Development of Edible Carbohydrate–Protein Sports Gels to Optimize the Muscle Glycogen Re-Synthesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
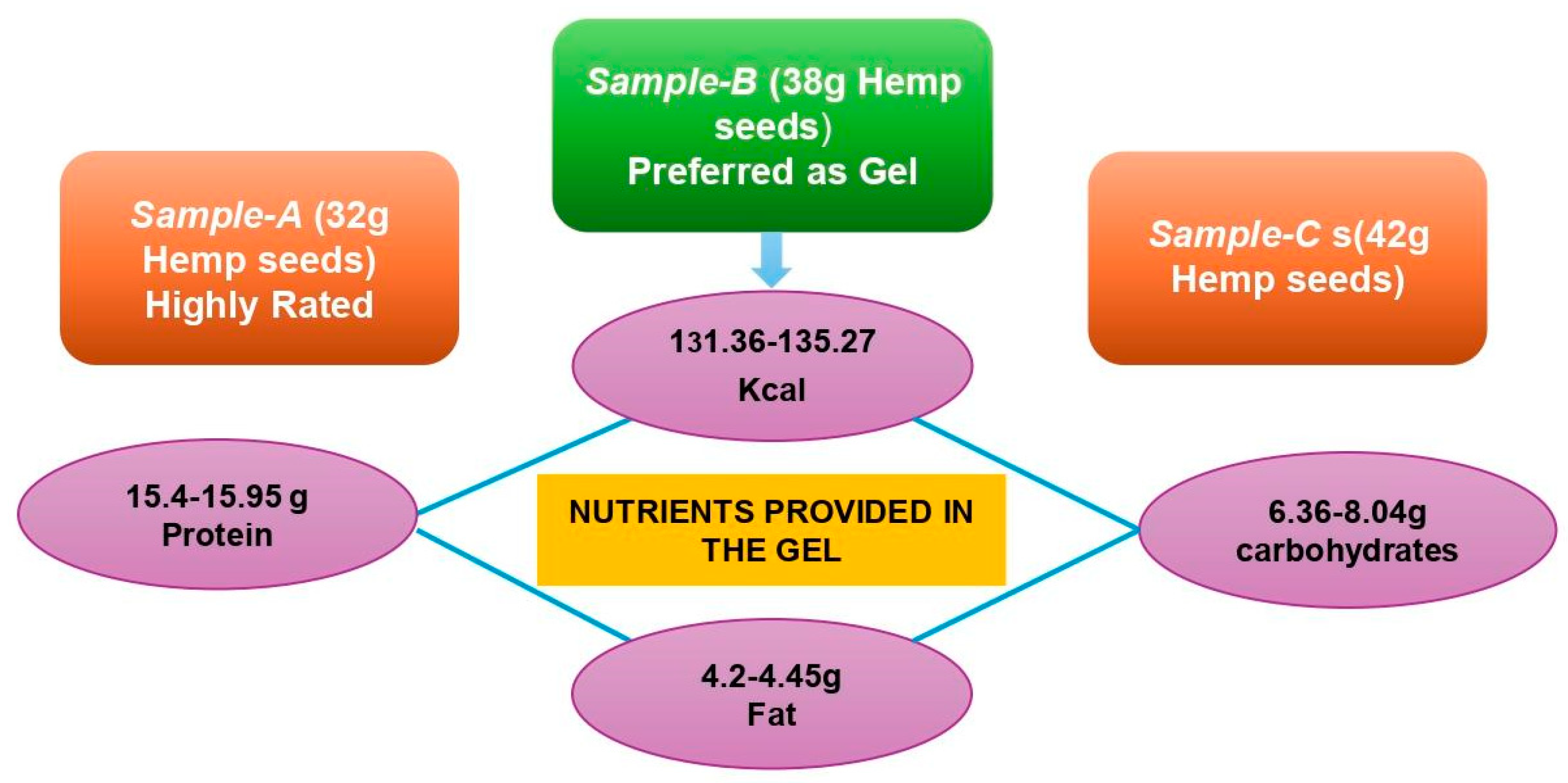
2.1. Physicochemical Characteristics
2.2. Sensory Characteristics of Sports Gel
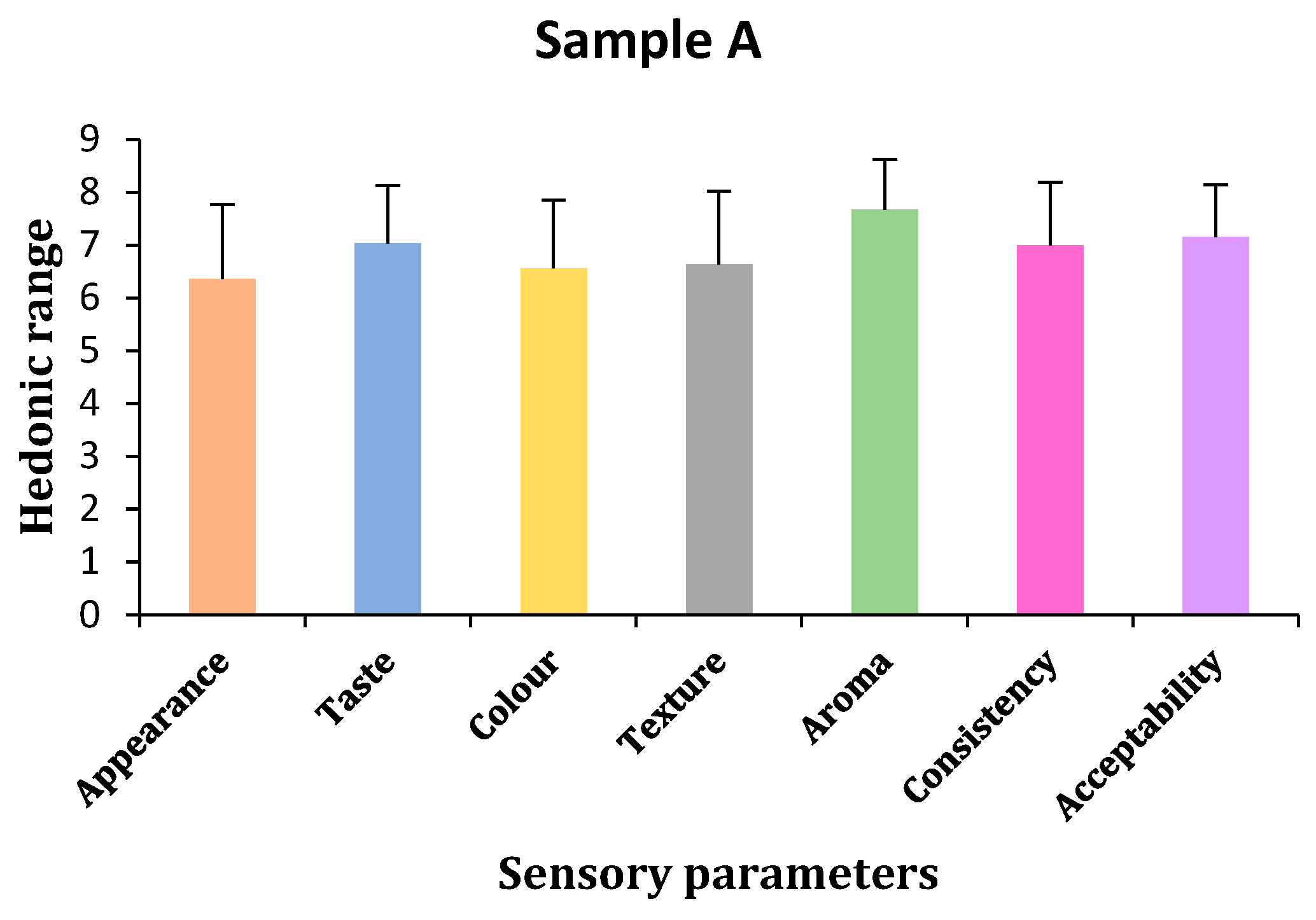
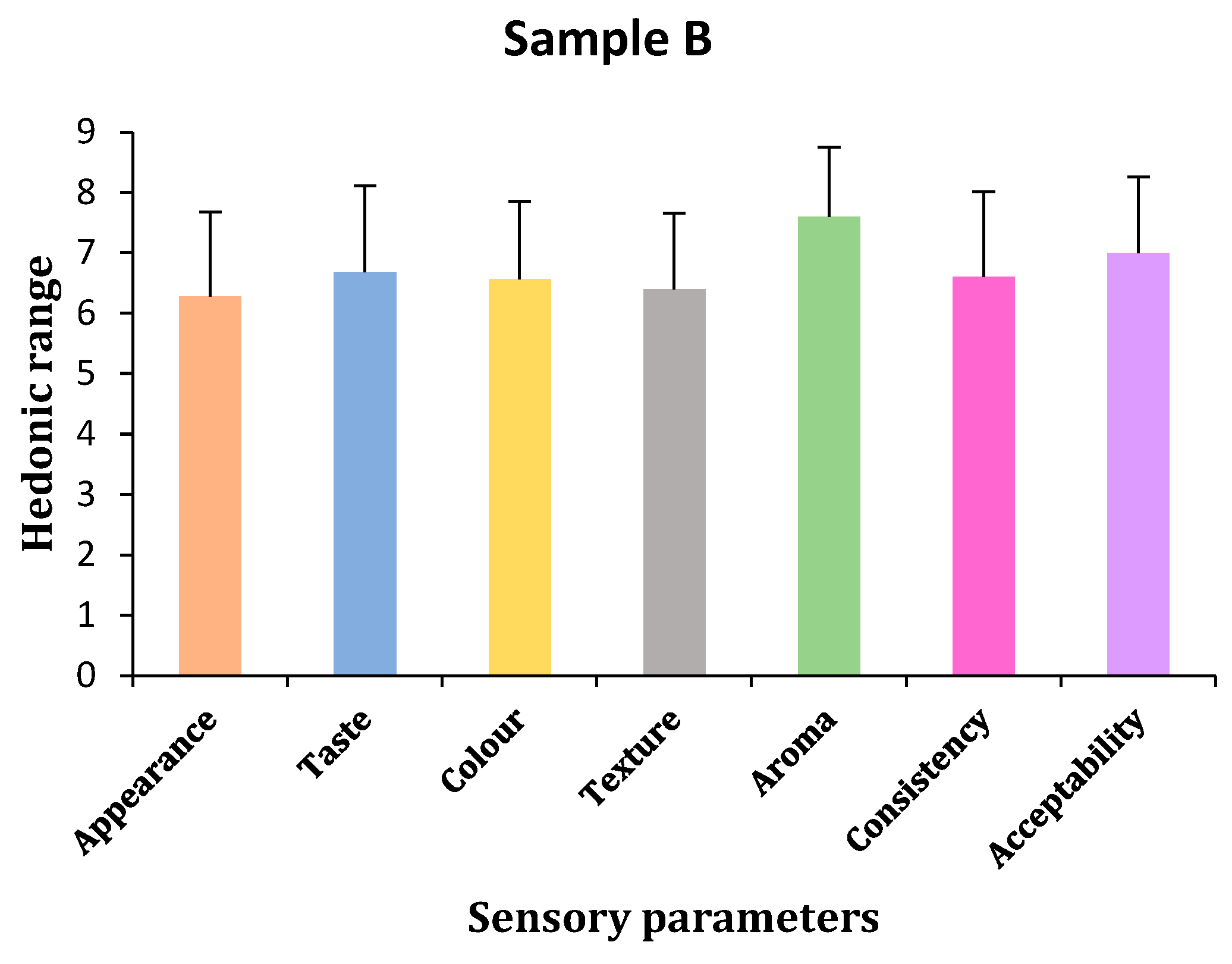
- (a)
- Appearance
- (b)
- Taste
- (c)
- Color
- (d)
- Texture
- (e)
- Aroma
- (f)
- Consistency
- (g)
- Acceptability
2.3. Correlation Between Sensory Parameters Evaluated
2.3.1. Intra-Sample Correlation (Within Each Sample)
2.3.2. Inter-Sample Correlation (Across Samples)
- Appearance and taste consistently demonstrate strong positive correlations with acceptability in all three samples. This indicates that visual appeal and flavor are the primary drivers of consumer preferences.
- Texture and color also show moderate-to-high correlations with acceptability, highlighting their secondary but significant roles in influencing sensory appeal.
- Aroma and consistency generally exhibit a weaker correlation with acceptability, suggesting that they have less influence on consumer preference compared to other attributes.
2.4. The Gel with the Best Formulation
2.5. Shelf Life of Samples
2.6. Toxicity Testing
2.7. Viscosity Testing
2.8. Texture Profile Analysis
- Sample A (32 g of hemp) displayed the least hardness (4.2 ± 0.5 N) and gumminess (3.8 ± 0.4 N), which matched its higher acceptability score (7.16 ± 0.99) due to its soft texture.
- Sample B (38 g of hemp) presented a moderate level of hardness (4.6 ± 0.6 N) and gumminess (4.2 ± 0.5 N), reflecting its texture score of 6.4 ± 1.26 and smooth consistency rating of 6.6 ± 1.41.
- Sample C (42 g of hemp) showed a slightly greater hardness (4.9 ± 0.7 N) and gumminess (4.5 ± 0.6 N) but remained within an easily chewable range, supported by its sensory texture score of 6.6 ± 1.71 and acceptability score of 7 ± 1.19.
3. Conclusions
Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
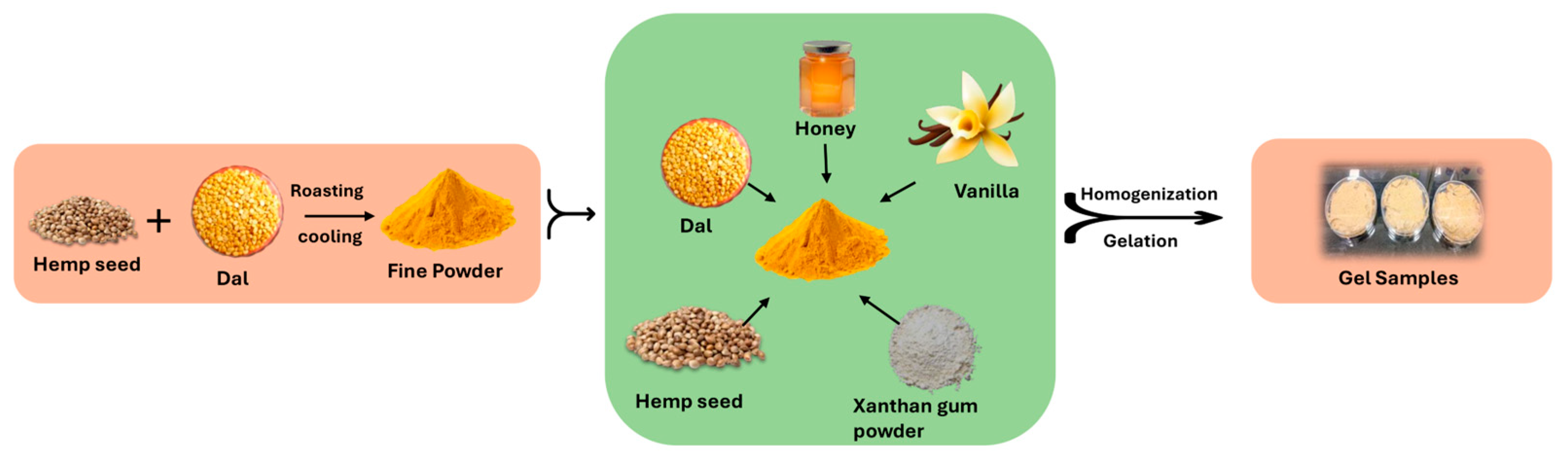
4.2. Preparation of Sports Carbohydrate–Protein Gels
4.3. Physicochemical Characteristics Analysis
4.4. Sensory Characteristics Analysis
4.5. Best Treatment Determination
4.6. Toxicity Analysis
4.7. Viscosity Analysis
4.8. Texture Profile Analysis
4.9. Data Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ivy, J.L. Muscle Glycogen Synthesis Before and After Exercise. Sports Med. 1991, 11, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunders, M.J.; Luden, N.D.; Herrick, J.E. Consumption of an oral carbohydrate-protein gel improves cycling endurance and prevents postexercise muscle damage. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2007, 21, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, A. Nutrition and health benefits of hemp-seed protein (Cannabis sativa L.). Pharma Innov. J. 2021, 10, 16–19. [Google Scholar]
- Barbara, F.; Romina, M.; Lara, C.; Merendino, N. The seed of industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.): Nutritional quality and potential functionality for human health and nutrition. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irakli, M.; Tsaliki, E.; Kalivas, A.; Kleisiaris, F.; Sarrou, E.; Cook, C.M. Effect of genotype and growing year on the nutritional, phytochemical, and antioxidant properties of industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seeds. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Zha, F.; Peckrul, A.; Hanson, B.; Johnson, B.; Rao, J.; Chen, B. Genotype x Environmental Effects on Yielding Ability and Seed Chemical Composition of Industrial Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Varieties Grown in North Dakota, USA. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2019, 96, 1417–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sohaimy, S.A.; Androsova, N.V.; Toshev, A.D.; El Enshasy, H.A. Nutritional quality, chemical, and functional characteristics of hemp (Cannabis sativa ssp. sativa) protein Isolate. Plants 2022, 11, 2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, L.; Ballesteros-Vivas, D.; Gonzalez-Barrios, A.F.; Sánchez-Camargo, A.d.P. Hemp seeds: Nutritional value, associated bioactivities and the potential food applications in the Colombian context. Front. Nutr. 2023, 9, 1039180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tănase Apetroaei, V.; Pricop, E.M.; Istrati, D.I.; Vizireanu, C. Hemp Seeds (Cannabis sativa L.) as a Valuable Source of Natural Ingredients for Functional Foods—A Review. Molecules 2024, 29, 2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamle, M.; Mahato, D.K.; Sharma, B.; Gupta, A.; Shah, A.K.; Mahmud, M.C.; Agrawal, S.; Singh, J.; Rasane, P.; Shukla, A.C. Nutraceutical potential, phytochemistry of hemp seed (Cannabis sativa L.) and its application in food and feed: A review. Food Chem. Adv. 2024, 4, 100671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jukanti, A.K.; Gaur, P.M.; Gowda, C.L.L.; Chibbar, R.N. Nutritional quality and health benefits of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.): A review. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, S11–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samarghandian, S.; Farkhondeh, T.; Samini, F. Honey and health: A review of recent clinical research. Pharmacogn. Res. 2017, 9, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, H. Honey on Basketball Players’ Physical Recovery and Nutritional Supplement. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 6953568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subaraj, S.; Priyadharshini, S.; Manimegalai, R.; Sarubala, S.; Soundararajan, D.K.; Meenakumari, R. A Review on potential value of Bengal gram in Siddha for a healthy lifestyle. Int. J. Adv. Multidiscip. Res. 2023, 10, 88–92. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, C. Modern Techniques of Raising Field Crops; Oxford and IBH Publishing: Delhi, India, 1983; Available online: https://books.google.com/books?hl=en&lr=&id=CmiB0VKMTU4C&oi=fnd&pg=PA1&dq=13.%09Singh,+C.+(1988).+Modern+Techniques+of+raising+field+crops.+Oxford+%26+IBH+Publishing+Co.+Pvt.+Ltd.,+New+Delhi,+523-524.&ots=QXucl6Pm3j&sig=kN7JKYMaqTk_sfkrFb4xIluXzW8 (accessed on 8 January 2025).
- Singh, R.P. Status of chickpea in the world. Int. Chickpea Newsl. 1990, 22, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Longvah, T.; Ananthan, R.; Bhaskarachary, K.; Venkaiah, K. Indian Food Composition Table; National Institute of Nutrition, Indian Council of Medical Research: Hyderabad, India, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, P.C.; Singh, U. Quality Screening and Evaluation in Pulse Breeding; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Mandal, M.; Mishra, S. Nutritional and Therapeutic Potential of Superseeds and it used in Preparation of Ready to Eat Food- Superseeds Dalupma/Uppindi. Int. J. Sci. Res. (IJSR) 2010, 8, 582–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atrouse, O.M.; Oran, S.A.; Al-Abbadi, S.Y. Chemical analysis and identification of pollen grains from different jordanian honey samples. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2004, 39, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranneh, Y.; Akim, A.M.; Hamid, H.A.; Khazaai, H.; Fadel, A.; Zakaria, Z.A.; Albujja, M.; Bakar, M.F.A. Honey and its nutritional and anti-inflammatory value. BMC Complement. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küçük, M.; Kolaylı, S.; Karaoğlu, Ş.; Ulusoy, E.; Baltacı, C.; Candan, F. Biological activities and chemical composition of three honeys of different types from Anatolia. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergström, J.; Hultman, E.; Roch-Norlund, A.E. Muscle Glycogen Synthetase in Normal Subjects: Basal Values, Effect of Glycogen Depletion by Exercise and of a Carbohydrate-Rich Diet Following Exercise. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 1972, 29, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeva-Andany, M.M.; González-Lucán, M.; Donapetry-García, C.; Fernández-Fernández, C.; Ameneiros-Rodríguez, E. Glycogen metabolism in humans. BBA Clin. 2016, 5, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, B.; Rosenbloom, C. Fundamentals of glycogen metabolism for coaches and athletes. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 243–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, E.A.; Derave, W.; Wojtaszewski, J.F.P. Glucose, exercise and insulin: Emerging concepts. J. Physiol. 2001, 535, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, L.M.; Van Loon, L.J.C.; Hawley, J.A. Postexercise muscle glycogen resynthesis in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 2017, 122, 1055–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikines, K.J.; Farrell, P.A.; Sonne, B.; Tronier, B.; Galbo, H. Postexercise dose-response relationship between plasma glucose and insulin secretion. J. Appl. Physiol. 1988, 64, 988–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
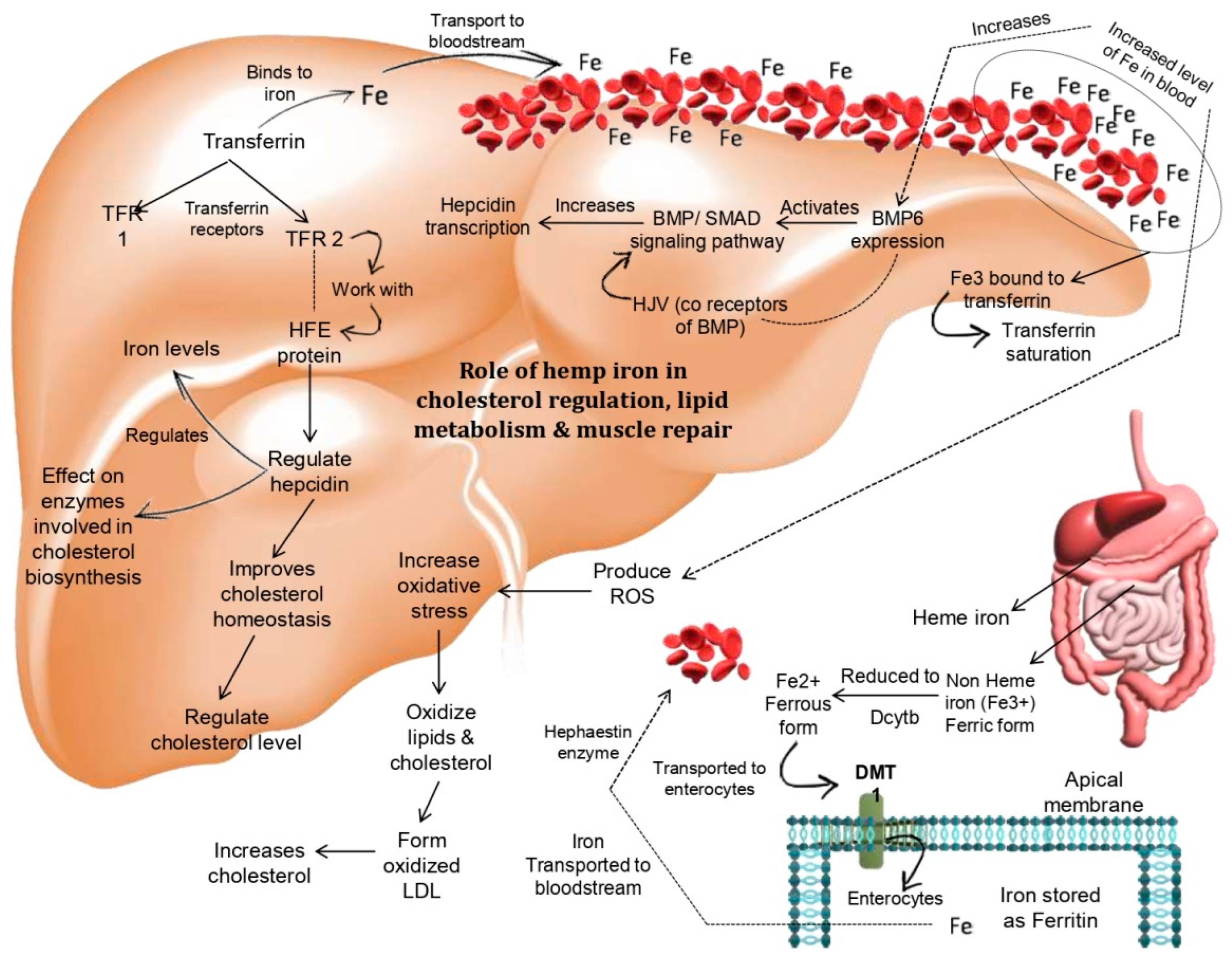
- Mohammadrezaei, A.; Kavakeb, A.; Abbasalizad-Farhangi, M.; Mesgari-Abbasi, M. Effects of hemp seed alone and combined with aerobic exercise on metabolic parameters, oxidative stress, and neurotrophic factors in young sedentary men. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCartney, D.; Benson, M.J.; Desbrow, B.; Irwin, C.; Suraev, A.; McGregor, I.S. Cannabidiol and Sports Performance: A Narrative Review of Relevant Evidence and Recommendations for Future Research. Sports Med. Open 2020, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahinovic, A.; Irwin, C.; Doohan, P.T.; Kevin, R.C.; Cox, A.J.; Lau, N.S.; Desbrow, B.; Johnson, N.A.; Sabag, A.; Hislop, M.; et al. Effects of Cannabidiol on Exercise Physiology and Bioenergetics: A Randomised Controlled Pilot Trial. Sports Med.-Open 2022, 8, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, M.; Tong, C.; Cong, P.; Mao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Hou, M.; Piao, Y. Protective effect and mechanism of cannabidiol on myocardial injury in exhaustive exercise training mice. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2022, 365, 110079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Valverde, D.; Fallas-Campos, A. Cannabidiol in sports: Insights on how CBD could improve performance and recovery. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1210202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamelin, F.-X.; Cuvelier, G.; Mendes, A.; Aucouturier, J.; Berthoin, S.; Di Marzo, V.; Heyman, E. Cannabidiol in sport: Ergogenic or else? Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 156, 104764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitriani, P.; Mulyana, M.; Simbolon, M.; Hamzah, A.; Sartika, D. Effect of honey on measurable sport. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Sport Science, Health, and Physical Education (ICSSHPE 2019), Bandung, Indonesia, 8–9 October 2019; Atlantis Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 351–354. Available online: https://www.atlantis-press.com/proceedings/icsshpe-19/125934719 (accessed on 8 January 2025).
- Yusof, A.; Ahmad, N.S.; Hamid, A.; Khong, T.K. Effects of honey on exercise performance and health components: A systematic review. Sci. Sports 2018, 33, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, S.P.; Mitchell, P.; Wells, C.; Russell, M. Honey supplementation and exercise: A systematic review. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Xu, B.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; He, D.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Xing, X. Emerging natural hemp seed proteins and their functions for nutraceutical applications. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2023, 12, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiroodi, S.G.; Lo, Y.M. The effect of pH on the rheology of mixed gels containing whey protein isolate and xanthan-curdlan hydrogel. J. Dairy Res. 2015, 82, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suksaard, C.; Masashi, M.; Kuenpetch, K.; Nokkaew, N. Consumer behavior of energy gel in male runners: Oral Presentation. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference of Sports Science-AESA, Virtual, 10 March 2022; Volume 6, p. 11. Available online: https://www.journal.aesasport.com/index.php/AESA-Conf/article/view/292 (accessed on 8 January 2025).
- Van Loon, L.J.; Saris, W.H.; Kruijshoop, M.; Wagenmakers, A.J. Maximizing postexercise muscle glycogen synthesis: Carbohydrate supplementation and the application of amino acid or protein hydrolysate mixtures. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beriziky, P.; Cherkaoui, M.; Linxe, L.; Perrin, E.; Rogniaux, H.; Denery-Papini, S.; Morisset, M.; Larré, C.; Dijk, W. Hemp seed: An allergen source with potential cross-reactivity to hazelnut. Food Res. Int. 2023, 169, 112932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.P.; Niphadkar, P.V.; Bapat, M.M. Chickpea: A major food allergen in the Indian subcontinent and its clinical and immunochemical correlation. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001, 87, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, G.; Phillips, S.M. Nutrition guidelines for strength sports: Sprinting, weightlifting, throwing events, and bodybuilding. In Food, Nutrition and Sports Performance III; Routledge: London, UK, 2013; pp. 67–77. Available online: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/edit/10.4324/9781315873268-7/nutrition-guidelines-strength-sports-gary-slater-stuart-phillips (accessed on 9 January 2025).
- Vijayakumar, P.; Adedeji, A. Measuring the pH of Food Products. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lestari, Y.N.; Farida, E.; Amin, N.; Afridah, W.; Fitriyah, F.K.; Sunanto, S. Chia seeds (Salvia hispanica L.): Can they be used as ingredients in making sports energy gel? Gels 2021, 7, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardozo, C.J.M.; Castañeda, C.A.J.; Ripoll, C.S.S. Development of mango (Mangifera indica L.) energy drinks. Rev. Fac. Nac. Agron. Medellín 2017, 70, 8115–8121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friday, O.A.; Julius, A.; Precious, E.-P.; Giacomo, S.; Gioacchino, B.; Małgorzata, K. Functional and sensory properties of jam with different proportions of pineapple, cucumber, and Jatropha leaf. Foods Raw Mater. 2021, 9, 192–200. [Google Scholar]
- Kurni, A.R.; Prameswari, G.N.; Susilo, M.T.; Melinda, A.; Nasiha, N.; Hidayatun, N. Comparing macronutrient compositions and sensory characteristics of jackfruit nugget formulations and commercially available chicken nugget. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Physical Education, Sport, and Health (ACPES 19), Semerang, Indonesia, 10–12 September 2019; Atlantis Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 233–236. Available online: https://www.atlantis-press.com/proceedings/acpes-19/125921460 (accessed on 8 January 2025).
- Febrianto, N.A.; Sa’diyah, K.; Tejasari, T. Red kidney bean powder substituted milk in cinnamon herbal coffee: Consumer perception, sensory properties and nutrition content. Pelita Perkeb. 2016, 32, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubrow, G.A.; Pawar, R.S.; Srigley, C.; Sam, J.F.; Talavera, C.; Parker, C.H.; Noonan, G.O. A survey of cannabinoids and toxic elements in hemp-derived products from the United States marketplace. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 97, 103800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, E.; Kim, H.; Jang, S.; Lee, J.; Baeck, S.; In, S.; Kim, E.; Kim, Y.; Han, E. Concentrations of THC, CBD, and CBN in commercial hemp seeds and hempseed oil sold in Korea. Forensic Sci. Int. 2020, 306, 110064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Lewis, M.M.; Bello, A.M.; Wasilewski, E.; Clarke, H.A.; Kotra, L.P. Cannabis sativa (Hemp) Seeds, Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol, and Potential Overdose. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2017, 2, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroyi, S.A.H.M.; Yusof, Y.A.; Ghazali, N.S.M.; Al-Awaadh, A.M.; Kadota, K.; Mustafa, S.; Abu Saad, H.; Shah, N.N.A.K.; Fikry, M. Determination of physicochemical, textural, and sensory properties of date-based sports energy gel. Gels 2023, 9, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
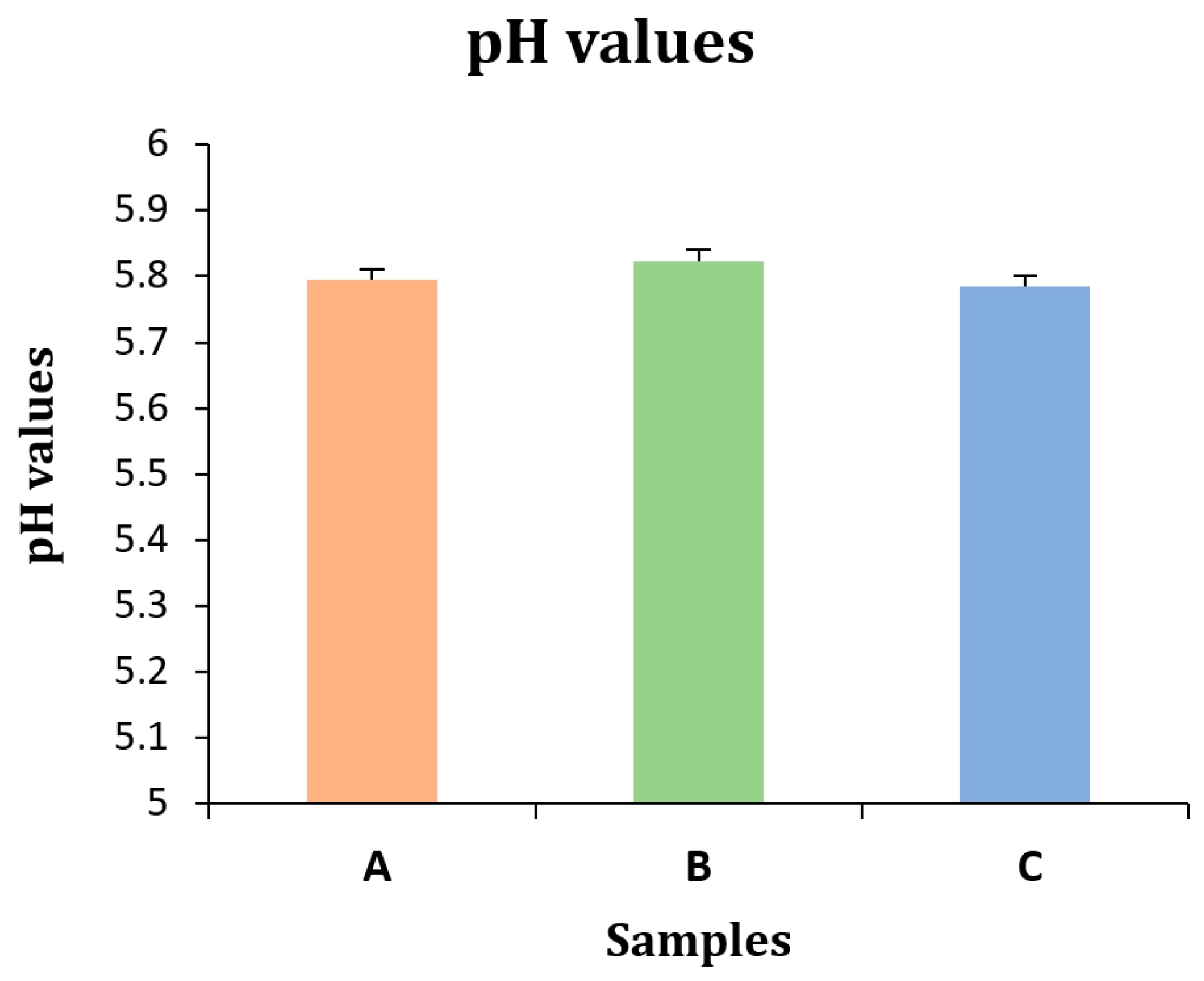



| Sample No. | pH ± SD |
|---|---|
| A | 5.794 ± 0.016 |
| B | 5.822 ± 0.0183 |
| C | 5.785 ± 0.015 |
| Sample No. | Energy (Kcal) | Carbohydrates (g) | Protein (g) | Fat (g) | Ash (g) | Moisture (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 262.7 | 12.73 | 30.9 | 8.9 | 1.92 | 44.65 |
| B | 263.2 | 16.09 | 30.8 | 8.4 | 1.77 | 42.94 |
| C | 270.5 | 15.71 | 31.9 | 8.9 | 1.85 | 41.64 |
| Sensory Characteristics | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment 1 | Appearances ± SD | Taste ± SD | Color ± SD | Texture ± SD | Aroma ± SD | Consistency ± SD | Acceptability ± SD |
| Sample A | 6.36 ± 1.41 | 7.04 ± 1.10 | 6.56 ± 1.29 | 6.64 ± 1.38 | 7.68 ± 0.94 | 7 ± 1.19 | 7.16 ± 0.99 |
| Sample B | 6.28 ± 1.40 | 6.68 ± 1.44 | 6.56 ± 1.29 | 6.4 ± 1.26 | 7.6 ± 1.16 | 6.6 ± 1.41 | 7 ± 1.26 |
| Sample C | 6.68 ± 1.11 | 6.96 ± 1.17 | 6.48 ± 1.36 | 6.6 ± 1.71 | 7.48 ± 1.09 | 6.96 ± 1.31 | 7 ± 1.19 |
| Variables | BV | BN | Sample A | Sample B | Sample C | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NE | NH | NE | NH | NE | NH | |||
| Appearances | 0.805 | 0.126 | 0.590 | 0.073 | 0.570 | 0.071 | 0.560 | 0.073 |
| Taste | 0.766 | 0.120 | 0.510 | 0.062 | 0.613 | 0.072 | 0.592 | 0.071 |
| Color | 0.726 | 0.113 | 0.512 | 0.058 | 0.593 | 0.068 | 0.496 | 0.055 |
| Texture | 0.727 | 0.114 | 0.528 | 0.060 | 0.567 | 0.064 | 0.600 | 0.068 |
| Aroma | 0.843 | 0.132 | 0.560 | 0.074 | 0.650 | 0.087 | 0.620 | 0.080 |
| Consistency | 0.761 | 0.119 | 0.500 | 0.060 | 0.520 | 0.060 | 0.592 | 0.071 |
| Acceptability | 0.784 | 0.122 | 0.540 | 0.066 | 0.600 | 0.074 | 0.500 | 0.060 |
| pH | 0.995 | 0.155 | 0.480 | 0.074 | 0.533 | 0.084 | 0.500 | 0.077 |
| Total | 6.408 | 1.000 | 0.527 | 0.580 1 | 0.556 | |||
| Ingredients (g) | Treatments | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample A | Sample B | Sample C | |
| Bengal gram dal | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Hemp seeds | 32 | 38 | 42 |
| Honey | 40 | 40 | 40 |
| Water | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| Xanthan gum | 0.82 | 0.89 | 0.96 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Verma, V.; Gill, V.; Kumar, A.; Singh, S.P. Development of Edible Carbohydrate–Protein Sports Gels to Optimize the Muscle Glycogen Re-Synthesis. Gels 2025, 11, 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11050341
Verma V, Gill V, Kumar A, Singh SP. Development of Edible Carbohydrate–Protein Sports Gels to Optimize the Muscle Glycogen Re-Synthesis. Gels. 2025; 11(5):341. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11050341
Chicago/Turabian StyleVerma, Vishal, Vishal Gill, Avinash Kumar, and Shailendra Pratap Singh. 2025. "Development of Edible Carbohydrate–Protein Sports Gels to Optimize the Muscle Glycogen Re-Synthesis" Gels 11, no. 5: 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11050341
APA StyleVerma, V., Gill, V., Kumar, A., & Singh, S. P. (2025). Development of Edible Carbohydrate–Protein Sports Gels to Optimize the Muscle Glycogen Re-Synthesis. Gels, 11(5), 341. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11050341









