Self-Healing and Tough Polyacrylic Acid-Based Hydrogels for Micro-Strain Sensors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
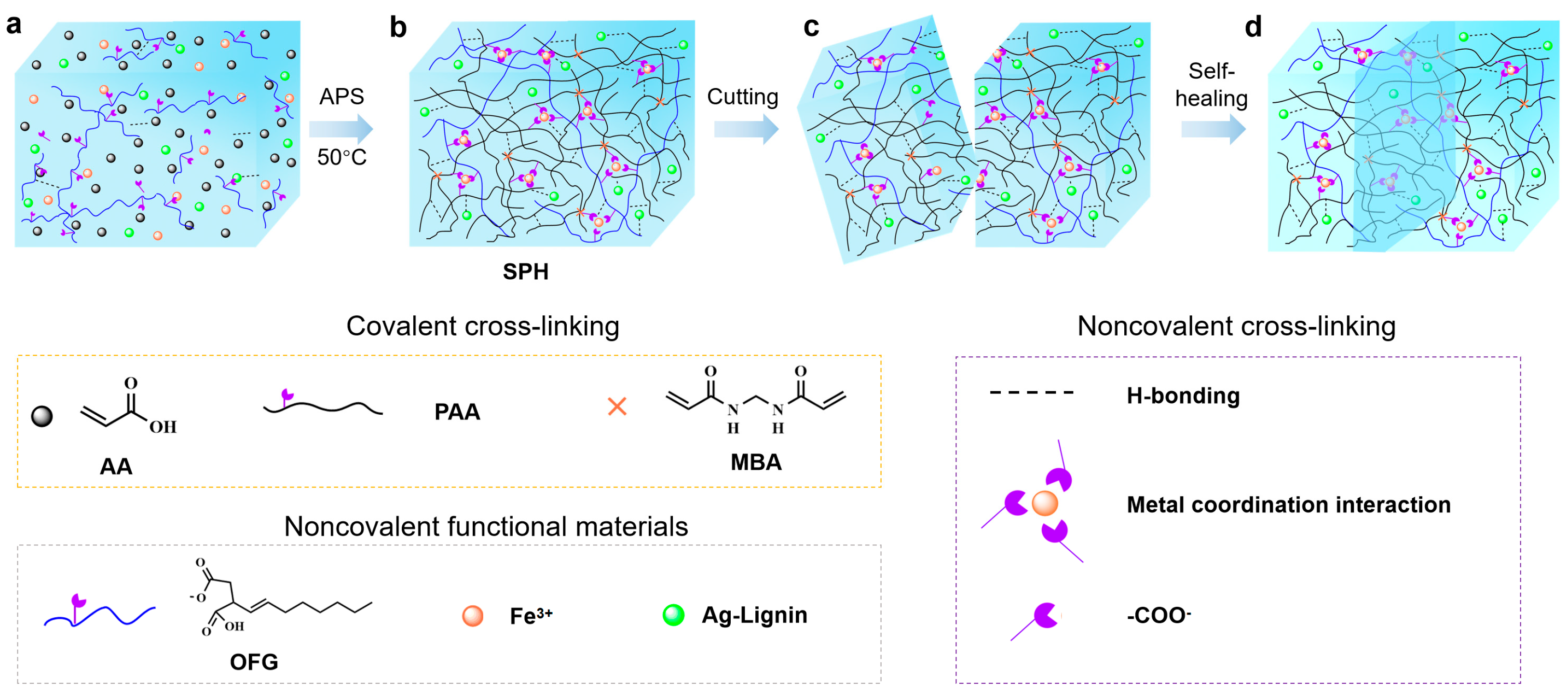
2.1. Characterization Results of the Hydrogel
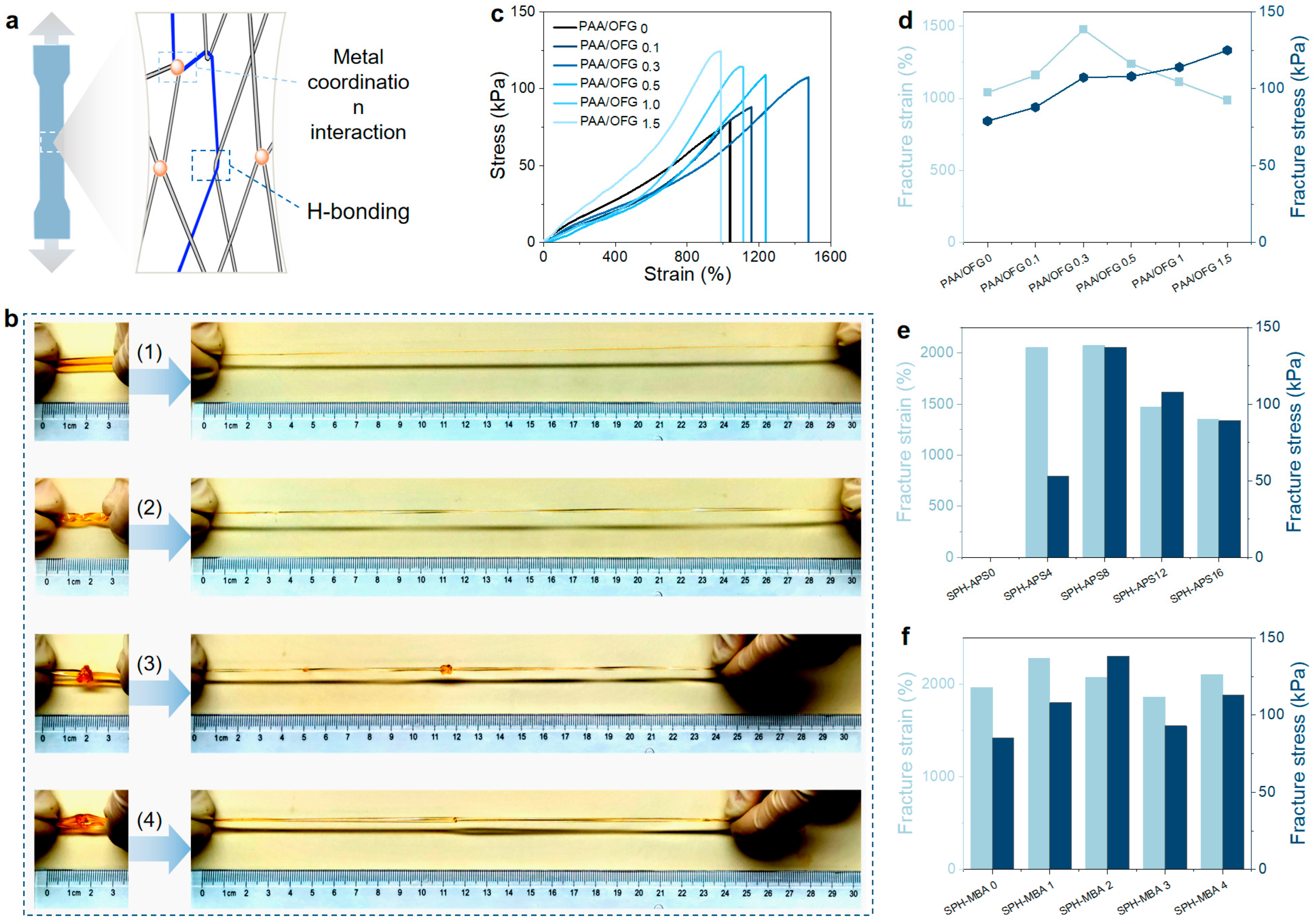
2.2. Mechanical Properties of the Hydrogel
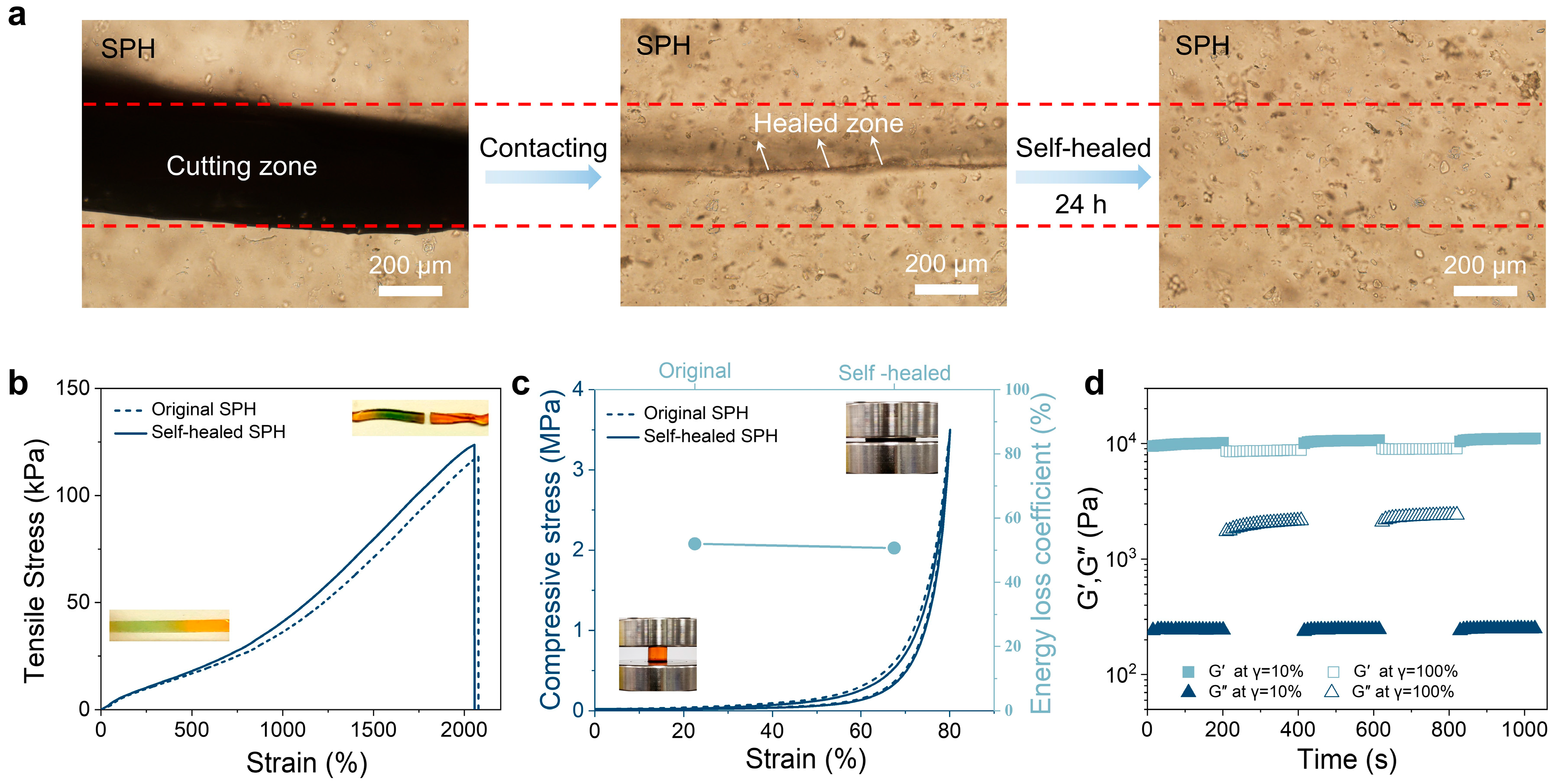
2.3. Self-Healing Properties of the Hydrogel
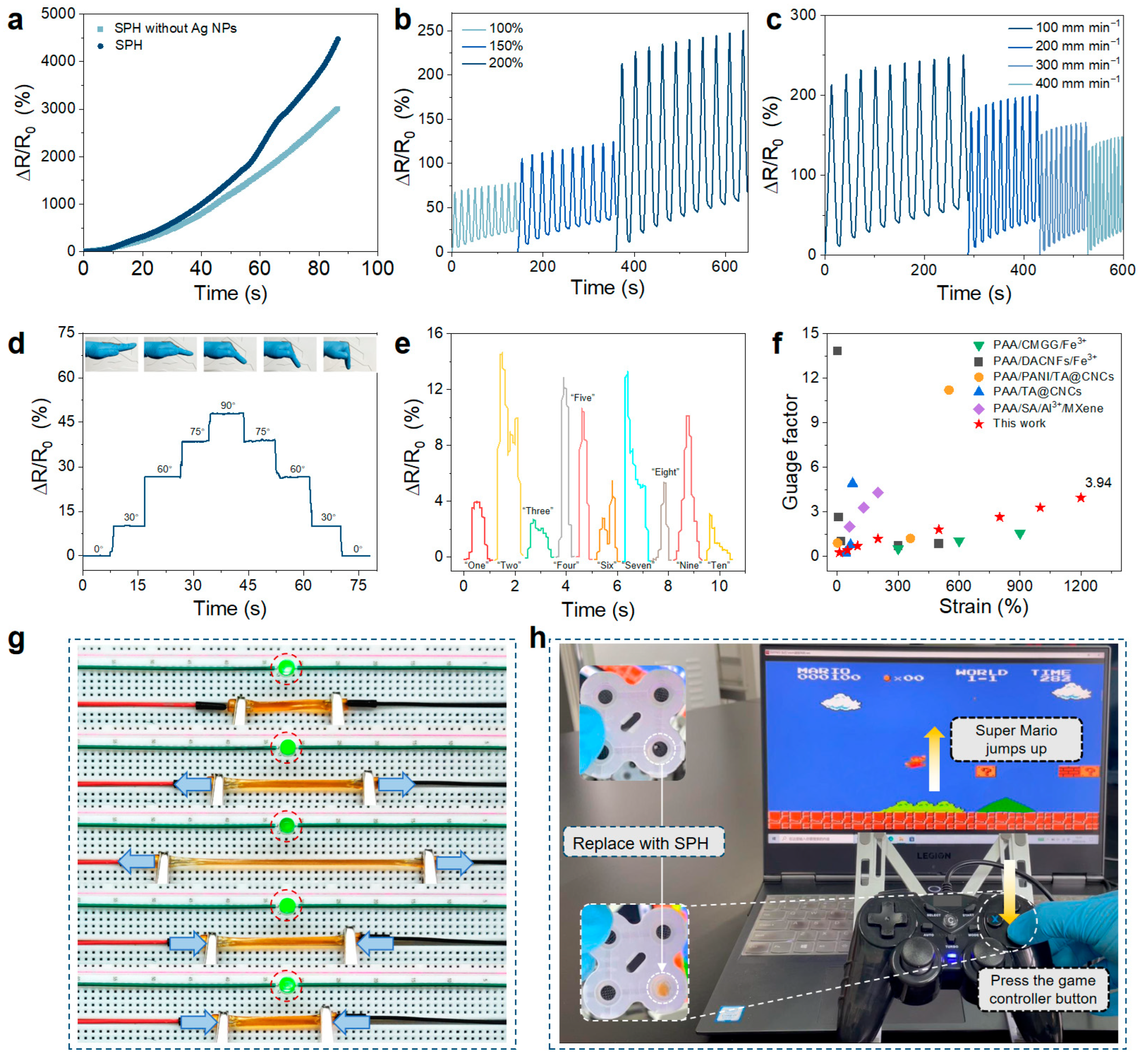
2.4. Sensing Properties of the Hydrogel
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Hydrogels
4.3. Characterization
4.4. Mechanical Testing
4.5. Self-Healing Testing
4.6. Fabrication Strain Sensors
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OFG | Modified fenugreek galactomannan |
| PAA | Polyacrylic acid |
| Ag-NPs | Lignin–silver nanoparticles |
| SPH | Self-healing PAA/OFG-Fe3+ hydrogel |
References
- Chen, K.Y.; Xu, Y.T.; Zhao, Y.; Li, J.K.; Wang, X.P.; Qu, L.T. Recent progress in graphene-based wearable piezoresistive sensors: From 1D to 3D device geometries. Nano Mater. Sci. 2023, 5, 247–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Zhao, F.; Cheng, Z.H.; Deng, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, P.; Huang, Y.; Shao, H.; Qu, L. Electric power generation via asymmetric moisturizing of graphene oxide for flexible, printable and portable electronics. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 1730–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Qiao, C.Y.; Sui, P.F.; Luo, J.; Li, Z.; Cao, Y.; Pei, R.; Peng, X.; Zeng, H. Stratum corneum-inspired zwitterionic hydrogels with intrinsic water retention and anti-freezing properties for intelligent flexible sensors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 2422755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, M.Y.; Li, Z.H.; Dou, H.; Zhang, W.; Yang, J.; Wu, P.; Li, D.; Mu, X. Machine learning-assisted wearable sensing systems for speech recognition and interaction. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchantchane, R.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, S.; Alici, G. Fabrication and characterization of a soft and stretchable capacitive strain sensor for hand gesture recognition. IEEE Sens. J. 2025, 25, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.L.; Chen, X.L.; Yang, B.; Luo, S.; Guo, M.; An, N.; Tian, H.; Li, X.; Shao, J. Advancements in functionalizable metal-organic frameworks for flexible sensing electronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 2501683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, B.; Jones, M.; Ionescu, C.; Walker, D.; Wagle, S.; Chester, J.; Foster, T.; Brown, D.; Mikov, M.; Mooranian, A.; et al. The emerging role of bile acids as critical components in nanotechnology and bioengineering: Pharmacology, formulation optimizers and hydrogel-biomaterial applications. Biomaterials 2022, 283, 121459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.; Ni, Y.; Kong, X.; Li, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.L. Self-healing and elastic triboelectric nanogenerators for muscle motion monitoring and photothermal treatment. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 14653–14661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liang, Y.; Gao, G.; Wei, S.; Jian, Y.; Le, X.; Lu, W.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Chen, T. Asymmetric bilayer CNTs-elastomer/hydrogel composite as soft actuators with sensing performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 415, 128988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Ji, X.; Gong, J.; Hu, Y.; Wu, W.; Wang, X.; Peng, H.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Lam, J.W.Y.; et al. Bioinspired simultaneous changes in fluorescence color, brightness, and shape of hydrogels enabled by AIEgens. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Yan, M.X.; Dong, H.Q.; Wang, C.; Shao, L.; Xiao, X.; Li, W.; Ji, Z.; Ling, Z. Biomimetic construction of adhesive, self-healing and antifatigue hydrogels via galactomannan-induced double-network cross-linking for flexible strain sensors. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2025, 7, 2517–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.S.; Wei, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Qin, X.; Zhang, L. Ultra-stretchable, tough, and self-healing polyurethane with tunable microphase separation for flexible wearable electronics. Nano Energy 2025, 139, 110908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robby, A.I.; Lee, G.; Park, S.Y. NIR-induced pH-reversible self-healing monitoring with smartphone by wireless hydrogel sensor. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2019, 297, 126783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.K.; Shauloff, N.; Sui, X.; Wagner, H.D.; Jelinek, R. Polydiacetylene hydrogel self-healing capacitive strain sensor. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 6034–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Shen, B.; Mo, J.; Tang, F.; Feng, J. Highly stretchable and self-healing double network hydrogel based on polysaccharide and polyzwitterion for wearable electric skin. Polymer 2020, 194, 122381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Ke, T.; Ling, Q.; Zhao, L.; Gu, H. Rapid self-healing and self-adhesive chitosan-based hydrogels by host-guest interaction and dynamic covalent bond as flexible sensor. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 273, 118533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Li, L.; Pan, L.; Wang, H.; Bin, Y. MWCNTsreinforced conductive, self-healing polyvinyl alcohol/carboxymethyl chitosan/oxidized sodium alginate hydrogel as the strain sensor. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 49800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Tang, F.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Q.; Liu, S.; Li, L. Self-healing and highly stretchable gelatin hydrogel for self-powered strain sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 1558–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Bu, Y.H.; Li, D.L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, G.; Wan, X.; Li, N. Development of high-strength, tough, and self-healing carboxymethyl guar gum-based hydrogels for human motion detection. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Bu, Y.H.; Li, D.L.; Liu, C.; Chen, G.; Wan, X.; Li, N. High-strength, tough, and self-healing hydrogel based on carboxymethyl cellulose. Cellulose 2019, 27, 853–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Ning, R.X.; Lei, F.H.; Li, P.; Wang, K.; Jiang, J. Study on the structure and physicochemical properties of fenugreek galactomannan modified via octenyl succinic anhydride. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 214, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.J.; Cheng, X.C.; Zhang, F.L.; Lei, F.; Li, P.; Wang, K.; Jiang, J. Preparation and application of galactomannan-based green hydrogels initiated by lignin-Ag NPs. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 105256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.H.; Yu, D.H.; Gong, X.; Li, Z.; Zhao, R.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Li, G.; Wang, H.; Liu, W.; et al. Amylopectin-enhanced MXene/gallium hydrogels: High-performance flexible conductive materials for multifunctional sensing, EMI shielding, and energy storage applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 510, 161793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, L.Z.; Sufu, A.; Liu, F.F. Stretchable and self-healing carboxymethyl cellulose/polyacrylic acid conductive hydrogels for monitoring human motions and electrophysiological signals. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 293, 138900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, D.; Xing, W.; Jiang, L.; Fang, J.; Zhao, C.; Ren, F.; Fang, L.; Wang, K.; Lu, X. Plant-inspired adhesive and tough hydrogel based on Ag-Lignin nanoparticles-triggered dynamic redox catechol chemistry. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Li, B.; Fu, S. Synergy coordination of cellulose-based dialdehyde and carboxyl with Fe3+ recoverable conductive self-healing hydrogel for sensor. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2021, 125, 112094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.Y.; Meng, L.; Cui, C.; Yang, J. An integrated self-healable and robust conductive hydrogel for dynamically self-adhesive and highly conformable electronic skin. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 15208–15218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, C.; Wang, M.; Meng, L.; Chang, H.; Wang, B.; Xu, F.; Yang, J.; Wan, P. Mussel-inspired cellulose nanocomposite tough hydrogels with synergistic self-healing, adhesive, and strain-sensitive properties. Chem. Mater. 2018, 30, 3110–3121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.H.; Wang, D.; Huang, J.Y.; Ke, H.Z.; Wei, Q.F. A highly sensitive epidermal sensor based on triple-bonded hydrogels for strain/pressure sensing. Compos. Commun. 2021, 28, 100951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, C.; Liu, Z.; Lu, B. Self-Healing and Tough Polyacrylic Acid-Based Hydrogels for Micro-Strain Sensors. Gels 2025, 11, 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070475
Liu C, Liu Z, Lu B. Self-Healing and Tough Polyacrylic Acid-Based Hydrogels for Micro-Strain Sensors. Gels. 2025; 11(7):475. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070475
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Chuanjie, Zhihong Liu, and Bing Lu. 2025. "Self-Healing and Tough Polyacrylic Acid-Based Hydrogels for Micro-Strain Sensors" Gels 11, no. 7: 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070475
APA StyleLiu, C., Liu, Z., & Lu, B. (2025). Self-Healing and Tough Polyacrylic Acid-Based Hydrogels for Micro-Strain Sensors. Gels, 11(7), 475. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11070475





