Five-Cavity Resonance Inspired, rGO Nano-Sheet Reinforced, Multi-Site Voice Synergetic Detection Hydrogel Sensors with Diverse Self-Adhesion and Robust Wireless Transmissibility
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
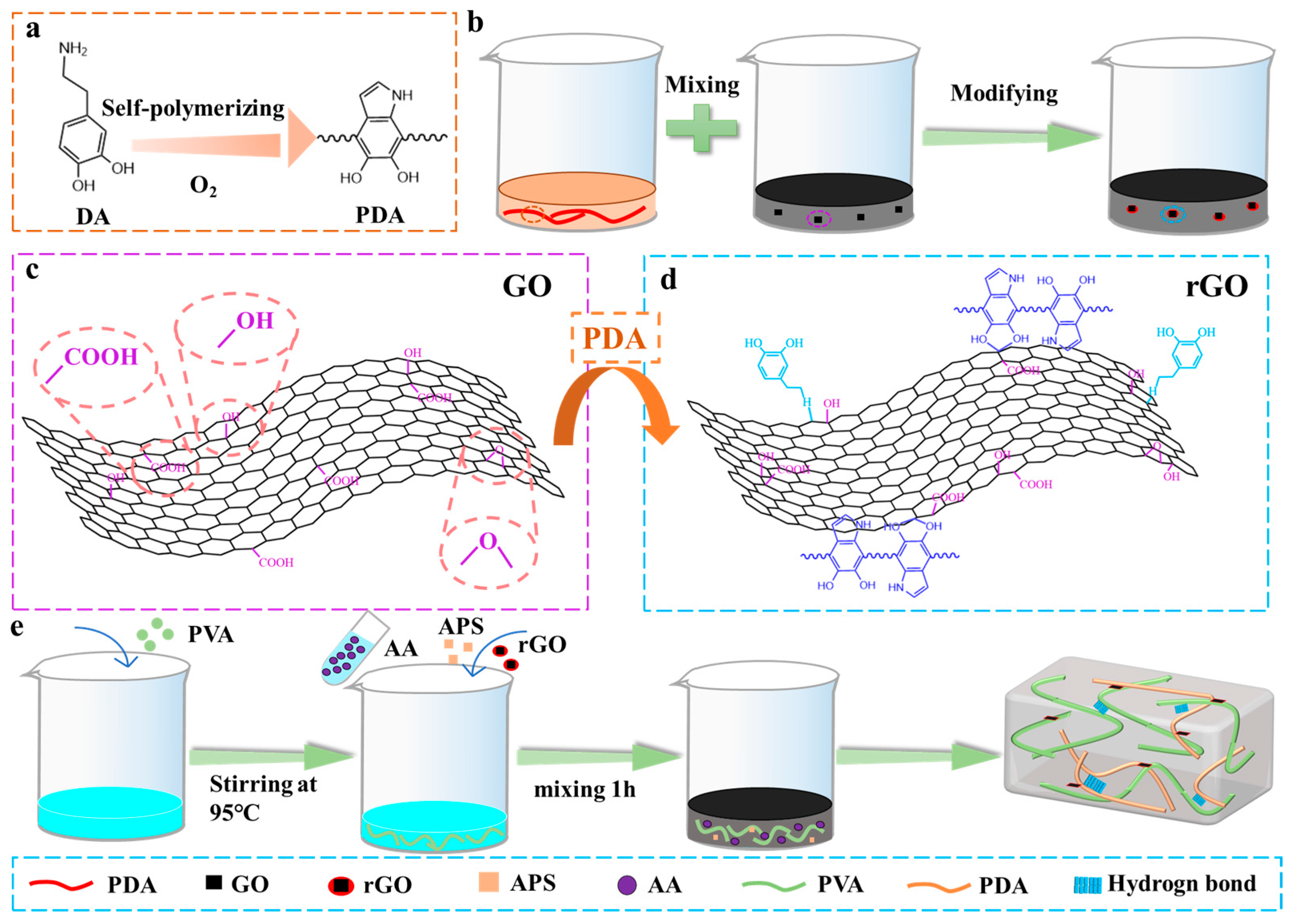
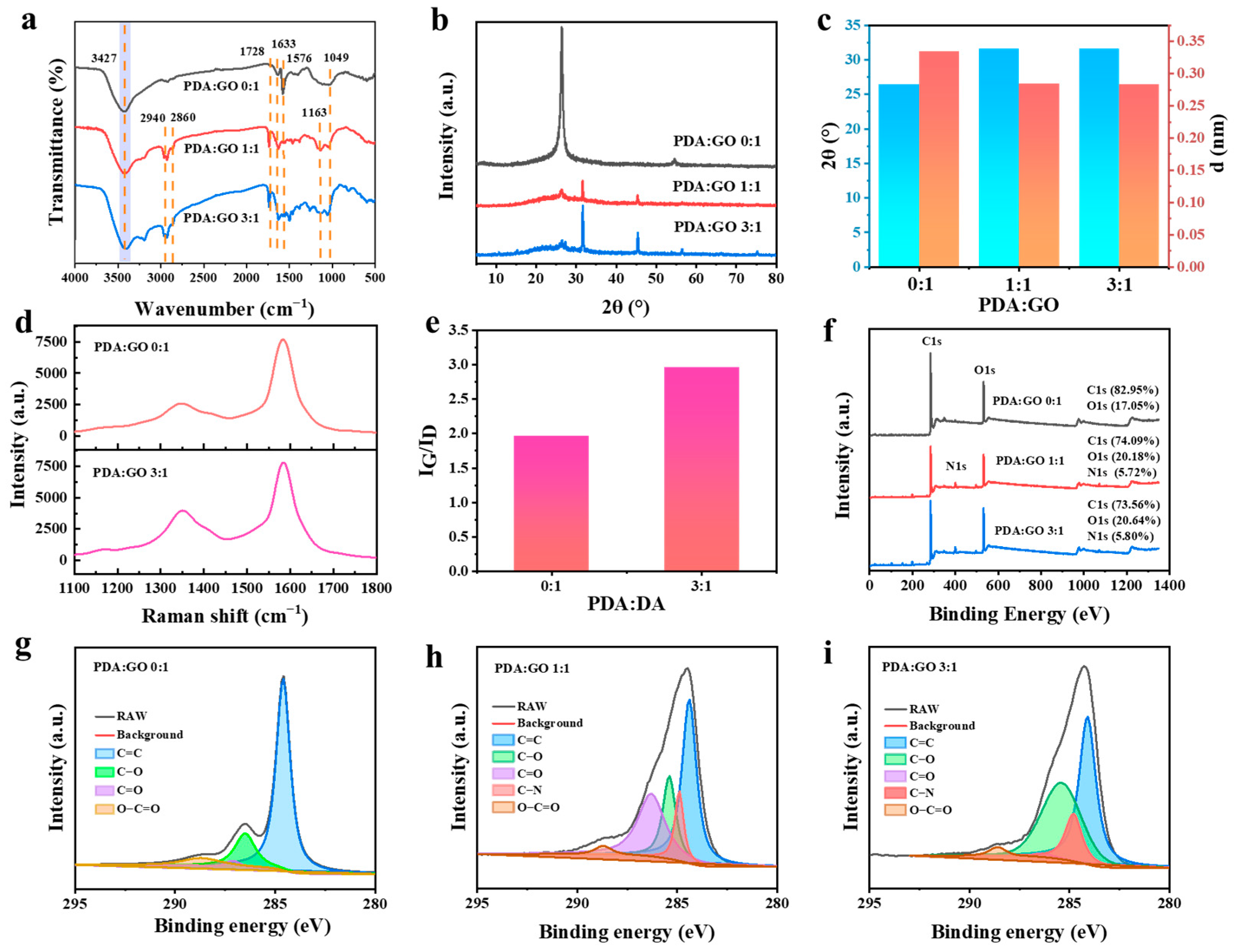
2.1. Preparation and Characteristic of rGO@PVA-PAA
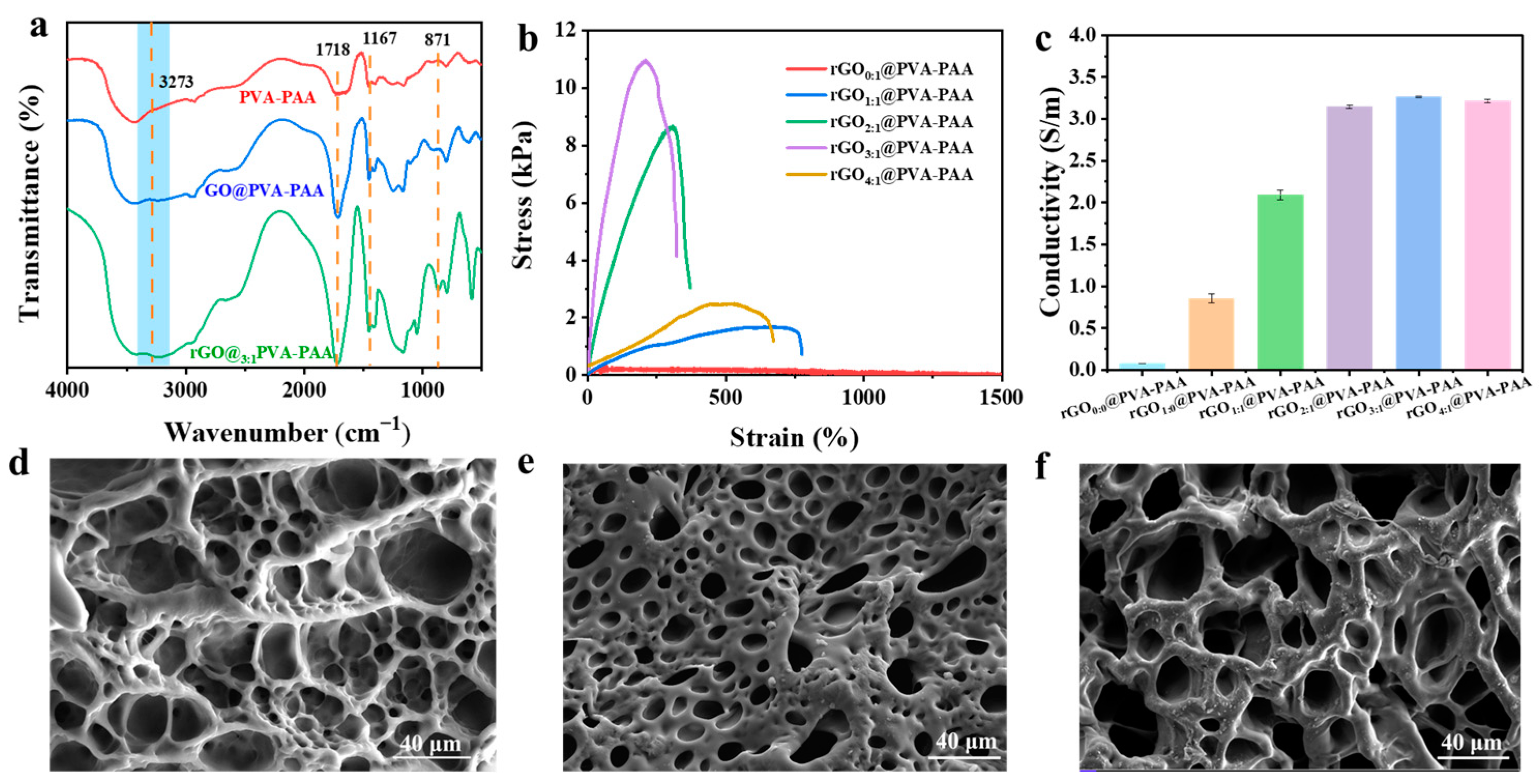
2.2. Characteristic of rGO@PVA-PAA Composite Hydrogels
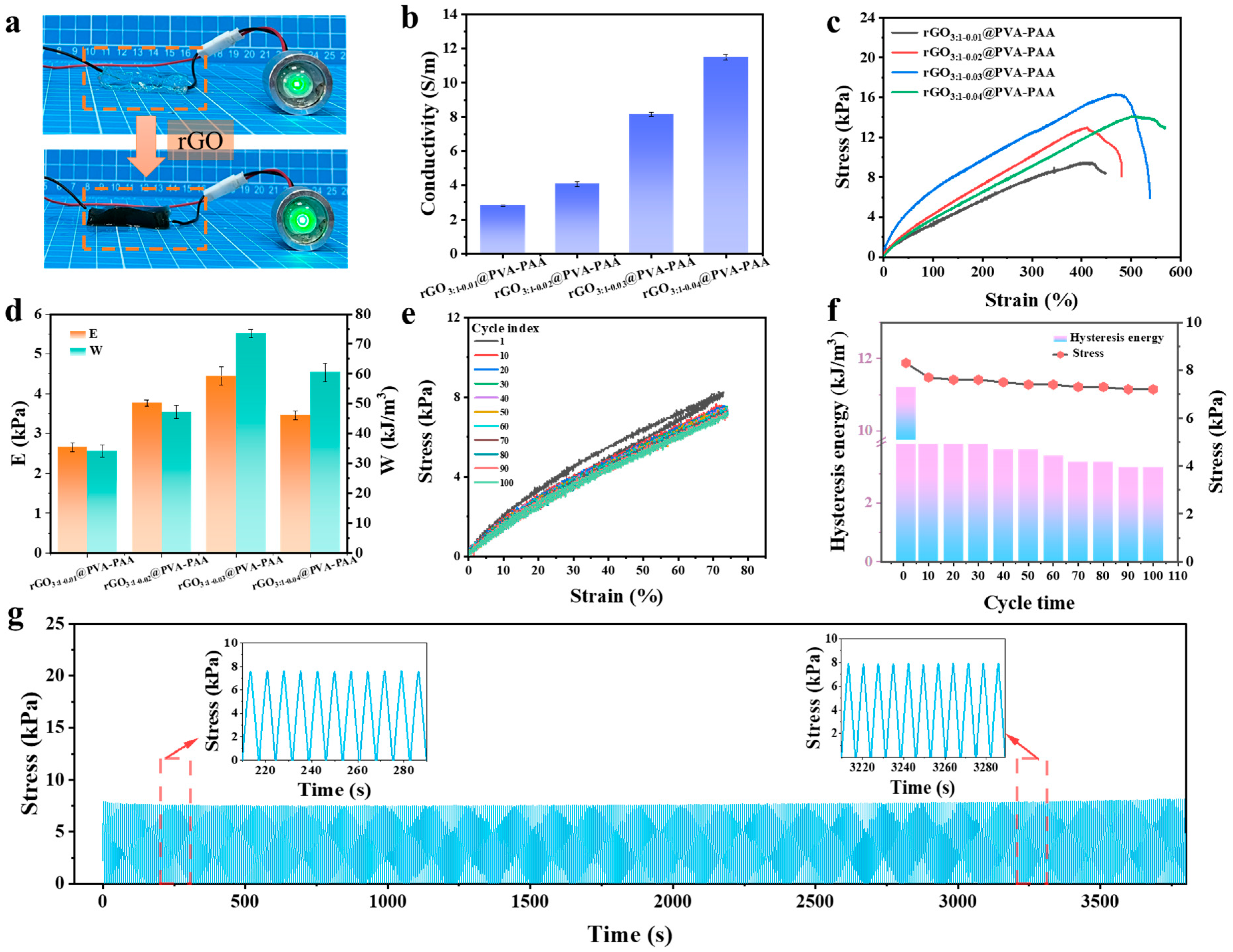
2.3. Mechanical Properties and Conductivity of rGO@PVA-PAA Hydrogels
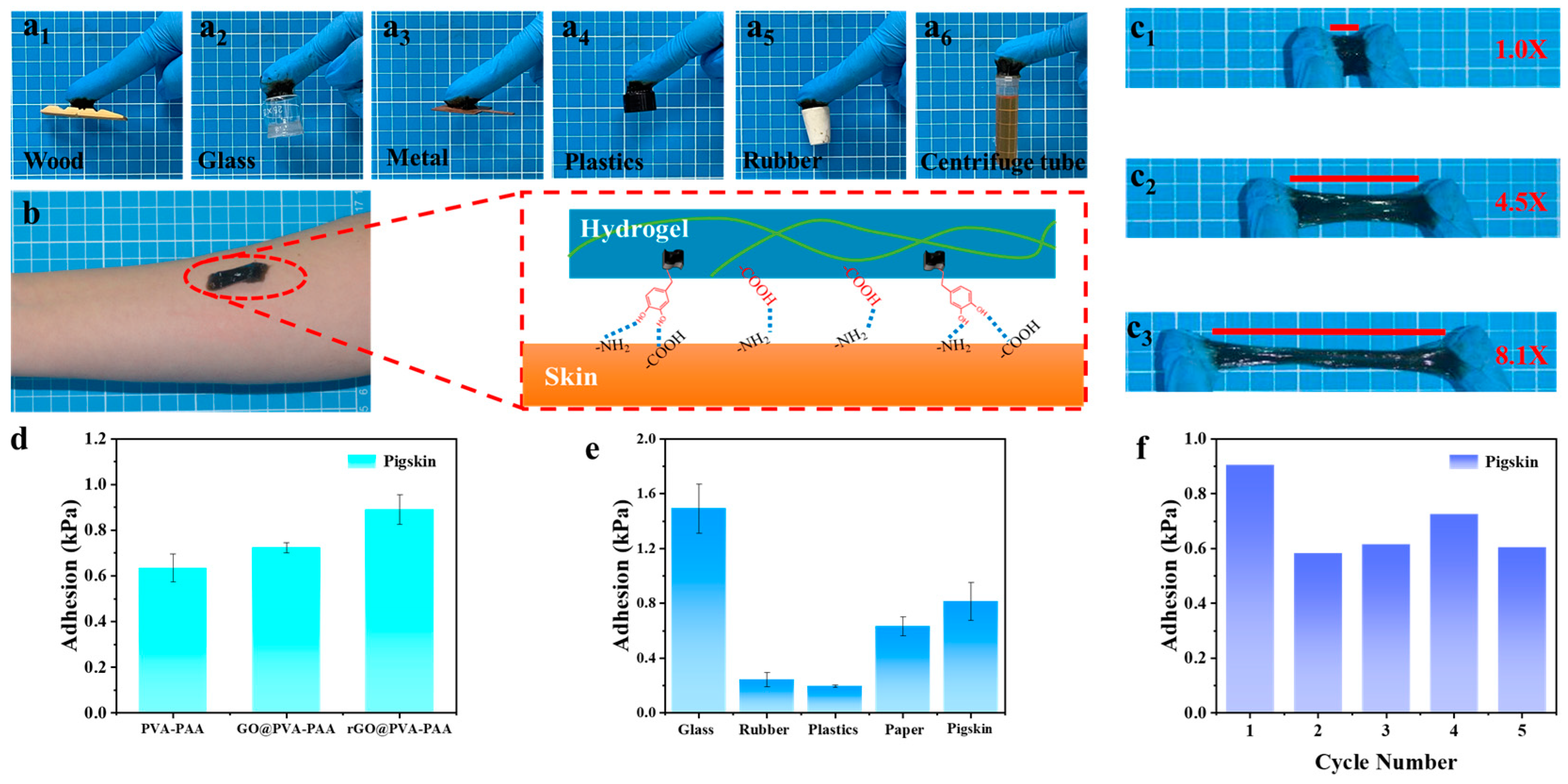
2.4. Adhesion Property of rGO3:1-0.03@PVA-PAA Hydrogel
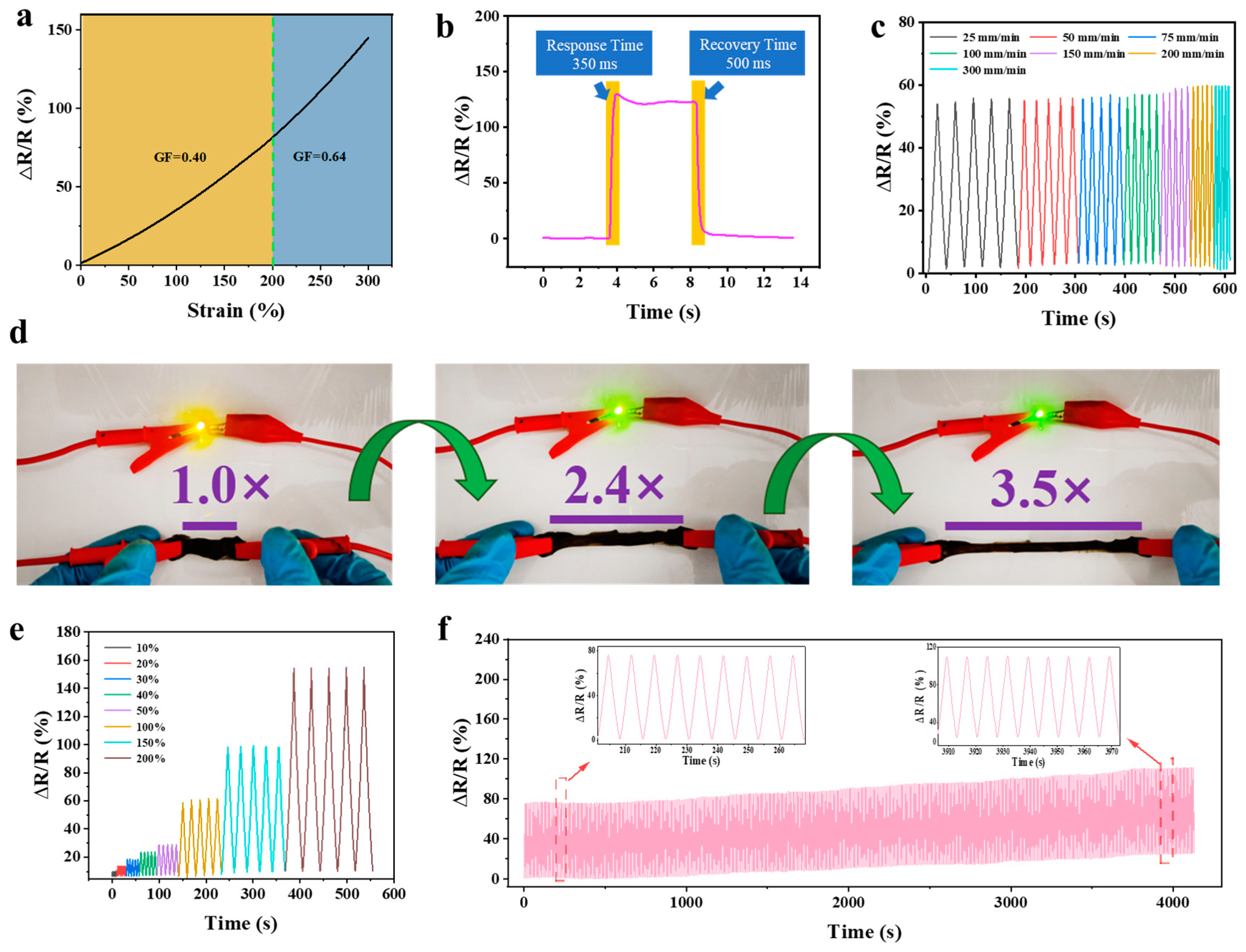
2.5. Sensing Performance of rGO3:1-0.03@PVA-PAA Hydrogel
2.6. rGO3:3-0.03@PVA-PAA Hydrogel Based Sensor
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of rGO@PVA-PAA Composite Hydrogel
4.3. Characterization
4.4. Mechanical Property
4.5. Conductivity Measurement
4.6. Adhesion Property
4.7. Fabrication of the Flexible Strain Sensor
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AA | Acrylic acid |
| APS | Ammonium persulfate |
| DA | Dopamine hydrochloride |
| EDS | Energy-dispersive spectrometer |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared spectrometer |
| GO | Graphene oxide |
| HCI | Hydrochloric acid |
| PVA | Polyvinyl alcohol |
| PDA | Polydopamine |
| PAA | Polyacrylic acid |
| rGO | Reduced graphene oxide |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscope |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| XPS | X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy |
References
- Zhang, M.; Yan, W.; Ma, W.; Deng, Y.; Song, W. Self-powered hybrid motion and health sensing system based on triboelectric nanogenerators. Small 2024, 20, 2402452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, R.; Tarique, M.; Abdel-Raheem, E. A survey on signal processing based pathological voice detection techniques. IEEE Access 2022, 8, 66749–66776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillivan-Murphy, P.; Miller, N.; Carding, P. Voice tremor in parkinson’s disease: An acoustic study. J. Voice 2019, 33, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqudaihi, K.S.; Aslam, N.; Khan, I.U.; Almuhaideb, A.M.; Alsunaidi, S.J.; Ibrahim, N.M.A.R.; Alshahrani, F.A.; Alharthi, H.M.; Alghamdi, W.M.; Alshahrani, M.S. Cough sound detection and diagnosis using artificial intelligence techniques: Challenges and opportunities. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 102327–102344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Dai, G.; Li, J.; Zhu, X.; Huang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Tan, M.; Wang, L.; Fang, P.; et al. An interpretable model based on graph learning for diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease with voice-related EEG. npj Digit. Med. 2024, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Jain, S.; Miranda, R.; Patil, S.; Pandya, S.; Kotecha, K. Deep learning based respiratory sound analysis for detection of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horáček, J.; Radolf, V.; Laukkanen, A.M. Low frequency mechanical resonance of the vocal tract in vocal exercises that apply tubes. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 37, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaide, J.; Lukacova, K.; Orije, J.; Keliris, G.A.; Verhoye, M.; Van der Linden, A. In vivo assessment of the neural substrate linked with vocal imitation accuracy. eLife 2020, 9, e49941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhatre, N.; Montealegre-Z, F.; Balakrishnan, R.; Robert, D. Changing resonator geometry to boost sound power decouples size and song frequency in a small insect. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, e1444–e1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivas, A.; Deshpande, S.; Gidaye, G.; Nirmal, J.; Ezzine, K.; Frikha, M.; Desai, K.; Shinde, S.; Oza, A.D.; Burduhos-Nergis, D.D.; et al. Employing energy and statistical features for automatic diagnosis of voice disorders. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, D.; Sun, X.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Song, Y.; Jiang, F. An environmentally tolerant, highly stable, cellulose nanofiber-reinforced, conductive hydrogel multifunctional sensor. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 284, 119199. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, S.; Chhetry, A.; Kim, D.; Yoon, H.; Park, J.Y. Hysteresis-free double-network hydrogel-based strain sensor for wearable smart bioelectronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 31363–31372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Wang, L.; Jiang, X.; Bai, L.; Wang, W.; Chen, H.; Yang, L.; Yang, H.; Wei, D. Self-healing, sensitive and antifreezing biomass nanocomposite hydrogels based on hydroxypropyl guar gum and application in flexible sensors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 1569–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, E.; Wallmersperger, T.; Gwosch, T.; Menning, J.D.M.; Peters, J.; Breimann, R.; Kraus, B.; Welzbacher, P.; Küchenhof, J.; Krause, D.; et al. A Review on sensor-integrating machine elements. Adv. Sens. Res. 2024, 3, 2300113. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, Z.; Cheng, N.; Zhang, L.; Liu, L.; Zhao, J.; Yu, H. Wearable strain sensor based on highly conductive carbon nanotube/polyurethane composite fibers. Nanotechnology 2020, 31, 205701. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; He, Q.; Cai, J.; Shen, D.; Hu, X.; Zhang, D. Flexible strain sensor with tunable sensitivity via microscale electrical breakdown in graphene/polyimide thin films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 58317–58325. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Luo, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Q.M. Carbon based polyimide nanocomposites thin film strain sensors fabricated by ink-jet printing method. Sens. Actuators A 2019, 300, 111664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, R.; Xu, J.; Duan, L.; Gao, G. Chitosan-driven skin-attachable hydrogel sensors toward human motion and physiological signal monitoring. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 268, 118240. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, B.; Wu, S.; Wang, R.; Yan, Y.; Cardenas, A.; Wu, D.; Alsaid, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhu, X.; He, X. Hydrogel ionotronics with ultra-low impedance and high signal fidelity across broad frequency and temperature ranges. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2109506. [Google Scholar]
- Das, P.; Ganguly, S.; Marvi, P.K.; Sherazee, M.; Tang, X.; Srinivasan, S.; Rajabzadeh, A.R. Carbon dots infused 3D printed cephalopod mimeticbactericidal and antioxidant hydrogel for uniaxial mechano-fluorescent tactile sensor. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2409819. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, X.; Qing, Y.; Lou, Y.; Gao, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Qin, Y.; Sun, J. Degradable, recyclable, water-resistant, and eco-friendly poly(vinyl alcohol)-based supramolecular plastics. ACS Mater. Lett. 2022, 4, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, Y.; Zang, X.; Yang, Y.; Gong, Z.; Li, H.; Chen, J.; Wu, C.; Huang, J.; Lai, Y. Environmental stability stretchable organic hydrogel humidity sensor for respiratory monitoring with ultrahigh sensitivity. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2402853. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Luo, H.; Ou, J.; Zheng, J.; Huang, C.; Liu, F.; Ou, S. Preparation of a chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol-based dual-network hydrogel for use as a potential wound-healing material for the sustainable release of drugs. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 348, 122822. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guo, P.; Zhang, Z.; Qian, C.; Wang, R.; Cheng, L.; Tian, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhu, S.; Liu, A. Programming hydrogen bonds for reversible elastic-plastic phase transition in aconductive stretchable hydrogel actuator with rapid ultra-high-density energy conversion and multiple sensory properties. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, e2410324. [Google Scholar]
- Narita, T.; Hsieh, W.C.; Ku, Y.T.; Su, Y.C.; Inoguchi, H.; Takeno, H. Fracture behavior and biocompatibility of cellulose nanofiber-reinforced poly(vinyl alcohol) composite hydrogels cross-linked with borax. Biomacromolecules 2025, 26, 374–386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Yu, X. Ultra-stretchable, dhesive, conductive, and ntifreezing Mmultinetwork orateester-based hydrogel for wearable strain sensor and VOC absorption. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 5322–5332. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Zhou, G.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Fu, X.; Chi, J.; Chen, X.; Fang, H.; et al. Insight into photo-fenton catalytic degradation of tetracycline by environmental friendly nanocomposite 1T-2H hybrid phases MoS2/Fe3O4/g-C3N4. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 383, 135406. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Lu, X.; Wang, M.; Gan, D.; Deng, W.; Wang, K.; Fang, L.; Liu, K.; Chan, C.; Tang, Y.; et al. A mussel-inspired conductive, self-adhesive, and self-healable tough hydrogel as cell stimulators and implantable bioelectronics. Small 2017, 13, 1601916. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yao, Y.; Bao, X.; Hu, Q. Ultrastretchable, self-adhesive, strain-sensitive and self-healing GO@DA/Alginate/P(AAc-co-AAm) multifunctional hydrogels via mussel-inspired chemistry. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 254, 117316. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Khan, R.; Liu, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, T.; Zhang, R.; Li, H. A fast self-healing and conductive nanocomposite hydrogel as soft strain sensor. Colloids Surf. A 2019, 567, 139–149. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.P.; Qu, K.Y.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.Y.; Abodunrin, O.D.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, N.P. Electrical stimulation of neonatal rat cardiomyocytes using conductive polydopamine-reduced graphene oxide-hybrid hydrogels for constructing cardiac microtissues. Colloids Surf. B 2021, 205, 111844. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Z.; Yang, L.; Shi, S.; Wang, T.; Duan, G.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. Flexible polydopamine bioelectronics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2103391. [Google Scholar]
- Cozens, E.J.; Roohpour, N.; Gautrot, J.E. Comparative adhesion of chemically and physically crosslinked poly(acrylic acid)-based hydrogels to soft tissues. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 146, 110250. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Ma, Q.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, H. Polydopamine reduced graphene oxide/chitosan-based hydrogel for the therapy of diabetic wound. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 39, 109319. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhouzaam, A.; Qiblawey, H. Novel polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes incorporating polydopamine functionalized graphene oxide with enhanced flux and fouling resistance. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 620, 118900. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Ren, P.; Yang, F.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, J. Biomimetic epidermal sensors assembled from polydopamine-modified reduced graphene oxide/polyvinyl alcohol hydrogels for the real-time monitoring of human motions. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 10549–10558. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meng, F.; Wang, W.; Zeng, Y.; Gao, Z.; Li, J.; Jia, H.; Ji, Q. An attachable, self-healing and durable TiO2/rGO/PVA photocatalytic hydrogel band for dye degradation. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 15946–15954. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; An, X.; An, W.; Hu, J.; Wu, P.; Cui, W. Efficient adsorption of anionic and cationic dyes by PVA/PAA/GO composite hydrogel with three-dimensional porous double network structure. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 313, 128716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Hu, Y.; Tang, P.; Wang, H.; Bin, Y. High stretchable, pH-sensitive and self-adhesive rGO/CMCNa/PAA composite conductive hydrogel with good strain-sensing performance. Compos. Commun. 2021, 24, 100669. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, X.; Mu, X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y.; Gao, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, C.; et al. Reduced graphene oxide reinforced PDA-Gly-PVA composite hydrogel as strain sensors for monitoring human motion. Soft Sci. 2023, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Lin, Y.; Qiao, C.; Wang, L.; Cai, C.; He, H.; Tian, X. Construction of the Au nanoparticle/graphene xide/Au Nnanotube (AuNP/GO/AuNT) andwich membrane for urface-enhanced raman scattering sensing. Langmuir 2024, 40, 6806–6815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Fang, S.; Chang, G.; Han, H.; Teng, H.; Wei, Z. Megawatt peak power, octave-spanning Ti:sapphire oscillators. Appl. Phys. Express 2019, 12, 102009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, S.; Li, K.; Cui, M.; Wu, Y.; Ren, S. Static and dynamic mechanical properties of polyurea nanocomposites reinforced by polydopamine functionalized graphene oxide. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 29, 2889–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shang, T.; Yang, W.; Yang, H.; Lin, S.; Jia, X.; Cai, Q.; Yang, X. Effectively exerting the reinforcement of dopamine educed raphene oxide on epoxy-based composites via strengthened interfacial bonding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 13037–13050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z. Mussel-inspired hydrogels: From design principles to promising applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 3605–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Pei, M.; Du, J.; Yang, R.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, D.; Qin, S. A tough, anticorrosive hydrogel consisting of bio-friendly resources for conductive and electromagnetic shielding materials. New J. Chem. 2023, 47, 13721–13728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Pei, M.; Zhan, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, D.; Qin, S. Mechanical, robust and conductive eco-friendly self-assembling hydrogel: A novel material for electromagnetic shielding. New J. Chem. 2023, 47, 21475–21484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, B.; Jiang, Q.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Xiong, X. Flexible and wearable sensor based on graphene nanocomposite hydrogels. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 075027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Chen, S.; Ding, X.; Wang, M.; Yu, F.; Yuan, M.; Lu, C.; Yang, H. Application of polydopamine and graphene oxide combination in poly (N-isopropylacrylamide)/poly (acrylamide-co-acrylic acid) bilayer hydrogels. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2025, 303, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Li, S.; Xie, H.; Wu, Y.; Zou, X.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J. Construction of polydopamine reduced graphene oxide/sodium carboxymethyl cellulose/polyacrylamide double network conductive hydrogel with high stretchable, pH-sensitive and strain-sensing properties. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 642, 128428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Mi, H.-Y.; Peng, X.-F.; Turng, L.-S. Biocompatible, self-healing, highly stretchable polyacrylic acid/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite hydrogel sensors via mussel-inspired chemistry. Carbon 2018, 136, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Maktedar, S.S. Structural, functional and mechanical performance of advanced Graphene-based composite hydrogels. Results Chem. 2023, 6, 101029. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Z.; Li, H.; Mi, H.Y.; Feng, P.Y.; Liu, Y.; Jing, X. Freezing-tolerant, widely detectable and ultra-sensitive composite organohydrogel for multiple sensing applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2021, 9, 10127–10137. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, J.; Li, C.; Ji, X.; Tao, Y.; Lu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Du, J.; Wang, H. Highly tough and conductive hydrogel based on defect-patched reduction graphene oxide for high-performance self-powered flexible sensing micro-system. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 466, 143358. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, J.; Fei, Y.; Lu, L. An all-natural strategy for versatile interpenetrating network hydrogels with self-healing, super-adhesion and high sensitivity. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 129736. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, R.; Xu, X.; Hu, L. Highly Strong, Stretchable, and Conductive Reduced Graphene Oxide Composite Hydrogel-Based Sensors for Motoring Strain and Pressure. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 5155–5161. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.; Wang, Z.; Chen, S.; Shen, Y.; Yin, J.; Wang, R. Phytic Acid-Induced Gradient Hydrogels for Highly Sensitive and Broad Range Pressure Sensing. Adv. Mater. 2025, 37, 2417978. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Q.; Zhang, C.; Guo, T.; Tian, Y.; Song, W.; Lei, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, A.; Zhang, M.; Bai, S.; et al. Hydrogel nanoarchitectonics of a flexible and self-adhesive electrode for long-term wireless electroencephalogram recording and high-accuracy sustained attention evaluation. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2209606. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yang, D.; Wu, Z.; Gao, F.L.; Gao, X.Z.; Zhao, H.Y.; Li, X.; Yu, Z.Z. Self-adhesive, self-healing, biocompatible and conductive polyacrylamide nanocomposite hydrogels for reliable strain and pressure sensors. Nano Energy 2023, 109, 108324. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Pan, W.; Dong, Y.; Ding, J.; Xu, L. Stretchable, fast response and adhesive MXene-based hydrogels for wearable strain sensor. Compos. Commun. 2025, 53, 102245. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Y.; Liu, H.; He, R.; Luo, M.; Shu, M.; Xu, F. Environmentally compatible earable electronics based on ionically conductive rganohydrogels for health monitoring with thermal compatibility, nti-dehydration, and underwater adhesion. Small 2021, 17, e2101151. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Bai, H.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; Dong, W. Anti-freezing, tough, and stretchable ionic conductive hydrogel with multi-crosslinked double-network for a flexible strain sensor. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 148192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Shu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Ji, W.; Chen, J.; Wei, Y. Highly elastic, sensitive, tretchable, and skin-inspired conductive sodium alginate/polyacrylamide/gallium composite ydrogel with toughness as a flexible strain sensor. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 2603–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, B.; Wu, Y.; He, S.; Wang, C.; Yao, M.; Yu, Q.; Wu, X.; Yu, C.; Liu, M.; Liang, L.; et al. Anisotropic and super-strong conductive hydrogels enabled by mechanical stretching combined with the Hofmeister effect. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 8038–8047. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, B.; Wu, S.; Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Gong, L.; Tang, J.; Tang, L. Water and stress tension dual-response antifreeze conductive hydrogel with optically tunable behavior and sensing applications. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2024, 113, 696–707. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; He, M.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Bai, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, T.; Meng, L.; Meng, F.; Ma, Q.; et al. Tunicate cellulose nanocrystal reinforced conductive multi-responsive hydrogel with super flexible, fatigue resistant and self-healable capability for antibacterial flexible sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 495, 153567. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Chen, E.; Wu, Y.; Yang, H.; Huang, K.; Chang, G.; Pan, X.; Huang, K.; He, Z.; Lei, M. Silver nanosheets doped polyvinyl alcohol hydrogel piezoresistive bifunctional sensor with a wide range and high resolution for human motion detection. Adv. Compos. Hybrid. Mater. 2022, 5, 1196–1205. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Li, Q.; Zheng, S.; Liu, Z.; Li, W.; Yan, F. Low-hysteresis and high-toughness hydrogels regulated by porous cationic polymers: The effect of counteranions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2024, 63, e202316375. [Google Scholar]
- Ling, Q.; Liu, W.; Liu, J.; Zhao, L.; Ren, Z.; Gu, H. Highly sensitive and robust polysaccharide-based composite hydrogel sensor integrated with underwater repeatable self-adhesion and rapid self-Hhealing for human motion detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 24741–24754. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, B.; Miyata, H.; Wang, Y.; Nayeem, M.O.G.; Kim, J.J.; Lee, S.; Yokota, T.; Onodera, H.; et al. On-skin paintable biogel for long-term high-fidelity electroencephalogram recording. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabo1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Z.; Wang, X.E.; Zou, K.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, X.; Mu, E.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; et al. Visual-audio thermoelectric detectors for images and sound recognition. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2406110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Y.; Zhao, K.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Y.; Gu, X. Five-Cavity Resonance Inspired, rGO Nano-Sheet Reinforced, Multi-Site Voice Synergetic Detection Hydrogel Sensors with Diverse Self-Adhesion and Robust Wireless Transmissibility. Gels 2025, 11, 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040233
Wu Y, Zhao K, Wang J, Li C, Jiang X, Wang Y, Gu X. Five-Cavity Resonance Inspired, rGO Nano-Sheet Reinforced, Multi-Site Voice Synergetic Detection Hydrogel Sensors with Diverse Self-Adhesion and Robust Wireless Transmissibility. Gels. 2025; 11(4):233. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040233
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Yue, Kewei Zhao, Jingliu Wang, Chunhui Li, Xubao Jiang, Yudong Wang, and Xiangling Gu. 2025. "Five-Cavity Resonance Inspired, rGO Nano-Sheet Reinforced, Multi-Site Voice Synergetic Detection Hydrogel Sensors with Diverse Self-Adhesion and Robust Wireless Transmissibility" Gels 11, no. 4: 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040233
APA StyleWu, Y., Zhao, K., Wang, J., Li, C., Jiang, X., Wang, Y., & Gu, X. (2025). Five-Cavity Resonance Inspired, rGO Nano-Sheet Reinforced, Multi-Site Voice Synergetic Detection Hydrogel Sensors with Diverse Self-Adhesion and Robust Wireless Transmissibility. Gels, 11(4), 233. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11040233





