Protein–Protein Interactions and Structure of Heat-Set Gels Based on Pea Protein and Egg White Mixtures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Thermal Gelation and Viscoelastic Properties of PPI-EWP Gels
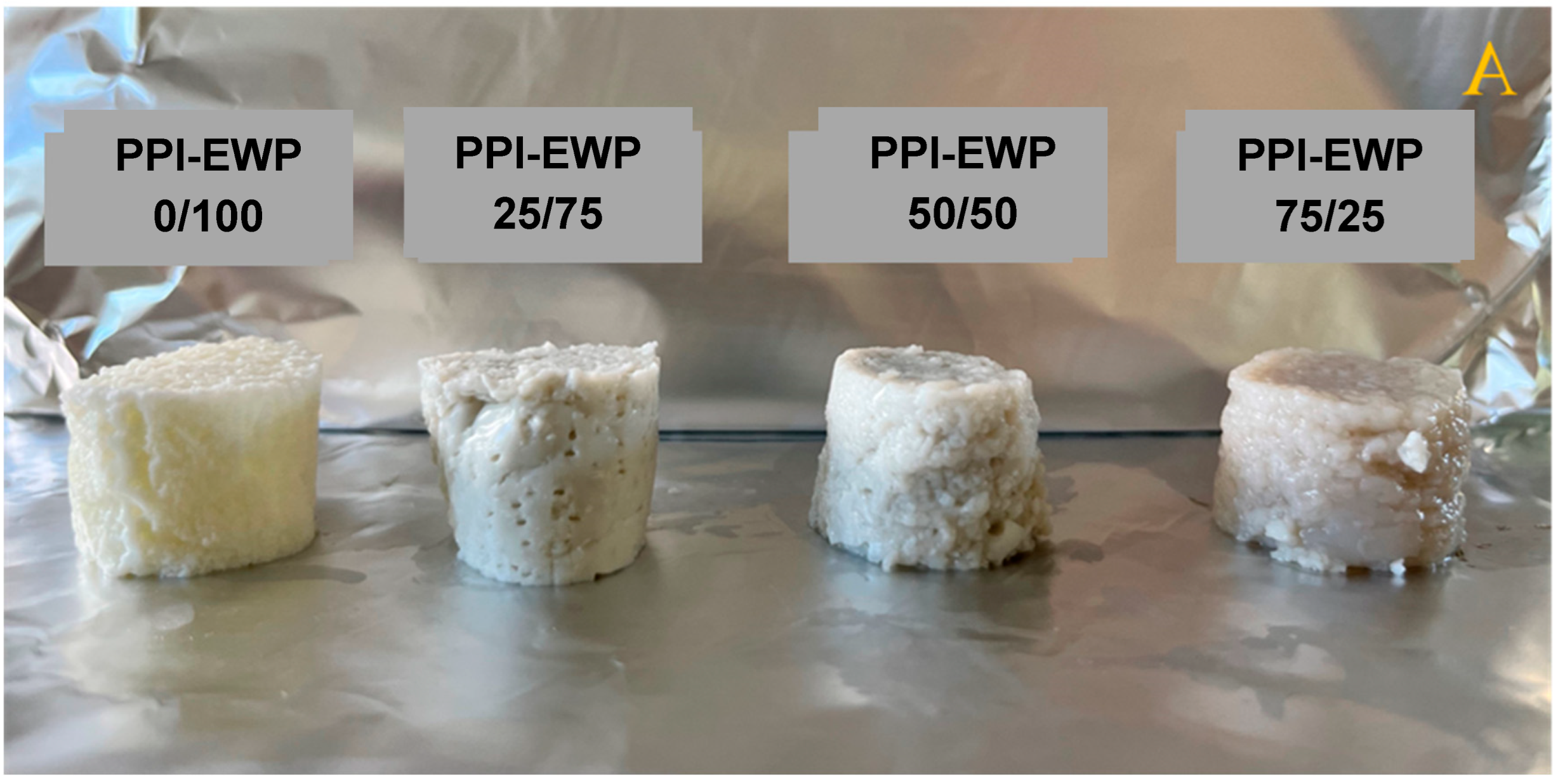
2.2. Macrostructure of PPI-EWP Gels
2.3. Microstructure of PPI-EWP Gels
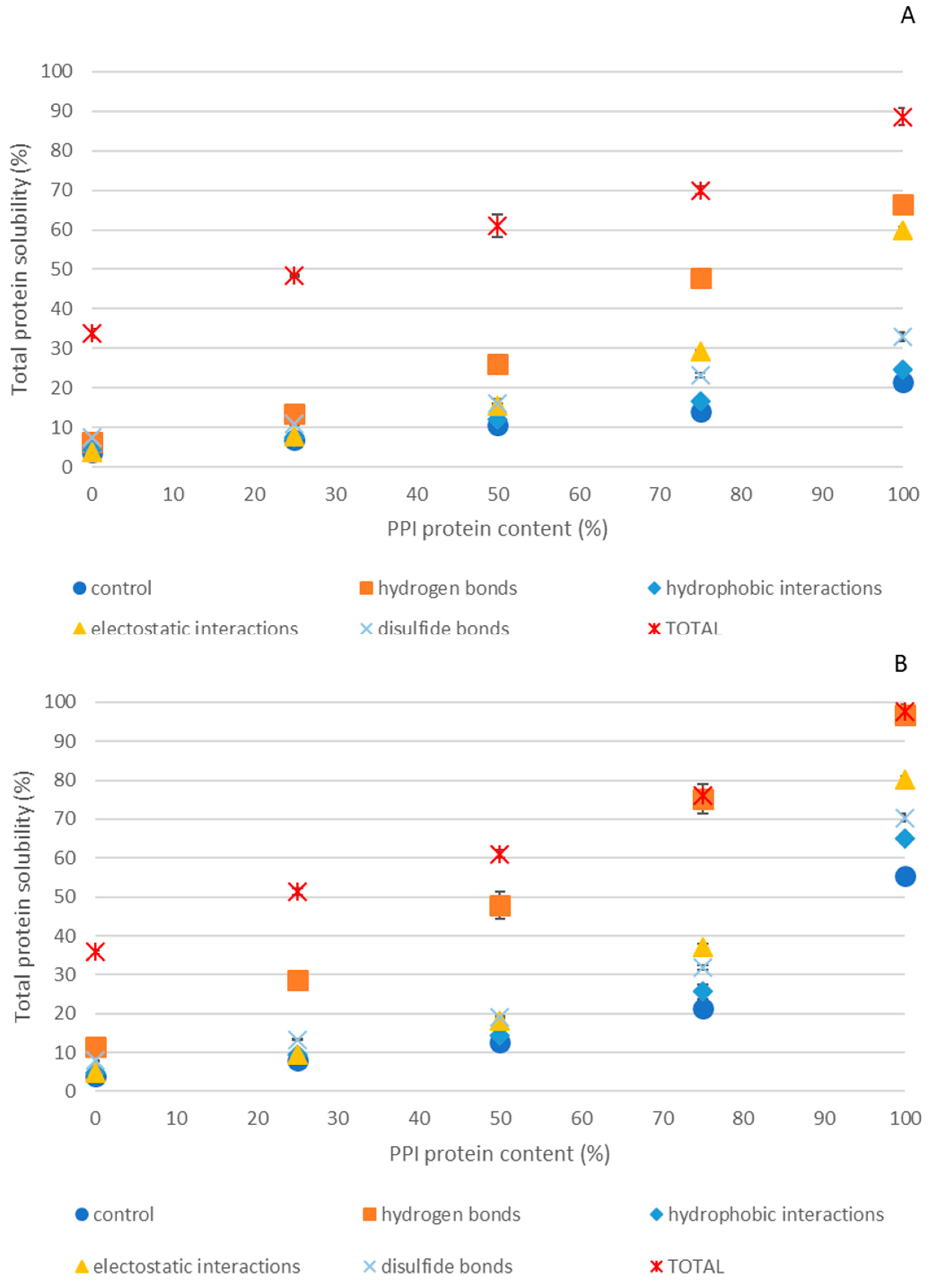
2.4. Intermolecular Interactions Involved in PPI-EWP Gels
2.4.1. Effect of Dissociating Agents on 100% PPI and 100% EWP Gels
2.4.2. Effect of Dissociating Agents on PPI-EWP Mixed Gels
3. Conclusions
- proposal of a mechanism for gelation of PPI-EWP mixtures
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Samples Preparation
4.2. Gel Preparation
4.3. Small-Strain Dynamic Rheology
4.4. Texture Profile Analysis
4.5. Confocal Microscopy (CLSM)
4.6. Gel Dissolution by Dissociating Agents
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). The State of Food Insecurity in the World 2013. The Multiple Dimensions of Food Security; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2013; Available online: http://www.fao.org/docrep/018/i3434e/i3434e.pdf (accessed on 16 October 2024).
- Chihi, M.L.; Sok, N.; Saurel, R. Acid gelation of mixed thermal aggregates of pea globulins and β-lactoglobulin. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 85, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCann, T.H.; Guyon, L.; Fischer, P.; Day, L. Rheological properties and microstructure of soy-whey protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2018, 82, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harfmann, B. The winning wheys of proteins. Beverage Ind. 2016, 107, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Su, Y.; Chang, C.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Gu, L. Preparation and characterization of hen egg proteins-soybean protein isolate composite gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 97, 105191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aluko, R.E.; Mofolasayo, O.A.; Watts, B.M. Emulsifying and foaming properties of commercial yellow pea (Pisum sativum L.) seed flours. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 9793–9800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havemeier, S.; Erickson, J.; Slavin, J. Dietary guidance for pulses: The challenge and opportunity to be part of both the vegetable and protein food groups. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2017, 1392, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.C.; Tavares, G.M. Mixing animal and plant proteins: Is this a way to improve protein techno-functionalities? Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 97, 105171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, T.G.; Zhang, Y. Recent progress in the utilization of pea protein as an emulsifier for food applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 86, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.X.; He, J.F.; Zhang, Y.C.; Bing, D.J. Composition, physicochemical properties of pea protein and its application in functional foods. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Dietary protein quality evaluation in human nutrition: Report of an FAO expert consultation. FAO Food Nutr. Paper 2013, 92, 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- Shand, P.J.; Ya, H.; Pietrasik, Z.; Wanasundara, P.K.J.P.D. Physicochemical and textural properties of heat-induced pea protein isolate gels. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.D.; Arntfield, S.D. Molecular forces involved in heat-induced pea protein gelation: Effects of various reagents on the rheological properties of salt-extracted pea protein gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2012, 28, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Kane, F.E.; Happe, R.P.; Vereijken, J.M.; Gruppen, H.; van Boekel, M.A. Characterization of pea vicilin. 1. Denoting convicilin as the α-subunit of the Pisum vicilin family. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3141–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Kane, F.E.; Happe, R.P.; Vereijken, J.M.; Gruppen, H.; van Boekel, M.A. Characterization of pea vicilin. 2. Consequences of compositional heterogeneity on heat-induced gelation behavior. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 3149–3154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Kane, F.E.; Vereijken, J.M.; Gruppen, H.; Van Boekel, M.A. Gelation behavior of protein isolates extracted from 5 cultivars of Pisum sativum L. J. Food Sci. 2005, 70, C132–C137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mession, J.L.; Chihi, M.L.; Sok, N.; Saurel, R. Effect of globular pea proteins fractionation on their heat-induced aggregation and acid cold-set gelation. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 46, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zamani, S.; Liang, L.; Chen, L. Extraction methods significantly impact pea protein composition, structure and gelling properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 117, 106678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Q.; Teng, C.; Xie, W.; Shi, Y.; Yang, Y. Combination effects of NaOH and NaCl on the rheology and gel characteristics of hen egg white proteins. Food Chem. 2018, 250, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mine, Y. Recent advances in the understanding of egg white protein functionality. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1995, 6, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, D.; Laca, A.; Estrada, L.N.; Paredes, B.; Rendueles, M.; Díaz, M. Egg yolk and egg yolk fractions as key ingredient for the development of a new type of gels. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2016, 3, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razi, S.M.; Bagheri, H.; Mohammadian, M.; Mirarab-Razi, V.; Rashidinejas, A. Gelation properties of egg white proteins: A review. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 40, 2751–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Dong, Y.; Niu, F.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Y. Study on the gel properties and secondary structure of soybean protein isolate/egg white composite gels. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 240, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavi, F.; Emam-Djomeh, Z.; Chen, L. Acid-induced gelation of thermal co-aggregates from egg white and hempseed protein: Impact of microbial transglutaminase on mechanical and microstructural properties of gels. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 107, 105960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyńska-Mleko, M.; Terpiłowski, K.; Pérez-Huertas, S.; Sapiga, V.; Polischuk, G.; Sołowiej, B.; Nastaj, M.; Wesołowska-Trojanowska, M.; Mleko, S. Co-Gelation of Pumpkin-Seed Protein with Egg-White Protein. Foods 2023, 12, 2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Xu, X.; Sheng, L. Effects of different plant proteins on the quality and characteristics of heat induced egg white protein gel under freezing conditions. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 146 Pt A, 109281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, J. Etude des Interactions et des Propriétés Physico-Chimiques de mélanges de Protéines de Pois et de Blanc d’œuf: De l’état Colloidal à l’état Gelifié. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Bourgogne Franche Comté, Dijon, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kuang, J.; Hamon, P.; Lechevalier, V.; Saurel, R. Thermal behavior of pea and egg white protein mixtures. Foods 2023, 12, 2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.H.; Ross-Murphy, S.B. Structural and mechanical properties of biopolymer gels. Adv. Poly. Sci. 1987, 83, 57–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, J.F. Weak and Strong Gels and the Emergence of the Amorphous Solid State. Gels 2018, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.Y.; Yiu, S.H.; Harwalkar, V.R. Rheological and structural properties of egg-white oat globulin co-gels. J. Food Sci. 1990, 1, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, A.; Takahashi, K.; Kuroda, N.; Froning, G.W. Heat-induced egg white gels as affected by pH. J. Food Sci. 1998, 63, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alleoni, A.C.C.; Antunes, A.J. Texture profile and expressible moisture in albumen gels of eggs coated with whey. Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 25, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somaratne, G.; Ye, A.; Nau, F.; Ferrua, M.J.; Dupont, D.; Singh, R.P.; Singh, J. Egg white gel structure determines biochemical digestion with consequences on softening and mechanical disintegration during in vitro gastric digestion. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Vu, G.; McClements, D.J. Formulation and characterization of plant-based egg white analogs using RuBisCO protein. Food Chem. 2022, 397, 133808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, X.; Guo, N.; Dai, H.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, G. Influence of different pH values on gels produced from tea polyphenols and low acyl gellan gum. Gels 2023, 9, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez-Lopez, J.; Martínez, A.; Fernandez-Gines, J.M.; Sayas-Barbera, E.; Sendra, E.; Perez-Alvares, J.A. Gelling and color properties of ostrich (Struthio camelus) egg white. J. Food Qual. 2006, 29, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyemb, K.; Guérin-Dubiard, C.; Pézennec, S.; Jardin, J.; Briard-Bion, V.; Cauty, C.; Nau, F. The structural properties of egg white gels impact the extent of in vitro protein digestion and the nature of peptides generated. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 54, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, A.H.; Kavanagh, G.M.; Ross-Murphy, S.B. Globular protein gelation—Theory and experiment. Food Hydrocoll. 2001, 15, 383–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somaratne, G.; Nau, F.; Ferrua, M.J.; Singh, J.; Ye, A.; Dupont, D.; Floury, J. Characterization of egg white gel microstructure and its relationship with pepsin diffusivity. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 98, 105258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Plancken, I.; Van Loey, A.; Hendrickx, M.E. Effect of heat-treatment on the physico-chemical properties of egg white proteins: A kinetic study. J. Food Eng. 2006, 75, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornet, R.; Veenemans, J.; Venema, P.; van der Goot, A.J.; Meinders, M.; Sagis, L.; van der Linden, E. Less is more: Limited fractionation yields stronger gels for pea proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 112, 106285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.V.; Cochereau, R.; Schmitt, C.; Chassenieux, C.; Nicolai, T. Heat-induced gelation of mixtures of micellar caseins and plant proteins in aqueous solution. Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roesch, R.R.; Corredig, M. Heat-induced soy–whey proteins interactions: Formation of soluble and insoluble protein complexes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 3476–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Mascaraque, L.G.; Pinho, S.C. Microstructural Analysis of Whey/Soy Protein Isolate Mixed Gels Using Confocal Raman Microscopy. Foods 2021, 10, 2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, J.; Hamon, P.; Rousseau, F.; Cases, E.; Bouhallab, S.; Saurel, R.; Lechevalier, V. Interactions Between Isolated Pea Globulins and Purified Egg White Proteins in Solution. Food Biophys. 2023, 18, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstoguzov, V.B. Some physico-chemical aspects of protein processing in foods. Multicomponent gels. Food Hydrocoll. 1995, 9, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstoguzov, V. Some thermodynamic considerations in food formulation. Food Hydrocoll. 2003, 17, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgeon, S.L.; Beaulieu, M.; Schmitt, C.; Sanchez, C. Protein–polysaccharide interactions: Phase-ordering kinetics, thermodynamic and structural aspects. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 8, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, V.I.; Grinberg, V.Y.; Tolstoguzov, V.B. Thermodynamic incompatibility of proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 1997, 11, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.I.; Chen, T.C. Functional and gel characteristics of liquid whole egg as affected by pH alteration. J. Food Eng. 2000, 45, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rüegg, U.T.; Rudinger, J. Cleavage of disulfide bonds in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1977, 47, 111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Léger, L.W.; Arntfield, S.D. Thermal gelation of the 12S canola globulin. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1993, 70, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanford, C. Protein denaturation. Adv. Prot. Chem. 1968, 23, 121e282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanford, C. Contribution of hydrophobic interactions to the stability of the globular conformation of proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1962, 84, 4240–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustunol, Z.; Xiong, Y.L.; Means, W.J.; Decker, E.A. Forces involved in mixed pork myofibrillar protein and calcium alginate gels. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1992, 40, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utsumi, S.; Kinsella, J.E. Forces involved in soy protein gelation: Effects of various reagents on the formation, hardness and solubility of heat-induced gels made from 7S, 11S and soy isolate. J. Food Sci. 1985, 50, 1278–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uruakpa, F.O.; Arntfield, S.D. Impact of urea on the microstructure of commercial canola protein–carrageenan network: A research note. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2006, 38, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozaki, Y.; Tanford, C. The solubility of amino acids and related compounds in aqueous urea solutions. J. Biol. Chem. 1963, 238, 4074–4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanger, C.; Müller, M.; Andlinger, D.; Kulozik, U. Influence of pH and ionic strength on the thermal gelation behavior of pea protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 123, 106903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, J.; Chang, C.; Gu, L.; Su, Y.; Yang, Y. Effects of NaOH/NaCl pickling on heat-induced gelation behavior of egg white. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, M.; Gu, L.; Chang, C.; Yang, Y. Molecular forces and gelling properties of heat-induced gel from egg white protein glycated with isomalto-oligosaccharide. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 99, 105356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Sheng, L. Impact of phosphates on heat-induced egg white gel properties: Texture, water state, micro-rheology and microstructure. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 110, 106200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourne, M.C. Texture Profile Analysis. Food Technol. 1978, 32, 62–66+72. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.; Hsieh, F.H. Protein–protein interactions during high-moisture extrusion for fibrous meat analogues and comparison of protein solubility methods using different solvent systems. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 2681–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhu, X.; Ilavsky, J.; Whitmer, T.; Hatzakis, E.; Jones, O.G.; Campanella, O.H. Polyphenols weaken pea protein gel by formation of large aggregates with diminished noncovalent interactions. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 1001–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
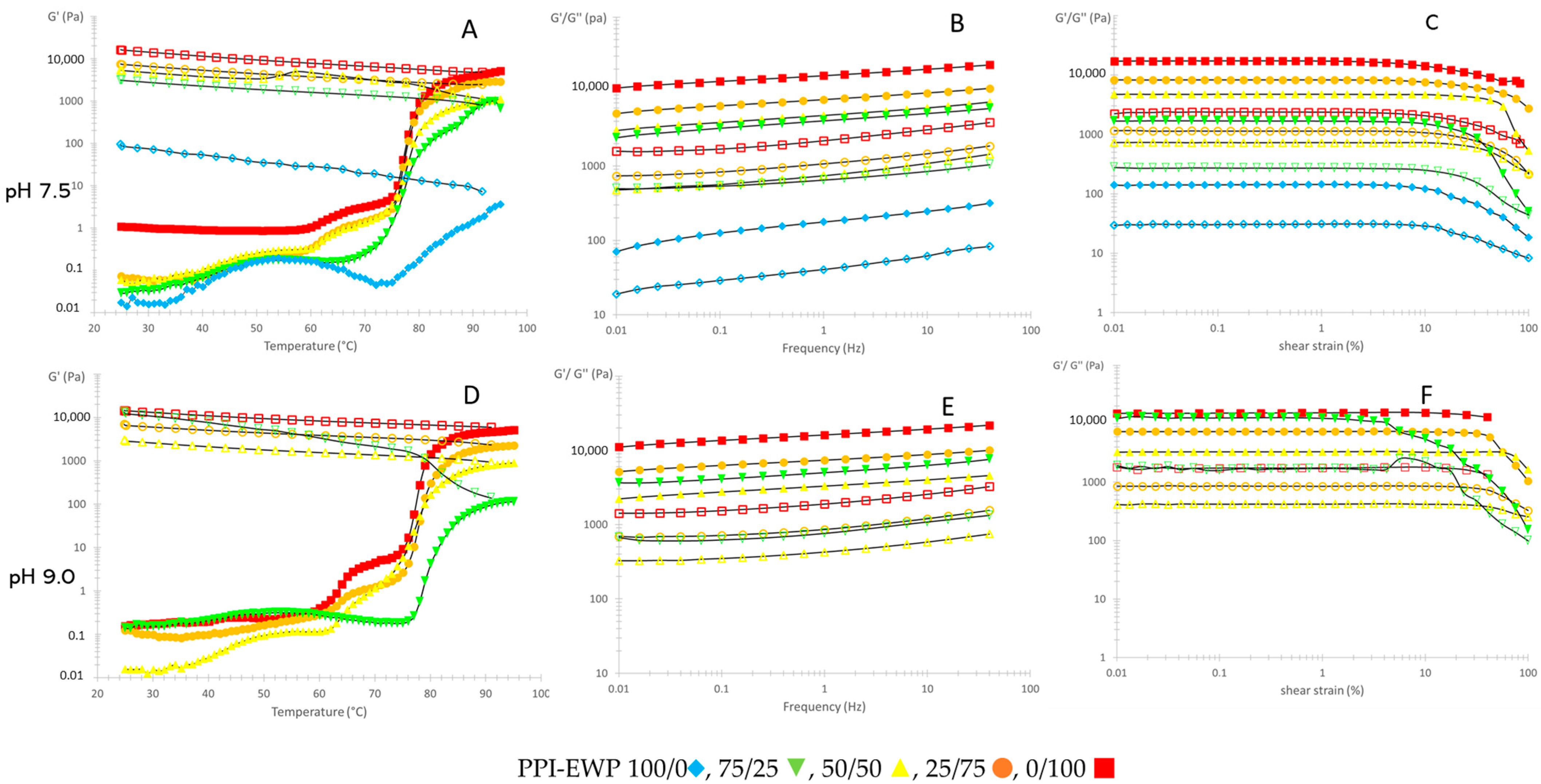

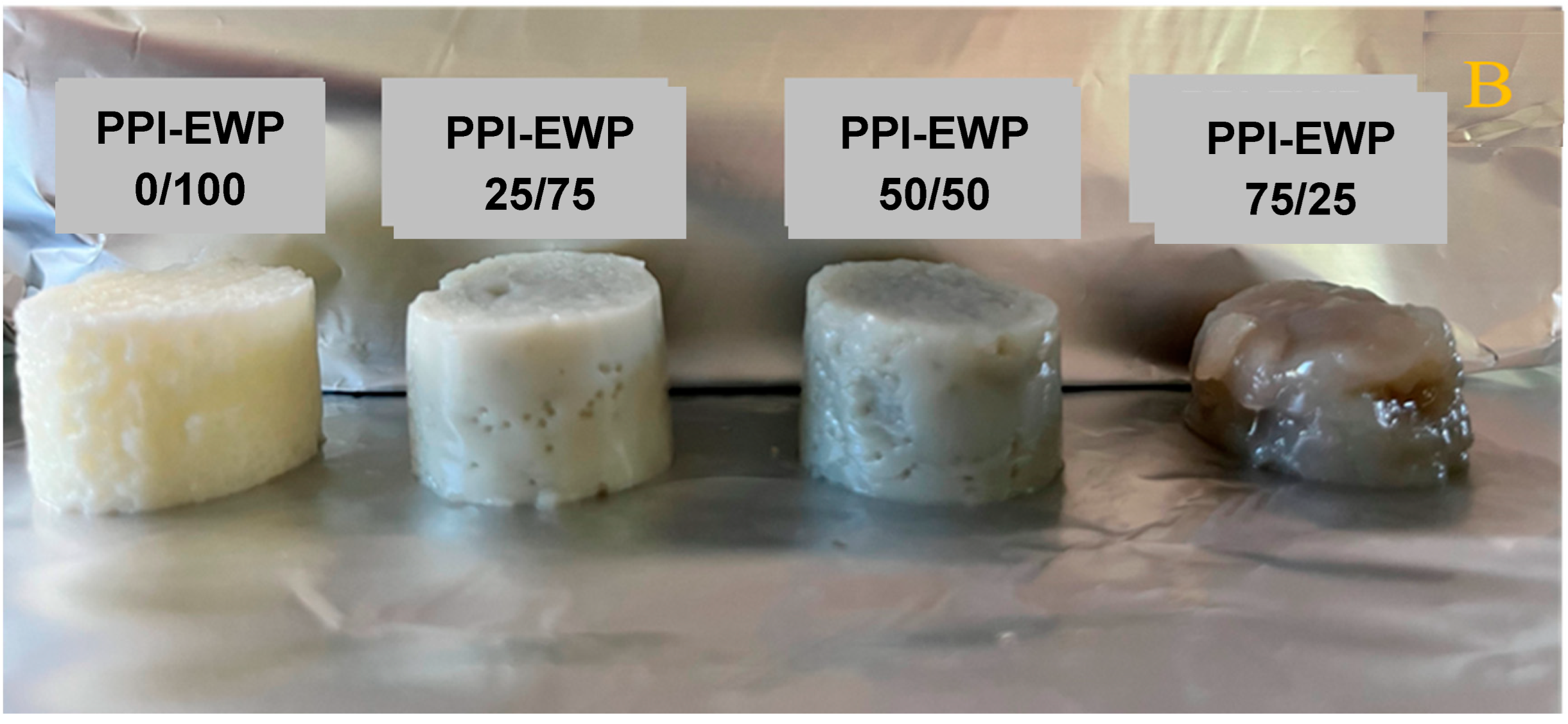
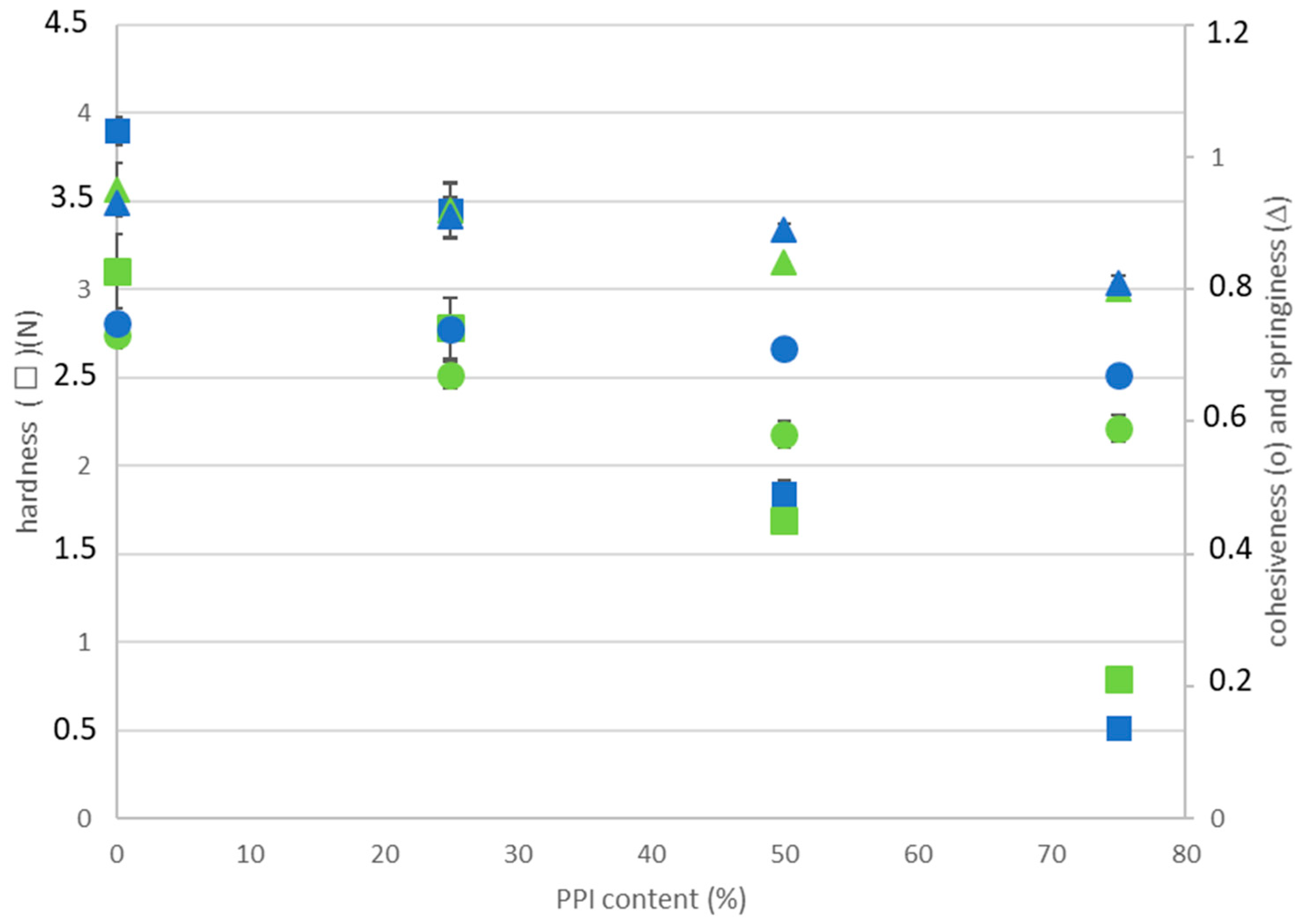
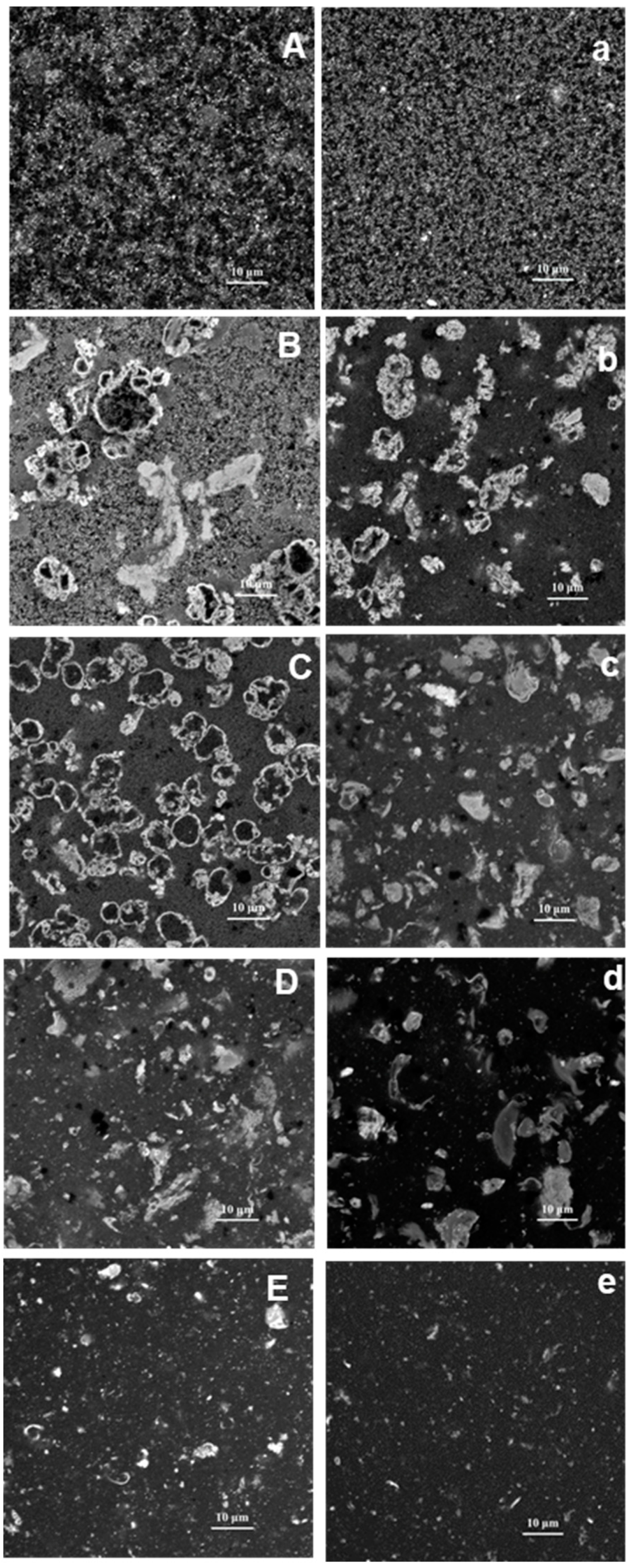
| PPI-EWP Ratio | G′ (Pa) | Tan (δ) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 7.5 | pH 9.0 | pH 7.5 | pH 9.0 | |
| 0/100 | 15,115 ± 632 aA | 14,446 ± 413 aA | 0.135 ± 0.002 aA | 0.115 ± 0.001 aB |
| 25/75 | 7284 ± 192 bA | 7204 ± 281 bA | 0.138 ± 0.001 aA | 0.118 ± 0.003 aB |
| 50/50 | 4725 ± 324 cA | 4182 ± 440 cA | 0.151 ± 0.002 bA | 0.134 ± 0.004 bB |
| 75/25 | 3446 ± 331 cA | 9237 ± 3249 bB | 0.157 ± 0.003 bA | 0.158 ± 0.008 cA |
| 100/0 | 97 ± 4 d | no gel | 0.227 ± 0.005 c | no gel |
| PPI-EWP Ratio | Yield Point (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| pH 7.5 | pH 9.0 | |
| 0/100 | 5.5 ± 0.1 a | 16.6 ± 0.6 a |
| 25/75 | 9.7 ± 0.6 b | 41.6 ± 5.4 b |
| 50/50 | 11.4 ± 0.6 b | 52.3 ± 2.0 b |
| 75/25 | 3.9 ± 0.2 a | 9.7 ± 3.8 a |
| 100/0 | 5.6 ± 0.3 a | no gel |
| Non-Covalent Bonds | Covalent Bonds | References | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ionic Effect/Electrostatic Interactions | Hydrophobic Interactions | Hydrogen Bonds | Disulfide Bonds | ||
| Dithiothreitol (DTT) | Disrupt | [13,52,53] | |||
| Guanidinium–HCl (GuHCl) | Disrupt | Weaken | Disrupt | [13,53,54] | |
| Propylene glycol (PG) | Promote | Disrupt | Promote | [55,56,57] | |
| Urea | Disrupt | Disrupt | [56,58,59] | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuang, J.; Hamon, P.; Lee, J.; Bouhallab, S.; Cases, E.; Saurel, R.; Lechevalier, V. Protein–Protein Interactions and Structure of Heat-Set Gels Based on Pea Protein and Egg White Mixtures. Gels 2025, 11, 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11030176
Kuang J, Hamon P, Lee J, Bouhallab S, Cases E, Saurel R, Lechevalier V. Protein–Protein Interactions and Structure of Heat-Set Gels Based on Pea Protein and Egg White Mixtures. Gels. 2025; 11(3):176. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11030176
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuang, Jian, Pascaline Hamon, Jeehyun Lee, Said Bouhallab, Eliane Cases, Remi Saurel, and Valérie Lechevalier. 2025. "Protein–Protein Interactions and Structure of Heat-Set Gels Based on Pea Protein and Egg White Mixtures" Gels 11, no. 3: 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11030176
APA StyleKuang, J., Hamon, P., Lee, J., Bouhallab, S., Cases, E., Saurel, R., & Lechevalier, V. (2025). Protein–Protein Interactions and Structure of Heat-Set Gels Based on Pea Protein and Egg White Mixtures. Gels, 11(3), 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11030176









