neck. Once the body had filled by diffusive mass transport, the menisci formed at the ends of the body then invaded the necks. This mechanism is very different to what has been observed in experiments where the intrusion process can be frozen and inspected at various stages, such as via the use of low-melting-point metal alloys coupled with serial-sectioning and SEM or with CXT [25,84], which suggest an intrusion mechanism more like invasion percolation with no evidence for isolated ganglia ahead of the main meniscus.
Figure 18.
Snapshots representative of the intrusion (top) and extrusion (bottom) states of the liquid in the (12−6) ink-bottle pore during Kawasaki dynamics model for mercury porosimetry. From top to bottom, the snapshots are obtained at βμ = −4.95, −4.90, −4.85, and −4.80 (corresponding to increasing capillary pressure) for intrusion and at βμ = −5.00, −5.05, −5.15, and −5.20 (corresponding to decreasing capillary pressure) for extrusion, where μ is chemical potential and β (here) is equal to 1/kT, wherein k is Boltzmann’s constant. Reprinted with permission from [82]. Copyright 2005 American Chemical Society.
During extrusion, similarly, a droplet of nwp liquid was trapped within the wider pore body, with only slow exiting mass transport by diffusion. Snapshots of the extrusion process showed that the liquid phase first fragmented and then retreated from the necks. However, for relatively wide ink-bottle pores, the whole system behaved like a regular slit-shaped pore for both intrusion and retraction. In all cases, the surface layer of lattice sites filled and emptied only after and just before, respectively, the bulk sites within the core of the pore. Monson and co-workers also conducted simulations of mercury intrusion and extrusion in more disordered model systems, representing Vycor porous glass, using the hybrid Glauber–Kawasaki dynamics [82,83]. They found that intrusion involved advancement of the mercury meniscus but also included nucleation of droplets of liquid ahead of the front. This is not what is typically observed in glass micro-model experiments [30,37] and may only be a feature of very small pores or where the mass transport of nwp is somehow limited to diffusion, as in the simulated mechanism. During extrusion simulations, cavitation and fragmentation of the liquid phase occurred leading to isolated ganglia of nwp akin to entrapment. Overall, Monson and co-workers [82,83] suggested their simulations showed that mercury extrusion was not a percolation-type process and consisted of an initial, rapid transport-regime process, followed by a much slower quasi-equilibrium regime which involved redistribution of the remaining fluid within the porous material. They suggested this mechanism was consistent with experimental observations which showed the slow extrusion of (initially) entrapped mercury over an extended period [82,83]. However, many materials, such as some catalyst pellets, show no evidence of further extrusion, or even internal re-organisation (assessed by SAXS and/or CXT), of the initial entrapment at the end of the porosimetry experiment even after many days at ambient conditions [11,66,84]. This may mean that, if it exists for these materials, the quasi-equilibrium regime involves physical processes with very long characteristic time-scales indeed.
Thermodynamics have also been incorporated into LBM algorithms. Alpak et al. [85] used a Helmholtz free-energy-minimising phase-field model that was solved using LBM to simulate two-phase flow on structural models derived directly from CXT images. The continuity and Navier–Stokes equations were coupled to an advection–diffusion equation and solved with a free-energy LBM algorithm. The key element of the method was a free-energy functional that described the equilibrium properties of the binary fluid. The model was of the diffuse-interface type whereby the fluid–fluid interface has a finite thickness. Far from the contact line, the LBM algorithm solves the hydrodynamic equations of fluid motion; near the contact line, the method introduced a diffusive mechanism which allowed the contact line to slip on a solid substrate. However, there were some limitations on the fluid properties such that both fluids were of the same density and contact angle hysteresis was assumed to be negligible. Test simulations of snap-off in a simple constriction suggested that it occurred close to the quasi-static ratio of 2. The flow model was also used to simulate capillary desaturation in structural models of sandstone rocks. Capillary desaturation is when the nwp is mobilised by increasing the ratio of viscous to capillary forces. It was found that the predicted curve of residual nwp saturation against capillary number for simulations on a model of Berea sandstone closely matched the equivalent experimental curve for similar real systems.
8. Discussion
The foregoing survey of the literature would suggest that the ideal, “maximally realistic” model for predicting nwp entrapment in disordered porous media would consist of the following. It would employ a structural model for the void space derived directly from a single imaging modality with sufficient resolution, to capture even surface roughness on the smallest pore, across a sufficient field-of-view to encompass the complete representative elemental volume for the porous material. The technique for simulation of the multiphase fluid behaviour within the void space would need to be able to predict wetting properties from pore surface chemistry and texture, reproduce the complex menisci configurations arising within a disordered geometry, and cope with physical processes occurring over very different length- and time-scales. Unfortunately, the above survey has shown that such a maximally realistic model, with all the listed features, is not currently possible within existing computing power and imaging capabilities, and alternative strategies are required for the present. The various types of idealisations, away from the maximally realistic model, required are more restricted in the circumstances in which they can give predictions, but these can still be useful for more constrained problems.
As mentioned above, previous work has typically adopted one of three strategies to deal with this problem. The first is to employ phenomenological models based upon empirical findings. These provide no mechanistic understanding and are predictive only within their realm of applicability determined by the range of key input parameters tested in the experiments. They were, therefore, not discussed in detail in this work.
The second strategy is Galilean idealisation models which reduce the complexity of the problem until it becomes tractable with existing characterisation technology, mathematical techniques, and/or computational power. The biggest problem with this approach is that it is not possible to know in advance which aspects of the problem can be safely left out, or approximated, while still retaining empirical adequacy. A key type of Galilean idealisation is the PNM extracted from direct imaging data. The most appropriate overall form (pore bond only versus pore body–throat networks) and geometries of individual lattice elements can be decided based upon the pore-scale imaging data. As mentioned above, it remains difficult to represent the complex configurations and dynamic behaviour of menisci even in the simplified PNM. This issue is compounded by the fact that testing of PNM extraction algorithms on model structures, as reviewed elsewhere [14,15], has suggested that they often misidentify, or falsely create or remove, individual pore bonds and/or necks, and fail to retain the correct connectivity of the original void space, and thus the resulting model would misrepresent the behaviour of the menisci therein. Notwithstanding these issues, in some cases, it has been seen that PNMs derived from imaging data are predictive of some key observables, such as the general level of residual saturation of nwp.
Further, even simulations of fluid behaviour on models constructed directly from imaging datasets themselves have issues. Image segmentation can give rise to false pores and/or incorrect texture [14,15]. Low-resolution images can miss micropores where residual wp saturation remains at the end of the initial drainage process before imbibition commences, thereby missing key seed sites for the initiation of imbibition. Simulation techniques that can cope with complex void space geometry still have problems with meniscus tracking.
As mentioned above, disordered porous media often have void spaces that cannot be comprehensively imaged with one modality alone. Hierarchical models e.g., [70] have attempted to bridge the gaps between different imaging modalities with different resolution and field-of-view trade-offs.
A further modelling strategy is to develop a minimal idealisation representation of the system. The basic physical problem considered here has a series of levels of phenomena occurring over a hierarchy of length- and time-scales. For example, the work considered above has shown that snap-off of menisci can happen at the edges of macroscopic heterogeneities in the spatial distribution of pore sizes, and/or at the edges of smaller local clusters of pores, and/or within individual pore necks. In some cases, one of these levels is dominant, and the others can be neglected. This means that the model can be simplified such that it only includes the key processes controlling entrapment. Further, it has been seen that dynamical effects can also be neglected under certain conditions, particularly at low capillary number in the quasi-static regime, and the model predictions still remain empirically adequate.
PNMs can also be implemented as a form of minimalist model whereby increasing levels of complexity, in the form of ever more pore structural features, such as irregular pore cross-section or axial corrugation, variable connectivity, spatial correlations in pore sizes, etc., can be progressively incorporated until empirical adequacy is achieved with ever more experimental data types, including imaging. The increased complexity resulting from this “building up” approach can also bring the PNM close to the edge of practical feasibility due to computing limitations. However, the above surveyed findings have shown that, for some materials, only incorporation of a limited set of void space features is necessary to achieve empirical adequacy, and so the minimalist approach can be successful.
A range of different analytical calculation methods for predicting snap-off in pore bonds have been described above, but each relies upon different assumptions or approximations that give rise to different predictions of snap-off pressure. For example, the analytical methods have been seen to require approximation that sometimes ignores the variable finite length of pore bonds, but studies have shown that accounting for the explicit length of a pore matters [50]. Further, the fixed pore connectivity in some simpler PNMs discussed above [24,25,26,27] is an issue for low-connectivity networks where connectivity matters most [36,37]. Hence, some of the very simplest PNMs incorporate less than the minimum level of detail needed to be predictive.
Percolation models and PNMs give rise to similar findings for the impact of snap-off and spatial correlation in pore sizes. This is probably because more detailed dynamic simulations, conducted at a low capillary number, have shown that simpler sets of rules, developed for menisci behaviour under the quasi-static regime, are sufficient. However, it is also important to check that a low overall capillary number does not hide local high-capillary-number processes.
9. Conclusions and Future Perspective
Empirical models are limited in their scope and ability to improve understanding of the underlying mechanisms of entrapment. Hence, the other more detailed modelling approaches described here are required to supply explanations for nwp entrapment levels observed in real porous media. PNMs, models derived from imaging data, percolation theory, and thermodynamic and statistical mechanical approaches can also improve fundamental understanding of the entrapment process. PNMs, as a form of Galilean idealisation, greatly reduce the demands on computing power compared with the original dataset derived directly from imaging, thereby improving the tractability of datasets and the feasibility of predictions. However, it is not possible to know in advance whether a given degree of simplification will retain empirical adequacy, and, thus, this must be tested—it is not always the case—or the scope of potential model predictions is reduced. A key issue is that the necessary simplification process to create PNMs from imaging data means that they are still limited in their ability to represent the true configurational complexity of the meniscus boundaries in disordered porous materials. It has been seen that this can limit their ability to accurately predict withdrawal pressures for nwp, etc.
Full dynamic simulations of fluid flow processes at a low capillary number, within both PNMs and direct visualisations of the void space provided by imaging data, have shown that the quasi-static approximation, based upon fixed rules for discrete, individual flow events, provides an empirically adequate description of entrapment for some systems, such as during mercury porosimetry experiments. However, there is still some uncertainty for more complex systems, especially at higher capillary numbers. Simulations on models derived directly from images have also shown the validity of approaches based upon percolation theory in some circumstances.
Thermodynamics-based approaches have shown some capability for describing and understanding chemically heterogeneous, and thus mixed-wettability, systems. However, while statistical mechanical methods can reproduce some major empirical features of entrapment, such as the predominant localisation of residual nwp in larger pores, the proposed mass transfer mechanisms are not those occurring in most real systems—leading to the incorrect prediction of phenomena not observed in experiments.
It has been seen that the overall pore connectivity (average pore co-ordination number) is particularly important in determining the behaviour of the menisci, and the level of entrapment of nwp, for flows with a wide range of capillary pressures. However, in some cases, even the full distribution of pore co-ordination number was found to be insufficient to predict entrapment levels. The width (coefficient of variation) of the pore size distribution is also important. However, in certain types of porous media, with long-range correlations in local pore sizes, it is the connectivity and spatial distribution of extended regions of similar pore size that control the entrapment. For flows with higher capillary number, such that they begin to lie outside the quasi-static regime controlled by capillary forces, the overall migration of the fluid–fluid displacement front becomes more uniform and is less affected by local pore structural heterogeneity.
Improvements in the spatial and temporal resolution possible for CXT imaging data of individual fluid–fluid displacements during imbibition will resolve the uncertainties around the validity of PNMs of quasi-static flow. This will enable the remaining doubt about whether any discrepancies in model predictions and experimental data arise from limitations in the imaging data or in the model to be dispelled. Further developments in imaging methods may enable the mapping of surface characteristics, such as chemistry and roughness, that affect wettability, and thus the a priori prediction of spatial distribution of wettability in complex void spaces.
For systems where the resolution and field-of-view of a single imaging modality are insufficient to comprehensively map the whole void space, appropriate new scale-up and/or hierarchical modelling approaches incorporating data from multiple imaging modalities at different length-scales are required. This is because existing scale-up methodologies would struggle to cope with highly heterogeneous systems where local regions at lower length-scales differ significantly in key descriptors such as pore size and wettability.
Previous work discussed above has suggested that scenarios exist where the snap-off ratio (SOR) varies from the classical value of 2. More detailed study is required to establish the continued viability of the SOR concept and establish appropriate guidance on its use. Further, more detailed consideration of particular pore-scale processes, such as lid–cavity driven flow, is required to determine their level of importance for potential inclusion in minimalist models.
The thermodynamic and statistical mechanical approaches have been somewhat neglected of late. However, these approaches have been shown to be able to cope with chemical heterogeneity. Hence, they may still have further potential for addressing such systems.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fetter, C. Contaminant Hydrogeology; Prentice Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Kota, A.K.; Kwon, G.; Choi, W.; Mabry, J.M.; Tuteja, A. Hygro-responsive membranes for effective oil-water separation. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Li, Q.; Kühn, M.; Nakaten, N. Power-to-gas based subsurface energy storage: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 97, 478–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyne, N.J. Nontechnical Guide to Petroleum Geology, Exploration, Drilling and Production; PennWell Books, LLC: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Rigby, S.P.; Alsayah, A.; Seely, R. Impact of Exposure to Supercritical Carbon Dioxide on Reservoir Caprocks and Inter-Layers during Sequestration. Energies 2022, 15, 7538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, S.P. Structural Characterisation of Natural and Industrial Porous Materials: A Manual; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ellman, S.; Mascini, A.; Bultreys, T. Validating mechanistic models of fluid displacement during imbibition. Adv. Water Resour. 2024, 183, 104590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blunt, M.J. Multiphase Flow in Permeable Media: A Pore-Scale Perspective; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, R.; Nisar, V.; Erfani, H.; Martinez-Ferrer, P.J. Impact of pore morphology on two-phase flow dynamics under wettability alteration. Fuel 2020, 268, 117315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Gharbi, M.S.; Blunt, M.J. Dynamic network modeling of two-phase drainage in porous media. Phys. Rev. E 2005, 71, 016308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, S.P.; Chigada, P.I.; Evbuomvan, I.O.; Chudek, J.A.; Miri, T.; Wood, J.; Bakalis, S. Experimental and modelling studies of the kinetics of mercury retraction from highly confined geometries during porosimetry in the transport and the quasi-equilibrium regimes. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2008, 63, 5771–5788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, G.; Morrow, N.R. Developments in spontaneous imbibition and possibilities for future work. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2013, 110, 268–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisberg, M. Simulation and Similarity: Using Models to Understand the World; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rigby, S.P. Do Pores Exist?—Foundational Issues in Pore Structural Characterisation. Foundations 2024, 4, 225–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, S.P.; Himona, E. Methods of Pore Structural Characterisation of Sedimentary Rocks and Their Constituent Minerals. Minerals 2024, 14, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, C.T.; Christakos, G.; Imhoff, P.T.; McBride, J.F.; Pedit, J.A.; Trangenstein, J.A. Multiphase flow and transport modeling in heterogeneous porous media: Challenges and approaches. Adv. Water Resour. 1998, 21, 77–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhaj, M.A.; Niah, M.I.; Hossain, M.E. State-of-the-art on capillary pressure hysteresis: Productive techniques for better reservoir performance. Upstream Oil Gas Technol. 2021, 7, 100040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Guo, P.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Cao, S.; Zhang, J.; Sun, W.; Qi, D.; Ji, Q. State of the art relative permeability hysteresis in porous media: Petroleum engineering applications. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 46396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Y.; Sedghi, M.; Piri, M. Dynamic pore-scale modelling of residual trapping following imbibition in a rough-walled fracture. Transp. Porous Media 2021, 140, 143–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Land, C.S. Calculation of imbibition relative permeability for two- and three-phase flow from rock properties. SPE J. 1968, 8, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmas, C.E.; Androutsopoulos, G.P. A novel pore structure tortuosity concept based on nitrogen sorption hysteresis data. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, S.P.; Hasan, M.; Hitchcock, I.; Fletcher, R.S. Detection of the delayed condensation effect and determination of its impact on the accuracy of gas adsorption pore size distributions. Colloids Surf. A 2017, 517, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadasi, R.; Foroughi, S.; Goodarzi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Bijeljic, B.; Blunt, M.J.; Niemi, A. Trapping and remobilization during geological CO2 storage: A pore-scale imaging and modeling study. Adv. Water Resour. 2025, 205, 105092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androutsopoulos, G.P.; Mann, R. Evaluation of mercury porosimeter experiments using a network pore structure model. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1979, 34, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, R.; Allamy, A.; Holt, A. Visualized porosimetry for pore structure characterization of a nickel/alumina reforming catalyst. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 1995, 73, 147–153. [Google Scholar]
- Mata, V.G.; Lopes, J.C.B.; Dias, M.M. Porous media characterization using mercury porosimetry simulation. 1. Description of the simulator and its sensitivity to model parameters. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 3511–3522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, V.G.; Lopes, J.C.B.; Dias, M.M. Porous media characterization using mercury porosimetry simulation. 2. An iterative method for the determination of the real pore size distribution and the mean coordination number. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2001, 40, 4836–4843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portsmouth, R.L.; Gladden, L.F. Determination of pore connectivity by mercury porosimetry. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1991, 46, 3023–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portsmouth, R.L.; Gladden, L.F. Mercury porosimetry as a probe of pore connectivity. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 1992, 70, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Wardlaw, N.C.; McKellar, M. Mercury porosimetry and the interpretation of pore geometry in sedimentary rocks and artificial models. Powder Technol. 1981, 29, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Dullien, F.A.L.; Dai, L.; Li, D. Immiscible displacement in the interacting capillary bundle model part I. Development of interacting capillary bundle model. Trans. Porous Med. 2005, 59, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.; Dullien, F.A.L.; Dai, L.; Li, D. Immiscible displacement in the interacting capillary bundle model part II. Applications of model and comparison of interacting and non-interacting capillary bundle models. Trans. Porous Med. 2006, 63, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Liu, H.; Wang, J. Entrapment of the non-wetting phase during co-current spontaneous imbibition. Energy Fuels 2015, 29, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dong, M. Trapping of the non-wetting phase in an interacting triangular tube bundle model. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felipe, C.; Cordero, S.; Kornhauser, I.; Zgrablich, G.; López, R.; Rojas, F. Domain Complexion Diagrams Related to Mercury Intrusion-Extrusion in Monte Carlo-Simulated Porous Networks. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2006, 23, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiroglou, C.D.; Payatakes, A.C. A new simulator of mercury porosimetry for the characterization of porous materials. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1990, 137, 315–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiroglou, C.D.; Payatakes, A.C. Mercury intrusion and retraction in model porous media. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1998, 75, 215–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Ju, B.; Chen, X.; Chen, Z.; Dong, Y.; Wu, D. Pore-scale investigation of waterflooding based on experiments and numerical simulations considering the change in geometry and wettability. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 17617–17628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavuluri, S.; Seers, T.D.; Shokri, N.; Alyafei, N.; Rabbani, H.S. Capillary trapping in mixed-wet porous media: Implications for subsurface carbon dioxide sequestration. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2025, 191, 105307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, F.G.; Siebert, D.N.; Surmas, R. Influence of wettability on the residual fluid saturation for homogeneous and heterogeneous systems. Phys. Fluids 2020, 32, 052008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Song, R.; Liu, J.; Lei, Y.; Zhu, X. Pore-scale visualization and quantitative analysis of the spontaneous imbibition based on experiments and micro-CT technology in low-permeability mixed-wettability rock. Energy Sci. Eng. 2020, 8, 1840–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Li, J.; Liang, B.; Liu, J.; Sun, W.; He, J.; Lei, Y. Complex wettability behaviour triggering mechanism on imbibition: A model construction and comparative study based on analysis at multiple scales. Energy 2023, 275, 127434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, M.G.; Bondino, J.; Hamon, G.; McDougall, S.R. A pore-scale investigation of low-salinity waterflooding in porous media: Uniformly wetted systems. Transp. Porous Media 2017, 118, 201–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raeesi, B.; Piri, M. The effects of wettability and trapping on relationships between interfacial area, capillary pressure and saturation in porous media: A pore-scale network modelling approach. J. Hydrol. 2009, 376, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stauffer, D.; Aharony, A. Introduction to Percolation Theory, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Avnir, D. The Fractal Approach to Heterogeneous Chemistry; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, R.G.; Scriven, L.E.; Davis, H.T. Percolation theory of two phase flow in porous media. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1981, 36, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, M.A.; Chatzis, I. A mixed-percoaltion model of capillary hysteresis and entrapment in mercury porosimetry. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1993, 161, 278–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonormand, R.; Zarone, C.; Sarr, A. Mechanisms of The Displacement of One Fluid by Another in a Network of Capillary Ducts. J. Fluid Mech. 1983, 135, 337–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, M.A.; Chatzis, I. The effect of spatial correlations on the accessibility characteristics of three-dimensional cubic networks as related to drainage displacements in porous media. Water Resour. Res. 1993, 29, 1777–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, W.M.; Nguyen, V.H. Effects of snap-off in imbibition in porous media with different spatial correlations. Transp. Porous Media 2006, 64, 279–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Avraham, D.; Havlin, S. Diffusion and Reactions in Fractals and Disordered Systems; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rodenas, T.; Prieto, G. FIB-SEM tomography in catalysis and electrochemistry. Catal. Today 2022, 405–406, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Sun, M.; Sun, X.; Liu, B.; Ostadhassan, M.; Huang, W.; Chen, X.; Pan, Z. Pore network characterization of shale reservoirs through state-of-the-art X-ray computed tomography: A review. Gas Sci. Eng. 2023, 113, 204967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Qin, X.; Wang, H.; Xia, Y.; Zou, S. Pore-scale investigation of forced imbibition in porous rocks through interface curvature and pore topology analysis. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2025, 17, 245–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namaee-Ghasemi, A.; Ayatollahi, S.; Mahani, H. Pore-scale simulation of the interplay between wettability, capillary number, and salt dispersion on the efficiency of oil mobilization by low-salinity waterflooding. SPE J. 2021, 26, 4000–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Zhao, L.; Li, P.; Yang, F.; Cai, J. Experiments and phase-field simulation of counter-current imbibition in porous media with different pore structure. J. Hydrol. 2022, 608, 127670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Xie, Q.; Wang, H.; Su, Y.; Rezaei-Gomari, S. Pseudopotential-based multiple-relaxation-time lattice Boltzmann model for multicomponent and multiphase slip flow. Adv. Geo-Energy Res. 2023, 9, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwandi, N.; Jiang, F.; Tsuji, T. Relative permeability variation depending on viscosity ratio and capillary number. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR031501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashirbekov, A.; Kabdenova, B.; Kuljabekov, A.; Monaco, E.; Wang, L.; Rojas-Solórzano, L. Lattice Boltzmann pseudopotential multiphase modeling of transcritical CO2 flow using a crossover formulation. Adv. Geo-Energy Res. 2022, 6, 539–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambekar, A.S.; Mondal, S.; Buwa, V.V. Pore-resolved volume-of-fluid simulations of two-phase flow in porous media: Pore-scale flow mechanisms and regime map. Phys. Fluids 2022, 33, 102119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cai, S.; Yao, J.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, K.; Song, W.; Zhang, L.; Sun, H.; Lisitsa, V. Pore-scale simulation of remaining oil distribution in 3D porous media affected by wettability and capillarity based upon volume of fluid method. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2021, 143, 103746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.; Mahmoud, Y.; Zhang, S.; Iglauer, S. X-ray tomography imaging of shale microstructures: A review in the context of multiscale correlative imaging. Int. J. Coal Geol. 2020, 233, 103641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Dowey, P.J.; Rutter, E.; Taylor, K.G.; Lee, P.D. A novel upscaling procedure for characterising heterogeneous shale porosity from nanometer-to millimetre-scale in 3D. Energy 2019, 181, 1285–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, A.J.; Ziese, U.; Verkleij, A.J.; Janssen, A.H.; de Jong, K.P. Three-dimensional transmission electron microscopy: A novel imaging and characterization technique with nanometer scale resolution for materials science. J. Phys. Chem. B 2000, 104, 9368–9370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nepryahin, A.; Fletcher, R.; Holt, E.M.; Rigby, S.P. Structure-transport relationships in disordered solids using integrated rate of gas sorption and mercury porosimetry. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 152, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollewand, M.P.; Gladden, L.F. Heterogeneities in Structure and Diffusion within Porous Catalyst Support Pellets Observed by NMR Imaging. J. Catal. 1993, 144, 254–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, S.P.; Watt-Smith, M.J.; Chigada, P.; Chudek, J.A.; Fletcher, R.S.; Wood, J.; Bakalis, S.; Miri, T. Studies of the entrapment of non-wetting fluid within nanoporous media using a synergistic combination of MRI and micro-computed X-ray tomography. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2006, 61, 7579–7592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt-Smith, M.J.; Rigby, S.P.; Chudek, J.A.; Fletcher, R.S. Simulation of non-wetting phase entrapment within porous media using MRI. Langmuir 2006, 22, 5180–5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, S.P. A hierarchical structural model for the interpretation of mercury porosimetry and nitrogen sorption. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2000, 224, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sok, R.M.; Knackstedt, M.A.; Sheppard, A.P.; Pinczewski, W.V.; Lindquist, W.B.; Venkatarangan, A.; Paterson, L. Direct and stochastic generation of network models from tomographic images: Effect of topology on residual saturations. Transp. Porous Media 2002, 46, 345–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.J.; Niu, Y.; Manoorkar, S.; Mostaghimi, P.; Armstrong, R.T. Deep Learning of Multiresolution X-Ray Micro-Computed-Tomography Images for Multiscale Modeling. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2022, 17, 054046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Qian, M. Deep-learning-based porous media microstructure quantitative characterization and reconstruction method. Phys. Rev. E 2022, 105, 015308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaei, A.; Piri, M. Direct pore-to-core up-scaling of displacement processes: Dynamic pore network modelling and experimentation. J. Hydrol. 2015, 522, 488–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyväluoma, J.; Raiskinmäki, P.; Jäsberg, A.; Koponen, A.; Kataja, M.; Timonen, J. Evaluation of a lattice-Boltzmann method for mercury intrusion porosimetry simulations. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2004, 20, 1003–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, M.; Singh, K.; Bijeljic, B.; Blunt, M.J. Direct numerical simulation of pore-scale trapping events during capillary-dominated two-phase flow in porous media. Transp. Porous Media 2021, 138, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, D.; Sun, H.; Zhong, J.; Yao, J.; Lisitsa, V. Correlations of residual oil distribution with pore structure during the water flooding process in sandstone reservoirs. Adv. Geo-Energy Res. 2024, 12, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bultreys, T.; Lin, Q.; Gao, Y.; Raeini, A.Q.; AlRatrout, A.; Bijeljic, B.; Blunt, M.J. Validation of model predictions of pore-scale fluid distributions during two-phase flow. Phys. Rev. E 2018, 97, 053104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bultreys, T.; Singh, K.; Raeini, A.Q.; Ruspini, L.C.; Øren, P.E.; Berg, S.; Rücker, M.; Bijeljic, B.; Blunt, M.J. Verifying pore network models of imbibition in rocks using time-resolved synchrotron imaging. Water Resour. Res. 2020, 56, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowell, S.; Shields, J.E. Influence of pore potential on hysteresis and entrapment in mercury porosimetry. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1982, 90, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcheron, F.; Monson, P.A. Modeling mercury porosimetry using statistical mechanics. Langmuir 2004, 20, 6482–6489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porcheron, F.; Monson, P.A. Dynamic aspects of mercury porosimetry: A lattice model study. Langmuir 2005, 21, 3179–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porcheron, F.; Thommes, M.; Ahmad, R.; Monson, P.A. Mercury porosimetry in mesoporous glasses: A comparison of experiments with results from a molecular model. Langmuir 2007, 23, 3372–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffino, L.; Mann, R.; Oldman, R.; Stitt, E.H.; Boller, E.; Cloetens, P.; DiMichiel, M.; Merino, J. Using x-ray microtomography for characterisation of catalyst particle pore structure. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2005, 83, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpak, F.O.; Zacharoudiou, I.; Dietderich, J.; Saxena, N. Direct simulation of pore-scale two-phase visco-capillary flow on large digital rock images using a phase-field lattice Boltzmann method on general purpose graphics processing units. Comput. Geosci. 2019, 23, 849–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).