Preparation and Evaluation of Polymer-Based Ultrasound Gel and Its Application in Ultrasonography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Characterization
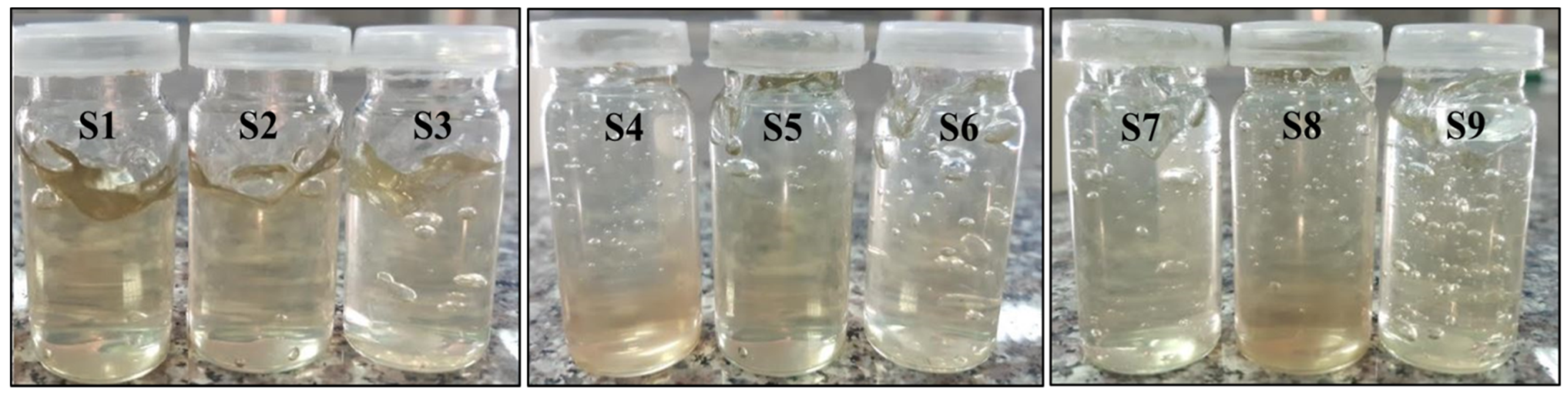
2.1. Visual Inspection
2.2. Homogeneity
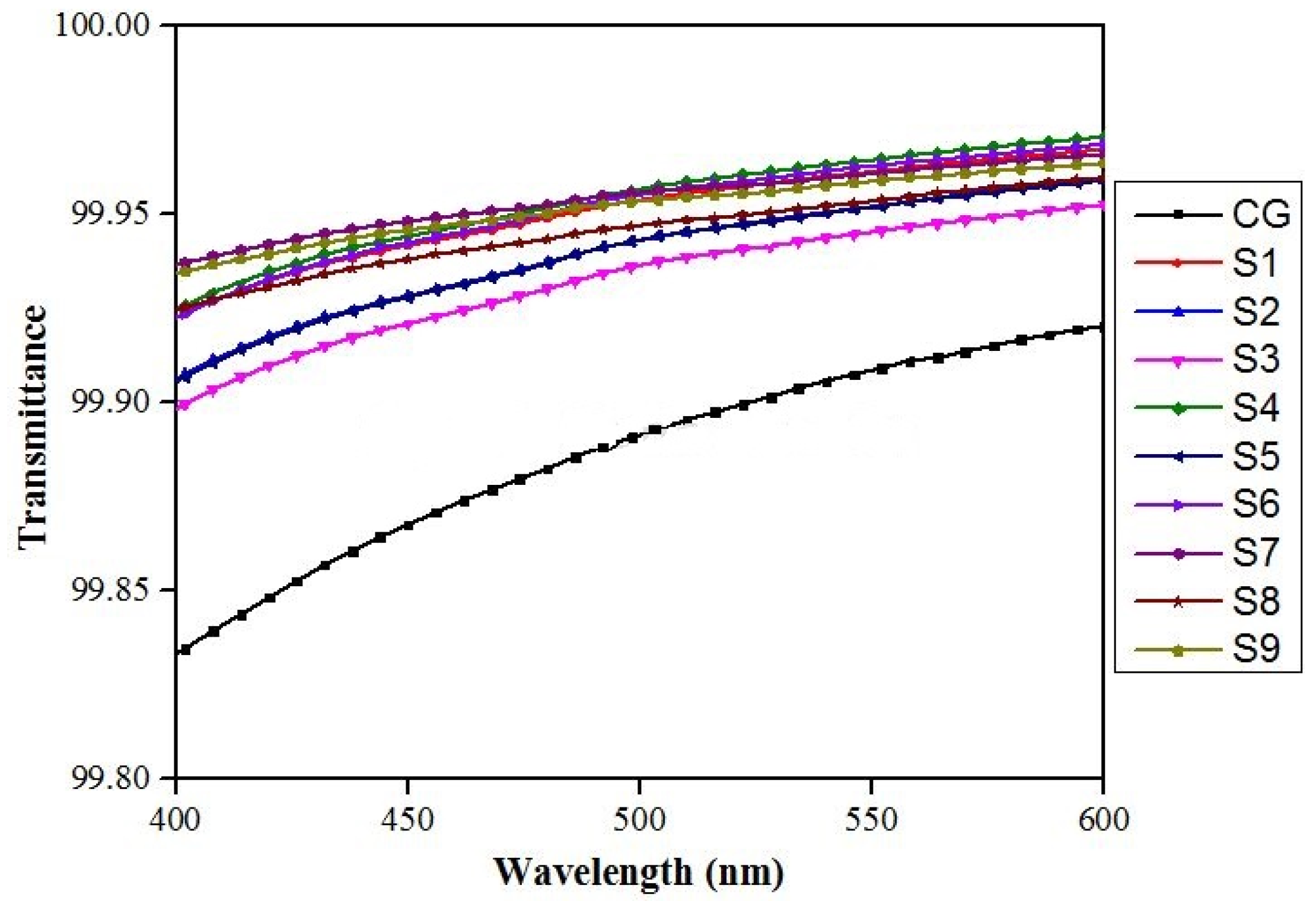
2.3. UV-Vis-NIR Spectrophotometry
2.4. pH Determination
2.5. Skin Irritation Test
2.6. Viscosity Determination
2.7. Antibacterial Activity
2.8. Conductivity
2.9. Further Evaluation of the Selected Formulation
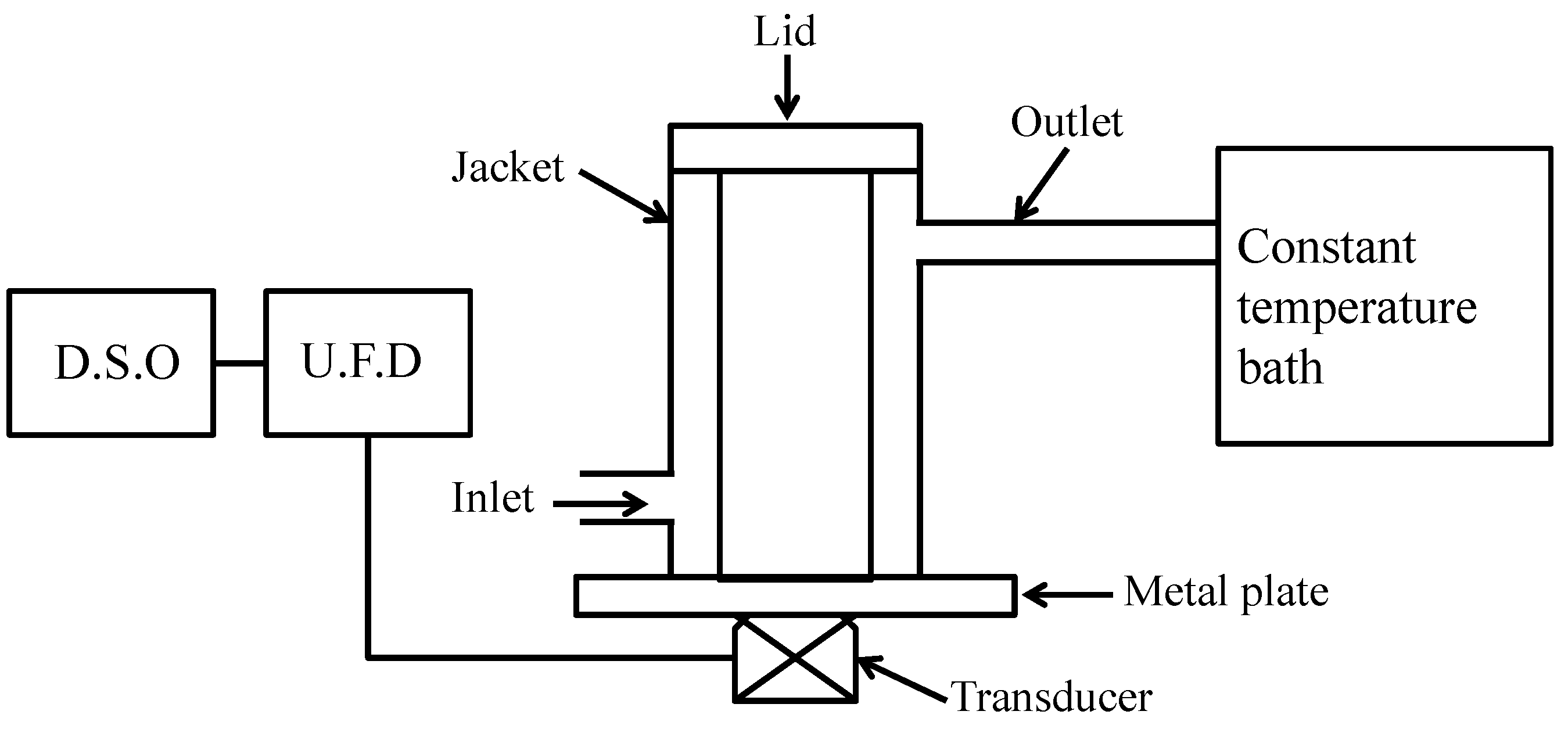
2.9.1. Acoustic Impedance
2.9.2. Accelerated Stability Test
2.9.3. Evaluation of Images Produced
2.9.4. Cost
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Visual Inspection
3.2. Homogeneity
3.3. VIS-Spectrophotometry
3.4. pH
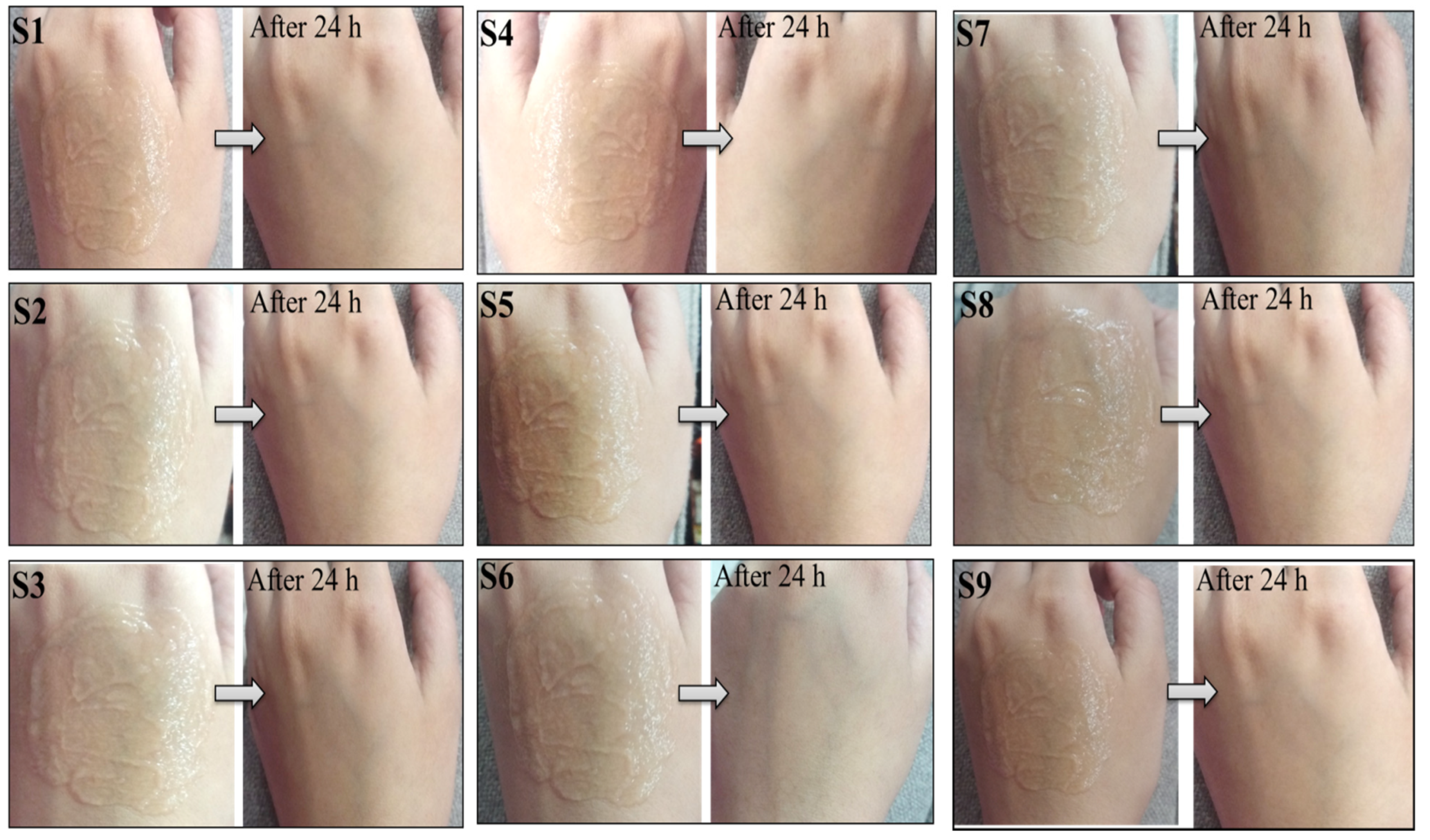
3.5. Skin Irritation Test
3.6. Viscosity Determination
3.7. Antibacterial Activity
3.8. Conductivity
3.9. Further Evaluation of the Selected Formulation
3.9.1. Acoustic Impedance
3.9.2. Accelerated Stability Test
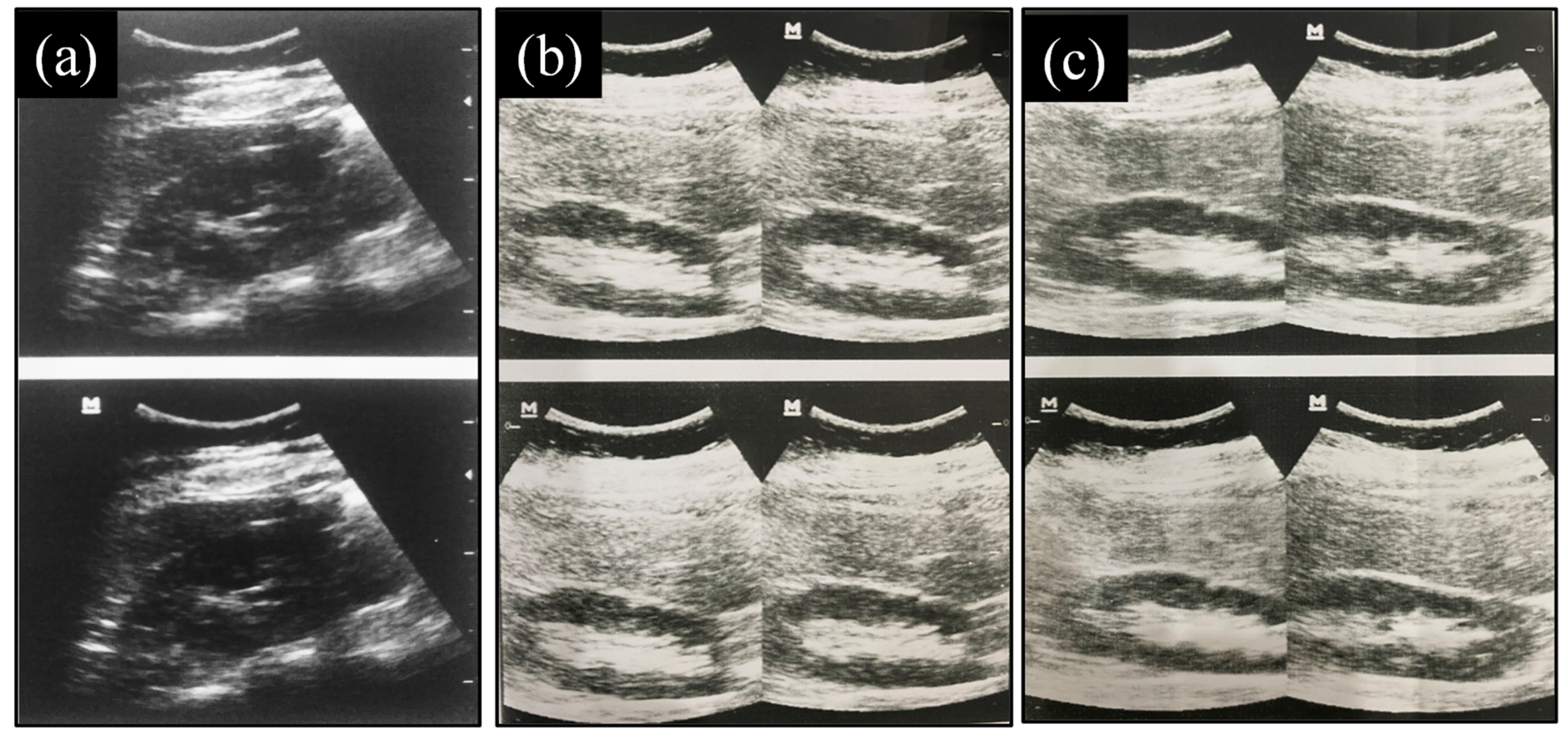
3.9.3. Evaluation of Images Produced
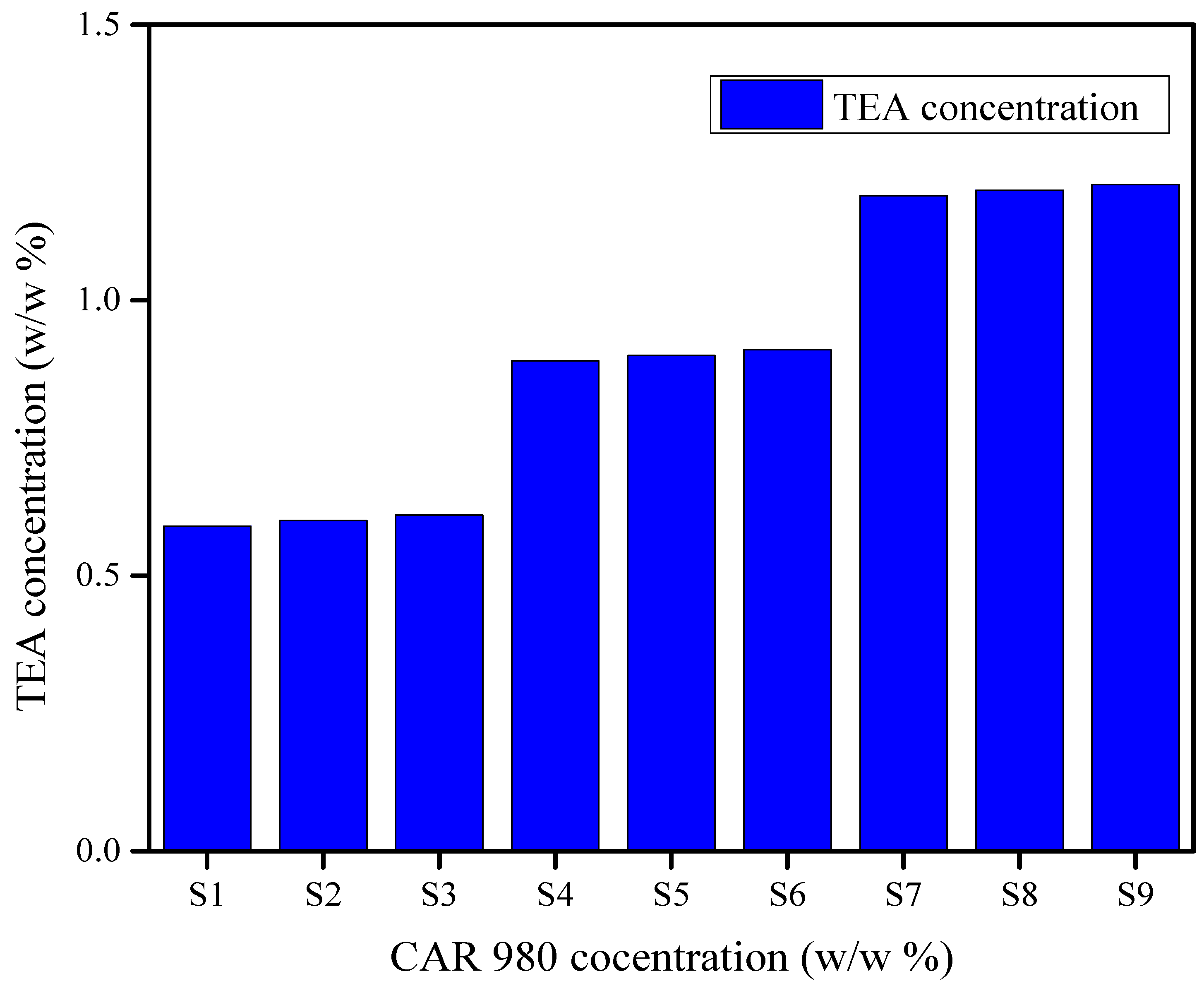
3.9.4. Cost
4. Conclusions
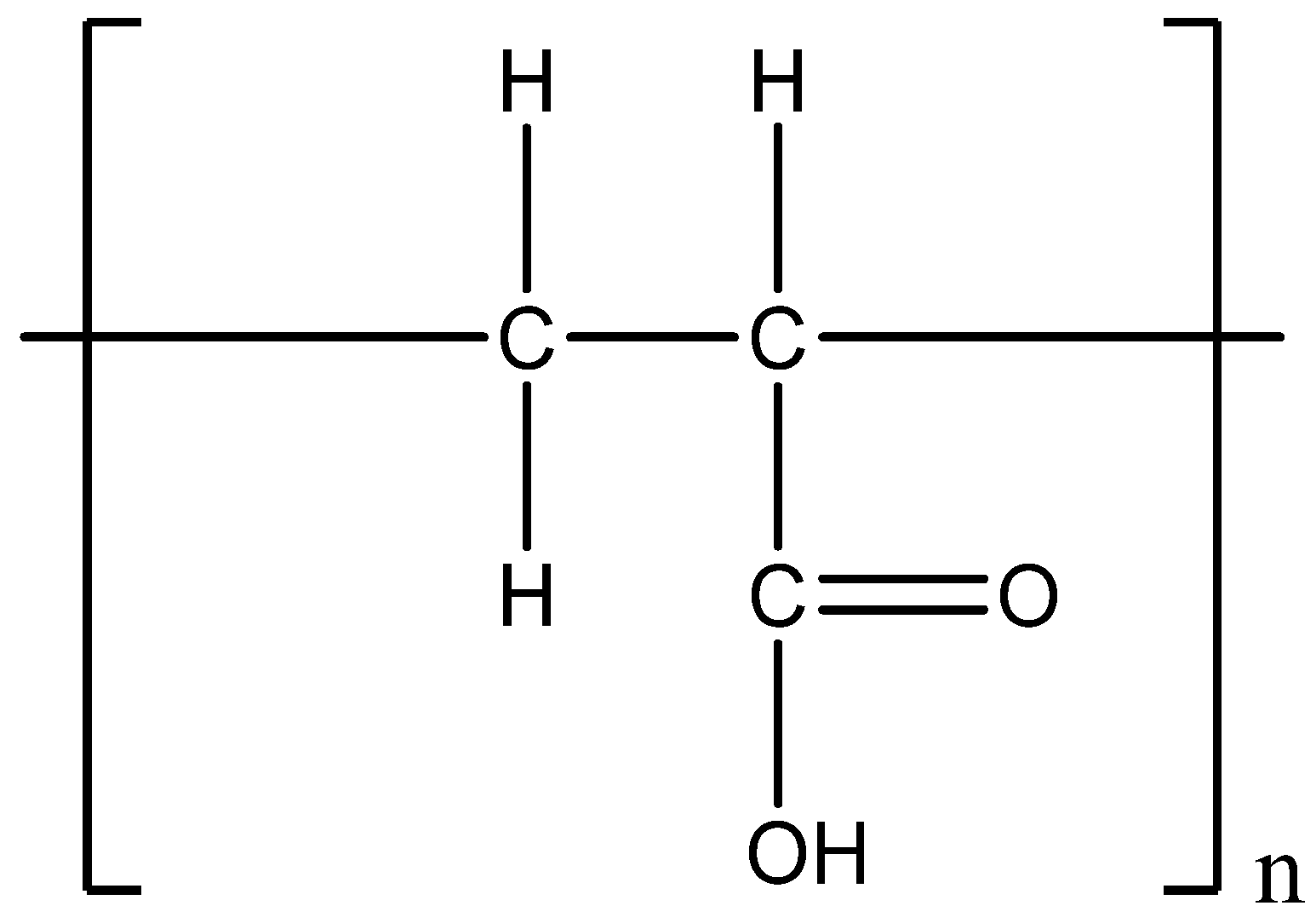
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Materials
5.2. Method
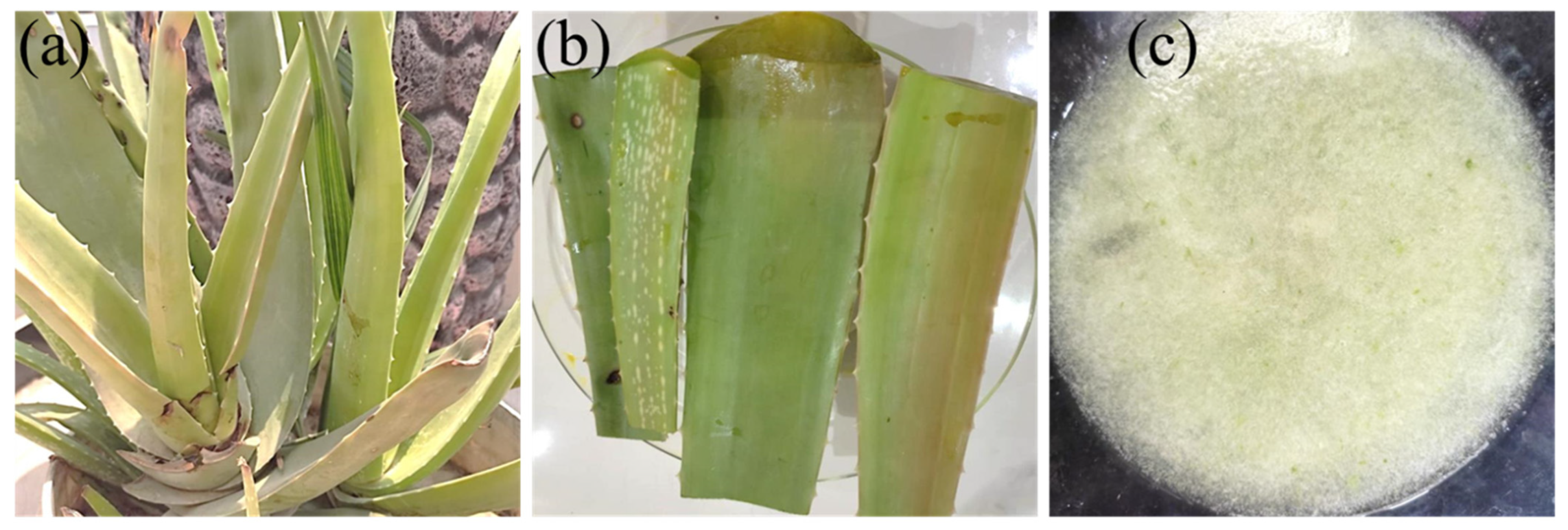
5.2.1. Preparation of Aloe Vera Gel
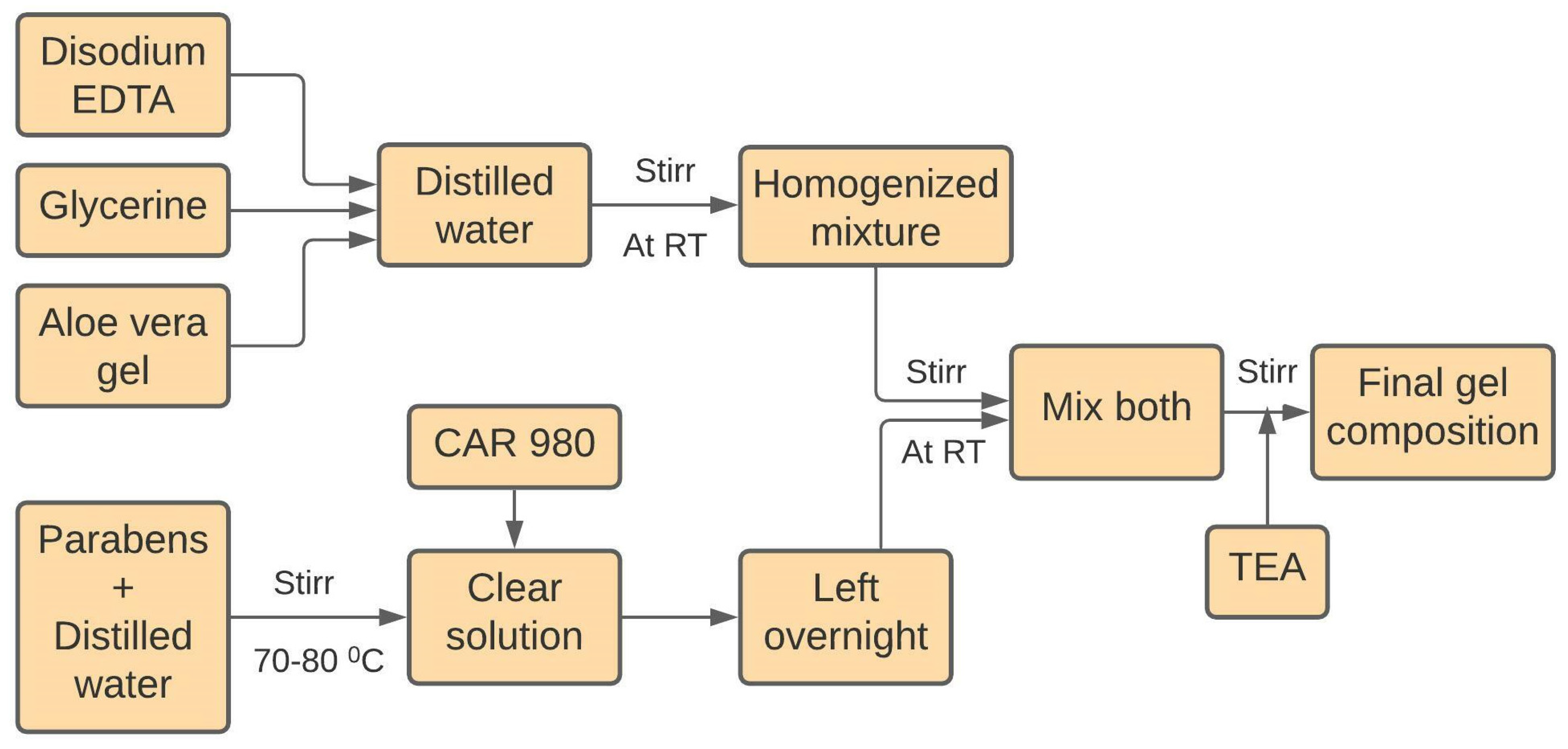
5.2.2. Preparation of Ultrasound Gel Formulations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tola, J.; Hoelscher, T.; Doyle, T.F. Ultrasound Gel Module Assemblies. U.S. Patent 15/883,880, 2 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, L.M. Gel Composition for Ultrasound Procedure and Related Methods. U.S. Patent 15/354,16, 6 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Prachasilchai, W.; Punyanitya, S.; Thiansem, S.; Ruksanti, A.; Koonawoot, R.; Chankachang, P. Clinical Trial of Rice-Based Ultrasound Gel. In Key Engineering Materials; Trans Tech Publications: Zurich, Switzerland, 2020; Volume 862, pp. 125–129. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, C.M.; Thomson, A.J.W. Preclinical ultrasound imaging—A review of techniques and imaging applications. Front. Phys. 2020, 8, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Roh, Y. Ultrasonic transducers for medical diagnostic imaging. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 2017, 7, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munagsomboon, K. Ultrasonography of the liver for non-radiologist. Thai J. Hepatol. 2018, 1, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohm, R. Ultrasound Gel Container. U.S. Patent 15/624,096, 20 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Castellan, R.F.P.; Thomson, A.; Moran, C.M.; Gray, G.A. Electrocardiogram-gated kilohertz visualisation (EKV) ultrasound allows assessment of neonatal cardiac structural and functional maturation and longitudinal evaluation of regeneration after injury. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2020, 46, 167–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vedamurthy, M.; Raghupathy, S.; Vanasekar, P. Use of ultrasound gel to increase efficacy of cryotherapy in treatment of warts. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 85, e275–e277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.L.; Yan, J.P.; Li, Y.F.; Liu, H. Multi-frequency ultrasound transducers for medical applications: A survey. Int. J. Intell. Robot. Appl. 2018, 2, 296–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nima, A.M.; Al-Kotaji, M.; Al-Iraqi, O.; Ali, Z.H. Preparation and evaluation of ultrasound transmission gel. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2019, 12, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Zeng, G.; Guo, D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Lin, S.; Zhang, K. Soft elastic hydrogel couplants for ultrasonography. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 119, 111609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, F.; Momen, M.A.; Happy, A.A.; Hossain, M.H.; Akbor, M.A.; Ahmed, S. Formulation and Evaluation of Herbal Ultrasound Gel for Ultrasonography. J. Dis. Med. Plants 2020, 6, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myasar, A.; Mudhafar, A.-N.A.; Ahmed, Z.A. Comparative study of new formula of ultrasound gel with commercial ultrasound gel. Drug Invent. Today 2019, 12, 2822. [Google Scholar]
- Oglat, A.A.; Matjafri, M.Z.; Suardi, N.; Oqlat, M.A.; Abdelrahman, M.A.; Oqlat, A.A.; Farhat, O.F.; Alkhateb, B.N.; Abdalrheem, R.; Ahmad, M.S.; et al. Chemical items used for preparing tissue-mimicking material of wall-less flow phantom for doppler ultrasound imaging. J. Med. Ultrasound 2018, 26, 123–127. [Google Scholar]
- Culjat, M.O.; Goldenberg, D.; Tewari, P.; Singh, R.S. A review of tissue substitutes for ultrasound imaging. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2010, 36, 861–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riguzzi, C.; Binkowski, A.; Butterfield, M.; Sani, F.; Teismann, N.; Fahimi, J. A randomised experiment comparing low-cost ultrasound gel alternative with commercial gel. Emerg. Med. J. 2017, 34, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherukuri, A.R.; Lane, L.; Guy, D.; Perusse, K.; Keating, D.P.; DeStigter, K.K. Shake No Bake: A Homemade Ultrasound Gel Recipe for Low-Resource Settings. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahid, M.; Lodhi, M.; Rehan, Z.A.; Tayyab, H.; Javed, T.; Shabbir, R.; Mukhtar, A.; El Sabagh, A.; Adamski, R.; Sakran, M.I.; et al. Sustainable development of chitosan/Calotropis procera based hydrogels to stimulate formation of granulation tissue and angiogenesis in wound healing applications. Molecules 2021, 26, 3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahid, M.; Lodhi, M.; Afzal, A.; Rehan, Z.A.; Mehmood, M.; Javed, T.; Shabbir, R.; Siuta, D.; Althobaiti, F.; Dessok, E.S. Development of hydrogels with the incorporation of Raphanus sativus L. seed extract in sodium alginate for wound-healing application. Gels 2021, 7, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, A.; Dar, P.; Hughes, F.; Solorzano, C.; Muller, M.M.; Salmon, C.; Salmon, M.; Benfield, N. Cassava flour slurry as a low-cost alternative to commercially available gel for obstetrical ultrasound: A blinded non-inferiority trial comparison of image quality. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2018, 125, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sekar, M.; Ali, A.S.A.; Subramanian, G.S.; Manoharan, V.S.; Jason, I.J.; Yean, P.A. Formulation and evaluation of natural ultrasound gel for physiotherapy treatment. Indo Am. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 4, 2548–2554. [Google Scholar]
- Chasset, F.; Soria, A.; Moguelet, P.; Mathian, A.; Auger, Y.; Francès, C.; Barete, S. Contact dermatitis due to ultrasound gel: A case report and published work review. J. Dermatol. 2016, 43, 318–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binkowski, A.; Riguzzi, C.; Price, D.; Fahimi, J. Evaluation of a cornstarch-based ultrasound gel alternative for low-resource settings. J. Emerg. Med. 2014, 47, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, M.D.A.; Jáuregui, I.; Galán, C.; de Vicente, J.S.; Segurola, A.; Seras, Y.; García Lirio, E.; Irazábal, B.; Gamboa, P.M. Two cases of allergic contact dermatitis to different elements in identical ultrasound gels. Contact Dermat. 2021, 85, 477–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, O.H.; Wilkinson, J.P. Cost-effective innovations in low-resource settings. BJOG Int. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2018, 125, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Zuo, X.; Fang, S.; Xu, H.; Chen, J.; Meng, Y.; Chen, T. Effects of cellulose derivative hydrocolloids on pasting, viscoelastic, and morphological characteristics of rice starch gel. J. Texture Stud. 2017, 48, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punyanitya, S.; Koonawoot, R.; Thiensem, S.; Punyanitya, W. Novel Rice Gel for Ultrasound Applications: Physical and Chemical Properties. In Key Engineering Materials; Trans Tech Publications: Zurich, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 773, pp. 344–348. [Google Scholar]
- Vinograd, A.M.; Fasina, A.; Dean, A.J.; Shofer, F.; Panebianco, N.L.; Lewiss, R.E.; Gupta, S.; Rao, A.K.R.; Henwood, P.C. Evaluation of Noncommercial Ultrasound Gels for Use in Resource-Limited Settings. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 38, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jadhav, A.S.; Patil, O.A.; Kadam, S.V.; Bhutkar, M.A. Review on Aloe Vera is used in medicinal plant. Asian J. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 10, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scurtescu, C.; Gill, G. Viscosity and Stability Modified Ultrasound Gel. U.S. Patent 16/068,946, 17 January 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Shafiei, M.; Balhoff, M.; Hayman, N.W. Chemical and microstructural controls on viscoplasticity in Carbopol hydrogel. Polymer 2018, 139, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R. Varges, P.; M. Costa, C.; S. Fonseca, B.; F. Naccache, M.; De Souza Mendes, P.R. Rheological characterization of carbopol® dispersions in water and in water/glycerol solutions. Fluids 2019, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.-S.; Song, K.-W. Rheological characterization of carbopol 940 in steady shear and start-up flow fields. Annu. Trans. Nord. Rheol. Soc. 2011, 19. [Google Scholar]
- Desai, D.D.; Schmucker, J.F.; Light, D. Carbopol Ultrez 10 Polymer: A New Universal Thickener fort the Personal Care Industry; Noveon Lubrizol Corp.: Clevelend, OH, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Prasanthi, D.; Lakshmi, P.K. Optimisation of transdermal gel formulations of tolterodine tartrate by experimental design. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 10, 273–286. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, S.; Kadam, A.; Bandgar, S.; Patil, S. Formulation and evaluation of an in situ gel for ocular drug delivery of anticonjunctival drug. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2015, 49, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Kiyotake, E.A.; Douglas, A.W.; Thomas, E.E.; Nimmo, S.L.; Detamore, M.S. Development and quantitative characterization of the precursor rheology of hyaluronic acid hydrogels for bioprinting. Acta Biomater. 2019, 95, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmonem, R.; Hamed, R.R.; Abdelhalim, S.A.; ElMiligi, M.F.; El-Nabarawi, M.A. Formulation and Characterization of Cinnarizine Targeted Aural Transfersomal Gel for Vertigo Treatment: A Pharmacokinetic Study on Rabbits. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 6211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahid, F.; Zhou, Y.-N.; Wang, H.-S.; Wan, T.; Zhong, C.; Chu, L.-Q. Injectable self-healing carboxymethyl chitosan-zinc supramolecular hydrogels and their antibacterial activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, D.; Bhatnager, D.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, R. Direct measurement of acoustic impedance in liquids by a new pulse echo technique. Mapan 2009, 24, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.N.; Jha, S.; Dubey, S.D. Formulation & Evaluation of curcuminoid based herbal face cream. Indo-Global J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 1, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Grimm, W. Extension of the International Conference on Harmonization Tripartite Guideline for Stability Testing of New Drug Substances and Products to countries of climatic zones III and IV. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1998, 24, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

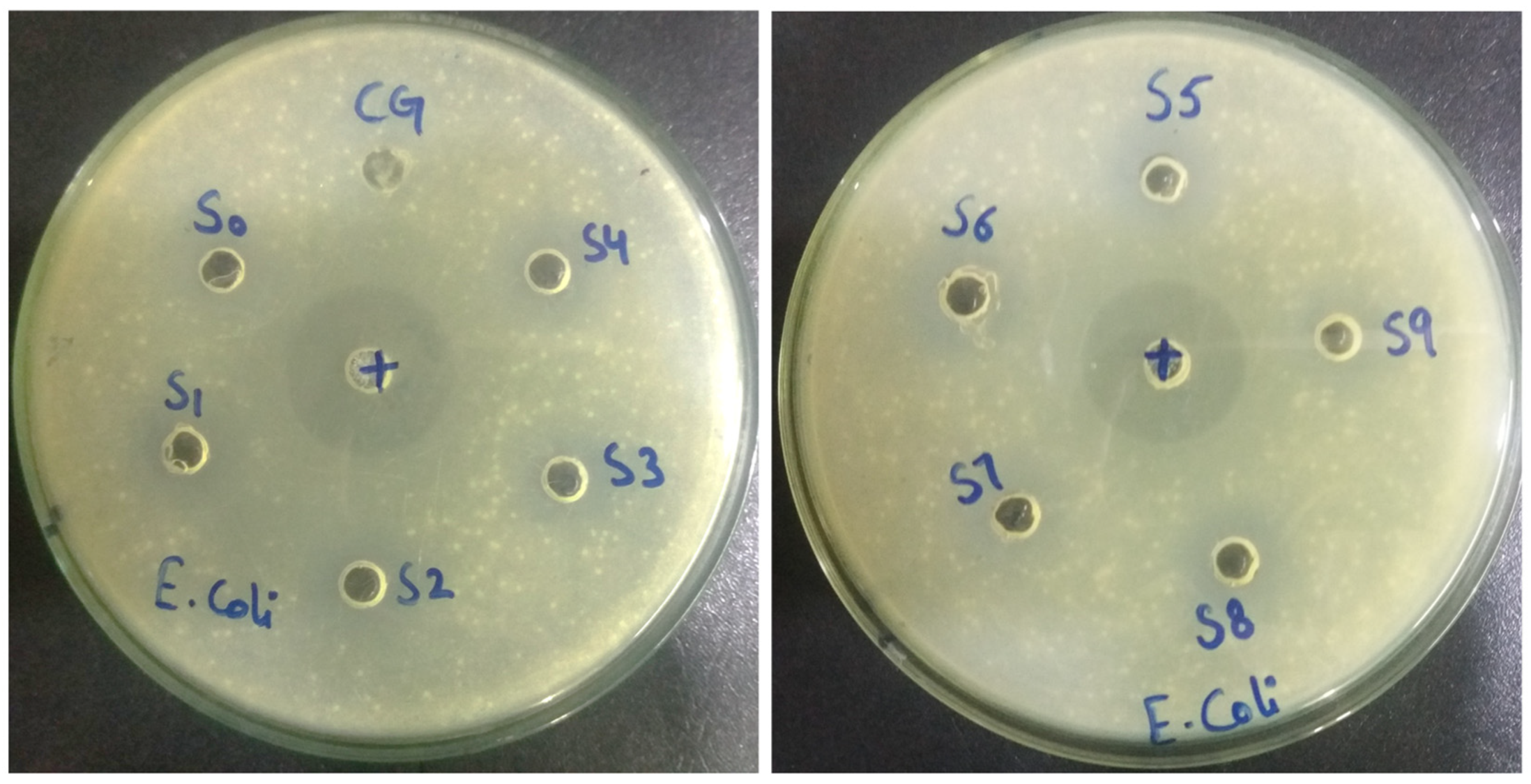
| Samples | Inhibition Zone (mm) against Escherichia Coli |
|---|---|
| Control antibacterial (Ciprofloxacin) | 32 |
| CG (Commercial Gel) | 15 |
| S0 | 10 |
| S1 | 18 |
| S2 | 23 |
| S3 | 26 |
| S4 | 21 |
| S5 | 24 |
| S6 | 26.5 |
| S7 | 21 |
| S8 | 24.5 |
| S9 | 27 |
| Samples | Conductivity Values at 28 °C |
|---|---|
| CG (commercial gel) | 0.70 mS/cm |
| S1 | 2.10 mS/cm |
| S2 | 2.14 mS/cm |
| S3 | 2.12 mS/cm |
| S4 | 2.27 mS/cm |
| S5 | 2.25 mS/cm |
| S6 | 2.20 mS/cm |
| S7 | 2.50 mS/cm |
| S8 | 2.48 mS/cm |
| S9 | 2.52 mS/cm |
| Characteristics | Before Incubation | After Incubation |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 7 | 7 |
| Color | Slight green | Slight green |
| Transparency | Yes | Yes |
| Viscosity | 8.92 Pa.s | 8.82 Pa.s |
| Antimicrobial activity | Yes | Yes |
| Conductivity | 2.10 mS/cm | 2.12 mS/cm |
| Materials | Price Per kg ($) | w/w% of Materials Required Per kg | Cost ($) | Total Cost of S1 Per kg | Cost of Commercial Gel (Aquasonic 100) Per kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAR 980 | 19 | 4 | 0.07 | 5.5 $ | 19.99 $ |
| Methylparaben | 928 | 2 | 1.85 | ||
| Propylparaben | 217 | 0.5 | 0.10 | ||
| Disodium EDTA | 427 | 0.2 | 0.08 | ||
| Glycerine | 2 | 40 | 0.08 | ||
| Distilled water | 3 | ≈900 | 2.7 | ||
| Aloe vera gel | 0.5 | 50 | 0.02 | ||
| TEA | 76 | ≈8.62 | 0.65 |
| Samples | Carbopol | Methylparaben | Distill. Water | Propylparaben | Disodium EDTA | Glycerine | Aloe Vera Gel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 0.4 | 0.2 | Remaining | 0.05 | 0.02 | 4 | 5 |
| S2 | 0.3 | ||||||
| S3 | 0.4 | ||||||
| S4 | 0.6 | 0.2 | |||||
| S5 | 0.3 | ||||||
| S6 | 0.4 | ||||||
| S7 | 0.8 | 0.2 | |||||
| S8 | 0.3 | ||||||
| S9 | 0.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Afzal, S.; Zahid, M.; Rehan, Z.A.; Shakir, H.M.F.; Javed, H.; Aljohani, M.M.H.; Mustafa, S.K.; Ahmad, M.; Hassan, M.M. Preparation and Evaluation of Polymer-Based Ultrasound Gel and Its Application in Ultrasonography. Gels 2022, 8, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8010042
Afzal S, Zahid M, Rehan ZA, Shakir HMF, Javed H, Aljohani MMH, Mustafa SK, Ahmad M, Hassan MM. Preparation and Evaluation of Polymer-Based Ultrasound Gel and Its Application in Ultrasonography. Gels. 2022; 8(1):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8010042
Chicago/Turabian StyleAfzal, Sadia, Muhammad Zahid, Zulfiqar Ahmad Rehan, H. M. Fayzan Shakir, Hamza Javed, Meshari M. H. Aljohani, Syed Khalid Mustafa, Maqsood Ahmad, and Montaser M. Hassan. 2022. "Preparation and Evaluation of Polymer-Based Ultrasound Gel and Its Application in Ultrasonography" Gels 8, no. 1: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8010042
APA StyleAfzal, S., Zahid, M., Rehan, Z. A., Shakir, H. M. F., Javed, H., Aljohani, M. M. H., Mustafa, S. K., Ahmad, M., & Hassan, M. M. (2022). Preparation and Evaluation of Polymer-Based Ultrasound Gel and Its Application in Ultrasonography. Gels, 8(1), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8010042






