Optical, Electrical, and Structural Properties of NiO Thin Films, Derived by Sol–Gel Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. XRD Analysis
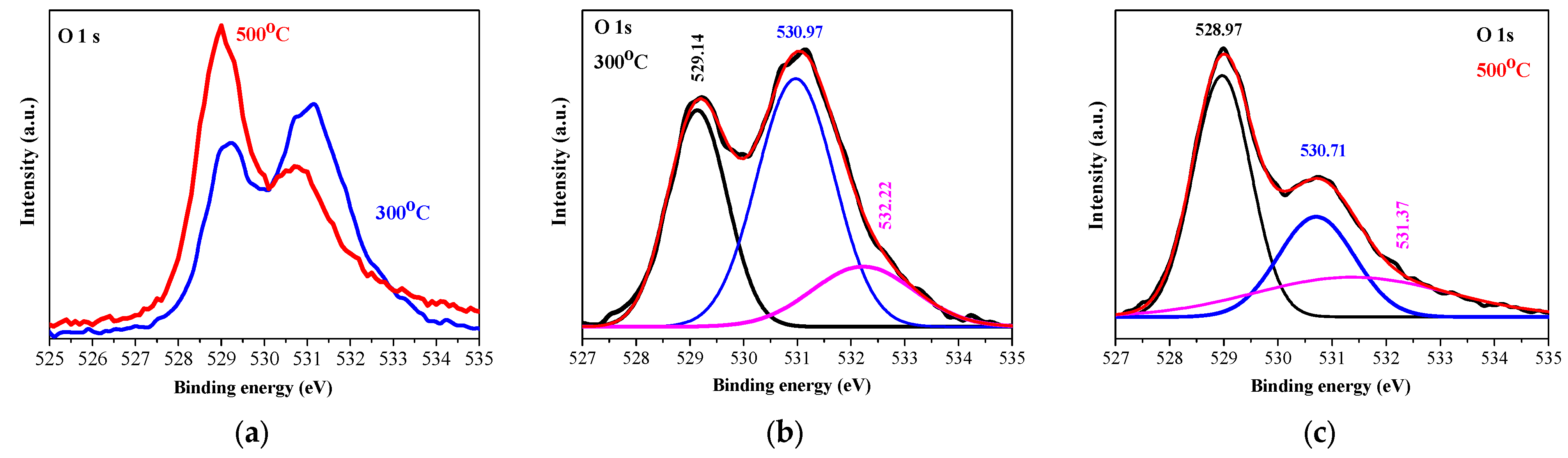
2.2. XPS Characterization
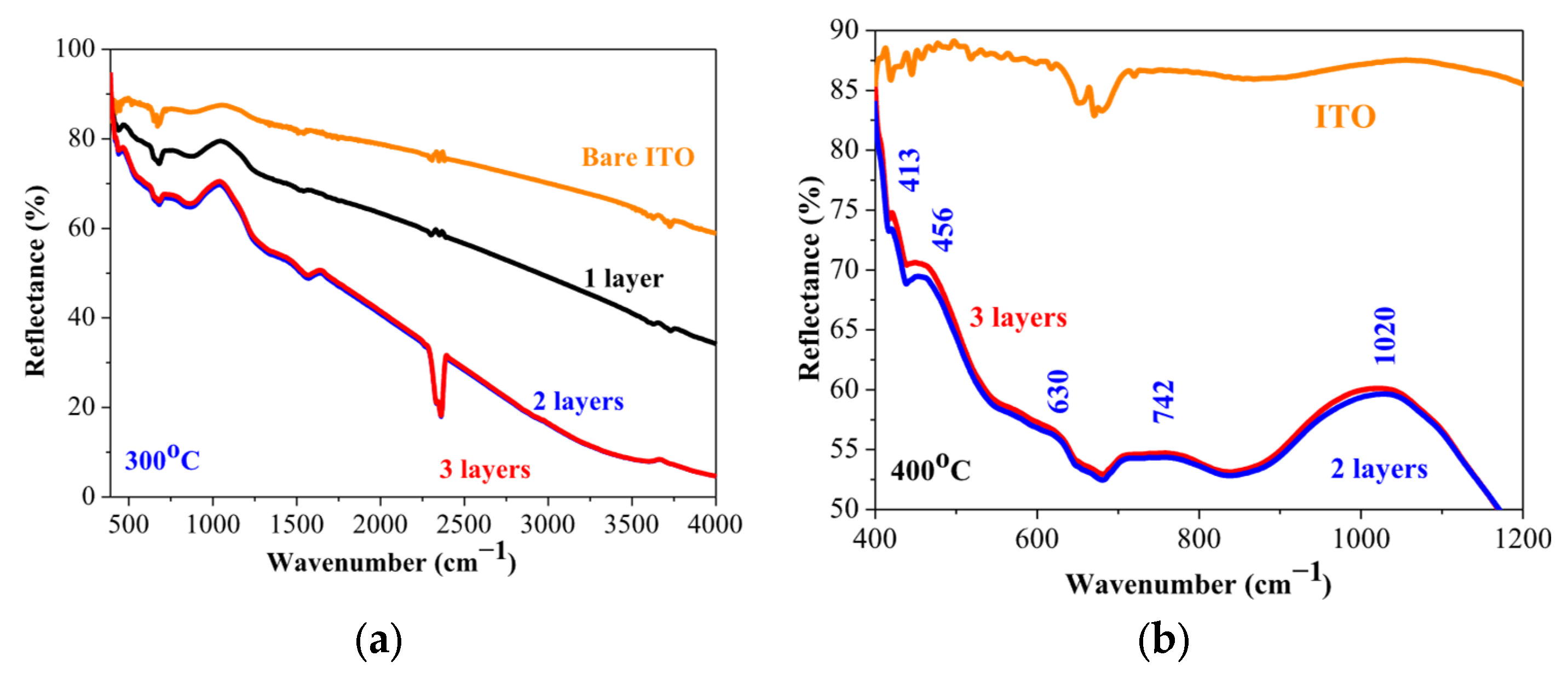
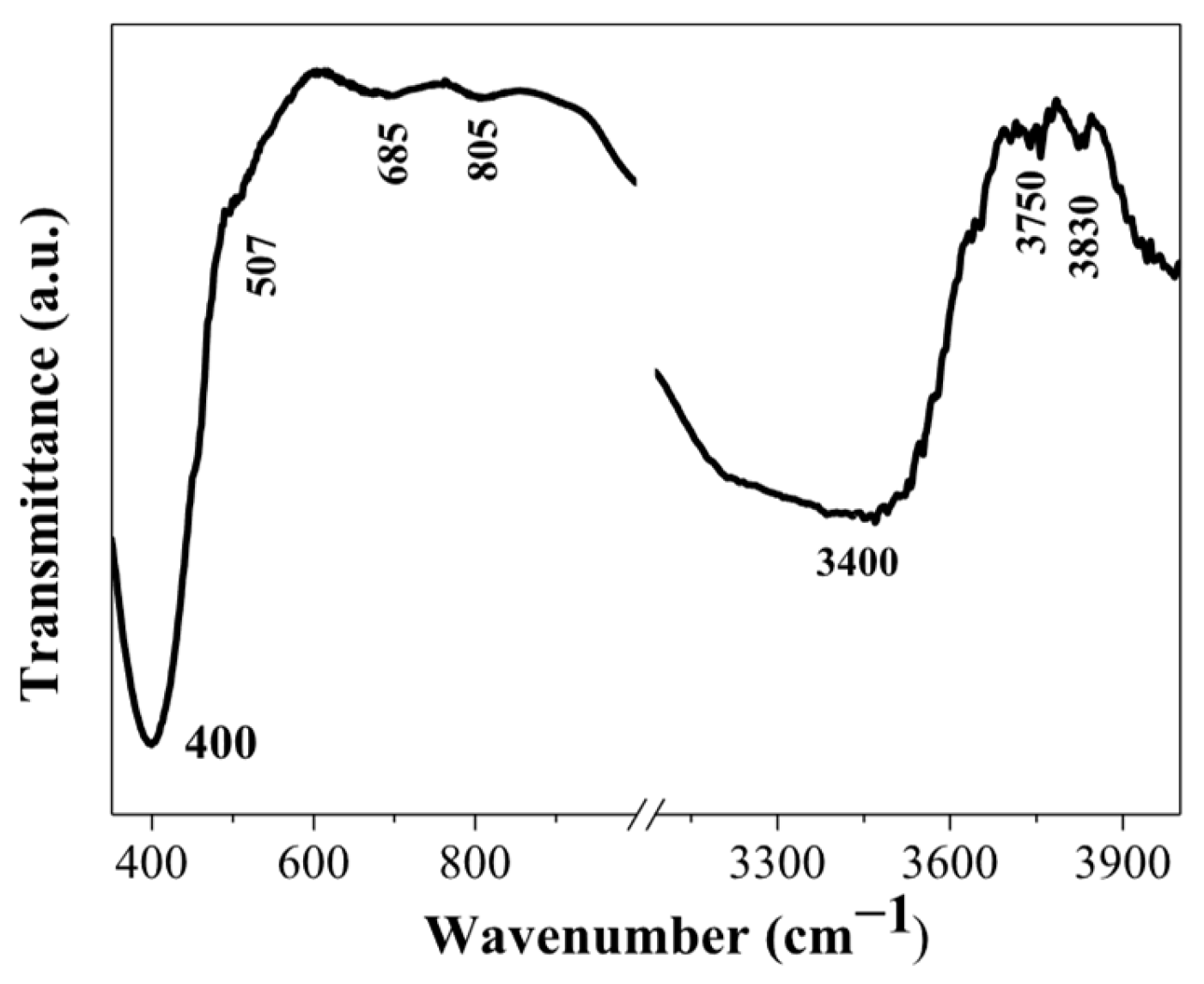
2.3. FTIR Study
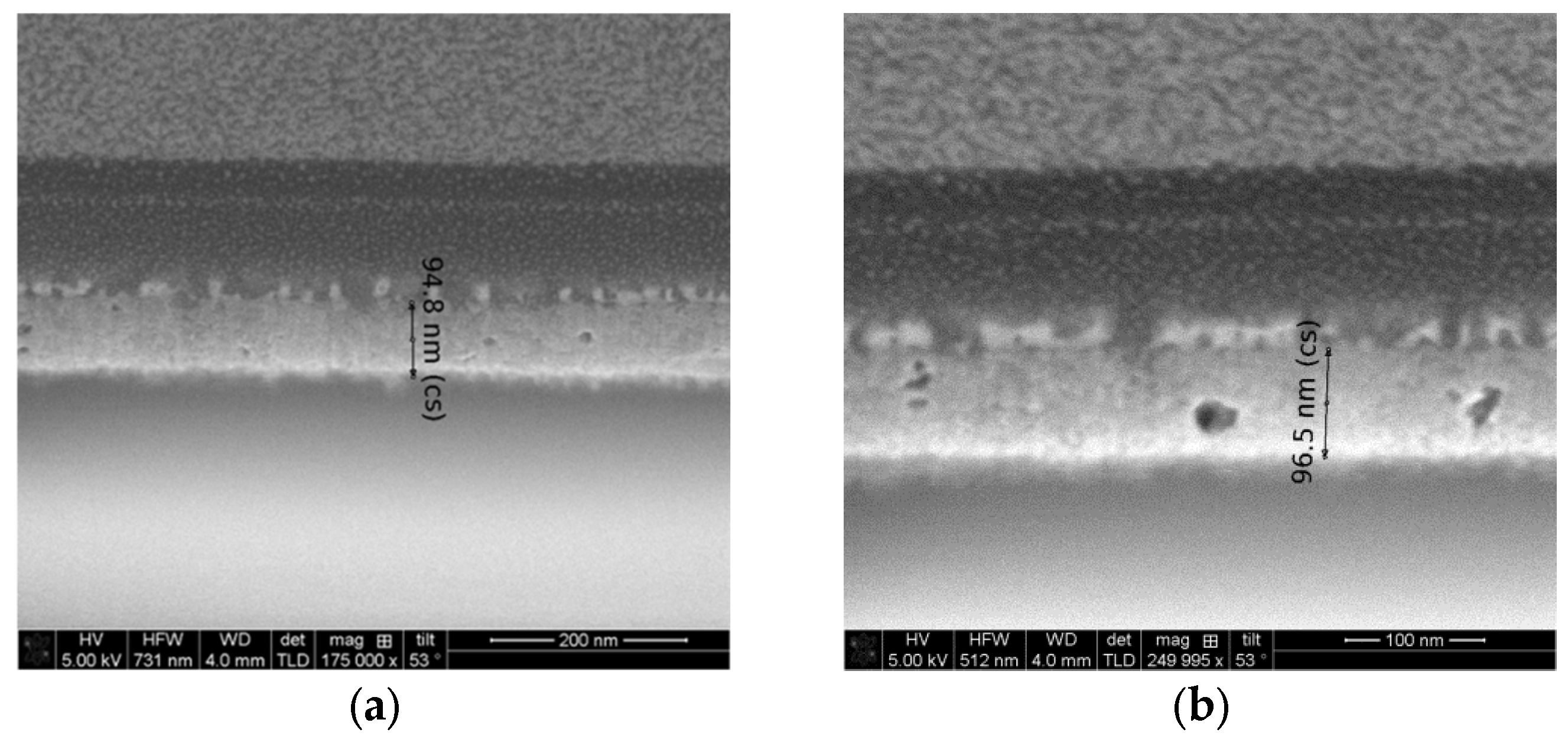
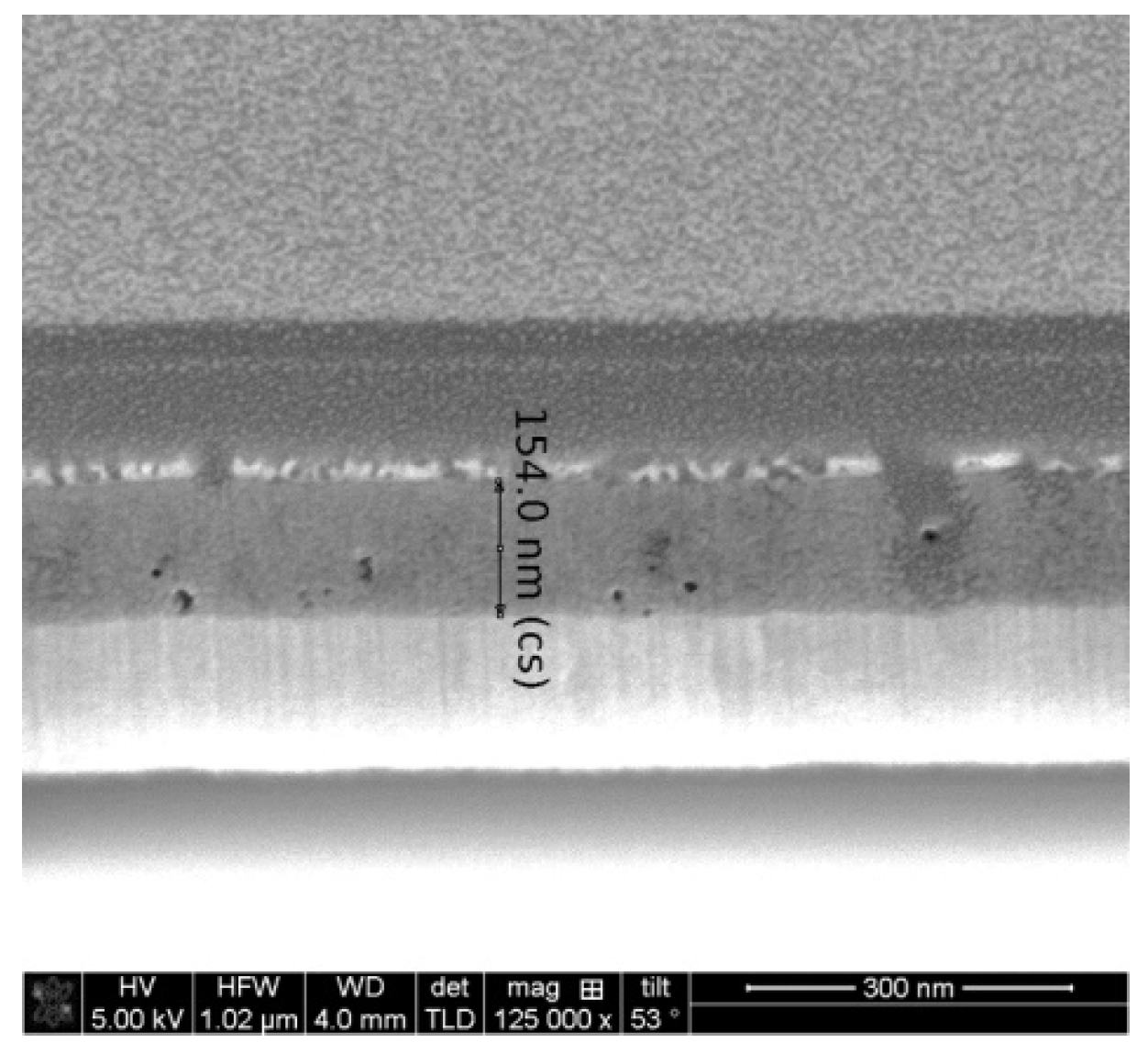
2.4. FESEM Observation
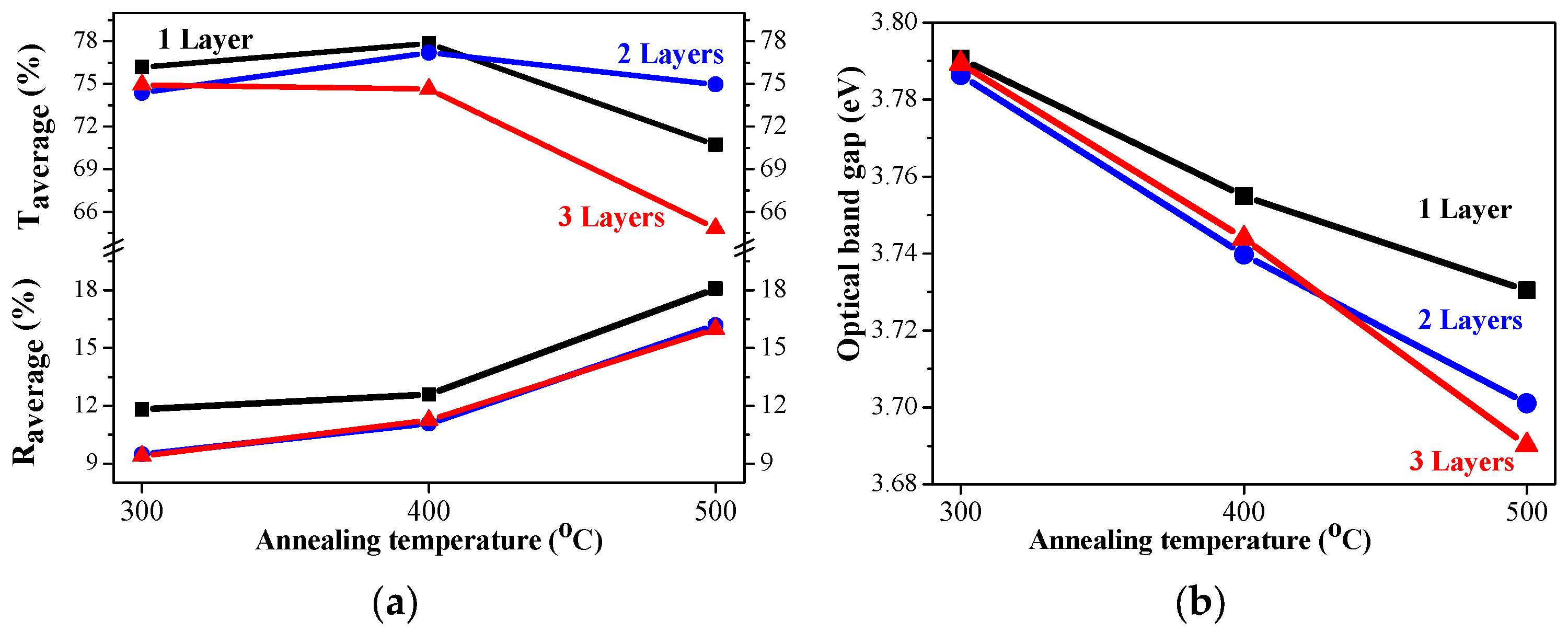
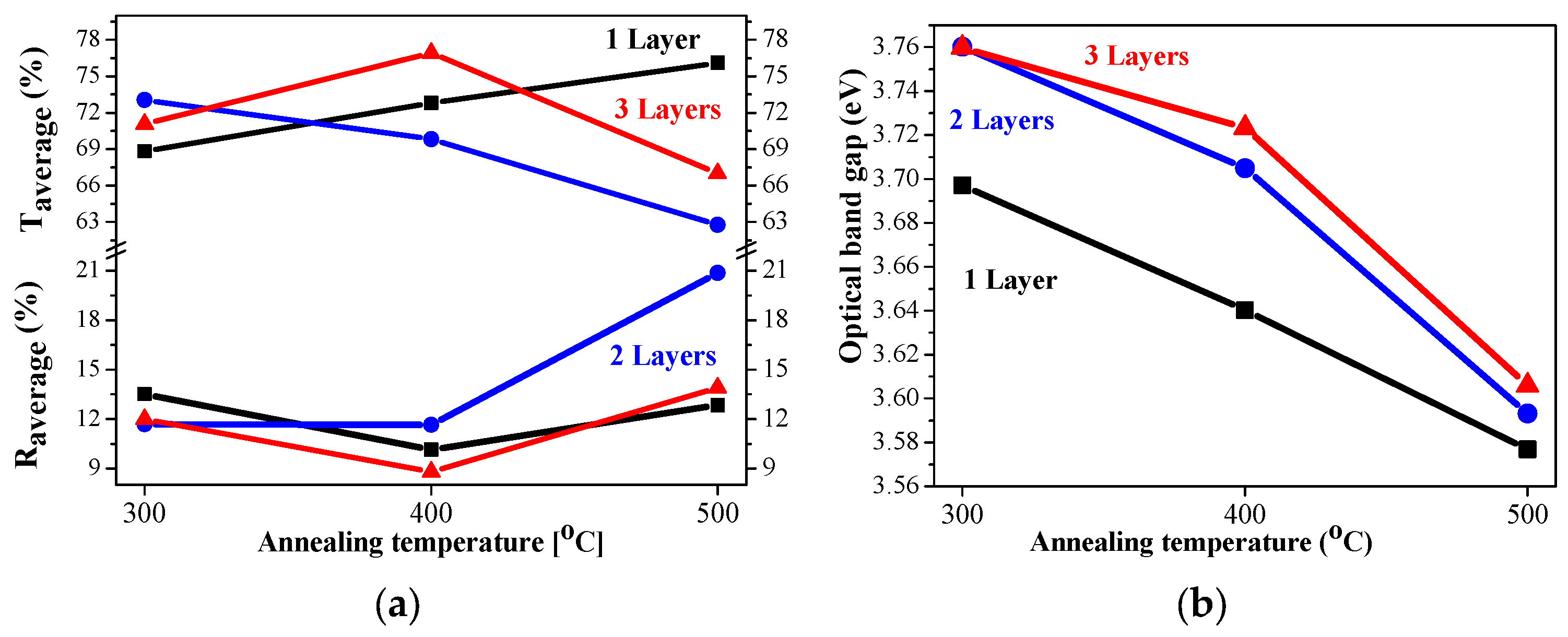
2.5. Optical Properties
2.6. Electrical Properties of Sol–Gel NiO Films
2.6.1. Sheet Resistance
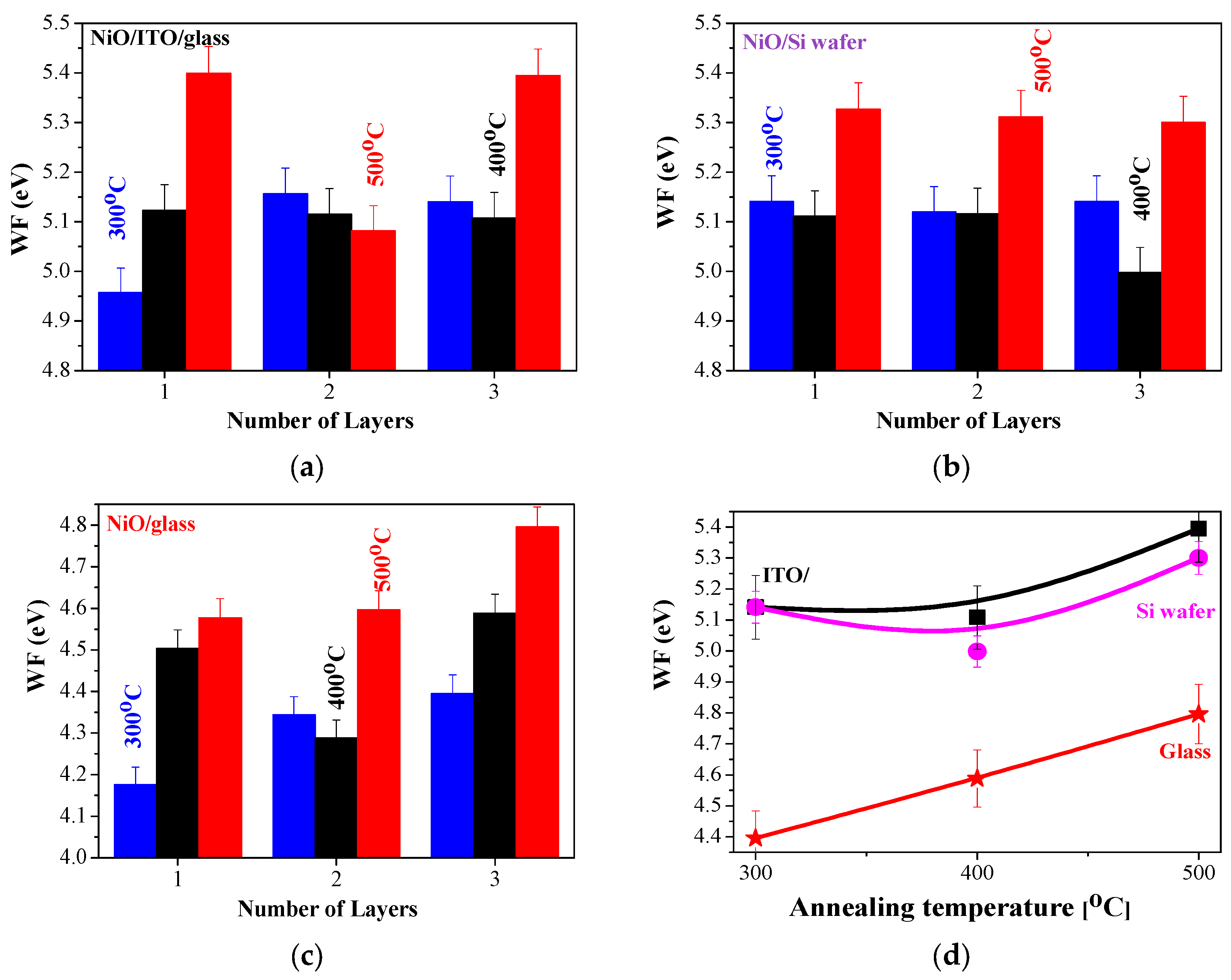
2.6.2. Work Function (WF) of Sol–Gel NiO Films, Deposited on Si, Glass, and ITO Substrates
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ukoba, K.O.; Eloka-Eboka, A.C.; Inambao, F.L. Review of nanostructured NiO thin film deposition using the spray pyrolysis Technique. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 2900–2914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshnev, S.; Kazakin, A.; Shubina, K.; Andreeva, V.; Fedorenko, E.; Koroleva, A.; Zhizhin, E.; Koval, O.; Kurinnaya, A.; Shalin, A.; et al. Annealing Temperature Effect on the Physical Properties of NiO Thin Films Grown by DC Magnetron Sputtering. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 11, 2300815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, P.; Kaurav, N.; Devan, R.S.; Okram, G.S.; Kuo, Y.K. The effect of stoichiometry on the structural, thermal and electronic properties of thermally decomposed nickel oxide. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 5882–5890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayansal, F.; Ilhom, S.; Ocak, Y.S.; Grasso, J.; Willis, B.G.; Biyikli, N. Crystalline NiO films by hollow-cathode plasma-enhanced atomic layer deposition: Material properties and heterojunction device performance. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1018, 179279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caglar, M.; Sever, K.; Aktas, S.; Demiroglu, A. Improving the electrical performance of NiO based photodiode fabricated by sol-gel process with Al doping. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2023, 350, 114099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, W.; Samir, S.; Habib, M.A.; El-Shaer, A. Effect of annealing temperature on physical properties and photoelectrochemical behavior of electrodeposited nanostructured NiO thin films for optoelectronic applications. Opt. Mater. 2024, 153, 115595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athira, M.; Bharath, S.P.; Angappane, S. SnO2 -NiO heterojunction based self-powered UV photodetectors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2022, 340, 113540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, M.S.; Shahahmadi, S.A.; Chelvanathan, P.; Alharbi, H.F.; Karim, M.R.; Dar, M.A.; Luqman, M.; Alharthi, N.H.; Al-Harthi, Y.S.; Aminuzzaman, M.; et al. Effects of growth temperature on the photovoltaic properties of RF sputtered undoped NiO thin films. Res. Phys. 2019, 14, 102360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owoeye, V.A.; Adewinbi, S.A.; Salau, A.O.; Orelusi, A.N.; Adeoye, A.E.; Akindadelo, A.T. Effect of precursor concentration on stoichiometry and optical properties of spray pyrolyzed nanostructured NiO thin films. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdag, A.; Iskenderoglu, D.; Gulduren, M.E.; Karadeniz, S.M.; Guney, H. Altering the physical properties of NiO thin films grown through the ultrasonic spray pyrolysis method by incorporating impurity lead dopants. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 32430–32438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Hu, T.; Hou, H.; Zhu, P.; Liu, R.; Peng, J.; Luo, W.; Yu, H. A review for nickel oxide hole transport layer and its application in halide perovskite solar cells. Mater. Today Sustain. 2023, 23, 100438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, A.; Mondal, P. Optimization of ZnO films for the development of ZnO/NiO heterojunction solar cells. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2025, 36, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, D. Self-Powered p-NiO/n-ZnO Heterojunction Ultraviolet Photodetector Based on Honeycomb Nano-Mesh Structure. Sensors 2024, 24, 7733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aivalioti, C.; Androulidaki, M.; Tsagaraki, K.; Manidakis, E.G.; Koliakoudakis, C.; Pelekanos, N.T.; Modreanu, M.; Aperathitis, E. The Effect of Nitrogen as a Co-Dopant in p-Type NiO:Nb Films on the Photovoltaic Performance of NiO/TiO2 Transparent Solar Cells. Solids 2024, 5, 651–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usha, K.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Sivakumar, R.; Sanjeeviraja, C. Ultra-fast switching of energy efficient electrochromic nickel oxide thin films for smart window applications. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 36651–36665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Tan, Q.; Li, Z.; Xiu, J.; Wang, J.; Cheng, T.; He, D.; Sun, Q.; Ma, X.; Lamberti, F.; et al. Magnetron sputtered nickel oxide with suppressed interfacial defect states for efficient inverted perovskite solar cells. J. Energy Chem. 2025, 100, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaoudhary, S.; Midhun, A.R.; Aissa, B.; Rastogi, V.; Mitra, A. Impact of ambient oxygen pressure on the structural and optical properties of NiO thin films deposited using pulsed laser deposition and the performance of self-driven p-NiO/n-Si as UV-Visible-NIR photodetectors. Thin Solid Films 2025, 824, 140703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napari, M.; Huq, T.N.; Hoye, R.L.Z.; MacManus-Driscoll, J.L. Nickel oxide thin films grown by chemical deposition techniques: Potential and challenges in next-generation rigid and flexible device applications. Infomat 2021, 3, 536–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, M.; Vengatesan, K.; Aly, M.H.; Sitharthan, R.; Dhanabalan, S.S.; Karthikeyan, M. Electrical and optical properties of sol–gel-deposited NiO films and corresponding response to annealing temperature. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2023, 55, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, G.; Sonmez, E.; Duman, S. Determination of certain sol-gel growth parameters of nickel oxide films. Ceram. Int. 2015, 42, 2976–2989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.J.; Su, T.H.; Kuo, P.C.; Chang, H.C. A source of free holes in NiO thin films with different nickel content that are prepared using the sol-gel method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 276, 125345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beisembekov, M.K.; Omarbekova, G.I.; Tazhibayev, S.K.; Aimukhanov, A.K.; Baltabekov, A.S.; Ziyat, A.Z.; Zeinidenov, A.K. The role of annealing temperature on the optical and electrical transport properties of NiOx films. Opt. Mater. 2024, 151, 115398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Gil, M.; Cabrera-German, D.; Rodríguez-Curiel, M.; Abundiz-Cisneros, N.; Vargas-Viveros, E.; Cota, L.; De La Cruz, W. Role of different atmosphere gasses during annealing in chemical-solution-deposition NiO thin films processing. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2023, 600, 122012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Hui, K.N.; Hui, K.S. High conductivity nickel oxide thin films by a facile sol–gel method. Mater. Lett. 2013, 92, 201–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, T.; Harizanova, A.; Shipochka, M.; Vitanov, P. Nickel Oxide Films Deposited by Sol-Gel Method: Effect of Annealing Temperature on Structural, Optical, and Electrical Properties. Materials 2022, 15, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-J.; Mun, H.-J.; Kim, B.-J.; Kim, Y.-S. Characterization of Nickel Oxide Nanoparticles Synthesized under Low Temperature. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Thimont, Y.; Presmanes, L.; Diao, X.; Barnabé, A. The effect of the oxygen ratio control of DC reactive magnetron sputtering on as-deposited non stoichiometric NiO thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 419, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén, C.; Herrero, J. Influence of Acceptor Defects on the Structural, Optical and Electrical Properties of Sputtered NiO Thin Films. Phys. Status Solidi A 2021, 218, 2100237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshtyal, Y.; Nazarov, D.; Ezhov, I.; Mitrofanov, I.; Kim, A.; Rymyantsev, A.; Lyutakov, O.; Popovich, A.; Maximov, M. Atomic Layer Deposition of NiO to Produce Active Material for Thin-Film Lithium-Ion Batteries. Coatings 2019, 9, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulla, M.G.; Pittala, R.K. Fabrication and physicochemical properties of nickel oxide (NiO) thin films. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 22255–22265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, E.; Coban, O.; Saritas, S.; Tuzemen, S.; Yildirimc, M.; Gurc, E. Oxygen partial pressure effects on the RF sputtered p-type NiO hydrogen gas sensors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 435, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Li, L.; Yu, S.; Zheng, H.; Peng, W. The annealing temperature and films thickness effect on the surface morphology, preferential orientation and dielectric property of NiO films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 493, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, B.; Wang, L.; Lin, J. The electronic structures of NiO NPs coated with stearates. Solid State Commun. 1995, 94, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaf, A.; Saghir, R.; Abdallah, A.M.; Noun, R.; Awad, R. Influence of Mo doping on the structural, Raman scattering, and magnetic properties of NiO nanostructures. Appl. Phys. A 2024, 130, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, U.; Kim, B.G.; Nguyen, D.; Park, G.H.; Ha, N.S.; Kim, S.J.; Ko, S.H.; Lee, S.; Park, H.J. Solution-Processible Crystalline NiO Nanoparticles for High-Performance Planar Perovskite Photovoltaic Cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Wu, Y.; Wei, H.; Shi, Y.; Hu, C. Synthesis and characteristics of NiO nanowire by a solution method. Mater. Lett. 2004, 58, 2700–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalmi, Y.; Habelhames, F.; Sayah, A.; Bahloul, A.; Nessark, B.; Shalabi, M.; Nunzi, J.M. Capacitance performance of NiO thin films synthesized by direct and pulse potentiostatic methods. Ionics 2019, 25, 6025–6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, H.; Wei, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhu, L.; Yan, X. Preparation and Characterization of NiO Nanoparticles by Anodic Arc Plasma Method. J. Nanomater. 2009, 2009, 795928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, G.; Al-Sehemi, A.S.; Al-Shihri, A.K.; Gaohui, D.; Tokeer, A. Microwave synthesis, optical properties and surface area studies of NiO nanoparticles. J. Mol. Struct. 2014, 1058, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.K.H.; Tran, B.Q.; Nguyen, K.B.; Pham, N.Y.N.; Nguyen, T.H.Y.; Nguyen, A.H.T.; Nguyen, N.P.; Ngo, H.D.; Pham, H.P. Oxygen partial pressure effects on nickel oxide thin films and NiO/Si diode performance. Mater. Adv. 2025, 6, 1719–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandy, S.; Maiti, U.N.; Ghosh, C.K.; Chattopadhyay, K.K. Enhanced p-type conductivity and band gap narrowing in heavily Al doped NiO thin films deposited by RF magnetron sputtering. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2009, 21, 115804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Y.; Rasadujjaman; Bhuyan, D.I.; Ali, H.; Karim, R.; Uddin, S.; Jamil, A.T.K.; Ahmed, S.J.; Ali, A.; Hossain, A. Annealing temperature effect on the optical properties of spin-coated Ru-doped NiO films. Opt. Mater. 2025, 167, 117345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejam, L.; Sabbaghzadeh, J.; Ghaderi, A.; Solaymani, S.; Matos, R.S.; Țălu, S.; da Fonseca Filho, H.D.; Sari, A.H.; Kiani, H.; Shayegan, A.H.S.; et al. Advanced nano-texture, optical bandgap, and Urbach energy analysis of NiO/Si heterojunctions. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.R.; Feng, B.X.; Yan, P.X.; Cai, X.M.; Lu, S.Y. The effect of annealing on the electrochromic properties of microcrystalline NiOx films prepared by reactive magnetron rf sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2001, 174, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasi, B.; Gopchandran, K.G.; Manoj, P.K.; Koshy, P.; Rao, P.; Vaidyan, V.K. Preparation of transparent and semiconducting NiO films. Vacuum 2003, 68, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaida, M.; Fathi, A.M.; Moussa, I.; Afify, H.H. Characterization and electrochromic properties of NiO thin films prepared using a green aqueous solution by pulsed spray pyrolysis technique. J. Mater. Res. 2022, 37, 2282–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelghani, L.; Said, L.; Said, B.; Okba, B. Spin coating method deposited nickel oxide thin films with various film thicknesses. J. Chem. Res. 2022, 46, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, C.-C.; Huang, C.-Y.; Yang, C.-F.; Wu, C.-C. Morphological, Optical, and Electrical Properties of p-Type Nickel Oxide Thin Films by Nonvacuum Deposition. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.C.; Dai, M.J.; Lin, S.S.; Chen, S.C.; Ding, A.N.; Gong, G.H.; Sun, H. Effect of annealing temperature on the optoelectronic properties and structure of NiO films. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 2820–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haacke, G. New figure of merit for transparent conductors. J. Appl. Phys. 1976, 47, 4086–4089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hettiaratchy, E.C.; Rockett, A.A.; Hill, T.D.; Grover, S. NiO as a P-Type TCO for Inorganic Thin-Film Photovoltaics. In Proceedings of the IEEE 50th Photovoltaic Specialists Conference (PVSC), San Juan, PR, USA, 11–16 June 2023; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Sayed, A.M. Exploring the morphology, optical and electrical properties of nickel oxide thin films under lead and iridium doping. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2021, 60, 412601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, M.T.; Helander, M.G.; Wang, Z.B.; Tang, W.M.; Lu, Z.H. Effects of processing conditions on the work function and energy-level alignment of NiO thin films. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 19777–19781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Gil, M.; Pintor-Monroy, M.I.; Cota-Leal, M.; Cabrera-German, D.; Garzon-Fontecha, A.; Quevedo-Lopez, M.A.; Sotelo-Lerma, M. Influence of annealing temperature on nickel oxide thin films grown by chemical bath deposition. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2017, 72, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, M.D.; Servaites, J.D.; Buchholz, D.B.; Leever, B.J.; Liu, J.; Emery, J.D.; Zhang, M.; Song, J.H.; Durstock, M.F.; Freeman, A.J.; et al. Structural and Electrical Functionality of NiO Interfacial Films in Bulk Heterojunction Organic Solar Cells. Chem. Mater. 2011, 23, 2218–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hietzschold, S.; Hillebrandt, S.; Ullrich, F.; Bombsch, J.; Rohnacher, V.; Ma, S.; Liu, M.; Kohn, A.; Jaegermann, W.; Pucci, A.; et al. Functionalized Nickel Oxide Hole Contact Layers: Work Function versus Conductivity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 39821–39829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zuo, J.; Li, P.; Gao, Y.; He, W.; Zheng, Z. Study of the nanoscale electrical performance of NiO thin films by C-AFM and KPFM techniques: The effect of grain boundary barrier. Phys. E Low Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2019, 111, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Song, h.; Kim, K.H.; Oh, J. Investigation of surface reactions in metal oxide on Si for efficient heterojunction Si solar cells. APL Mater. 2019, 7, 071106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Jacobs, R.; Ma, T.; Chen, D.; Booske, J.; Morgan, D. Work Function: Fundamentals, Measurement, Calculation, Engineering, and Applications. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2023, 19, 037001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Punia, R.; Pant, K.K.; Biswas, P. Effect of work-function and morphology of heterostructure components on CO2 reduction photo-catalytic activity of MoS2-Cu2O heterostructure. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 132709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

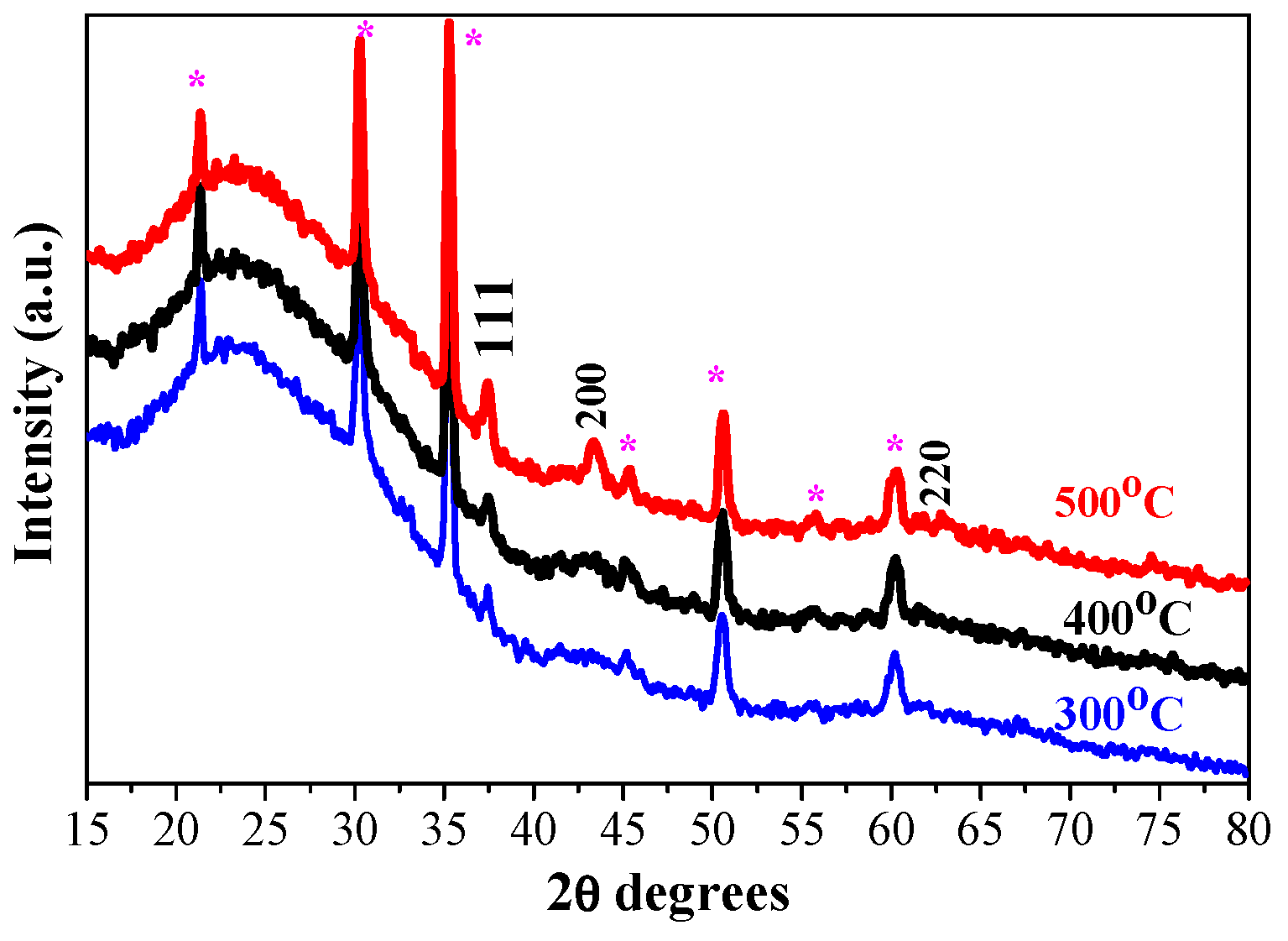
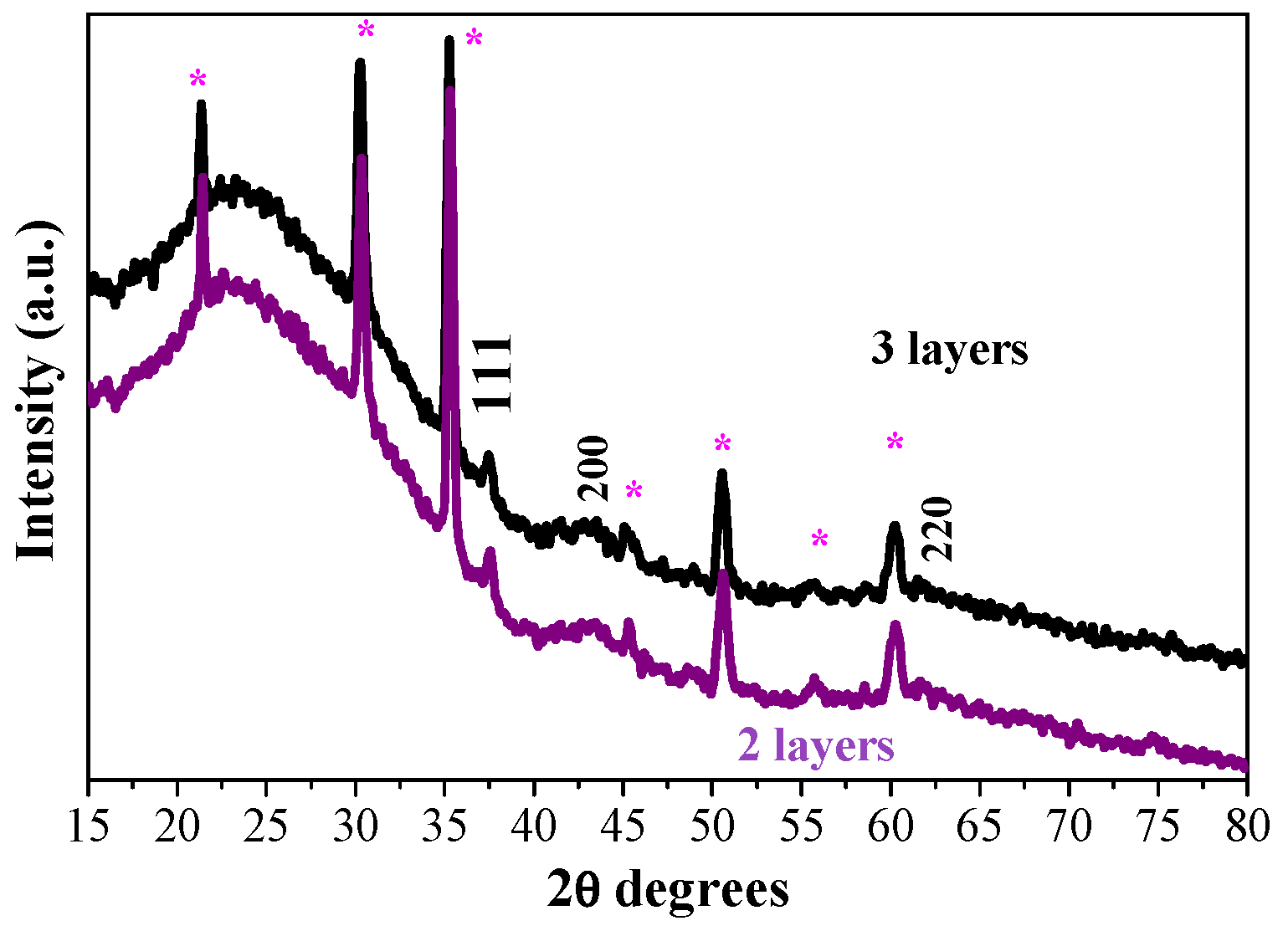
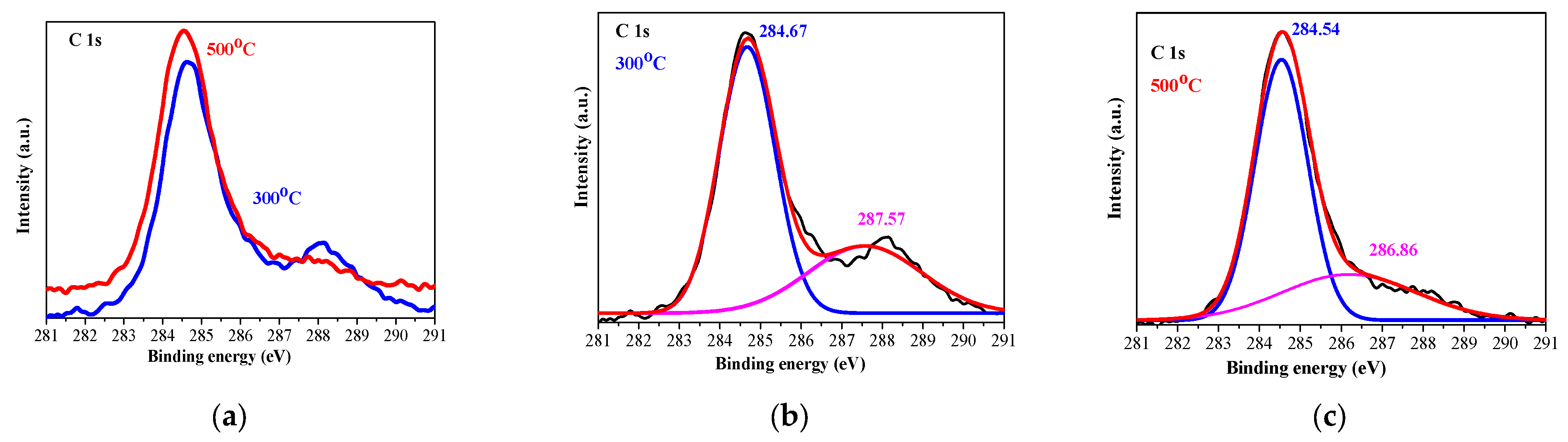
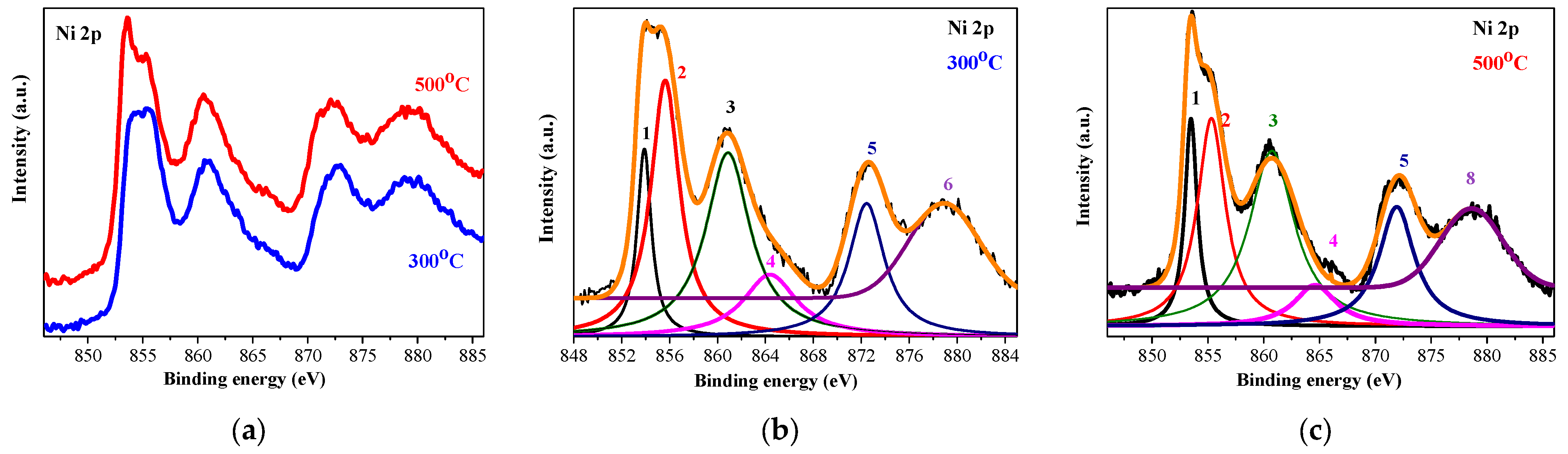



| Substrate | Number of Layers | Annealing (°C) | 2θ Degrees | Miller Indices | FWHM | Crystallite Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass | 3 | 400 | 37.21 43.13 | 111 200 | Weak, broad 1.15049 | - 7.58 |
| 3 | 500 | 37.42 43.35 | 111 200 | 2.07068 0.6358 | 4.23 13.73 | |
| ITO | 3 | 300 | 37.36 | 111 200 | 0.69502 - | 12.60 - |
| 3 | 400 | 37.44 43.35 | 111 200 | 0.33477 broad | 26.18 - | |
| 3 | 500 | 37.42 43.36 | 111 200 | 0.42876 0.92663 | 20.42 9.52 | |
| 2 | 400 | 37.21 43.13 | 111 200 | 0.28302 broad | 30.33 - |
| IR Line (cm−1) | Assigned to |
|---|---|
| 413 | Ni-O stretching mode [36] |
| 459 | stretching vibration Ni-O, NiO, or Ni2O3 [37] |
| 630 | defects and surface oxygen interstitials from Ni-O vibrations [38] |
| 742 | Ni-O stretching vibration [38] |
| 1020 | C-O modes due to the deposition process [19] |
| Number of Layers | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Rsheet, (Ω/□) | Taverage (%) λ = 450–700 nm | Figure of Merit ×10−5 (Ω−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 300 | 688 | 76.18 | 9.56 |
| 400 | 691 | 77.85 | 11.83 | |
| 500 | 220 | 70.71 | 14.20 | |
| 2 | 300 | 377 | 74.36 | 13.71 |
| 400 | 255 | 77.19 | 29.45 | |
| 500 | 242 | 74.97 | 23.18 | |
| 3 | 300 | 168 | 74.93 | 33.21 |
| 400 | 235 | 74.64 | 22.84 | |
| 500 | 250 | 64.85 | 5.26 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ivanova, T.; Harizanova, A.; Petkov, N. Optical, Electrical, and Structural Properties of NiO Thin Films, Derived by Sol–Gel Method. Gels 2025, 11, 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11120944
Ivanova T, Harizanova A, Petkov N. Optical, Electrical, and Structural Properties of NiO Thin Films, Derived by Sol–Gel Method. Gels. 2025; 11(12):944. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11120944
Chicago/Turabian StyleIvanova, Tatyana, Antoaneta Harizanova, and Nikolay Petkov. 2025. "Optical, Electrical, and Structural Properties of NiO Thin Films, Derived by Sol–Gel Method" Gels 11, no. 12: 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11120944
APA StyleIvanova, T., Harizanova, A., & Petkov, N. (2025). Optical, Electrical, and Structural Properties of NiO Thin Films, Derived by Sol–Gel Method. Gels, 11(12), 944. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11120944






