Drug-Induced Phase Separation in Polyelectrolyte Microgels
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
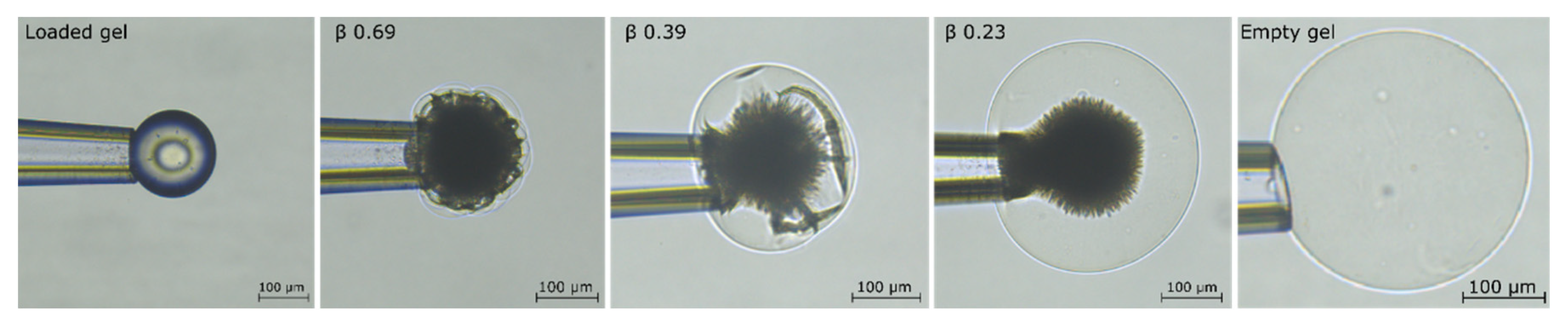
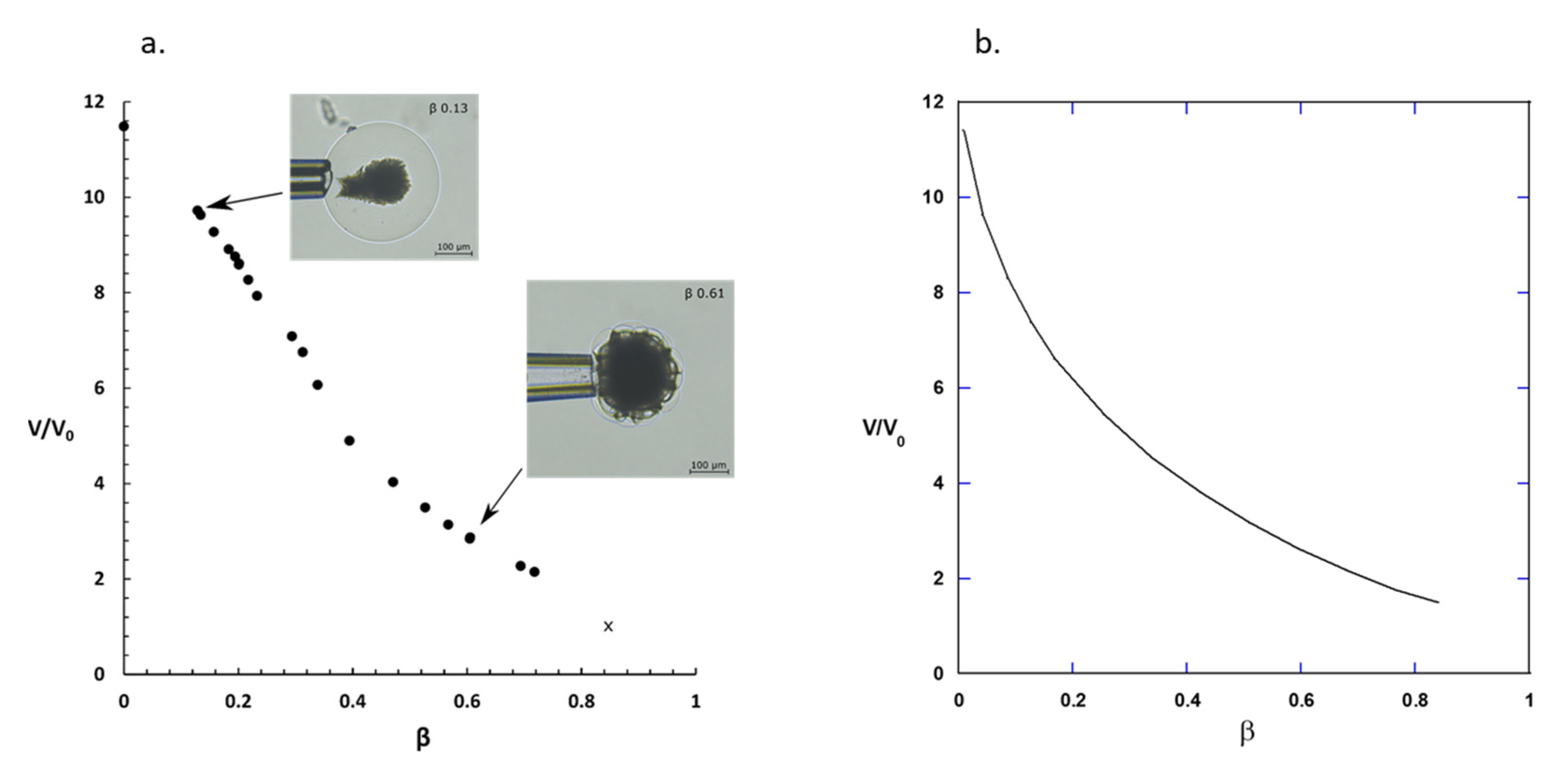
2.1. Drug Loading at 10 mM Ionic Strength
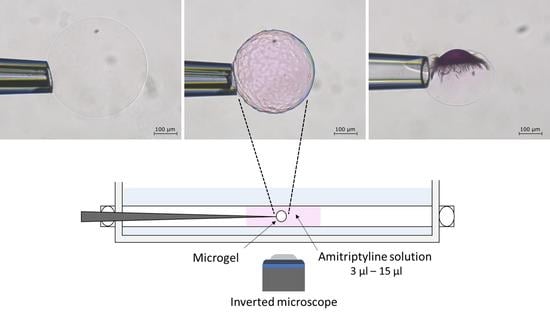
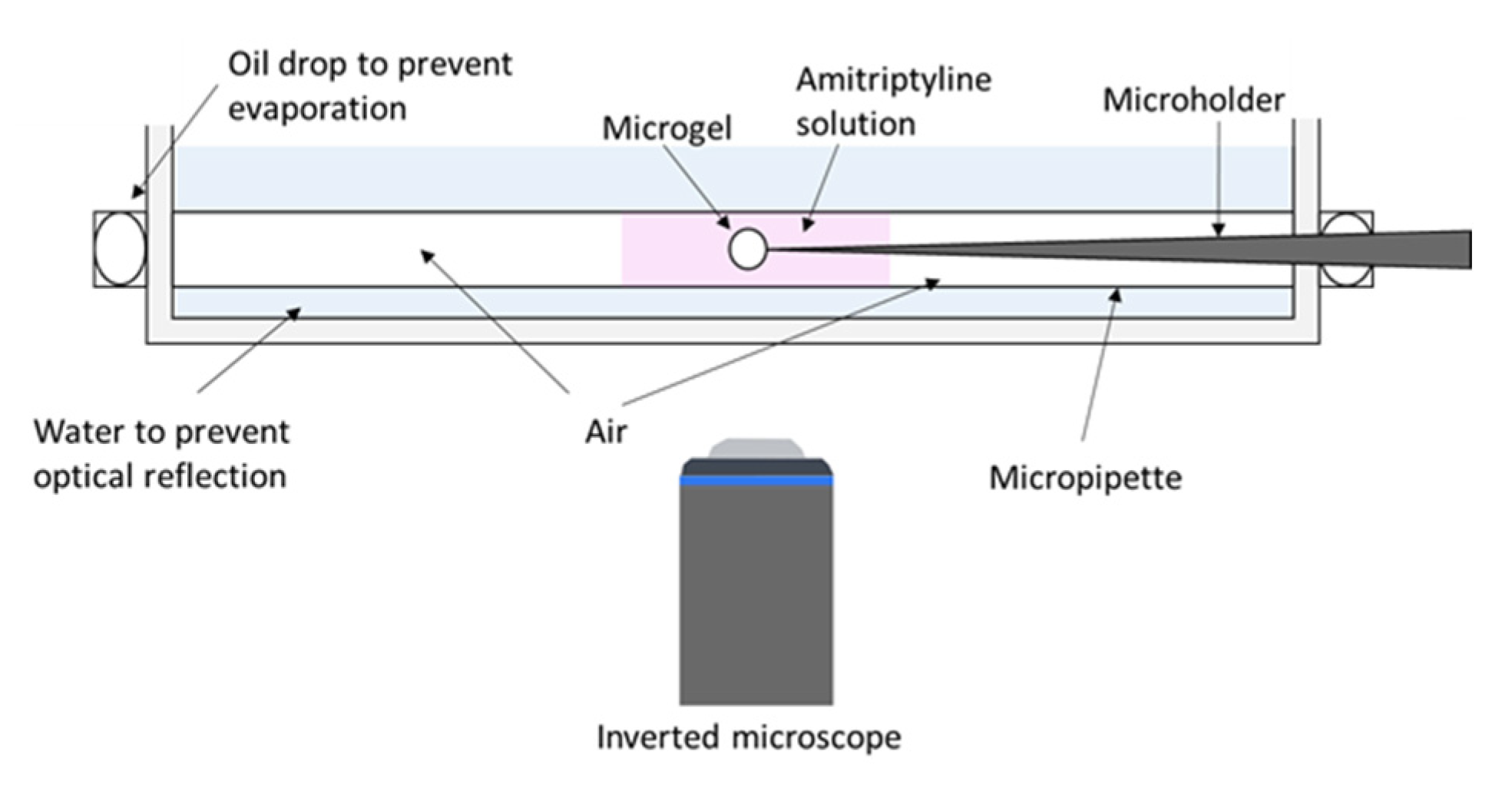
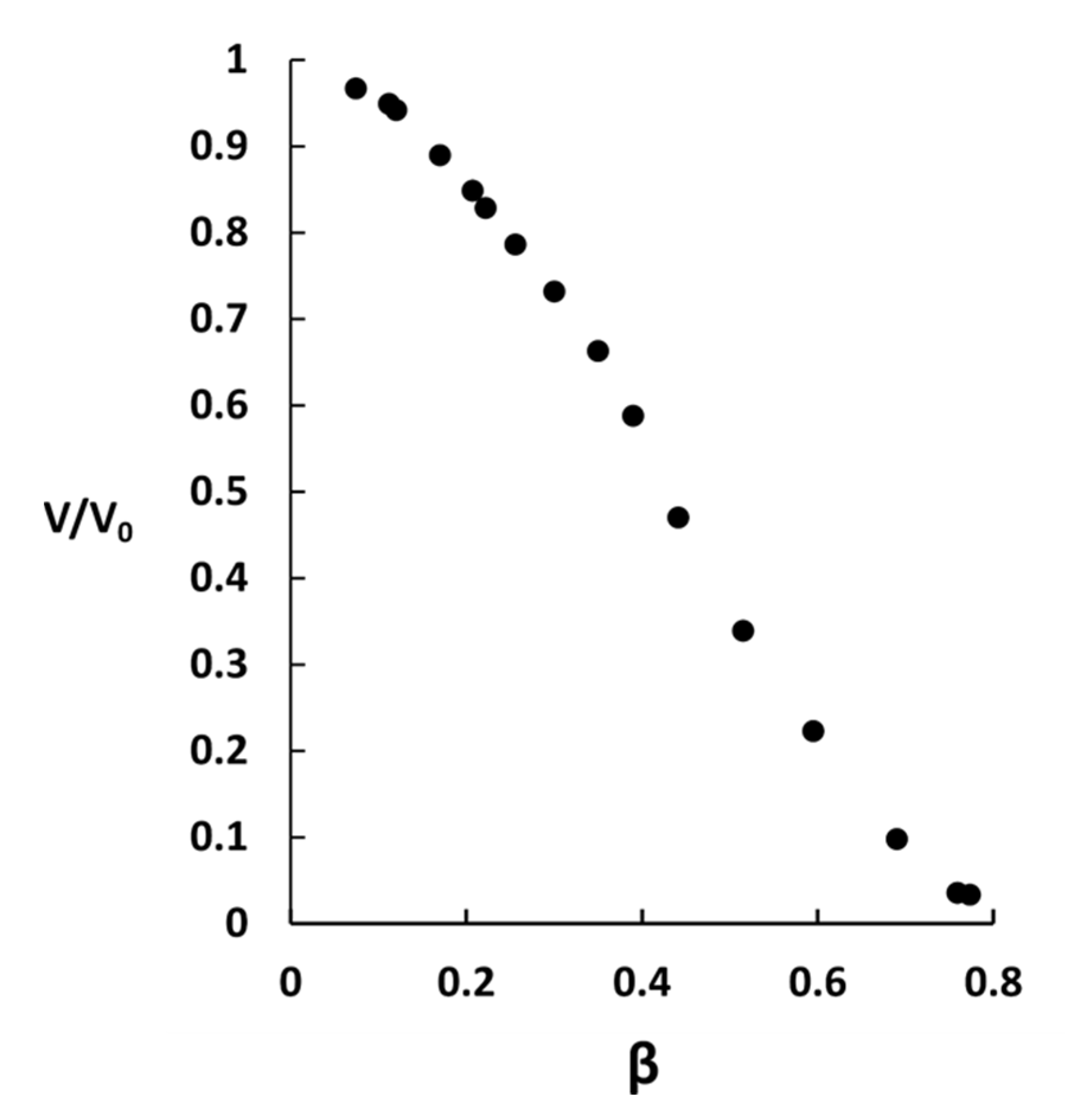
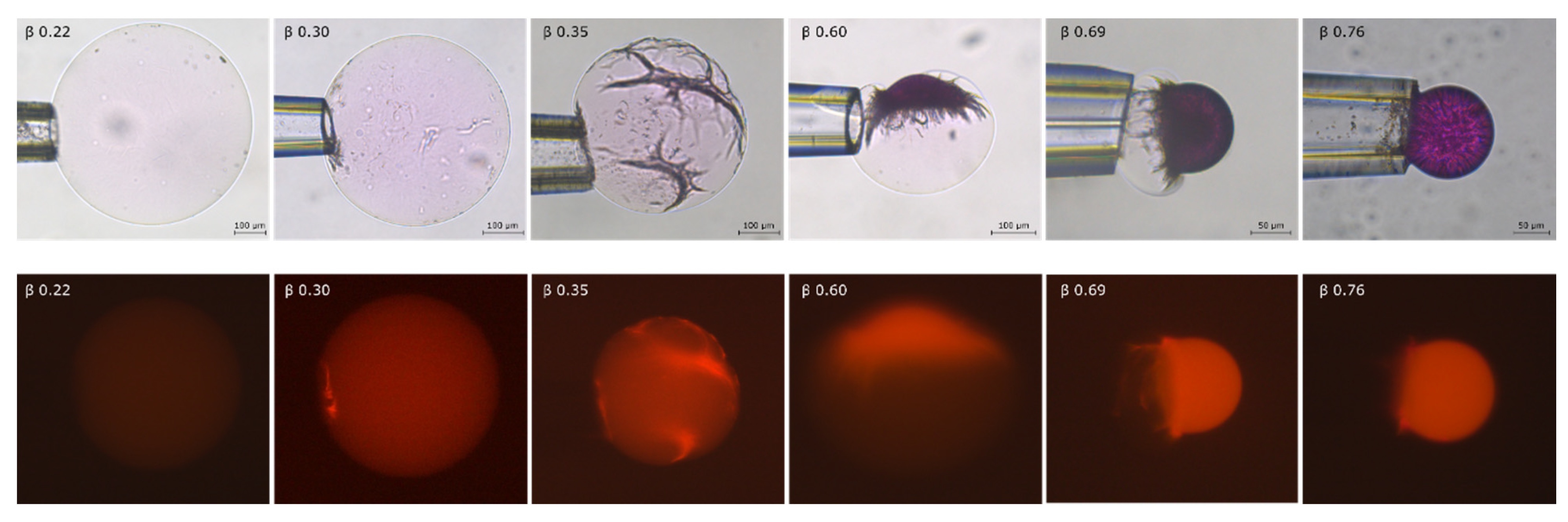
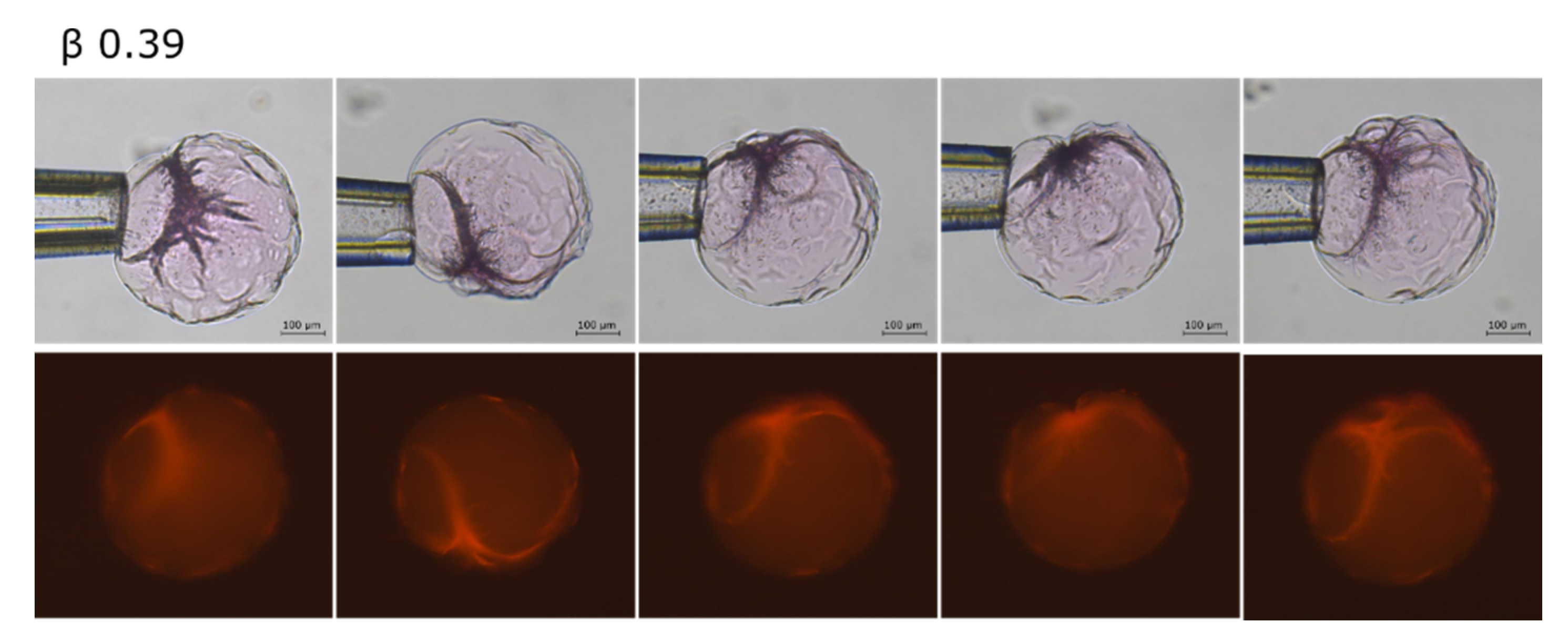
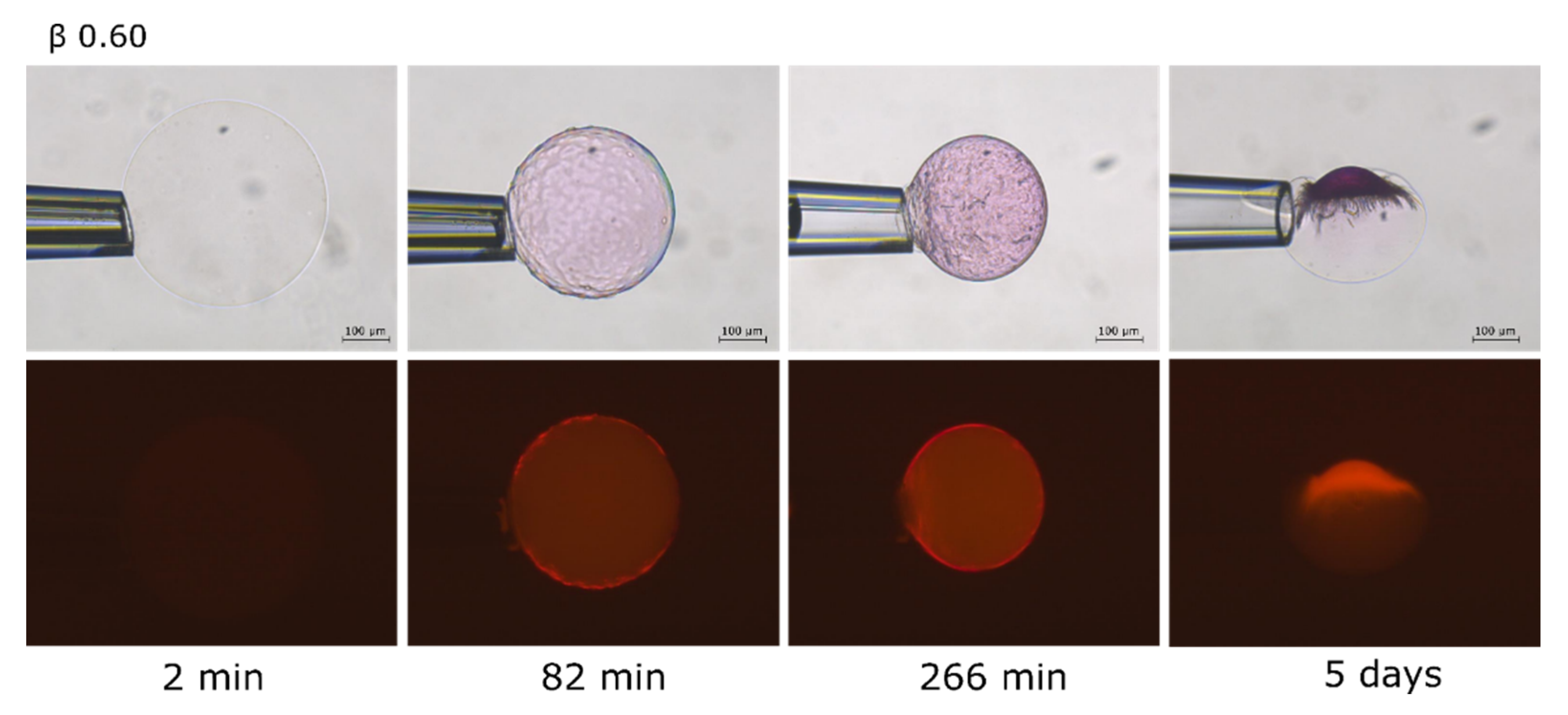
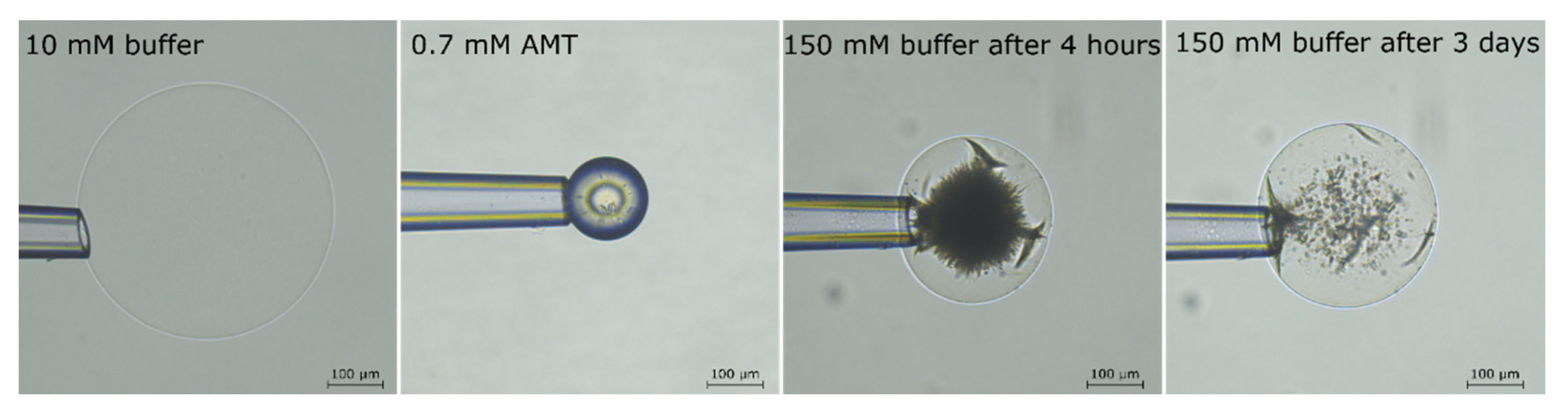
2.2. Phase Coexistence after Partial Release of AMT at Physiological Ionic Strength
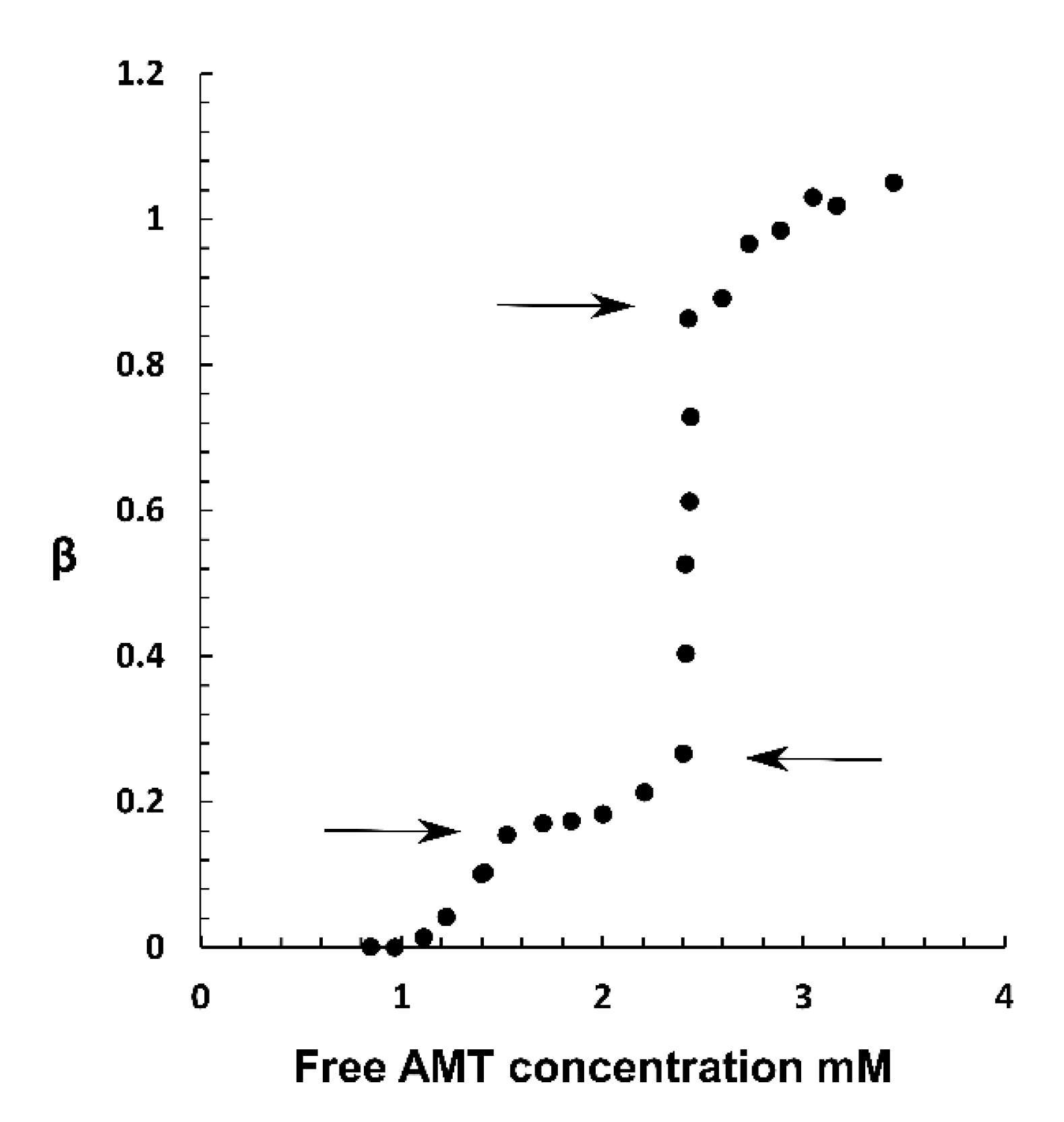
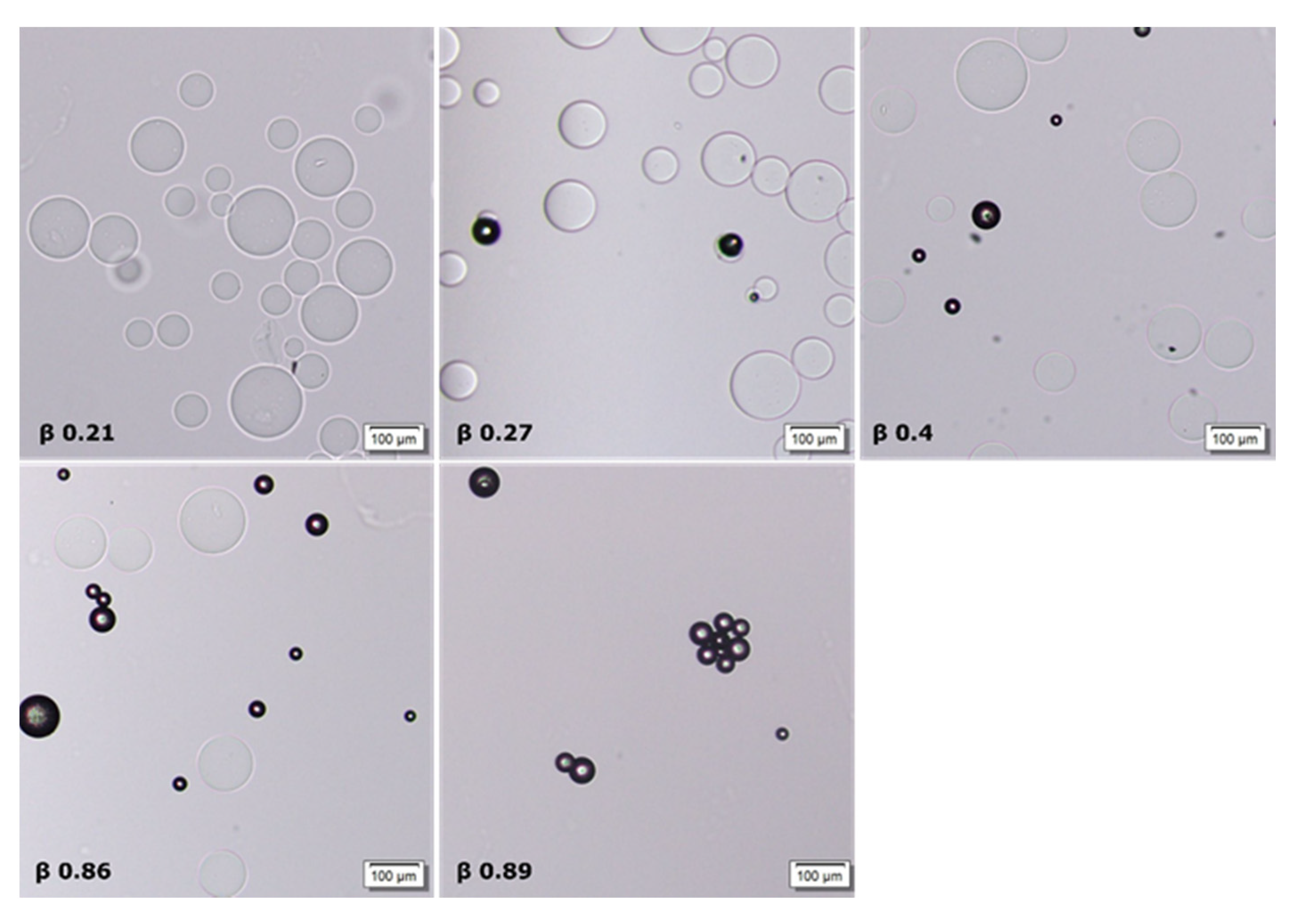
2.3. Phase Coexistence in Microgel Suspension at Elevated Ionic Strength
3. Discussion
3.1. Drug Loading at 10 mM Ionic Strength
3.2. Phase Separation in Microgels at Physiological Ionic Strength
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Materials
5.2. Microgels Synthesis
5.3. Swelling Isotherm in 10 mM Ionic Strength
5.4. Swelling Isotherm at 155 mM Ionic Strength
5.5. Binding Isotherm in Microgel Suspension at 155 mM Ionic Strength
5.6. The Concentration of Polyacrylate Segments in Microgels
5.7. Determination of CMC
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brannon-Peppas, L.; Peppas, N.A. Equilibrium swelling behavior of pH-sensitive hydrogels. Chem. Eng. Sci. 1991, 46, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitura, S.; Sionkowska, A.; Jaiswal, A. Biopolymers for hydrogels in cosmetics: Review. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2020, 31, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Censi, R.; Di Martino, P.; Vermonden, T.; Hennink, W.E. Hydrogels for protein delivery in tissue engineering. J. Control. Release 2012, 161, 680–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ende, M.T.; Peppas, N.A. Transport of ionizable drugs and proteins in crosslinked poly(acrylic acid) and poly(acrylic acid-co-2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) hydrogels. II. Diffusion and release studies. J. Control. Release 1997, 48, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoare, T.R.; Kohane, D.S. Hydrogels in drug delivery: Progress and challenges. Polymer 2008, 49, 1993–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, C.-C.; Metters, A.T. Hydrogels in controlled release formulations: Network design and mathematical modeling. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 1379–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanaswamy, R.; Torchilin, V.P. Hydrogels and Their Applications in Targeted Drug Delivery. Molecules 2019, 24, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peppas, N.A.; Buresa, P.; Leobandunga, W.; Ichikawa, H. Hydrogels in pharmaceutical formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 27–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, M.E.; Stephenson, R.E.; Murphy, A.C.; Oldenkamp, H.F.; Singh, A.; Peppas, N.A. Engineered microscale hydrogels for drug delivery, cell therapy, and sequencing. Biomed. Microdevices 2019, 21, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, R.; Sakai, K.; Okano, T.; Sakurai, Y. Pulsatile drug delivery systems using hydrogels. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1993, 11, 85–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfferich, F. Ion Exchange; McGraw-Hill Book Company Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Dadsetan, M.; Liu, Z.; Pumberger, M.; Giraldo, C.V.; Ruesink, T.; Lu, L.; Yaszemski, M.J. A stimuli-responsive hydrogel for doxorubicin delivery. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 8051–8062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sjöberg, H.; Persson, S.; Caram-Lelham, N. How interactions between drugs and agarose-carrageenan hydrogels influence the simultaneous transport of drugs. J. Control. Release 1999, 59, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malmsten, M.; Bysell, H.; Hansson, P. Biomacromolecules in microgels-opportunities and challanges for drug delivery. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 15, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bysell, H.; Hansson, P.; Malmsten, M. Transport of poly-L-lysine into oppositely charged poly(acrylic acid) microgels and its effect on gel deswelling. J. Colloid Int. Sci. 2008, 323, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bysell, H.; Hansson, P.; Malmsten, M. Effect of charge density on the interaction between cationic peptides and oppositely charged microgels. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 7207–7215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bysell, H.; Hansson, P.; Schmidtchen, A.; Malmsten, M. Effect of hydrophobicity on the interaction between antimicrobial peptides and poly(acrylic acid) microgels. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bysell, H.; Malmsten, M. Visualizing the interaction between poly-L-lysine and poly(acrylic acid) microgels using microscopy techniques: Effect of electrostatics and peptide size. Langmuir 2006, 22, 5476–5484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bysell, H.; Malmsten, M. Interactions between homopolypeptides and lightly cross-linked microgels. Langmuir 2009, 25, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bysell, H.; Månsson, R.; Malmsten, M. Effects of peptide cyclization on the interaction with oppositely charged microgels. Colloids Surf. A 2011, 391, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bysell, H.; Schmidtchen, A.; Malmsten, M. Binding and Release of Consensus Peptides by Poly(acrylic acid) Microgels. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 2162–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, P.; Bysell, H.; Månsson, R.; Malmsten, M. Peptide-microgel interaction in the strong coupling regime. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 10964–10975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, C.; Hansson, P.; Malmsten, M. Interaction between lysozyme and poly(acrylic acid) microgels. J. Coll. Int. Sci. 2007, 316, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, C.; Hansson, P.; Malmsten, M. Mechanism of lysozyme uptake in poly(acrylic acid) microgels. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 6183–6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Månsson, R.; Bysell, H.; Hansson, P.; Schmitdchen, A.; Malmsten, M. Effect of peptide secondary structure on the interaction with oppositely charged microgels. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenbaum, G.M.; Kiser, P.F.; Dobrynin, A.V.; Simon, S.A.; Needham, D. Investigation of the swelling response and loading of ionic microgels with drugs and proteins: The dependence on cross-link density. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 4867–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernandt, J.; Hansson, P. Core-shell separation of a hydrogel in a large solution of proteins. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 10905–10913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, P. Volume transition and phase coexistence in polyelectrolyte gels interacting with amphiphiles and proteins. Gels 2020, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, D.; Li, V.; Qian, Q.; Kobyayshi, T. Temperature-pH sensitivity of bovine serum albumin protein-microgels based on cross-linked poly(N-isopropylacryalmide-co-acrylic acid). Colloids Surf. B 2006, 50, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigit, C.; Welsch, N.; Ballauff, M.; Dzubiella, J. Protein Sorption to Charged Microgels: Characterizing Binding Isotherms and Driving Forces. Langmuir 2012, 28, 14373–14385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jidheden, C.; Hansson, P. Single microgels in core-shell equilibrium: A novel method for limited volume studies. J. Phys. Chem. B 2016, 120, 10030–10042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, C.; Gernandt, J.; Bradley, M.; Vincent, B.; Hansson, P. Interaction between lysozyme and colloidal poly(NIPAM-co-AAc) microgels. J. Colloid. Int. Sci. 2010, 347, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, C.; Hansson, P. Distribution of cytochrome c in polyacrylate microgels. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 3970–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; de Vries, R.; Kleijn, M.; Slaghek, T.; Timmermans, J.; Cohen Stuart, M.; Norde, W. Lysozyme uptake by oxidized starch polymer microgels. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1754–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; de Vries, R.; Slaghac, T.; Timmermans, J.; Cohen Stuart, M.A.; Norde, W. Preparation and characterization of oxidized starch polymer microgels for encapsulation and controlled release of functional ingredients. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 1931–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahnfelt, E.; Gernandt, J.; Al-Tikriti, Y.; Sjögren, E.; Lennernäs, H.; Hansson, P. Single bead investigation of a clinical drug delivery system—A novel release mechanism. J. Control. Release 2018, 292, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.; Hansson, P. Phase Behavior of Salt-Free Polyelectrolyte Gel–Surfactant Systems. J. Phys. Chem. B 2017, 121, 6064–6080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, M.; Råsmark, P.J.; Elvingson, C.; Hansson, P. Single microgel particle studies demonstrate the influence of hydrophobic interactions between charged micelles and oppositely charged polyions. Langmuir 2005, 21, 3773–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernandt, J.; Hansson, P. Hysteresis in the surfactant-induced volume transition of hydrogels. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 1717–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gernandt, J.; Hansson, P. Surfactant-induced core/shell phase equilibrium in hydrogels. J. Chem. Phys. 2016, 144, 064902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göransson, A.; Hansson, P. Shrinking kinetics of polyacrylate gels in surfactant solution. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 9203–9213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, P.; Hansson, P. Ion-exchange controls the kinetics of deswelling of polyelectrolyte microgels in solutions of oppositely charged surfactant. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 23843–23856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, P.; Hansson, P. Deswelling kinetics of polyacrylate gels in solutions of cetyltrimethylammunium bromide. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 9770–9778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, P.; Hansson, P. Regular and Irregular deswelling of polyacrylate and hyaluronate gels induced by oppositely charged surfactants. J. Colloid Int. Sci. 2008, 325, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, P.; Unga, J.; Hansson, P. Effect of salt and surfactant concentration on the structure of polyacrylate gel/surfactant complexes. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 10959–10964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khokhlov, A.R.; Kramarenko, E.Y.; Makhaeva, E.E.; Starodoubtzev, S.G. Collapse of polyelectrolyte networks induced by their interaction with an oppositely charged surfactant. Theory. Makromol. Chem. Theory Simul. 1992, 1, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, P. Interaction between polyelectrolyte gels and surfactants of opposite charge. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 11, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tikriti, Y.; Hansson, P. Drug-Eluting Polyacrylate Microgels: Loading and Release of Amitriptyline. J. Phys. Chem. B 2020, 124, 2289–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biondi, M.; Fusco, S.; Lewis, A.L.; Netti, P.A. New Insights into the Mechanisms of the Interactions between Doxorubicin and the Ion-Exchange Hydrogel DC Bead™ for Use in Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE). J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2012, 23, 333–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, O.; Denys, A.; De Baere, T.; Boulens, N.; Doelker, E. Comparative Study of Chemoembolization Loadable Beads: In vitro Drug Release and Physical Properties of DC Bead and Hepasphere Loaded with Doxorubicin and Irinotecan. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2010, 21, 1084–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.L.; Gonzalez, M.V.; Lloyd, A.W.; Hall, B.; Tang, Y.; Willis, S.L.; Leppard, S.W.; Wolfenden, L.C.; Palmer, R.R.; Stratford, P.W. DC Bead: In Vitro Characterization of a Drug-delivery Device for Transarterial Chemoembolization. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2006, 17, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.L.; Holden, R.R. DC Bead embolic drug-eluting bead: Clinical applications in the locoregional treatment of tumors. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2011, 8, 153–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, F.; Wennerström, H. The Colloidal Domain: Where Physics, Chemistry, Biology, and Technology Meet; VCH Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Hansson, P. Surfactant self-assembly in polyelectrolyte gels: Aggregation numbers and their relation to the gel collapse and the appearance of ordered structures in the NaPA/C12TAB system. Langmuir 1998, 14, 4059–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordling, C.; Österman, J. Physics Handbook, 3rd ed.; Chartwell-Bratt Ltd.: Bromley, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Hansson, P.; Schneider, S.; Lindman, B. Phase separation in polyelectrolyte gels interacting with surfactants of opposite charge. J. Phys. Chem. B 2002, 106, 9777–9793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukerjee, P.; Mysels, K.J. Critical Micelle Concentrations of Aquesous Micelle Systems; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1971; p. 57.
- Efthymiuo, C.; Bergström, L.M.; Nedergaard Pedersen, J.; Pedersen, J.S.; Hansson, P. Self-assembling properties of ionisable amphiphilic drugs in aqueous solution. J. Colloid Int. Sci. 2021, 600, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, P.; Schneider, S.; Lindman, B. Macroscopic phase separation in a polyelectrolyte gel interacting with oppositely charged surfactant: Correlation between anomalous deswelling and microstructure. Prog. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2000, 115, 342–346. [Google Scholar]
- Onuki, A. Paradox in phase transitions with volume change. Phys. Rev. A 1988, 38, 2192–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekimoto, K. Temperature hysteresis and morphology of volume phase transitions of gels. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1993, 70, 4154–4157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomari, T.; Doi, M. Hysteresis and incubation in the dynamics of volume transition of spherical gels. Macromolecules 1995, 28, 8334–8343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, P. Phase behavior of aqueous polyion-surfactant ion complex salts: A theoretical analysis. J. Colloid Int. Sci. 2009, 332, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, A.; Piculell, L.; Karlsson, L.; Cabane, B.; Jönsson, B. Phase behavior of an ionic surfactant with mixed monovalent/polymeric counterions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 8119–8130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Tikriti, Y.; Hansson, P. Drug-Induced Phase Separation in Polyelectrolyte Microgels. Gels 2022, 8, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8010004
Al-Tikriti Y, Hansson P. Drug-Induced Phase Separation in Polyelectrolyte Microgels. Gels. 2022; 8(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Tikriti, Yassir, and Per Hansson. 2022. "Drug-Induced Phase Separation in Polyelectrolyte Microgels" Gels 8, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8010004
APA StyleAl-Tikriti, Y., & Hansson, P. (2022). Drug-Induced Phase Separation in Polyelectrolyte Microgels. Gels, 8(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8010004