Palm Olein Organogelation Using Mixtures of Soy Lecithin and Glyceryl Monostearate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Model Fitting and Regression Modelling
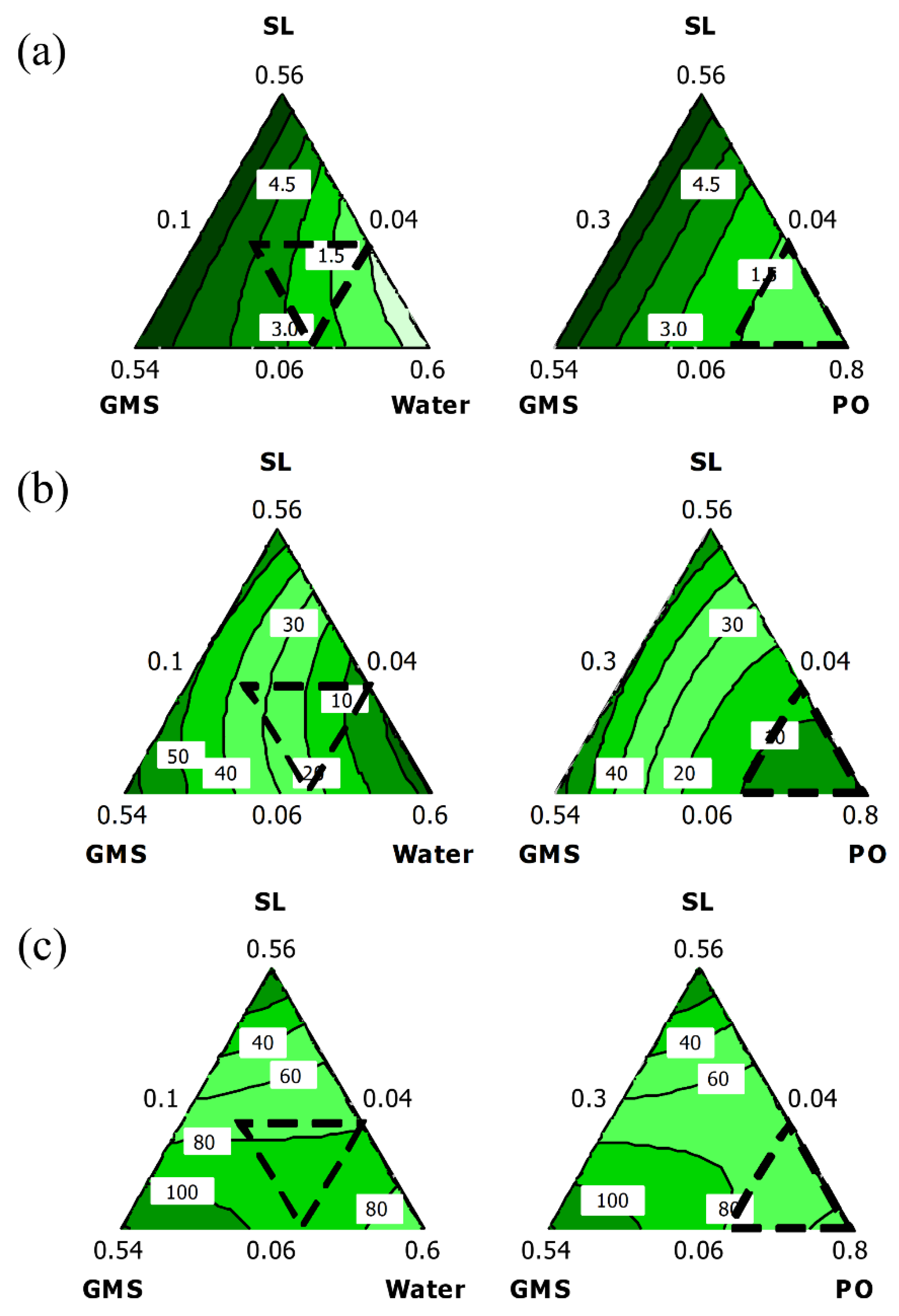
2.2. Interaction between Organogel Components and Their Effect on Firmness, Spreadability, and OBC
2.3. Optimization and Verification of Results
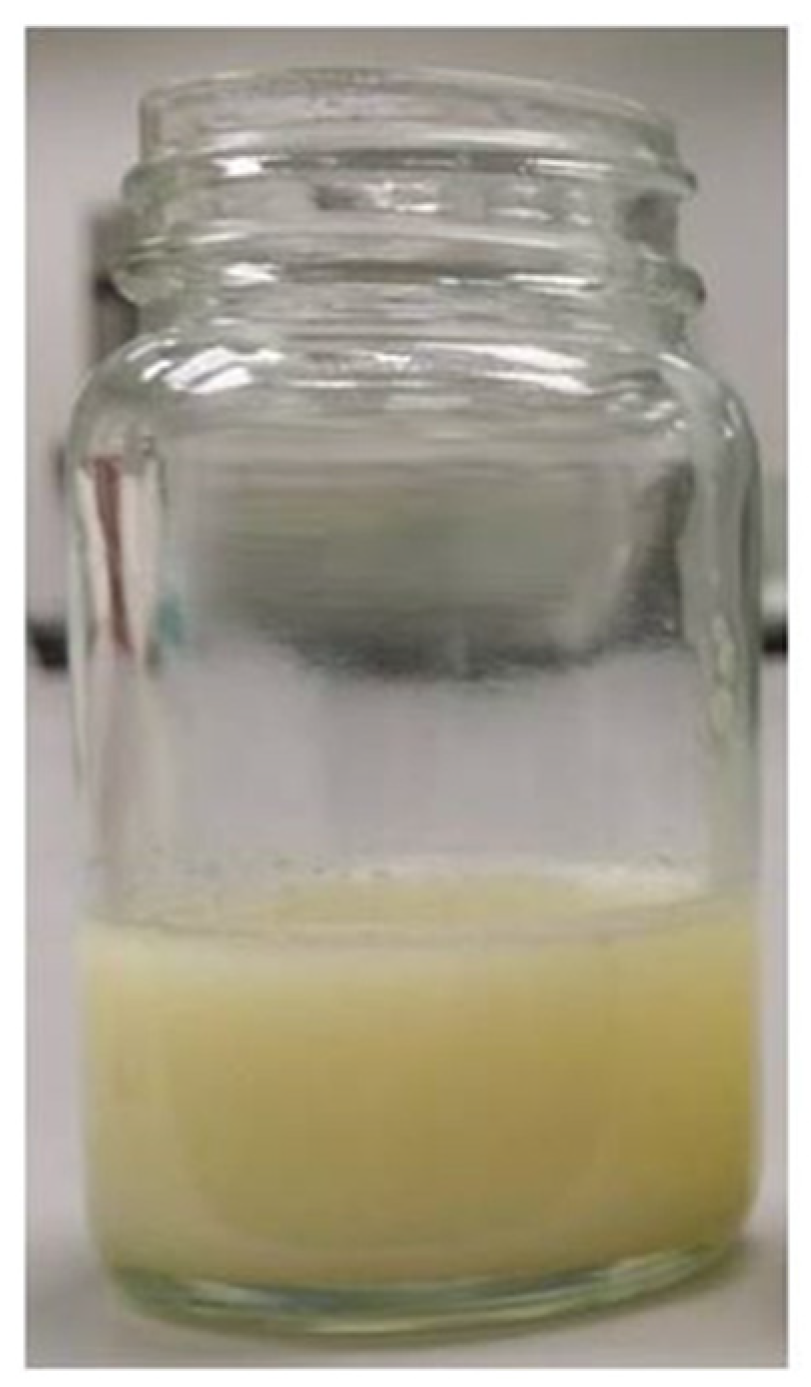
2.4. Evaluation of Prepared Organogels
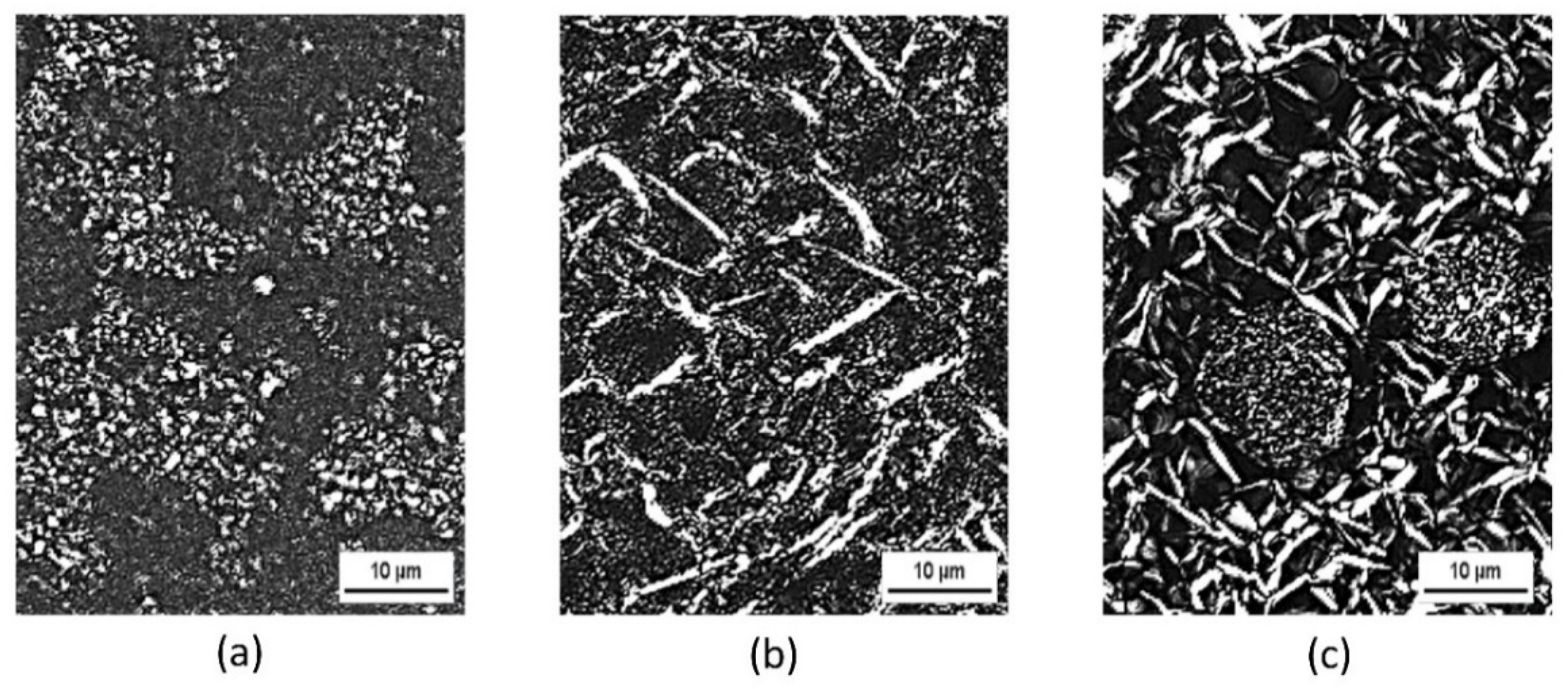
2.4.1. Polarized Microscopy Analysis
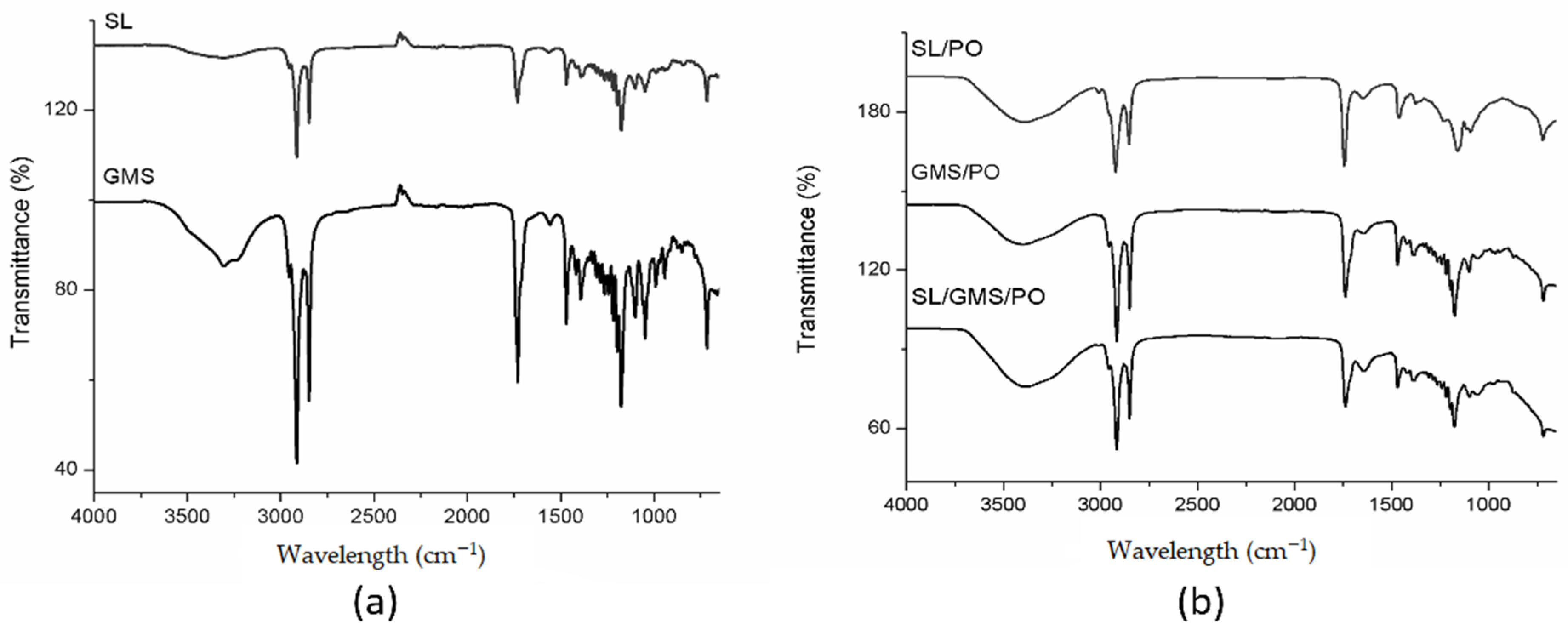
2.4.2. FTIR
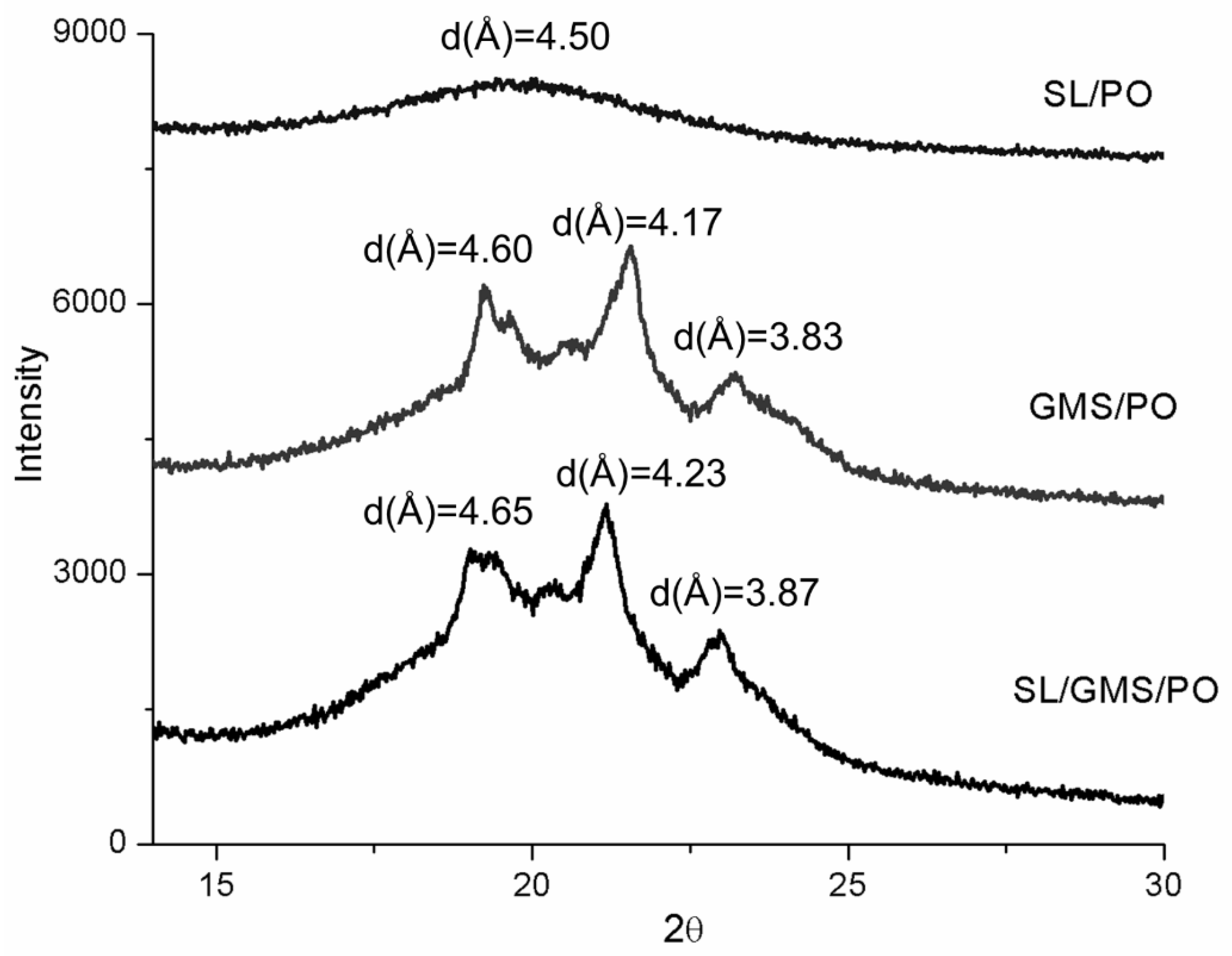
2.4.3. XRD
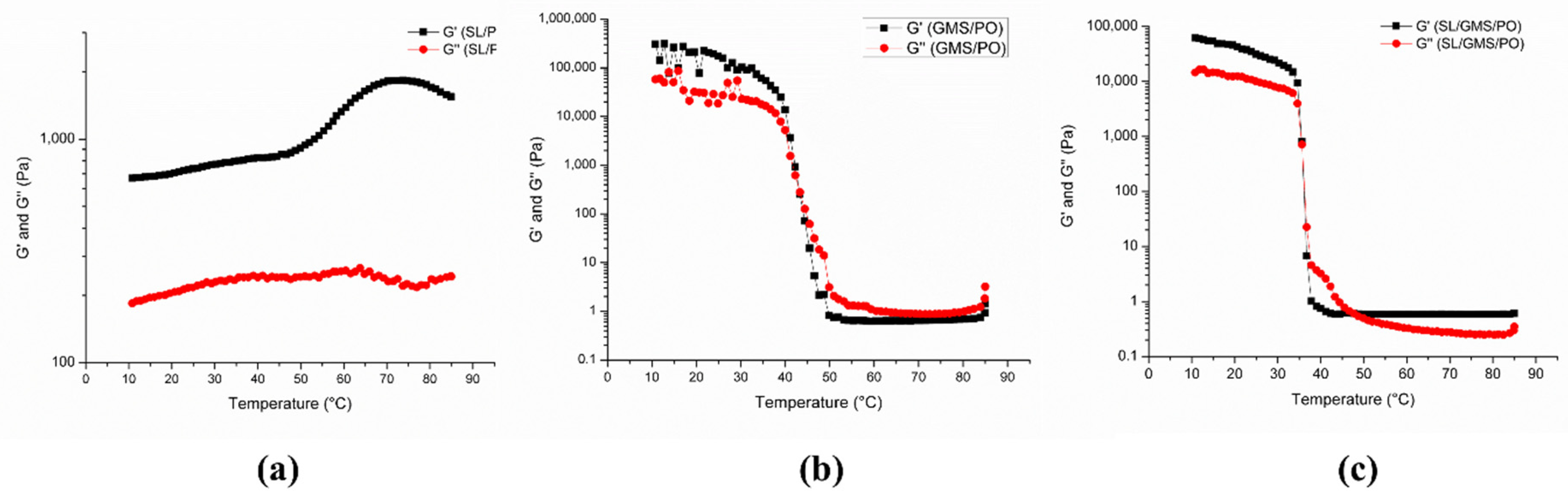
2.4.4. Rheology
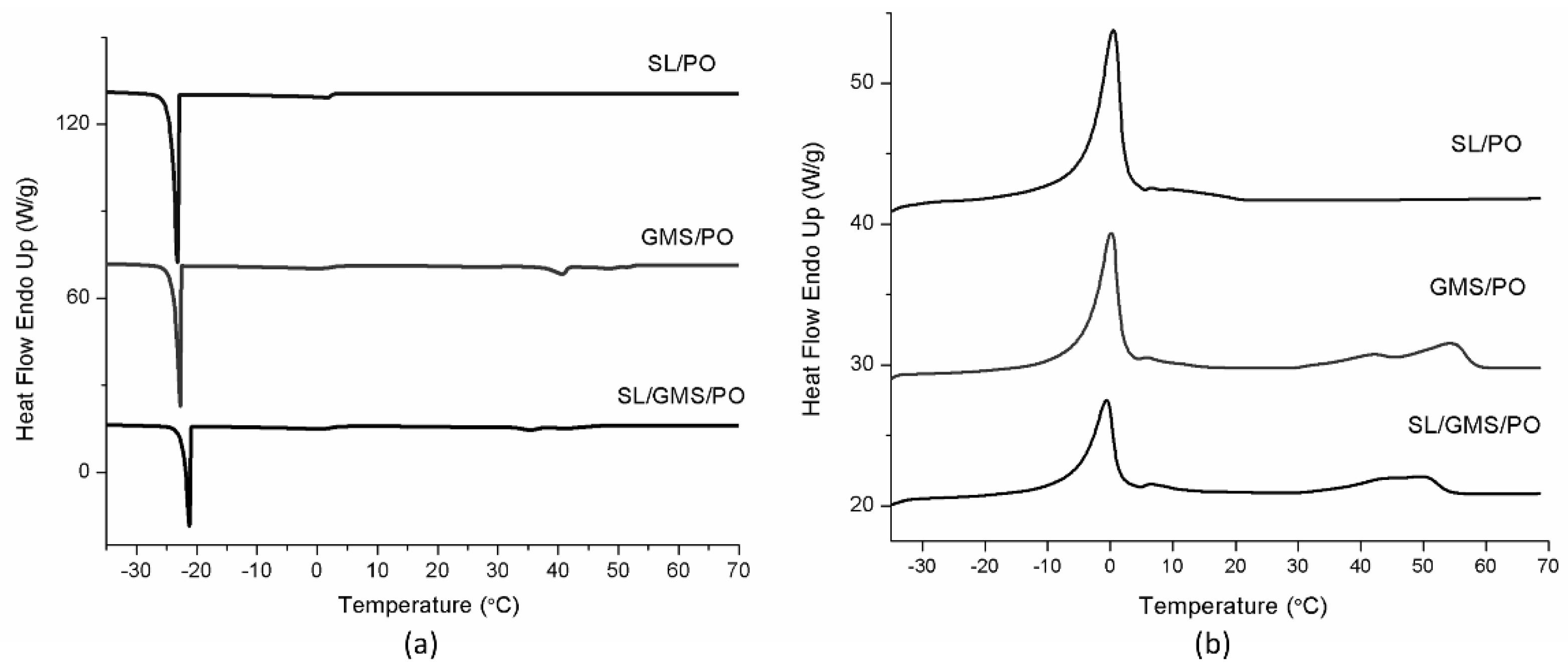
2.4.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Experimental Design
4.3. Preparation of Organogels
4.4. Mechanical Properties
4.5. Oil Binding Capacity (OBC)
4.6. Optimization and Verification of Models
4.7. Organogel Characterization
4.7.1. Polarized Microscope Observation
4.7.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
4.7.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
4.7.4. Rheological Analysis
4.7.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gravelle, A.J.; Davidovich-Pinhas, M.; Zetzl, A.K.; Barbut, S.; Marangoni, A.G. Influence of solvent quality on the mechanical strength of ethylcellulose oleogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 135, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palla, C.; Giacomozzi, A.; Genovese, D.B.; Carrín, M.E. Multi–objective optimization of high oleic sunflower oil and monoglycerides oleogels: Searching for rheological and textural properties similar to margarine. Food Struct. 2017, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, D.K.; Sagiri, S.S.; Behera, B.; Pal, K.; Pramanik, K. Development of olive oil based organogels using sorbitan monopalmitate and sorbitan monostearate: A comparative study. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbut, S.; Wood, J.; Marangoni, A. Quality effects of using organogels in breakfast sausage. Meat Sci. 2016, 122, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidovich-Pinhas, M.; Barbut, S.; Marangoni, A.G. Development, characterization, and utilization of food-grade polymer oleogels. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 7, 65–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Estaca, J.; Pintado, T.; Jiménez-Colmenero, F.; Cofrades, S. Assessment of a healthy oil combination structured in ethyl cellulose and beeswax oleogels as animal fat replacers in low-fat, PUFA-enriched pork burgers. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2019, 12, 1068–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lupi, F.R.; Shakeel, A.; Greco, V.; Baldino, N.; Calabrò, V.; Gabriele, D. Organogelation of extra virgin olive oil with fatty alcohols, glyceryl stearate and their mixture. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 77, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, N.; Singh, V.K.; Pal, K.; Anis, A.; Pradhan, D.K.; Pramanik, K. Development and characterization of soy lecithin and palm oil-based organogels. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2014, 53, 865–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sintang, M.D.; Danthine, S.; Patel, A.R.; Rimaux, T.; Walle, D.V.D.; Dewettinck, K. Mixed surfactant systems of sucrose esters and lecithin as a synergistic approach for oil structuring. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 504, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Li, L.; Li, B.; Zhao, L.; Liu, G.Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. Structure and physical properties of organogels developed by sitosterol and lecithin with sunflower oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2014, 91, 1783–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikiforidis, C.V.; Scholten, E. Self-assemblies of lecithin and α-tocopherol as gelators of lipid material. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 2466–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wendt, A.; Abraham, K.; Wernecke, C.; Pfeiffer, J.; Flöter, E. Application of β-sitosterol + γ-oryzanol-structured organogel as migration barrier in filled chocolate products. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2017, 94, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawalha, H.; Venema, P.; Bot, A.; Flöter, E.; den Adel, R.; van der Linden, E. The phase behavior of γ-oryzanol and β-sitosterol in edible oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2015, 92, 1651–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cerqueira, M.A.; Fasolin, L.H.; Picone, C.S.F.; Pastrana, L.M.; Cunha, R.L.; Vicente, A.A. Structural and mechanical properties of organogels: Role of oil and gelator molecular structure. Food Res. Int. 2017, 96, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sawalha, H.; den Adel, R.; Venema, P.; Bot, A.; Floter, E.; van der Linden, E. Organogel-emulsions with mixtures of β -sitosterol and γ -oryzanol: Influence of water activity and type of oil phase on gelling capability. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 3462–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, K.M.; Cardoso, L.P.; Ribeiro, A.P.B.; Kieckbusch, T.G.; Buscato, M.H.M. Crystallization of low saturated lipid blends of palm and canola oils with sorbitan monostearate and fully hydrogenated palm oil. J. Food Sci Technol. 2018, 55, 1104–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norhaizan, M.E.; Hosseini, S.; Gangadaran, S.; Lee, S.T.; Kapourchali, F.R.; Moghadasian, M.H. Palm oil: Features and applications. Lipid Technol. 2013, 25, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheong, A.M.; Tan, K.W.; Tan, C.P.; Nyam, K.L. Improvement of physical stability properties of kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) seed oil-in-water nanoemulsions. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 80, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama, A.P.; Hung, Y.C.; Adhikari, K. Optimization of emulsifier and stabilizer concentrations in a model peanut-based beverage system: A mixture design approach. Foods 2019, 8, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ntsoane, M.L.; Sivakumar, D.; Mahajan, P.V. Optimisation of O2 and CO2 concentrations to retain quality and prolong shelf life of ‘shelly’ mango fruit using a simplex lattice mixture design. Biosyst. Eng. 2020, 192, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonda, A.F.; Candiani, A.; Pertile, M.; Giovannelli, L.; Segale, L. Shellac gum/carrageenan alginate-based core-shell systems containing peppermint essential oil formulated by mixture design approach. Gels 2021, 7, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, R.; Hosseini, H.; Bondarianzadeh, D.; Jiménez, F. Optimization of prebiotic sausage formulation: Effect of using β-glucan and resistant starch by D-optimal mixture design approach. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carr, L.G.; Tadini, C.C. Influence of yeast and vegetable shortening on physical and textural parameters of frozen part baked French bread. LWT—Food Sci.Technol. 2003, 36, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.S.; Singh, M.; Winkler-Moser, J.K.; Bakota, E.L.; Liu, S.X. Preparation of margarines from organogels of sunflower wax and vegetable oils. J. Food Sci. 2014, 79, C1926–C1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, A.; Singh, B.; Raza, K.; Wadhwa, S.; Katare, O.P. Tamoxifen-loaded lecithin organogel (LO) for topical application: Development, optimization and characterization. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 444, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, A.C.; Okuro, P.K.; Badan, A.P.; Cunha, R.L. Role of the oil on glyceryl monostearate based oleogels. Food Res. Int. 2019, 120, 610–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelico, R.; Ceglie, A.; Colafemmina, G.; Delfine, F.; Olsson, U.; Palazzo, G. Phase behavior of the lecithin/water/isooctane and lecithin/water/decane systems. Langmuir 2004, 20, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Saleh, A.S.M.; Wang, P.; Wang, Q.; Yang, S.; Zhu, M.; Duan, Y.; Xiao, Z. Characterization of organogel prepared from rice bran oil with cinnamic acid. Food Biophys. 2017, 12, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Co, E.D.; Marangoni, A.G. Organogels: An alternative edible oil-structuring method. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2012, 89, 749–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Sher, A.; Rousset, P.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Formulation of food emulsions using natural emulsifiers: Utilization of quillaja saponin and soy lecithin to fabricate liquid coffee whiteners. J. Food Eng. 2017, 209, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raut, S.; Bhadoriya, S.S.; Uplanchiwar, V.; Mishra, V.; Gahane, A.; Jain, S.K. Lecithin organogel: A unique micellar system for the delivery of bioactive agents in the treatment of skin aging. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2012, 2, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lupi, F.R.; Greco, V.; Baldino, N.; de Cindio, B.; Fischer, P.; Gabriele, D. The effects of intermolecular interactions on the physical properties of organogels in edible oils. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 483, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Nakajima, Y.; Yumoto, M.; Kimura, M.; Shirai, H.; Hanabusa, K. Effects of hydrogen bonding and van der Waals interactions on organogelation using designed low-molecular-weight gelators and gel formation at room temperature. Langmuir 2003, 19, 8622–8624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brad, K.; Chen, C. Physicochemical properties of diosmetin and lecithin complex. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2013, 12, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, E.; Ogutcu, M. Properties and stability of hazelnut oil organogels with beeswax and monoglyceride. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2014, 91, 1007–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguna, L.; Farrell, G.; Bryant, M.; Morina, A.; Sarkar, A. Relating rheology and tribology of commercial dairy colloids to sensory perception. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.R.; Rajarethinem, P.S.; Grędowska, A.; Turhan, O.; Lesaffer, A.; De Vos, W.H.; Van de Walle, D.; Dewettinck, K. Edible applications of shellac oleogels: Spreads, chocolate paste and cakes. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, M.; Sharma, V.; Pathak, K. Nanovesicles for transdermal delivery of felodipine: Development, characterization, and pharmacokinetics. Int. J. Pharm. Investig. 2014, 4, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basu, S.; Shivhare, U.S. Rheological, textural, microstructural, and sensory properties of sorbitol-substituted mango jam. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 1401–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, A.J.; Vicente, A.A.; Cunha, R.L.; Cerqueira, M.A. Edible oleogels: An opportunity for fat replacement in foods. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 758–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, B.; Sagiri, S.S.; Pal, K.; Srivastava, A. Modulating the physical properties of sunflower oil and sorbitan monopalmitate-based organogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 4910–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample Number | Independent Variables (% w/w) | Response Variables | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X1: SL | X2: GMS | X3: Water | X4: PO | Y1: Firmness (N) | Y2: Spreadability (N S−1) | Y3: OBC (%) | |
| 1 | 13.00 | 10.00 | 10.00 | 67.00 | 1.17 | 7.84 | 74.69 |
| 2 | 19.00 | 7.00 | 18.00 | 56.00 | 0.78 | 9.05 | 80.26 |
| 3 | 26.00 | 4.00 | 40.00 | 30.00 | 0.28 | 4.56 | 82.14 |
| 4 | 13.00 | 10.00 | 40.00 | 37.00 | 0.45 | 5.05 | 78.26 |
| 5 | 6.00 | 14.00 | 40.00 | 40.00 | 0.82 | 7.69 | 80.93 |
| 6 | 16.00 | 4.00 | 10.00 | 70.00 | 0.84 | 8.88 | 73.85 |
| 7 | 16.00 | 14.00 | 25.00 | 45.00 | 1.52 | 15.59 | 82.77 |
| 8 | 6.00 | 4.00 | 10.00 | 80.00 | 0.20 | 2.00 | 50.03 |
| 9 | 6.00 | 24.00 | 25.00 | 45.00 | 3.62 | 17.08 | 86.09 |
| 10 | 6.00 | 14.00 | 25.00 | 55.00 | 1.06 | 6.81 | 75.15 |
| 11 | 13.00 | 10.00 | 25.00 | 52.00 | 0.78 | 7.01 | 71.74 |
| 12 | 16.00 | 14.00 | 40.00 | 30.00 | 1.20 | 12.81 | 85.38 |
| 13 | 9.00 | 7.00 | 18.00 | 66.00 | 0.56 | 5.84 | 62.30 |
| 14 | 9.00 | 17.00 | 33.00 | 41.00 | 1.20 | 10.41 | 78.70 |
| 15 | 6.00 | 4.00 | 25.00 | 65.00 | 0.33 | 4.07 | 58.07 |
| 16 | 26.00 | 4.00 | 10.00 | 60.00 | 1.36 | 13.52 | 71.12 |
| 17 | 13.00 | 10.00 | 25.00 | 52.00 | 0.74 | 6.22 | 70.89 |
| 18 | 6.00 | 14.00 | 10.00 | 70.00 | 0.99 | 6.33 | 63.37 |
| 19 | 16.00 | 4.00 | 40.00 | 40.00 | 1.00 | 8.86 | 81.11 |
| 20 | 16.00 | 14.00 | 10.00 | 60.00 | 2.31 | 19.97 | 76.76 |
| 21 | 16.00 | 4.00 | 25.00 | 55.00 | 0.28 | 3.74 | 59.21 |
| 22 | 9.00 | 17.00 | 18.00 | 56.00 | 1.31 | 8.22 | 66.20 |
| 23 | 13.00 | 10.00 | 25.00 | 52.00 | 0.68 | 3.98 | 74.45 |
| 24 | 6.00 | 24.00 | 10.00 | 60.00 | 1.67 | 10.11 | 69.05 |
| 25 | 6.00 | 4.00 | 40.00 | 50.00 | 0.23 | 1.29 | 63.67 |
| 26 | 6.00 | 24.00 | 40.00 | 30.00 | 2.52 | 23.93 | 91.50 |
| 27 | 9.00 | 7.00 | 33.00 | 51.00 | 0.24 | 1.65 | 65.85 |
| 28 | 26.00 | 4.00 | 25.00 | 45.00 | 0.35 | 5.82 | 74.46 |
| 29 | 19.00 | 7.00 | 33.00 | 41.00 | 0.39 | 5.16 | 77.87 |
| Independent Variables | Regression Coefficients | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Firmness | Spreadability | OBC | |
| Linear | |||
| SL | 26.12 | 200.50 | −326.80 |
| GM | 19.24 | 216.20 | 206.10 |
| Water | −1.90 | −5.30 | 66.00 |
| PO | 2.08 | 26.20 | 20.50 |
| Quadratic | |||
| SL × Water | −40.68 * | −290.30 * | 634.00 * |
| SL × PO | −35.99 * | −270.30 * | 736.50 * |
| GMS × PO | −28.16 * | −366.10 * | - |
| R2 | 0.9412 | 0.9699 | 0.8970 |
| Predicted R2 | 0.8150 | 0.9231 | 0.8197 |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.9216 | 0.9548 | 0.8712 |
| Lack of fit | |||
| F value | 10.1400 | 0.3700 | 3.5300 |
| p value | 0.0930 | 0.9010 | 0.2430 |
| Factors | Dependent Variables (Response) | Optimum Value | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SL | GMS | Water | PO | Experimental a | Predicted | p-Value | |
| 8.00 | 22.00 | 28.00 | 42.00 | Firmness | 1.91 ± 0.04 | 1.91 | 0.923 |
| Spreadability | 15.28 ± 0.66 | 15.68 | 0.372 | ||||
| OBC | 83.83 ± 4.14 | 85.15 | 0.568 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ghan, S.Y.; Siow, L.F.; Tan, C.P.; Cheong, K.W.; Thoo, Y.Y. Palm Olein Organogelation Using Mixtures of Soy Lecithin and Glyceryl Monostearate. Gels 2022, 8, 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8010030
Ghan SY, Siow LF, Tan CP, Cheong KW, Thoo YY. Palm Olein Organogelation Using Mixtures of Soy Lecithin and Glyceryl Monostearate. Gels. 2022; 8(1):30. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8010030
Chicago/Turabian StyleGhan, Sheah Yee, Lee Fong Siow, Chin Ping Tan, Kok Whye Cheong, and Yin Yin Thoo. 2022. "Palm Olein Organogelation Using Mixtures of Soy Lecithin and Glyceryl Monostearate" Gels 8, no. 1: 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8010030
APA StyleGhan, S. Y., Siow, L. F., Tan, C. P., Cheong, K. W., & Thoo, Y. Y. (2022). Palm Olein Organogelation Using Mixtures of Soy Lecithin and Glyceryl Monostearate. Gels, 8(1), 30. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels8010030







