Update on the Research of an Emulgel for the Effective Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis: Clinical Investigation in Children
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
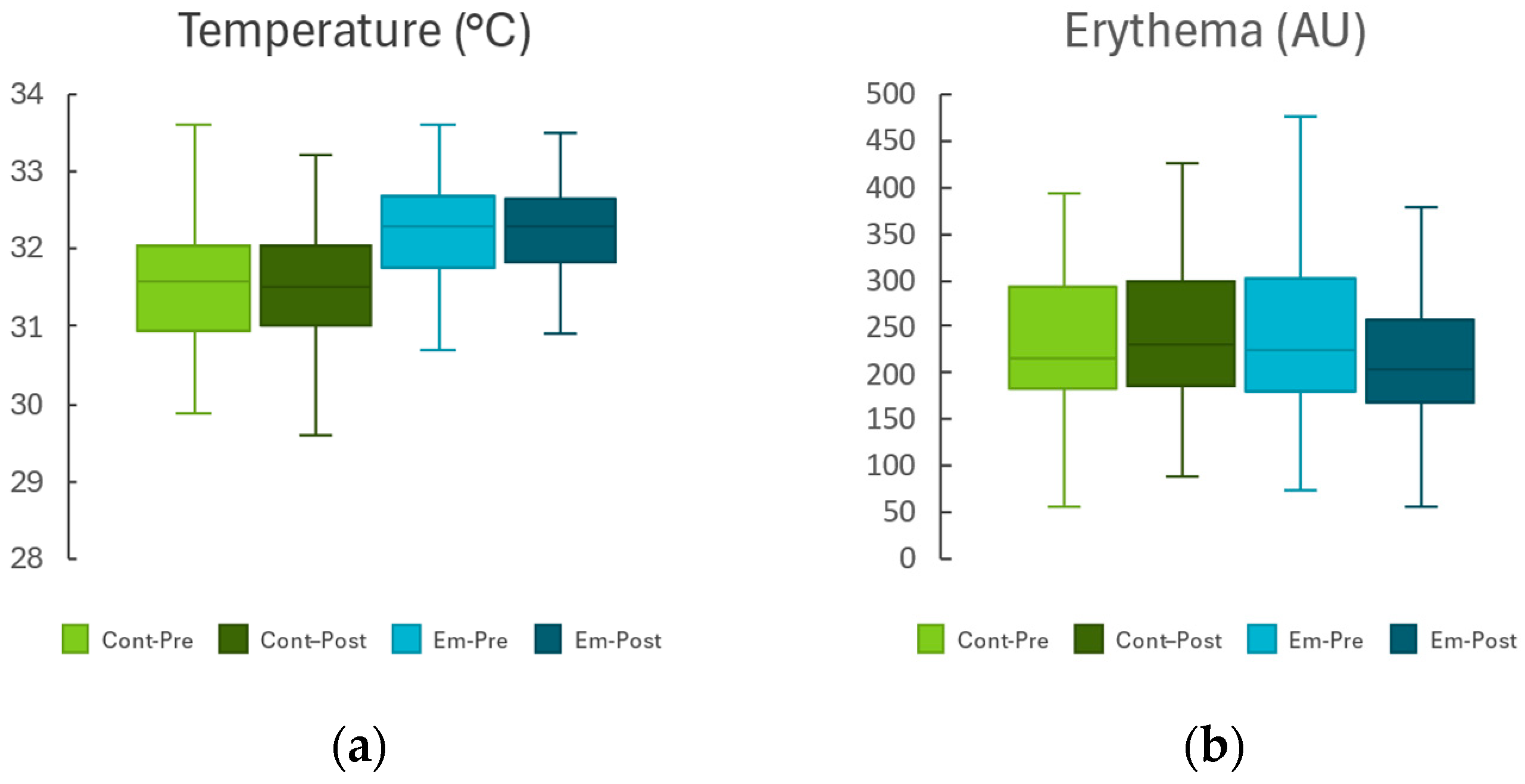
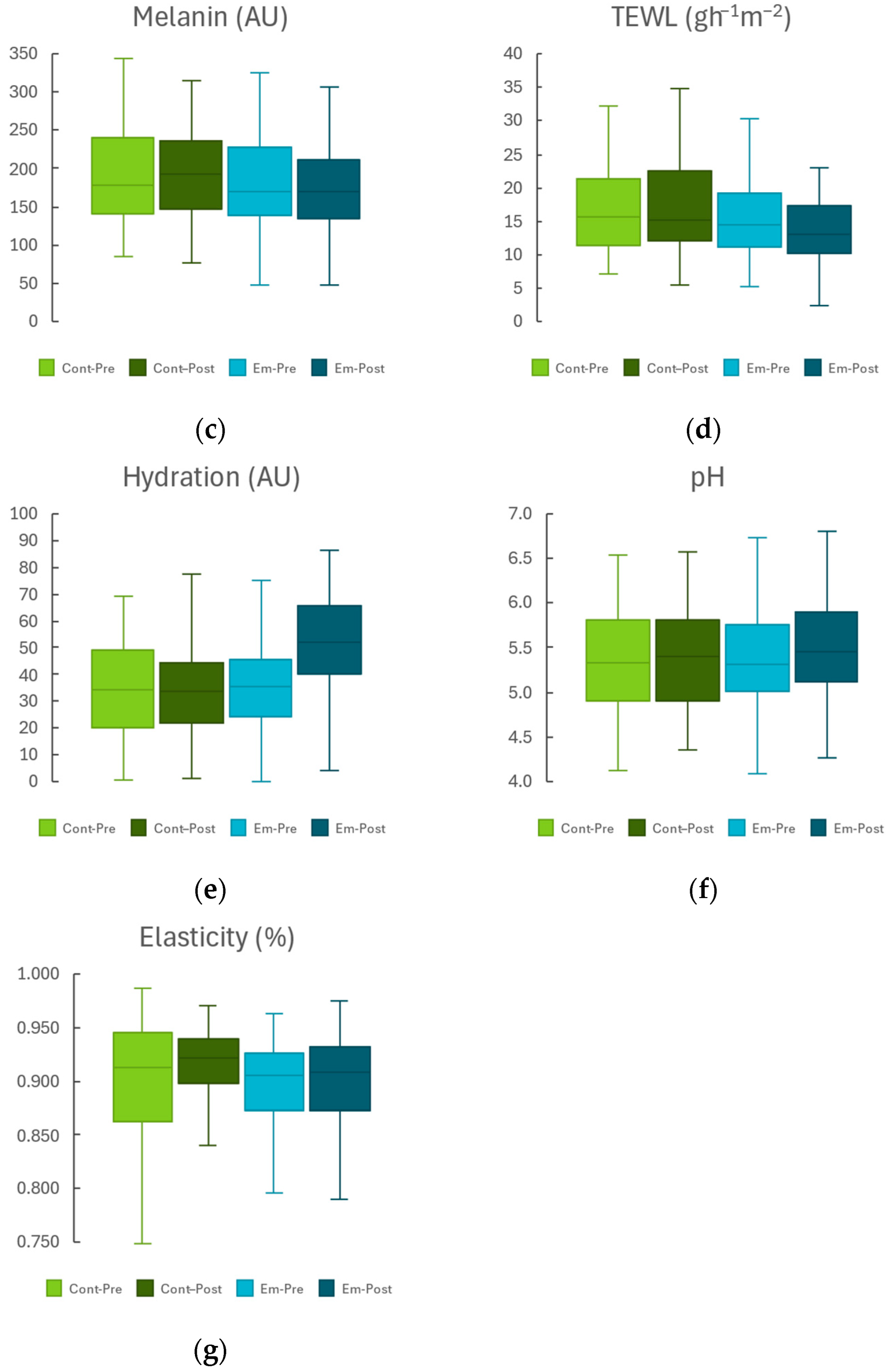
2.1. Non-Lesional Skin Area
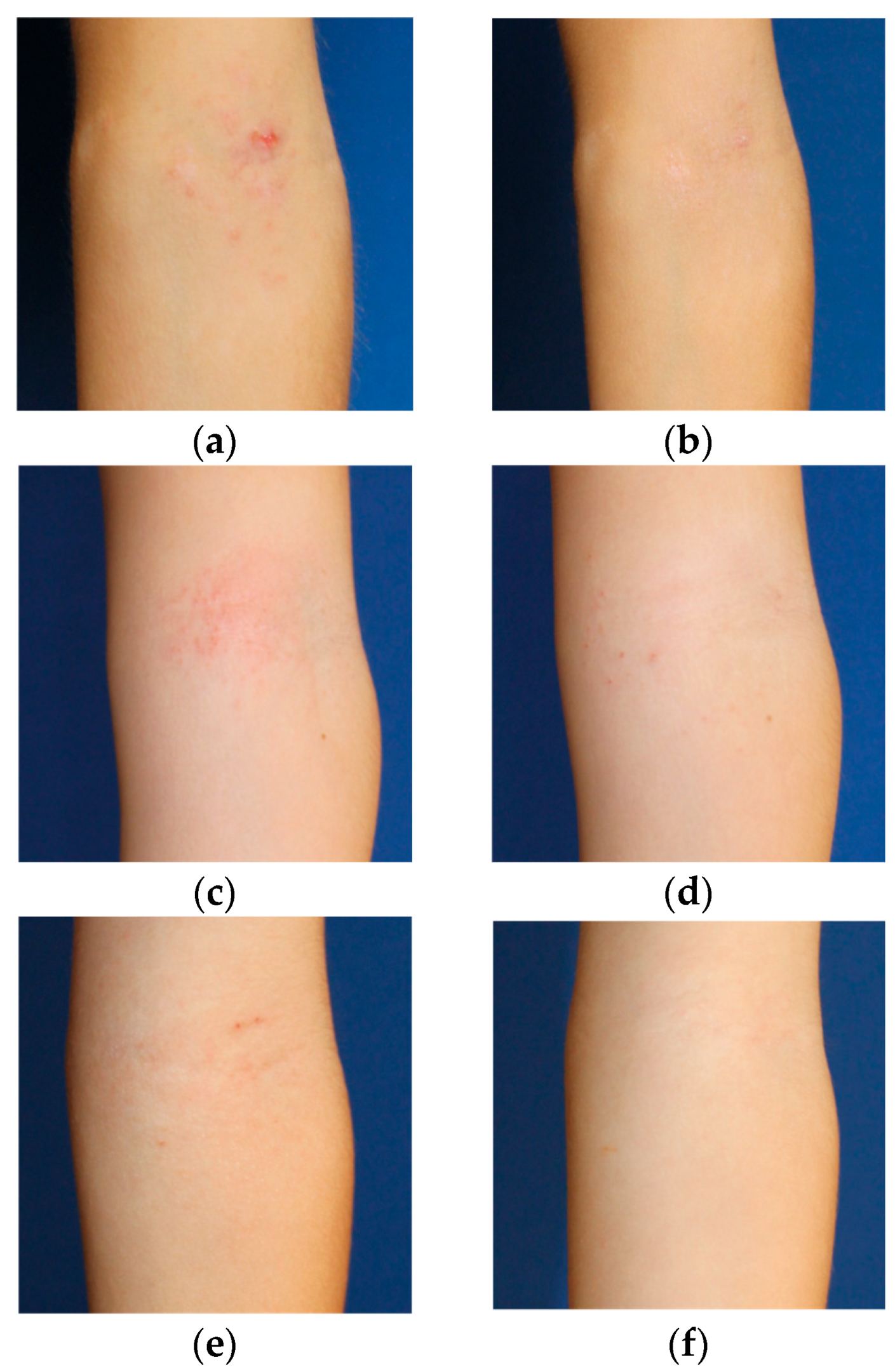
2.2. Lesional Skin Area
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Emulgel Characteristics
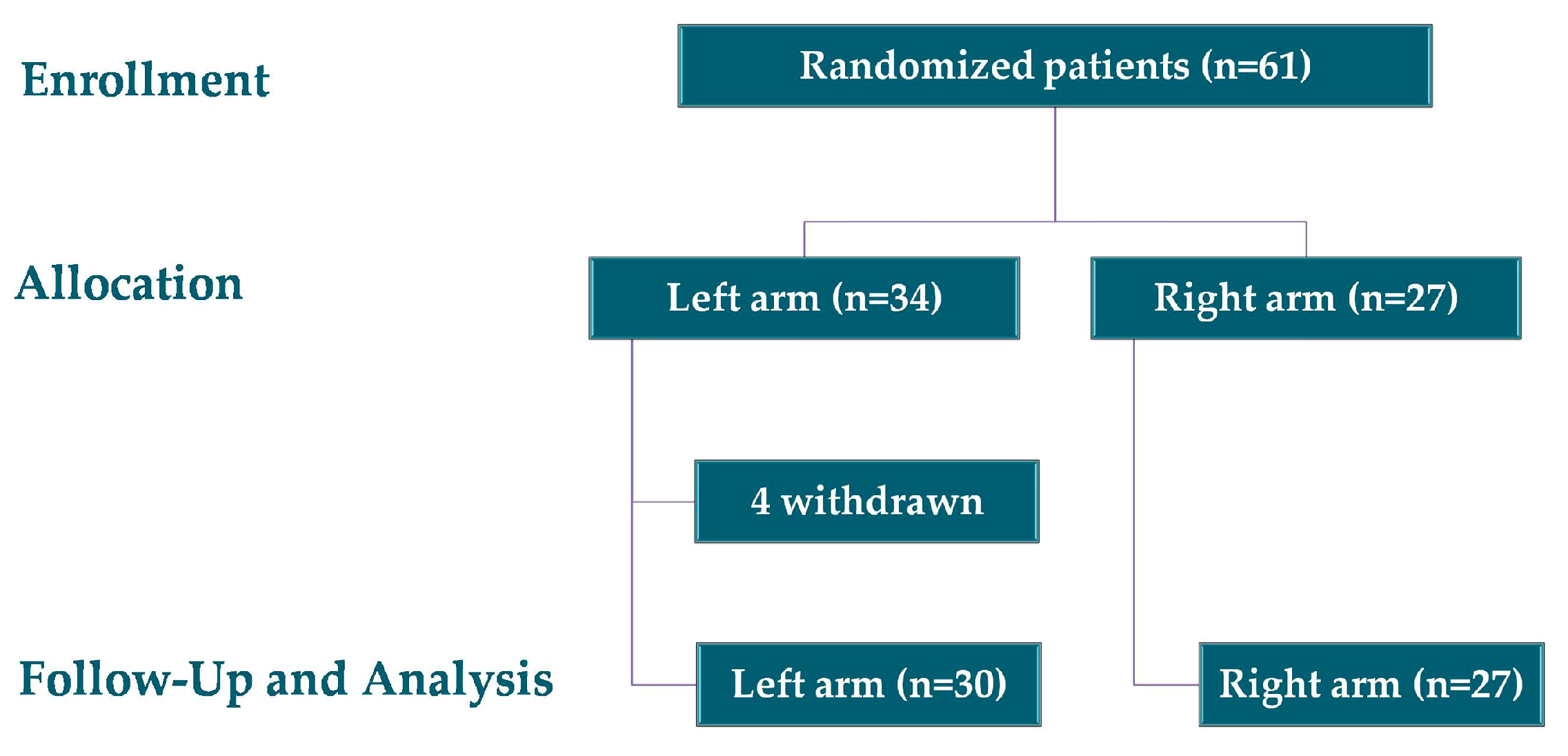
4.2. Study Design
- Children aged 2 to 14 years diagnosed with AD by a dermatologist according to Hanifin and Rajka criteria, with a disease duration of at least six months.
- Patients who had attended the AD clinic at the Dermatology Department of Hospital Universitario Virgen de las Nieves.
- Presence of any clinical infection in the area designated for measurement.
- History of cancer or immunosuppression.
- Coexisting inflammatory skin conditions such as psoriasis or hidradenitis suppurativa.
4.3. Sociodemographic Variables
4.4. Skin Barrier Function
- Skin temperature, which reflects changes in microcirculation and tends to rise in cases of barrier dysfunction [42].
- Melanin and erythema index, which are associated with skin exposure to irritants, allergens, or UV radiation [43].
- Transepidermal Water Loss (TEWL), which is an indicator of water diffusion through the stratum corneum, with increased values reflecting impaired barrier function [44].
- Skin surface pH, which is important for lipid organisation and metabolism within the stratum corneum [14].
- Skin elasticity, which reflects the condition of dermal elastic fibres [46].
4.5. Severity and Quality of Life
4.6. User Perception Assessment
4.7. Statistical Analyses
4.8. Ethical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Atopic Dermatitis |
| TEWL | Transepidermal water loss |
| SCH | Stratum corneum hydration |
| SCORAD | SCORing Atopic Dermatitis |
| EASI | Eczema Area and Severity Index |
References
- Wang, Y.; Yue, Y.; Jia, R.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xie, Z.; Xia, H. Design and Evaluation of Paeonol-Loaded Liposomes in Thermoreversible Gels for Atopic Dermatitis. Gels 2023, 9, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharwade, R.; Ali, N.; Gangane, P.; Pawar, K.; More, S.; Iqbal, M.; Bhat, A.R.; AlAsmari, A.F.; Kaleem, M. DOE-Assisted Formulation, Optimization, and Characterization of Tioconazole-Loaded Transferosomal Hydrogel for the Effective Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis: In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation. Gels 2023, 9, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savva, M.; Papadopoulos, N.G.; Gregoriou, S.; Katsarou, S.; Papapostolou, N.; Makris, M.; Xepapadaki, P. Recent Advancements in the Atopic Dermatitis Mechanism. Front. Biosci. 2024, 29, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Marín, H.A.; Silverberg, J.I. Differences between pediatric and adult atopic dermatitis. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2022, 39, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.R.; Sandhu, V.K.; Drucker, A.M.; Fleming, P.; Lynde, C.W. Adult-Onset Atopic Dermatitis: Presentations and Progress. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2020, 24, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, A.Y.; Høj, S.; Thomsen, S.F.; Meteran, H. Vitamin D Supplementation for Treating Atopic Dermatitis in Children and Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Ion, A.; Orzan, O.A.; Bălăceanu-Gurău, B. Emerging Treatments and New Vehicle Formulations for Atopic Dermatitis. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollefson, M.M.; Bruckner, A.L.; Section On Dermatology; Cohen, B.A.; Antaya, R.; Bruckner, A.; Horii, K.; Silverberg, N.B.; Wright, T. Atopic Dermatitis: Skin-Directed Management. Pediatrics 2014, 134, e1735–e1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, N.K. ʟ-Histidine Supplementation in Adults and Young Children with Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema). J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 2576S–2579S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, P.P. Recent insights into the management of treatment-resistant pediatric atopic dermatitis. Int. J. Women’s Dermatol. 2022, 8, e023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavkova, M.; Lazov, C.; Spassova, I.; Kovacheva, D.; Tibi, I.P.-E.; Stefanova, D.; Tzankova, V.; Petrov, P.D.; Yoncheva, K. Formulation of Budesonide-Loaded Polymeric Nanoparticles into Hydrogels for Local Therapy of Atopic Dermatitis. Gels 2024, 10, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero-Vilchez, T.; Segura-Fernández-Nogueras, M.-V.; Pérez-Rodríguez, I.; Soler-Gongora, M.; Martinez-Lopez, A.; Fernández-González, A.; Molina-Leyva, A.; Arias-Santiago, S. Skin Barrier Function in Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis: Transepidermal Water Loss and Temperature as Useful Tools to Assess Disease Severity. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubel, D.; Thirumoorthy, T.; Soebaryo, R.W.; Weng, S.C.K.; Gabriel, T.M.; Villafuerte, L.L.; Chu, C.-Y.; Dhar, S.; Parikh, D.; Wong, L.-C.; et al. Consensus guidelines for the management of atopic dermatitis: An Asia–Pacific perspective. J. Dermatol. 2013, 40, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Farto, A.; Jiménez-Escobar, A.L.; Pérez-González, N.; Castán, H.; Clares, B.; Arias-Santiago, S.; Montero-Vílchez, T. Development of an Emulgel for the Effective Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis: Biocompatibility and Clinical Investigation. Gels 2024, 10, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chylińska, N.; Maciejczyk, M. Hyaluronic Acid and Skin: Its Role in Aging and Wound-Healing Processes. Gels 2025, 11, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagrafena, I.; Morin, M.; Paraskevopoulos, G.; Nilsson, E.J.; Hrdinová, I.; Kováčik, A.; Björklund, S.; Vávrová, K. Structure and function of skin barrier lipids: Effects of hydration and natural moisturizers in vitro. Biophys. J. 2024, 123, 3951–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Korponyai, C.; Szél, E.; Behány, Z.; Varga, E.; Mohos, G.; Dura, Á.; Dikstein, S.; Kemény, L.; Erős, G. Effects of Locally Applied Glycerol and Xylitol on the Hydration, Barrier Function and Morphological Parameters of the Skin. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2017, 97, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdier-Sévrain, S.; Bonté, F. Skin hydration: A review on its molecular mechanisms. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2007, 6, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawawi, N.A.; Ahmad, H.; Madatheri, R.; Fadilah, N.I.M.; Maarof, M.; Fauzi, M.B. Flavonoids as Natural Anti-Inflammatory Agents in the Atopic Dermatitis Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2025, 17, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivero-Verbel, J.; Quintero-Rincón, P.; Caballero-Gallardo, K. Aromatic plants as cosmeceuticals: Benefits and applications for skin health. Planta 2024, 260, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shahane, K.; Kshirsagar, M.; Tambe, S.; Jain, D.; Rout, S.; Ferreira, M.K.M.; Mali, S.; Amin, P.; Srivastav, P.P.; Cruz, J.; et al. An Updated Review on the Multifaceted Therapeutic Potential of Calendula officinalis L. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sánchez, M.; González-Burgos, E.; Iglesias, I.; Gómez-Serranillos, M.P. Pharmacological Update Properties of Aloe Vera and its Major Active Constituents. Molecules 2020, 25, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Shin, S.H.; Koh, Y.G.; Lee, W.G.; Seok, J.; Park, K.Y. The use of epidermal growth factor in dermatological practice. Int. Wound J. 2023, 20, 2414–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panther, D.J.; Jacob, S.E. The Importance of Acidification in Atopic Eczema: An Underexplored Avenue for Treatment. J. Clin. Med. 2015, 4, 970–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Schmid-Wendtner, M.H.; Korting, H.C. The pH of the skin surface and its impact on the barrier function. Ski. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2006, 19, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, M.K.; Orłowska, S.M.; Bednarczyk, Ł. Applied Research on Atopic Dermatitis with Special Emphasis on the Role of Emollients in This Disorder: A Review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hon, K.L.; Kung, J.S.C.; Ng, W.G.G.; Leung, T.F. Emollient treatment of atopic dermatitis: Latest evidence and clinical considerations. Drugs Context 2018, 7, 212530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Prakoeswa, C.R.S.; Damayanti; Anggraeni, S.; Umborowati, M.A.; Sari, M.; Hendaria, M.P.; Thahir, T.F. The Role of Moisturizer Containing Anti-inflammatory on Skin Hydration in Mild-Moderate Atopic Dermatitis Patients. Dermatol. Res. Pract. 2024, 2024, 3586393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Grimalt, R.; Mengeaud, V.; Cambazard, F. The steroid-sparing effect of an emollient therapy in infants with atopic dermatitis: A randomized controlled study. Dermatology 2007, 214, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basra, M.K.; Salek, M.S.; Camilleri, L.; Sturkey, R.; Finlay, A.Y. Determining the minimal clinically important difference and responsiveness of the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI): Further data. Dermatology 2015, 230, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenninkmeijer, E.E.; Legierse, C.M.; Sillevis Smitt, J.H.; Last, B.F.; Grootenhuis, M.A.; Bos, J.D. The course of life of patients with childhood atopic dermatitis. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2009, 26, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery, M.J.; Essex, M.J.; Paletz, E.M.; Vanness, E.R.; Infante, M.; Rogers, G.M.; Gern, J.E. Depression, anxiety, and dermatologic quality of life in adolescents with atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 668–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelsay, K. Management of sleep disturbance associated with atopic dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Shobaili, H.A. The impact of childhood atopic dermatitis on the patients’ family. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2010, 27, 618–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.; Almeida, I.F. Patient-Centric Design of Topical Dermatological Medicines. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaux, S.; Castela, A.; Archier, E.; Gallini, A.; Joly, P.; Misery, L.; Aractingi, S.; Aubin, F.; Bachelez, H.; Cribier, B.; et al. Adherence to topical treatment in psoriasis: A systematic literature review. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2012, 26 (Suppl. 3), 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cork, M.J.; Danby, S. Skin barrier breakdown: A renaissance in emollient therapy. Br. J. Nurs. 2009, 18, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, S.W.; Jamil, A.; Safian, N.; Nor, N.; Muhammad, N.; Saharudin, N.L. A randomized half-body, double blind, controlled trial on the effects of a pH-modified moisturizer vs. standard moisturizer in mild to moderate atopic dermatitis. Bras. Dermatol. 2020, 95, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatas, G.N.; Nikolovski, J.; Mack, M.C.; Kollias, N. Infant skin physiology and development during the first years of life: A review of recent findings based on in vivo studies. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2011, 33, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douladiris, N.; Vakirlis, E.; Vassilopoulou, E. Atopic Dermatitis and Water: Is There an Optimum Water Intake Level for Improving Atopic Skin? Children 2023, 10, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 17516:2014; Cosmetics—Microbiology—Microbiological Limits. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014.
- Gonzalez-Bravo, A.; Montero-Vilchez, T.; Arias-Santiago, S.; Buendia-Eisman, A. The Effect of Sunscreens on the Skin Barrier. Life 2022, 12, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosrowpour, Z.; Ahmad Nasrollahi, S.; Ayatollahi, A.; Samadi, A.; Firooz, A. Effects of four soaps on skin trans-epidermal water loss and erythema index. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2019, 18, 857–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akdeniz, M.; Gabriel, S.; Lichterfeld-Kottner, A.; Blume-Peytavi, U.; Kottner, J. Transepidermal water loss in healthy adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis update. Br. J. Dermatol. 2018, 179, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montero-Vilchez, T.; Soler-Góngora, M.; Martínez-López, A.; Ana, F.; Buendía-Eisman, A.; Molina-Leyva, A.; Arias-Santiago, S. Epidermal barrier changes in patients with psoriasis: The role of phototherapy. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2021, 37, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pullar, J.M.; Carr, A.C.; Vissers, M.C.M. The Roles of Vitamin C in Skin Health. Nutrients 2017, 9, 866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 14155:2020; Clinical Investigation of Medical Devices for Human Subjects—Good Clinical Practice. Standarization IOf: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020.


| Characteristics | Mean/No. (n = 57) | % |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 6.72 ± 3.82 | |
| Sex | ||
| Women | 34 | 59.6 |
| Men | 23 | 40.4 |
| Phototype | ||
| I | 10 | 17.5 |
| II | 25 | 43.9 |
| III | 19 | 33.3 |
| IV | 1 | 1.8 |
| V | 1 | 1.8 |
| VI | 1 | 1.8 |
| Sun exposure | ||
| Frequently | 14 | 24.6 |
| Occasionally | 39 | 68.4 |
| Never | 4 | 7.0 |
| Frequency of moisturiser use | ||
| Several times a day | 13 | 22.8 |
| Rarely | 3 | 5.3 |
| Once a day | 29 | 50.9 |
| Sometimes | 9 | 15.8 |
| Never | 3 | 5.3 |
| Treatment | ||
| None | 25 | 43.9 |
| Topical | 25 | 43.9 |
| Cyclosporine | 3 | 5.3 |
| Biological | 4 | 7.0 |
| Comorbidities | ||
| Asthma | 13 | 22.8 |
| Allergies | 17 | 29.8 |
| Prurigo nodularis | 0 | 0 |
| Rhinitis | 2 | 3.5 |
| Conjunctivitis | 2 | 3.5 |
| Contact dermatitis | 4 | 7.0 |
| Diaper dermatitis | 1 | 1.8 |
| Homeostasis Parameter | Non-Lesional Skin | ||||
| Control Forearm | Emulgel-Treated Forearm | p * | |||
| ΔBefore/After | p 1 | ΔBefore/After | p 2 | ||
| Temperature (°C) | −0.14 ± 0.14 | 0.298 | −0.19 ± 0.14 | 0.193 | 0.693 |
| Erythema (AU) | −0.19 ± 5.24 | 0.971 | −0.66 ± 5.42 | 0.903 | 0.941 |
| TEWL (g·m−2·h−1) | −1.21 ± 0.78 | 0.128 | −1.64 ± 0.83 | 0.053 | 0.412 |
| SCH (AU) | −2.18 ± 1.53 | 0.159 | 10.13 ± 1.31 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| pH | −0.02 ± 0.09 | 0.839 | −0.03 ± 0.08 | 0.722 | 0.820 |
| Elasticity (%) | −0.001 ± 0.008 | 0.883 | −0.006 ± 0.006 | 0.300 | 0.587 |
| Homeostasis Parameter | Lesional Skin | ||||
| Control Forearm | Emulgel-Treated Forearm | p * | |||
| ΔBefore/After | p 1 | ΔBefore/After | p 2 | ||
| Temperature (°C) | −0.02 ± 0.13 | 0.857 | −0.05 ± 0.12 | 0.667 | 0.781 |
| Erythema (AU) | 5.43 ± 8.86 | 0.542 | −26.48 ± 9.38 | 0.007 | 0.002 |
| TEWL (g·m−2·h−1) | −1.99 ± 0.97 | 0.045 | −5.59 ± 1.69 | 0.002 | 0.021 |
| SCH (AU) | 0.90 ± 2.06 | 0.665 | 17.44 ± 2.14 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| pH | −0.01 ± 0.08 | 0.930 | 0.10 ± 0.07 | 0.151 | 0.020 |
| Elasticity (%) | 0.006 ± 0.009 | 0.497 | −0.004 ± 0.008 | 0.562 | 0.295 |
| Before Treatment n = 57 (%) | After Treatment n = 57 (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| SCORAD | Mild | 37 (64.9%) | 46 (80.7%) |
| Moderate | 14 (24.6%) | 9 (15.8%) | |
| Severe | 6 (10.5%) | 2 (3.5%) | |
| EASI | Mild | 47 (82.5%) | 53 (93.0%) |
| Moderate | 10 (17.5%) | 4 (7.0%) | |
| Severe | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gómez-Farto, A.; Jiménez-Escobar, A.L.; Pérez-González, N.; Lozano-White, A.; Expósito-Herrera, J.; Montero-Vílchez, T.; Clares, B.; Arias-Santiago, S. Update on the Research of an Emulgel for the Effective Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis: Clinical Investigation in Children. Gels 2025, 11, 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11110880
Gómez-Farto A, Jiménez-Escobar AL, Pérez-González N, Lozano-White A, Expósito-Herrera J, Montero-Vílchez T, Clares B, Arias-Santiago S. Update on the Research of an Emulgel for the Effective Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis: Clinical Investigation in Children. Gels. 2025; 11(11):880. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11110880
Chicago/Turabian StyleGómez-Farto, Almudena, Ana Leticia Jiménez-Escobar, Noelia Pérez-González, Amy Lozano-White, Jésica Expósito-Herrera, Trinidad Montero-Vílchez, Beatriz Clares, and Salvador Arias-Santiago. 2025. "Update on the Research of an Emulgel for the Effective Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis: Clinical Investigation in Children" Gels 11, no. 11: 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11110880
APA StyleGómez-Farto, A., Jiménez-Escobar, A. L., Pérez-González, N., Lozano-White, A., Expósito-Herrera, J., Montero-Vílchez, T., Clares, B., & Arias-Santiago, S. (2025). Update on the Research of an Emulgel for the Effective Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis: Clinical Investigation in Children. Gels, 11(11), 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11110880








