(W/O/W) Double Emulsions-Filled Chitosan Hydrogel Beads for Topical Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
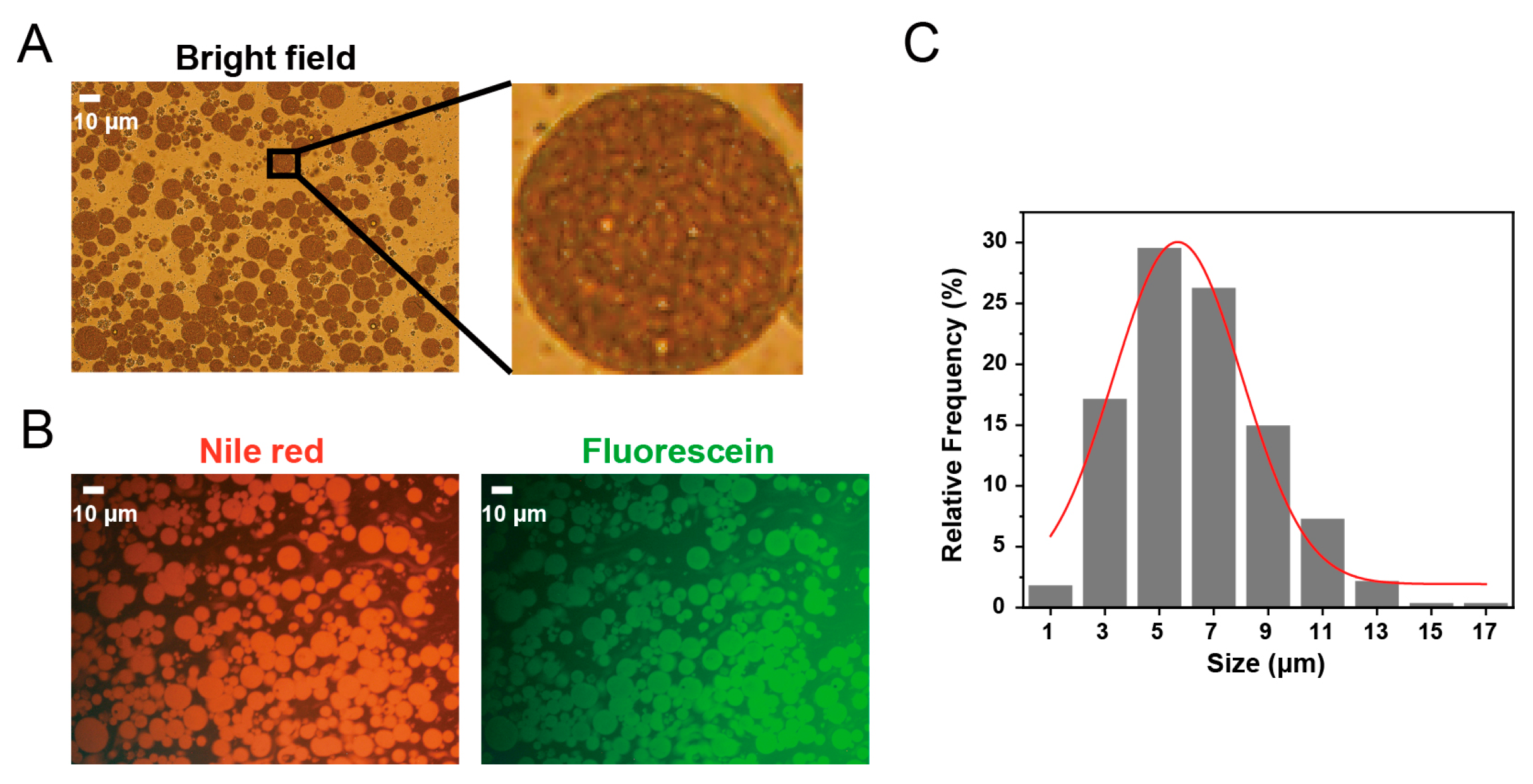
2.1. Characterization of the Original (W/O/W) Double Emulsions
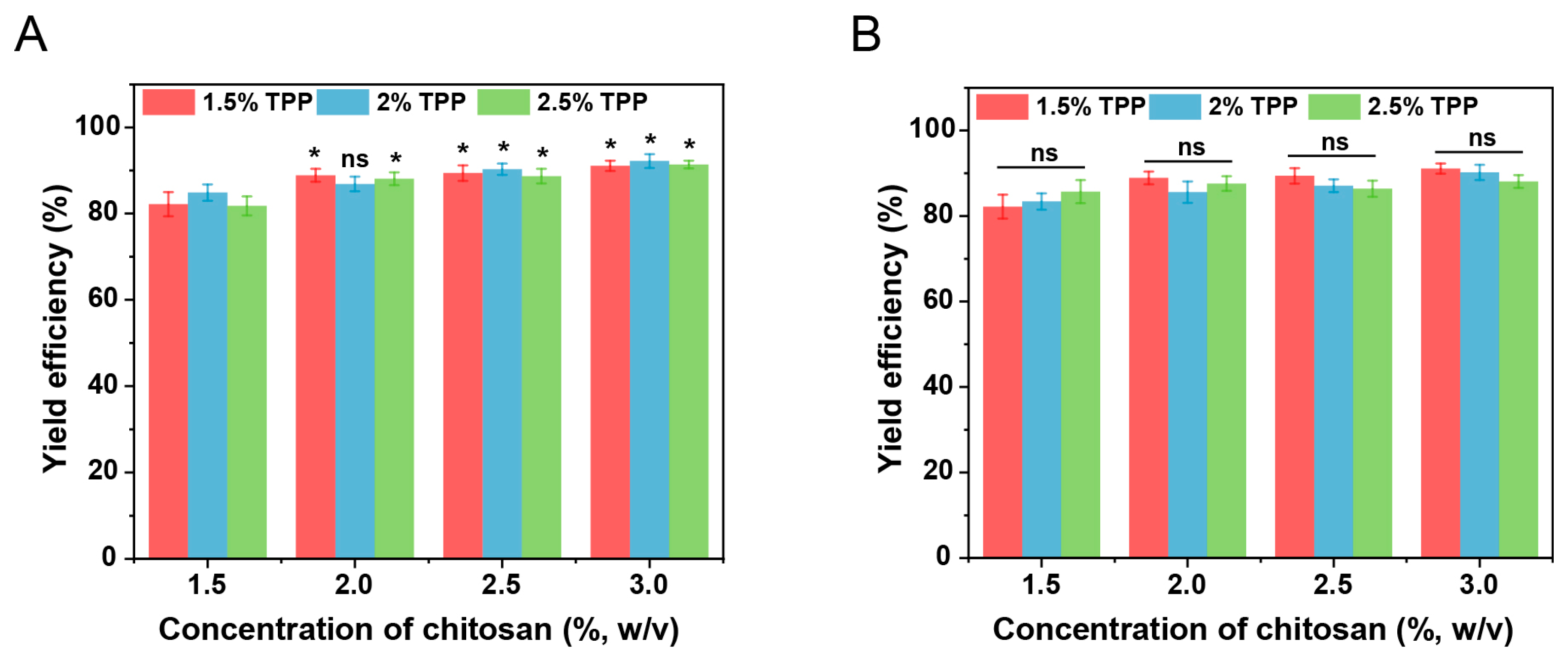
2.2. Incorporation of Double Emulsions in Chitosan Hydrogel Beads
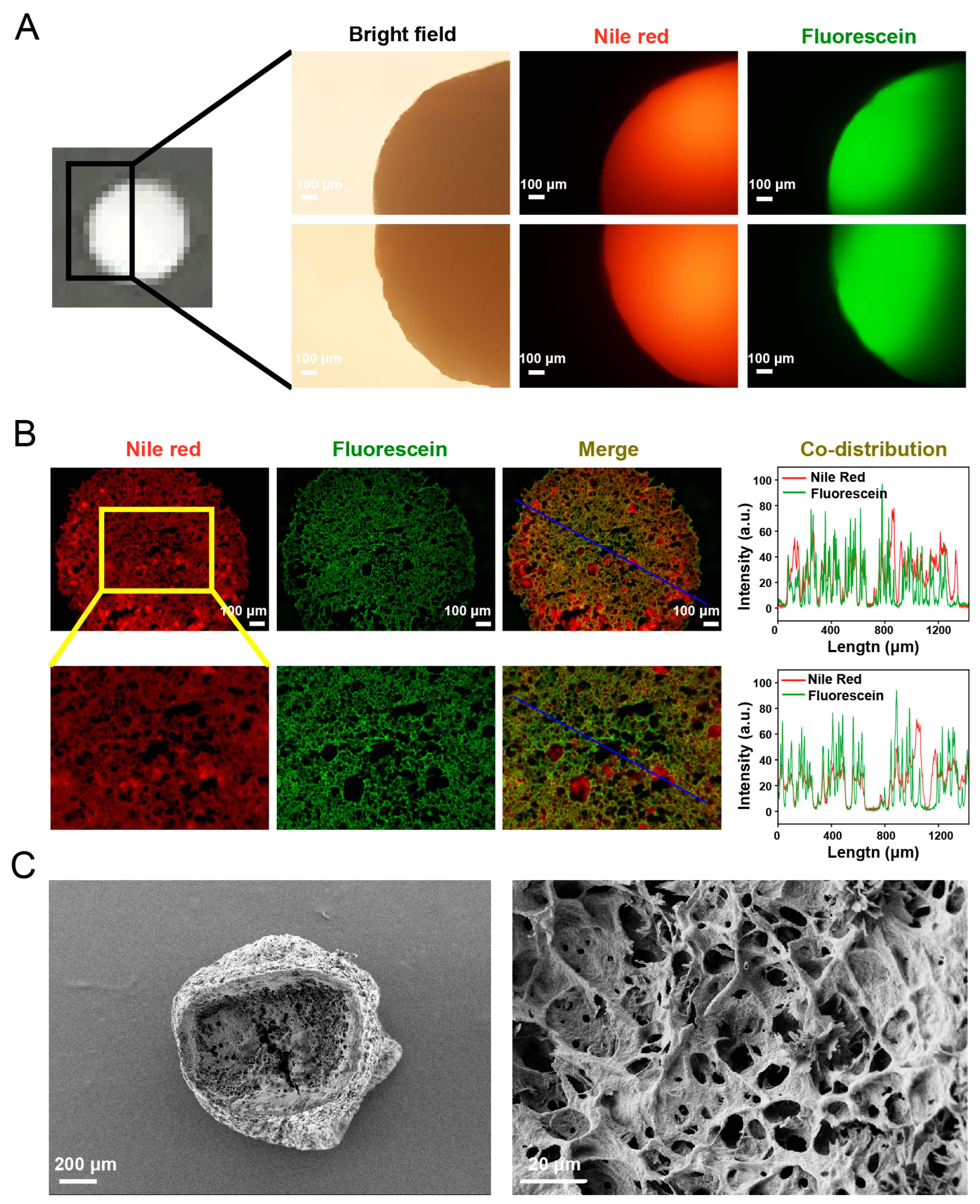
2.3. Characterization of Double Emulsions-Filled Chitosan Hydrogel Beads
2.4. Stability Study
2.5. Skin Permeation of Hydrophilic Active Ingredients
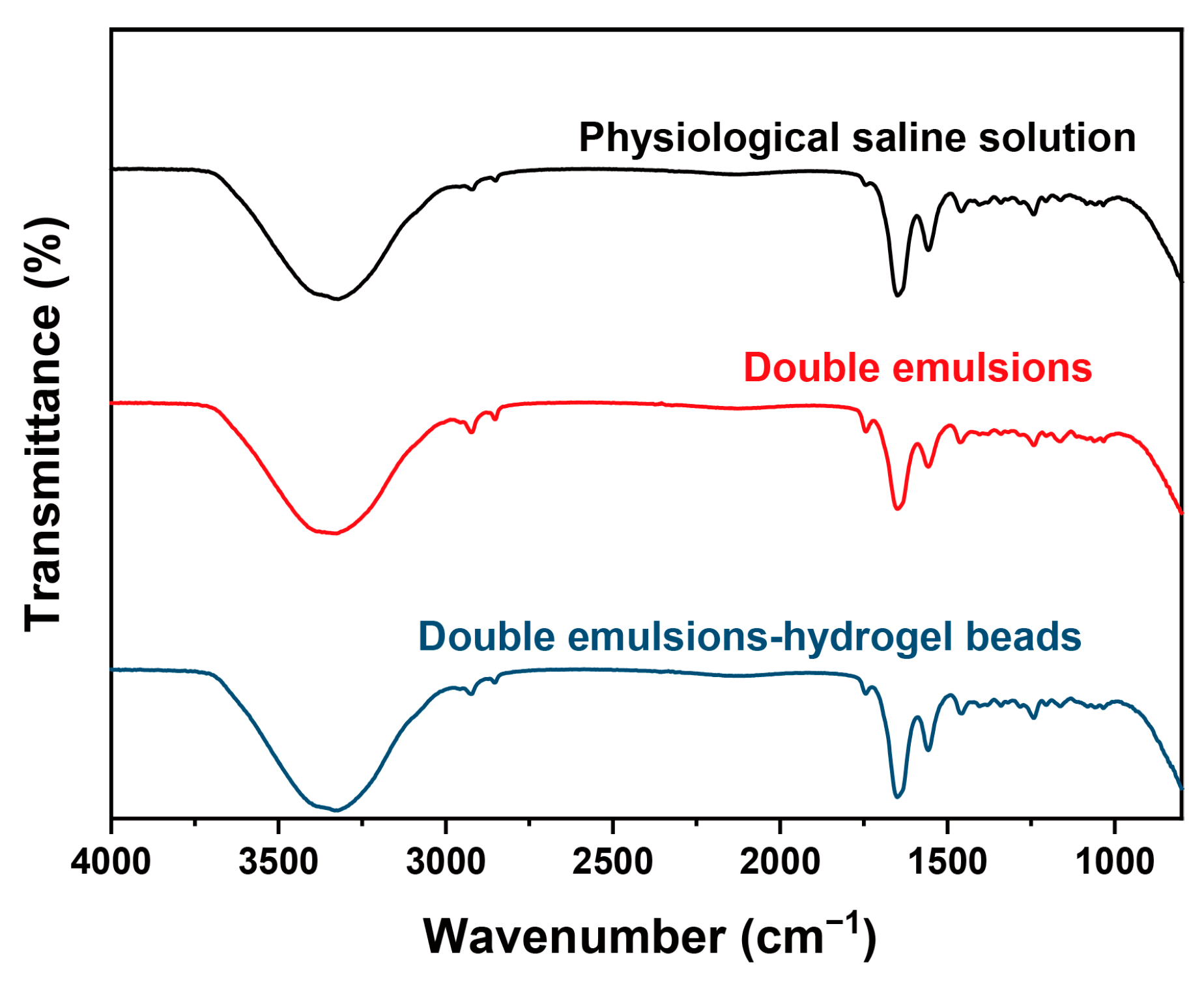
2.6. Skin Permeation Behavior Study Based on ATR-FTIR
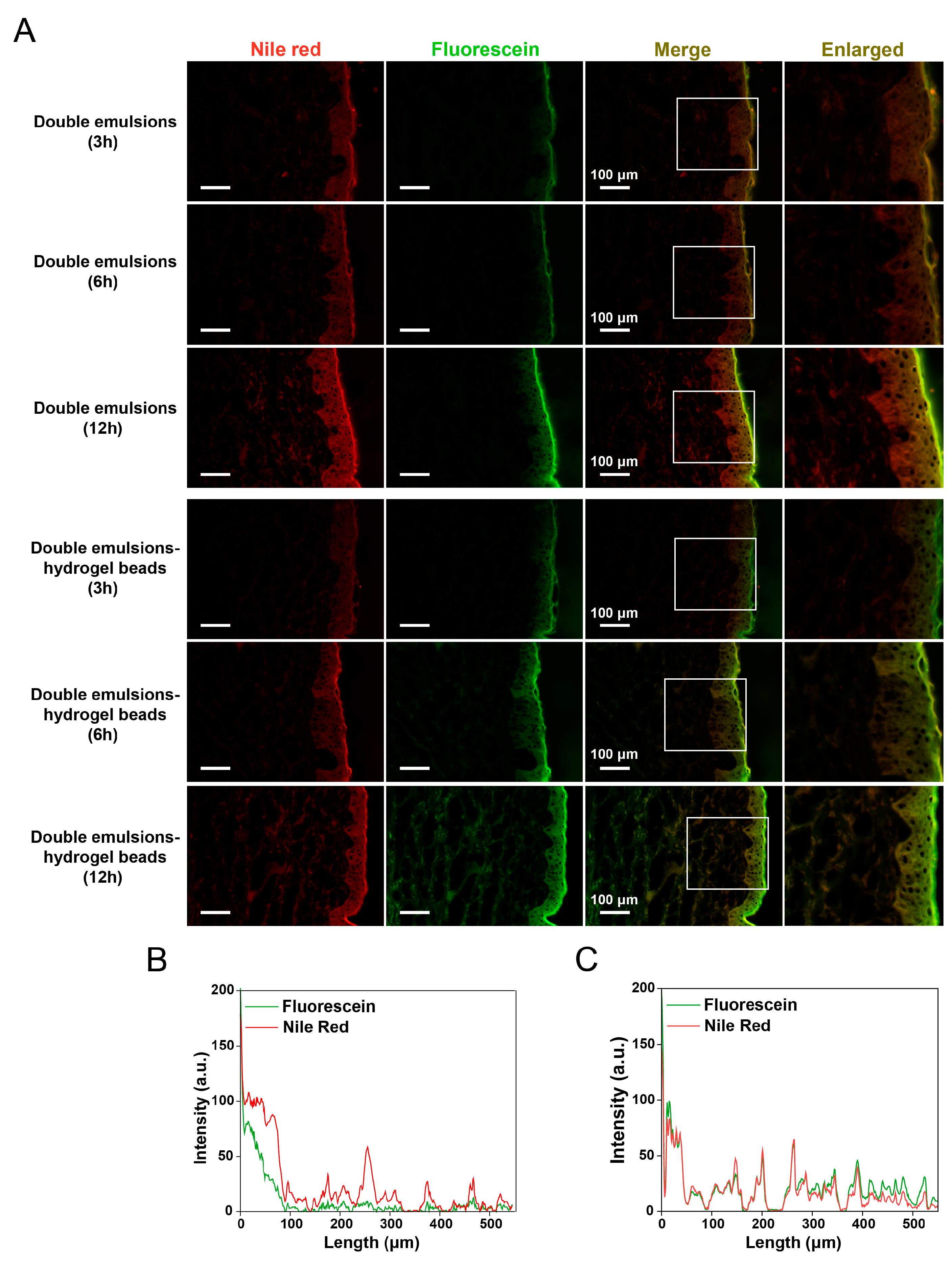
2.7. Skin Permeation Behavior Study Based on Fluorescent Probes
2.8. Skin Permeation of Hydrophobic Active Ingredients
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Double Emulsions
4.3. Preparation of Double Emulsions-Filled Chitosan Hydrogel Beads
4.4. Encapsulation Efficiency of Double Emulsions
4.5. Yield Efficiency of Double Emulsions-Filled Chitosan Hydrogel Beads
4.6. Analysis of Diameter and Void Fraction
4.7. Analysis of Morphology
4.8. Storage Stability
4.9. Skin Permeation Study
4.10. Skin Permeation Study Based on ATR-FTIR
4.11. Skin Permeation Study Based on Fluorescent Probes
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, H.; Kuang, H.; Huang, X.; Li, X.; Zhao, R.; Shang, G.; Wang, Z.; Liao, Y.; He, J.; Li, D. 3D printing of drug delivery systems enhanced with micro/nano-technology. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2025, 216, 115479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, T.; Hu, Y.; Wu, J.; van der Meeren, P. Designing delivery systems for functional ingredients by protein/polysaccharide interactions. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 119, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulchar, R.J.; Singh, R.; Ding, S.; Alexander, E.; Daniell, H.; Leong, K.W. Delivery of biologics: Topical administration. Biomaterials 2023, 302, 122312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastav, A.K.; Karpathak, S.; Rai, M.K.; Kumar, D.; Misra, D.P.; Agarwal, V. Lipid based drug delivery systems for oral, transdermal and parenteral delivery: Recent strategies for targeted delivery consistent with different clinical application. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 85, 104526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareek, A.; Kapoor, D.U.; Yadav, S.K.; Rashid, S.; Fareed, M.; Akhter, M.S.; Muteeb, G.; Gupta, M.M.; Prajapati, B.G. Advancing lipid nanoparticles: A pioneering technology in cosmetic and dermatological treatments. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2025, 64, 100814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kaur, R.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, S.; Gehlot, R.; Aggarwal, P. New insights into water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) double emulsions: Properties, fabrication, instability mechanism, and food applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 128, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, F.; Jafari, S.M.; Ziaiifar, A.M.; Malekjani, N. Stability and release mechanisms of double emulsions loaded with bioactive compounds; a critical review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 299, 102567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Ko, J.; Park, S.-B.; Kim, J.-Y.; Ha, J.-H.; Roh, S.; An, Y.-H.; Hwang, N.S. Double Emulsion-Mediated Delivery of Polyphenol Mixture Alleviates Atopic Dermatitis. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, e2300998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhu, X.; Shi, F.; Liu, Y.; Hu, W.; Yang, Z. Influence of β-cyclodextrin concentration on the physicochemical properties and skin permeation behavior of vitamin C-loaded Pickering water-in-oil-in-water (W1/O/W2) double emulsions. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 72, 103368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppel, M.; Mahrhauser, D.; Stallinger, C.; Wagner, F.; Wirth, M.; Valenta, C. Natural polymer-stabilized multiple water-in-oil-in-water emulsions: A novel dermal drug delivery system for 5-fluorouracil. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 66, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppel, M.; Reznicek, G.; Kaehlig, H.; Kotisch, H.; Resch, G.P.; Valenta, C. Topical delivery of acetyl hexapeptide-8 from different emulsions: Influence of emulsion composition and internal structure. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 68, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaimes-Lizcano, Y.A.; Lawson, L.B.; Papadopoulos, K.D. Oil-Frozen W1/O/W2 Double Emulsions for Dermal Biomacromolecular Delivery Containing Ethanol as Chemical Penetration Enhancer. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidts, T.; Dobler, D.; Schlupp, P.; Nissing, C.; Garn, H.; Runkel, F. Development of multiple W/O/W emulsions as dermal carrier system for oligonucleotides: Effect of additives on emulsion stability. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 398, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, B.; Luo, Y. Chitosan-based hydrogel beads: Preparations, modifications and applications in food and agriculture sectors—A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 152, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Li, B.; Li, Y.; McClements, D.J. Construction of biopolymer-based hydrogel beads for encapsulation, retention, and colonic delivery of tributyrin: Development of functional beverages (fortified bubble tea). Food Res. Int. 2024, 197, 115165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letocha, A.; Miastkowska, M.; Sikora, E. Preparation and Characteristics of Alginate Microparticles for Food, Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Applications. Polymers 2022, 14, 3834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Chen, F.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, J.; Wu, T.; Wang, P.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, Q. Co-encapsulation of collagen peptide and astaxanthin in WG/OG/W double emulsions-filled alginate hydrogel beads: Fabrication, characterization and digestion behaviors. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 651, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xie, L.; Liang, S.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhan, X. Carboxymethyl konjac glucomannan-chitosan complex nanogels stabilized double emulsions incorporated into alginate hydrogel beads for the encapsulation, protection and delivery of probiotics. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 289, 119438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozcan, B.E.; Saroglu, O.; Karakas, C.Y.; Karadag, A. Encapsulation of purple basil leaf extract by electrospraying in double emulsion (W/O/W) filled alginate-carrageenan beads to improve the bioaccessibility of anthocyanins. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 250, 126207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Sun, R.; Xia, Q. An ascorbic acid delivery system based on (W1/O/W2) double emulsions encapsulated by Ca-alginate hydrogel beads. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 101929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Sun, R.; Xia, Q. Influence of gelation of internal aqueous phase on in vitro controlled release of W1/O/W2 double emulsions-filled alginate hydrogel beads. J. Food Eng. 2023, 337, 111246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenorio-Garcia, E.; Araiza-Calahorra, A.; Simone, E.; Sarkar, A. Recent advances in design and stability of double emulsions: Trends in Pickering stabilization. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 128, 107601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Li, W.; Wang, W.; Cao, Y.; Lan, Y.; Huang, Q.; Xiao, J. Effects of gelation on the stability, tribological properties and time-delayed release profile of double emulsions. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Sun, R.; Dong, Z.; Ji, S.P.; Xia, Q. Preparation of a stable gel-in-crystallized oil-in-gel type structured W1/O/W2 double emulsions: Effect of internal aqueous phase gelation on the system stability. J. Dispers. Sci. Technol. 2023, 44, 1873–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Yuan, M.; Gao, P.; Wang, L.; Qi, Y.; Chen, J.; Bai, K.; Fan, Y.; Liu, X. Microemulsion-Based Keratin-Chitosan Gel for Improvement of Skin Permeation/Retention and Activity of Curcumin. Gels 2023, 9, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, P.; Furlani, F.; de Marzo, G.; Marsich, E.; Paoletti, S.; Donati, I. Concepts for Developing Physical Gels of Chitosan and of Chitosan Derivatives. Gels 2018, 4, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Hua, S.; Huang, Z.; Gu, Z.; Cheng, L.; Hong, Y. Comparison of bioaccessibility of astaxanthin encapsulated in starch-based double emulsion with different structures. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 272, 118475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florence, A.T.; Whitehill, D. Some features of breakdown in water-in-oil-in-water multiple emulsions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1981, 79, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liang, Y.; Huang, S.; Guo, B. Chitosan-based self-healing hydrogel dressing for wound healing. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2024, 332, 103267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidts, T.; Marquardt, K.; Schlupp, P.; Dobler, D.; Heinz, F.; Maeder, U.; Garn, H.; Renz, H.; Zeitvogel, J.; Werfel, T.; et al. Development of drug delivery systems for the dermal application of therapeutic DNAzymes. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 431, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.A.M.; Seiller, M.; Grossiord, J.L.; Marty, J.P.; Wepierre, J. Vehicle influence on in vitro release of metronidazole: Role of w/o/w multiple emulsion. Int. J. Pharm. 1994, 109, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-L.; Chen, P.-P.; Wang, L.-f.; Xue, W.; Fu, T.-L. Hair regenerative effect of silk fibroin hydrogel with incorporation of FGF-2-liposome and its potential mechanism in mice with testosterone-induced alopecia areata. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 48, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Han, L.; Lian, G. Recent advances in predicting skin permeability of hydrophilic solutes. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Liu, W.; Zou, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, C.; Liang, R.; Chen, J. Storage stability and skin permeation of vitamin C liposomes improved by pectin coating. Colloids Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2014, 117, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Huang, J.; Xia, N.; Li, T.; Xia, Q. Self-double-emulsifying drug delivery system incorporated in natural hydrogels: A new way for topical application of vitamin C. J. Microencapsul. 2018, 35, 90–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, M.S.; GuhaSarkar, S.; Banerjee, R. Stratum corneum modulation by chemical enhancers and lipid nanostructures: Implications for transdermal drug delivery. Ther. Deliv. 2017, 8, 701–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subongkot, T.; Sirirak, T. Development and skin penetration pathway evaluation of microemulsions for enhancing the dermal delivery of celecoxib. Colloids Surf. B-Biointerfaces 2020, 193, 111103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppel, M.; Holper, E.; Baurecht, D.; Valenta, C. Monitoring the Distribution of Surfactants in the Stratum Corneum by Combined ATR-FTIR and Tape-Stripping Experiments. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2015, 28, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.C.; Barry, B.W. Penetration enhancers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funke, A.P.; Schiller, R.; Motzkus, H.W.; Gunther, C.; Muller, R.H.; Lipp, R. Transdermal delivery of highly lipophilic drugs: In vitro fluxes of antiestrogens, permeation enhancers, and solvents from liquid formulations. Pharm. Res. 2002, 19, 661–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathout, R.M.; Mansour, S.; Geneidi, A.S.; Mortada, N.D. Visualization, dermatopharmacokinetic analysis and monitoring the conformational effects of a microemulsion formulation in the skin stratum corneum. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 354, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, A.; Pechtold, L.A.R.M.; Potts, R.O.; Guy, R.H. Mechanism of oleic acid-induced skin penetration enhancement in vivo in humans. J. Control. Release 1995, 37, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitragotri, S. Modeling skin permeability to hydrophilic and hydrophobic solutes based on four permeation pathways. J. Control. Release 2003, 86, 69–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youenang Piemi, M.P.; de Luca, M.; Grossiord, J.-L.; Seiller, M.; Marty, J.-P. Transdermal delivery of glucose through hairless rat skin in vitro: Effect of multiple and simple emulsions. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 171, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Zhang, M.; Xia, Q. Improved stability of (W1/O/W2) double emulsions based on dual gelation: Oleogels and hydrogels. J. Food Process Eng. 2019, 42, e13186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robitzer, M.; Di Renzo, F.; Quignard, F. Natural materials with high surface area. Physisorption methods for the characterization of the texture and surface of polysaccharide aerogels. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2011, 140, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, Q.; Chu, L.; Xia, Q. Liposome-chitosan hydrogel bead delivery system for the encapsulation of linseed oil and quercetin: Preparation and in vitro characterization studies. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 117, 108615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
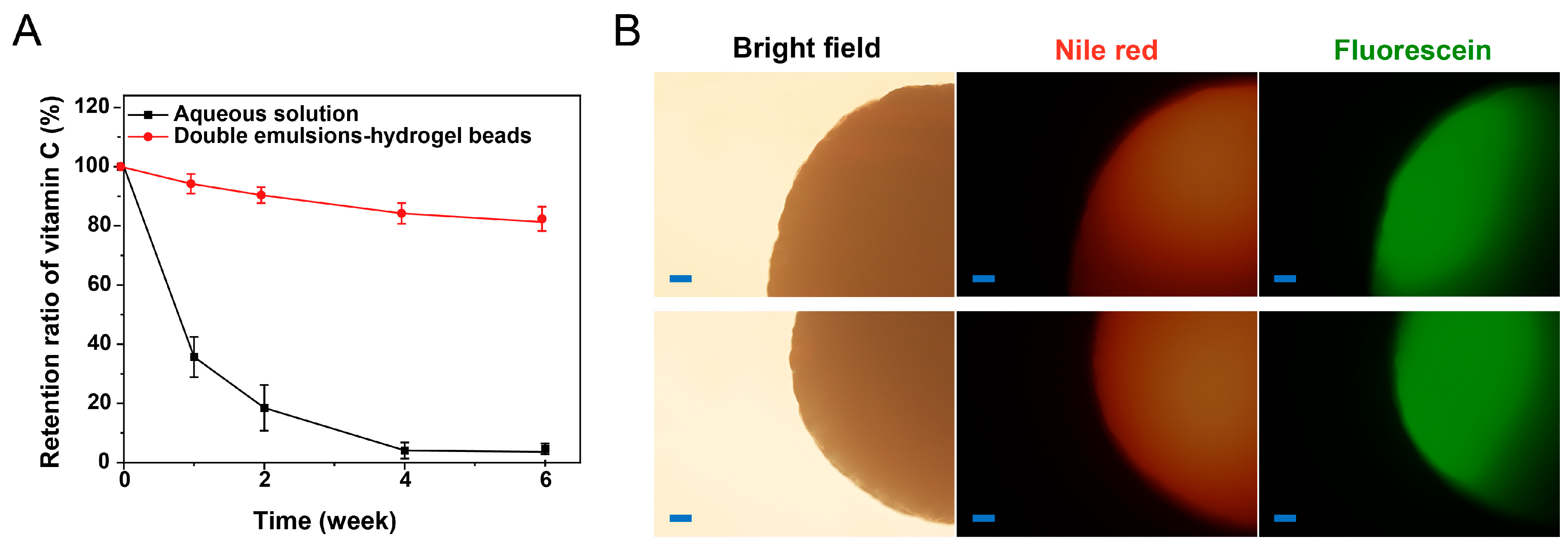
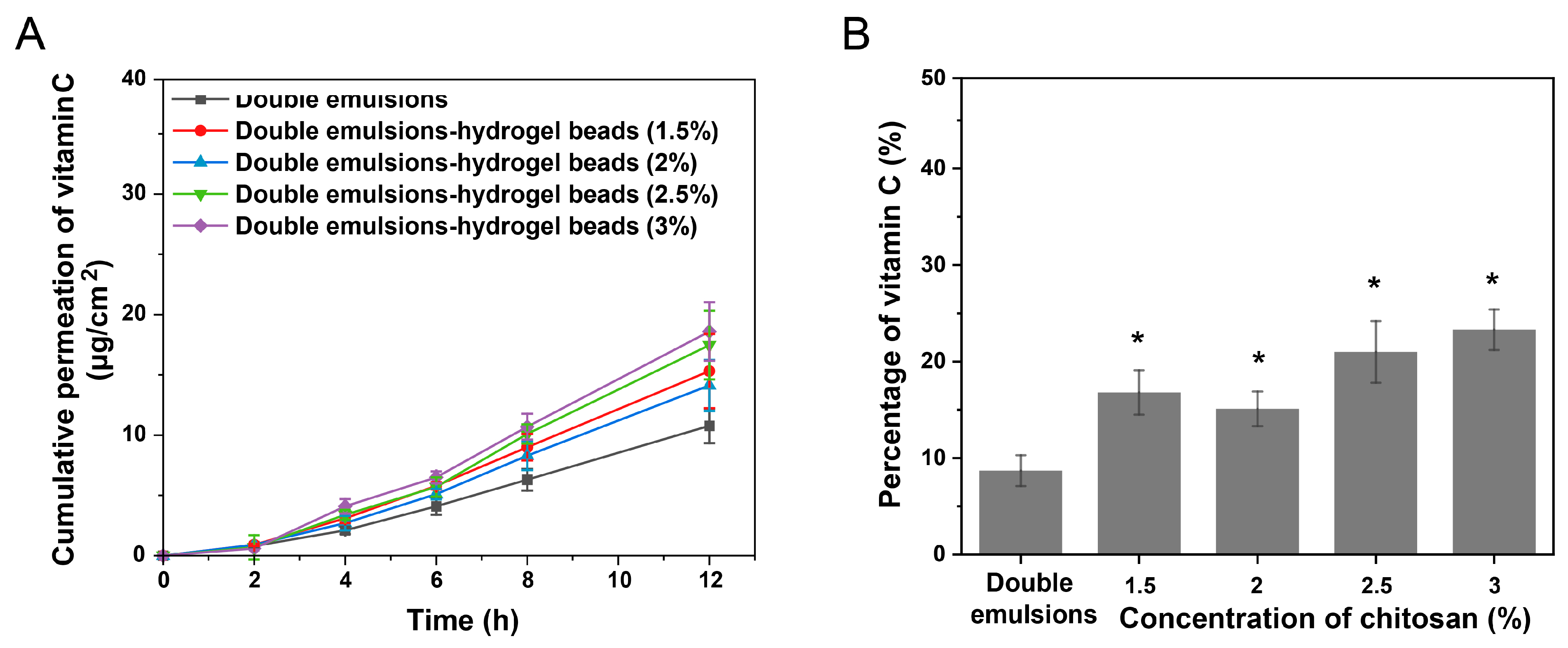

| Period | Morphology | Color | Diameter (mm) | Retention Ratio of Vitamin C (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 week | Spherical and smooth | White | 2.31 ± 0.14 | 100 ± 0.5 |
| 1 week | Spherical and smooth | White | 2.34 ± 0.16 | 94.2 ± 3.3 |
| 2 week | Spherical and smooth | White | 2.41 ± 0.21 | 90.4 ± 2.7 |
| 4 week | Spherical and smooth | White | 2.39 ± 0.17 | 84.2 ± 3.5 |
| 6 week | Spherical and smooth | White | 2.36 ± 0.19 | 81.3 ± 4.1 |
| Flux (Jss) (μg/(cm2·h)) | Lag Time (h) | Permeability Coefficient (Kp) (10−4 cm/h) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Double emulsions | 1.089 ± 0.1370 | 2.165 ± 0.095 | 3.630 ± 0.456 | |
| Double emulsions- hydrogel beads | 1.5% | 1.538 ± 0.3585 | 2.027 ± 0.496 | 5.128 ± 1.196 |
| 2% | 1.445 ± 0.2125 | 2.271 ± 0.221 | 4.818 ± 0.708 | |
| 2.5% | 1.801 ± 0.2970 * | 2.394 ± 0.181 | 6.004 ± 0.990 * | |
| 3% | 1.856 ± 0.2430 * | 2.117 ± 0.085 | 6.186 ± 0.809 * |
| Asymmetric CH2 (cm−1) | Symmetric CH2 (cm−1) | |
|---|---|---|
| Physiological saline solution | 2918.86 ± 0.64 | 2850.46 ± 0.25 |
| Double emulsions | 2922.68 ± 0.52 * | 2852.38 ± 0.71 * |
| Double emulsions-hydrogel beads | 2923.95 ± 0.47 * | 2852.87 ± 0.21 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, R.; Sun, Y.; Tang, X.; Ji, J. (W/O/W) Double Emulsions-Filled Chitosan Hydrogel Beads for Topical Application. Gels 2025, 11, 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070504
Sun R, Sun Y, Tang X, Ji J. (W/O/W) Double Emulsions-Filled Chitosan Hydrogel Beads for Topical Application. Gels. 2025; 11(7):504. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070504
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Rui, Yufeng Sun, Xiaoyan Tang, and Juling Ji. 2025. "(W/O/W) Double Emulsions-Filled Chitosan Hydrogel Beads for Topical Application" Gels 11, no. 7: 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070504
APA StyleSun, R., Sun, Y., Tang, X., & Ji, J. (2025). (W/O/W) Double Emulsions-Filled Chitosan Hydrogel Beads for Topical Application. Gels, 11(7), 504. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070504






