Effects of Different Dual-Modified Jujube Juicing Residue Dietary Fibers on the Properties of Egg Protein Gels Induced by Alkalinity and Heat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Effect of Dual Modifications on Chemical Composition of JJRDFs
2.2. Colour and Size of JJRDFs
2.3. Structural Characteristics
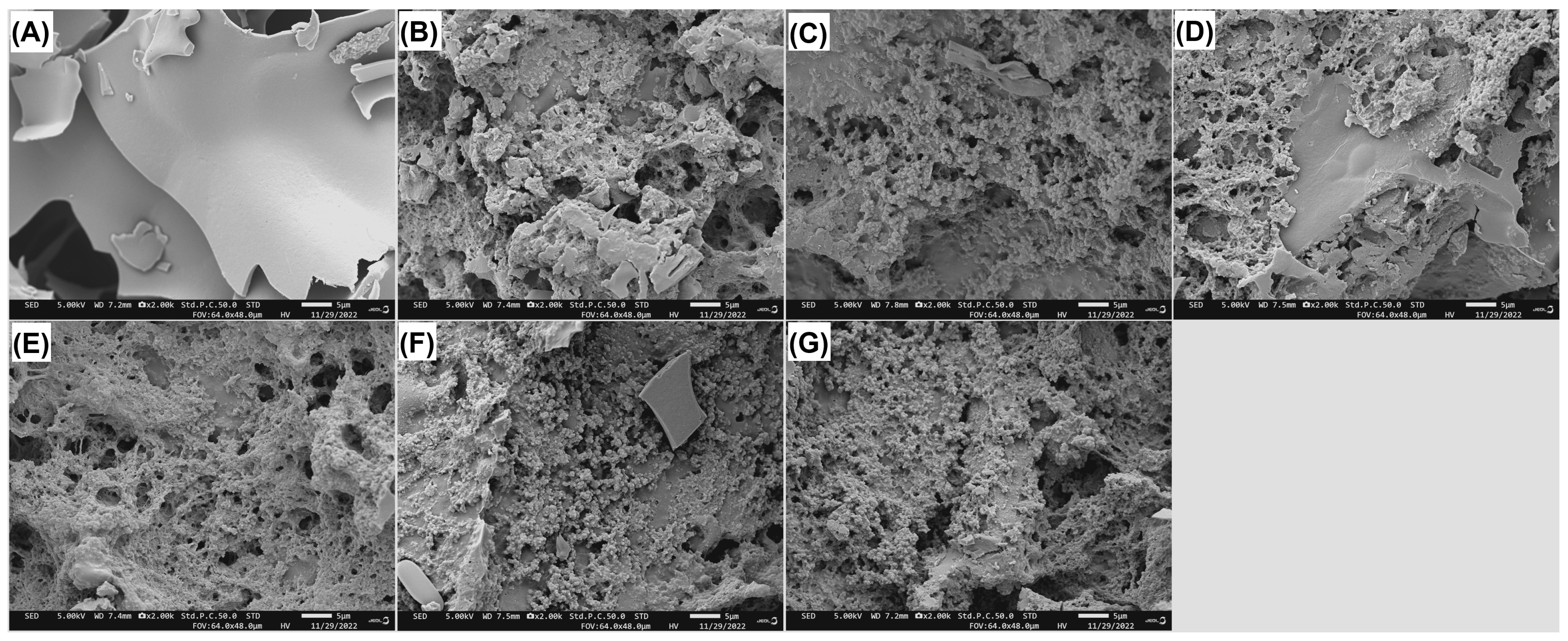
2.3.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy of JJRDFs
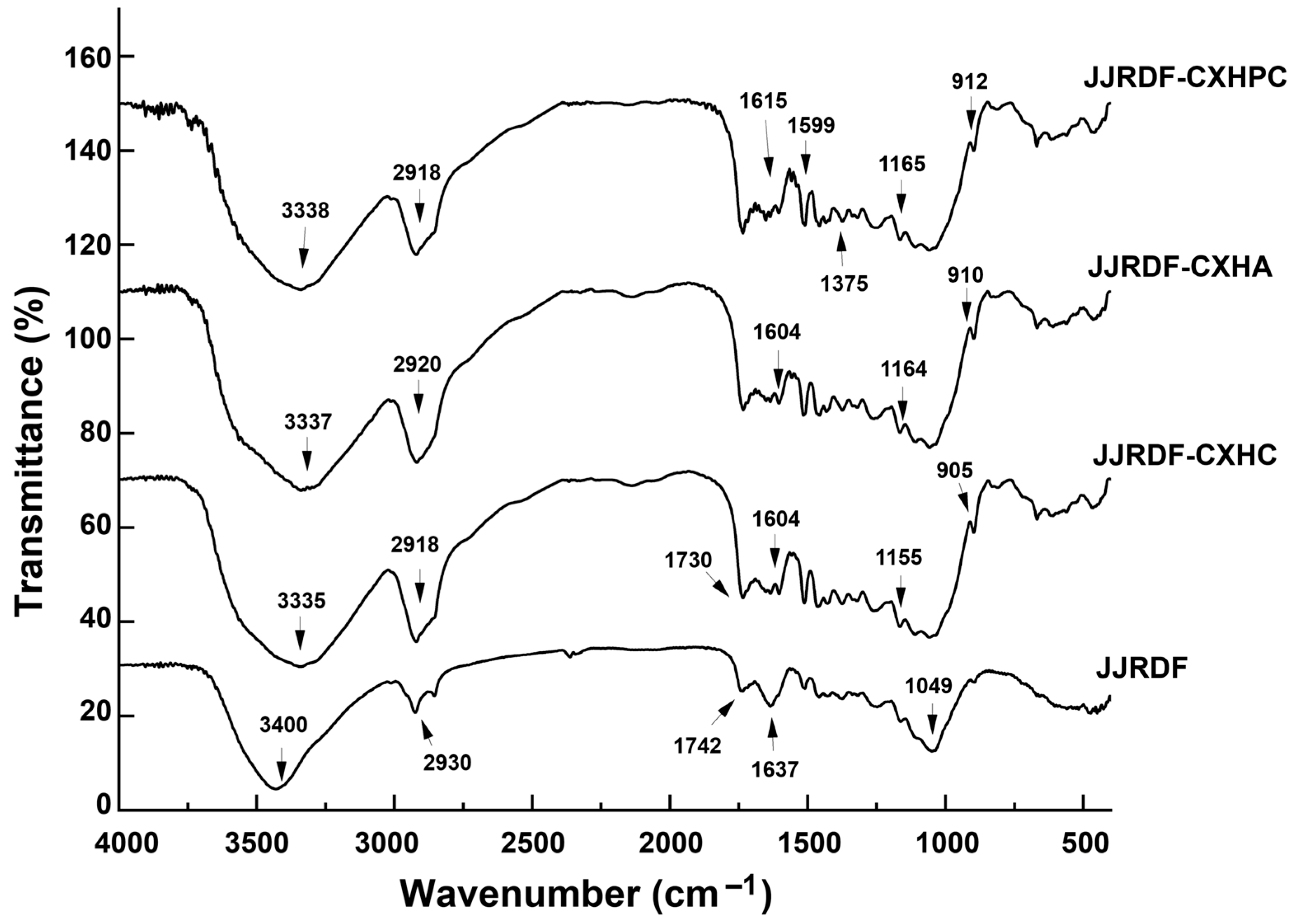
2.3.2. Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectra
2.4. Viscosity, ARW, and EVW of JJRDFs
2.5. HA-EPG Structure
2.5.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy
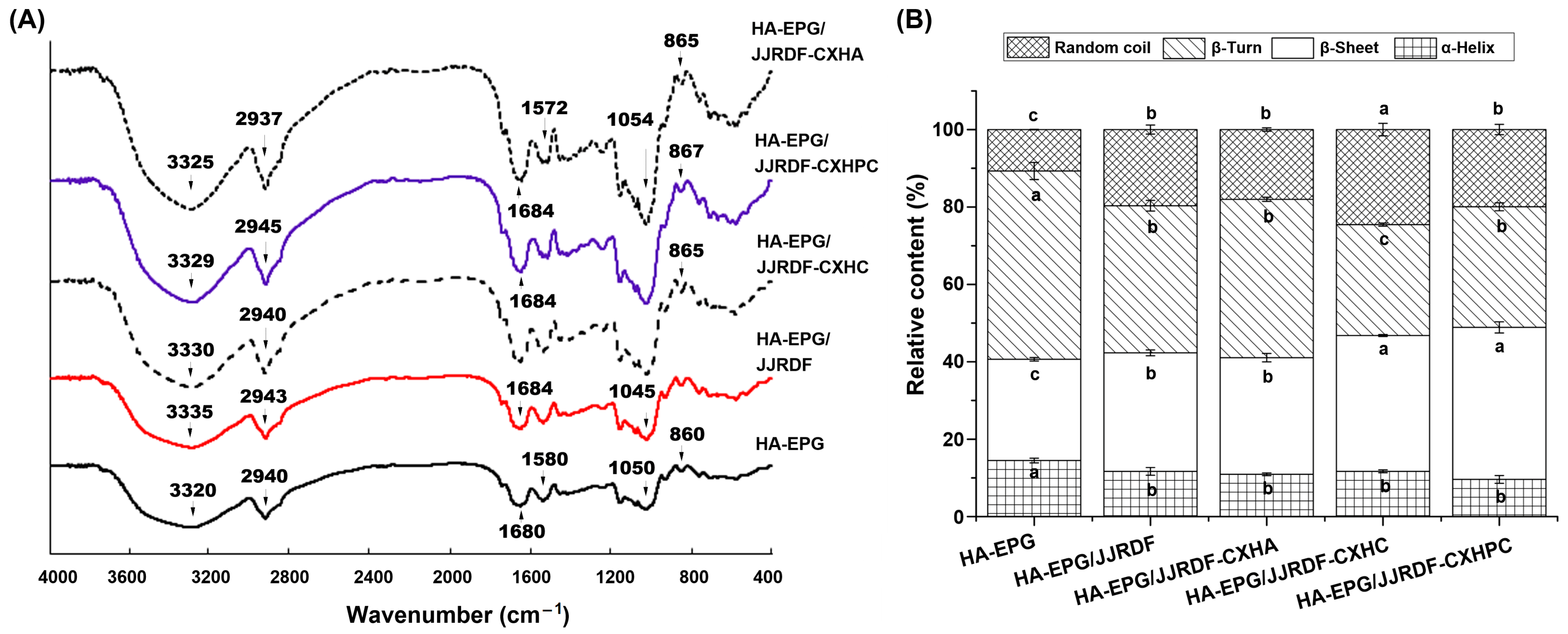
2.5.2. Secondary Structure
2.6. Effect of the Addition of JJRDFs on the Morphological Diagram and Color of HA-EPGs
2.7. Physicochemical Properties of HA-EPGs
2.7.1. Ability of HA-EPGs to Retain Water
2.7.2. pH Values
2.7.3. Water-Losing Rate After Freeze–Thaw
2.7.4. Light Transmittance
2.8. Textural Qualities
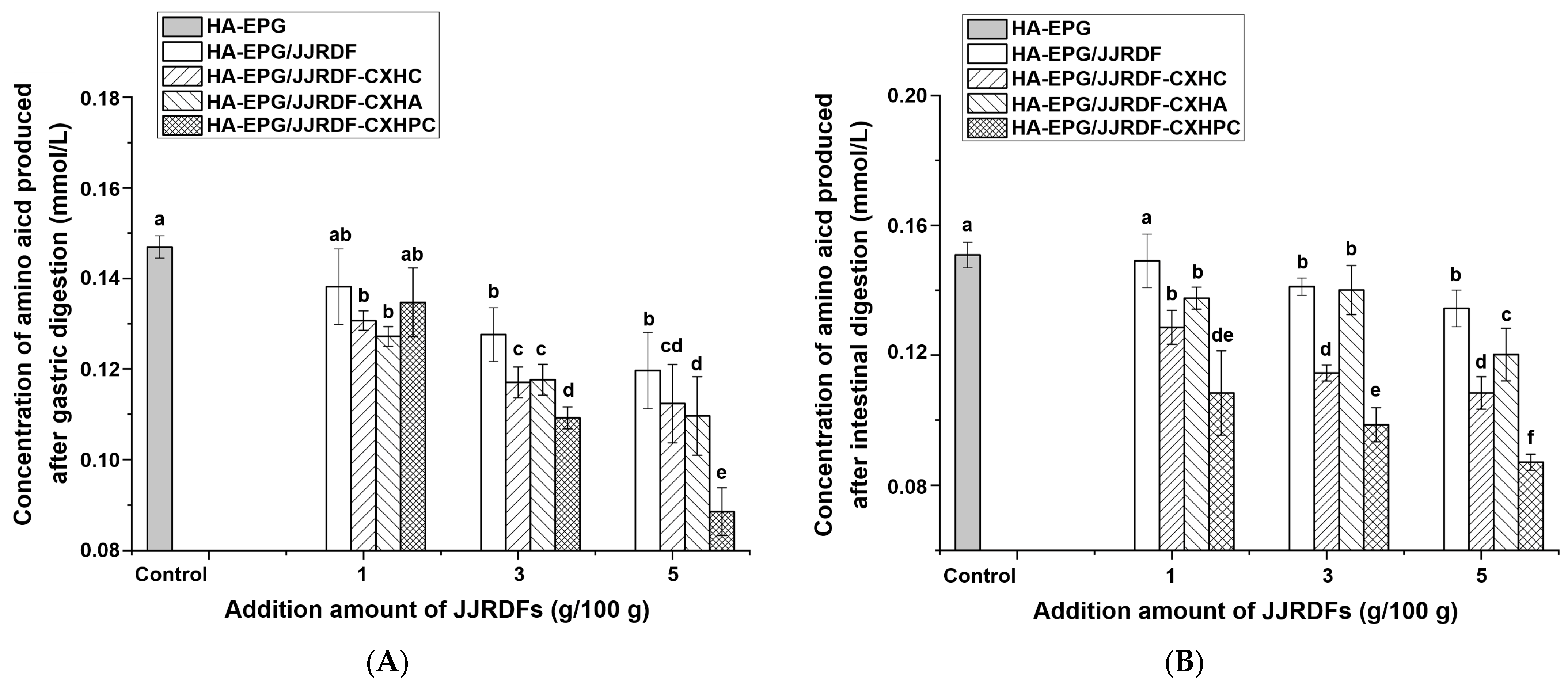
2.9. Simulated Gastrointestinal Hydrolysis of HA-EPGs
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Extraction of JJRDF
4.3. Xylanase and Cellulase Hydrolysis
4.4. Carboxymethylation of JJRDF-CXH
4.5. Phosphate Crosslinking of JJRDF-CXH
4.6. Acetylation of JJRDF-CXH
4.7. Preparation of Heat- and Alkaline-Induced Egg Protein Gels Fortified with JJRDFs
4.8. Determination of Constituent
4.9. Colour Difference and Surface Area Measurement
4.10. Surface Microstructure Scanning
4.11. Fourier-Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy
4.12. Physicochemical Properties
4.12.1. Ability to Retain Water
4.12.2. Expansion Volume in Water
4.12.3. Viscosity
4.13. Gel Characteristics
4.13.1. Optical Transparency and Water-Retention Ability of HA-EPGs
4.13.2. Water-Losing Rate During Freeze–Thaw of HA-EPGs
4.13.3. Textural Quality
4.14. Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion
4.15. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| JJRDF | Jujube juicing residue dietary fiber |
| JJRDF-CXHC | Jujube juicing residue dietary fiber modified by cellulase and xylanase hydrolysis coupled with carboxymethylation |
| JJRDF-CXHA | Jujube juicing residue dietary fiber modified by cellulase and xylanase hydrolysis coupled with acetylation |
| JJRDF-CXHPC | Jujube juicing residue dietary fiber modified by cellulase and xylanase hydrolysis coupled with phosphate crosslinking |
| HA-EPG | Heat- and alkaline-induced egg protein gel |
| ARW | Ability to retention water |
References
- Zhang, J.; Ye, Z. Influences of superfine-grinding and mix enzymatic hydrolysis combined with hydroxypropylation or acetylation on the structure and physicochemical properties of jujube kernel fiber. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1382314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Hou, C.; Yan, Y.; Shi, M.; Liu, Y. Comparison of structural characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) fruit. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 149, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farahani, Z.K.; Mousavi, M.; Ardebili, M.S.; Bakhoda, H. The effects of Ziziphus jujuba extract-based sodium alginate and proteins (whey and pea) beads on characteristics of functional beverage. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2022, 16, 2782–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashwan, A.K.; Karim, N.; Shishir, M.R.I.; Bao, T.; Lu, Y.; Chen, W. Jujube fruit: A potential nutritious fruit for the development of functional food products. J. Funct. Foods 2020, 75, 104205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, P.; Singh, T.; Pathak, D.; Chopra, H. An updated review of Ziziphus jujube: Major focus on its phytochemicals and pharmacological properties. Pharmacol. Res.-Mod. Chin. Med. 2023, 8, 100297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Tirpanalan-Staben, Ö.; Franke, K. Modification of Dietary Fibers to Valorize the By-Products of Cereal, Fruit and Vegetable Industry—A Review on Treatment Methods. Plants 2022, 11, 3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.M.; Zhang, X.; Wei, X.Y.; Wu, R.Q.; Gu, Q.; Zhou, T. Hypoglycemic and Gut Microbiota-Modulating Effects of Pectin from Citrus aurantium “Changshanhuyou” Residue in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 9088–9102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwar, P.; Yadav, R.B.; Yadav, B.S. Cross-linking, carboxymethylation and hydroxypropylation treatment to sorghum dietary fiber: Effect on physicochemical, micro structural and thermal properties. J. Cereal Sci. 2023, 233, 123638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berktas, S.; Cam, M. Effects of acid, alkaline and enzymatic extraction methods on functional, structural and antioxidant properties of dietary fiber fractions from quince (Cydonia oblonga Miller). Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, H.; Sultan, Z.; Yousuf, O.; Malik, M.; Younis, K. A review of the health benefits, functional properties, and ultrasound-assisted dietary fiber extraction. Bioact. Carbohydr. Diet. Fibre 2023, 30, 100356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, A.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Zheng, X.; Jin, Z.; Liu, D.; Wang, N.; Kan, Y. Influences of superfine-grinding and enzymolysis separately assisted with carboxymethylation and acetylation on the in vitro hypoglycemic and antioxidant activities of oil palm kernel expeller fibre. Food Chem. 2024, 449, 139192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.R.; Park, J.Y.; Park, E.Y. Effect of ethanol, phytic acid and citric acid treatment on the physicochemical and heavy metal adsorption properties of corn starch. Food Chem. 2024, 431, 137167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, A.; Olenskyj, A.G.; Guerrero, M.G.; Graham, R.; Bornhorst, G.M. Interplay of egg white gel pH and intragastric pH: Impact on breakdown kinetics and mass transport processes. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J.; Hamon, P.; Lee, J.; Bouhallab, S.; Cases, E.; Saurel, R.; Lechevalier, V. Protein–Protein Interactions and Structure of Heat-Set Gels Based on Pea Protein and Egg White Mixtures. Gels 2025, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoor, A.; Dar, A.H.; Pandey, V.K.; Shams, R.; Khan, S.; Panesar, P.S.; Kennedy, J.F.; Fayaz, U.; Khan, S.A. Recent insights into polysaccharide-based hydrogels and their potential applications in food sector: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 213, 987–1006. [Google Scholar]
- Muhedaner, M.; Hadiza Kabir Bako, H.K.; Zhou, G. Impact of egg white protein on mycoprotein gel: Insights into rheological properties, protein structure and Molecular interactions. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grootaert, C.; Monge-Morera, M.; Delcour, J.A.; Skirtach, A.G.; Rousseau, F.; Schymkowitz, J.; Dewettinck, K.; Van der Meeren, P. Impact of heat and enzymatic treatment on ovalbumin amyloid-like fibril formation and enzymeinduced gelation. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 131, 107784. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, M.; Lei, Y.; Huo, J.; Ma, L.; Li, S. Chain reactions of temperature-induced egg white protein amorphous aggregates: Formation, structure and material composition of thermal gels. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baquero-Aznar, V.; Salvador, M.; Fernández-Cuello, Á.; Clavería, I.; González-Buesa, J. Role of egg white protein gelling capacity on the processability and properties of compression-moulded films. Future Foods 2025, 11, 100616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Qin, X.; Sang, X.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, Y. DNAzyme ampliffed dispersion state change of gold nanoparticles and its dual optical channels for ultrasensitive and facile detection of lead ion in preserved eggs. Food Chem. 2024, 435, 137538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Hu, Y.; You, J.; Yin, T.; Xiong, S.; Din, Z.U.; Huang, Q.L.; Liu, R. Influence of okara dietary fiber with varying particle sizes on gelling properties, water state and microstructure of tofu gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 89, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, L.; Tan, B.; Li, R. Effect of structural characteristics on the physicochemical properties and functional activities of dietary fiber: A review of structure-activity relationship. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 269, 132214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, B.; Liu, T.; Cai, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, Q. The formation, structural and rheological properties of emulsion gels stabilized by egg white protein-insoluble soybean fiber complex. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 134, 108035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, K.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y. The impact of dietary fibers on the construction and molecular network of extrusion-based 3D-printed chicken noodles: Unlocking the potential of specialized functional food. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.J.; Li, Y. Physicochemical and functional properties of coconut (Cocos nucifera L) cake dietary fibres: Effects of cellulase hydrolysis, acid treatment and particle size distribution. Food Chem. 2018, 257, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Shen, J.; Tang, C.; Lu, Z.; Lu, F.; Bie, X.; Meng, F.; Zhao, H. Prevention of high-fat-diet-induced obesity in mice by soluble dietary fiber from fermented and unfermented millet bran. Food Res. Int. 2024, 179, 113974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Lu, L.; Zhao, L.; Peng, L.; Zhou, W. Improvement of okara noodle quality by modifying the soluble/insoluble dietary fibre ratio. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.J.; Xu, B.F.; Shi, P.Q.; Tian, H.L.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.Y.; Wu, S.; Liang, P.F. The influences of acetylation, hydroxypropylation, enzymatic hydrolysis and crosslinking on improved adsorption capacities and in vitro hypoglycemic properties of millet bran dietary fibre. Food Chem. 2022, 368, 130883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.; Chen, J.; Hong, Z.; Guo, R.; Huang, Q. Insights into the Pickering emulsions stabilized by yeast dietary fiber: Interfacial adsorption kinetics, rheological characteristics, and stabilization mechanisms. Food Chem. 2025, 464, 141924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, M.; Norlander, S.; Hedstrm, M.; Adlercreutz, P.; Grey, C. Xylanases and high-degree wet milling improve soluble dietary fibre content in liquid oat base. Food Chem. 2025, 442, 138619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Qi, J.; Yu, M.; Zhang, R.; Lin, H.; Yan, H.; Li, C.; Jia, J.M.; Hu, Y. Insight into the mechanism of water-insoluble dietary fiber from star anise (Illicium verum Hook. f.) on water-holding capacity of myofibrillar protein gels. Food Chem. 2023, 423, 136348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Yuan, Y.Y.; Wu, X.L.; Yu, P.X.; Ji, J.H.; Chai, J.L.; Sainic, R.K.; Liu, J.B.; Shang, X.M. The level of sulfate substitution of polysaccharide regulates thermal-induced egg white protein gel properties: The characterization of gel structure and intermolecular forces. Food Res. Int. 2023, 173, 113349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhu, D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, C.; Han, J. Influence of soybean dietary fiber on the properties of konjac glucomannan/κ-carrageenan corn oil composite gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 129, 107602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Wu, T.; Quan, Z.; Wang, C. Effects of cavitation jet combined with ultrasound, alkaline hydrogen peroxide and Bacillus subtilis treatment on the properties of dietary fiber. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 103895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazarika, B.J.; Sit, N. Effect of dual modification with hydroxypropylation and cross-linking on physicochemical properties of taro starch. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 140, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khemakhem, M.; Attia, H.; Ayadi, M.A. The effect of pH, sucrose, salt and hydrocolloid gums on the gelling properties and water holding ability of egg white gel. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.Q.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.L.; Tang, T.T.; Su, Y.J.; Gu, L.P.; Chang, C.H.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Y.J.; Li, J.H. Gel properties of okara dietary fiber-fortified soy protein isolate gel with/without NaCl. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 103, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Jeong, S.K.C.; Jeon, H.; Kim, Y.J.; Choi, Y.S.; Jung, S. Heat-induced gelation of egg white proteins depending on heating temperature: Insights into protein structure and digestive behaviors in the elderly in vitro digestion model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 262, 130053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis; Association of Official Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, J.; Zhao, H.; Lu, Z.; Lu, F.; Bie, X.; Zhang, C. Improved physicochemical and functional properties of dietary fiber from millet bran fermented by Bacillus natto. Food Chem. 2019, 294, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, F.C.; Swaisgood, H.E.; Porter, D.H.; Catignani, G.L. Spectrophotometric assay using o-phthaldialdehyde for determination of proteolysis in milk and isolated milk Proteins1. J. Dairy Sci. 1983, 66, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Proximate Composition | JJRDF | JJRDF-CXHA | JJRDF-CXHC | JJRDF-CXHPC |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture (g/100 g) | 7.47 ± 0.20 c | 5.99 ± 0.24 c | 5.95 ± 0.37 c | 6.46 ± 0.17 c |
| Fat (g/100 g) | 1.28 ± 0.09 c | 1.12 ± 0.09 c | 1.22 ± 0.08 c | 1.41 ± 0.03 c |
| Protein (g/100 g) | 2.19 ± 0.21 c | 2.07 ± 0.09 c | 1.89 ± 0.08 c | 1.79 ± 0.07 c |
| Ash (g/ 100 g) | 1.38 ± 0.08 d | 1.74 ± 0.08 d | 4.22 ± 0.27 c | 2.89 ± 0.09 c |
| TDF (g/ 100 g) | 75.38 ± 2.28 d | 76.93 ± 4.82 c | 77.43 ± 4.24 c | 78.09 ± 3.58 c |
| IDF (g/100 g) | 69.72 ± 4.52 c | 65.92 ± 1.79 d | 60.47 ± 2.61 e | 60.56 ± 4.95 e |
| SDF (g/100 g) | 5.66 ± 0.11 e | 11.01 ± 2.56 d | 16.96 ± 0.42 c | 17.53 ± 2.32 c |
| Hemicellulose (g/100 g) | 43.56 ± 3.47 c | 30.28 ± 3.17 d | 29.38 ± 2.77 d | 30.99 ± 3.67 d |
| Cellulose (g/100 g) | 16.53 ± 0.55 c | 9.85 ± 0.08 d | 10.79 ± 0.34 d | 10.73 ± 1.05 d |
| Lignin (g/100 g) | 9.63 ± 0.39 c | 6.89 ± 3.11 d | 8.79 ± 2.66 c | 5.97 ± 0.39 e |
| D3,2 (μm) | 116.47 ± 4.71 c | 76.71 ± 2.07 e | 59.38 ± 3.35 f | 95.23 ± 4.05 d |
| Specific surface area (m2∙kg−1) | 64.53 ± 3.74 f | 105.15 ± 4.74 d | 167.35 ± 4.42 c | 86.44 ± 2.95 e |
| L | 53.8 ± 1.02 c | 40.75 ± 3.13 d | 36.95 ± 2.44 d | 38.56 ± 3.34 d |
| a | 7.95 ± 0.23 d | 10.57 ± 0.32 c | 11.75 ± 0.37 c | 9.36 ± 0.27 c |
| b | 11.32 ± 0.26 e | 14.26 ± 0.26 d | 19.54 ± 0.37 c | 15.08 ± 1.42 d |
| ΔE | Control | 13.63 | 19.13 | 15.76 |
| Ability to retain water (g/g) | 6.02 ± 0.34 d | 7.17 ± 0.36 d | 12.83 ± 0.56 c | 14.75 ± 0.23 c |
| Expansion volume in water (mL/g) | 5.60 ± 0.20 e | 8.42 ± 0.40 d | 10.40 ± 0.20 c | 9.80 ± 0.20 c |
| Viscosity (cP) | 7.01 ± 0.33 f | 10.56 ± 0.08 e | 18.46 ± 0.36 c | 13.92 ± 0.43 d |
| Gels | L | a | b | ΔE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA-EPG | 89.37 ± 1.19 a | –1.13 ± 0.07 c | 13.34 ± 1.02 c | Control |
| HA-EPG/JJRDF | 77.98 ± 6.67 c | 3.36 ± 0.07 b | 15.16 ± 0.54 b | 12.378 |
| HA-EPG/JJRDF-XCHC | 78.90 ± 3.33 c | 4.13 ± 0.12 ab | 15.30 ± 1.07 b | 11.88 |
| HA-EPG/JJRDF-XCHPC | 78.18 ± 2.67 c | 5.46 ± 0.19 a | 22.30 ± 0.33 a | 15.78 |
| HA-EPG/JJRDF-XCHA | 83.08 ± 1.33 b | 3.35 ± 0.33 b | 15.96 ± 0.45 b | 8.16 |
| Gels | Amount (g/100 g) | Hardness (g) | Adhesiveness | Springiness | Cohesiveness | Gumminess | Chewiness (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HA-EPG | 0 | 93.16 ± 4.85 f | −47.32 ± 1.38 d | 0.91 ± 0.02 a | 0.77 ± 0.02 a | 83.99 ± 5.72 e | 80.14 ± 3.77 e |
| HA-EPG/JJRDF | 1 | 95.87 ± 3.40 f | −34.92 ± 0.78 b | 0.91 ± 0.01 a | 0.81 ± 0.01 a | 69.07 ± 3.65 f | 78.65 ± 4.53 e |
| 3 | 109.87 ± 7.56 e | −33.41 ± 0.18 b | 0.90 ± 0.00 a | 0.77 ± 0.01 a | 93.58 ± 7.11 d | 97.38 ± 0.77 d | |
| 5 | 127.93 ± 7.47 d | −26.21 ± 0.35 a | 0.89 ± 0.00 a | 0.82 ± 0.02 a | 99.33 ± 0.67 d | 101.01 ± 4.75 d | |
| HA-EPG/JJRDF-XCHC | 1 | 116.53 ± 4.99 e | −40.26 ± 1.94 c | 0.87 ± 0.01 a | 0.79 ± 0.02 a | 98.25 ± 6.75 d | 94.68 ± 7.34 d |
| 3 | 141.82 ± 9.11 c | −36.53 ± 2.66 b | 0.89 ± 0.03 a | 0.81 ± 0.02 a | 124.56 ± 7.99 d | 111.39 ± 6.42 cd | |
| 5 | 177.93 ± 5.26 b | −39.84 ± 4.73 c | 0.90 ± 0.01 a | 0.79 ± 0.01 a | 159.17 ± 9.84 b | 118.01 ± 3.99 c | |
| HA-EPG/JJRDF-XCHPC | 1 | 79.44 ± 4.59 g | −48.78 ±3.29 d | 0.91 ± 0.02 a | 0.74 ± 0.02 a | 94.79 ± 6.94 d | 72.56 ± 8.33 e |
| 3 | 148.83 ± 11.55 c | −43.95 ±7.54 d | 0.90 ± 0.01 a | 0.81 ± 0.01 a | 147.66 ± 1.48 c | 149.62 ± 9.12 b | |
| 5 | 201.41 ± 8.83 a | −46.00 ±3.42 d | 0.88 ± 0.02 a | 0.82 ± 0.01 a | 173.56 ± 7.48 a | 177.99 ± 7.58 a | |
| HA-EPG/JJRDF-XCHA | 1 | 117.28 ± 11.06 e | −36.39 ± 1.58 b | 0.87 ± 0.02 a | 0.81 ± 0.02 a | 90.01 ± 4.55 d | 87.96 ± 4.98 d |
| 3 | 142.12 ± 7.43 c | −30.23 ± 0.72 b | 0.89 ± 0.01 a | 0.83 ± 0.01 a | 120.75 ± 9.58 d | 105.44 ± 9.72 d | |
| 5 | 157.67 ± 5.79 c | −39.21 ± 1.15 b | 0.93 ± 0.01 a | 0.81 ± 0.02 a | 139.88 ± 9.77 c | 123.55 ± 9.13 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, X.; Dang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Y.; Song, X.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X. Effects of Different Dual-Modified Jujube Juicing Residue Dietary Fibers on the Properties of Egg Protein Gels Induced by Alkalinity and Heat. Gels 2025, 11, 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060399
Zheng X, Dang L, Zhang Y, Liu X, Wang H, Zheng Y, Song X, Wei Z, Zhang J, Guo X. Effects of Different Dual-Modified Jujube Juicing Residue Dietary Fibers on the Properties of Egg Protein Gels Induced by Alkalinity and Heat. Gels. 2025; 11(6):399. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060399
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Xinyu, Ling Dang, Yichan Zhang, Xinyu Liu, Hui Wang, Yajun Zheng, Xinling Song, Zhihui Wei, Jiayao Zhang, and Xiaoyang Guo. 2025. "Effects of Different Dual-Modified Jujube Juicing Residue Dietary Fibers on the Properties of Egg Protein Gels Induced by Alkalinity and Heat" Gels 11, no. 6: 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060399
APA StyleZheng, X., Dang, L., Zhang, Y., Liu, X., Wang, H., Zheng, Y., Song, X., Wei, Z., Zhang, J., & Guo, X. (2025). Effects of Different Dual-Modified Jujube Juicing Residue Dietary Fibers on the Properties of Egg Protein Gels Induced by Alkalinity and Heat. Gels, 11(6), 399. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11060399






