A Scientific Framework for Comparing Hyaluronic Acid Filler Crosslinking Technologies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sample Selection
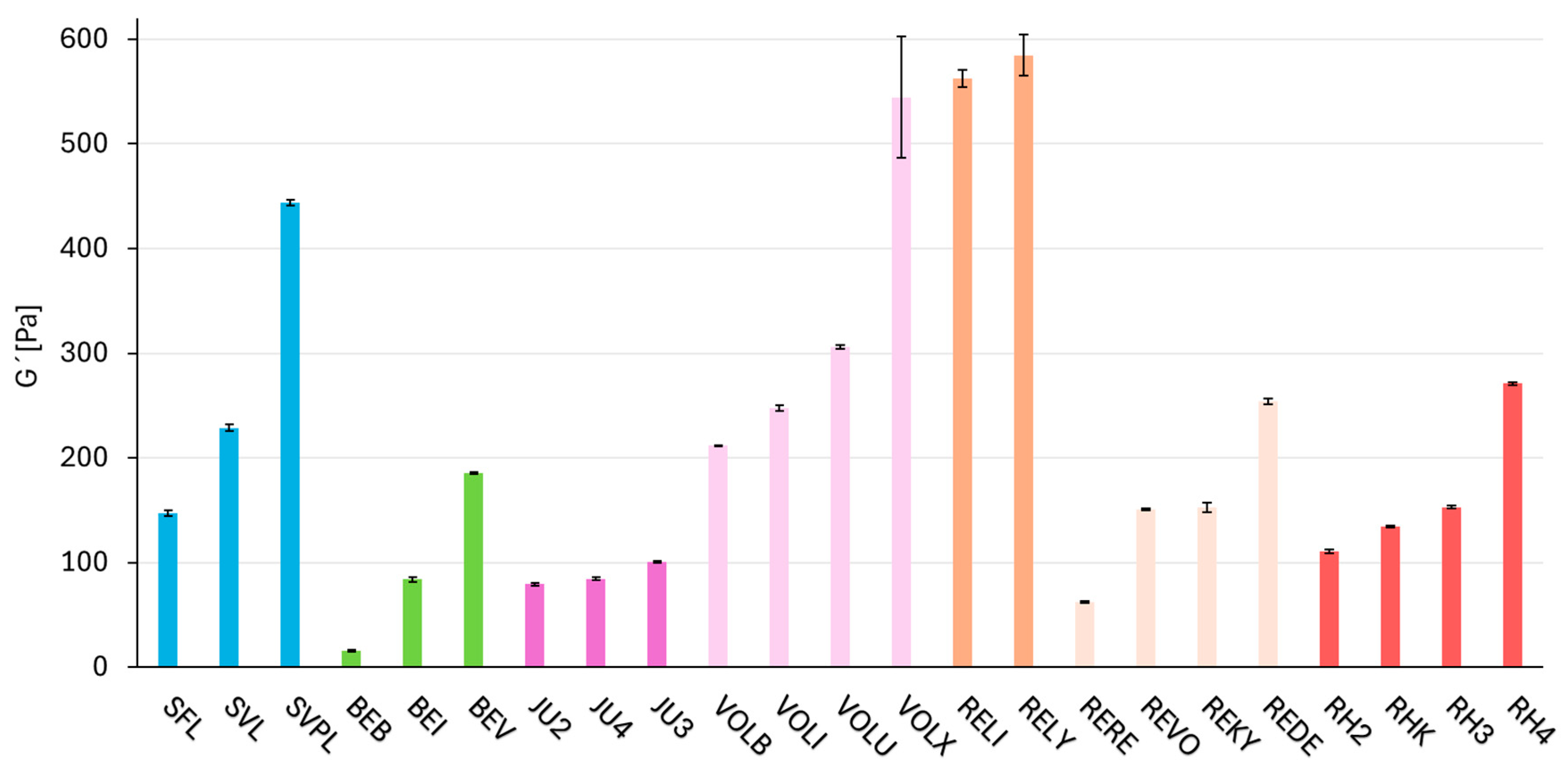
2.2. Dynamic Parameter—Rheology (Storage Modulus G′)
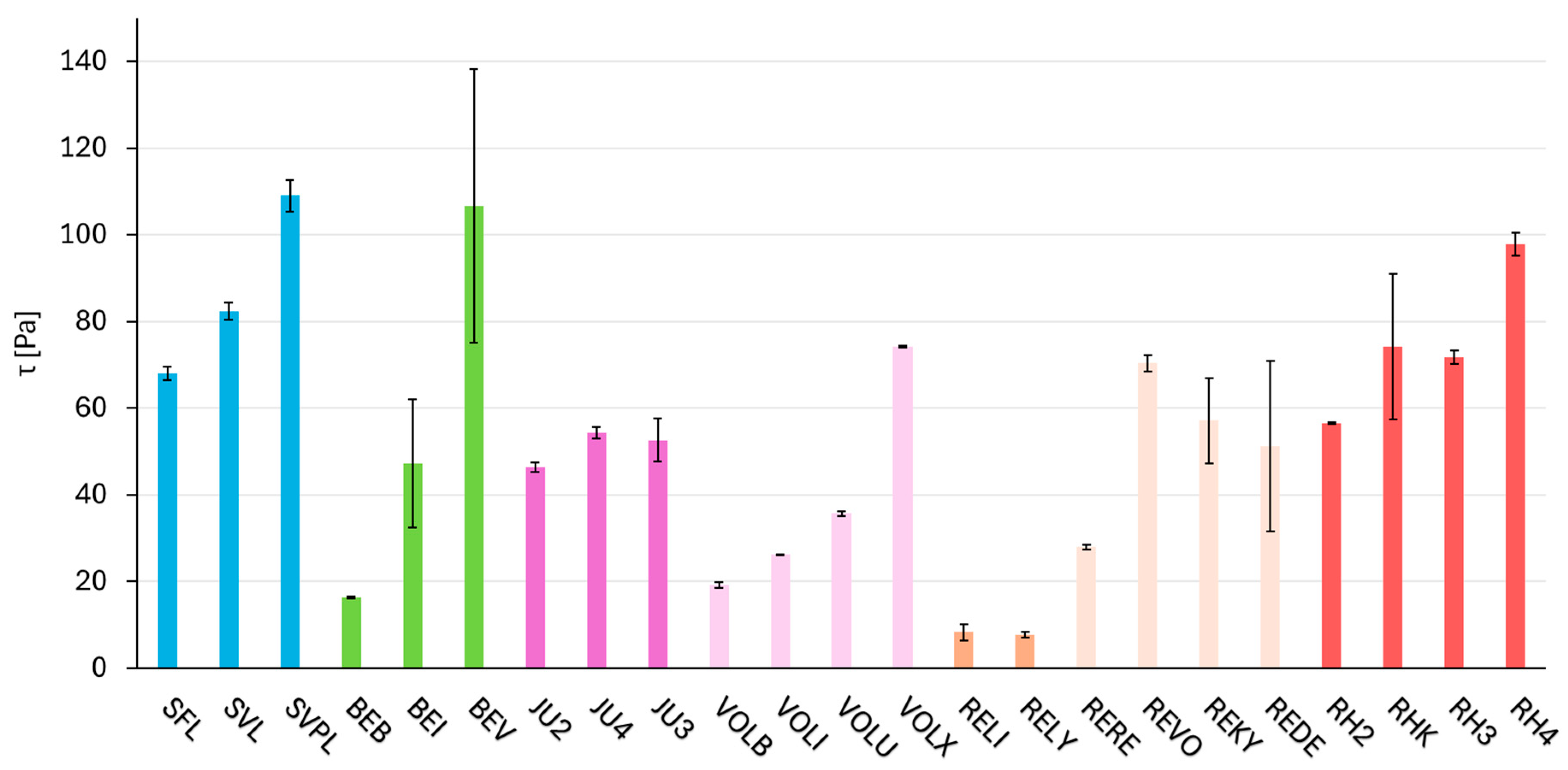
2.3. Dynamic Parameter—Rheology (Shear Stress τ)
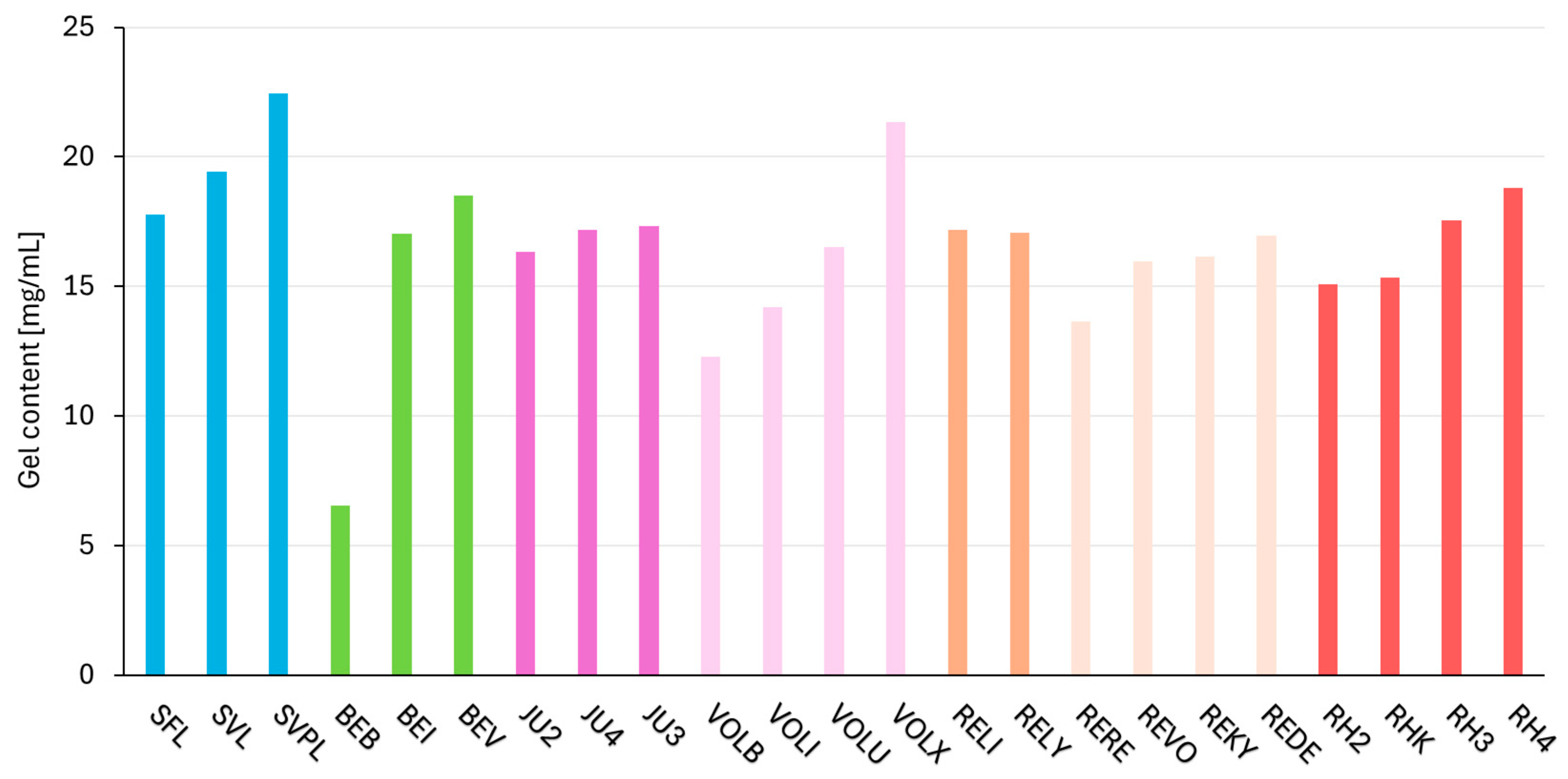
2.4. Dynamic Parameter—Gel Content
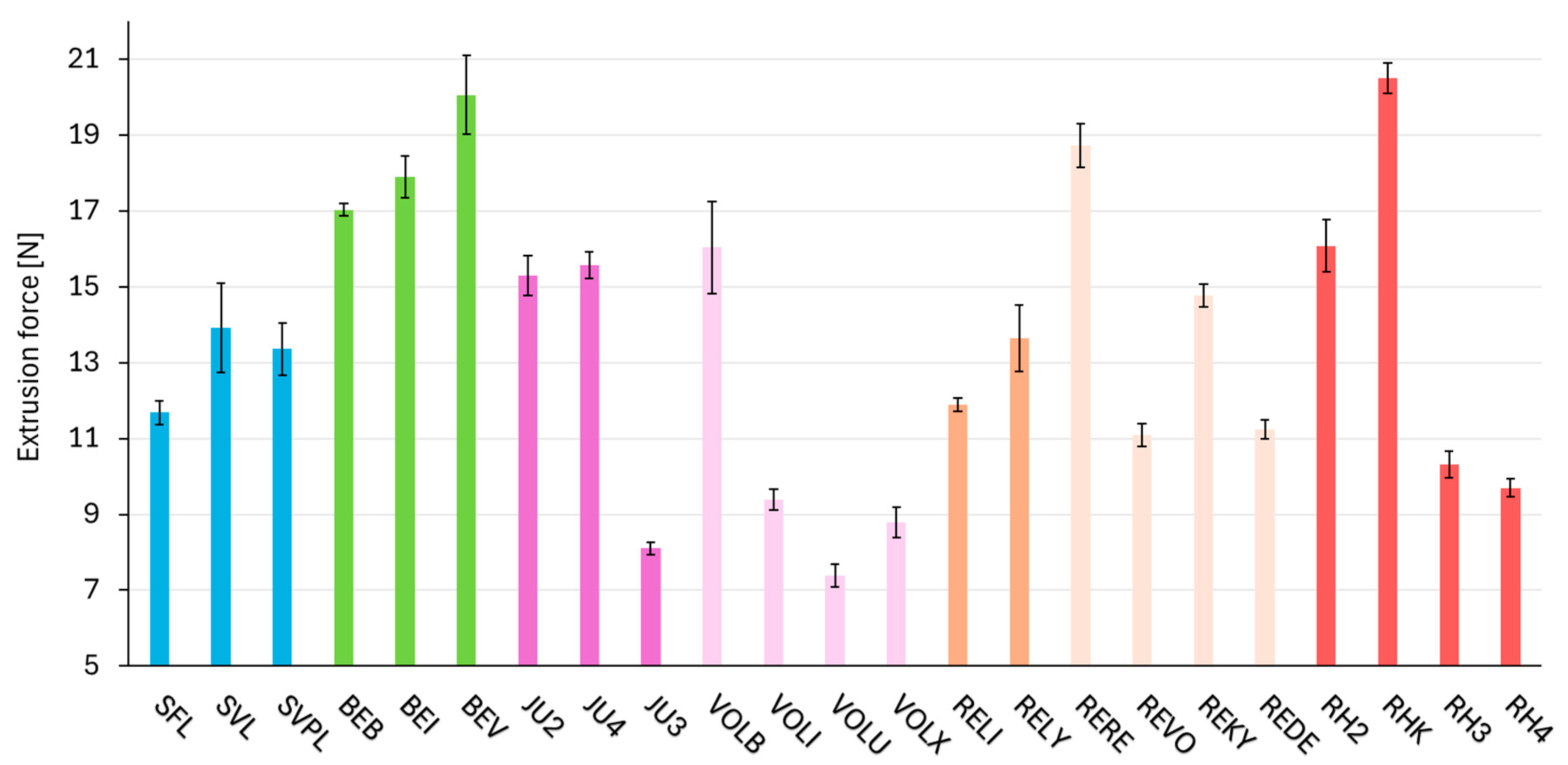
2.5. Consistency Parameter—Extrusion Force
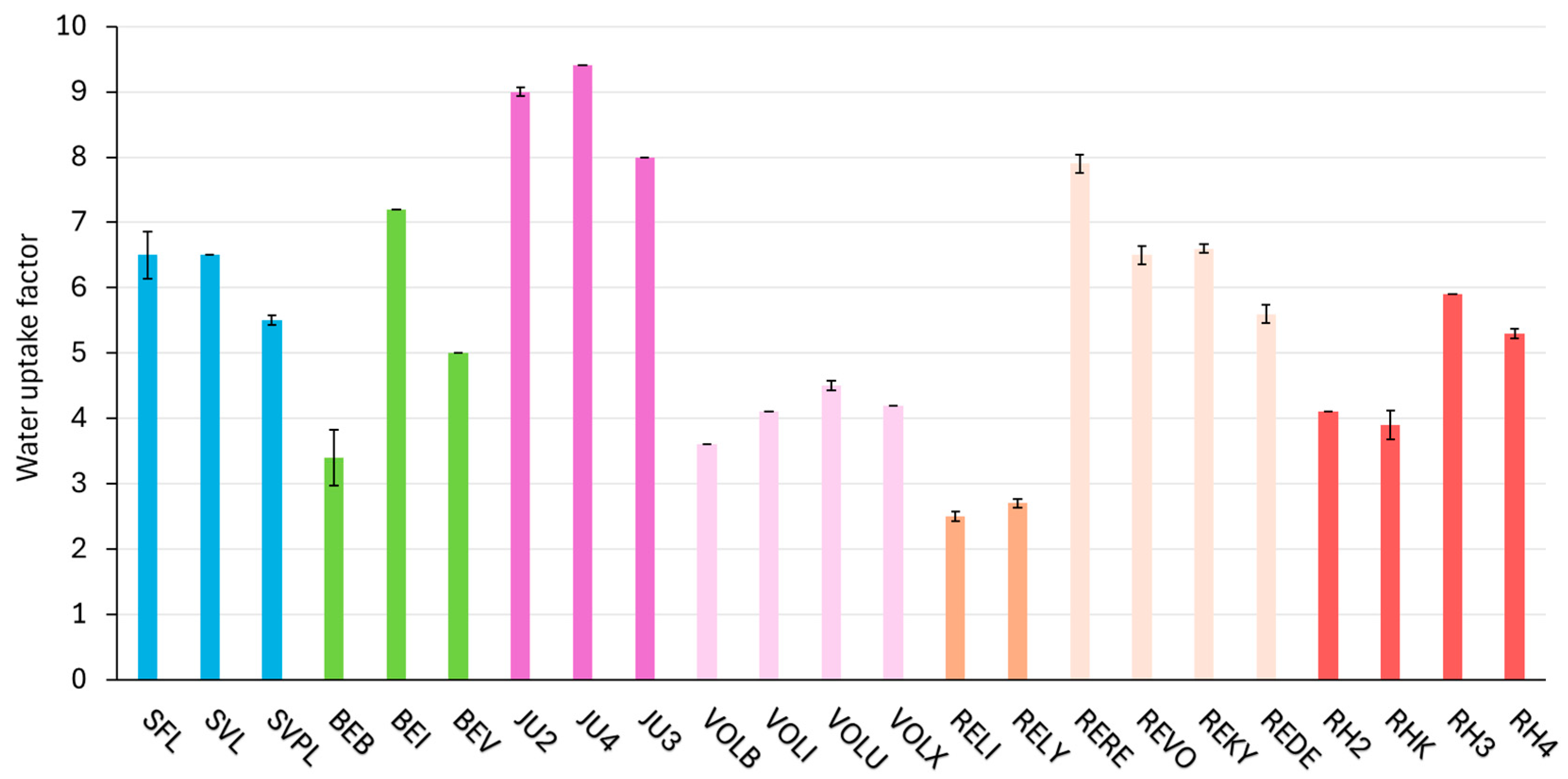
2.6. Consistency Parameter—Water Uptake
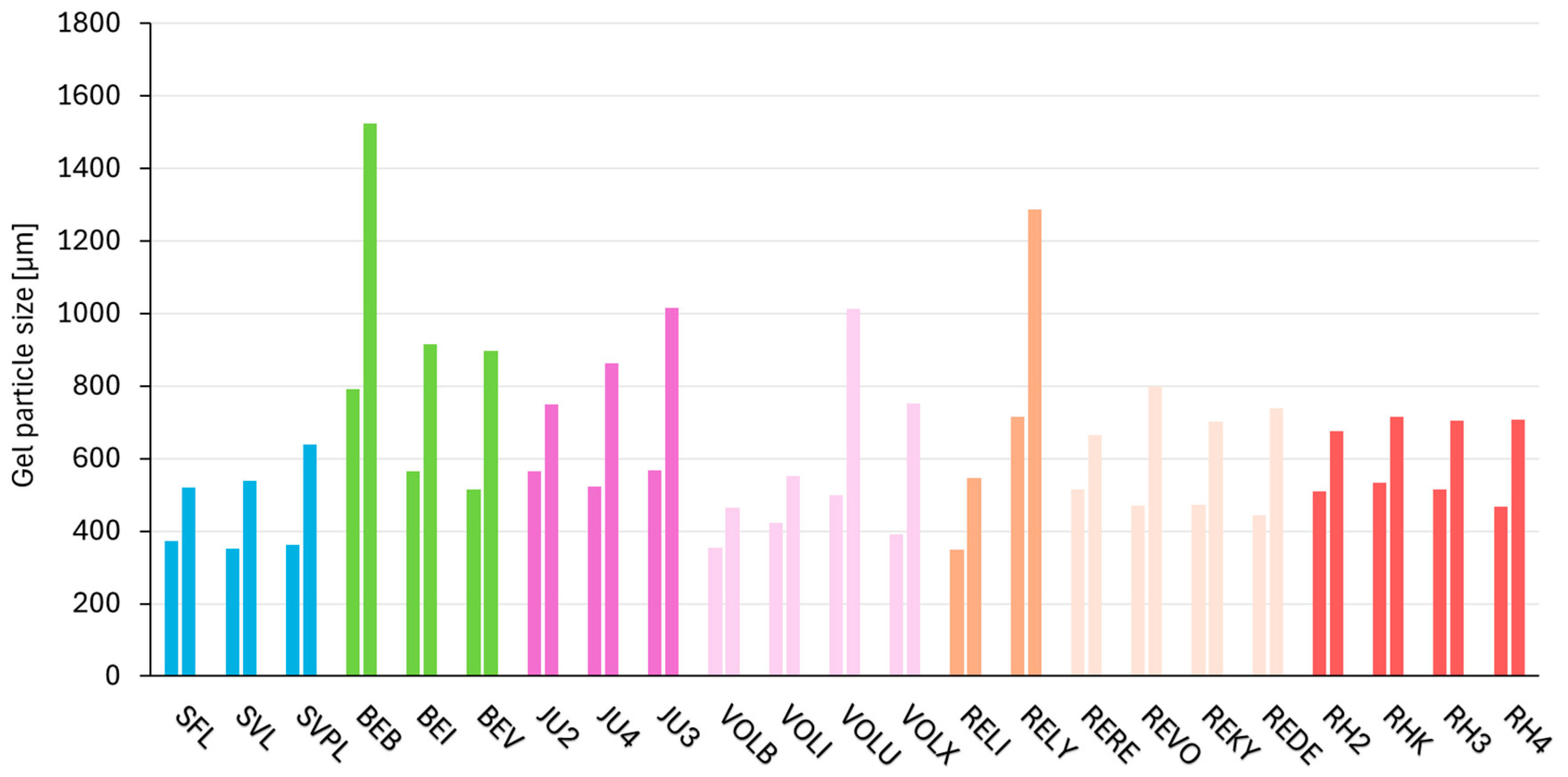
2.7. Consistency Parameter—Gel Particle Size Distribution
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Sample Selection and Data Analysis
5.2. Rheology
5.3. Gel Content
5.4. Extrusion Force
5.5. Water Uptake
5.6. Gel Particle Size Distribution
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HA | Hyaluronic acid |
| G′ | Storage modulus (elastic modulus) |
| G″ | Loss modulus (viscous modulus) |
| tan δ | Loss factor |
| τ (tau) | Shear stress |
| γ (gamma) | Shear deformation |
| ω (omega) | Angular frequency |
| LVR | linear viscoelastic range |
| DV10 | Gel particle diameter below which 10% of the total sample volume is contained |
| DV50 | Median gel particle diameter (50% of particle volume is below this size) |
| DV90 | Gel particle diameters below which 90% of the total sample volume is contained |
| DV90–10 | Difference between DV90 and DV10 (particle size range of the central 80% of the volume) |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| BDDE | 1,4-Butanediol diglycidyl ether |
| RSD | Relative standard deviation |
| G | Gauge (used for needle size, e.g., 27 G) |
| TW | Thin wall (needle type) |
| UTW | Ultra-thin wall (needle type) |
Appendix A
| Product | G′ [Pa] | G″ [Pa] | tan δ [-] |
|---|---|---|---|
| SFL | 147.3 | 26.3 | 0.18 |
| SVL | 228.8 | 26.1 | 0.11 |
| SVPL | 443.9 | 45.0 | 0.10 |
| BEB | 15.7 | 12.9 | 0.82 |
| BEI | 83.9 | 33.0 | 0.39 |
| BEV | 185.4 | 44.9 | 0.24 |
| JU2 | 79.2 | 21.5 | 0.27 |
| JU4 | 84.4 | 17.7 | 0.21 |
| JU3 | 100.4 | 21.3 | 0.21 |
| VOLB | 212.1 | 30.4 | 0.14 |
| VOLI | 247.4 | 31.6 | 0.13 |
| VOLU | 306.3 | 30.1 | 0.10 |
| VOLX | 544.7 | 58.8 | 0.11 |
| RELI | 562.3 | 123.3 | 0.22 |
| RELY | 584.8 | 107.6 | 0.18 |
| RERE | 62.0 | 14.7 | 0.24 |
| REVO | 150.8 | 16.6 | 0.11 |
| REKY | 152.7 | 17.3 | 0.11 |
| REDE | 253.6 | 25.2 | 0.10 |
| RH2 | 110.6 | 34.6 | 0.31 |
| RHK | 134.4 | 38.6 | 0.29 |
| RH3 | 153.0 | 29.1 | 0.19 |
| RH4 | 270.9 | 40.2 | 0.15 |
| Product | LVR | LVR | LVR | LVR | LVR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| γ [%] | τ [Pa] | G′ [Pa] | G″ [Pa] | tan δ [-] | |
| SFL | 36.6 | 68.0 | 176.1 | 46.0 | 0.26 |
| SVL | 32.3 | 82.3 | 245.2 | 47.1 | 0.19 |
| SVPL | 23.0 | 109.0 | 459.9 | 89.5 | 0.19 |
| BEB | 30.7 | 16.3 | 39.0 | 35.2 | 0.88 |
| BEI | 31.8 | 47.3 | 133.3 | 61.6 | 0.45 |
| BEV | 43.7 | 106.7 | 231.7 | 66.4 | 0.28 |
| JU2 | 38.9 | 46.3 | 108.7 | 43.7 | 0.39 |
| JU4 | 48.0 | 52.6 | 126.9 | 40.8 | 0.32 |
| JU3 | 47.5 | 54.3 | 107.2 | 37.6 | 0.35 |
| VOLB | 8.3 | 19.2 | 224.0 | 47.4 | 0.21 |
| VOLI | 9.9 | 26.2 | 254.8 | 52.0 | 0.20 |
| VOLU | 11.2 | 35.7 | 309.5 | 43.9 | 0.14 |
| VOLX | 13.0 | 74.2 | 561.6 | 98.1 | 0.17 |
| RELI | 1.1 | 8.3 | 722.7 | 148.2 | 0.20 |
| RELY | 1.1 | 7.8 | 701.6 | 124.2 | 0.17 |
| RERE | 32.8 | 27.9 | 79.9 | 29.6 | 0.37 |
| REVO | 33.9 | 57.1 | 166.8 | 36.8 | 0.22 |
| REKY | 43.7 | 70.4 | 158.5 | 23.1 | 0.14 |
| REDE | 19.8 | 51.2 | 261.2 | 45.7 | 0.18 |
| RH2 | 33.8 | 56.6 | 153.9 | 55.3 | 0.35 |
| RHK | 31.2 | 97.8 | 300.3 | 47.9 | 0.15 |
| RH3 | 37.7 | 74.1 | 184.5 | 59.2 | 0.31 |
| RH4 | 37.3 | 71.7 | 182.1 | 46.5 | 0.25 |
| Product | HA Content [mg/mL] 1 | Gel Content [%] 2 | Gel Content [mg/mL] 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| SFL | 23.0 | 76.0 | 17.5 |
| SVL | 23.0 | 86.0 | 19.8 |
| SVPL | 25.0 | 90.0 | 22.5 |
| BEB | 22.5 | 29.0 | 6.5 |
| BEI | 25.5 | 66.8 | 17.0 |
| BEV | 26.0 | 71.3 | 18.5 |
| JU2 | 24.0 | 68.1 | 16.3 |
| JU4 | 24.0 | 71.5 | 17.2 |
| JU3 | 24.0 | 72.2 | 17.3 |
| VOLB | 15.0 | 82.0 | 12.3 |
| VOLI | 17.5 | 81.1 | 14.2 |
| VOLU | 20.0 | 82.6 | 16.5 |
| VOLX | 25.0 | 85.3 | 21.3 |
| RELI | 20.0 | 86.0 | 17.2 |
| RELY | 20.0 | 85.4 | 17.1 |
| RERE | 20.0 | 68.3 | 13.7 |
| REVO | 20.0 | 79.8 | 16.0 |
| REKY | 20.0 | 80.7 | 16.1 |
| REDE | 20.0 | 84.9 | 17.0 |
| RH2 | 23.0 | 65.5 | 15.1 |
| RHK | 23.0 | 66.8 | 15.4 |
| RH3 | 23.0 | 76.2 | 17.5 |
| RH4 | 23.0 | 81.7 | 18.8 |
| Product | Extrusion Force [N] | Needle Type Used |
|---|---|---|
| SFL | 12 | 27 G ½″ TW Terumo K-Pack II |
| SVL | 14 | 27 G ½″ TW Terumo K-Pack II |
| SVPL | 13 | 27 G ½″ TW Terumo K-Pack II |
| BEB | 17 1 | 30 G ½″ TSK PRC-30013I |
| BEI | 18 1 | 27 G ½″ TSK HPC-27013I |
| BEV | 20 | 30 G ½″ TSK PRC-30013I |
| JU2 | 15 | 30 G ½″ TSK HPC-30013A |
| JU4 | 16 | 27 G ½″ TSK HPC-27013A |
| JU3 | 8 | 27 G ½″ TSK HPC-27013A |
| VOLB | 16 | 32 G ½″ TSK HPC-32013A |
| VOLI | 9 | 30 G ½″ TSK HPC-30013A |
| VOLU | 7 | 27 G ½″ TSK HPC-27013A |
| VOLX | 9 | 27 G ½″ TSK HPC-27013A |
| RELI | 12 1 | 29 G ½″ TW Terumo K-Pack II |
| RELY | 14 | 27 G ½″ TW Terumo K-Pack II |
| RERE | 19 1 | 30 G ½″ TSK HPC-30013I |
| REVO | 11 1 | 27 G ½″ TSK HPC-27013I |
| REKY | 15 1 | 30 G ½″ UTW Terumo K-Pack II |
| REDE | 11 1 | 27 G ½″ TSK HPC-27013I |
| RH2 | 16 | 30 G ½″ TSK HPC-30013I |
| RHK | 21 | 30 G ½″ TW Terumo K-Pack II |
| RH3 | 10 | 27 G ½″ TSK HPC-27013I |
| RH4 | 10 | 27 G ½″ TSK HPC-27013I |
| Product | Gel Particle Size Distribution [µm] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DV10 | DV50 | DV90 | DV90-10 | |
| SFL | 182 | 374 | 703 | 521 |
| SVL | 164 | 351 | 704 | 540 |
| SVPL | 152 | 361 | 791 | 639 |
| BEB | 346 | 792 | 1870 | 1524 |
| BEI | 275 | 566 | 1190 | 915 |
| BEV | 214 | 514 | 1110 | 896 |
| JU2 | 280 | 566 | 1030 | 750 |
| JU4 | 236 | 523 | 1100 | 864 |
| JU3 | 253 | 569 | 1270 | 1017 |
| VOLB | 174 | 354 | 639 | 465 |
| VOLI | 198 | 424 | 751 | 553 |
| VOLU | 176 | 498 | 1190 | 1014 |
| VOLX | 140 | 390 | 891 | 751 |
| RELI | 123 | 348 | 669 | 546 |
| RELY | 152 | 716 | 1440 | 1288 |
| RERE | 247 | 515 | 912 | 665 |
| REVO | 198 | 470 | 999 | 801 |
| REKY | 203 | 474 | 904 | 701 |
| REDE | 177 | 443 | 917 | 740 |
| RH2 | 245 | 511 | 920 | 675 |
| RHK | 252 | 534 | 968 | 716 |
| RH3 | 238 | 514 | 943 | 705 |
| RH4 | 195 | 468 | 902 | 707 |
| Manufacturer 1 | Crosslinking Technology | Product Name | Abbreviation | Provided Needle | Product Batch Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Croma | Macro | Saypha Filler Lidocaine | SFL | 27 G ½″ TW Terumo K-Pack II | 905015 |
| Saypha Volume Lidocaine | SVL | 27 G ½″ TW Terumo K-Pack II | 106024 | ||
| Saypha Volume Plus Lidocaine | SVPL | 27 G ½″ TW Terumo K-Pack II | 206020 | ||
| Merz Aesthetics | DCLT | Belotero Balance Lidocaine | BEB | 27 G ½″ TSK PRC-27013I 30 G ½″ TSK PRC-30013I | B00021100 |
| Belotero Intense Lidocaine | BEI | 27 G ½″ TSK HPC-27013I | B00030380 | ||
| Belotero Volume Lidocaine | BEV | 27 G ½″ TSK PRC-27013I 30 G ½″ TSK PRC-30013I | B00021920 | ||
| Allergan Aesthetics | Hylacross | Juvéderm Ultra 2 | JU2 | 30 G ½″ TSK HPC-30013A | 1000610608 |
| Juvéderm Ultra 3 | JU3 | 27 G ½″ TSK HPC-27013A | 1000648446 | ||
| Juvéderm Ultra 4 | JU4 | 27 G ½″ TSK HPC-27013A | 1000749866 | ||
| Vycross | Juvéderm Volbella | VOLB | 32 G ½″ TSK HPC-32013A | 1000594126 | |
| Juvéderm Volift | VOLI | 30 G ½″ TSK HPC-30013A | 1000568917 | ||
| Juvéderm Voluma | VOLU | 27 G ½″ TSK HPC-27013A | 1000609303 | ||
| Juvéderm Volux | VOLX | 27 G ½″ TSK HPC-27013A | 1000546997 | ||
| Galderma | NASHA | Restylane Lidocaine | RELI | 29 G ½″ TW Terumo K-Pack II | 21568-1 |
| Restylane Lyft Lidocaine | RELY | 27 G ½″ TW Terumo K-Pack II | 21775-1 | ||
| OBT | Restylane Refyne | RERE | 30 G ½″ TSK HPC-30013I | 21497-1 | |
| Restylane Kysse | REKY | 30 G ½″ UTW Terumo K-Pack II | 21642 | ||
| Restylane Volyme | REVO | 27 G ½″ TSK HPC-27013I | 21641 | ||
| Restylane Defyne | REDE | 27 G ½″ TSK HPC-27013I | 21545 | ||
| Teoxane | RHA | Teosyal RHA 2 | RH2 | 30 G ½″ TSK HPC-30013I | 23171DLO |
| Teosyal RHA 3 | RH3 | 27 G ½″ TSK HPC-27013I | 23171JLO | ||
| Teosyal RHA 4 | RH4 | 27 G ½″ TSK HPC-27013I | 23341FLO | ||
| Teosyal RHA Kiss | RHK | 30 G ½″ Thin wall Terumo K-Pack II | 23221ALO |
References
- Laurent, T.C.; Fraser, J.R. Hyaluronan. FASEB J. 1992, 6, 2397–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallacara, A.; Baldini, E.; Manfredini, S.; Vertuani, S. Hyaluronic Acid in the Third Millennium. Polymers 2018, 10, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Garza, L.A.; Kang, S.; Varani, J.; Orringer, J.S.; Fisher, G.J.; Voorhees, J.J. In vivo stimulation of de novo collagen production caused by cross-linked hyaluronic acid dermal filler injections in photodamaged human skin. Arch. Dermatol. 2007, 143, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Necas, J.; Bartosikova, L.; Brauner, P.; Kolář, J. Hyaluronic acid (Hyaluronan): A review. Vet. Med. 2008, 53, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/europe-facial-injectables-market-report (accessed on 11 June 2025).
- Edsman, K.; Nord, L.I.; Ohrlund, A.; Larkner, H.; Kenne, A.H. Gel properties of hyaluronic acid dermal fillers. Dermatol. Surg. 2012, 38, 1170–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, H.; Cassuto, D. Biophysical characteristics of hyaluronic acid soft-tissue fillers and their relevance to aesthetic applications. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 132, 5S–21S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Gatta, A.; De Rosa, M.; Frezza, M.A.; Catalano, C.; Meloni, M.; Schiraldi, C. Biophysical and biological characterization of a new line of hyaluronan-based dermal fillers: A scientific rationale to specific clinical indications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2016, 68, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Gatta, A.; Salzillo, R.; Catalano, C.; D’Agostino, A.; Pirozzi, A.V.A.; De Rosa, M.; Schiraldi, C. Hyaluronan-based hydrogels as dermal fillers: The biophysical properties that translate into a “volumetric” effect. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0218287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagien, S.; Bertucci, V.; von Grote, E.; Mashburn, J.H. Rheologic and Physicochemical Properties Used to Differentiate Injectable Hyaluronic Acid Filler Products. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 143, 707e–720e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.W.; Moon, H.J.; Lee, H.M.; Kim, D.K.; Lee, K.H. Deformation characteristics of hydrogel products based on cross-linked hyaluronic acid. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 3118–3124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fundaro, S.P.; Salti, G.; Malgapo, D.M.H.; Innocenti, S. The Rheology and Physicochemical Characteristics of Hyaluronic Acid Fillers: Their Clinical Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluda, S.; Salvagnini, C.; Fontana, A.; Marchetti, A.; Di Lucia, A.; Galesso, D.; Guarise, C. Investigation of Crosslinking Parameters and Characterization of Hyaluronic Acid Dermal Fillers: From Design to Product Performances. Gels 2023, 9, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierre, S.; Liew, S.; Bernardin, A. Basics of dermal filler rheology. Dermatol. Surg. 2015, 41 (Suppl S1), S120–S126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavard Molliard, S.; Albert, S.; Mondon, K. Key importance of compression properties in the biophysical characteristics of hyaluronic acid soft-tissue fillers. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 61, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulino, P.; Santos, V.; Silva, N.; Mata, A.; da Cruz, M.B. Water Absorption and 3D Expansion of Different Injectable Hyaluronic Acids. J. Dermatol. Res. Rev. Rep. 2024, 5, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Hou, S.; Deng, S.; Peng, Y.; Fu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, J.; Peng, C. The Intrinsic Relation between the Hydrogel Structure and In Vivo Performance of Hyaluronic Acid Dermal Fillers: A Comparative Study of Four Typical Dermal Fillers. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2023, 20, 503–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheels, P.; Porcello, A.; Bezzola, T.; Perrenoud, D.; Quinodoz, P.; Kalia, Y.; Allemann, E.; Laurent, A.; Jordan, O. Clinical Perspectives on the Injectability of Cross-Linked Hyaluronic Acid Dermal Fillers: A Standardized Methodology for Commercial Product Benchmarking with Inter-Injector Assessments. Gels 2024, 10, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander Daoud, R.W. Hyaluronic Acid Fillers: Where We Have Been and Where We Are Going. In Extracellular Matrix—Developments and Therapeutics; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; pp. 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molliard, S.G.; Bétemps, J.B.; Hadjab, B.; Topchian, D.; Micheels, P.; Salomon, D. Key rheological properties of hyaluronic acid fillers: From tissue integration to product degradation. Plast. Aesthet. Res. 2018, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, D.S.; Grablowitz, D.; Krames-Juerss, A.; Worseg, A. Lip Augmentation with Saypha LIPS Lidocaine: A Postmarket, Prospective, Open-Label, Randomized Clinical Study to Evaluate Its Efficacy and Short- and Long-term Safety. Aesthet. Surg. J. 2024, 45, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohrlund, A.; Winlof, P.; Bromee, T.; Prygova, I. Differentiation of NASHA and OBT Hyaluronic Acid Gels According to Strength, Flexibility, and Associated Clinical Significance. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2024, 23, 1332–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merza Aesthetics. Available online: https://merzaesthetics.com.sg/belotero/ (accessed on 11 June 2025).
- Faivre, J.; Gallet, M.; Tremblais, E.; Trevidic, P.; Bourdon, F. Advanced Concepts in Rheology for the Evaluation of Hyaluronic Acid-Based Soft Tissue Fillers. Dermatol. Surg. 2021, 47, e159–e167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, H.; Voigts, B.; Beer, K.; Meland, M. Comparison of the rheological properties of viscosity and elasticity in two categories of soft tissue fillers: Calcium hydroxylapatite and hyaluronic acid. Dermatol. Surg. 2010, 36 (Suppl S3), 1859–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, M. The science and art of hyaluronic acid dermal filler use in esthetic applications. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2009, 8, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hee, C.K.; Shumate, G.T.; Narurkar, V.; Bernardin, A.; Messina, D.J. Rheological Properties and In Vivo Performance Characteristics of Soft Tissue Fillers. Dermatol. Surg. 2015, 41 (Suppl S1), S373–S381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, S.; Russo, L.; Argenzio, V.; Borzacchiello, A. Rheological properties of cross-linked hyaluronic acid dermal fillers. J. Appl. Biomater. Biomech. 2011, 9, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Öhrlund, Å. Evaluation of Rheometry Amplitude Sweep Cross-Over Point as an Index of Flexibility for HA Fillers. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. Sci. Appl. 2018, 08, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kablik, J.; Monheit, G.D.; Yu, L.; Chang, G.; Gershkovich, J. Comparative physical properties of hyaluronic acid dermal fillers. Dermatol. Surg. 2009, 35 (Suppl S1), 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraser, J.R.; Laurent, T.C.; Laurent, U.B. Hyaluronan: Its nature, distribution, functions and turnover. J. Intern. Med. 1997, 242, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegeau, K.; Jing, J.; Vantou, C.; Brusini, R.; Bourdon, F.; Faivre, J. Strengthening the Key Features of Volumizing Fillers: Projection Capacity and Long-Term Persistence. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.; Dodou, K. Current Knowledge and Regulatory Framework on the Use of Hyaluronic Acid for Aesthetic Injectable Skin Rejuvenation Treatments. Cosmetics 2024, 11, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, G.W.; Wan, J.; Chang, K.; Park, Y.; Yi, K.H. Decomposition and Changes in In Vivo Post-HA Filler Injection: A Review. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2025, 24, e16652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Boulle, K.; Glogau, R.; Kono, T.; Nathan, M.; Tezel, A.; Roca-Martinez, J.X.; Paliwal, S.; Stroumpoulis, D. A review of the metabolism of 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether-crosslinked hyaluronic acid dermal fillers. Dermatol. Surg. 2013, 39, 1758–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Manufacturer | Crosslinking Technology | Product Name | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Allergan Aesthetics | Hylacross | Juvéderm Ultra 2 | JU2 |
| Juvéderm Ultra 3 | JU3 | ||
| Juvéderm Ultra 4 | JU4 | ||
| Vycross | Juvéderm Volbella | VOLB | |
| Juvéderm Volift | VOLI | ||
| Juvéderm Voluma | VOLU | ||
| Juvéderm Volux | VOLX | ||
| Croma | Macro | Saypha Filler Lidocaine | SFL |
| Saypha Volume Lidocaine | SVL | ||
| Saypha Volume Plus Lidocaine | SVPL | ||
| Galderma | NASHA | Restylane Lidocaine | RELI |
| Restylane Lyft Lidocaine | RELY | ||
| OBT | Restylane Refyne | RERE | |
| Restylane Kysse | REKY | ||
| Restylane Volyme | REVO | ||
| Restylane Defyne | REDE | ||
| Merz Aesthetics | DCLT | Belotero Balance Lidocaine | BEB |
| Belotero Intense Lidocaine | BEI | ||
| Belotero Volume Lidocaine | BEV | ||
| Teoxane | RHA | Teosyal RHA 2 | RH2 |
| Teosyal RHA 3 | RH3 | ||
| Teosyal RHA 4 | RH4 | ||
| Teosyal RHA Kiss | RHK |
| Crosslinking Technology | Crosslinking Description |
|---|---|
| Hylacross | HAs of the same molecular weight are crosslinked together, creating a relatively uniform product of set viscosity and thickness [19]. |
| Vycross | Utilizes a novel mix of low-molecular-weight HA (<1 MDa) and high-molecular-weight HA (>1 MDa); low HA concentration [20]. |
| Macro | Predefined viscoelastic characteristics. High molecular weight HA undergoes controlled processing to maintain consistency in the crosslinking process [21] |
| NASHA | Preservation of naturally long HA chains resulting in strong gels with high G′. Minimal modification and controlled particle sizing [22]. |
| OBT | Flexible HA Fillers. Strength/firmness varied by applying different degrees of crosslinking [22]. |
| DCLT | DCLT includes two additional phases. This provides a combination of cohesivity, elasticity, and plasticity [23]. |
| RHA | Improved HA chain integrity, preserving long (high Mw) HA, with low amounts of crosslinker to achieve clinically desirable mechanical properties and durability [24]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Puljic, A.; Frank, K.; Cohen, J.; Otto, K.; Mayr, J.; Hugh-Bloch, A.; Kuroki-Hasenöhrl, D. A Scientific Framework for Comparing Hyaluronic Acid Filler Crosslinking Technologies. Gels 2025, 11, 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070487
Puljic A, Frank K, Cohen J, Otto K, Mayr J, Hugh-Bloch A, Kuroki-Hasenöhrl D. A Scientific Framework for Comparing Hyaluronic Acid Filler Crosslinking Technologies. Gels. 2025; 11(7):487. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070487
Chicago/Turabian StylePuljic, Anto, Konstantin Frank, Joel Cohen, Karine Otto, Josef Mayr, Andreas Hugh-Bloch, and David Kuroki-Hasenöhrl. 2025. "A Scientific Framework for Comparing Hyaluronic Acid Filler Crosslinking Technologies" Gels 11, no. 7: 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070487
APA StylePuljic, A., Frank, K., Cohen, J., Otto, K., Mayr, J., Hugh-Bloch, A., & Kuroki-Hasenöhrl, D. (2025). A Scientific Framework for Comparing Hyaluronic Acid Filler Crosslinking Technologies. Gels, 11(7), 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070487







