Abstract
Ion-conductive gels (ICGs) are essential for achieving human–machine interfaces, bioelectronic applications, or durable wearable sensors. However, traditional solvent-dependent ICGs face bottlenecks such as dehydration-induced failure and challenges in achieving a balance between conductivity and mechanical properties. Here, this work developed a novel ternary ion-conductive xerogel (PEM-Li ICXG) system based on polyethylene glycol (PEG), poly (2-methoxyethyl acrylate) (PMEA), and LiTFSI. PEM-Li ICXGs exhibit high conductivity (2.7 × 10−2 S/m), high adhesive capability (0.34 MPa), and solvent-free characteristics. Remarkably, the incorporation of ions into ICXGs simultaneously optimizes their mechanical performance. We demonstrate the application of ICGs in flexible sensors for strain or temperature sensing. The proposed synthesis strategy is straightforward and may further inspire the design of novel high-performance ICXGs.
1. Introduction
Against the backdrop of the rapid advancement of Internet of Things technology, the growing demand for wearable devices, miniaturized instruments, and attachable sensors has significantly driven innovative breakthroughs in flexible electronics [1,2,3]. The field has successfully developed novel solutions applicable to cutting-edge scenarios, such as biomedical monitoring [4] and bio-inspired robotics [5,6,7,8]. Notably, current electronic systems predominantly employ electrons as information carriers [9,10,11,12], which fundamentally differs from the ion-mediated conduction mechanisms in biological organisms [13,14,15]. Flexible polymer materials with ion-conductive properties through dynamic ion–polymer interactions (i.e., ion-conductive gels, ICGs) demonstrate immense potential in bridging the electromechanical performance gap [16,17,18,19]. To meet the application requirements of next-generation intelligent soft devices, such materials must integrate exceptional electrical conductivity, reliable mechanical properties, as well as environmentally responsive functionalities and other comprehensive performance metrics [20,21].
Previous research focused on constructing highly ionically conductive gels by integrating flexible polymer networks with liquid electrolytes, such as ionic hydrogels or ionic liquid gels. For instance, polyacrylamide/lithium chloride (PAAm/LiCl)-based ionic hydrogels achieve high conductivity (>0.1 S m−1), approaching biological tissue conductivity levels, and demonstrate potential in flexible sensing applications [22]. However, such systems heavily rely on solvation to maintain ion transport channels. Prolonged environmental exposure leads to water evaporation, causing conductive network collapse and conductivity decay exceeding 80% [23]. More critically, under dynamic cyclic strain (e.g., 100% stretching amplitude over 1000 cycles), the modulus mismatch between the liquid electrolyte and polymer network exacerbates interfacial slippage, forming millimeter-scale conductive phase-separation regions and resulting in resistance fluctuations exceeding 200% [24]. To eliminate solvent dependency, solvent-free ICXGs chemically anchor electrolyte salts within polymer networks [25]. A representative strategy involves metal-coordination systems based on polyethylene oxide and zinc bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide, where dynamic coordination between Zn2+ and ether oxygen groups forms crosslinked networks. This enables the material to retain an elastic modulus of 0.15 MPa at 60 °C without leakage risks [26]. However, strong coordination interactions significantly suppress Li+ mobility, yielding a room-temperature conductivity of only 0.017 S m−1, which is two orders of magnitude lower than liquid-based systems [27]. Additionally, constrained by the solubility threshold of salts in polymer matrices (typically <30 wt%), synergistic optimization of network crosslinking density and ion transport capability faces fundamental challenges [28]. Recent breakthrough studies have attempted to merge the advantages of solvent-based and solvent-free systems, such as composite electrolytes employing polyethylene glycol (PEG) and dual-network designs [29]. By dissolving lithium bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (LiTFSI) salts in PEG solvents while forming hydrogen bonds with poly (urethane acrylate) networks, a conductivity of 0.08 S m−1 at 25 °C is achieved, alongside a 40% improvement in anti-swelling performance compared to conventional hydrogels [30]. Nevertheless, such systems still face mechanical limitations: when PEG content exceeds 50 wt%, the elastic modulus drops below 0.5 MPa. Although fracture elongation reaches 800%, plastic deformation readily occurs under high-frequency loading scenarios (e.g., >10 N cyclic loads in soft robotic joints), with residual strain accumulation reaching 35% after 100 cycles [31], where these limitations severely hinder the application of ICXGs [32].
This study developed high-performance ICXGs by constructing a PEG/poly (2-methoxyethyl acrylate) (PMEA)/LiTFSI ternary system, which is abbreviated as PEM-Li. The chemical structures and compositions of PEM-Li ICXGs are presented in Scheme 1. We discovered that Li+ dynamic coordination establishes a reversible ion-dipole energy dissipation network [33], endowing it with a high work of extension at the fracture of 0.36 MJ/m3. The presence of PMEA imparts universal adhesion to wood, ceramic, and metal substrates (0.28–0.33 MPa), and LiTFSI’s dual antibacterial mechanism achieves an inhibition zone diameter of 7 ± 0.4 mm. Electrically, as an organic salt widely used in solid polymer electrolytes, LiTFSI was employed in this work to enhance conductivity. Considering the good compatibility between LiTFSI and the polymer matrix PEM, LiTFSI can dissociate as the cations Li+ and anions TFSI− within PEM-Li ICXGs to provide charge carriers [34,35,36]. PEM-Li yields a conductivity of 2.7 × 10−2 S/m with dual-temperature–strain response characteristics: a temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) of −1.54% °C−1 in the physiological range (30–45 °C), a gauge factor (GF) of 1.78 under 60% strain, and a response time <535 ms. After 200 cycles, the dynamic network demonstrates efficient energy dissipation and self-recovery capabilities [37]. As a multifunctional sensor, it successfully achieves synchronized monitoring of joint motion and temperature signals. We believe that this work opens a new pathway for developing high-performance ion-conductive intelligent materials [38,39].
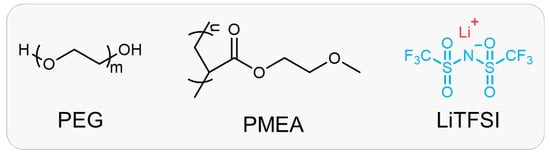
Scheme 1.
Chemical structures and compositions of PEM-Li ICXGs.
2. Results and Discussion
We successfully constructed ternary PEMx-Liy ICXGs through a free radical copolymerization strategy, where “x” represents the mass ratios of MEA (ωMEA) to the total MEA and PEG monomers, and “y” denotes the mass ratios of Li (ωLi) to the total precursor solution. The system employs PEG4000 as a flexible backbone, MEA as a functional building unit, and LiTFSI as a dynamic ionic regulation medium. As shown in Figure 1, when ωLi increases from 0 to 20%, both the optical appearances of the PEM50 and PEM50-Li systems are turbid, suggesting distinct phase-separation phenomena formed by the PEG crystals. Of note is that the PEM50-Li samples with ωLi ≥ 30% fail to form stable films and are excluded from further consideration. Subsequently, by systematically investigating the uniaxial tensile behavior of PEM50-Li ICXGs with ωLi from 0 to 20% (Figure 2a), we can see that the elastic modulus (E) drastically decreases from 16.9 to 2.04 MPa with increasing ωLi. On the contrary, the work of extension at fracture (Wextf) increases from 0.03 to 0.36 MJ/m3, showing a 12-fold enhancement [40]. In terms of adhesive performance, lap-shear testing results show that the PEM elastomer without LiTFSI exhibits an initial adhesive strength of 0.8 MPa (Figure 3a) due to the methoxyethyl (-OCH2CH2O-) and ester (-COO-) groups in MEA molecules forming a multi-noncovalent bonding network with the glass substrates [41]. As ωLi increases to 5%, 10%, and 20%, the adhesive strength progressively declines in a stepwise manner from 0.34 to 0.22 MPa and finally to 0.1 MPa (Figure 3b). This degradation likely stems from two factors: (1) the competitive coordination between Li+ and the polar functional groups of MEA reduces the density of effective adhesive sites, and (2) the steric hindrance effect of TFSI− anions weakens the physical entanglement capability of polymer chains [42,43].
Figure 1.
Optical images of PEM-Li membranes with varying LITFSI addition ratios: (a) 0%, (b) 5%, (c) 10%, and (d) 20%. Scale bar: 1 cm. Scale bar: 1 cm.
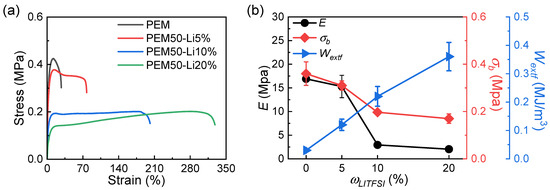
Figure 2.
(a) Tensile stress–strain curves of PEM-Li ICXGs. (b) Mechanical properties. Elastic modulus, E; fracture stress, σb; work of extension at fracture, Wextf.
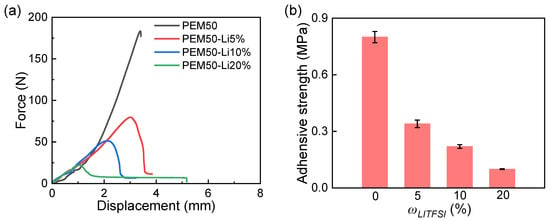
Figure 3.
(a) Displacement–force curves of PEM-Li ICXGs. (b) Comparative analysis of interfacial bonding strength of PEM-Li ICXGs.
As shown in Figure 4a, when ωLi is 5%, the conductivity of PEM50-Li ICXG achieves the peak conductivity of 2.7 × 10−2 S/m, surpassing that of various ICGs reported before. It is noted that the electrical conductivity measured in this study by the DC electricity reflects the combined contributions of ionic and electronic conductivity in the material. Future work will include impedance measurements (e.g., electrochemical impedance spectroscopy) to further distinguish ionic conductivity from electrical conductivity. Specifically, its conductivity not only far exceeds that of traditional ionogels (e.g., polyurethane ionogels ~1.5 × 10−2 S/m, starch/gelatin-based systems ~1 × 10−2 S/m), glycerol hydrogels (~1.2 × 10−2 S/m), and silicone rubber elastomers (~3 × 10−3 S/m, Figure 4b) [44,45,46,47,48,49,50]. This optimization arises from the uniform dispersion of Li+ in the polymer matrix, forming a continuous conductive network, and the synergistic enhancement of carrier mobility through moderate ion–polymer interactions [51]. When the ωLi exceeds 5%, it may trigger ion cluster aggregation, obstructing ion migration pathways and causing conductivity decline (Figure 4a). Based on the study of multi-parameter synergistic evolution, when the ωLi is 5%, the PEM50-Li ICXGs achieve the relative optimal balance among mechanical, adhesive, and conductive properties.
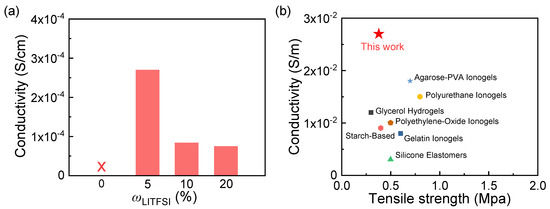
Figure 4.
(a) Statistics of the conductivity of PEM-Li ICXGs. (b) Comparison of the tensile strength and conductivity between PEM-Li ICXGs and other reported ion-conductive materials [44,45,46,47,48,49,50].
Then, we examined the effects of the mass ratio of PEG and PMEA (ωPMEA) on the tensile and adhesion properties of PEM-Li5% ICXGs. As shown in Figure 5a, by investigating the influence of ωPMEA from 40% to 70% on the uniaxial tensile behavior of ICG samples, it is found that the fracture elongation rate achieves a 40-fold leap from 15% to 580%, but the elastic modulus E decreases from 12.5 to 2.8 MPa, with a 77.6% reduction. This drastic mechanical transformation originates from structural reorganization involving PEG crystalline domain dissociation and PMEA dynamic network formation [52]; the former weakens the strong interchain constraints, while the latter enhances the motional freedom through chain slippage mechanisms [53]. In addition, the work of extension at fracture Wextf exhibits stepwise growth, rising from 0.05 to 4.92 MJ/m3, whereas the fracture stress follows a nonmonotonic trend, where it is decreasing first and then increasing as ωPMEA >50%. The initial decline likely stems from the rigidity loss due to the PEG crystalline network dissociation, while the subsequent recovery may be dominated by phase-separation-induced crack blunting effects [54]. After comprehensive performance evaluation, the PEM50-Li5% ICXGs are ultimately selected as the optimal ratio.
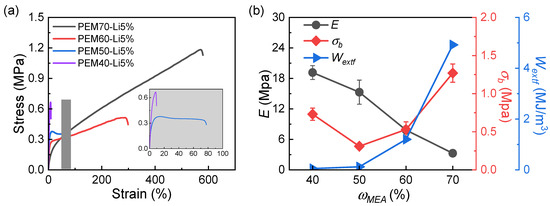
Figure 5.
(a) Uniaxial tensile stress–strain curves of PEM-Li ICXGs. (b) Mechanical properties. Elastic modulus, E; fracture stress, σb; work of extension at fracture, Wextf.
The cyclic tensile testing results in Figure 6a demonstrate that the PEM50-Li5% ICXGs exhibit good energy dissipation characteristics during 50 cycles at 40% strain. The first cycle generates a significant hysteresis loop due to molecular chain reorganization and energy dissipation, but the hysteresis rate rapidly stabilizes around 3.98% after subsequent cycles (Figure 6b), attributed to the dynamic entanglement network achieving rapid equilibrium of energy dissipation pathways via reversible disentanglement mechanisms [55]. A residual strain of 14.33% was observed, confirming that the segmental slippage effect within the entropy–elastic network endows the materials with excellent deformation recovery [56]. Quantitative analysis of stabilized hysteresis rates and residual strain reveals the dual advantages of efficient energy dissipation and structural self-recovery in the PEM50-Li5% ICXGs.

Figure 6.
(a) Successive cyclic tensile stress–strain curves at 40% strain. (b) Hysteresis energy and residual strain.
Notably, the PEM50-Li5% sample demonstrates exceptional interfacial adhesion adaptability across diverse materials. As shown in Figure 7a, experimental comparisons of its adhesive performance on substrates including wood, ceramic, rubber, glass, and metal reveal stable adhesion strengths within the range of 0.28–0.33 MPa (Figure 7b,c). This universal adhesion capability arises from the dual mechanisms of methoxyethyl and ester groups in MEA molecules: for highly polar substrates (e.g., metal, glass), ether oxygen (-O-) and ester (-COO-) groups form strong interactions with surface hydroxyls or oxides via hydrogen bonding; for low-polarity substrates (e.g., rubber, wood), the conformational adaptability of flexible polyether chains enables the accommodation of surface roughness, enhancing the interfacial bonding through chain penetration and mechanical interlocking effects [57,58,59]. The retention of such broad-spectrum adhesion, combined with the optimized electrical and mechanical properties discussed earlier, further highlights the unique advantages of PEM50-Li5% ICXGs for integration with flexible sensors and complex surfaces (e.g., bio-inspired skins).

Figure 7.
(a) Universal adhesion of PEM50-Li5% to various substrates (i: wood, ii: ceramic, iii: glass, iv: rubber, v: stell). (b) Force–displacement curves during lap-shear tests. (c) Adhesion strength on various substrates. Scale bar: 1 cm.
Leveraging the synergistic effects of free Li+ and TFSI− ions in the PEM50-Li5% ICXG, it exhibits a pronounced temperature-responsive characteristic. To validate its temperature-sensing performance, we quantitatively analyzed the temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR) as a key metric [60]. Experimental data show an outstanding TCR value of −1.54% °C−1 at 36 °C (near human body temperature, Figure 8a), strongly confirming its potential as a temperature sensor. Further studies reveal that under varying heating/cooling rates (e.g., 10, 25, 40 °C min−1) within the 30–40 °C range, the final relative resistance change (ΔR/R0) variation remains constant (Figure 8b), demonstrating reliable electrical response characteristics. To address practical application requirements for sensor devices, we systematically evaluated the cyclic stability of PEM50-Li5% ICXGs in the 35–40 °C range. After 100 consecutive heating–cooling cycles, the ΔR/R0 signal amplitude remains stable (Figure 8c), with long-term stability tests fully verifying the performance reliability of PEM50-Li5% ICXGs under repeated usage conditions. The combined validation of reproducibility and long-term stability provides the critical experimental evidence for assessing the suitability of PEM50-Li5% ICXGs in biomedical temperature monitoring and related fields.

Figure 8.
(a) ∆R/R0 changes in PEM-Li ICXGs in the temperature range of 30–50 °C. The resistance at 36 °C was taken as the reference resistance. (b) Comparison of temperature-resistance response under different ramp rates (i.e., 10, 25, and 50 °C min−1) from 30 to 40 °C. (c) Cyclic stability test under repeated heating–cooling in the 35−40 °C temperature range at a ramp rate of 10 °C min−1 for 100 cycles.
Likewise, systematic studies on strain-resistance response characteristics reveal that PEM50-Li5% ICXGs also exhibit exceptional strain-sensing performance (Figure 9). The PEM50-Li5% ICXGs present a high-strain responsive window from 0 to 60% (Figure 9a). The results of the gauge factor (GF = 1.78) and correlation coefficient (R2 = 0.993), calculated by linearly fitting the ∆R/R0 with loading strain, indicate the good linearity of sensing signals. Notably, this gauge factor significantly surpasses those of conventional strain-sensitive materials [61,62,63,64]. To further evaluate the practical device performance, multi-parameter cyclic testing was conducted. Under varying fixed strain levels (5–50%, Figure 9b) and loading rates (5–100 mm/min, Figure 9c), the material exhibits stable resistance responses during continuous stretch–release cycles. This high repeatability primarily stems from the three-dimensional crosslinked network structure, which endows the ICG with superior elastic recovery and microstructural stability [65].

Figure 9.
(a) ∆R/R0 changes in PEM50-Li5% ICXGs as a function of tensile strain. The red dots denote the experiment data, and the gray dashed line represents the linear fitting curve. (b,c) ∆R/R0 signals measured (b) under different tensile strains (5−50%) with the strain rate of 5 mm min−1 and (c) at different strain rates (5−100 mm min−1) upon stretching to 50% strain.
Dynamic mechanical response testing highlights the superior sensing properties of PEM50-Li5% ICXGs. As illustrated in Figure 10a, under 40% strain, the material displays exceptional dynamic responsiveness, with stretching and recovery response times of 535 and 360 ms, respectively. Notably, after 200 cyclic loading tests at 50% strain, the sensor retains stable resistance output (Figure 10b), which is a critical durability feature for dynamic monitoring applications. Combined with its sensitive temperature/strain response (Figure 9 and Figure 10), the material demonstrates significant advantages as a multifunctional wearable sensor, capable of addressing multi-parameter detection requirements in complex operational scenarios.
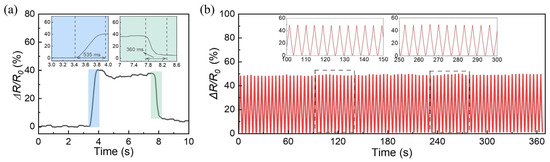
Figure 10.
(a) Determination of response time and recovery time of PEM50-Li5% ICXGs at 40% strain. (b) Cyclic stability test under the repeated loading–unloading strain of 50% for 200 cycles. Insets exhibit the enlarged view of some periods during the whole cyclic test.
The application potential of PEM50-Li5% ICXGs in biomedical sensing is particularly remarkable, as its unique temperature–strain-coupled response characteristics are fully demonstrated under human body surface temperature conditions (~36 °C). As shown in Figure 11, the PEM50-Li5% ICXGs achieve synchronous capture of multimodal biomechanical signals through flexible device integration, with core advantages manifested in two aspects: (1) stable adhesion at the material–skin interface ensures signal transmission reliability; (2) the linear mapping relationship between dynamic deformation and electrical signals enables precise motion resolution. Specifically, when deployed as a finger joint sensor (inset in Figure 11a), the device can record bending angle variations of the finger in the 15°–90° range in real time. The ΔR/R0 value exhibits a monotonic increasing trend with angle increments and rapidly returns to baseline within 1.2 s after reverting to the initial state (State I). Furthermore, these PEM50-Li5% ICXGs were also applied to monitor other body joints, such as the elbow, wrist, and knee joint. Figure 11b–d show that the PEM50-Li5% ICXGs can discern the flexure of the elbow joint and the bending of the wrist and knee joint.
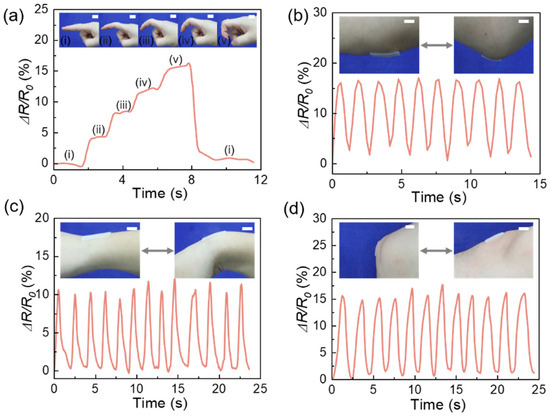
Figure 11.
Human motion detections for the movements of (a) finger (i: 0°, ii: 15°, iii: 30°, iv: 45°, v: 90°), (b) elbow, (c) wrist, and (d) knee by the strain sensor of PEM50-Li5% ICXGs. Scale bar: 1 cm. (a) Human motion detections for the movements of (a) finger (i: 0°, ii: 15°, iii: 30°, iv: 45°, v: 90°).
In biosafety evaluation, the antibacterial efficacy of PEM50-Li5% against Staphylococcus aureus was systematically investigated via inhibition zone assays (Figure 12a). The results show that the samples with ωLi = 5% form inhibition zones of 7 ± 0.4 mm diameter on agar plates, which is significantly larger than that of the control group without LiTFSI (3 ± 0.2 mm). After 5 days of continuous culture, the inhibition zone area of LiTFSI-containing samples remains at 108% of the initial value, while the control group maintains stable antibacterial efficacy (Figure 12b). This long-lasting antimicrobial property likely stems from the dual mechanisms of fluorinated species in LiTFSI: (1) TFSI− anions penetrate bacterial cell membranes to inhibit activity; (2) gradually released Li+ competitively binds with phosphate groups of phospholipid head groups, disrupting membrane integrity [66]. These mechanisms collectively endow PEM50-Li5% with robust antibacterial performance.
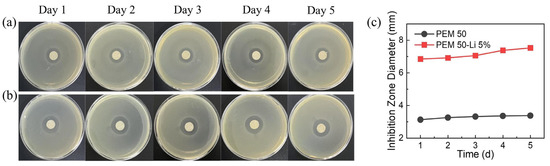
Figure 12.
(a,b) Time-dependent variation in inhibition zones of (a) PEM50 and (b) PEM50-Li5% gels against S. aureus (ATCC 25923). (c) Comparative analysis of inhibition zone diameters between PEM50 and PEM50-Li5% gels. Scale bar: 1 cm.
3. Conclusions
In summary, this study successfully constructed PEM-Li ICXGs that leverage the dynamic coordination effects of LiTFSI to achieve synergistic regulation of mechanical, electrical, and interfacial properties. The PEM50-Li5% ICXGs have good flexibility with damage resistance while maintaining robust adhesion and high conductivity. More importantly, the PEM50-Li5% ICXGs exhibit dual-mode temperature/strain-sensing capabilities, with rapid response characteristics and cyclic stability that provide a reliable solution for human motion monitoring. The unique dynamic ionic network endows the materials with self-recovery properties and long-lasting antibacterial performance, offering a novel design strategy for the development of intelligent flexible electronic devices. Despite these promising results, challenges remain that must be addressed to facilitate real-world applications. Long-term stability under varying environmental conditions, such as humidity and temperature fluctuations, is critical for practical use. In addition, improving the environmental robustness and scalability of the fabrication process and seamless integration with existing electronic systems are essential for further advancement. Future work should focus on optimizing the material’s durability and adaptability in complex environments, while enhancing its compatibility with diverse technologies for commercialization and biomedical applications. Addressing these challenges will not only solidify the current contributions, but also pave the way for broader practical implementation and future innovations.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
Polyethylene glycol (PEG, Mn = 4000, Shanghai Macklin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), 2-methoxyethyl acrylate (MEA, purity 98%), lithium bis (trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide (LiTFSI, purity 99%), dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, ≥99.9%), potassium persulfate (KPS), and N,N′-methylenebisacrylamide (MBAA) were purchased from Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China. All reagents were used without further purification.
4.2. Preparation of PEM-Li ICXGs
The preparation method described in this article is a universally applicable protocol, and samples with other different proportions can all be prepared through the same process. For example, polyethylene glycol (PEG, 15 g) and 2-methoxyethyl acrylate (MEA) at a mass ratio of 1:1 (PEG:MEA) were first dissolved in DMSO under a nitrogen atmosphere. The mixture was magnetically stirred at 70 °C for 1 h until complete homogenization. Subsequently, LiTFSI with 5 wt% of the total polymer mass was added in three equal portions at 15 min intervals to prevent localized crystallization. The final mixture was continuously stirred at 70 °C for an additional 1 h to obtain a transparent and homogeneous electrolyte solution. After allowing the solution to cool naturally to 40 °C, 1 wt% thermal initiator KPS and 0.2 wt% crosslinker MBAA (relative to the total monomer mass) were added sequentially. The mixture was continuously stirred for 30 min at 40 °C and 500 rpm using a constant-temperature magnetic stirrer until complete dissolution. The solution was then transferred to an ultrasonic cleaner (40 kHz) for a 15 min degassing treatment. Subsequently, the degassed solution was poured into a custom glass–rubber composite mold (100 × 100 × 1 mm3) and subjected to gradient polymerization in a programmable temperature oven. The polymerization protocol was set as follows: linear heating from 25 to 80 °C at a rate of 2 °C/min, followed by isothermal curing at 80 °C for 2 h to complete crosslinking. After natural cooling to room temperature, the system was demolded to obtain a white solid material with excellent ductility. Finally, the sample was placed in a polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Petri dish and dried in a vacuum oven (80 °C, −0.1 MPa) for 2 h to completely remove DMSO solvent, yielding the target polymer.
4.3. Mechanical Property Testing
The mechanical properties of samples were evaluated using a universal material testing machine (UTM4304, Shenzhen SUNS Testing Machine Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China) via the uniaxial tensile method. The stress–strain curve was measured to calculate the tensile strength, elongation at break, and elastic modulus of the samples. Prior to testing, the samples were cut into standard dumbbell-shaped specimens with a gauge length of 15 mm and a width of 3 mm. The ends of the specimens were clamped by fixtures, and a tensile force was applied at a constant speed of 5 mm/min until complete fracture of the specimen. To ensure data reliability, each sample was tested at least 5 times.
4.4. Adhesion Testing
This study employed lap-shear testing to evaluate the adhesive properties of the samples. To establish adhesive contact, the sample and substrate were first pre-compressed under 1.3 N normal pressure for 2 min to form a standardized contact interface. Subsequently, tensile loading was applied parallel to the contact surface at a constant rate of 1 mm/min until complete interfacial separation occurred. The adhesive strength was calculated by dividing the recorded maximum shear force by the pre-compressed contact area. To ensure data reliability, each experimental group underwent at least 5 independent replicate tests.
4.5. Electrical Conductivity Test
The bulk resistance, R, of PEM-Li ICXGs was detected using a two-probe measurement, with two copper electrodes attached to both ends of the samples (DMM7510 digital multimeter, Keithley, Cleveland, OH, USA). The samples were trimmed to a rectangle with a length (l) of 2 cm, a width (d) of 1 cm, and a thickness (h) of 1 mm and placed in a thermostatic chamber (25 °C) for 24 h before testing. The electrical conductivity σ of the samples was calculated as follows: σ = l/Rdh.
4.6. Strain-Sensing Performance Test
A strain sensor was fabricated using PEM50-Li5% ICXGs with dimensions of 25 mm in length, 10 mm in width, and 1 mm in thickness. Both ends of the PEM50-Li5% ICXGs were connected with copper wires and encapsulated with VHB adhesive as the strain sensor. The copper electrodes at both ends were then connected to a Keithley digital multimeter (DMM7510, Tektronix Technology (China) Co., Ltd., Beaverton, OR, USA) to collect real-time resistance signals. The hydrogel strain sensor was attached to human joints to monitor movement activities. The relative resistance change is defined as follows: ΔR/R0 = (R–R0)/R0 × 100%, where R0 represents the initial resistance, and R denotes the real-time resistance. The gauge factor (GF) is defined as follows: GF = (ΔR/R0)/ε, where ε indicates the strain applied to the sensor. It is calculated from the slope of the relative resistance–strain response curve.
4.7. Antibacterial Studies
Prepare a solid culture medium containing 4% glucose, 1% meat peptone broth (MPB), and 2% agar (dissolved in 100 mL deionized water). Autoclave the medium and cool it to below 40 °C. Pour 20 mL of the medium into a 90 mm sterile Petri dish and allow it to solidify for later use. Using an inoculation loop, pick a single colony of Staphylococcus aureus and transfer it to a test tube containing 10 mL of liquid MPB medium. Incubate the tube at 32 ± 2 °C in a constant-temperature incubator for 24 h to obtain logarithmic-phase bacterial culture. Mix 2 mL of the bacterial suspension uniformly into 20 mL of solid medium cooled to 40 °C. Quickly pour the mixture into a Petri dish, swirl gently to ensure even distribution, and allow it to solidify completely. Prepare PEM50-Li5% ICG discs (15 mm in diameter and 1 mm in thickness) and gently place them on the surface of the solidified agar containing the bacterial culture, ensuring full contact with the agar. Invert the plates and incubate them at 32 ± 2 °C. Observe the formation of inhibition zones every 24 h for five days. Measure the diameter (in cm) of the inhibition zones and record the data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Z. (Yicheng Zhu) and P.P.; methodology, Y.Z. (Yicheng Zhu) and Y.Z. (Yichen Zhou); validation, Y.Z. (Yicheng Zhu); formal analysis, Y.Z. (Yicheng Zhu) and C.Y.; investigation, Y.Z. (Yicheng Zhu) and X.Z.; data curation, Y.Z. (Yicheng Zhu); writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z. (Yicheng Zhu); writing—review and editing, C.Y. and J.Y.; supervision, C.Y. and J.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Key Laboratory of Energy Resource Utilization from Agriculture Residue, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, China (Grant No. KLERUAR2023-03); State Key Laboratory of Biobased Material and Green Papermaking, Qilu University of Technology, Shandong Academy of Sciences (Grant No. GZKF202317). National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52473021).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Li, H.B.; Ma, Y.J.; Huang, Y.G. Material innovation and mechanics design for substrates and encapsulation of flexible electronics: A review. Mater. Horiz. 2021, 8, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.Y.; Shen, Y.Y.; Zhu, F.B.; Yin, J.; Qian, J.; Fu, J.Z.; Wu, Z.L.; Zheng, Q. Programmed Deformations of 3D-Printed Tough Physical Hydrogels with High Response Speed and Large Output Force. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1803366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Zheng, Y.; Zhu, R.J.; Mu, Q.F.; Wang, X.Y.; Wang, Z.S.; Liu, S.Q.; Li, M.; Ran, R. Strong Tough Conductive Hydrogels via the Synergy of Ion-Induced Cross-Linking and Salting-Out. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2204823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.R.; Gao, W. Wearable and flexible electronics for continuous molecular monitoring. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 1465–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Lin, Y.; Shen, S.T.; Du, Z.H.; Lin, Z.Q.; Zhou, P.P.; Huang, H.L.; Lyu, X.L.; Zou, Z.G. Intrinsic Anti-Freezing, Tough, and Transparent Hydrogels for Smart Optical and Multi-Modal Sensing Applications. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2413856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi, M.H.; Qin, S.H.; Wen, S.H.; Wang, Z.S.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, M.; Lu, H.L.; Meng, Q.D.; Cui, W.; Ran, R. Rapid gelation of tough and anti-swelling hydrogels under mild conditions for underwater communication. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2210188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.X.; Yuan, F.Y.; Liu, J.Q.; Tian, L.F.; Chen, B.H.; Fu, Z.Q.; Mao, S.Z.; Jin, T.T.; Wang, Y.; He, X.; et al. Octopus-inspired sensorized soft arm for environmental interaction. Sci. Robot. 2023, 8, eadh7852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.T.; Zou, Y.; Deng, Y.L.; Li, Z. Bioinspired sensor system for health care and human-machine interaction. EcoMat 2022, 4, e12209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacour, S.P.; Courtine, G.; Guck, J. Materials and technologies for soft implantable neuroprostheses. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2016, 1, 16063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feiner, R.; Dvir, T. Tissue-electronics interfaces: From implantable devices to engineered tissues. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 17076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodelón, G.; Montes-García, V.; López-Puente, V.; Hill, E.H.; Hamon, C.; Sanz-Ortiz, M.N.; Rodal-Cedeira, S.; Costas, C.; Celiksoy, S.; Pérez-Juste, I.; et al. Detection and imaging of quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm communities by surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering. Nat. Mater. 2016, 15, 1203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zong, S.Y.; Lv, H.; Liu, C.J.; Zhu, L.W.; Duan, J.F.; Jiang, J.X. Mussel inspired Cu-tannic autocatalytic strategy for rapid self-polymerization of conductive and adhesive hydrogel sensors with extreme environmental tolerance. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 465, 142831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoul, D.; Hu, W.L.; Gao, M.M.; Mehta, V.; Pei, Q.B. Recent Advances in Stretchable and Transparent Electronic Materials. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2016, 2, 1500407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.Q.; Lieber, C.M. Nano-bioelectronics. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 215–257. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.Y.; Mao, S.H.; Yuan, J.F.; Wang, S.B.; He, X.M.; Zhang, X.N.; Du, C.; Zhang, D.; Wu, Z.L.; Yang, J.T. Molecularly Engineered Zwitterionic Hydrogels with High Toughness and Self-Healing Capacity for Soft Electronics Applications. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 8418–8429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuk, H.; Wu, J.J.; Zhao, X.H. Hydrogel interfaces for merging humans and machines. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 935–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tordi, P.; Ridi, F.; Samori, P.; Bonini, M. Cation-Alginate Complexes and Their Hydrogels: A Powerful Toolkit for the Development of Next-Generation Sustainable Functional Materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2416390. [Google Scholar]
- Boufidis, D.; Garg, R.; Angelopoulos, E.; Cullen, D.K.; Vitale, F. Bio-inspired electronics: Soft, biohybrid, and "living" neural interfaces. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1861. [Google Scholar]
- Afanasenkau, D.; Kalinina, D.; Lyakhovetskii, V.; Tondera, C.; Gorsky, O.; Moosavi, S.; Pavlova, N.; Merkulyeva, N.; Kalueff, A.V.; Minev, I.R.; et al. Rapid prototyping of soft bioelectronic implants for use as neuromuscular interfaces. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 1010–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.Y.; Jiang, Q.; Bisoyi, H.K.; Zhu, G.Q.; Nie, Z.Z.; Jiang, K.; Yang, H.; Li, Q. Multifunctional Ionic Conductive Anisotropic Elastomers with Self-Wrinkling Microstructures by In Situ Phase Separation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 28546–28554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.Y.; Wang, L.; Liang, C.Y.; Qiu, J.H.; Zhang, T.Y.; Xu, D.H.; Qi, D.P.; Luan, S.F.; Shi, H.C. Bioinspired Ionic Elastomer with Skin-Like Piezo-Ionic Dynamics Enabled by a Self-Confined Multi-Interaction Network. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, Early View, 2418583. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.X.; Zhou, J.L.; Lu, G.Q.; Sun, J.X.; Tang, L.Q. Highly Stretchable, Transparent, and Self-Adhesive Ionic Conductor for High-Performance Flexible Sensors. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 1610–1617. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, L.Y.; Li, W.W.; Zhang, T.H.; Ma, H.H.; Cao, Y.Q.; Wang, K.X.; Zhou, Y.L.; Shamim, A.; Zheng, L.; Wang, X.W.; et al. Wireless Technologies in Flexible and Wearable Sensing: From Materials Design, System Integration to Applications. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2400333. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, L.; Jia, K.; Gao, Y.Y.; Yang, H.; Ma, Y.M.; Lu, S.Y.; Gao, G.X.; Bu, H.T.; Lu, T.Q.; Ding, S.J. Highly Stretchable and Transparent Ionic Conductor with Novel Hydrophobicity and Extreme-Temperature Tolerance. Research 2020, 2020, 2505619. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Li, W.X.; Li, D.B.; Zhao, X.X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Qi, X.; Wu, M.; Fan, L.Z. High-Performance Solid-State Lithium Metal Batteries of Garnet/Polymer Composite Thin-Film Electrolyte with Domain-Limited Ion Transport Pathways. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 32175–32185. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Qu, X.X.; Hu, Z.Y.; Zhu, J.J.; Niu, W.W.; Liu, X.K.J. Highly elastic and mechanically robust polymer electrolytes with high ionic conductivity and adhesiveness for high-performance lithium metal. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 13597–13607. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.W.; Cui, H.J.; Liu, M.D.; Grage, S.L.; Hoffmann, M.; Sedghamiz, E.; Wenzel, W.; Levkin, P.A. Tough, Transparent, 3D-Printable, and Self-Healing Poly(ethylene glycol)-Gel (PEGgel). Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2107791. [Google Scholar]
- Stephan, A.M.; Nahm, K.S. Review on composite polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Polymer 2006, 47, 5952–5964. [Google Scholar]
- Manthiram, A.; Yu, X.W.; Wang, S.F. Lithium battery chemistries enabled by solid-state electrolytes. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 16103. [Google Scholar]
- Mendes-Felipe, C.; Barbosa, J.C.; Gonçalves, R.; Miranda, D.; Costa, C.M.; Vilas-Vilela, J.L.; Lanceros-Mendez, S.J. Lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide blended in polyurethane acrylate photocurable solid polymer electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. Energy Chem. 2021, 62, 485–496. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, N.X.; Wang, W.; Chen, Z.X.; Heng, Y.; Yuan, Z.D.; Xu, R.J.; Lei, C.H.J. Electrochemically stable poly (vinylidene fluoride)-polyurethane polymer gel electrolytes with polar β-phase in lithium batteries. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 907, 116026. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, M.; Yan, B.Y.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, L.Q.; Nishi, T.; Ning, N.Y.J. Largely improved actuation strain at low electric field of dielectric elastomer by combining disrupting hydrogen bonds with ionic conductivity. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 8388–8397. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuo, Y.Z.; Xia, Z.J.; Qi, Y.; Sumigawa, T.; Wu, J.Y.; Sesták, P.; Lu, Y.A.; Håkonsen, V.; Li, T.; Wang, F.; et al. Simultaneously Toughening and Stiffening Elastomers with Octuple Hydrogen Bonding. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2008523. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Gao, Y.Y.; Shi, L.; Yu, W.; Sun, Z.J.; Zhou, Y.F.; Liu, S.; Mao, H.; Zhang, D.Y.; Lu, T.Q.; et al. Phase-locked constructing dynamic supramolecular ionic conductive elastomers with superior toughness, autonomous self-healing and recyclability. Nat.Commun. 2022, 13, 4868. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xiang, H.; Li, X.X.; Wu, B.H.; Sun, S.T.; Wu, P.Y. Highly Damping and Self-Healable Ionic Elastomer from Dynamic Phase Separation of Sticky Fluorinated Polymers. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2209581. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, P.R.; Wang, Y.F.; Wan, K.N.; Zhang, C.; Liu, T.X. A Waterproof Ion-Conducting Fluorinated Elastomer with 6000% Stretchability, Superior Ionic Conductivity, and Harsh Environment Tolerance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2112293. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Morrissey, T.G.; Acome, E.; Allec, S.I.; Wong, B.M.; Keplinger, C.; Wang, C. A Transparent, Self-Healing, Highly Stretchable Ionic Conductor. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1605099. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, R.; Yuan, C. Modelling constrained recovery of UV-curable shape memory polymer toward 4D printing. Chem. Bio Eng. 2024, 1, 715–724. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Dong, P.; Yuan, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y. Manganese-based oxide cathode materials for aqueous zinc-ion batteries: Materials, mechanism, challenges, and strategies. Chem. Bio Eng. 2024, 1, 113–132. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.L.; Wang, X.; Feng, S.Y.; Li, L. Dynamic Boronic Ester Cross-Linked Polymers with Tunable Properties via Side-Group Engineering. Polymers 2024, 16, 3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Liu, Z.Y.; Lu, X.Q.; Zhang, S.T.; Tang, C.L.; Cheng, Y.F.; Zhang, H.; Liu, G.L.; Sui, C.; Ding, C.B.; et al. 3D printed multi-coupled bioinspired skin-electronic interfaces with enhanced adhesion for monitoring and treatment. Acta Biomater. 2024, 187, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, D.B.; Olson, K.R.; Karny, A.; Mecham, S.J.; DeSimone, J.M.; Balsara, N.P.J. Effect of Anion Size on Conductivity and Transference Number of Perfluoroether Electrolytes with Lithium Salts. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, A3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wu, N.Q. Ionic conductivity and ion transport mechanisms of solid-state lithium-ion battery electrolytes: A review. Energy Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1643–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Gu, K.; Yao, J.; Shao, Z.; Chen, X. Boronic ester-based self-healing hydrogels formed by using intermolecular BN coordination. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 29008–29020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Li, S.; Xu, M.; Yang, X.; Li, T.; Song, H.S. Stretchable and recyclable gelatin Ionogel based ionic skin with extensive temperature tolerant, self-healing, UV-shielding, and sensing capabilities. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 244, 125417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Zhang, R.; Han, L.; Zhao, C.; Yan, X.; Dai, M. An antifatigue and self-healable ionic polyurethane/ionic liquid composite as the channel layer for a low energy cost synaptic transistor. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 174, 111292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Liu, Q.; Qi, X.; Zhang, N.; Huang, T.; Yang, J.; Wang, Y. Silicon-based dielectric elastomer with amino-complexed hybrids towards high actuation performance. Nano Mater. Sci. 2024, 6, 576–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braganza, C.O.; Philamore, H.; Conn, A.T. Sustainable Fabrication of Biodegradable Soft Robotic Actuators. In Proceedings of the 8th IEEE RAS International Conference on Soft Robotics, Lausanne, Switzerland, 23–26 April 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, M.; Jose, S.J. Electrospun membrane of PVA and functionalized agarose with polymeric ionic liquid and conductive carbon for efficient dye sensitized solar cell. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2022, 425, 113666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.; Das, E.; Bhargava, A.; Deshmukh, S.; Modi, A.; Srivastava, R. Ionogels for flexible conductive substrates and their application in biosensing. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 254, 127736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Hori, S.; Saito, T.; Suzuki, K.; Hirayama, M.; Mitsui, A.; Yonemura, M.; Iba, H.; Kanno, R. High-power all-solid-state batteries using sulfide superionic conductors. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Han, Y.; Tan, Y. Boronic ester-based self-healing hydrogels formed by using intermolecular BN coordination. Polymer 2020, 202, 122624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inverardi, N.; Toselli, M.; Scalet, G.; Messori, M.; Auricchio, F.; Pandini, S. Stress-free two-way shape memory effect of poly (ethylene glycol)/poly (ε-caprolactone) semicrystalline networks. Macromolecules 2022, 55, 8533–8547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golitsyn, Y.; Pulst, M.; Samiullah, M.H.; Busse, K.; Kressler, J.; Reichert, D. Crystallization in PEG networks: The importance of network topology and chain tilt in crystals. Polymer 2019, 165, 72–82. [Google Scholar]
- Webber, M.J.; Tibbitt, M.W. Dynamic and reconfigurable materials from reversible network interactions. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 541–556. [Google Scholar]
- Denissen, W.; Winne, J.M.; Du Prez, F.E. Vitrimers: Permanent organic networks with glass-like fluidity. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 30–38. [Google Scholar]
- Si, M.J.; Jian, X.F.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, J.H.; Jian, W.; Lin, J.; Luo, Y.F.; Hu, J.Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, D.; et al. A Highly Damping, Crack-Insensitive and Self-Healable Binder for Lithium-Sulfur Battery by Tailoring the Viscoelastic Behavior. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 14, 2303991. [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura, S.; Tsuji, Y.; Yoshizawa, K. Role of Hydrogen-Bonding and OH-π Interactions in the Adhesion of Epoxy Resin on Hydrophilic Surfaces. Acs Omega 2020, 5, 26211–26219. [Google Scholar]
- Abe, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Tanaka, K. Effect of interfacial local conformation of polymer chains on adhesion strength. Polym. Chem. 2024, 15, 4425–4432. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, X.C.; Pei, K.; Peng, B.Y.; Zhang, Z.C.; Wang, Z.R.; Wang, X.Y.; Chan, P.K.L. A Low-Operating-Power and Flexible Active-Matrix Organic-Transistor Temperature-Sensor Array. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4832–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tordi, P.; Tamayo, A.; Jeong, Y.; Bonini, M.; Samorì, P. Multiresponsive Ionic Conductive Alginate/Gelatin Organohydrogels with Tunable Functions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2410663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.W.; Bai, H.Y.; Zhu, H.Y.; Zhang, S.W.; Wang, W.; Dong, W.F. Anti-freezing, tough, and stretchable ionic conductive hydrogel with multi-crosslinked double-network for a flexible strain sensor. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 148192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.W.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.F.; Gao, G.R.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, R.; Xu, T.; Yin, J.B.; Fu, J. Flexible and wearable strain sensors based on tough and self-adhesive ion conducting hydrogels. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, T.D.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, Q.S.; Wang, H.X.; Duan, X.R.; Yan, J.; Xia, Z.P.; Wang, R.; Shou, W.; Li, X.P.; et al. Ultra-stretchable and anti-freezing ionic conductive hydrogels as high performance strain sensors and flexible triboelectric nanogenerator in extreme environments. Nano Energy 2024, 126, 149633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.J.; Zhang, J.C.; Ji, Y.; Cao, J.W.; Xu, S.; Luo, P.; Liu, J.P.; Ma, L.A.; Gao, G.L.; Wu, Y.D.; et al. Self-healing polyurethane elastomers with dynamic crosslinked networks for complex structure 3D printing. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 507, 160193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.Q.; Xu, Q.M.; Guo, J.N.; Qin, J.; Mao, H.L.; Wang, B.; Yan, F. Structure–Antibacterial Activity Relationships of Imidazolium-Type Ionic Liquid Monomers, Poly(ionic liquids) and Poly(ionic liquid) Membranes: Effect of Alkyl Chain Length and Cations. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 12684–12692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).