Influence of Rice Physicochemical Properties on High-Quality Fresh Wet Rice Noodles: Amylose and Gel Consistency as Key Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. The Composition and Gel Consistency of Different Rice Varieties
2.1.1. The Composition of Different Rice Varieties
2.1.2. Gel Consistency of the Rice Varieties
2.2. Structural Characteristics of Rice Starches from Different Rice Varieties
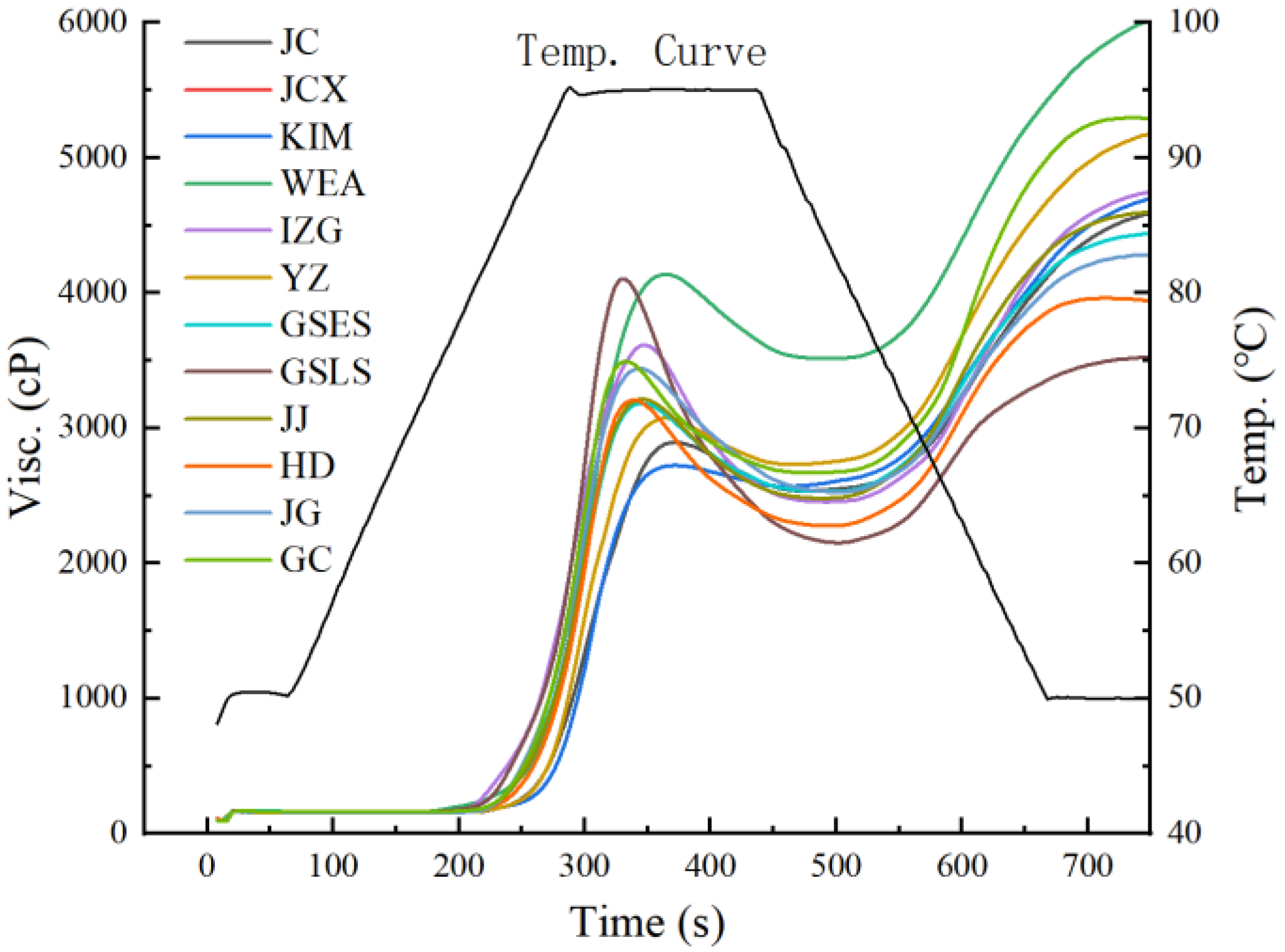
2.2.1. Pasting Properties
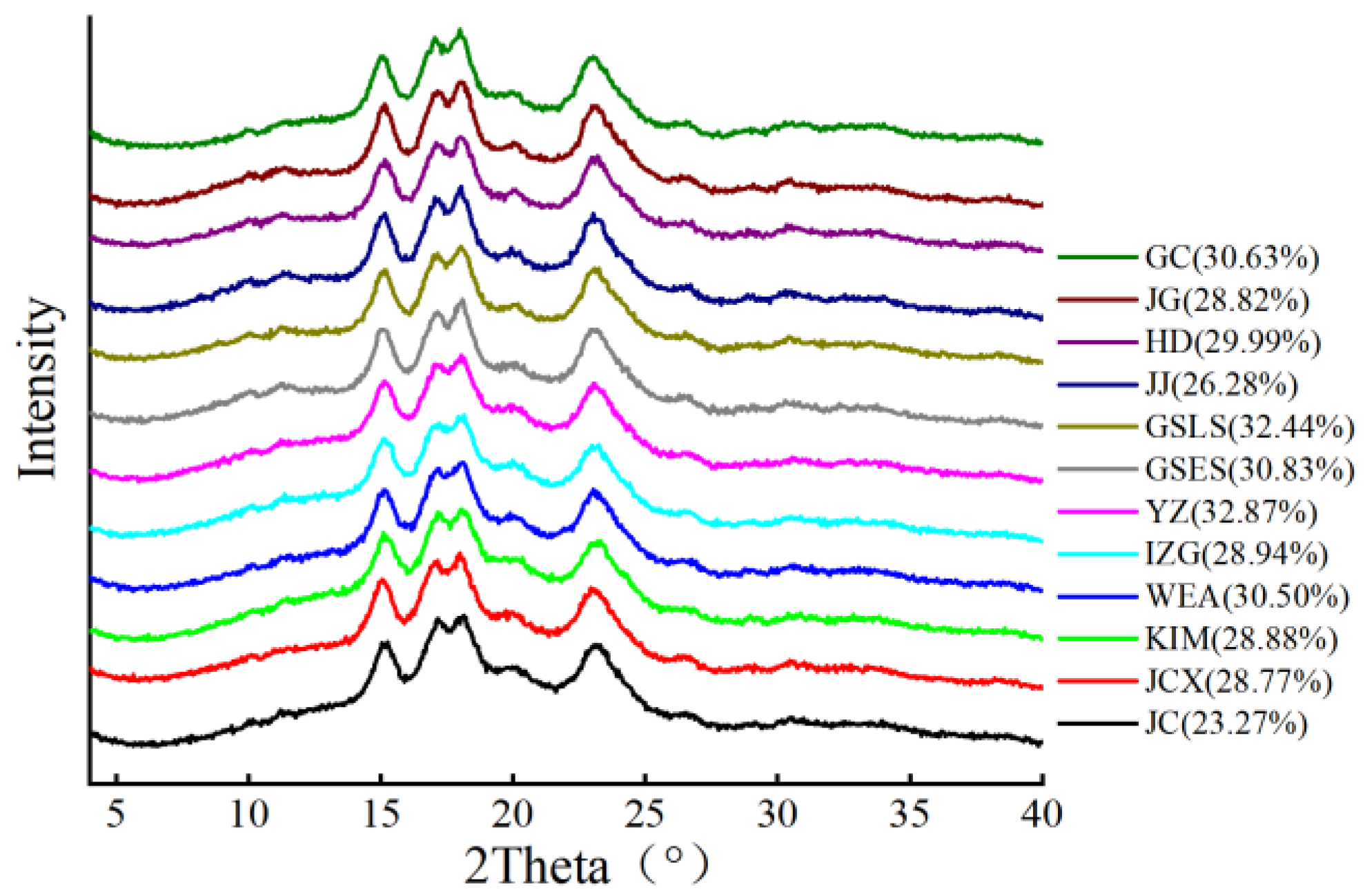
2.2.2. The Relative Crystallinity and Short-Range Order of Different Rice Starches
2.2.3. Thermal Properties of Different Rice Starches
2.3. Quality Evaluation of FWRNs Prepared from Different Rice Varieties
2.3.1. Appearance and Cooking Loss Rate of FWRNs Prepared from Different Rice Varieties
2.3.2. Texture of FWRNs Prepared from Different Rice Varieties
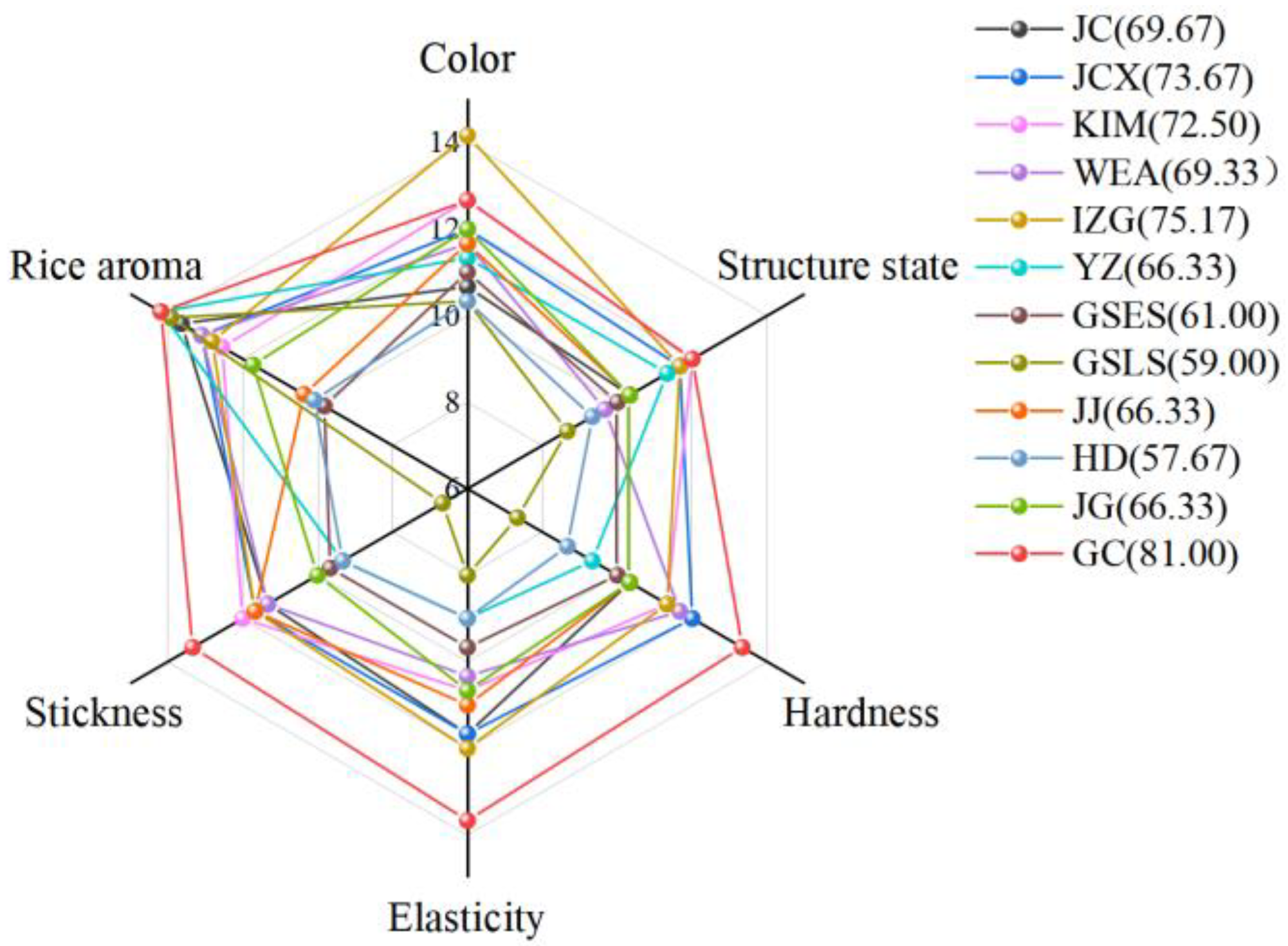
2.3.3. Sensory Evaluation of FWRNs Produced from Different Rice Varieties
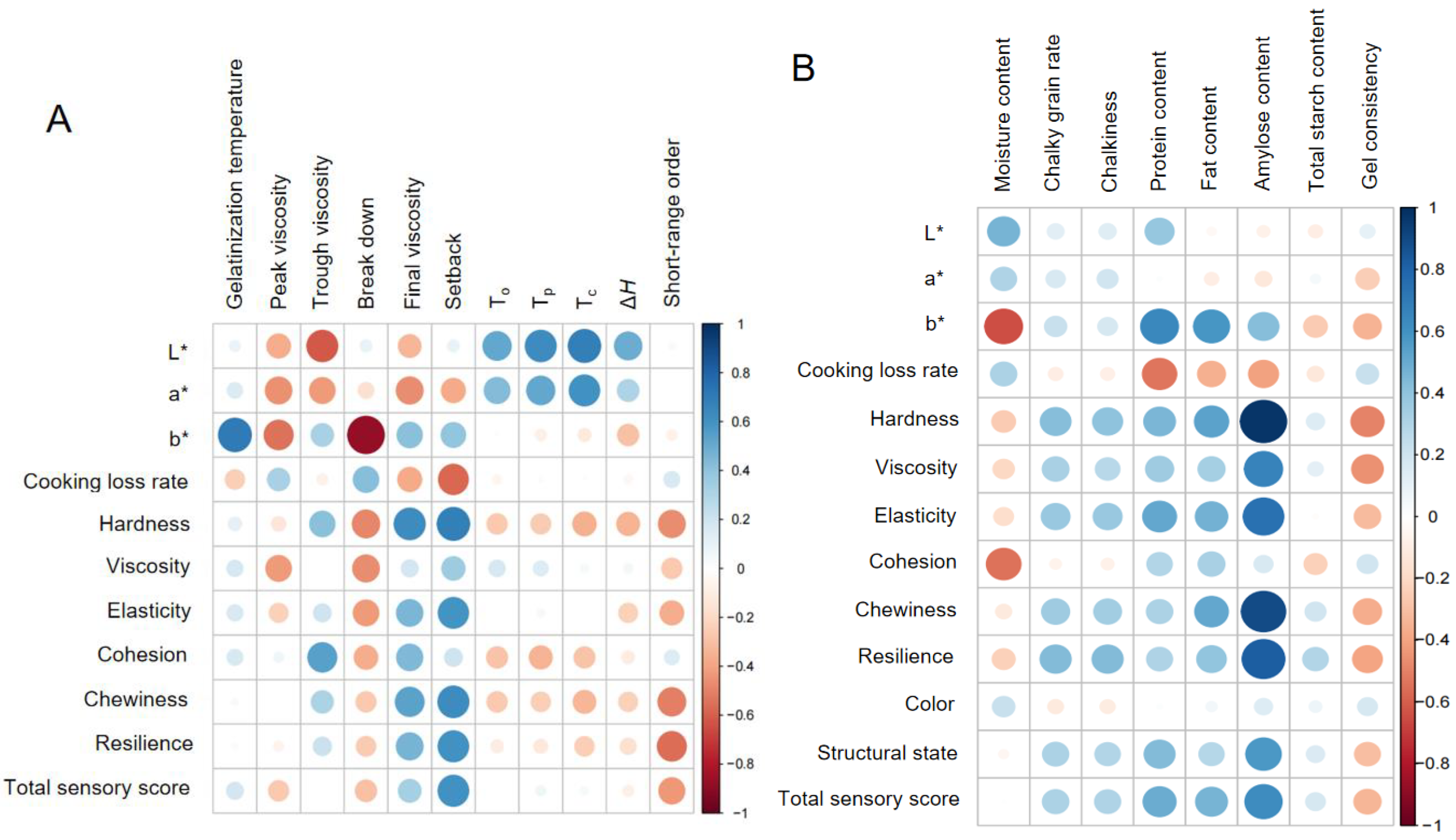
2.4. Correlation Analysis
2.4.1. Correlation of FWRN Quality and Rice Composition
2.4.2. Correlation of FWRN Quality and the Structural Properties of Rice Starch
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Measurements of Rice Quality
4.2.1. Chalkiness, Chalky Grain Rate, and Protein, Lipid and Starch Contents
4.2.2. Gel Consistency
4.3. The Characteristics of Rice Starch
4.3.1. Isolation of Rice Starch
4.3.2. Pasting Properties of Rice Starches
4.3.3. Thermal Properties of Rice Starches
4.3.4. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
4.3.5. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
4.4. Quality Assessment of FWRNs
4.4.1. Preparation of FWRNs
4.4.2. Color Analysis of FWRNs
4.4.3. Cooking Quality of FWRNs
4.4.4. Texture Determination of FWRNs
4.4.5. Sensory Evaluation
4.5. Data Processing and Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tian, Z.; Niu, Y.L.; Fan, D.L.; Sun, L.X.; Ficsher, G.; Zhong, H.L.; Deng, J.; Tubiello, F.N. Maintaining rice production while mitigating methane and nitrous oxide emissions from paddy fields in China: Evaluating tradeoffs by using coupled agricultural systems models. Agric. Syst. 2018, 159, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, Y.K.; Effarizah, M.E.; Cheng, L.H. Factors Influencing Rice Noodles Qualities. Food Rev. Int. 2020, 36, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, L.; Li, M.; Sun, Q. Inhibitory effects of sorbitol on the collapse and deterioration of gluten network in fresh noodles during storage. Food Chem. 2021, 44, 128638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Xiao, Z.W.; Chen, J.N.; Cao, F.B. Yield and quality of brown rice noodles processed from early-season rice grains. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hormdok, R.; Noomborm, A. Hydrothermal treatments of rice starch for improvement of rice noodle quality. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 1723–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.J.; Wang, B.J. Analysis on Quality Indicators Influencing Rice Noodle Quality. Qual. Saf. Agro-Prod. 2020, 3, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.G.Z.; Xiao, H.Q.; Lin, W.H.; Li, H.S.; Qin, S. The relationship between characteristics of rice raw material and quality of rice noodle. Cereal Feed. Ind. 2005, 9, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M.; Fitzgerald, M.A. Proteins in rice grains influence cooking properties. J. Cereal Sci. 2002, 36, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cham, S.; Suwannaporn, P. Effect of hydrothermal treatment of rice flour on various rice noodles quality. J. Cereal Sci. 2010, 51, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadan, R.S.; Bryant, R.I.; Miller, J.A. Effects of milling on functional properties of rice flour. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, E151–E154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Fang, Y.; Huang, Y.L.; Feng, C.; Yang, L.; Zhou, G.X.; Zhang, C.H. Analysis of the genotype and environment interactions as well as the correlation research of main taste quality in rice. China Rice 2020, 26, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.L.; Zhao, Z.M.; Wu, J.H.; Wu, Q.T.; Chen, J.D.; Ning, Z.X. Effect of ageing time of paddy on quality characteristics of rice noodles. J. South. China Univ. Technol. 2010, 38, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, R.P.; Fitzgerald, M.A. Genetic diversity of rice grain quality. Genet. Divers. Plants 2012, 10, 35119. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Kaur, L.; Sodhi, N.S.; Kaur, J. Physicochemical, cooking and textural properties of milled rice from different Indian rice cultivars. Food Chem. 2005, 90, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Vasanthan, T.; Hoover, R.; Rossnagel, B.G. Starch from hull-less barley: IV. Morphological and structural changes in waxy, normal and high-amylose starch granules during heating. Food Res. Int. 2004, 37, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterschoot, J.; Gomand, S.V.; Willebrords, J.K.; Fierens, E.; Delcour, J.A. Pasting properties of blends of potato, rice and maize starches. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 41, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Yang, X.; Li, C. Combined effects of starch fine molecular structures and storage temperatures on long-term rice amylopectin retrogradation property. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 201, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marti, A.; Pagani, M.A.; Seetharaman, K. Understanding starch organisation in gluten-free pasta from rice flour. Carbohyd. Polym. 2011, 84, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sárka, E.; Dvorácek, V. Waxy starch as a perspective raw material (a review). Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 69, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevenou, O.; Hill, S.E.; Farhat, I.A.; Mitchell, J.R. Organisation of the external region of the starch granule as determined by infrared spectroscopy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2002, 31, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Soest, J.J.G.; Tournois, H.; de Wit, D.; Vliegenthart, J.F.G. Short-range structure in (partially) crystalline potato starch determined with attenuated total reflectance Fourier-transform IR spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Res. 1995, 279, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.J.; Li, P.Y.; Yu, J.L.; Guo, P.; Wang, S. Multi-scale structures and functional properties of starches from hybrid, and waxy rice. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 102, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogracheva, T.Y.; Meares, C.; Hedley, C.L. The effect of heating on the thermodynamic characteristics of potato starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 63, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, C.; Gidley, M.J. Loss of crystalline and molecular order during starch gelatinisation: Origin of the enthalpic transition. Carbohydr. Res. 1992, 227, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.X. Asian noodles: History, classification, raw materials, and processing. Food Res. Int. 2008, 41, 888–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Niu, L.; Wu, L.; Xiao, J. The improved rehydration property, flavor characteristics and nutritional quality of freeze-dried instant rice supplemented with tea powder products. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 96, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, C.; Copeland, L.; Niu, Q.; Wang, S. Starch retrogradation: A comprehensive review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Safety 2019, 18, 1685–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wang, R.; Yoo, S.H.; Lim, S.T. Water effect on the interaction between amylose and amylopectin during retrogradation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 86, 1671–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Q.; Yi, C. Effect of Soy Protein Isolate on Textural Properties, Cooking Properties and Flavor of Whole-Grain Flat Rice Noodles. Foods 2021, 10, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, G.; Calle, M.L.; Serrat, C.; Curia, A. Number of consumers necessary for shelf life estimations based on survival analysis statistics. Food Qual. Prefer. 2007, 18, 771–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, K.; Yu, W.W.; Prakash, S.; Gilbert, R.G. High-amylose rice: Starch molecular structural features controlling cooked rice texture and preference. Carbohyd. Polym. 2019, 219, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCleary, B.V.; Charmier, L.M.J.; McKie, V.A. Measurement of Starch: Critical Evaluation of Current Methodology. Starch Starke 2019, 71, 1800146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Hu, Y.M.; Gu, F.T.; Gong, B. Causal relations among starch fine molecular structure, lamellar/crystalline structure and digestion kinetics of native rice starch. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.T.; Zhu, F. Physicochemical properties of quinoa flour as affected by starch interactions. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 1560–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Luo, X.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Effect of annealing on the physico-chemical properties of rice starch and the quality of rice noodles. J. Cereal Sci. 2018, 84, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swiader, K.; Marczewska, M. Trends of Using Sensory Evaluation in New Product Development in the Food Industry in Countries That Belong to the EIT Regional Innovation Scheme. Foods 2021, 10, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivek, K.; Subbarao, K.V.; Routray, W.; Kamini, N.R.; Dash, K.K. Application of Fuzzy Logic in Sensory Evaluation of Food Products: A Comprehensive Study. Food Bioprocess. Tech. 2020, 13, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, D.; Zeng, X. Intelligent Sensory Evaluation: Methodologies and Applications; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, W.Y.; Wu, W.G.; Liao, L.Y.; Ni, T.; Zhang, Y. Quality evaluation of and raw material selection for wet rice noodles. Shipin Kexue Food Sci. 2020, 41, 74–79. [Google Scholar]
| Samples 2 | Moisture Content/% | Chalky Grain Rates/% | Chalkiness /% | Protein Content/% | Lipid Content /% | Amylose Content/% | Total Starch Content/% | Gel Consistency |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JC | 11.48 ± 0.04 hi | 54.33 ± 1.35 cd | 22.97 ± 0.21 c | 7.46 ± 0.14 cd | 0.26 ± 0.04 ef | 22.61 ± 0.61 f | 86.07 ± 1.35 bcd | 36.57 ± 3.87 hi |
| JCX | 11.51 ± 0.06 hi | 31.57 ± 0.57 fg | 10.43 ± 0.40 g | 7.62 ± 0.23 c | 0.84 ± 0.03 a | 24.09 ± 0.02 e | 84.09 ± 1.94 defg | 37.77 ± 4.04 ghi |
| KIM | 12.19 ± 0.27 e | 82.53 ± 0.91 a | 35.43 ± 0.65 a | 6.68 ± 0.16 g | 0.31 ± 0.04 def | 27.66 ± 0.46 a | 90.44 ± 1.70 a | 33.97 ± 2.80 i |
| WEA | 11.72 ± 0.11 fg | 17.33 ± 1.40 h | 5.63 ± 0.51 h | 7.17 ± 0.07 f | 0.78 ± 0.04 ab | 23.81 ± 0.06 ef | 84.33 ± 1.19 cdefg | 66.83 ± 3.72 b |
| IZG | 12.56 ± 0.10 d | 14.73 ± 2.39 h | 4.13 ± 0.64 h | 7.20 ± 0.03 ef | 0.35 ± 0.07 cde | 25.58 ± 0.96 cd | 83.43 ± 0.37 defgh | 60.37 ± 3.01 d |
| YZ | 11.61 ± 0.04 gh | 52.43 ± 1.14 de | 17.57 ± 0.95 de | 8.98 ± 0.13 a | 0.45 ± 0.01 c | 22.62 ± 0.30 g | 80.83 ± 0.28 h | 60.60 ± 3.30 cd |
| GSES | 12.91 ± 0.05 b | 48.63 ± 12.43 de | 19.17 ± 5.36 d | 7.14 ± 0.08 f | 0.32 ± 0.16 def | 24.05 ± 1.43 e | 84.52 ± 1.14 cdefg | 41.40 ± 3.82 fgh |
| GSLS | 12.74 ± 0.04 c | 15.57 ± 0.40 h | 5.03 ± 0.06 h | 5.48 ± 0.05 i | 0.10 ± 0.02 gh | 14.61 ± 0.21 j | 84.42 ± 1.41 cdefg | 77.33 ± 1.20 a |
| JJ | 12.54 ± 0.06 d | 43.37 ± 14.72 e | 15.03 ± 5.65 ef | 7.19 ± 0.13 f | 0.30 ± 0.03 ef | 21.77 ± 1.41 gh | 85.84 ± 0.42 bcde | 48.10 ± 3.17 e |
| HD | 12.60 ± 0.03 cd | 15.73 ± 0.81 h | 4.20 ± 0.26 h | 6.27 ± 0.08 h | 0.08 ± 0.01 h | 16.60 ± 0.33 i | 85.03 ± 1.77 bcdef | 38.13 ± 3.56 ghi |
| JG | 12.17 ± 0.07 e | 61.97 ± 5.36 bc | 27.23 ± 3.21 b | 7.40 ± 0.07 de | 0.25 ± 0.11 ef | 21.05 ± 0.77 h | 84.77 ± 1.63 bcdefg | 65.63 ± 3.41 bc |
| GC | 13.49 ± 0.03 a | 81.87 ± 0.97 a | 34.53 ± 0.83 a | 8.31 ± 0.04 b | 0.31 ± 0.02 def | 26.81 ± 0.04 ab | 87.06 ± 0.40 bc | 35.87 ± 2.44 i |
| Samples 2 | Pasting Temperature (°C) | Peak Viscosity (cP) | Trough Viscosity (cP) | Final Viscosity (cP) | Breakdown (cP) | Set Back (cP) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JC | 86.22 ± 0.55 c | 2889.33 ± 35.74 g | 2528.67 ± 41.14 c | 4614.00 ± 39.13 e | 360.67 ± 5.69 hi | 2085.33 ± 30.92 e |
| JCX | 88.37 ± 0.03 a | 2693.33 ± 27.79 h | 2538.00 ± 30.81 c | 4645.00 ± 50.57 de | 155.33 ± 7.09 j | 2107.00 ± 41.39 e |
| KIM | 80.52 ± 0.42 i | 3530.00 ± 73.18 cd | 2387.33 ± 58.48 de | 4737.67 ± 57.59 d | 1142.67 ± 16.44 bc | 2350.33 ± 7.51 d |
| WEA | 83.28 ± 0.46 e | 4104.33 ± 68.89 a | 3332.67 ± 93.40 a | 5884.67 ± 64.28 a | 771.67 ± 91.70 f | 2552.00 ± 53.56 b |
| IZG | 79.52 ± 0.08 j | 3603.67 ± 51.62 bc | 2456.00 ± 44.51 cd | 4738.00 ± 36.66 d | 1147.67 ± 13.01 b | 2282.00 ± 11.53 d |
| YZ | 86.97 ± 0.51 bc | 3081.00 ± 14.42 f | 2726.67 ± 11.02 b | 5181.33 ± 79.25 c | 354.33 ± 25.32 hi | 2454.67 ± 89.67 c |
| GSES | 83.18 ± 0.51 ef | 3175.33 ± 7.57 e | 2511.67 ± 24.58 c | 4433.33 ± 5.13 f | 663.67 ± 19.35 fg | 1921.67 ± 22.81 f |
| GSLS | 81.37 ± 0.55 h | 4115.00 ± 12.29 a | 2192.67 ± 48.26 f | 3551.33 ± 36.36 i | 1922.33 ± 50.57 a | 1358.67 ± 13.87 i |
| JJ | 82.93 ± 0.49 efg | 3209.00 ± 11.27 e | 2481.67 ± 12.06 cd | 4576.67 ± 38.89 e | 727.33 ± 4.51 f | 2095.00 ± 27.73 e |
| HD | 84.33 ± 0.06 d | 3222.33 ± 30.29 e | 2303.67 ± 36.14 e | 3978.33 ± 46.69 h | 918.67 ± 19.69 e | 1674.67 ± 11.02 h |
| JG | 82.17 ± 0.42 g | 3454.33 ± 24.21 d | 2502.00 ± 35.79 c | 4285.33 ± 17.04 g | 952.33 ± 31.18 de | 1783.33 ± 25.54 g |
| GC | 82.45 ± 0.43 fg | 3643.67 ± 132.30 b | 2700.67 ± 76.58 b | 5383.67 ± 84.39 b | 943.00 ± 141.59 de | 2683.00 ± 75.03 a |
| Sample 2 | To (°C) | Tp (°C) | Tc (°C) | ΔH (J/g) | Short-Range Order (1045 cm−1/1022 cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JC | 74.30 ± 0.22 a | 78.44 ± 0.34 d | 84.29 ± 0.36 d | 8.74 ± 0.26 i | 3.72 ± 0.02 d |
| JCX | 65.16 ± 0.42 i | 69.78 ± 0.52 j | 74.35 ± 0.32 i | 9.98 ± 0.22 g | 4.14 ± 0.04 a |
| KIM | 73.41 ± 0.46 d | 77.50 ± 0.44 f | 82.52 ± 0.24 e | 12.52 ± 0.30 b | 2.13 ± 0.10 h |
| WEA | 64.51 ± 0.14 k | 69.22 ± 0.09 j | 74.62 ± 0.14 i | 8.55 ± 0.27 ij | 3.69 ± 0.02 d |
| IZG | 71.21 ± 0.04 f | 76.22 ± 0.09 g | 81.39 ± 0.26 f | 11.66 ± 0.35 bcde | 3.81 ± 0.06 cd |
| YZ | 73.72 ± 0.21 cd | 77.95 ± 0.25 e | 84.34 ± 0.13 d | 12.25 ± 1.01 bc | 3.86 ± 0.29 bcd |
| GSES | 73.37 ± 0.05 d | 79.11 ± 0.10 a | 86.29 ± 0.28 b | 11.11 ± 0.32 e | 3.97 ± 0.14 abc |
| GSLS | 69.85 ± 0.32 g | 74.25 ± 0.42 h | 77.15 ± 0.32 g | 8.98 ± 0.22 i | 4.06 ± 0.14 ab |
| JJ | 74.19 ± 0.12 ab | 79.00 ± 0.17 abc | 85.31 ± 0.14 c | 11.63 ± 0.28 bcde | 3.73 ± 0.10 cd |
| HD | 67.25 ± 0.32 h | 73.15 ± 0.42 i | 76.85 ± 0.52 h | 9.25 ± 0.22 h | 3.68 ± 0.16 d |
| JG | 73.71 ± 0.16 d | 78.72 ± 0.19 bcd | 87.57 ± 0.52 a | 14.65 ± 0.24 a | 2.51 ± 0.10 f |
| GC | 72.31 ± 0.32 e | 78.67 ± 0.29 cd | 85.22 ± 0.40 c | 10.15 ± 0.56 f | 2.14 ± 1.17 h |
| Samples 2 | L * | a * | b * | Brown Index | Cooking Loss Rate/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JC | 69.55 ± 0.32 de | 2.57 ± 0.02 cd | −0.80 ± 0.08 b | 1.52 ± 0.10 a | 0.12 ± 0.01 efg |
| JCX | 70.93 ± 0.87 cd | 2.56 ± 0.01 cd | −1.48 ± 0.04 cd | 0.56 ± 0.05 b | 0.12 ± 0.03 efg |
| KIM | 69.28 ± 1.14 e | 2.24 ± 0.07 hi | −2.38 ± 0.02 g | −0.98 ± 0.13 e | 0.11 ± 0.01 efg |
| WAA | 66.52 ± 1.25 fg | 2.17 ± 0.10 i | −1.27 ± 0.03 c | 0.48 ± 0.10 b | 0.10 ± 0.01 fg |
| IZG | 73.97 ± 1.17 ab | 2.30 ± 0.04 ghi | −2.36 ± 0.20 g | −0.84 ± 0.08 e | 0.13 ± 0.01 defg |
| YZ | 75.04 ± 0.16 a | 2.16 ± 0.05 i | −0.49 ± 0.25 ab | 1.42 ± 0.15 a | 0.07 ± 0.01 g |
| GSES | 73.39 ± 0.96 b | 3.17 ± 0.03 a | −1.90 ± 0.22 ef | 0.57 ± 0.13 b | 0.34 ± 0.20 b |
| GSLS | 71.75 ± 0.21 c | 2.35 ± 0.07 fgh | −3.54 ± 0.23 h | −2.36 ± 0.10 f | 0.49 ± 0.01 a |
| JJ | 71.65 ± 0.20 c | 2.64 ± 0.01 c | −1.75 ± 0.08 de | 0.27 ± 0.05 c | 0.19 ± 0.01 cdefg |
| HD | 67.69 ± 0.43 f | 2.53 ± 0.20 cde | −2.12 ± 0.42 fg | −0.34 ± 0.03 d | 0.14 ± 0.01 defg |
| JG | 71.59 ± 0.61 c | 2.80 ± 0.02 b | −2.32 ± 0.13 g | −0.32 ± 0.08 d | 0.20 ± 0.01 cdefg |
| GC | 74.59 ± 0.11 ab | 2.46 ± 0.03 def | −2.17 ± 0.21 fg | −0.44 ± 0.09 d | 0.18 ± 0.01 cdefg |
| Samples 2 | Hardness (g) | Stickiness (g·s) | Elasticity | Cohesion | Chewiness | Resilience |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JC | 2827.26 ± 72.40 e | −629.30 ± 226.22 bcd | 0.77 ± 0.01 a | 0.64 ± 0.06 bcdef | 2477.61 ± 118.83 hi | 0.16 ± 0.01 e |
| JCX | 3265.86 ± 9.00 cd | −635.03 ± 162.09 bcd | 0.74 ± 0.01 bcd | 0.73 ± 0.02 ab | 3527.59 ± 49.24 de | 0.17 ± 0.01 de |
| KIM | 3936.65 ± 102.35 a | −260.51 ± 15.46 a | 0.70 ± 0.01 cdef | 0.56 ± 0.07 ef | 4372.86 ± 418.35 a | 0.26 ± 0.02 a |
| WAA | 3149.90 ± 57.82 d | −985.69 ± 123.37 f | 0.72 ± 0.03 bcde | 0.73 ± 0.01 ab | 3448.54 ± 202.00 de | 0.17 ± 0.01 de |
| IZG | 3441.20 ± 134.44 b | −226.50 ± 55.58 a | 0.78 ± 0.02 ab | 0.58 ± 0.02 def | 4060.36 ± 191.27 ab | 0.19 ± 0.01 cd |
| YZ | 2822.92 ± 69.54 e | −604.63 ± 271.70 bcd | 0.66 ± 0.05 ef | 0.72 ± 0.06 ab | 2355.51 ± 129.30 hi | 0.17 ± 0.01 de |
| GSES | 3280.77 ± 40.58 cd | −601.95 ± 152.73 bcd | 0.69 ± 0.05 cdef | 0.62 ± 0.01 cdef | 2897.94 ± 50.58 fg | 0.16 ± 0.02 e |
| GSLS | 1237.08 ± 69.64 h | −1315.54 ± 56.51 g | 0.57 ± 0.02 g | 0.55 ± 0.01 f | 1785.83 ± 217.83 j | 0.11 ± 0.02 f |
| JJ | 2274.57 ± 49.25 f | −365.19 ± 125.47 ab | 0.65 ± 0.01 f | 0.66 ± 0.02 abcde | 2456.11 ± 268.10 hi | 0.13 ± 0.01 f |
| HD | 1492.42 ± 32.83 g | −1069.32 ± 193.30 fg | 0.55 ± 0.03 g | 0.55 ± 0.01 f | 1106.90 ± 217.35 k | 0.10 ± 0.01 f |
| JG | 2181.22 ± 166.16 f | −951.07 ± 45.49 ef | 0.68 ± 0.05 def | 0.73 ± 0.07 ab | 2231.17 ± 162.73 i | 0.11 ± 0.01 f |
| GC | 3812.54 ± 109.39 a | −794.75 ± 270.44 cdef | 0.81 ± 0.03 a | 0.56 ± 0.11 ef | 4341.10 ± 111.07 a | 0.21 ± 0.03 bc |
| Level 1 Indicators (Scores) | Secondary Indicators (Scores) | Specific Characteristic Description (Scores) |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance (30 points) | Color (15 points) | Uniform color, normal off-white, glossy surface (11–15 points) |
| Basically, uniform color, slightly yellowish skin color, glossy surface (6–10 points) | ||
| Uneven color, yellowish skin color, dull surface (1–5 points) | ||
| Structure (15 points) | Uniform and delicate cross-sectional structure, uniform thickness, smooth surface (11–15 points) | |
| Uniform cross-sectional structure, basically uniform thickness, smooth surface (6–10 points) | ||
| Granules in cross-sectional structure, uneven thickness, and rough surface (1–5 points) | ||
| Taste (50 points) | Hardness (15 points) | Moderately soft and hard (11–15 points) |
| Softer or harder (6–10 points) | ||
| Too soft or too hard (1–5 points) | ||
| Elasticity (15 points) | Chewy and elastic (11–15 points) | |
| Slightly chewy and generally elastic (6–10 points) | ||
| Poor chewiness and insufficient elasticity (1–5 points) | ||
| Viscosity (15 points) | Refreshing and not sticky (11–15 points) | |
| Refreshing and slightly sticky (6–10 points) | ||
| Not refreshing and sticky (1–5 points) | ||
| Flavor (20 points) | Rice aroma (20 points) | The rice aroma is strong and pure with no unpleasant odor (16–20 points) |
| The rice aroma is relatively light and pure with no unpleasant odor (11–15 points) | ||
| The rice aroma is average with a slight odor of raw noodles (6–10 points) | ||
| No rice aroma with sour or raw noodles odor (1–5 points) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, D.; Deng, Y.; Huang, Q.; Liu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhou, P.; Zhao, Z.; Zeng, J.; Liu, Y.; et al. Influence of Rice Physicochemical Properties on High-Quality Fresh Wet Rice Noodles: Amylose and Gel Consistency as Key Factors. Gels 2025, 11, 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090696
Zhao D, Deng Y, Huang Q, Liu G, Zhang Y, Tang X, Zhou P, Zhao Z, Zeng J, Liu Y, et al. Influence of Rice Physicochemical Properties on High-Quality Fresh Wet Rice Noodles: Amylose and Gel Consistency as Key Factors. Gels. 2025; 11(9):696. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090696
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Dezhi, Yuanyuan Deng, Qi Huang, Guang Liu, Yan Zhang, Xiaojun Tang, Pengfei Zhou, Zhihao Zhao, Jiarui Zeng, Ying Liu, and et al. 2025. "Influence of Rice Physicochemical Properties on High-Quality Fresh Wet Rice Noodles: Amylose and Gel Consistency as Key Factors" Gels 11, no. 9: 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090696
APA StyleZhao, D., Deng, Y., Huang, Q., Liu, G., Zhang, Y., Tang, X., Zhou, P., Zhao, Z., Zeng, J., Liu, Y., & Li, P. (2025). Influence of Rice Physicochemical Properties on High-Quality Fresh Wet Rice Noodles: Amylose and Gel Consistency as Key Factors. Gels, 11(9), 696. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11090696








