Effects of Formulation and Extrusion Conditions for Isolated Pea Protein-Based High-Moisture Meat Analogs: Insights into Gelation and Structural Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Fiber Structure
2.2. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA) and Cutting Strength
2.3. Water-Holding Capacity (WHC)
2.4. Integrity Index
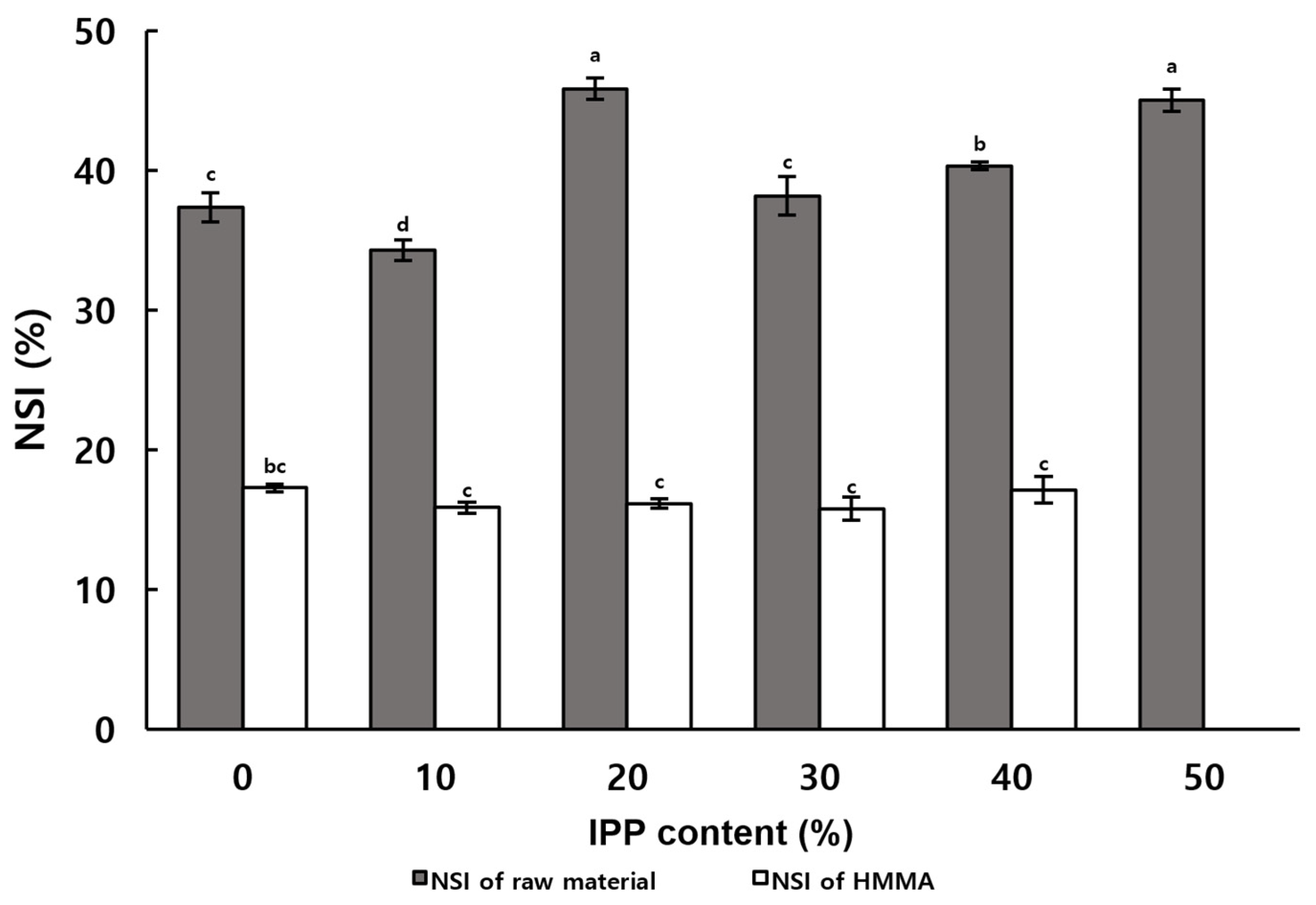
2.5. Nitrogen Solubility Index (NSI)
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
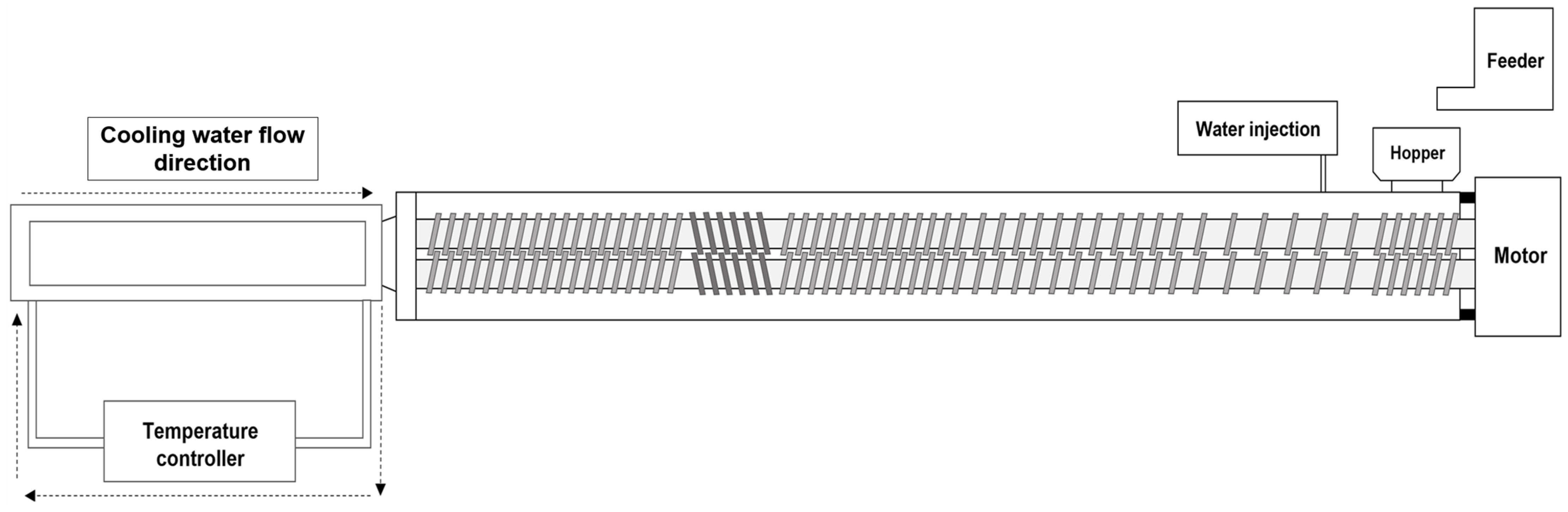
4.2. High-Moisture Extrusion Process
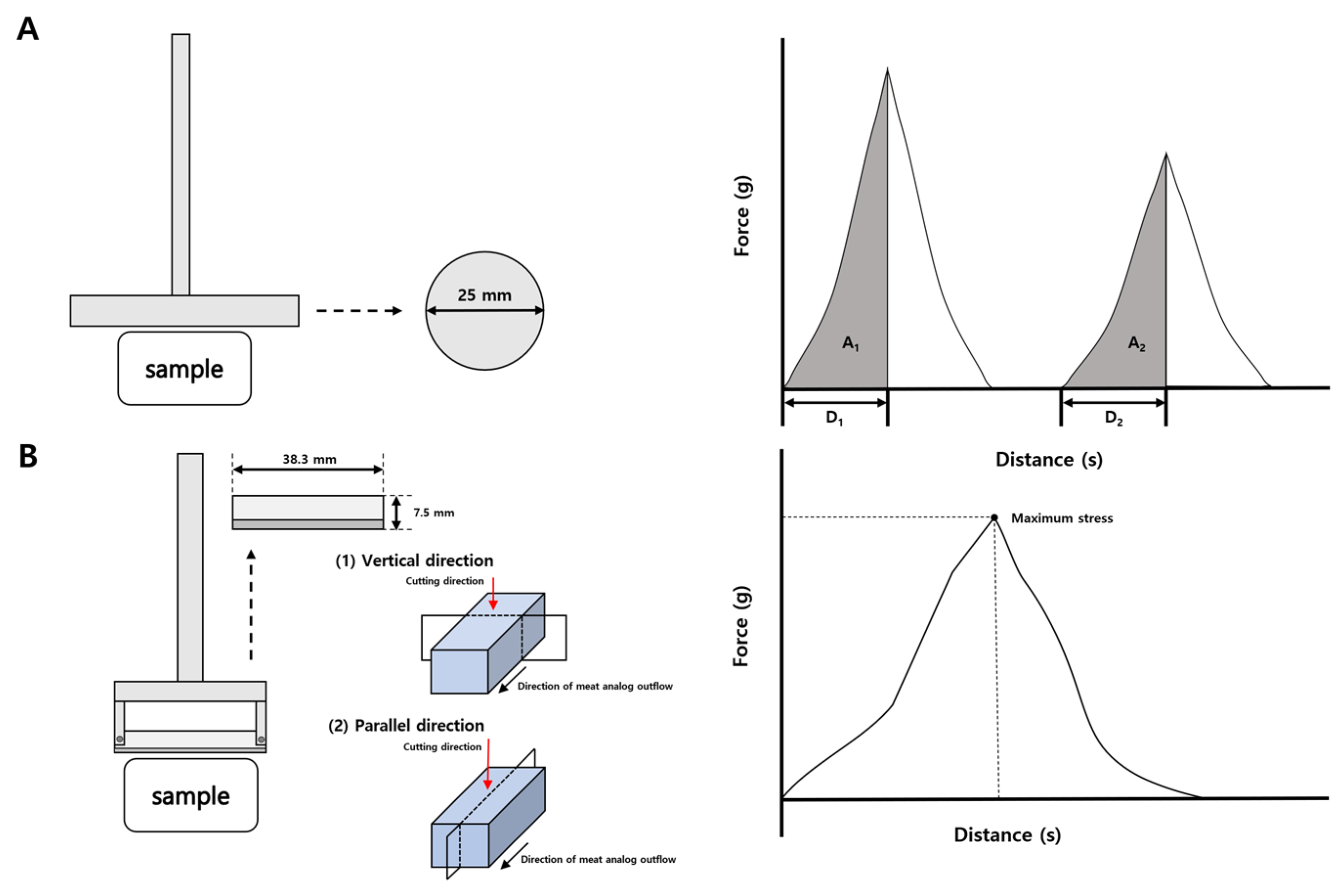
4.3. Texture Profile Analysis (TPA), Cutting Strength
4.4. Water-Holding Capacity (WHC)
4.5. Integrity Index
4.6. Nitrogen Solubility Index
4.7. Statistics Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ismail, I.; Hwang, Y.-H.; Joo, S.-T. Meat Analog as Future Food: A Review. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2020, 62, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottet, A.; de Haan, C.; Falcucci, A.; Tempio, G.; Opio, C.; Gerber, P. Livestock: On Our Plates or Eating at Our Table? A New Analysis of the Feed/Food Debate. Glob. Food Secur. 2017, 14, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.T.; Sobur, M.A.; Islam, M.S.; Ievy, S.; Hossain, M.J.; El Zowalaty, M.E.; Rahman, A.T.; Ashour, H.M. Zoonotic Diseases: Etiology, Impact, and Control. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira Mota, J.; Boué, G.; Guillou, S.; Pierre, F.; Membré, J.-M. Estimation of the Burden of Disease Attributable to Red Meat Consumption in France: Influence on Colorectal Cancer and Cardiovascular Diseases. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 130, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohrer, B.M. An Investigation of the Formulation and Nutritional Composition of Modern Meat Analogue Products. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arêas, J.A.G. Extrusion of Food Proteins. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1992, 32, 365–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langelaan, M.L.P.; Boonen, K.J.M.; Polak, R.B.; Baaijens, F.P.T.; Post, M.J.; van der Schaft, D.W.J. Meet the New Meat: Tissue Engineered Skeletal Muscle. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorani, B.; Tucker, N. Fundamentals of Electrospinning as a Novel Delivery Vehicle for Bioactive Compounds in Food Nanotechnology. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 51, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandraiah, K. Potential Development of Sustainable 3D-Printed Meat Analogues: A Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, E.-M.; Farahnaky, A.; Adhikari, B.; Torley, P.J. High Moisture Extrusion Cooking of Meat Analogs: A Review of Mechanisms of Protein Texturization. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 4573–4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniwal, A.S.; Singh, J.; Kaur, L.; Hardacre, A.; Singh, H. Meat Analogs: Protein Restructuring during Thermomechanical Processing. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 1221–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoval Murillo, J.L.; Osen, R.; Hiermaier, S.; Ganzenmüller, G. Towards Understanding the Mechanism of Fibrous Texture Formation during High-Moisture Extrusion of Meat Substitutes. J. Food Eng. 2019, 242, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, P.; Wang, T.; Luo, Y. A Review on Plant-Based Proteins from Soybean: Health Benefits and Soy Product Development. J. Agric. Food Res. 2022, 7, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordle, C.T. Soy Protein Allergy: Incidence and Relative Severity. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 1213S–1219S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Sun, C.-X.; Corke, H.; Gul, K.; Gan, R.-Y.; Fang, Y. The Health Benefits, Functional Properties, Modifications, and Applications of Pea (Pisum sativum L.) Protein: Current Status, Challenges, and Perspectives. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 1835–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hood-Niefer, S.D.; Tyler, R.T. Effect of Protein, Moisture Content and Barrel Temperature on the Physicochemical Characteristics of Pea Flour Extrudates. Food Res. Int. 2010, 43, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, A.C.Y.; Can Karaca, A.; Tyler, R.T.; Nickerson, M.T. Pea Protein Isolates: Structure, Extraction, and Functionality. Food Rev. Int. 2018, 34, 126–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osen, R.; Toelstede, S.; Wild, F.; Eisner, P.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U. High Moisture Extrusion Cooking of Pea Protein Isolates: Raw Material Characteristics, Extruder Responses, and Texture Properties. J. Food Eng. 2014, 127, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreuders, F.K.G.; Dekkers, B.L.; Bodnár, I.; Erni, P.; Boom, R.M.; van der Goot, A.J. Comparing Structuring Potential of Pea and Soy Protein with Gluten for Meat Analogue Preparation. J. Food Eng. 2019, 261, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ryu, G.-H. Effects of Pea Protein Content and Extrusion Types on Physicochemical Properties and Texture Characteristic of Meat Analogs. JSFA Rep. 2023, 3, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.-W.; Ryu, G.-H. Comparison of the Physicochemical Properties of Low and High-Moisture Extruded Meat Analog with Varying Moisture Content. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 51, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietsch, V.L.; Werner, R.; Karbstein, H.P.; Emin, M.A. High Moisture Extrusion of Wheat Gluten: Relationship between Process Parameters, Protein Polymerization, and Final Product Characteristics. J. Food Eng. 2019, 259, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Liu, H.; Yoon, A.; Rizvi, S.S.H.; Wang, Q. Changes in Conformation and Quality of Vegetable Protein During Texturization Process by Extrusion. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 3267–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trinh, K.T.; Glasgow, S. On the Texture Profile Analysis Test. In Proceedings of the Chemeca 2012, Wellington, New Zealand, 23–26 September 2012; Volume 2012, pp. 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Bhirud, P.R.; Tyler, R.T. Extrusion Texturization of Air-Classified Pea Protein. J. Food Sci. 1999, 64, 509–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Kane, F.E.; Happe, R.P.; Vereijken, J.M.; Gruppen, H.; van Boekel, M.A.J.S. Heat-Induced Gelation of Pea Legumin: Comparison with Soybean Glycinin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 5071–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazaheri Tehrani, M.; Ehtiati, A.; Sharifi Azghandi, S. Application of Genetic Algorithm to Optimize Extrusion Condition for Soy-Based Meat Analogue Texturization. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 1119–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samard, S.; Gu, B.Y.; Ryu, G.H. Effects of Extrusion Types, Screw Speed and Addition of Wheat Gluten on Physicochemical Characteristics and Cooking Stability of Meat Analogues. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 4922–4931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Shen, C.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, C. Comparison of Wheat, Soybean, Rice, and Pea Protein Properties for Effective Applications in Food Products. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Kang, D.I.; Ryu, G.H. Effects of Screw Speed, Moisture Content, and Die Temperature on Texturization of Extruded Soy Protein Isolate. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 45, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samard, S.; Ryu, G.-H. A Comparison of Physicochemical Characteristics, Texture, and Structure of Meat Analogue and Meats. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 2708–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Huff, H.E.; Hsieh, F. Extrusion Process Parameters, Sensory Characteristics, and Structural Properties of a High Moisture Soy Protein Meat Analog. J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brishti, F.H.; Chay, S.Y.; Muhammad, K.; Ismail-Fitry, M.R.; Zarei, M.; Saari, N. Texturized Mung Bean Protein as a Sustainable Food Source: Effects of Extrusion on Its Physical, Textural and Protein Quality. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2021, 67, 102591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starcher, B. A Ninhydrin-Based Assay to Quantitate the Total Protein Content of Tissue Samples. Anal. Biochem. 2001, 292, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
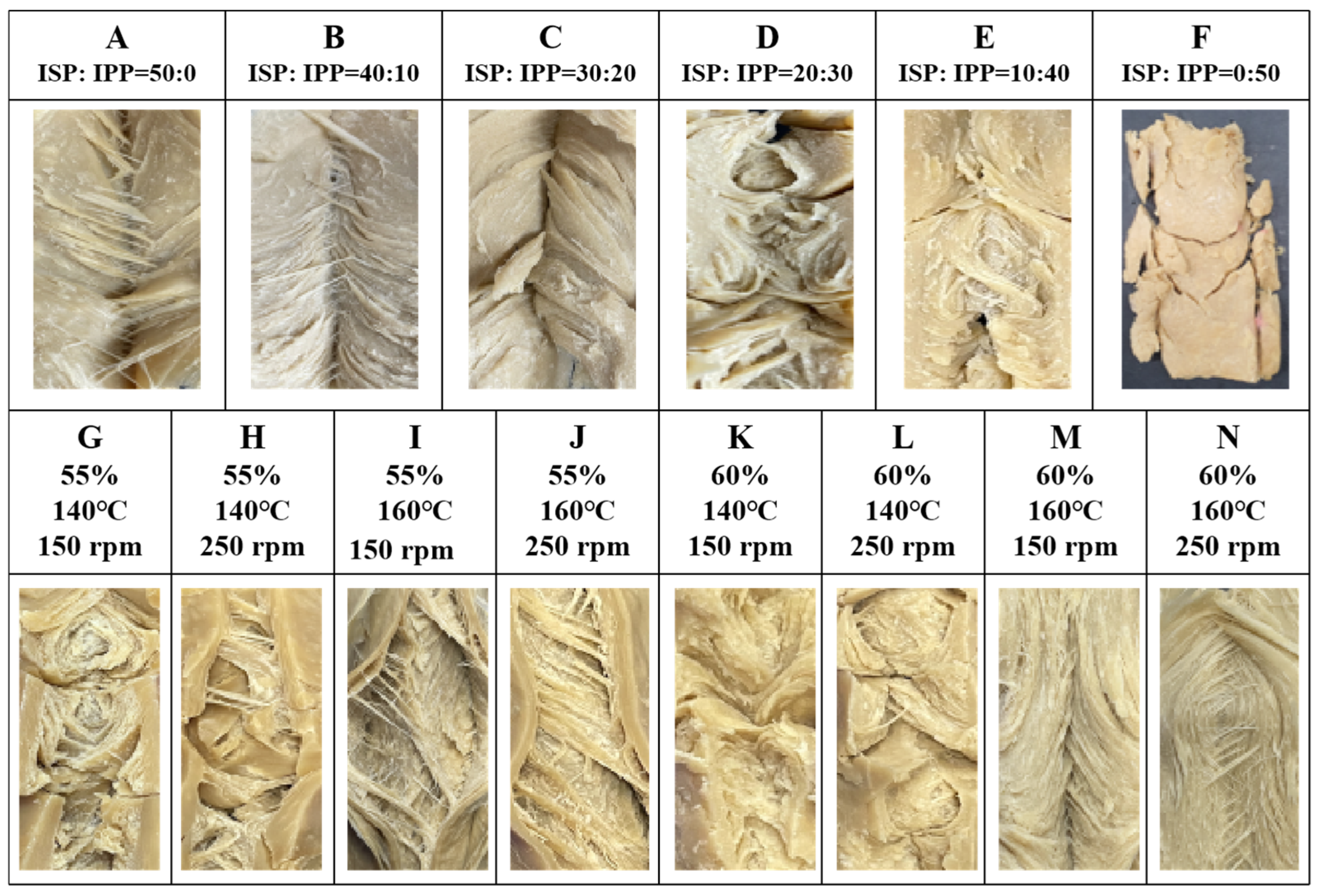

| Raw Material Content | Springiness (%) | Cohesiveness (%) | Chewiness (g) | Cutting Strength (g/cm2) | Integrity Index (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ISP (1) (%) | IPP (%) | Vertical Direction | Parallel Direction | ||||
| 50 | 0 | 92.45 ± 1.78 (2) a | 82.26 ± 0.73 bc | 5896.77 ± 246.10 a | 1205.63 ± 222.33 a | 860.36 ± 153.59 ab | 84.27 ± 0.49 a |
| 40 | 10 | 93.09 ± 0.91 a | 81.21 ± 0.35 bc | 4696.22 ± 163.35 b | 1027.93 ± 28.08 b | 933.08 ± 245.35 a | 81.26 ± 0.49 ab |
| 30 | 20 | 93.35 ± 1.22 a | 79.46 ± 2.07 cd | 3750.90 ± 337.33 c | 818.71 ± 43.86 c | 757.22 ± 133.58 b | 77.73 ± 1.27 abc |
| 20 | 30 | 89.95 ± 1.01 a | 74.86 ± 1.97 de | 3520.50 ± 193.36 c | 608.28 ± 30.27 ef | 564.54 ± 80.46 c | 76.91 ± 1.89 bc |
| 10 | 40 | 83.54 ± 2.96 b | 68.00 ± 5.26 fg | 2164.87 ± 373.33 d | 540.43 ± 30.10 f | 359.43 ± 67.86 de | 71.65 ± 1.86 cd |
| 0 | 50 | - | |||||
| M.C (1) (%) | B.T (°C) | S.S (rpm) | Springiness (%) | Cohesiveness (%) | Chewiness (g) | Cutting Strength (g/cm2) | WHC (g/g) | Integrity Index (%) | NSI (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vertical Direction | Parallel Direction | |||||||||
| 55 | 140 | 150 | 86.63 ± 0.74 (2) c | 70.37 ± 2.14 ef | 3804.47 ± 300.51 d | 810.12 ± 40.99 cd | 669.19 ± 96.05 ab | 2.78 ± 0.10 d | 77.33 ± 1.17 c | 11.76 ± 0.24 g |
| 250 | 88.81 ± 2.00 bc | 76.16 ± 2.42 bcd | 4521.01 ± 227.24 c | 910.48 ± 89.45 c | 743.05 ± 221.93 ab | 2.83 ± 0.04 d | 87.50 ± 0.12 a | 12.29 ± 0.14 efg | ||
| 160 | 150 | 92.71 ± 0.43 ab | 78.38 ± 0.54 abc | 5065.46 ± 142.85 b | 1391.11 ± 208.03 a | 713.62 ± 258.42 ab | 2.65 ± 0.26 def | 79.20 ± 0.46 bc | 14.80 ± 0.68 b | |
| 250 | 93.45 ± 0.59 a | 82.46 ± 1.25 a | 6374.08 ± 240.16 a | 1348.74 ± 126.25 a | 777.82 ± 86.36 a | 2.43 ± 0.12 fg | 88.27 ± 0.90 a | 13.87 ± 0.57 c | ||
| 60 | 140 | 150 | 81.63 ± 2.07 d | 64.02 ± 1.83 g | 1390.91 ± 179.24 h | 637.59 ± 58.88 ef | 581.02 ± 96.18 bcd | 2.85 ± 0.05 d | 58.30 ± 0.91 h | 14.59 ± 0.08 bc |
| 250 | 90.73 ± 1.04 ab | 72.19 ± 3.36 def | 2839.43 ± 315.75 g | 564.46 ± 12.04 f | 478.10 ± 116.59 cde | 2.81 ± 0.01 d | 71.49 ± 0.60 d | 16.52 ± 0.11 a | ||
| 160 | 150 | 91.44 ± 1.23 ab | 73.96 ± 1.61 cdef | 3180.68 ± 179.38 f | 812.28 ± 103.18 cd | 609.59 ± 139.45 bc | 2.47 ± 0.08 efg | 81.03 ± 1.10 b | 16.64 ± 0.38 a | |
| 250 | 93.87 ± 1.25 a | 80.19 ± 0.98 ab | 3515.33 ± 133.07 e | 1109.56 ± 123.43 b | 697.74 ± 82.04 ab | 2.70 ± 0.12 de | 80.70 ± 0.73 b | 16.14 ± 0.64 a | ||
| Extrusion Design | Formulation | Operation Parameters | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IPP (1) (%) | ISP (%) | WG (%) | CS (%) | MC (%) | BT (°C) | SS (rpm) | Feed Rate (g/min) | |
| Experiment 1 | 0 | 50 | 40 | 10 | 55 | 150 | 250 | 100 |
| 10 | 40 | |||||||
| 20 | 30 | |||||||
| 30 | 20 | |||||||
| 40 | 10 | |||||||
| 50 | 0 | |||||||
| Experiment 2 | 30 | 20 | 40 | 10 | 55 | 140 | 150 | |
| 250 | ||||||||
| 160 | 150 | |||||||
| 250 | ||||||||
| 60 | 140 | 150 | ||||||
| 250 | ||||||||
| 160 | 150 | |||||||
| 250 | ||||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Choi, H.-W.; Lee, Y.; Ryu, G.-H.; Gu, B.-J. Effects of Formulation and Extrusion Conditions for Isolated Pea Protein-Based High-Moisture Meat Analogs: Insights into Gelation and Structural Development. Gels 2026, 12, 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels12010042
Zhang Y, Choi H-W, Lee Y, Ryu G-H, Gu B-J. Effects of Formulation and Extrusion Conditions for Isolated Pea Protein-Based High-Moisture Meat Analogs: Insights into Gelation and Structural Development. Gels. 2026; 12(1):42. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels12010042
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yu, Hyun-Woo Choi, Yunju Lee, Gi-Hyung Ryu, and Bon-Jae Gu. 2026. "Effects of Formulation and Extrusion Conditions for Isolated Pea Protein-Based High-Moisture Meat Analogs: Insights into Gelation and Structural Development" Gels 12, no. 1: 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels12010042
APA StyleZhang, Y., Choi, H.-W., Lee, Y., Ryu, G.-H., & Gu, B.-J. (2026). Effects of Formulation and Extrusion Conditions for Isolated Pea Protein-Based High-Moisture Meat Analogs: Insights into Gelation and Structural Development. Gels, 12(1), 42. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels12010042










