Development and Characterization of a Wound-Healing System Based on a Marine Biopolymer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
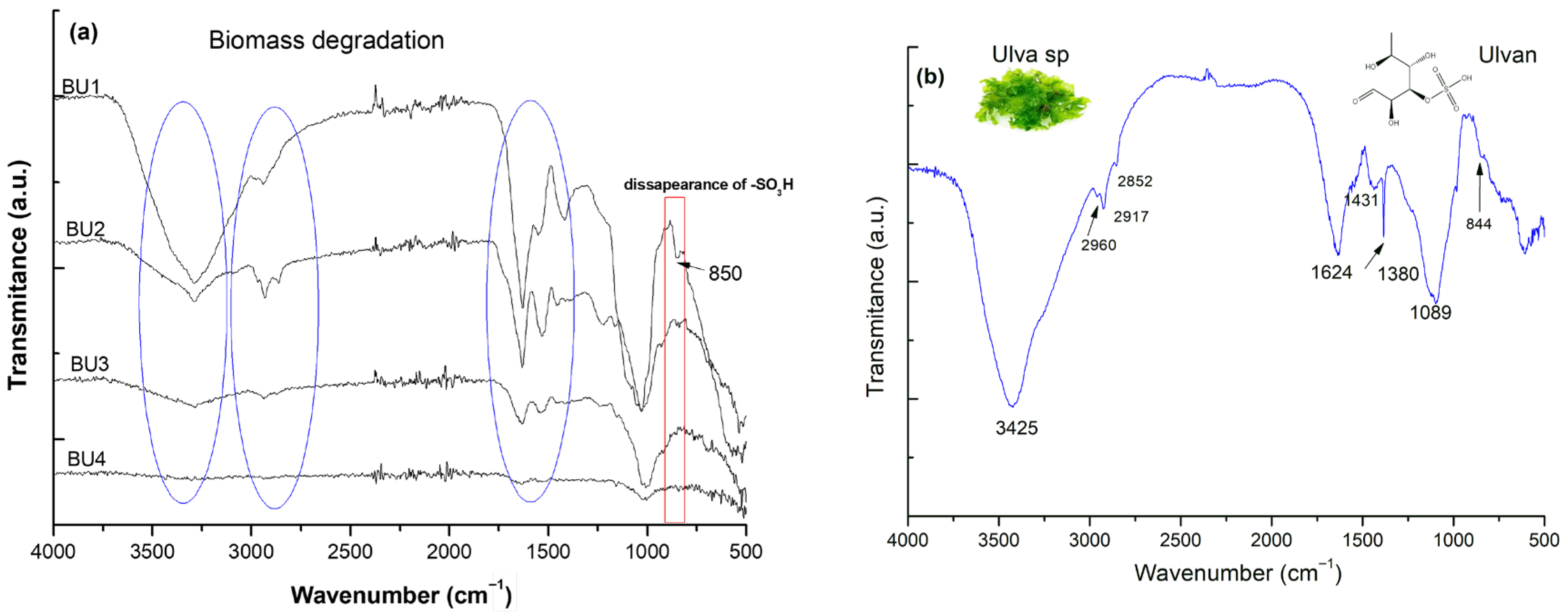
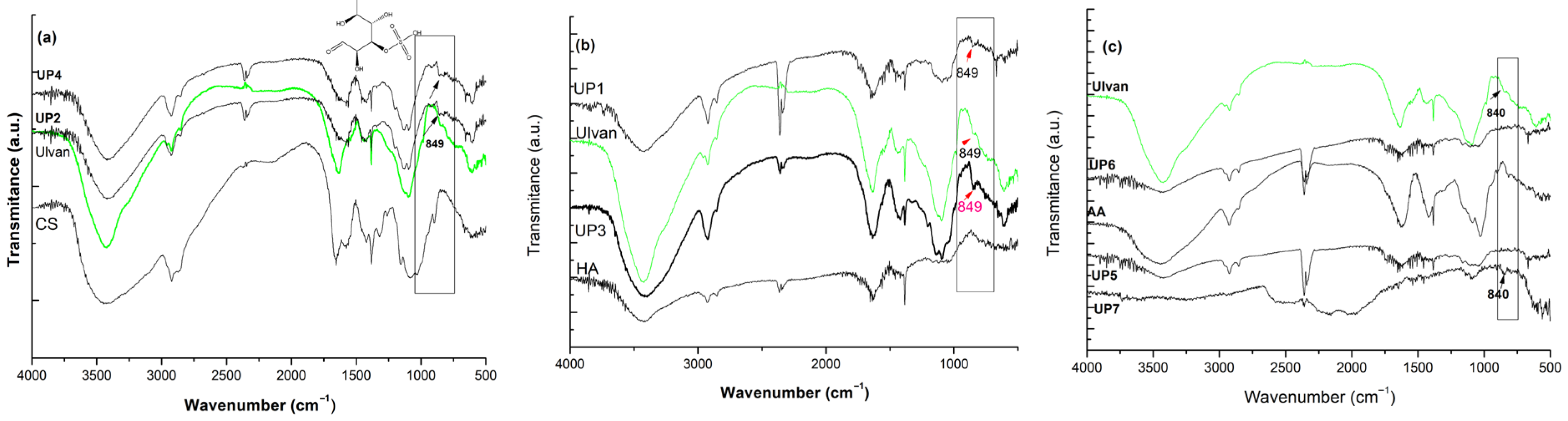
2.1. Structure Identity and the Extraction Efficiency of Ulvan
2.2. Thermal Properties
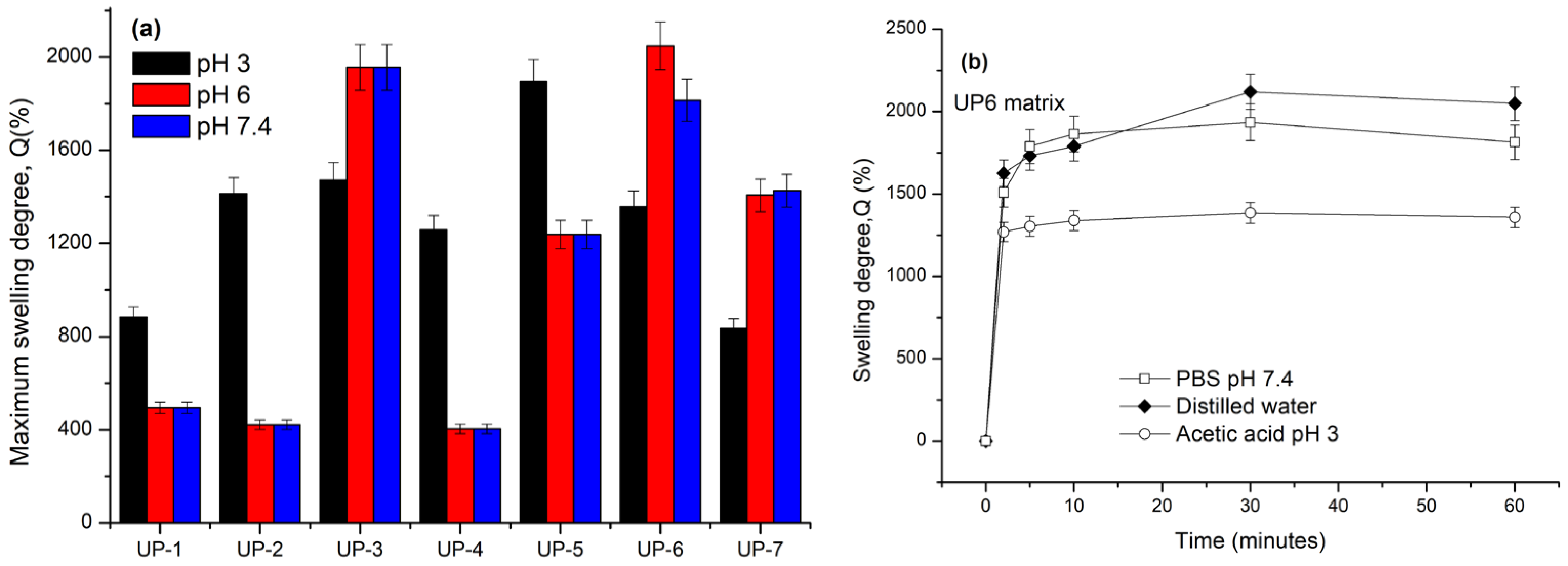
2.3. Swelling Ability
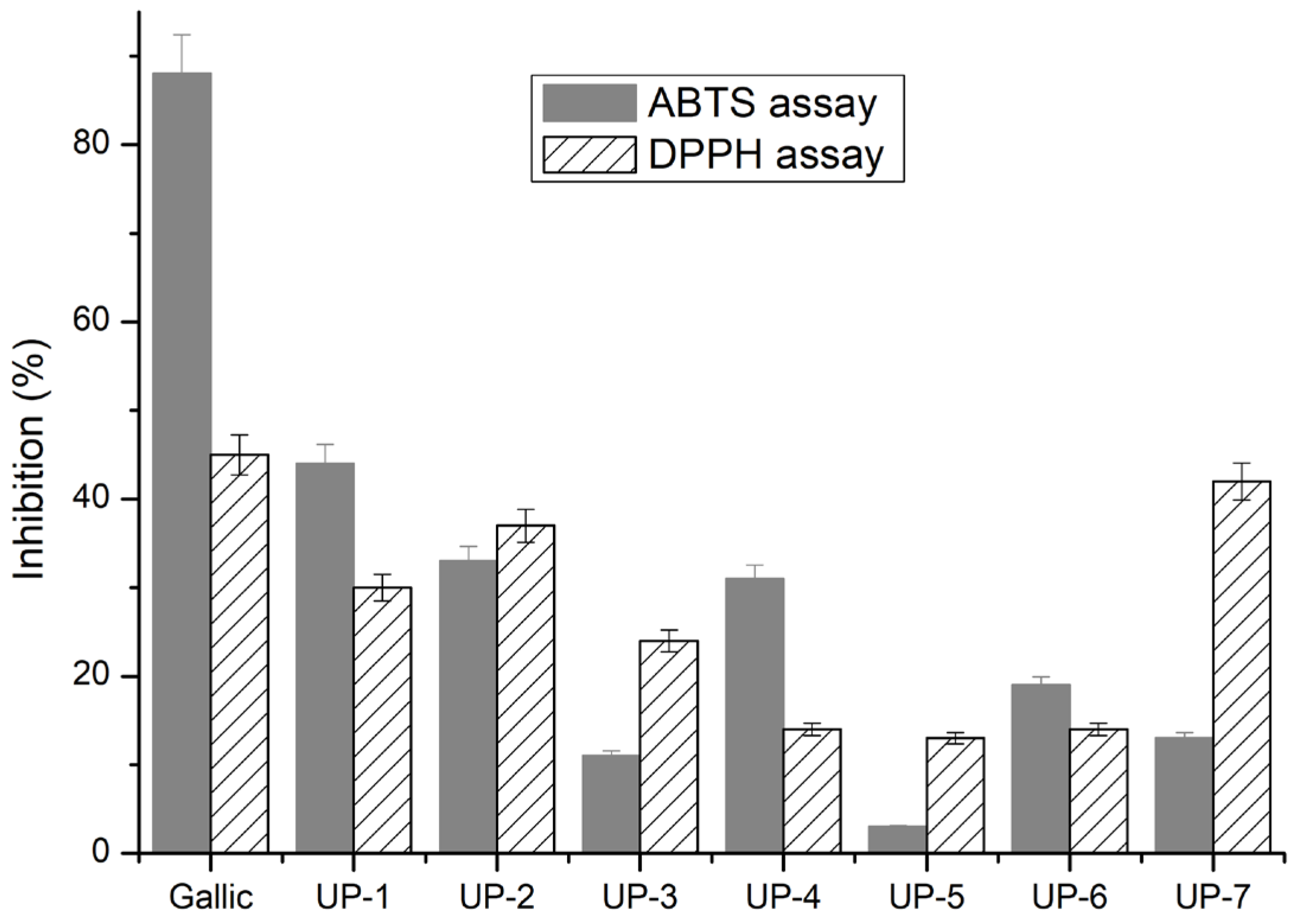
2.4. Antioxidant Activity of the Ulvan-Based Hydrogels
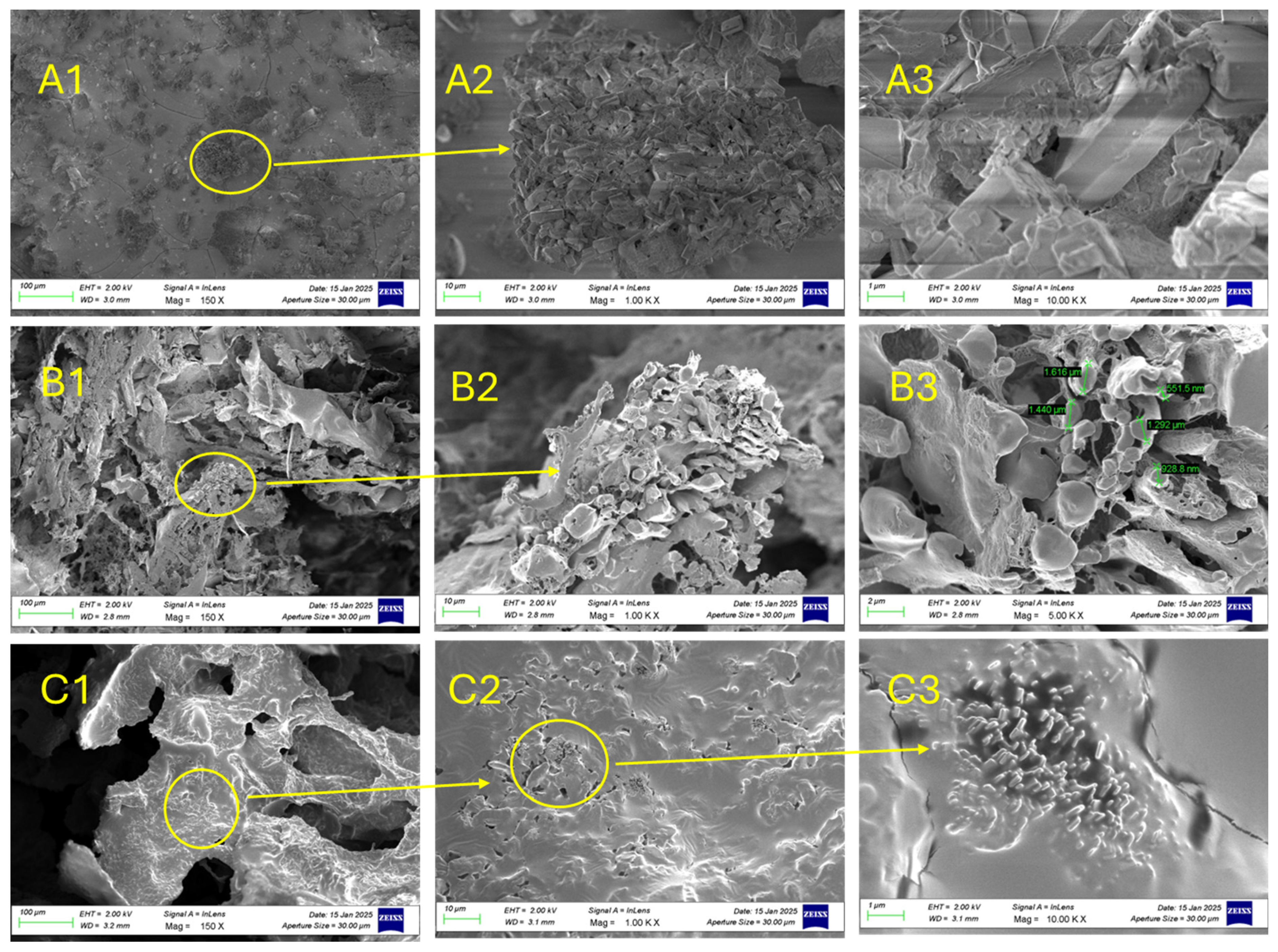
2.5. SEM Observations
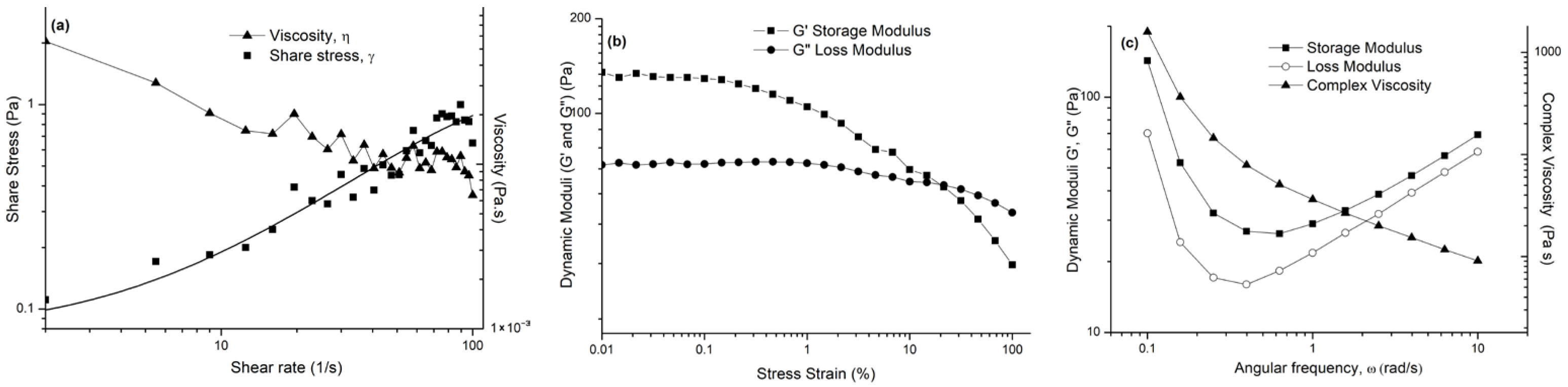
2.6. Rheological Behavior of the Prepared Semi-Solid Formulation
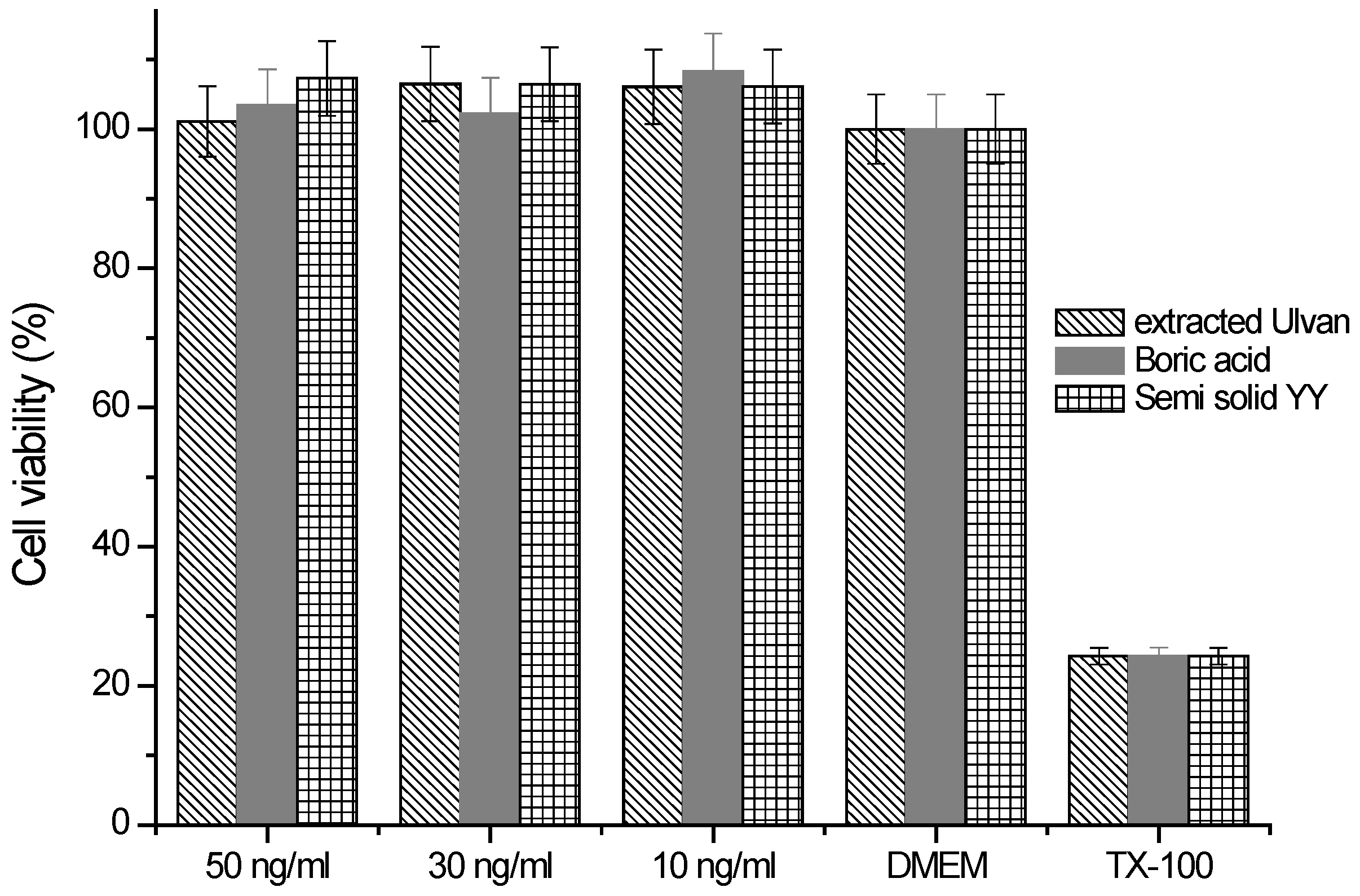
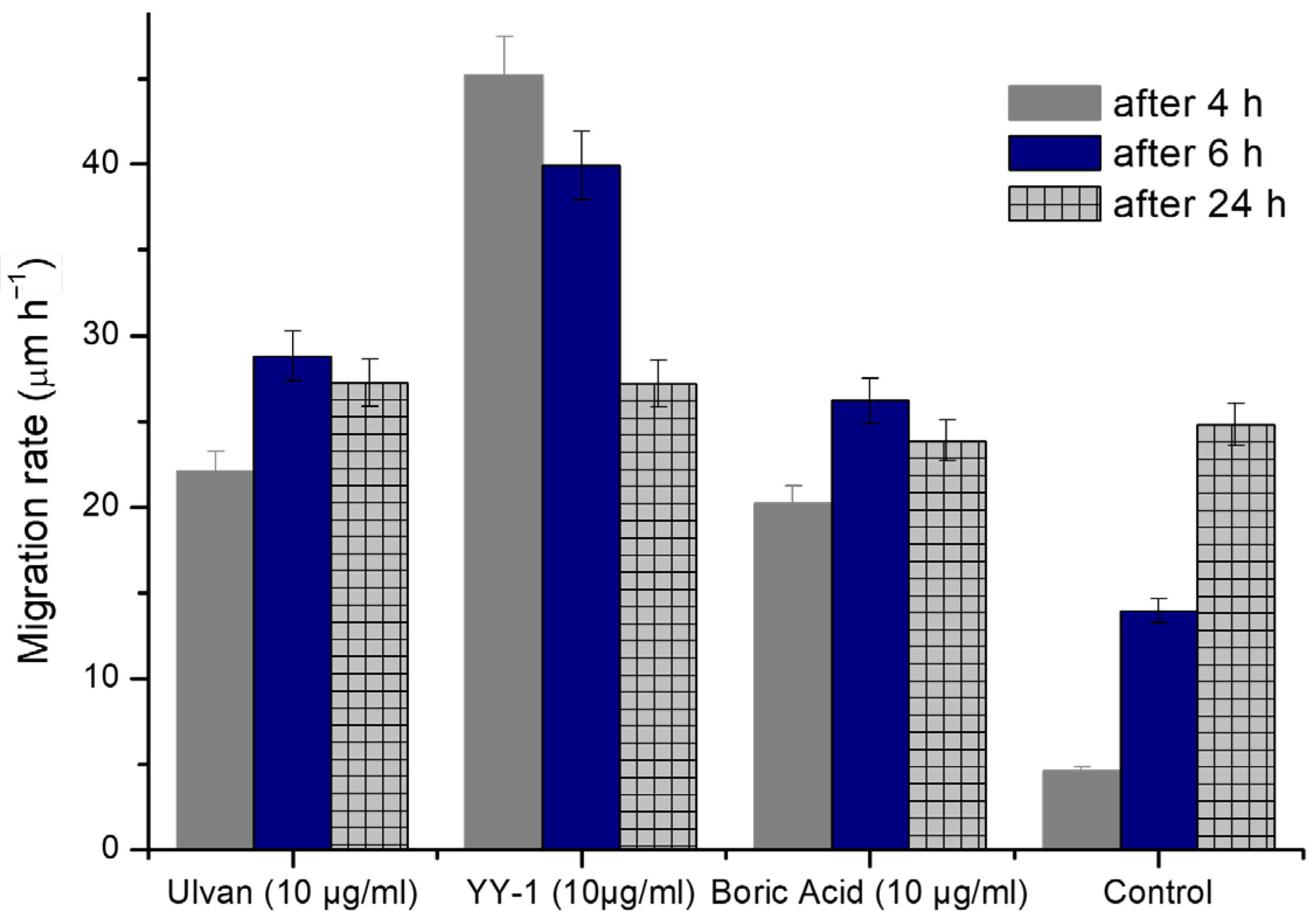
2.7. Cytotoxicity Assessment
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Reagents
4.2. Extraction of Ulvan
4.3. Preparation of Hydrogels
4.4. Characterization Methods
4.4.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) Analysis
4.4.2. Swelling Tests
4.4.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
4.4.4. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.4.5. Antioxidant Activity—DPPH and ABTS Analysis
4.4.6. Cell Viability Assay and Scratch Wound Healing Assay
4.5. Rheological Measurements
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boateng, J.S.; Matthews, K.H.; Stevens, H.N.; Eccleston, G.M. Wound healing dressings and drug delivery systems: A review. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 2892–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhivya, S.; Padma, V.V.; Santhini, E. Wound dressings—A review. BioMedicine 2015, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, E.M. Hydrogel: Preparation, characterization, and applications: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogoşanu, G.D.; Grumezescu, A.M. Natural and synthetic polymers for wounds and burns dressing. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 463, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamoun, E.A.; Kenawy, E.R.; Chen, X. A review on polymeric hydrogel membranes for wound dressing applications: PVA-based hydrogel dressings. J. Adv. Res. 2017, 8, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sood, A.; Granick, M.S.; Tomaselli, N.L. Wound dressings and comparative effectiveness data. Adv. Wound Care 2014, 3, 511–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Soratur, A.; Kumar, S.; Venmathi Maran, B.A. A review of marine algae as a sustainable source of antiviral and anticancer compounds. Macromol 2025, 5, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S. Therapeutic importance of sulfated polysaccharides from seaweeds: Updating the recent findings. 3 Biotech 2012, 2, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millotti, G.; Lagast, J.; Jurman, J.; Paliaga, P.; Laffleur, F. Ulvan as an underrated material for wound dressings: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 319, 145113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pari, R.F.; Uju, U.; Hardiningtyas, S.D.; Ramadhan, W.; Wakabayashi, R.; Goto, M.; Kamiya, N. Ulva seaweed-derived ulvan: A promising marine polysaccharide as a sustainable resource for biomaterial design. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnabosco, C.; Santaniello, G.; Romano, G. Microalgae: A promising source of bioactive polysaccharides for biotechnological applications. Molecules 2025, 30, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, J.; Reist, M.; Mayer, J.M.; Felt, O.; Gurny, R. Structure and interactions in chitosan hydrogels formed by complexation or aggregation for biomedical applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 57, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, M.N.; Birkinshaw, C. Hyaluronic acid based scaffolds for tissue engineering—A review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1262–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Alginate: Properties and biomedical applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 106–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, V.H.N.; Mikkelsen, M.D.; Truong, H.B.; Vo, H.N.M.; Pham, T.D.; Cao, H.T.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Meyer, A.S.; Thanh, T.T.T.; Van, T.T.T. Structural characterization and cytotoxic activity evaluation of ulvan polysaccharides extracted from the green algae Ulva papenfussii. Mar. Drugs 2023, 21, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidgell, J.T.; Carnachan, S.M.; Magnusson, M.; Lawton, R.J.; Sims, I.M.; Hinkley, S.F.R.; de Nys, R.; Glasson, C.R.K. Are all ulvans equal? A comparative assessment of the chemical and gelling properties of ulvan from blade and filamentous Ulva. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 264, 118010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tako, M.; Tamanaha, M.; Tamashiro, Y.; Uechi, S. Structure of ulvan isolated from the edible green seaweed, Ulva pertusa. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2015, 6, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, T.T.T.; Quach, T.M.T.; Nguyen, T.N.; Vu Luong, D.; Bui, M.L.; Van, T.T.T. Structure and cytotoxic activity of ulvan extracted from green seaweed Ulva lactuca. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabarsa, M.; You, S.G.; Dabaghian, E.H.; Surayot, U. Water-soluble polysaccharides from Ulva intestinalis: Molecular properties, structural elucidation and immunomodulatory activities. J. Food Drug Anal. 2018, 26, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, P.; Du, C.; Ye, H.; Zuo, S.; Guan, H.; Wang, P. Structural characterization of ulvan extracted from Ulva clathrata assisted by an ulvan lyase. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 229, 115497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, K.M.; Ismail, M.M.; Abou El Hassayeb, H.E.; El Sersy, N.A.; Elshobary, M.E. Chemical characterization and biological activities of ulvan extracted from Ulva fasciata (Chlorophyta). Rend. Fis. Acc. Lincei 2022, 33, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, R.; Piazzon, M.C.; Zarra, I.; Leiro, J.; Noya, M.; Lamas, J. Stimulation of turbot phagocytes by Ulva rigida C. Agardh polysaccharides. Aquaculture 2006, 254, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvasudha, S.; Viji, V.; Nagarajan, N. Seaweed-derived ulvan and alginate polysaccharides as food emulsifiers: Extraction, characterization and emulsification studies. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 6, 100555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulastri, M.R.; Wulandari, F.; Yusof, Y.A.; Rasyid, A. Development and characterization of ulvan extracted from green seaweed as a potential biomaterial for hydrogel. Polymers 2021, 13, 3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujalli, A.H.J.; Jubier, N.J. Thermal decomposition behavior and kinetic evaluation of chitosan/PEO blend films reinforced with Ag nanoparticles. J. Nanostruct. 2025, 15, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musa, M.T.; Shaari, N.; Kamarudin, S.K.; Wai Yin, W. Optimizing Sodium Alginate/PVA Polymer Electrolyte Membrane with Montmorillonite for Enhanced Architectural Features and Performance in DMFC Application. Arabian J. Sci. Eng. 2024, 49, 8099–8113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morelli, A.; Betti, M.; Puppi, D.; Chiellini, F. Design, preparation and characterization of ulvan based thermosensitive hydrogels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 136, 1108–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stan, D.; Mirica, A.-C.; Mocanu, S.; Stan, D.; Podolean, I.; Candu, N.; El Fergani, M.; Stefan, L.M.; Seciu-Grama, A.-M.; Aricov, L.; et al. Hybrid hydrogel supplemented with algal polysaccharide for potential use in biomedical applications. Gels 2025, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulastri, E.; Lesmana, R.; Zubair, M.S.; Elamin, K.M.; Wathoni, N. A comprehensive review on ulvan based hydrogel and its biomedical applications. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2021, 69, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. The study on antioxidant activity of ulvan-calcium derivative. J. Med. Plants Res. 2021, 15, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z. Antioxidant activities of natural polysaccharides and their applications. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 977495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floegel, A.; Kim, D.-O.; Chung, S.-J.; Koo, S.I.; Chun, O.K. Comparison of ABTS/DPPH assays to measure antioxidant capacity in popular antioxidant-rich US foods. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2011, 24, 1043–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y. The antioxidant activity of polysaccharides derived from marine organisms. Mar. Drugs 2019, 17, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gounden, V.; Singh, M. Hydrogels and wound healing: Current and future prospects. Gels 2024, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezger, T. The Rheology Handbook: For Users of Rotational and Oscillatory Rheometers; Vincentz Network: Hannover, Germany, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarentin, L.; Cardoso, C.; Miranda, M.; Vitorino, C. Rheology of Complex Topical Formulations: An Analytical Quality by Design Approach to Method Optimization and Validation. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calienni, M.N.; Martínez, L.M.; Izquierdo, M.C.; Alonso, S.d.V.; Montanari, J. Rheological and Viscoelastic Analysis of Hybrid Formulations for Topical Application. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Wan, Y.; Xu, H.; Zou, J.; Li, J.; Liang, S. Marine-derived polysaccharides in wound healing: Molecular mechanisms and biomedical applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 210, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, L.; Grenha, A. Sulfated polysaccharides as biomedical materials. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.; Caridade, S.G.; Mano, J.F.; Sousa, R.A. Marine polysaccharides in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: From structure to application. Polymers 2020, 12, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.; Critchley, A.T.; Neto, J.M. Ulvan-based hydrogels for biomedical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 181, 1196–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, W.-X.; Tang, S.; Chen, Y.; Lan, L.-M.; Li, S.; Xiong, M.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.-H.; Sun, J.; et al. A boron-based probe driven theranostic hydrogel dressing for visual monitoring and matching chronic wound healing. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2305580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, K.; Sivadasan, D.; Abderrahmen Al Weslati, M.; Gayasuddin Mouid, M.; Goyal, M.; Bansal, M.; Salama, M.E.-D.M.; Azizullah Ghori, S.; Ahmad, F. Protective effects of frankincense oil on wound healing: Downregulating caspase-3 expression to facilitate the transition from the inflammatory to proliferative phase. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, F.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, X. Alpha-boswellic acid accelerates acute wound healing via NF-κB signaling pathway. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0308028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Araby, E.; Raafat, A.; Elsonbaty, S. Radiation synthesis of psyllium/frankincense essential oil–based wound dressing hydrogels: Antimicrobial, antioxidant and wound healing performance. Arab J. Nucl. Sci. Appl. 2021, 54, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheaburu-Yilmaz, C.N.; Yilmaz, O.; Aydin Kose, F.; Bibire, N. Chitosan-Graft-Poly(N-Isopropylacrylamide)/PVA Cryogels as Carriers for Mucosal Delivery of Voriconazole. Polymers 2019, 11, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulcin, İ.; Alwasel, S.H. DPPH radical scavenging assay. Processes 2023, 11, 2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Property | UP6 (AA/PVA/Ulvan 35:30:35) | UP7 (PVA/Ulvan 80:20) |
|---|---|---|
| Swelling in PBS (max, %; mean ± SD) | 1700% (±5) | 1400% (±5) |
| ABTS inhibition @0.5 mg/mL (%) | 20.7 ± 1.2% | 40.3 ± 1.5% |
| DPPH inhibition @0.5 mg/mL (%) | 18.2 ± 1.1% | 42.1 ± 1.8% |
| DSC main transitions (°C) | 41; 223 | 50; 123; 226 |
| SEM (qualitative pore/connectivity) | Porous, Ulvan particles distributed partly homogeneously within the matrix | Less porous, Ulvan particles distributed homogeneously within the hydrogel matrix |
| Practical processing notes | The final formulation is not homogenous being present gel particles | Forms homogeneous a cream-textured material when mixed with the other actives |
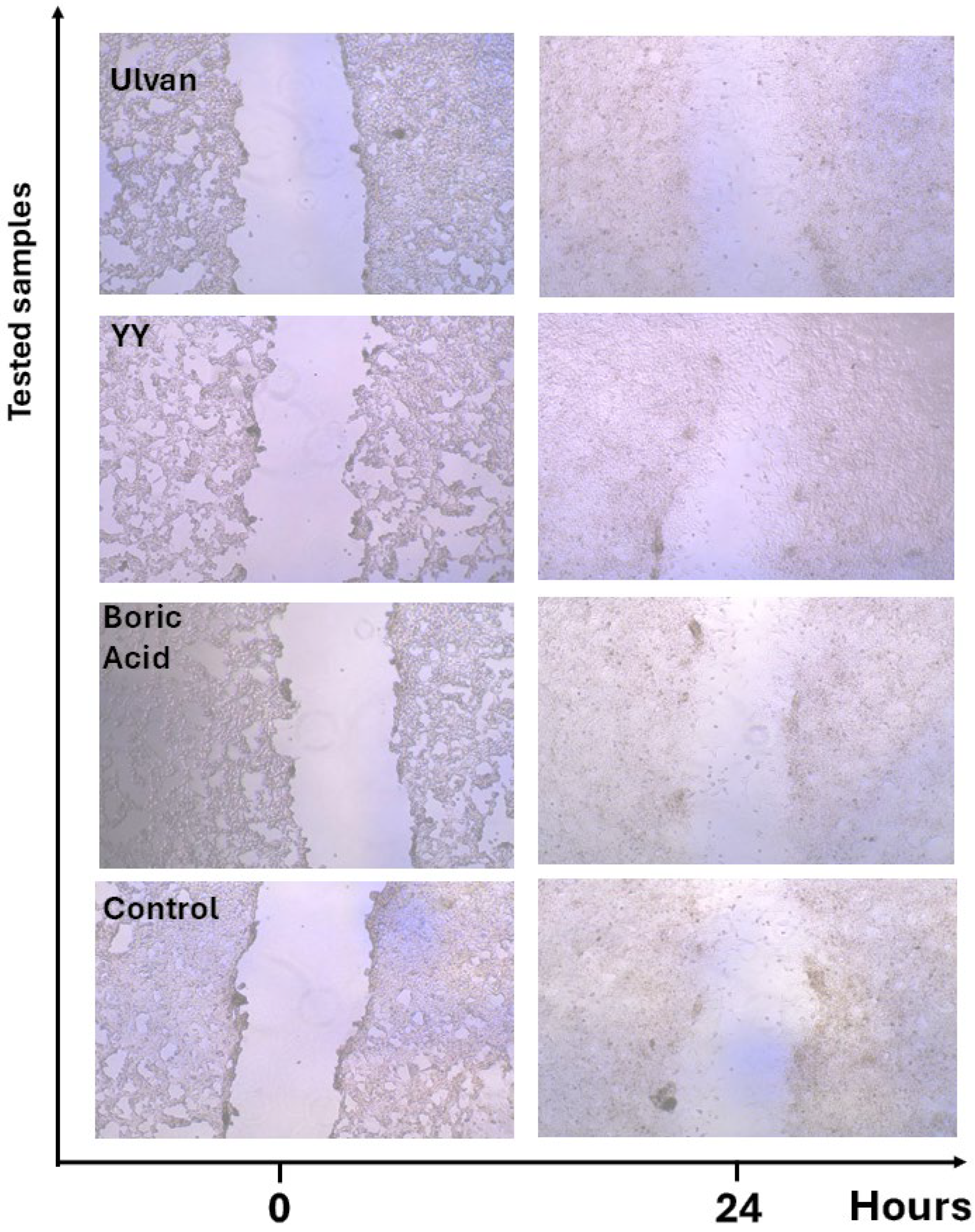
| RATE OF MIGRATION (µm/h) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Group | 4H | 6H | 24H |
| Ulvan (10 µg/mL) | 22.11 ± 1.5 | 28.79 ± 4.32 | 27.25 ± 4.09 |
| YY-1 (10 µg/mL) | 45.18 ± 6.78 | 39.92 ± 5.99 | 27.19 ± 4.08 |
| Boric Acid (10 µg/mL) | 20.20 ± 3.03 | 26.20 ± 3.93 | 23.86 ± 3.58 |
| Control | 4.59 ± 0.69 | 13.94 ± 2.09 | 24.80 ± 3.72 |
| Sample Code | Composition (wt%) | Solid Content (wt%) | Preparation Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| UP1 | HA/PVA/Ulvan (50:30:20) | 4 | Freeze–thaw, 2 cycles, 20 h at −20 °C and thawing for 4 h at RT followed by freeze-drying (lyophilization) to obtain white-like sponges to be tested for further characterization |
| UP2 | CS/PVA/Ulvan (50:30:20) | 4 | |
| UP3 | HA/PVA/Ulvan (35:30:35) | 4 | |
| UP4 | CS/PVA/Ulvan (35:30:35) | 4 | |
| UP5 | AA/PVA/Ulvan (50:30:20) | 4 | |
| UP6 | AA/PVA/Ulvan (35:30:35) | 4 | |
| UP7 | PVA/Ulvan (80:20) | 4 | |
| Semi-solid YY | Semi-solid formulation prepared by mixing Ulvan-based biopolymer (UP 7) with other ingredients such as UP7 4.5%; Boric acid 2.3%; ZnO 3.4%; CMC 1.2%; FE 0.5%; B 0.5%; and water 88 w/w. | 10 | The formulation was prepared by mechanical stirring by using an overhead mechanical stirrer with a speed between 200 and 800 rpm. After homogenizing and obtaining cream-like material for analysis purposes some part of the sample was lyophilized. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheaburu Yilmaz, C.N.; Yildirim, M.S.; Govem, D.; Ayar Kayali, H.; Yilmaz, O. Development and Characterization of a Wound-Healing System Based on a Marine Biopolymer. Gels 2025, 11, 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11110881
Cheaburu Yilmaz CN, Yildirim MS, Govem D, Ayar Kayali H, Yilmaz O. Development and Characterization of a Wound-Healing System Based on a Marine Biopolymer. Gels. 2025; 11(11):881. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11110881
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheaburu Yilmaz, Catalina Natalia, Melisa Sirin Yildirim, Defne Govem, Hulya Ayar Kayali, and Onur Yilmaz. 2025. "Development and Characterization of a Wound-Healing System Based on a Marine Biopolymer" Gels 11, no. 11: 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11110881
APA StyleCheaburu Yilmaz, C. N., Yildirim, M. S., Govem, D., Ayar Kayali, H., & Yilmaz, O. (2025). Development and Characterization of a Wound-Healing System Based on a Marine Biopolymer. Gels, 11(11), 881. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11110881







