Poly(curcumin β-amino ester)-Based Tablet Formulation for a Sustained Release of Curcumin
Abstract
:1. Introduction and Background
2. Results
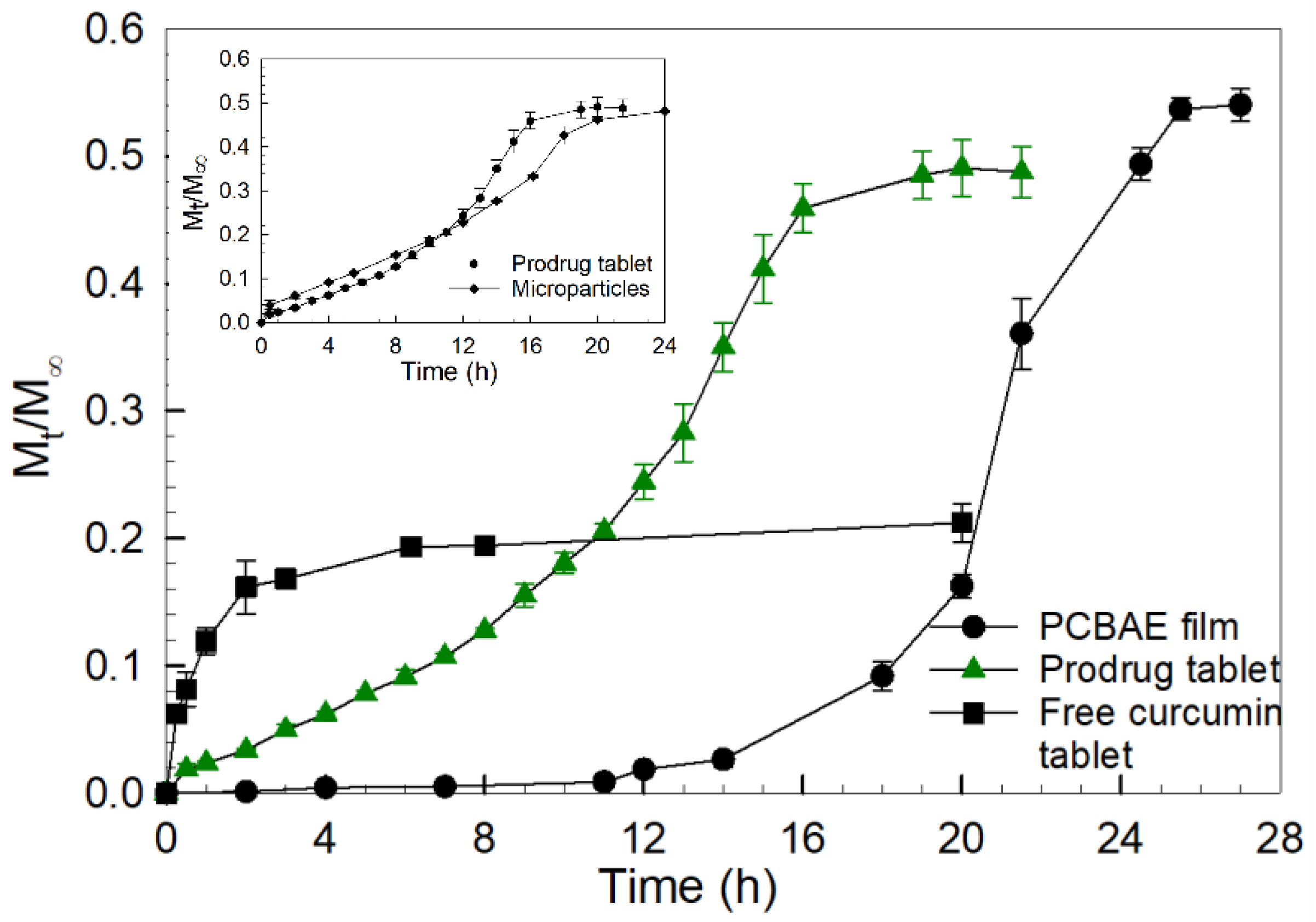
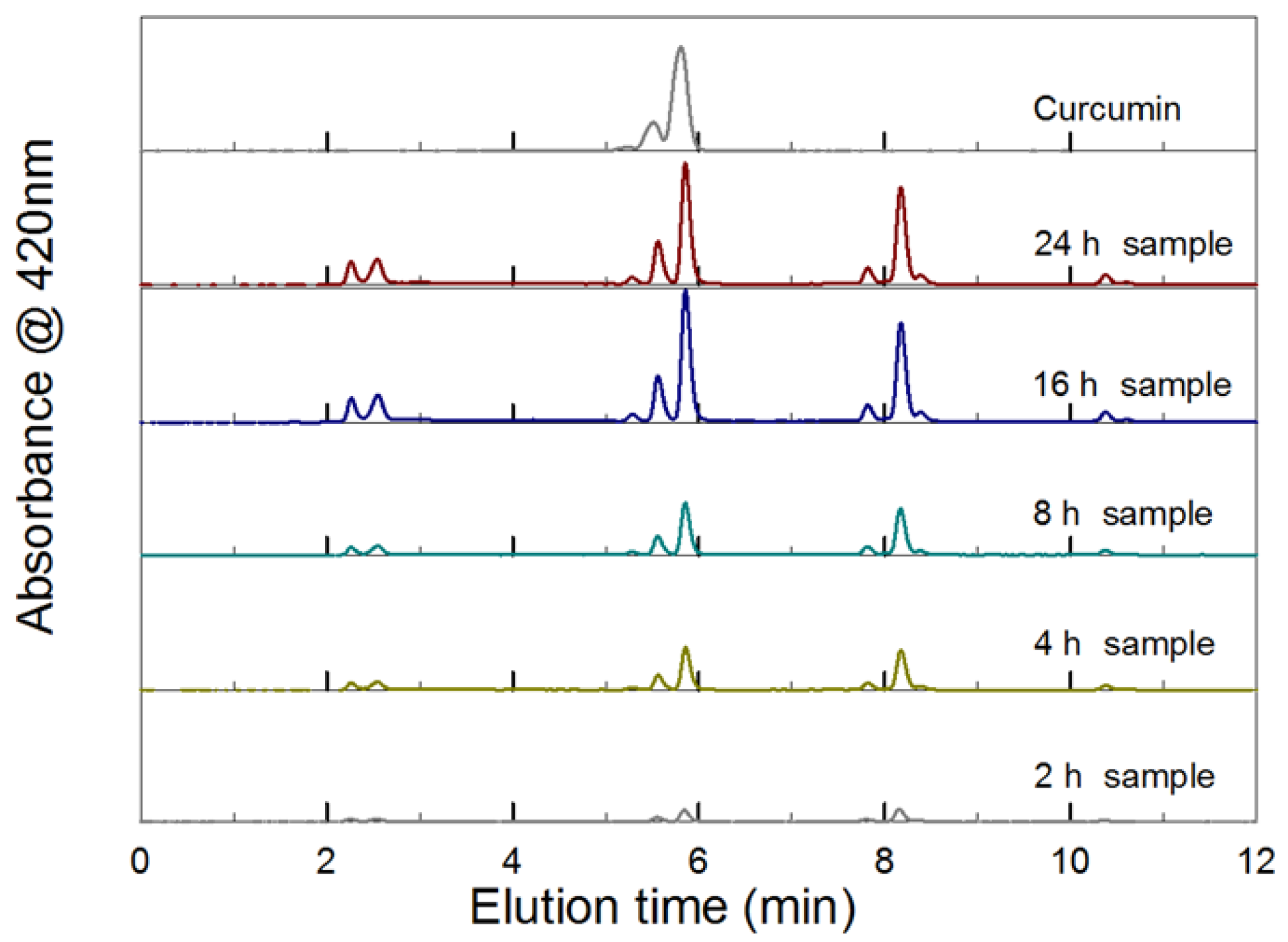
2.1. PCBAE Hydrogel Film Degradation and Tablet Dissolution
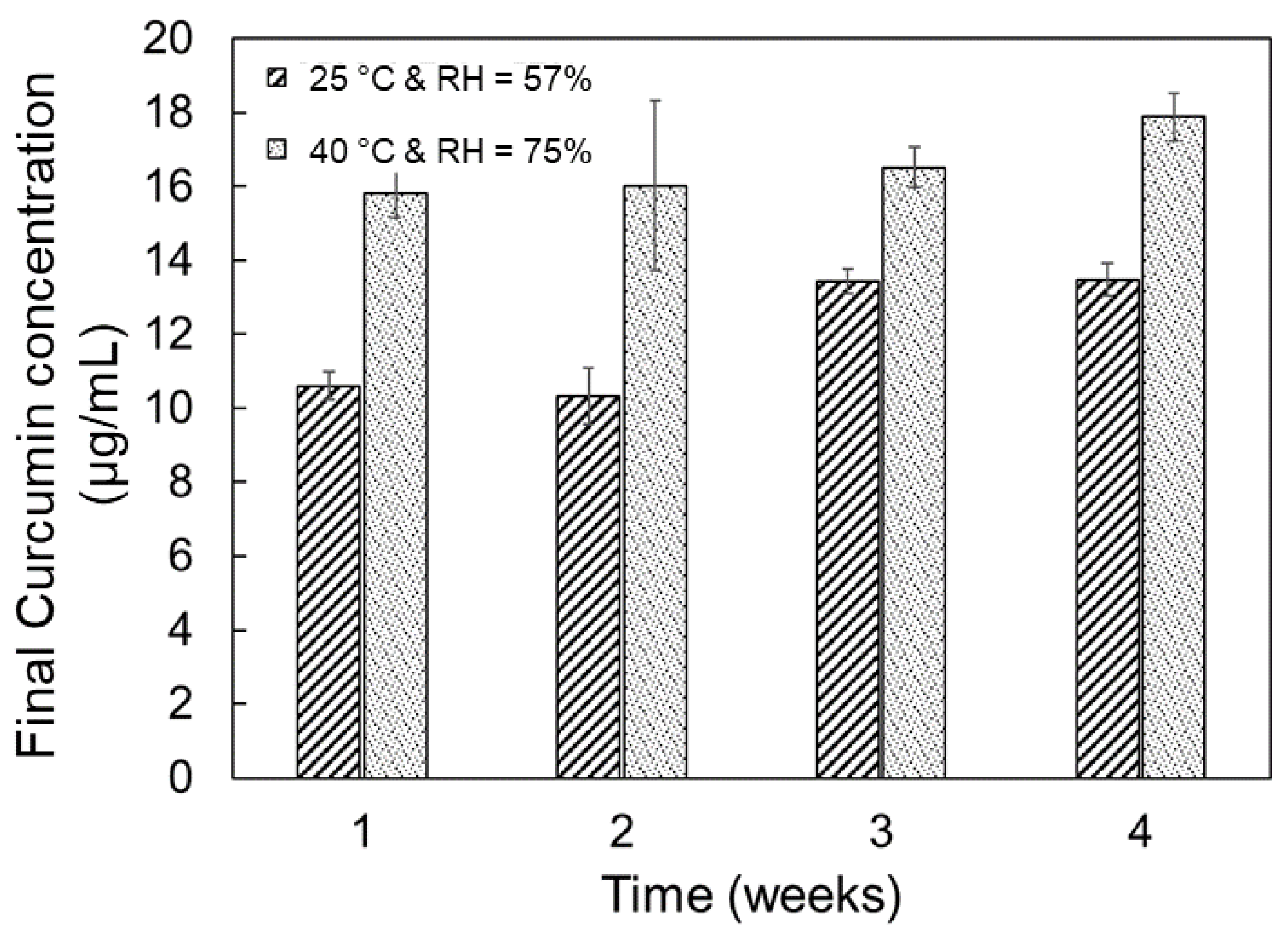
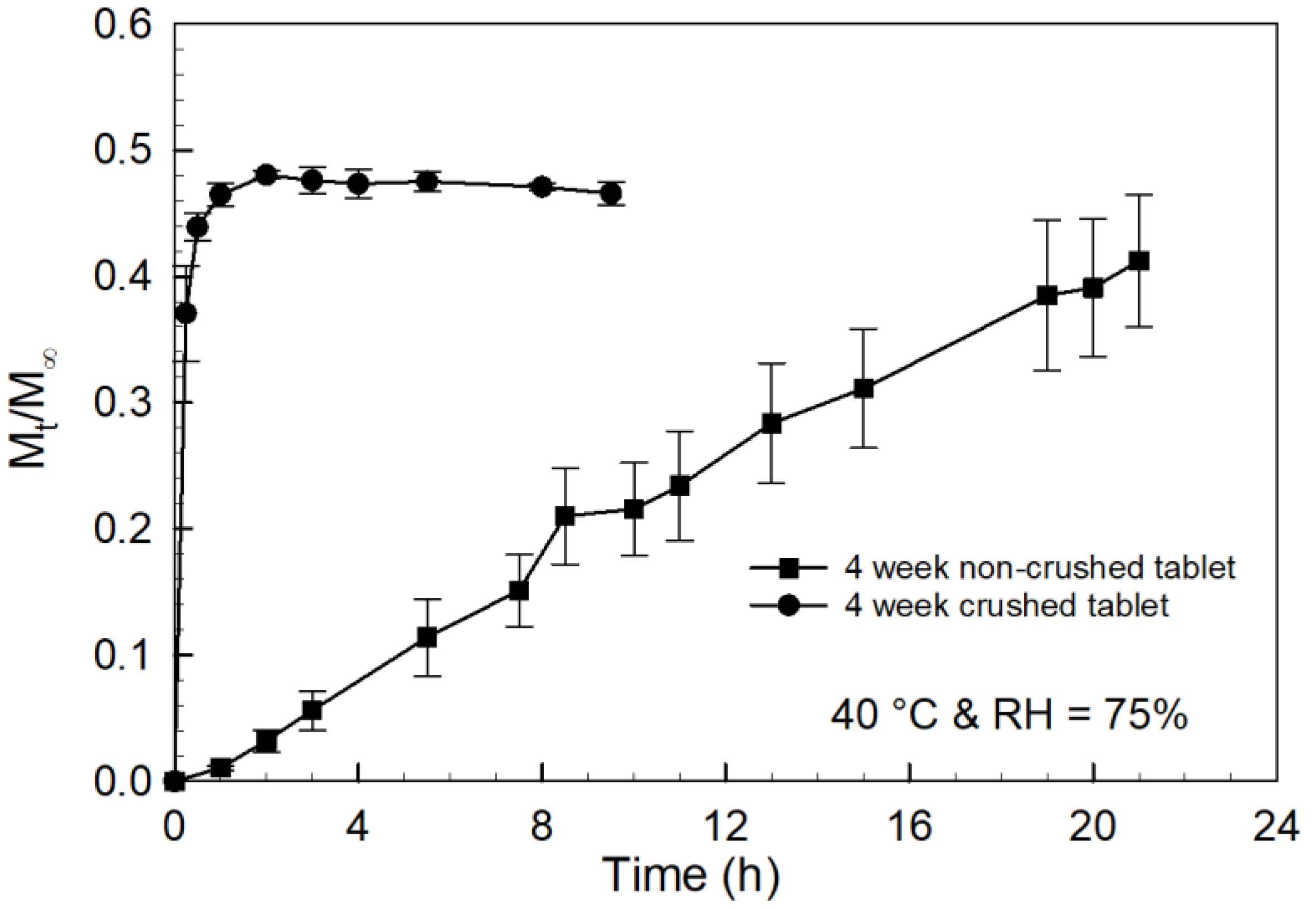
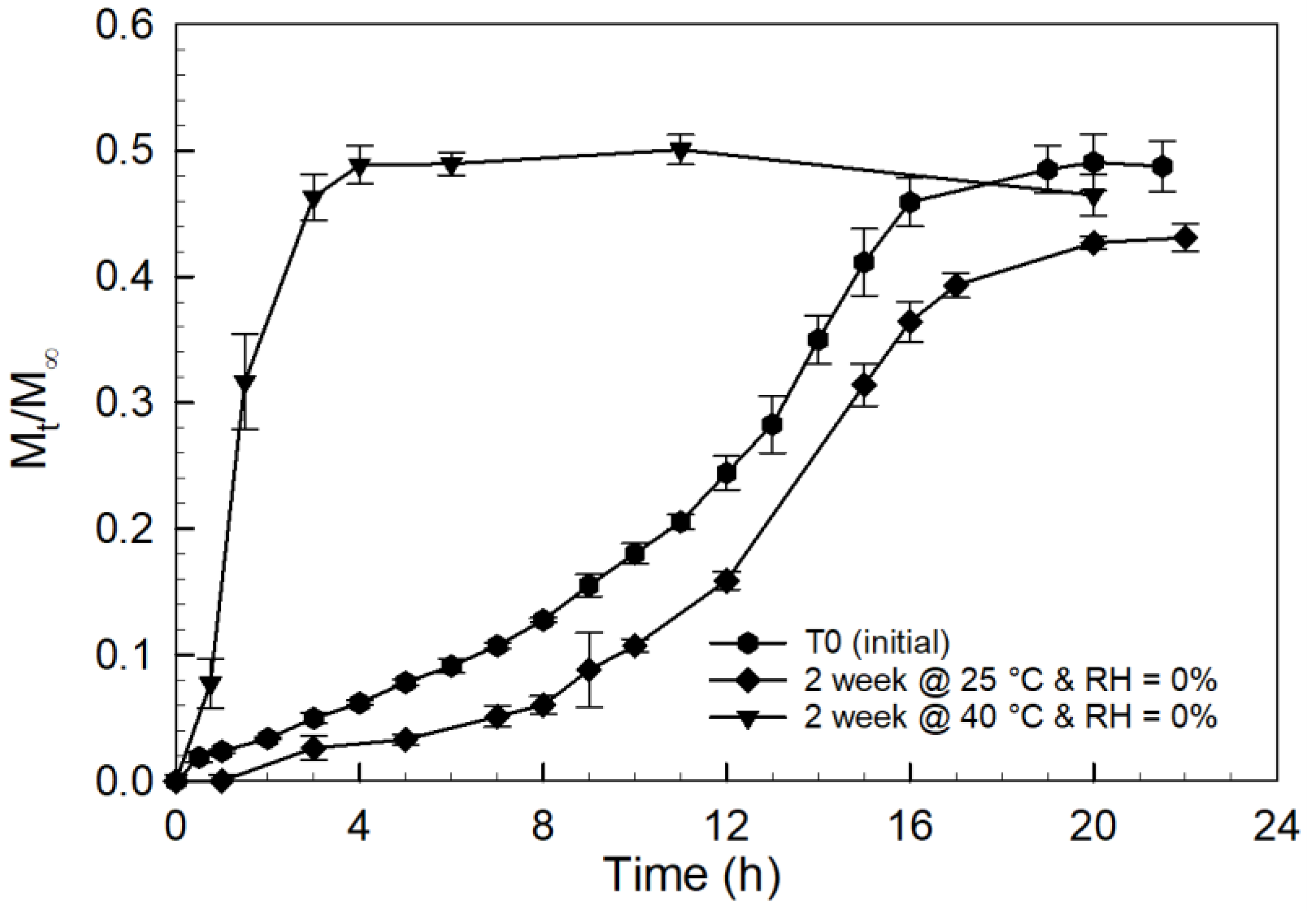
2.2. Tablet Storage Stability Study
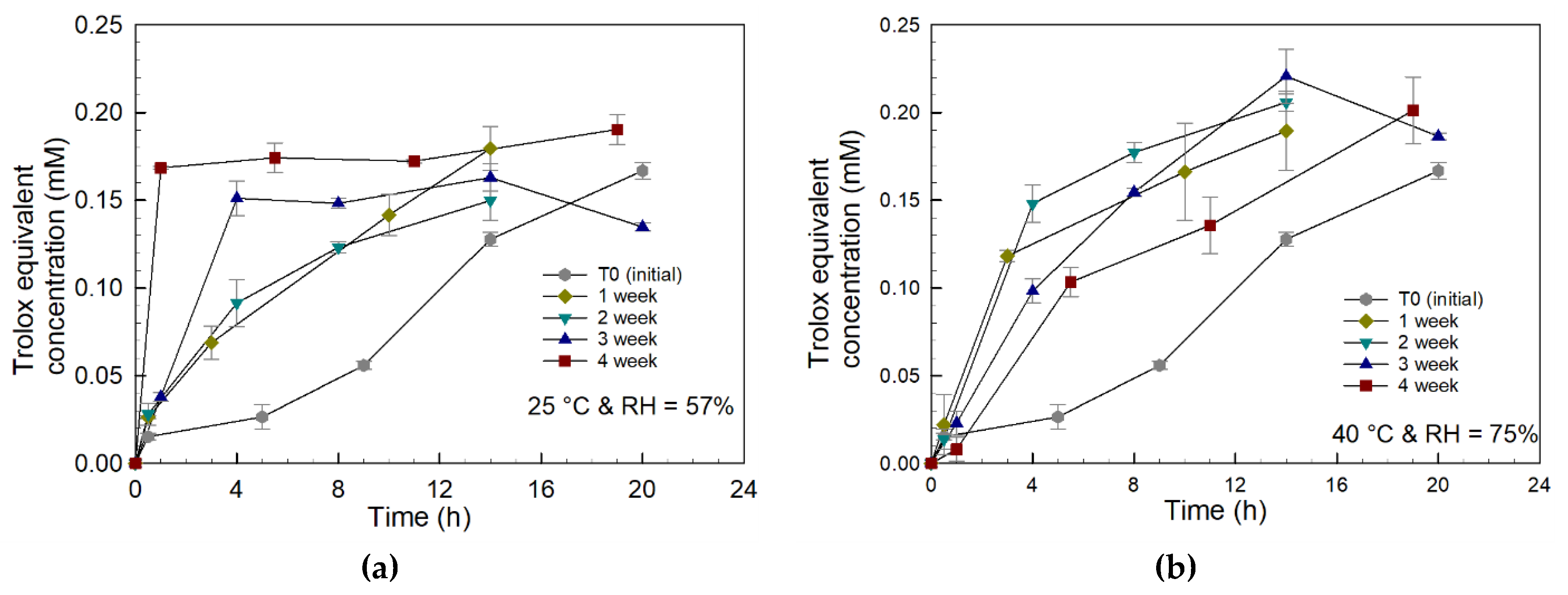
2.3. Antioxidant Activity
3. Discussion
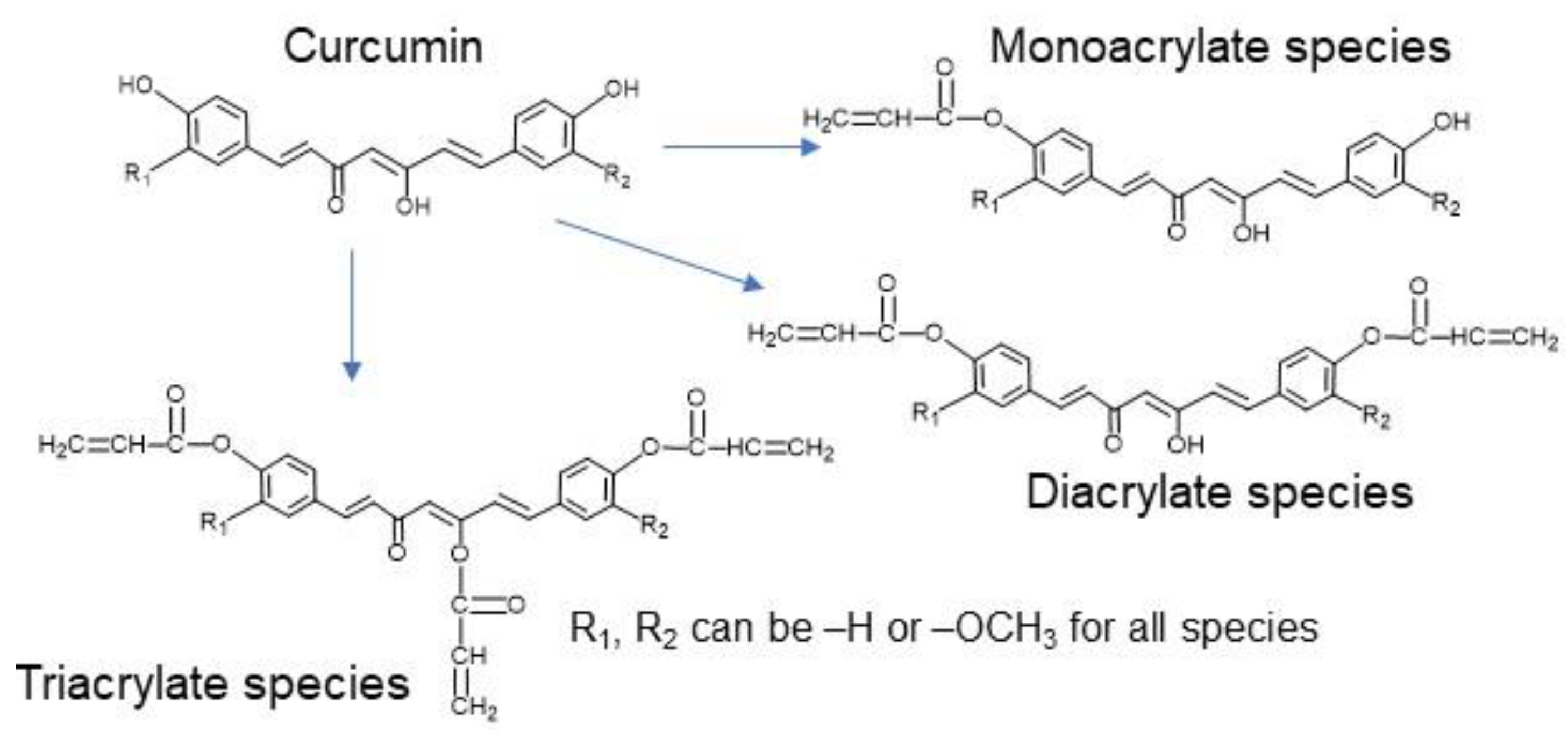
3.1. Difference in Curcumin Release Profile for PCAE Film Versus PCBAE Tablets
3.2. Superior Release Profile for PCBAE Tablets Compared to Free Curcumin Tablets
3.3. Storage Stability Assessment of PCBAE Tablets
3.4. Effect of Inherent Excipient Moisture on PCBAE Tablets
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Materials
5.2. Synthesis of Poly(Curcumin Β Amino Ester) (PCBAE) Hydrogel Films
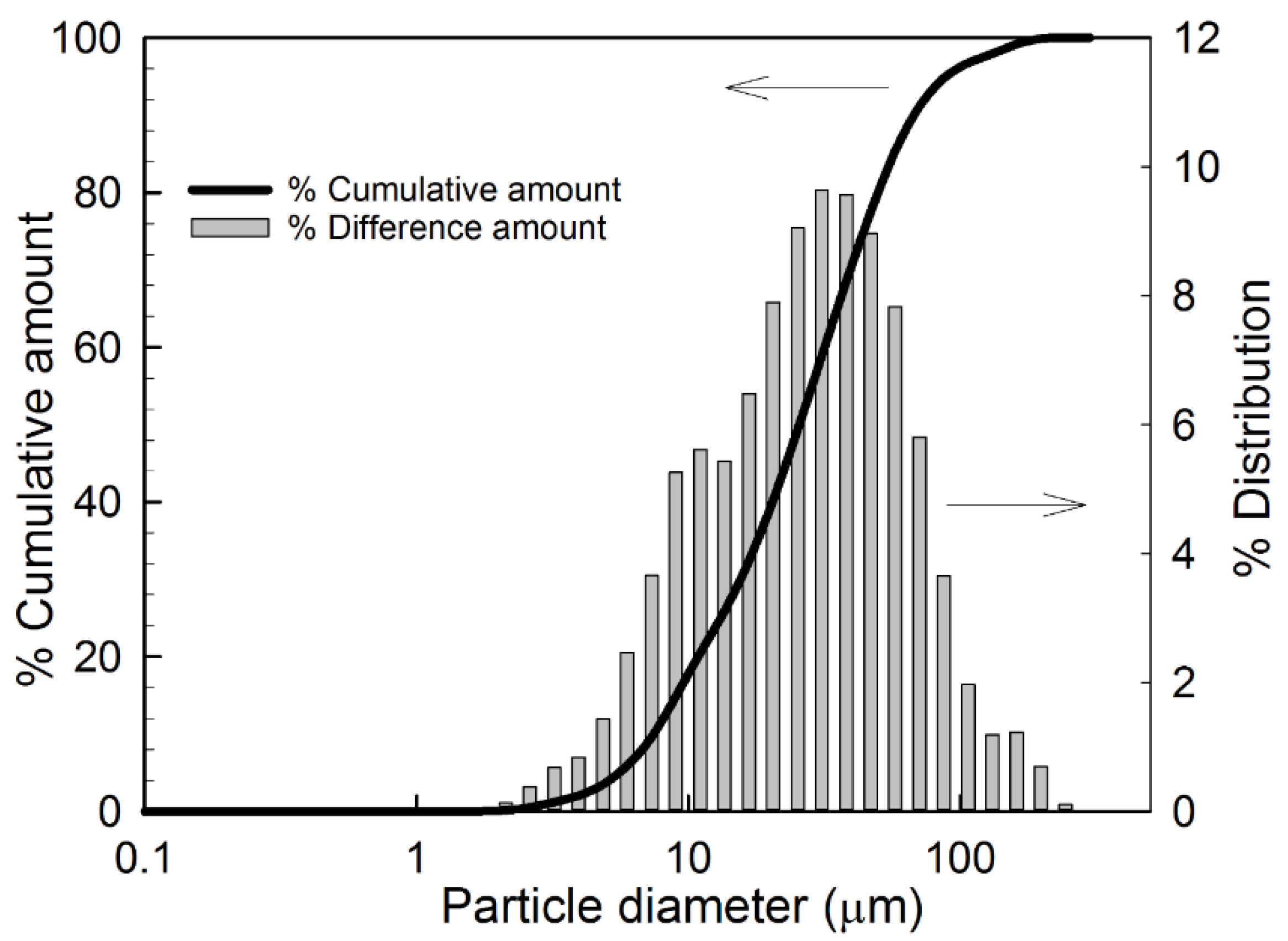
5.3. Particle Size Analysis
5.4. PCBAE Prodrug Tablet Synthesis
5.5. Tablet Dissolution and Curcumin Release
5.6. Antioxidant Activity Using TEAC Assay
5.7. Standard and Accelerated Storage Stability
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Enzmann, F.; Lachmann, B. Transdermal, Oral and Intravenous Formulations of 2,3-Dimethoxy-5-Methyl-6-Decaprenyl-1,4-Benzoquinone. U.S. Patent Application No. 10/783,029, 18 November 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, K.M.; Kass, M.; Wilson, R. Isolated Granulomatous Gastritis. Treatment with Corticosteroids. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 1987, 9, 442–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraser, A.G.; Orchard, T.R.; Jewell, D.P. The Efficacy of Azathioprine for the Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A 30 Year Review. Gut 2002, 50, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, K.; Wu, H.; Neish, A.S.; Champion, J.A. Alginate/Chitosan Microparticles for Gastric Passage and Intestinal Release of Therapeutic Protein Nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2019, 295, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, E.; Miyamura, N.; Uemura, K.; Kobayashi, M. Preparation of Enteric Coated Timed-Release Press-Coated Tablets and Evaluation of Their Function by in Vitro and in Vivo Tests for Colon Targeting. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 204, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchheiner, J.; Glatt, S.; Fuhr, U.; Klotz, U.; Meineke, I.; Seufferlein, T.; Brockmöller, J. Relative Potency of Proton-Pump Inhibitors—Comparison of Effects on Intragastric PH. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2009, 65, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calahan, J.L.; Azali, S.C.; Munson, E.J.; Nagapudi, K. Investigation of Phase Mixing in Amorphous Solid Dispersions of AMG 517 in HPMC-AS Using DSC, Solid-State NMR, and Solution Calorimetry. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 4115–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, E.; Rodríguez-Hornedo, N.; Suryanarayanan, R. A Rapid Thermal Method for Cocrystal Screening. CrystEngComm 2008, 10, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, V.S. OSD Formulations—Dissolving Bioavailability & Solubility Challenges in Formulation & Development. Drug Dev. Deliv. 2020, 20, 58–62. [Google Scholar]
- Serajuddin, A.T. Salt Formation to Improve Drug Solubility. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 603–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, S.P.; Arora, K.K.; Kwong, E.; Templeton, A.; Clas, S.-D.; Suryanarayanan, R. Correlation between Molecular Mobility and Physical Stability of Amorphous Itraconazole. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 694–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Dai, W.-G. Fundamental Aspects of Solid Dispersion Technology for Poorly Soluble Drugs. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2014, 4, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McNamara, D.; Yin, S.; Pan, D.; Crull, G.; Timmins, P.; Vig, B. Characterization of Phase Separation Propensity for Amorphous Spray Dried Dispersions. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, S.V.; Sharma, S.; Prasad, K.K.; Sinha, S.K.; Singh, K. Role of Oxidative Stress & Antioxidant Defence in Ulcerative Colitis Patients from North India. Indian J. Med. Res. 2014, 139, 568. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Solem, C.A.; Loftus Jr, E.V.; Tremaine, W.J.; Harmsen, W.S.; Zinsmeister, A.R.; Sandborn, W.J. Correlation of C-Reactive Protein with Clinical, Endoscopic, Histologic, and Radiographic Activity in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2005, 11, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millar, A.D.; Rampton, D.S.; Chander, C.L.; Claxson, A.W.; Blades, S.; Coumbe, A.; Panetta, J.; Morris, C.J.; Blake, D.R. Evaluating the Antioxidant Potential of New Treatments for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Using a Rat Model of Colitis. Gut 1996, 39, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mitov, M.I.; Patil, V.S.; Alstott, M.C.; Dziubla, T.; Butterfield, D.A. In Vitro Cellular Assays for Oxidative Stress and Biomaterial Response. In Oxidative Stress and Biomaterials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 145–186. [Google Scholar]
- Cuzzocrea, S.; Thiemermann, C.; Salvemini, D. Potential Therapeutic Effect of Antioxidant Therapy in Shock and Inflammation. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 1147–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, Y.R.; Krishnaiah, Y.S.R.; Satyanarayana, S. In Vitro Evaluation of Guar Gum as a Carrier for Colon-Specific Drug Delivery. J. Control. Release 1998, 51, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.Z.I.; Prebeg, Ž.; Kurjaković, N. A PH-Dependent Colon Targeted Oral Drug Delivery System Using Methacrylic Acid Copolymers: I. Manipulation of Drug Release Using Eudragit® L100-55 and Eudragit® S100 Combinations. J. Control. Release 1999, 58, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhija, S.N.; Vavia, P.R. Controlled Porosity Osmotic Pump-Based Controlled Release Systems of Pseudoephedrine: I. Cellulose Acetate as a Semipermeable Membrane. J. Control. Release 2003, 89, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngberg, C.A.; Berardi, R.R.; Howatt, W.F.; Hyneck, M.L.; Amidon, G.L.; Meyer, J.H.; Dressman, J.B. Comparison of Gastrointestinal PH in Cystic Fibrosis and Healthy Subjects. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1987, 32, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arévalo-Pérez, R.; Maderuelo, C.; Lanao, J.M. Recent Advances in Colon Drug Delivery Systems. J. Control. Release 2020, 327, 703–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wattamwar, P.P.; Biswal, D.; Cochran, D.B.; Lyvers, A.C.; Eitel, R.E.; Anderson, K.W.; Hilt, J.Z.; Dziubla, T.D. Synthesis and Characterization of Poly (Antioxidant β-Amino Esters) for Controlled Release of Polyphenolic Antioxidants. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 2529–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.; Lacerda, C.; Patil, V.S.; Biswal, D.; Wattamwar, P.; Zach Hilt, J.; Dziubla, T.D. Degradation of Poly (Β-amino Ester) Gels in Alcohols through Transesterification: Method to Conjugate Drugs to Polymer Matrices. J. Polym. Sci. Part Polym. Chem. 2017, 55, 2019–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynn, D.M.; Langer, R. Degradable Poly (β-Amino Esters): Synthesis, Characterization, and Self-Assembly with Plasmid DNA. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 10761–10768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.; Choi, Y.H.; Park, J. A Self-Destroying Polycationic Polymer: Biodegradable Poly (4-Hydroxy-L-Proline Ester). J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 5633–5639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, V.S.; Dziubla, T.D.; Kalika, D.S. Static and Dynamic Properties of Biodegradable Poly (Antioxidant β-Amino Ester) Networks Based on Incorporation of Curcumin Multiacrylate. Polymer 2015, 75, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, V.S. Formulation and Characterization of Poly(β-Amino Ester) Networks for Controlled Delivery of Antioxidants in Pharmaceutical Applications; University of Kentucky: Lexington, KY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Serra, L.; Doménech, J.; Peppas, N.A. Drug Transport Mechanisms and Release Kinetics from Molecularly Designed Poly (Acrylic Acid-g-Ethylene Glycol) Hydrogels. Biomaterials 2006, 27, 5440–5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, N.J.; Nangia, A. Solubility Advantage of Amorphous Drugs and Pharmaceutical Cocrystals. Cryst. Growth Des. 2011, 11, 2662–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, T.-X.; Anderson, B.D. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Amorphous Indomethacin-Poly(Vinylpyrrolidone) Glasses: Solubility and Hydrogen Bonding Interactions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 876–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Sperger, D.; Munson, E.J. Investigating Miscibility and Molecular Mobility of Nifedipine-PVP Amorphous Solid Dispersions Using Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayersohn, M.; Gibaldi, M. New Method of Solid-State Dispersion for Increasing Dissolution Rates. J. Pharm. Sci. 1966, 55, 1323–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, V.S.; Gutierrez, A.M.; Sunkara, M.; Morris, A.J.; Hilt, J.Z.; Kalika, D.S.; Dziubla, T.D. Curcumin Acrylation for Biological and Environmental Applications. J. Nat. Prod. 2017, 80, 1964–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arts, M.J.; Dallinga, J.S.; Voss, H.-P.; Haenen, G.R.; Bast, A. A New Approach to Assess the Total Antioxidant Capacity Using the TEAC Assay. Food Chem. 2004, 88, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Authimoolam, S.P.; Hilt, J.Z.; Dziubla, T.D. Quercetin Conjugated Poly (β-Amino Esters) Nanogels for the Treatment of Cellular Oxidative Stress. Acta Biomater. 2015, 27, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lao, L.L.; Peppas, N.A.; Boey, F.Y.C.; Venkatraman, S.S. Modeling of Drug Release from Bulk-Degrading Polymers. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 418, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basarkar, A.; Singh, J. Nanoparticulate Systems for Polynucleotide Delivery. Int. J. Nanomed. 2007, 2, 353. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.M.; Garreau, H.; Vert, M. Structure-Property Relationships in the Case of the Degradation of Massive Aliphatic Poly-(α-Hydroxy Acids) in Aqueous Media. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1990, 1, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunne, M.; Corrigan, O.I.; Ramtoola, Z. Influence of Particle Size and Dissolution Conditions on the Degradation Properties of Polylactide-Co-Glycolide Particles. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 1659–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panyam, J.; Dali, M.M.; Sahoo, S.K.; Ma, W.; Chakravarthi, S.S.; Amidon, G.L.; Levy, R.J.; Labhasetwar, V. Polymer Degradation and in Vitro Release of a Model Protein from Poly (D, L-Lactide-Co-Glycolide) Nano-and Microparticles. J. Control. Release 2003, 92, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, P.; Kunnumakkara, A.B.; Newman, R.A.; Aggarwal, B.B. Bioavailability of Curcumin: Problems and Promises. Mol. Pharm. 2007, 4, 807–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-H.; Cheng, A.-L. Clinical Studies with Curcumin. Mol. Targets Ther. Uses Curcumin Health Dis. 2007, 595, 471–480. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.A.; Euden, S.A.; Platton, S.L.; Cooke, D.N.; Shafayat, A.; Hewitt, H.R.; Marczylo, T.H.; Morgan, B.; Hemingway, D.; Plummer, S.M. Phase I Clinical Trial of Oral Curcumin: Biomarkers of Systemic Activity and Compliance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 6847–6854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, R.A.; McLelland, H.R.; Hill, K.A.; Ireson, C.R.; Euden, S.A.; Manson, M.M.; Pirmohamed, M.; Marnett, L.J.; Gescher, A.J.; Steward, W.P. Pharmacodynamic and Pharmacokinetic Study of Oral Curcuma Extract in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 1894–1900. [Google Scholar]
- Garcea, G.; Jones, D.J.L.; Singh, R.; Dennison, A.R.; Farmer, P.B.; Sharma, R.A.; Steward, W.P.; Gescher, A.J.; Berry, D.P. Detection of Curcumin and Its Metabolites in Hepatic Tissue and Portal Blood of Patients Following Oral Administration. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcea, G.; Berry, D.P.; Jones, D.J.; Singh, R.; Dennison, A.R.; Farmer, P.B.; Sharma, R.A.; Steward, W.P.; Gescher, A.J. Consumption of the Putative Chemopreventive Agent Curcumin by Cancer Patients: Assessment of Curcumin Levels in the Colorectum and Their Pharmacodynamic Consequences. Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark. 2005, 14, 120–125. [Google Scholar]
- Simanenko, Y.S.; Belousova, I.A.; Savelova, V.A.; Popov, A.F.; Vakhitova, L.N. The Effect of Temperature on the Rate of Alkaline Hydrolysis of Esters in Concentrated Aqueous Solutions of Et 4 NCl. Theor. Exp. Chem. 2004, 40, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Feng, Y.; Sun, C.C. Initial Moisture Content in Raw Material Can Profoundly Influence High Shear Wet Granulation Process. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 416, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, S.P.; Dave, R.H. To Prepare and Characterize Microcrystalline Cellulose Granules Using Water and Isopropyl Alcohol as Granulating Agents and Determine Its End-Point by Thermal and Rheological Tools. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2015, 41, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, V.P.; Konecny, J.J.; Everett, R.L.; McCullough, B.; Noorizadeh, A.C.; Skelly, J.P. In Vitro Dissolution Profile of Water-Insoluble Drug Dosage Forms in the Presence of Surfactants. Pharm. Res. 1989, 6, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rockland, L.B. Saturated Salt Solutions for Static Control of Relative Humidity between 5° and 40 °C. Anal. Chem. 1960, 32, 1375–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Ingredients | PCBAE Prodrug Tablet | Free Curcumin Tablet | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % w/w | mg/Tablet | % w/w | mg/Tablet | |
| 90:10 CMA:PEG400DA PCBAE (prodrug microparticles) a | 20.0 | 80.00 | NA | NA |
| Curcumin | NA | NA | 10.5 | 42.16 |
| 0:100 CMA:PEG400DA gel powder | NA | NA | 9.46 | 37.84 |
| MCC | 79.0 | 316.0 | 79.0 | 316.0 |
| Magnesium stearate | 1.0 | 4.000 | 1.0 | 4.000 |
| Total | 100.0 | 400.0 | 100.0 | 400.0 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Patil, V.S.; Burdette, B.C.; Hilt, J.Z.; Kalika, D.S.; Dziubla, T.D. Poly(curcumin β-amino ester)-Based Tablet Formulation for a Sustained Release of Curcumin. Gels 2022, 8, 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8060337
Patil VS, Burdette BC, Hilt JZ, Kalika DS, Dziubla TD. Poly(curcumin β-amino ester)-Based Tablet Formulation for a Sustained Release of Curcumin. Gels. 2022; 8(6):337. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8060337
Chicago/Turabian StylePatil, Vinod S., Benjamin C. Burdette, J. Zach Hilt, Douglass S. Kalika, and Thomas D. Dziubla. 2022. "Poly(curcumin β-amino ester)-Based Tablet Formulation for a Sustained Release of Curcumin" Gels 8, no. 6: 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8060337
APA StylePatil, V. S., Burdette, B. C., Hilt, J. Z., Kalika, D. S., & Dziubla, T. D. (2022). Poly(curcumin β-amino ester)-Based Tablet Formulation for a Sustained Release of Curcumin. Gels, 8(6), 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8060337







