Effect of Chitosan Properties and Dissolution State on Solution Rheology and Film Performance in Triboelectric Nanogenerators
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effect of Chitosan Molecular Weight
2.2. Effect of Chitosan Concentration
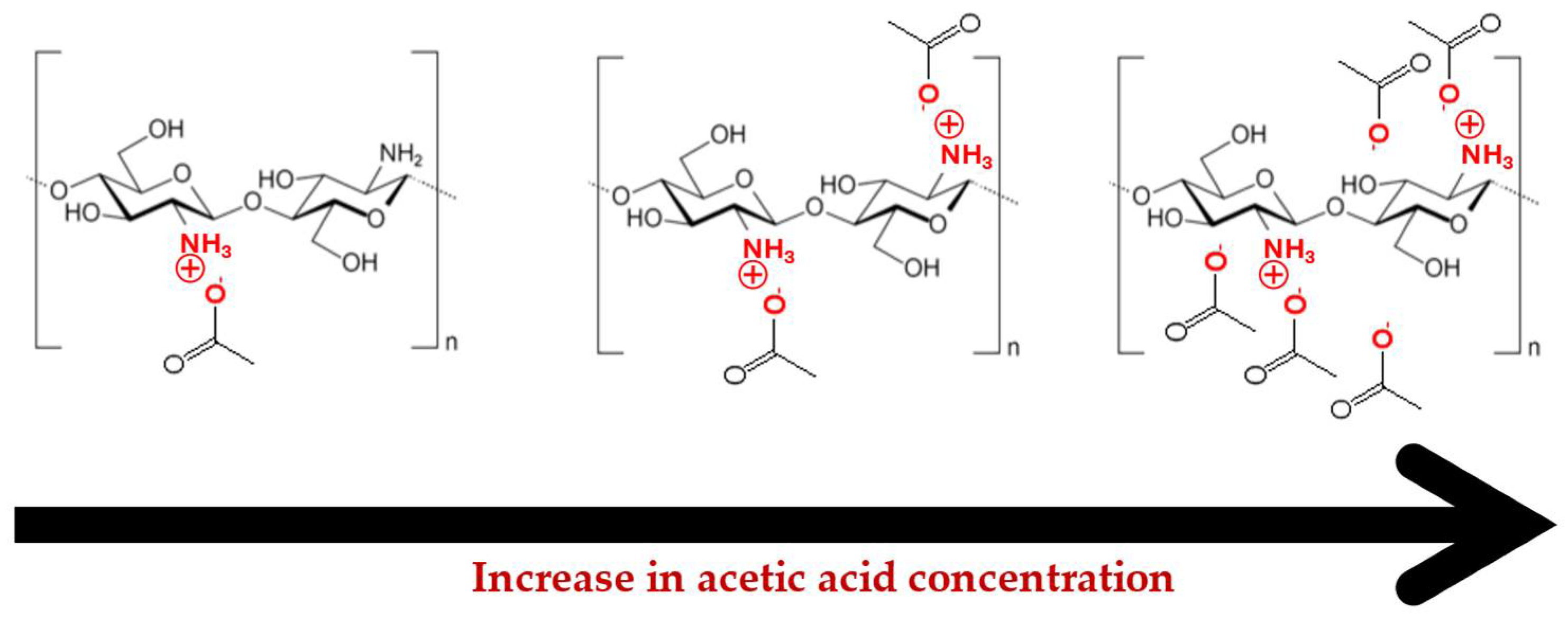
2.3. Effect of Acetic Acid Concentration
2.4. Deacetylation Effect
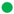
2.5. Oven Drying Time Effect
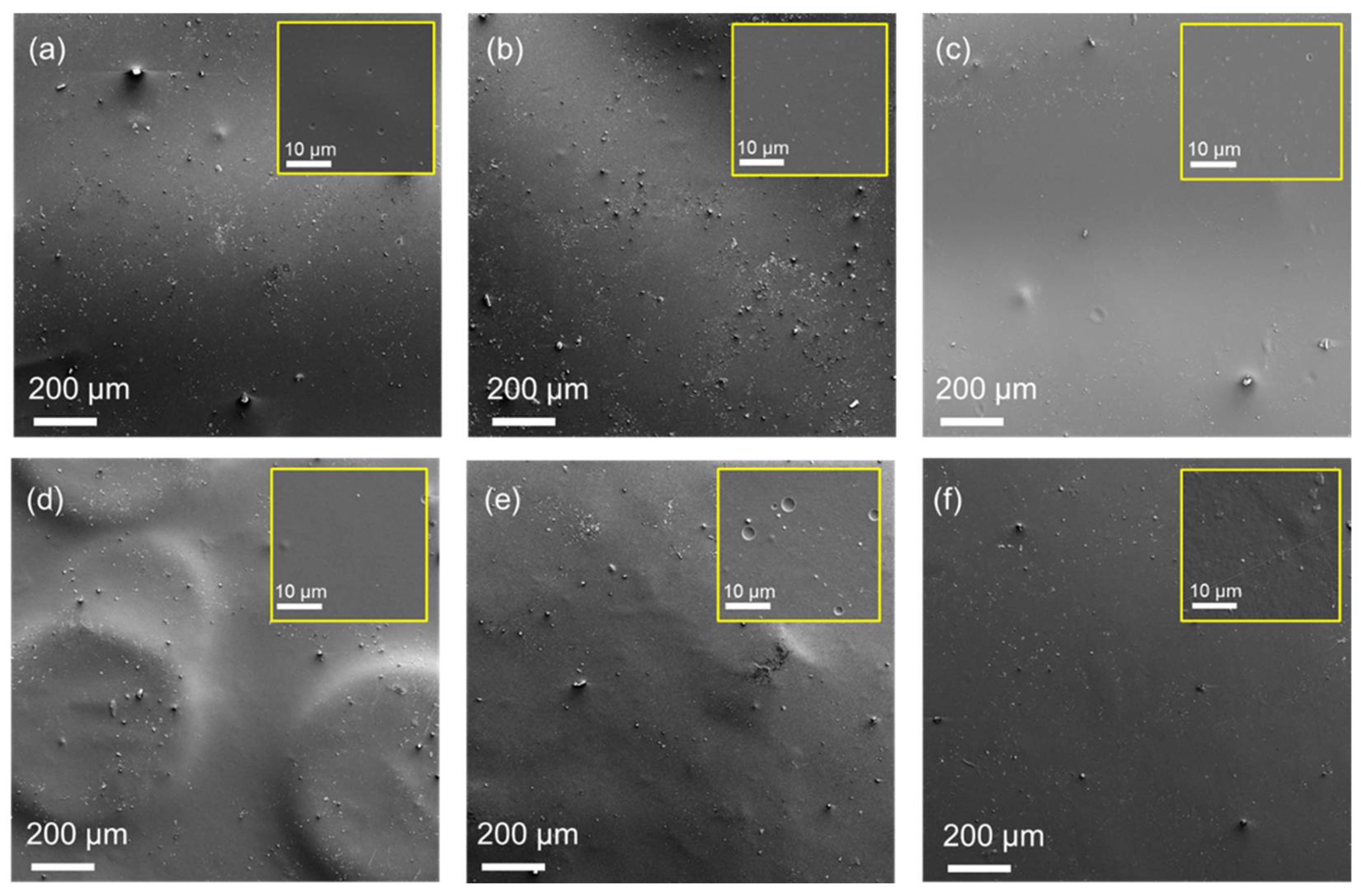
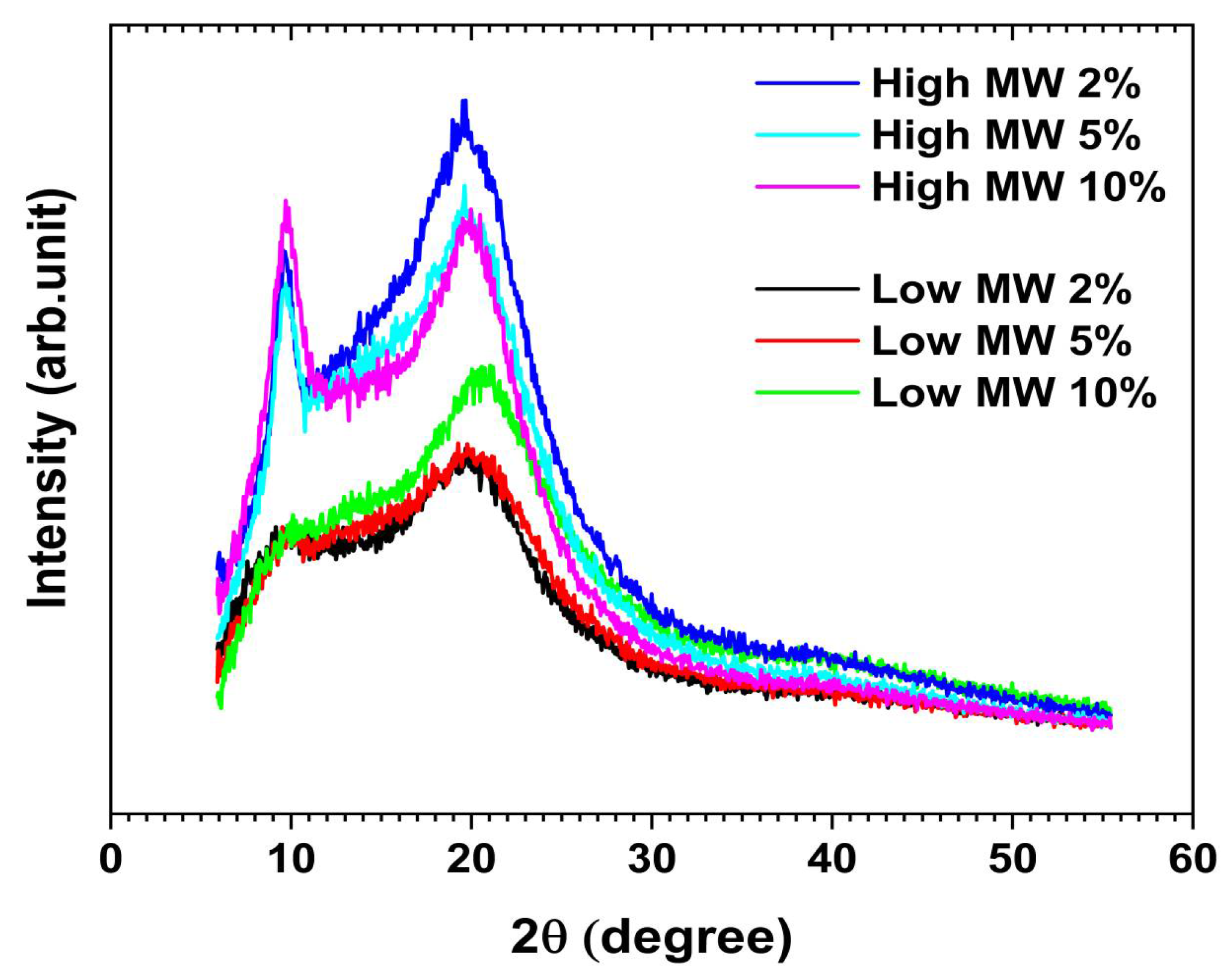
2.6. Characterisation of Chitosan Films
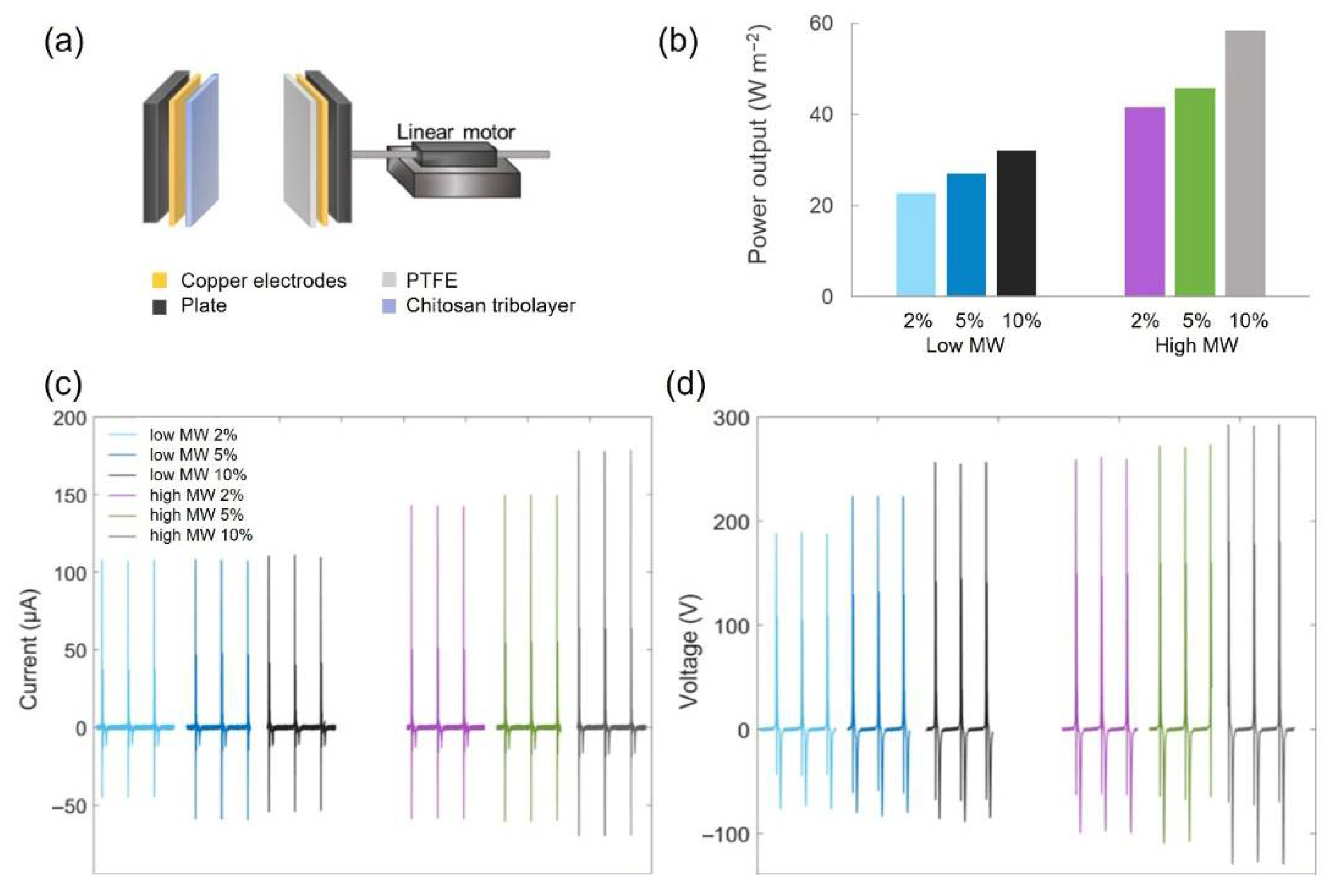
2.7. TENG Performance of the Chitosan Films
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Methods
4.2.1. Preparation and Characterisation of Highly Deacetylated Chitosan
4.2.2. Preparation of Chitosan Solutions and Films
4.2.3. Rheology of Chitosan Solutions
4.2.4. Characterisation of Chitosan Films
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography for the Determination of Residual Acetic Acid in Films
Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
X-Ray Diffraction Analysis
Atomic Force Microscopy
TENG Testing
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, R.; Hummelgård, M.; Örtegren, J.; Andersson, H.; Olsen, M.; Chen, D.; Li, J.; Eivazi, A.; Dahlström, C.; Norgren, M.; et al. Triboelectric nanogenerators with ultrahigh current density enhanced by hydrogen bonding between nylon and graphene oxide. Nano Energy 2023, 115, 108737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Sun, E.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, T.; Meng, S.; Ma, Z.; Shoaib, M.; Ur Rehman, H.; Cao, X.; Wang, N. Biopolymer Materials in Triboelectric Nanogenerators: A Review. Polymers 2024, 16, 1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Dahlström, C.; Zou, H.; Jonzon, J.; Hummelgård, M.; Örtegren, J.; Blomquist, N.; Yang, Y.; Andersson, H.; Olsen, M.; et al. Cellulose-Based Fully Green Triboelectric Nanogenerators with Output Power Density of 300 W m−2. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2002824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Tong, W.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y. Fully degradable chitosan–based triboelectric nanogenerators applying in disposable medical products for information transfer. Nano Energy 2023, 117, 108876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlieghere, F.; Vermeulen, A.; Debevere, J. Chitosan: Antimicrobial activity, interactions with food components and applicability as a coating on fruit and vegetables. Food Microbiol. 2004, 21, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- No, H.K.; Park, N.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Meyers, S.P. Antibacterial activity of chitosans and chitosan oligomers with different molecular weights. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2002, 74, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Romero, M.; Murphy, T.; Morris, M.; Cummins, E.; Kerry, J. Antimicrobial activity of chitosan, organic acids and nano-sized solubilisates for potential use in smart antimicrobially-active packaging for potential food applications. Food Control 2013, 34, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, P.; Tripathi, S.; Mehrotra, G.; Dutta, J. Perspectives for chitosan based antimicrobial films in food applications. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.N.R. A review of chitin and chitosan applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2000, 46, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melro, E.; Antunes, F.E.; da Silva, G.J.; Cruz, I.; Ramos, P.E.; Carvalho, F.; Alves, L. Chitosan Films in Food Applications. Tuning Film Properties by Changing Acidic Dissolution Conditions. Polymers 2021, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsabee, M.Z.; Abdou, E.S. Chitosan based edible films and coatings: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 1819–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, C.; Li, H.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Du, Y. Water-solubility of chitosan and its antimicrobial activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 63, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritthidej, G.C. Chapter 3—Nasal Delivery of Peptides and Proteins with Chitosan and Related Mucoadhesive Polymers. In Peptide and Protein Delivery; Van Der Walle, C., Ed.; Academic Press: Boston, MA, USA, 2011; pp. 47–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanazzi, G.; Gabler, F.M.; Margosan, D.; Mackey, B.E.; Smilanick, J.L. Effect of chitosan dissolved in different acids on its ability to control postharvest gray mold of table grape. Phytopathology 2009, 99, 1028–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdine, M.; Heuzey, M.-C.; Bégin, A. Effect of organic and inorganic acids on concentrated chitosan solutions and gels. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2005, 37, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bateman, D.N. Corrosives. Medicine 2012, 40, 118–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Rong, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Bao, J.; Shi, Z.; Xiong, C.; Yang, Q. Exploring the intrinsic mechanism of TOCN-based high-performance triboelectric positive material by oxygen-rich groups. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fu, Q.; Mo, J.; Lu, Y.; Cai, C.; Luo, B.; Nie, S. Chemically tailored molecular surface modification of cellulose nanofibrils for manipulating the charge density of triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2021, 89, 106369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, L.; Ferraz, E.; Lourenço, A.F.; Ferreira, P.J.T.; Rasteiro, M.G.; Gamelas, J.A.F. Tuning rheology and aggregation behaviour of TEMPO-oxidised cellulose nanofibrils aqueous suspensions by addition of different acids. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 237, 116109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribau Teixeira, M.; Ismail, A.; Medronho, B.; Alves, L.; Pedrosa, J.F.S.; Ferreira, P.J.T.; Serrão Sousa, V.; Rosa da Costa, A.M. Nanofibrillated cationic cellulose derivatives as flocculants for domestic wastewater treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 58, 104817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, L.; Magalhães, S.; Pedrosa, J.F.S.; Ferreira, P.J.T.; Gamelas, J.A.F.; Rasteiro, M.G. Rheology of Suspensions of TEMPO-Oxidised and Cationic Cellulose Nanofibrils—The Effect of Chemical Pre-Treatment. Gels 2024, 10, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pongampai, S.; Charoonsuk, T.; Pinpru, N.; Pulphol, P.; Vittayakorn, W.; Pakawanit, P.; Vittayakorn, N. Triboelectric-piezoelectric hybrid nanogenerator based on BaTiO3-Nanorods/Chitosan enhanced output performance with self-charge-pumping system. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 208, 108602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Lou, W.; Zhang, W.; Guan, X.; He, J.; Lin, J. Modulating crystallinity and dielectric constant of chitosan film for triboelectric polarity shift and performance enhancement in triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2023, 117, 108923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yar, A.; Okbaz, A.; Parlayıcı, Ş. A biocompatible, eco-friendly, and high-performance triboelectric nanogenerator based on sepiolite, bentonite, and kaolin decorated chitosan composite film. Nano Energy 2023, 110, 108354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Sridhar, T. Effects of the Polydispersity on Rheological Properties of Entangled Polystyrene Solutions. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 3442–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, D.P.; Inamdar, M.S. Aqueous Behaviour of Chitosan. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2010, 2010, 939536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, L.; Lindman, B.; Klotz, B.; Böttcher, A.; Haake, H.-M.; Antunes, F.E. Controlling the swelling and rheological properties of hydrophobically modified polyacrylic acid nanoparticles: Role of pH, anionic surfactant and electrolyte. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 459, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavoni, J.M.F.; Luchese, C.L.; Tessaro, I.C. Impact of acid type for chitosan dissolution on the characteristics and biodegradability of cornstarch/chitosan based films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Z.; Chen, X.G.; Liu, N.; Wang, S.X.; Liu, C.S.; Meng, X.H.; Liu, C.G. Protonation constants of chitosan with different molecular weight and degree of deacetylation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2006, 65, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Amaral Sobral, P.J.; Gebremariam, G.; Drudi, F.; De Aguiar Saldanha Pinheiro, A.C.; Romani, S.; Rocculi, P.; Dalla Rosa, M. Rheological and Viscoelastic Properties of Chitosan Solutions Prepared with Different Chitosan or Acetic Acid Concentrations. Foods 2022, 11, 2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanery, F.P.; Mansur, A.A.P.; Mansur, H.S. One-step colloidal synthesis of biocompatible water-soluble ZnS quantum dot/chitosan nanoconjugates. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ruvalcaba, A.; Chornet, E.; Rodrigue, D. Dynamic Rheological Properties of Concentrated Chitosan Soltions. Appl. Rheol. 2004, 14, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaün, F.; Chen, Y.; Ferri, A.; Giraud, S.; Roy, J.C.; Jinping, G.; Chen, G. Solubility of Chitin: Solvents, Solution Behaviors and Their Related Mechanisms. In Solubility of Polysaccharides; Xu, Z., Ed.; IntechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argüelles-Monal, W.; Goycoolea, F.M.; Peniche, C.; Higuera-Ciapara, I. Rheological study of the chitosan/glutaraldehyde chemical gel system. Polym. Gels Netw. 1998, 6, 429–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Kan, Y.; Huang, H.; Wu, W.; Lu, X. Probing the Molecular Interactions of Chitosan Films in Acidic Solutions with Different Salt Ions. Coatings 2020, 10, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes Queiroz, M.; Melo, K.R.T.; Sabry, D.A.; Sassaki, G.L.; Rocha, H.A.O. Does the Use of Chitosan Contribute to Oxalate Kidney Stone Formation? Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasweefali, M.K.; Sabu, S.; Sunooj, K.V.; Sasidharan, A.; Xavier, K.A.M. Consequences of chemical deacetylation on physicochemical, structural and functional characteristics of chitosan extracted from deep-sea mud shrimp. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2021, 2, 100032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaudo, M.; Milas, M.; Dung, P.L. Characterization of chitosan. Influence of ionic strength and degree of acetylation on chain expansion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1993, 15, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xue, C.; Xue, Y.; Gao, R.; Zhang, X. Determination of the degree of deacetylation of chitin and chitosan by X-ray powder diffraction. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 1914–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, C.; Ma, X.; Wang, X.; Liu, L. Structure and properties of chitosan films: Effect of the type of solvent acid. LWT 2021, 135, 109984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weißpflog, J.; Vehlow, D.; Müller, M.; Kohn, B.; Scheler, U.; Boye, S.; Schwarz, S. Characterization of chitosan with different degree of deacetylation and equal viscosity in dissolved and solid state—Insights by various complimentary methods. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 171, 242–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Hou, C.; Su, A.; Hu, S.; Yue, M.; Shan, X. The influence of functional groups on the triboelectric properties of chitosan derivatives and the electron transfer mechanism of insulators. Nano Energy 2025, 136, 110709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wu, P.; Chen, X.; Cui, E.; Liu, T.; Mu, X.; Yang, Y. Crystal boundary engineering-dominated high-performance chitosan-based triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered breath-activated ammonia sensors. InfoMat 2025, e12662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampim, I.T.; Wiggers, H.J.; Bueno, C.Z.; Chevallier, P.; Copes, F.; Mantovani, D. Sourcing Interchangeability in Commercial Chitosan: Focus on the Physical–Chemical Properties of Six Different Products and Their Impact on the Release of Antibacterial Agents. Polymers 2025, 17, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Chesnutt, B.M.; Haggard, W.O.; Bumgardner, J.D. Deacetylation of Chitosan: Material Characterization and in vitro Evaluation via Albumin Adsorption and Pre-Osteoblastic Cell Cultures. Materials 2011, 4, 1399–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, J.; Priyanka. A facile approach for the determination of degree of deacetylation of chitosan using acid-base titration. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
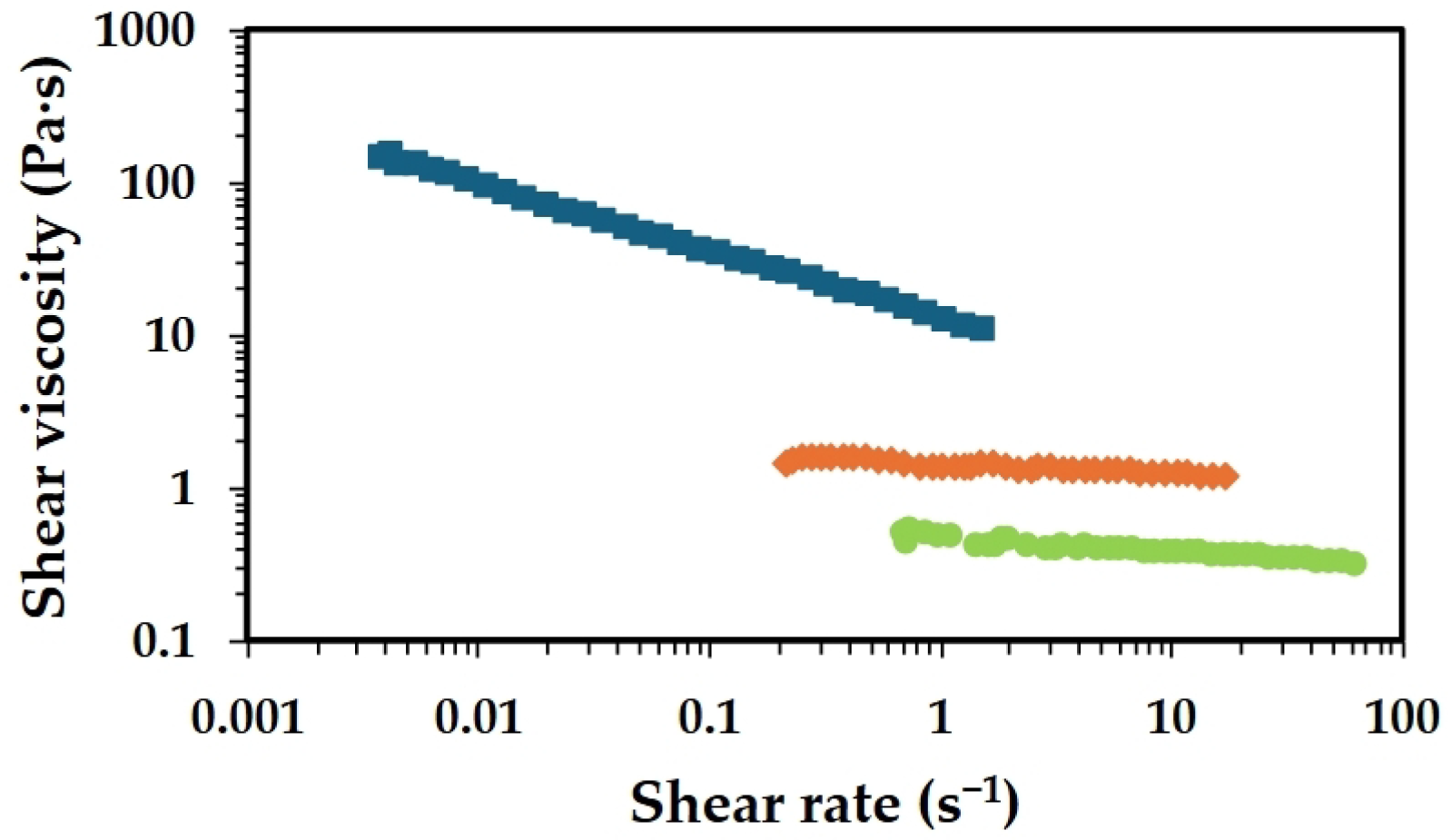
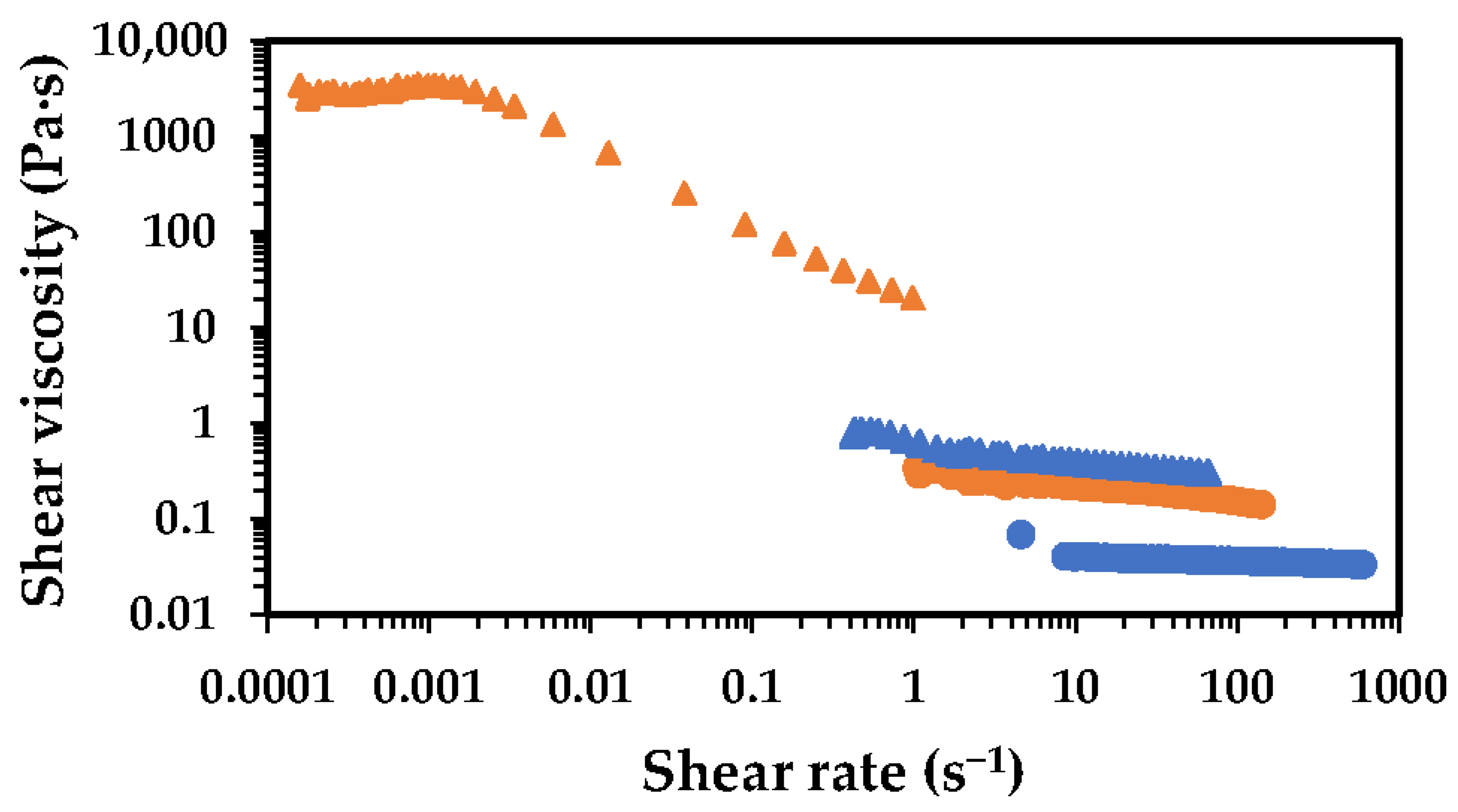

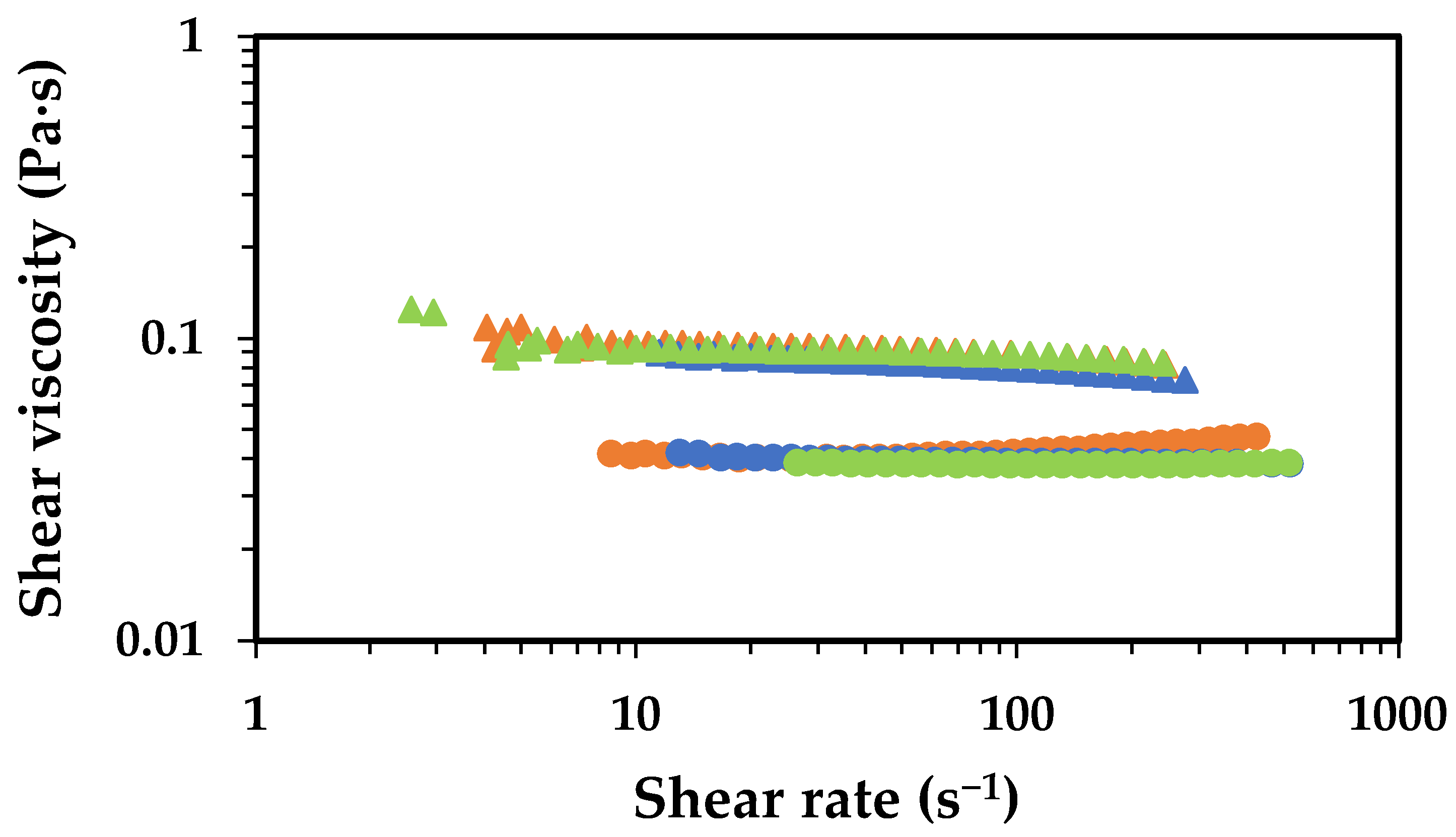
 ), 1 h (
), 1 h ( ), 2 h (
), 2 h ( ), 4 h (
), 4 h ( ) and 8 h (
) and 8 h ( ).
).
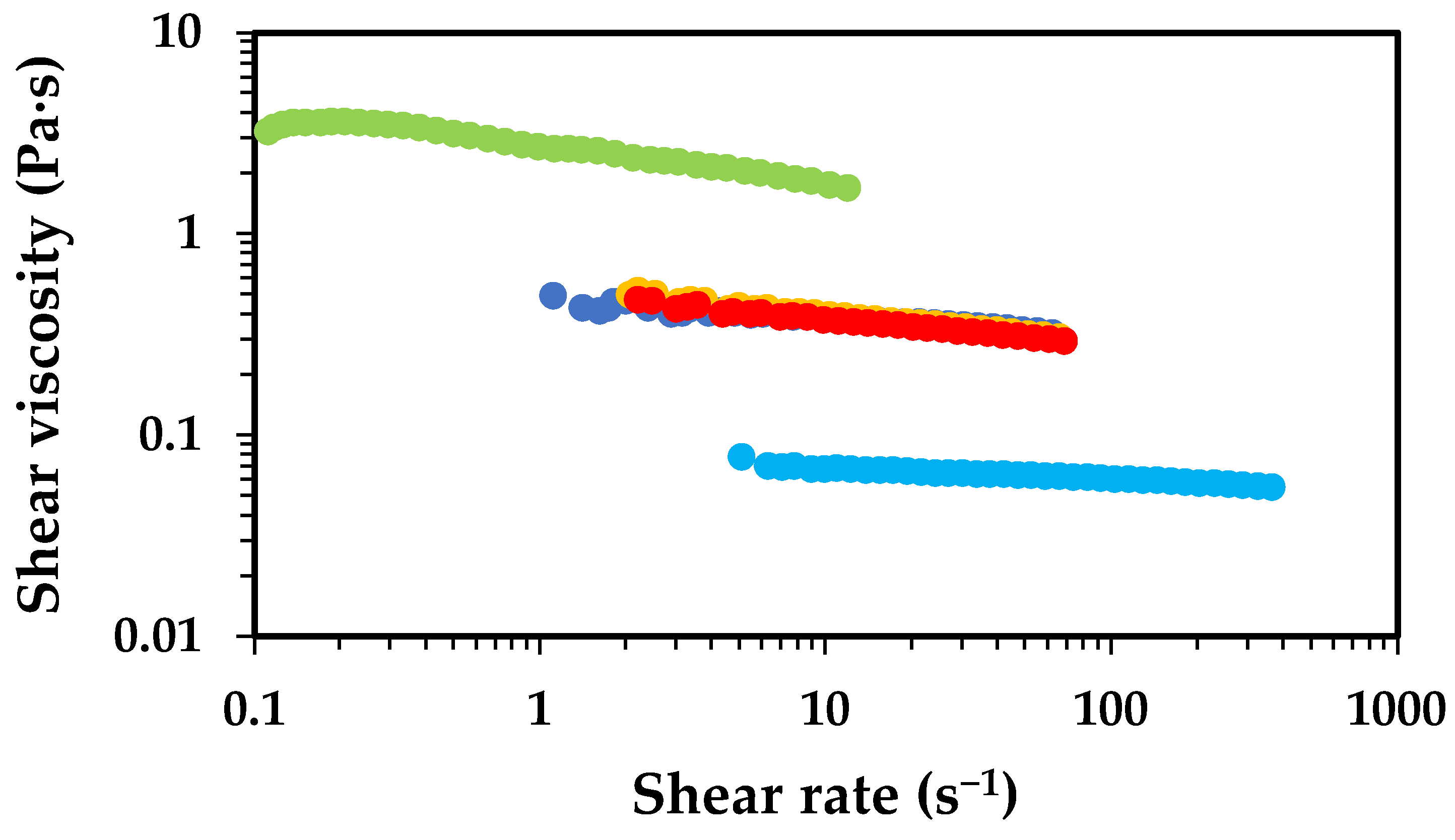
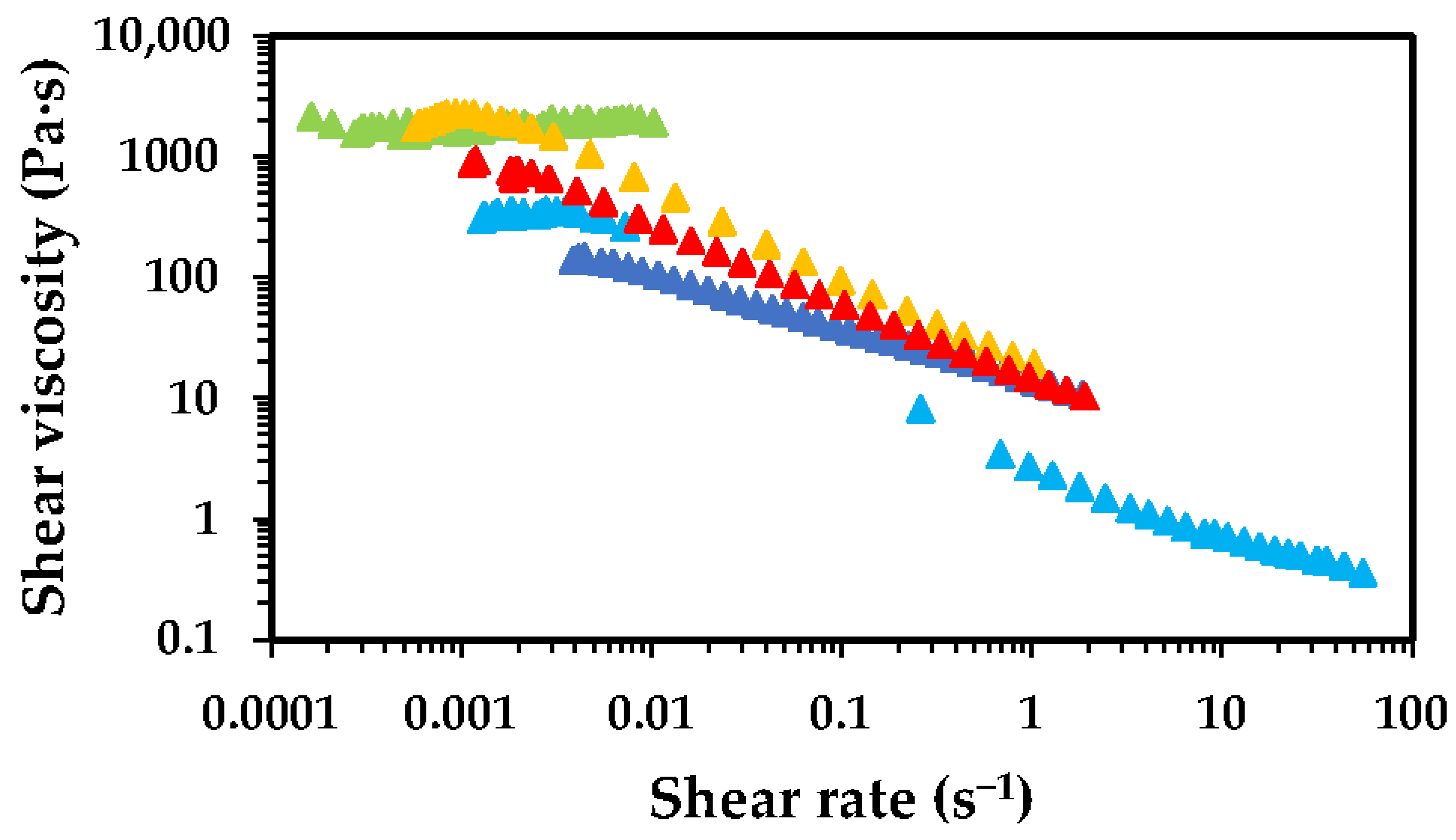
 ), 1 h (
), 1 h ( ), 2 h (
), 2 h ( ), 4 h (
), 4 h ( ) and 8 h (
) and 8 h ( ).
).

| Sample | K (Pa sn) | n | r |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 wt.% low-MW chitosan in 5.0 wt.% AA aq. | 0.04 | 0.96 | 0.997 |
| 1.0 wt.% high-MW chitosan in 5.0 wt.% AA aq. | 0.31 | 0.85 | 0.988 |
| 2.5 wt.% low-MW chitosan in 0.5 wt.% AA aq. | 0.07 | 0.95 | 0.990 |
| 2.5 wt.% low-MW chitosan in 1.0 wt.% AA aq. | 0.08 | 0.95 | 0.996 |
| 2.5 wt.% low-MW chitosan in 2.0 wt.% AA aq. | 0.45 | 0.93 | 0.986 |
| 2.5 wt.% low-MW chitosan in 5.0 wt.% AA aq. | 0.55 | 0.86 | 0.991 |
| 2.5 wt.% low-MW chitosan in 10.0 wt.% AA aq. | 0.50 | 0.87 | 0.991 |
| 2.5 wt.% high-MW chitosan in 0.5 wt.% AA aq. | 2205 | 1.03 | 0.985 |
| 2.5 wt.% high-MW chitosan in 1.0 wt.% AA aq. | 38.5 | 0.64 | 0.977 |
| 2.5 wt.% high-MW chitosan in 2.0 wt.% AA aq. | 14.2 | 0.56 | 0.999 |
| 2.5 wt.% high-MW chitosan in 5.0 wt.% AA aq. | 40.9 | 0.33 | 0.997 |
| 2.5 wt.% high-MW chitosan in 10.0 wt.% AA aq. | 29.2 | 0.49 | 0.987 |
| Sample | Current (µA) | Voltage (V) |
|---|---|---|
| low-MW 2 wt.% | 107.5 ± 0.3 | 188.8 ± 0.7 |
| low-MW 5 wt.% | 108.1 ± 0.3 | 223.6 ± 0.4 |
| low-MW 10 wt.% | 110.8 ± 0.9 | 255.7 ± 1.1 |
| high-MW 2 wt.% | 142.8 ± 0.3 | 259.8 ± 1.1 |
| high-MW 5 wt.% | 150.1 ± 0.3 | 271.4 ± 1.3 |
| high-MW 10 wt.% | 178.4 ± 0.4 | 291.9 ± 1.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Araújo, F.; Magalhães, S.; Medronho, B.; Eivazi, A.; Dahlström, C.; Norgren, M.; Alves, L. Effect of Chitosan Properties and Dissolution State on Solution Rheology and Film Performance in Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Gels 2025, 11, 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070523
Araújo F, Magalhães S, Medronho B, Eivazi A, Dahlström C, Norgren M, Alves L. Effect of Chitosan Properties and Dissolution State on Solution Rheology and Film Performance in Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Gels. 2025; 11(7):523. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070523
Chicago/Turabian StyleAraújo, Francisca, Solange Magalhães, Bruno Medronho, Alireza Eivazi, Christina Dahlström, Magnus Norgren, and Luís Alves. 2025. "Effect of Chitosan Properties and Dissolution State on Solution Rheology and Film Performance in Triboelectric Nanogenerators" Gels 11, no. 7: 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070523
APA StyleAraújo, F., Magalhães, S., Medronho, B., Eivazi, A., Dahlström, C., Norgren, M., & Alves, L. (2025). Effect of Chitosan Properties and Dissolution State on Solution Rheology and Film Performance in Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Gels, 11(7), 523. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070523









