Double-Network Hydrogels via Hybrid Strategies: Potential in Large-Scale Manufacturing for Colorimetric Indicator
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
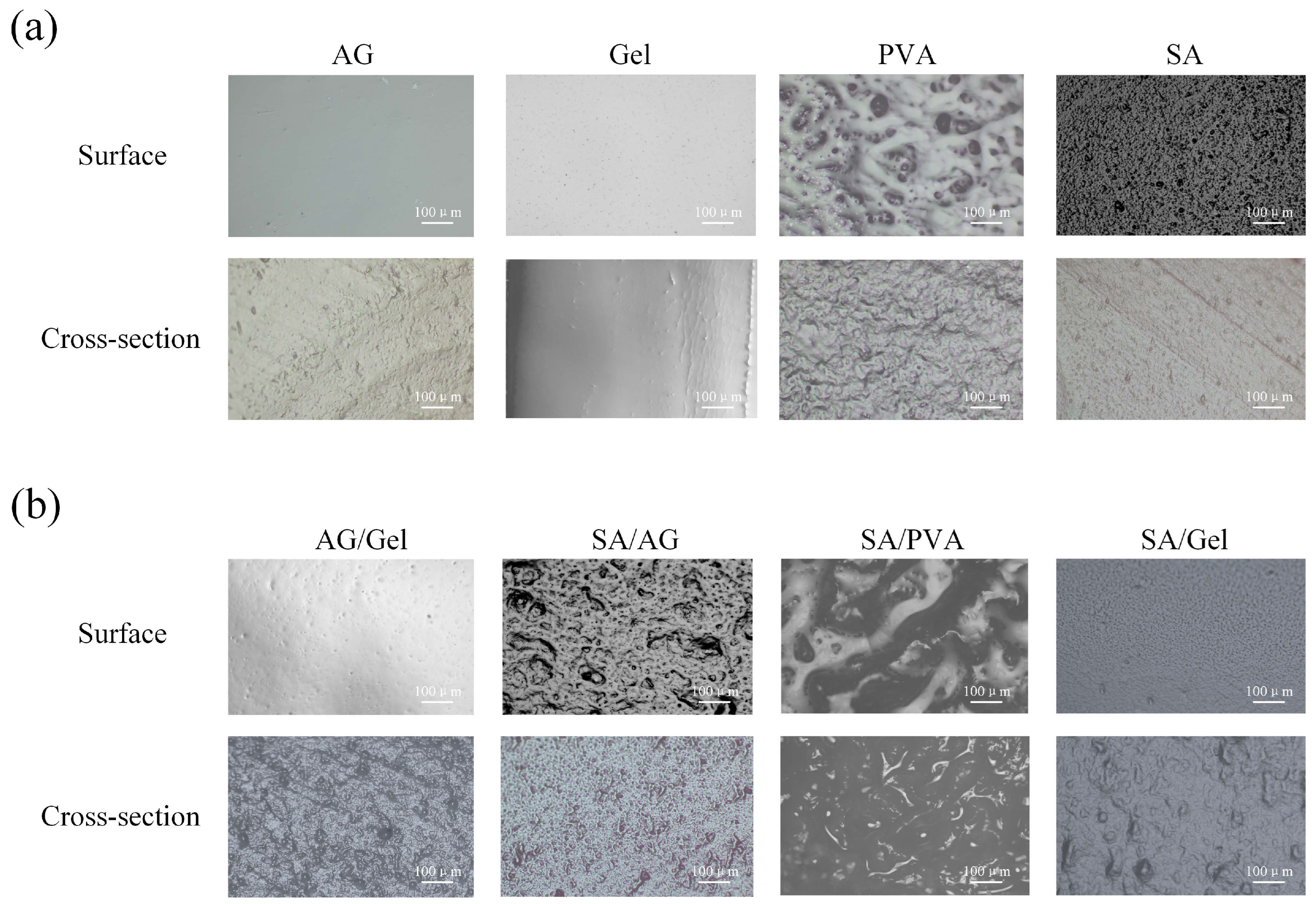
2.1. Surface Morphology of Dual-Network Hydrogels
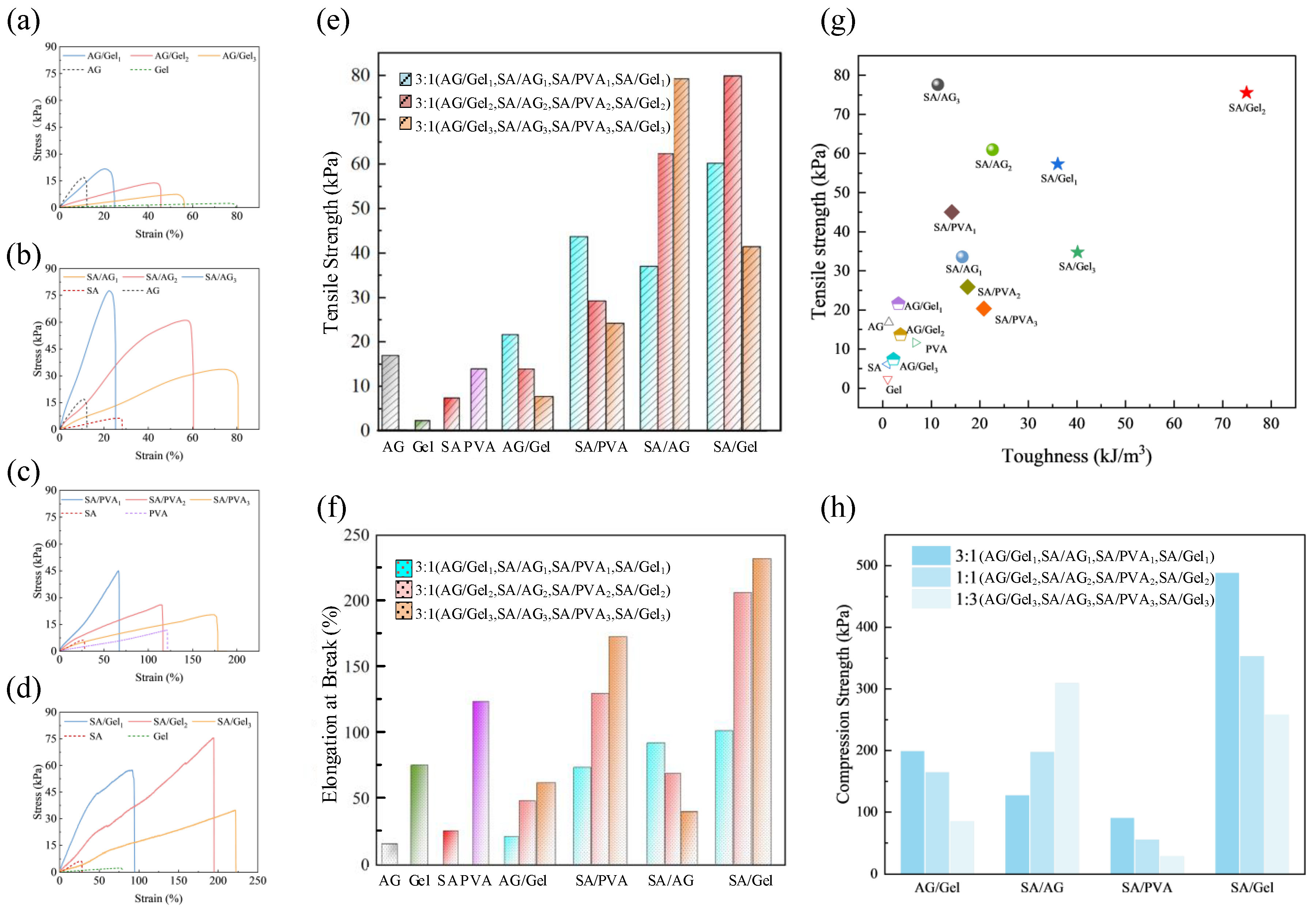
2.2. Mechanical Properties of Dual-Network Hydrogels
2.3. Structure of Dual-Network Hydrogels
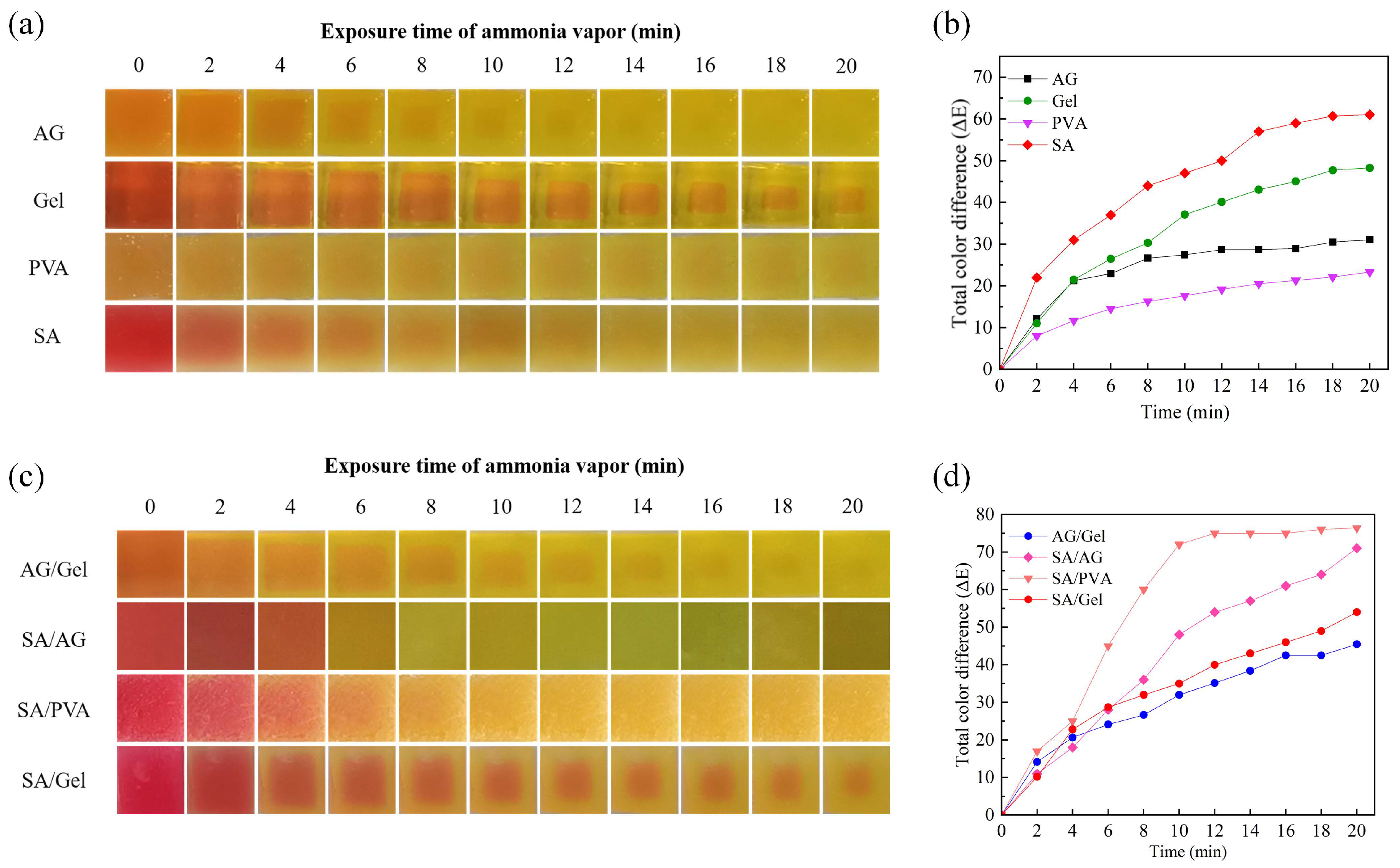
2.4. Color Response to Ammonia Vapor of Dual-Network Hydrogels
3. Conclusions
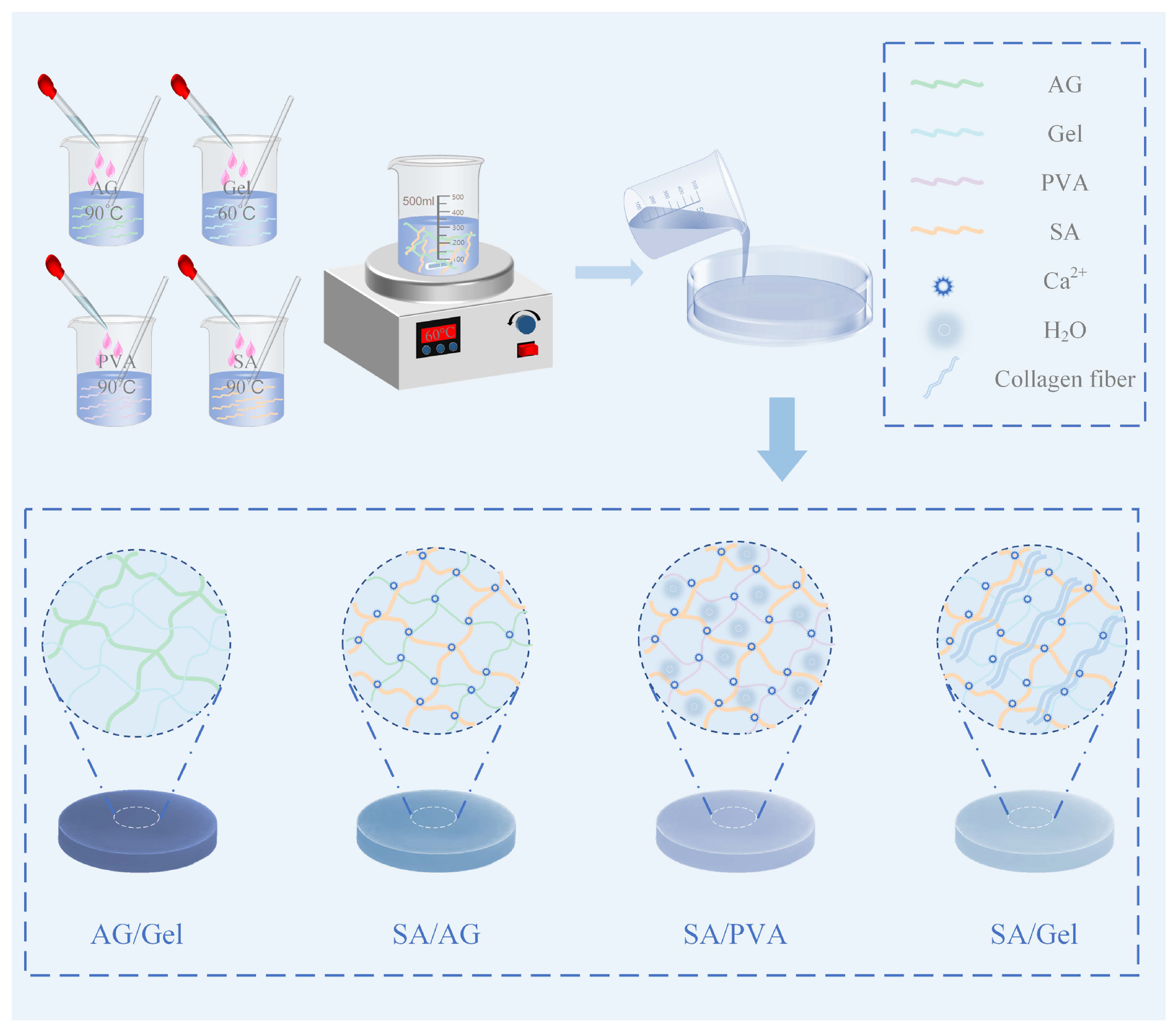
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of AG, Gel, PVA, and SA Films
4.3. Preparation of Double-Network Hydrogel Films
4.4. Characterization of Double-Network Hydrogel Films
4.4.1. Surface Morphology
4.4.2. Mechanical Properties
4.4.3. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
4.4.4. Ammonia Response of Hydrogel Films
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AG | Agar |
| Gel | Gelatin |
| SA | Sodium Alginate |
| PVA | Poly (vinyl alcohol) |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy |
| Gly | Glycerol |
| Calcium chloride | |
| MR | Methyl red |
References
- Liu, W.; Yao, C.; Wang, D.; Du, G.; Ji, Y.; Li, Q. Dynamic Double-Networked Hydrogels by Hybridizing PVA and Herbal Polysaccharides: Improved Mechanical Properties and Selective Antibacterial Activity. Gels 2024, 10, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Fu, Z.; Li, H.; Wei, R.; Guo, J.; Wang, H.; Qi, J. Smart hydrogel: A new platform for cancer therapy. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 340, 103470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Tao, J.; Yan, W.; Song, W. Pathways toward wearable and high-performance sensors based on hydrogels: Toughening networks and conductive networks. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwad180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Tan, Y.; Lao, J.; Gao, H.; Yu, J. Hydrogels for flexible electronics. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 9681–9693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wei, H.; Huang, Y.; Wei, Y.; Chen, J. Naturally sourced hydrogels: Emerging fundamental materials for next-generation healthcare sensing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 2992–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, L.; McClements, D.J.; Qiu, C.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z.; Miao, M.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, K.; Jin, Z. Stimulus-responsive hydrogels in food science: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 124, 107218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Jiménez, F.J.; Oliver-Simancas, R.; Castangia, I.; Rodriguez-Garcia, A.M.; Alañón, M.E. Comprehensive review of natural based hydrogels as an upcoming trend for food packing. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 135, 108124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; Yuk, H.; Lin, S.; Liu, X.; Parada, G. Soft materials by design: Unconventional polymer networks give extreme properties. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 4309–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Lu, W.; Mata, A.; Nishinari, K.; Fang, Y. Ions-induced gelation of alginate: Mechanisms and applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 177, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Liu, H.; Yan, K.; Li, X.; Lu, Z.; Wang, D. An ionic/thermal-responsive agar/alginate wet-spun microfiber-shaped hydrogel combined with grooved/wrinkled surface patterns and multi-functions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 304, 120501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.F.; Rhim, J.W. Preparation and application of agar/alginate/collagen ternary blend functional food packaging films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 80, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Bai, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Zou, J.; Fei, P.; Lai, W. Double network self-healing hydrogels based on carboxyethyl chitosan/oxidized sodium alginate/Ca2+: Preparation, characterization and application in dye absorption. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 264, 130564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.y.; Li, D.; Sun, W.; Wang, L.J.; Wang, Y. Green, tough, and heat-resistant: A GDL-induced strategy for starch-alginate hydrogels. Food Chem. 2024, 449, 139188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Zeng, L.; Cheng, X.; Yang, C.; Chen, J.; Chen, H.; Ni, H.; Bai, Y.; Yu, W.; Zhao, K.; et al. Shape memory composite hydrogel based on sodium alginate dual crosslinked network with carboxymethyl cellulose. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 156, 110592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, S.; Li, X.; Yan, Q.; Reaney, M.J.; Jiang, Z. Alginate oligosaccharides: Production, biological activities, and potential applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1859–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jiao, A.; Qiu, C.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Bian, S.; Zeng, F.; Jin, Z. A combined enzymatic and ionic cross-linking strategy for pea protein/sodium alginate double-network hydrogel with excellent mechanical properties and freeze-thaw stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panouillé, M.; Larreta-Garde, V. Gelation behaviour of gelatin and alginate mixtures. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Chawla, R.; Santhosh, R.; Thakur, R.; Sarkar, P.; Zhang, W. Agar-based edible films and food packaging application: A comprehensive review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 141, 104198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Xue, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yan, M.; Xia, Y. Preparation and properties of wet-spun agar fibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Pan, J.; Yao, Q.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, H.; Hu, Y.; Zheng, W.; Zhou, W.; et al. A good adhesion and antibacterial double-network composite hydrogel from PVA, sodium alginate and tannic acid by chemical and physical cross-linking for wound dressings. J. Mater. Sci. 2023, 58, 5756–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.M.; Nayak, S.K.; Shaw, G.S.; Uvanesh, K.; Banerjee, I.; Al-Zahrani, S.; Anis, A.; Pal, K. An in-depth analysis of the swelling, mechanical, electrical, and drug release properties of agar–gelatin co-hydrogels. Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2017, 56, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Yang, J.; Zhang, W.; Wei, Y.; Yuan, H.; Tan, Y. Seaweed polysaccharide fibers: Solution properties, processing and applications. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 140, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lin, X.; Wang, L. Design of mechanically strong and tough alginate hydrogels based on a soft-brittle transition. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 139, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Chen, H. A pH indicator film based on sodium alginate/gelatin and plum peel extract for monitoring the freshness of chicken. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, U.T.; Nguyen, Q.T.; Kim, J.; Luu, Q.S.; Park, Y.; Song, M.; Yang, S.; Choi, J.; Yun, S.; Kang, D.K.; et al. Tailored synthesis of pH-responsive biodegradable microcapsules incorporating gelatin, alginate, and hyaluronic acid for effective-controlled release. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 270, 132178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, H.J.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Liu, X.; You, X. A physically cross-linked sodium alginate–gelatin hydrogel with high mechanical strength. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 3197–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Gao, M.; Xiang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Yu, D.; Yan, R. A biomass-based colorimetric sulfur dioxide gas sensor for smart packaging. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 6849–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zou, X.; Zhai, X.; Huang, X.; Jiang, C.; Holmes, M. Preparation of an intelligent pH film based on biodegradable polymers and roselle anthocyanins for monitoring pork freshness. Food Chem. 2019, 272, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutthasupa, S.; Padungkit, C.; Suriyong, S. Colorimetric ammonia (NH3) sensor based on an alginate-methylcellulose blend hydrogel and the potential opportunity for the development of a minced pork spoilage indicator. Food Chem. 2021, 362, 130151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, N.; Zhou, W. Sodium alginate/ager colourimetric film on porous substrate layer: Potential in intelligent food packaging. Food Chem. 2024, 445, 138790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; He, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liang, Q. An insight into skeletal networks analysis for smart hydrogels. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2108489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Wang, H.; Xia, L.; Chen, M.; Li, L.; Cheng, J.; Li, X.; Jiang, S. Colorimetric film based on polyvinyl alcohol/okra mucilage polysaccharide incorporated with rose anthocyanins for shrimp freshness monitoring. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, M.; Kim, S.; Lee, W.; Lee, H. Fabrication of printable colorimetric food sensor based on hydrogel for low-concentration detection of ammonia. Biosensors 2022, 13, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, X.; Zhou, Y.; Hao, K.; Liu, C.; Yu, R.; Huang, A.; Wu, C.; Yang, Y. 3D printed all-natural hydrogels: Flame-retardant materials toward attaining green sustainability. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2306360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Lee, T.; Kim, M.; Park, S.; Hu, J.; Lee, K.; Hong, Y.; Park, I.; Lee, G. Fast responsive, reversible colorimetric nanoparticle-hydrogel complexes for pH monitoring. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Chu, F. Combination of acid treatment and dual network fabrication to stretchable cellulose based hydrogels with tunable properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 147, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, D.; Guo, N.; Wang, Y.; Ding, T.; Weng, L. A highly stretchable, sensing durability, transparent, and environmentally stable ion conducting hydrogel strain sensor built by interpenetrating Ca2+-SA and glycerol-PVA double physically cross-linked networks. Adv. Compos. Hybrid Mater. 2022, 5, 1712–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Tan, C.S.Y.; Yu, Z.; Lan, Y.; Abell, C.; Scherman, O.A. Biomimetic supramolecular polymer networks exhibiting both toughness and self-recovery. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1604951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Zhao, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Su, Z. Facile Synthesis of Dual-Network Polymer Hydrogels with Anti-Freezing, Highly Conductive, and Self-Healing Properties. Materials 2024, 17, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Gao, X.; Sun, K.; Xie, X.; Ma, G.; Zhou, X.; Lei, Z. Physically cross-linked dual-network hydrogel electrolyte with high self-healing behavior and mechanical strength for wide-temperature tolerant flexible supercapacitor. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 422, 130353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, Z.; Jia, L.; Wang, X.; He, T.; Wang, L.; Yao, G.; Xie, F. Soybean protein isolate-sodium alginate double network emulsion gels: Mechanism of formation and improved freeze-thaw stability. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 274, 133296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derkach, S.R.; Voron’ko, N.G.; Sokolan, N.I.; Kolotova, D.S.; Kuchina, Y.A. Interactions between gelatin and sodium alginate: UV and FTIR studies. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2020, 41, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarai, A.; Kasparkova, V.; Sedlacek, T.; Sáha, P. On the development and characterisation of crosslinked sodium alginate/gelatine hydrogels. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2013, 18, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohajer, S.; Rezaei, M.; Hosseini, S.F. Physico-chemical and microstructural properties of fish gelatin/agar bio-based blend films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavez-Granados, P.A.; Garcia-Contreras, R.; Reyes-Lopez, C.A.; Correa-Basurto, J.; Hernandez-Rojas, I.E.; Hernandez-Gomez, G.; Jurado, C.A.; Alhotan, A. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles with Roasted Green Tea: Applications in Alginate–Gelatin Hydrogels for Bone Regeneration. Gels 2024, 10, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, J.; Singh, B.; Vishavnath. Agar-gelatin-derived hydrogel-based controlled delivery devices for linuron herbicide to prevent environmental hazards. Environ. Chem. Ecotoxicol. 2024, 6, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Quan, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Tang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Qiang, X. Dual-network design to enhance the properties of agar aerogel adsorbent by incorporating in situ ion cross-linked alginate. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa-Enriquez, C.E.; Rodríguez-Félix, F.; Ruiz-Cruz, S.; Castro-Enriquez, D.D.; Gonzalez-Rios, H.; Perez-Alvarez, J.Á.; Madera-Santana, T.J.; Burruel-Ibarra, S.E.; Tapia-Hernández, J.A.; Estrella-Osuna, D.E. Edible Coating of Sodium Alginate With Gelatin Nanoparticles and Pitaya Extract (Stenocereus thurberi): Physicochemical and Antioxidant Properties. J. Food Qual. 2025, 2025, 5756522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Lan, X.; Guan, X.; Luo, R.; Zhang, Q.; Ren, H.; Xu, Z.; Tang, J. Comparative study on the effects of chitosan, carrageenan, and sodium alginate on the film-forming properties of fish skin gelatin. LWT 2024, 199, 116111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Ran, F.; Li, C.; Hao, Z.; He, H.; Dai, L.; Wang, J.; Yang, W. A lignin silver nanoparticles/polyvinyl alcohol/sodium alginate hybrid hydrogel with potent mechanical properties and antibacterial activity. Gels 2024, 10, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Fan, M.; Deng, S.; Tao, N. Characterization and application in packaging grease of gelatin–sodium alginate edible films cross-linked by pullulan. Polymers 2022, 14, 3199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, P.; Etxabide, A.; Leceta, I.; Peñalba, M.; De la Caba, K. Extraction of agar from Gelidium sesquipedale (Rodhopyta) and surface characterization of agar based films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Zhang, D.; Chen, X.; Liu, M. Self-cross-linked oxidized sodium alginate/gelatin/halloysite hydrogel as injectable, adhesive, antibacterial dressing for hemostasis. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 11739–11753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
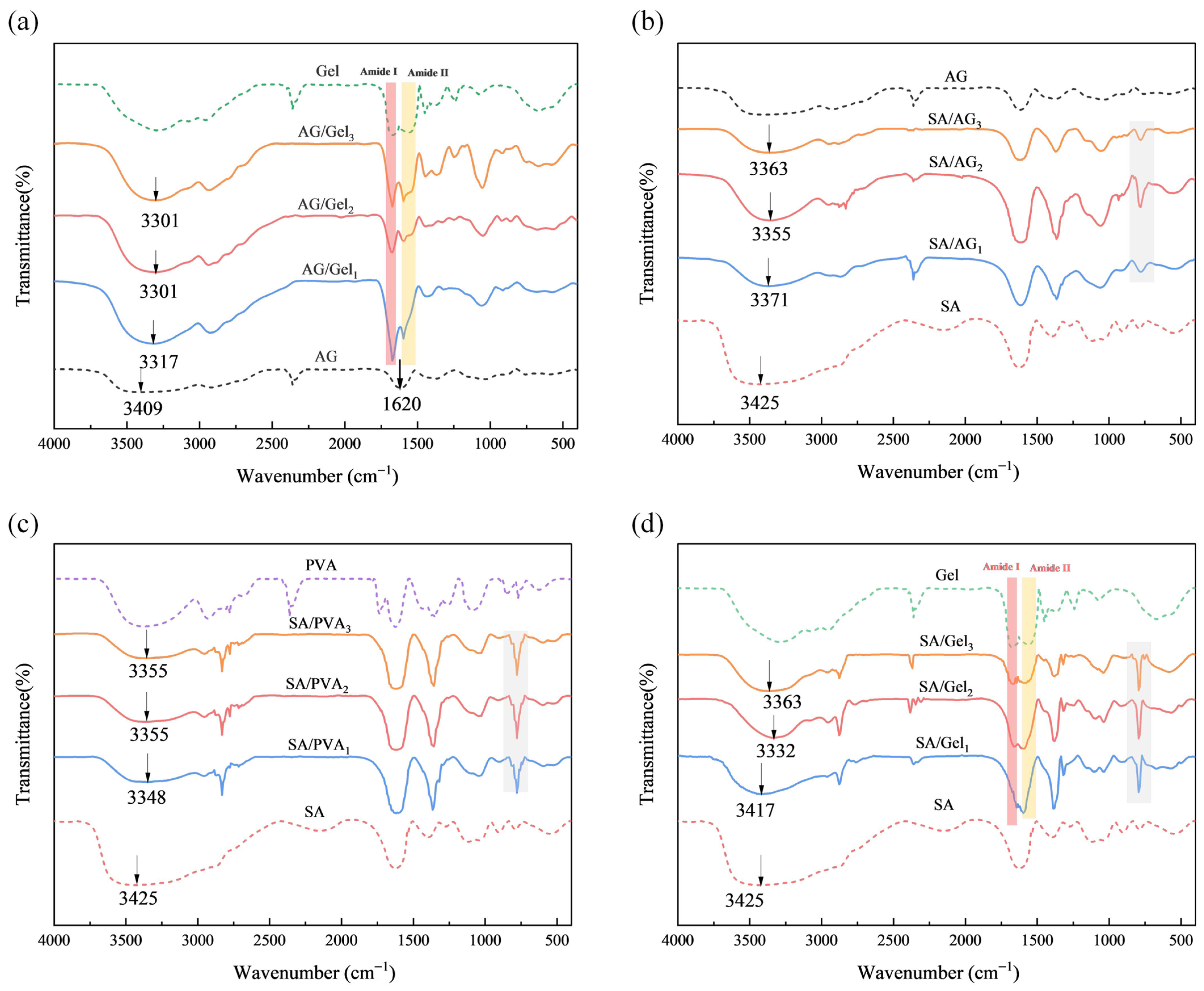
| Sample | -OH Peak Position (cm−1) | Shift Relative to SA (cm−1) |
|---|---|---|
| SA | 3425 | – |
| SA/AG1 | 3371 | 54 |
| SA/AG2 | 3355 | 70 |
| SA/AG3 | 3363 | 62 |
| SA/PVA1 | 3348 | 77 |
| SA/PVA2 | 3355 | 70 |
| SA/PVA3 | 3355 | 70 |
| SA/Gel1 | 3417 | 8 |
| SA/Gel2 | 3332 | 93 |
| SA/Gel3 | 3363 | 62 |
| Sample | AG | Gel | PVA | SA | AG/Gel | SA/AG | SA/PVA | SA/Gel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (min) | 8 | 18 | 6 | 16 | 16 | 20 | 10 | 20 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, N.; Liu, J.; Zhou, W.; He, Q.; Li, J.; Xiong, Y. Double-Network Hydrogels via Hybrid Strategies: Potential in Large-Scale Manufacturing for Colorimetric Indicator. Gels 2025, 11, 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090697
An N, Liu J, Zhou W, He Q, Li J, Xiong Y. Double-Network Hydrogels via Hybrid Strategies: Potential in Large-Scale Manufacturing for Colorimetric Indicator. Gels. 2025; 11(9):697. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090697
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Ningli, Jiwen Liu, Wentao Zhou, Qing He, Jianan Li, and Yali Xiong. 2025. "Double-Network Hydrogels via Hybrid Strategies: Potential in Large-Scale Manufacturing for Colorimetric Indicator" Gels 11, no. 9: 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090697
APA StyleAn, N., Liu, J., Zhou, W., He, Q., Li, J., & Xiong, Y. (2025). Double-Network Hydrogels via Hybrid Strategies: Potential in Large-Scale Manufacturing for Colorimetric Indicator. Gels, 11(9), 697. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090697






