Recent Advances in Dielectric Elastomer Actuator-Based Soft Robots: Classification, Applications, and Future Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Factors Influencing the Performance of Dielectric Elastomer Films
2.1. Effect of Actuating Voltage on the Performance of DEAs
2.2. Effect of Actuating Frequency on the Performance of DEAs
2.3. Effect of Pre-Stretching on the Performance of DEAs
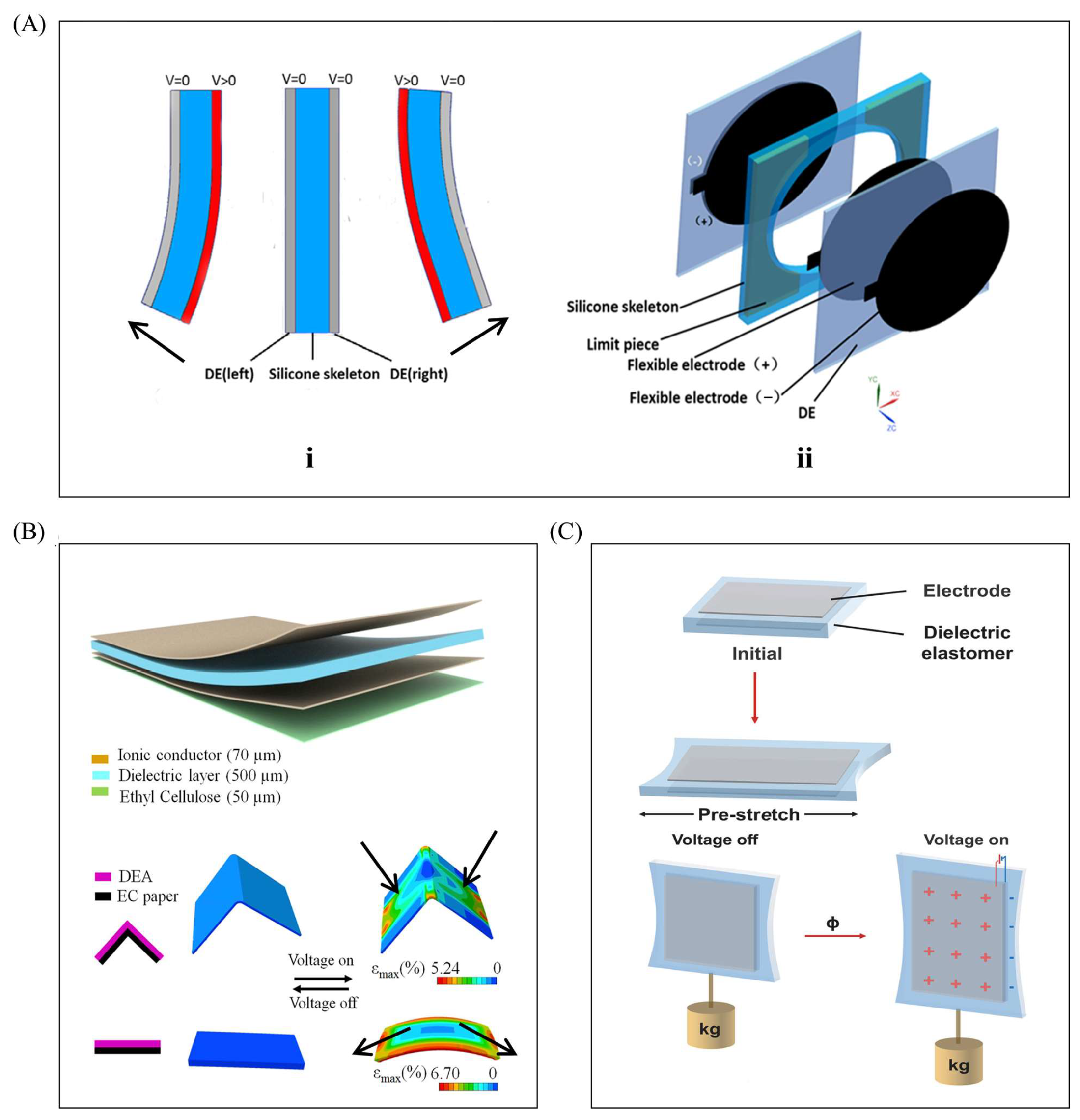
3. Planar DEAs
3.1. Working Principle of Planar DEAs
3.2. Robots Based on Planar DEAs
4. Saddle-Shaped DEAs
4.1. Working Principle of Saddle-Shaped DEAs
4.2. Robots Based on Saddle-Shaped DEAs

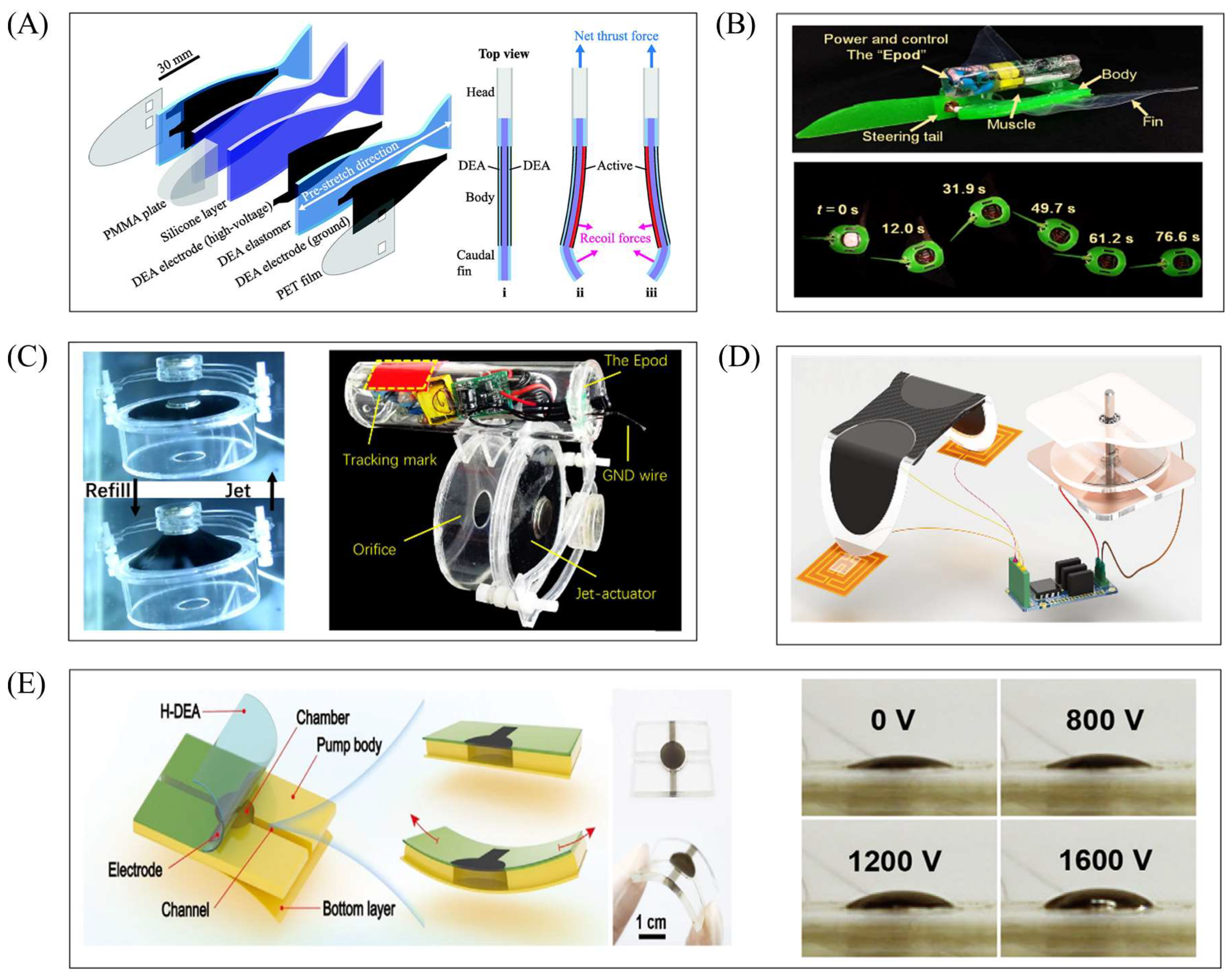
5. Cylindrical DEAs
5.1. Working Principle of Cylindrical DEAs
5.2. Robots Based on Axially Elongating Cylindrical DEAs

5.3. Robots Based on Bending–Oscillating Cylindrical DEAs
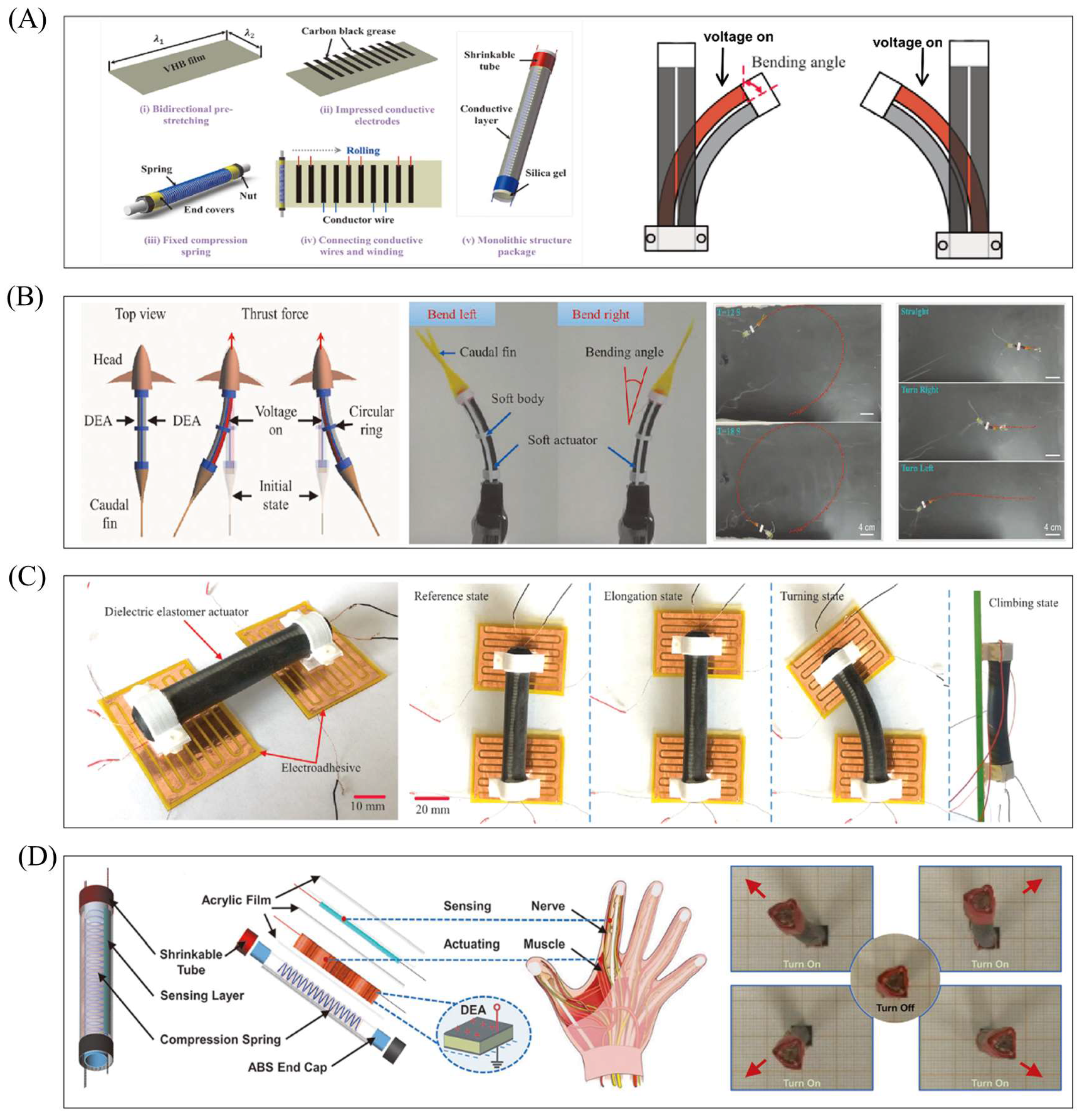
6. Conical DEAs
6.1. Working Principle of Conical DEAs
6.2. Robots Based on Conical DEAs
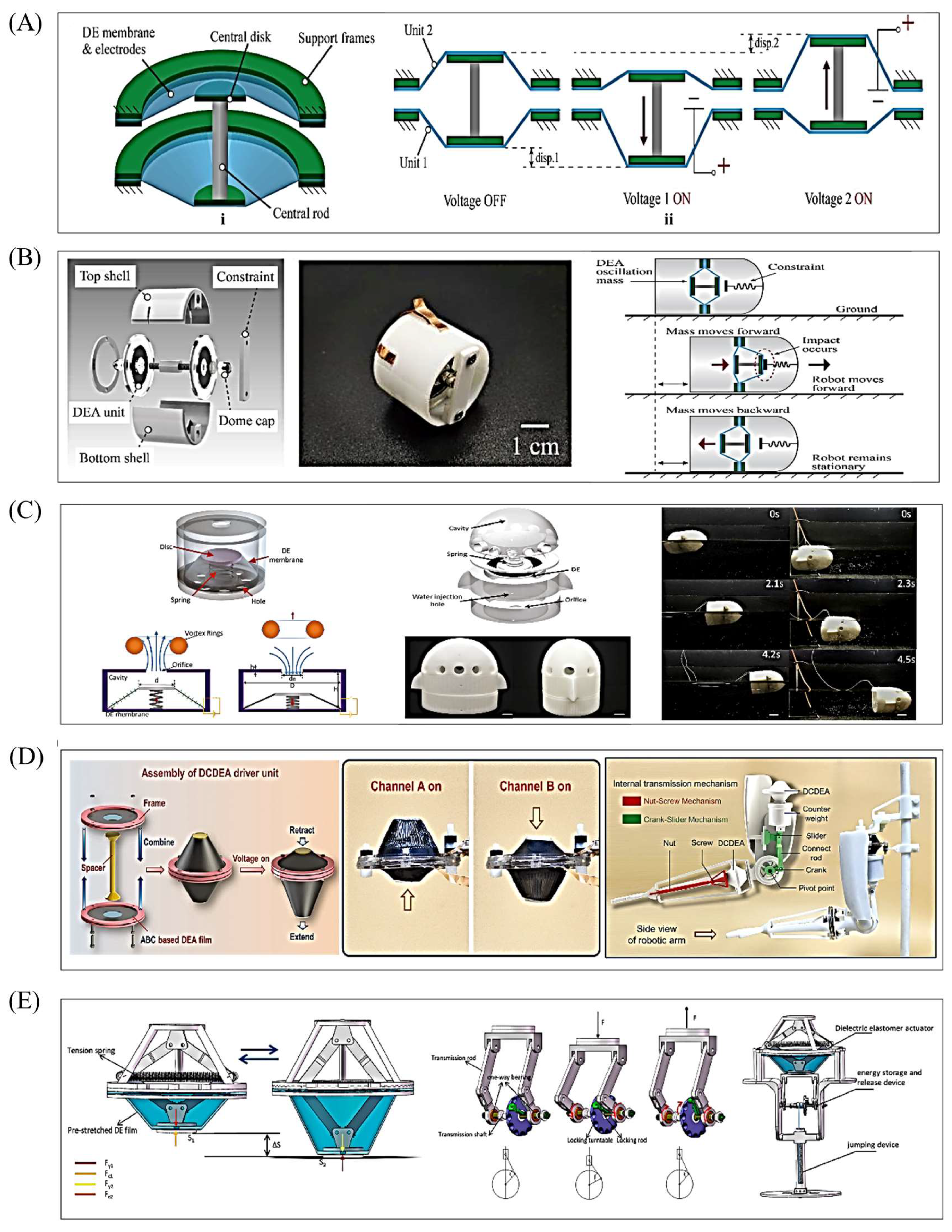
7. Design of Underwater and Terrestrial Robots Based on the Four Types of DEAs
7.1. Underwater DE Robots
7.2. Terrestrial DE Robots
8. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, C.; Yao, K.; Zong, Y.; Ye, J.; Chen, J. Rigid-Body Guidance Synthesis of Noncircular Gear-Five-Bar Mechanisms and Its Application in a Knee Joint Rehabilitation Device. Machines 2022, 10, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Gu, H. Backlash Elimination Control for Robotic Joints with Dual–Motor Drive. Actuators 2024, 13, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Kim, M.; Park, D.; Cheong, J. Control of a worm-wheel gear driven rescue robot with friction compensation and its experimental verification. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2023, 15, 16878132231191031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakilinejad, M.; Olabi, A.; Gibaru, O. Identification and Compensation of periodic gear transmission errors in Robot Manipulators. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Melbourne, Australia, 13–15 February 2019; pp. 126–132. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, W.; Wu, L.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, K. Dynamic Analysis of Geared Rotor System with Hybrid Uncertainties. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2024, 37, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alici, G. Softer is Harder: What Differentiates Soft Robotics from Hard Robotics? MRS Adv. 2018, 3, 1557–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Son, J.; Jin, M.; Kang, S.H. Experimental verification on the robustness and stability of an interaction control: Single-degree-of-freedom robot case. Electron. Lett. 2021, 57, 433–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonin, A.; Semprini, M.; Kiper, P.; Mantini, D. Brain-Computer Interfaces for Stroke Motor Rehabilitation. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lequan, L. Fire Recognition and Path Planning for Fire Fighting Robots Based on Machine Vision Slam Technology. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Communication (ICAIC 2024), Davos, Switzerland, 10–11 July 2024; pp. 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, J.; Li, J.; Peng, Y.; Mao, Z. Large language models for human–robot interaction: A review. Biomim. Intell. Robot. 2023, 3, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Wang, Y.; Yao, M.; Liu, S.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, B. Long-span delivery of differentiable hybrid robots for restoration of neural connections. Matter 2025, 8, 101942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Liu, M.; Li, L.; Gui, L. Hydrophilic hard-magnetic soft robots: A new approach for precise droplet manipulation. Nanotechnol. Precis. Eng. 2025, 8, 043012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortez, R.; Sandoval-Chileño, M.A.; Lozada-Castillo, N.; Luviano-Juárez, A. Snake Robot with Motion Based on Shape Memory Alloy Spring-Shaped Actuators. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Ma, X.; Deng, W.; Zhang, J.; Tang, S.; Pak, O.S.; Zhu, L.; Criado-Hidalgo, E.; Gong, C.; Karshalev, E.; et al. Imaging-guided bioresorbable acoustic hydrogel microrobots. Sci. Robot. 2024, 9, eadp3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shigemune, H.; Sugano, S.; Nishitani, J.; Yamauchi, M.; Hosoya, N.; Hashimoto, S.; Maeda, S. Dielectric Elastomer Actuators with Carbon Nanotube Electrodes Painted with a Soft Brush. Actuators 2018, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrico, J.D.; Kim, K.J.; Leang, K.K. 3D-printed ionic polymer-metal composite soft crawling robot. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 4313–4320. [Google Scholar]
- Acome, E.; Mitchell, S.K.; Morrissey, T.G.; Emmett, M.B.; Benjamin, C.; King, M.; Radakovitz, M.; Keplinger, C. Hydraulically amplified self-healing electrostatic actuators with muscle-like performance. Science 2018, 359, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, C.; Chen, D.; Wen, X.; Jin, B.; He, Y.; Xie, T.; Zhao, Q. High speed underwater hydrogel robots with programmable motions powered by light. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Pan, H.; Chen, Z.; Yin, T.; Zheng, M.; Cai, L. Twin-bioengine self-adaptive micro/nanorobots using enzyme actuation and macrophage relay for gastrointestinal inflammation therapy. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadc8978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Teng, Y.; Xu, Y. A Pneumatic Soft Quadruped Robot Based on a Bistable Actuator. ROBOT 2024, 46, 294–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Cao, L.; Lu, G.; Wang, P.; Ran, L.; Peng, B. Untethered soft microrobot driven by a single actuator for agile navigations. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 6842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Chan, K.H.; Wang, X.-Q.; Ding, T.; Li, T.; Zhang, C.; Lu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Ho, G. A Fast Autonomous Healing Magnetic Elastomer for Instantly Recoverable, Modularly Programmable, and Thermorecyclable Soft Robots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2101825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.H.; Won, S.; Lee, J.M.; Cho, W.; Park, S.; Kim, H.; Chae, C.-G.; Lee, W.; Kim, D.-G.; Wie, J.J.; et al. Closed-Loop and Sustainable 4D Printing of Multi-Stimuli-Responsive Sulfur-Rich Polymer Composites for Autonomous Task Execution. Adv. Mater. 2025, e07057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Cao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, H. Muscle-inspired elasto-electromagnetic mechanism in autonomous insect robots. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 6813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, S.; Wei, X.; Weng, M.; Zhao, F.; Chen, P.; Hong, J.; Xiang, S.; Shi, Q.; Sun, L.; Shen, G.; et al. Venus Flytrap-Inspired Data-Center-Free Fast-Responsive Soft Robots Enabled by 2D Ni3(HITP)2 MOF and Graphite. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2313089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, R.; Li, S.; Wang, F. Design and motion characteristics analysis of underwater biomimetic jellyfish based on shape memory alloy springs. Ocean Eng. 2024, 297, 117069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neil, T.R.; Askew, G.N. Jet-paddling jellies: Swimming performance in the Rhizostomeae jellyfish Catostylus mosaicus. J. Exp. Biol. 2018, 221, jeb191148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Monfort, G.M.; Costello, J.H.; Colin, S.P.; Morandini, A.C.; Migotto, A.E.; Maronna, M.M.; Reginato, M.; Miyake, H.; Nagata, R.M. Ontogenetic transitions, biomechanical trade-offs and macroevolution of scyphozoan medusae swimming patterns. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Qiao, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, A.; Zhu, B.; Yue, X.; Chen, Y.; Wong, T.-W.; Li, G. Jellyfish-Inspired Soft Robot Driven by Pneumatic Bistable Actuators. Soft Robot. 2024, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Kawakami, S.; Hayashi, K.; Mori, Y.; Hashida, M.; Konishi, S. Implantable pneumatically actuated microsystem for renal pressure-mediated transfection in mice. J. Control. Release 2012, 159, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, S.; Kawai, F.; Cusin, P. Thin flexible end-effector using pneumatic balloon actuator. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2001, 89, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Wei, F.; Fu, S.; Zhai, Z.; Ge, Z.; Yao, L.; Jiang, M.; Liu, M. Visible Light-Driven Jellyfish-like Miniature Swimming Soft Robot. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 47147–47154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.-M. High-Performance Carbon Nanotube Thin-Film Transistor Technology. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 22156–22166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righi, M.; Moretti, G.; Forehand, D.; Agostini, L.; Vertechy, R.; Fontana, M. A broadbanded pressure differential wave energy converter based on dielectric elastomer generators. Nonlinear Dyn. 2021, 105, 2861–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Cao, C.; Wu, X.; Xue, J.; Wang, L.; Gao, X. A Low-profile Vibration Crawling Robot Driven by A Planar Dielectric Elastomer Actuator. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Real-time Computing and Robotics (RCAR), Guiyang, China, 17–22 July 2022; pp. 413–418. [Google Scholar]
- Goh, Y.F.; Akbari, S.; Khanh Vo, T.V.; Koh, S.J.A. Electrically-Induced Actuation of Acrylic-Based Dielectric Elastomers in Excess of 500% Strain. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.-l.; Jin, X.-l.; Ruan, R.-h.; Zhu, W.-q. Typical dielectric elastomer structures: Dynamics and application in structural vibration control. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. A 2016, 17, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Y.-P. Active control of electro-visco-fingering in Hele-Shaw cells using Maxwell stress. iScience 2022, 25, 105204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, L.Y.; Chang, H.-C. Electrowetting films on parallel line electrodes. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 73, 011605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Cui, Y.; Sun, H.; Shao, Q.; Zhao, H. Active-Cooling-in-the-Loop Controller Design and Implementation for an SMA-Driven Soft Robotic Tentacle. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2023, 39, 2325–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadesse, Y.; Thayer, N.; Priya, S. Tailoring the Response Time of Shape Memory Alloy Wires through Active Cooling and Pre-stress. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2009, 21, 19–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, U.; Park, C.H. A Novel Fabric Muscle Based on Shape Memory Alloy Springs. Soft Robot. 2019, 7, 321–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chu, H.; Yuan, H.; Li, D.; Deng, W.; Fu, Z.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Han, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Bioinspired Multifunctional Self-Sensing Actuated Gradient Hydrogel for Soft-Hard Robot Remote Interaction. Nano-Micro Lett. 2024, 16, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.Y.; Zhu, Q.L.; Cheng, H.L.; Wen, X.L.; Wang, Z.J.; Zheng, Q.; Wu, Z.L. Muscle-like hydrogels with fast isochoric responses and their applications as soft robots: A minireview. Mater. Horiz. 2025, 12, 719–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zuo, L. A highly stretchable hydrogel sensor for soft robot multi-modal perception. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2021, 331, 113006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelrine, R.; Kornbluh, R.; Pei, Q.; Joseph, J. High-Speed Electrically Actuated Elastomers with Strain Greater Than 100%. Science 2000, 287, 836–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glick, P.; Suresh, S.A.; Ruffatto, D.; Cutkosky, M.; Tolley, M.T.; Parness, A. A Soft Robotic Gripper With Gecko-Inspired Adhesive. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2018, 3, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keplinger, C.; Li, T.; Baumgartner, R.; Suo, Z.; Bauer, S. Harnessing snap-through instability in soft dielectrics to achieve giant voltage-triggered deformation. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Hu, L.; Zhou, Y. Pneumatic Soft Robotic Crawler Integrated With a Precurved Actuator Enables Fast Locomotion. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics (ROBIO), Jinghong, China, 5–9 December 2022; pp. 507–512. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Gao, Z.; Li, Y.; Pan, J. Closed-loop Control of a Pneumatic Soft Gripper for Fast and Accurate Response. In Proceedings of the 2020 8th International Conference on Power Electronics Systems and Applications (PESA), Hong Kong, China, 7–10 December 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes, E.W.; Christensen, D.L.; Okamura, A.M. Design and implementation of a 300% strain soft artificial muscle. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 4022–4029. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, B.-K.; Ju, M.-S.; Lin, C.-C.K. A new approach to develop ionic polymer–metal composites (IPMC) actuator: Fabrication and control for active catheter systems. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2007, 137, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MohdIsa, W.; Hunt, A.; HosseinNia, S.H. Sensing and Self-Sensing Actuation Methods for Ionic Polymer–Metal Composite (IPMC): A Review. Sensors 2019, 19, 3967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbar, A.; Joseph, N.; Donald, L.; John, B. Design and development of bio-inspired underwater jellyfish like robot using ionic polymer metal composite (IPMC) actuators. In Proceedings of the SPIE Smart Structures and Materials + Nondestructive Evaluation and Health Monitoring 2011, San Diego, CA, USA, 6–10 March 2011; p. 797624. [Google Scholar]
- Jiao, Z.-W.; Wang, H.-Y.; Luo, B.; Yang, W.-M.; Yu, Y. A BCF Bionic Robot Fish Driven by A Dielectric Elastomer Actuator. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2022, 2331, 012010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Chen, T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z. An underwater bionic crab soft robot with multidirectional controllable motion ability. Ocean Eng. 2023, 278, 114412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Tan, W.; Qin, H.; Wang, F.; Liu, L. Fast-Swimming Soft Robotic Fish Actuated by Bionic Muscle. Soft Robot. 2024, 11, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Yan, H.; Cai, A.; Cao, C. A Dielectric Elastomer Actuator-Driven Vibro-Impact Crawling Robot. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, S.; Gao, D.; Xiong, J.; Lee, P.S. Reconfigurable and programmable origami dielectric elastomer actuators with 3D shape morphing and emissive architectures. NPG Asia Mater. 2019, 11, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Guo, J.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Leng, J. Bioinspired multimodal soft robot driven by a single dielectric elastomer actuator and two flexible electroadhesive feet. Extrem. Mech. Lett. 2022, 53, 101720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Lu, X.; Liu, J. Inchworm-Like Soft Robot with Multimodal Locomotion Using an Acrylic Stick-Constrained Dielectric Elastomer Actuator. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2023, 5, 2200209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Ma, W.; Li, B.; Jin, M.; Chen, H. Cephalopod-Inspired Swimming Robot Using Dielectric Elastomer Synthetic Jet Actuator. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2020, 22, 1901130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keplinger, C.; Kaltenbrunner, M.; Arnold, N.; Bauer, S. Capacitive extensometry for transient strain analysis of dielectric elastomer actuators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 192903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Vudayagiri, S.; Jensen, L.A.; Skov, A.L. Temperature dependence of dielectric breakdown of silicone-based dielectric elastomers. Int. J. Smart Nano Mater. 2020, 11, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, F.; Zuo, Y.-j.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, N.; Niu, G.; Ren, W.; Ye, Z. Improving actuation strain and breakdown strength of dielectric elastomers using core-shell structured CNT-Al2O3. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2020, 200, 108393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheima, Y.; Caspari, P.; Opris, D.M. Artificial Muscles: Dielectric Elastomers Responsive to Low Voltages. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2019, 40, 1900205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Liu, X.-J.; Zhao, H. Portable, High-Frequency, and High-Voltage Control Circuits for Untethered Miniature Robots Driven by Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.06166. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, L.-J.; Du, B.; Hu, H.-Y.; Dong, W.-Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Zhong, S.-L.; Yi, C.; Qu, L.; et al. A high-response-frequency bimodal network polyacrylate elastomer with ultrahigh power density under low electric field. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Sun, L.; Jin, Z.; Chen, L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Wang, C. A large-strain and ultrahigh energy density dielectric elastomer for fast moving soft robot. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannes, E.; Peter, L.; Holger, B. High-performance dielectric elastomer unimorph bending actuators without pre-stretch. In Proceedings of the SPIE Smart Structures + Nondestructive Evaluation 2023, Long Beach, CA, USA, 12–17 March 2023; p. 124820W. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, B.; Chen, H. Viscoelastic performance of dielectric elastomer subject to different voltage stimulation. In Proceedings of the SPIE Smart Structures and Materials + Nondestructive Evaluation and Health Monitoring 2017, Portland, OR, USA, 25–29 March 2017; p. 1016329. [Google Scholar]
- Kühnel, S.; Kornhuber, S.; Bärsch, R.; Lambrecht, J. On the arc-resistance when tested with DC- and AC-stress by the example of silicone elastomers. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Phenomena (CEIDP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 16–19 October 2016; pp. 501–505. [Google Scholar]
- Cole, K.S.; Cole, R.H. Dispersion and Absorption in Dielectrics I. Alternating Current Characteristics. J. Chem. Phys. 1941, 9, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Chen, H.; Sheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Jia, S. Experimental study on the dynamic response of in-plane deformation of dielectric elastomer under alternating electric load. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 025037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolazizi, K.P.; Linka, K.; Cyron, C.J. Viscoelastic constitutive artificial neural networks (vCANNs)—A framework for data-driven anisotropic nonlinear finite viscoelasticity. J. Comput. Phys. 2024, 499, 112704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, Y.; Tao, J.; Jia, B.; Li, D.; Zhai, Y. A viscoelastic constitutive relation for the rate-dependent mechanical behavior of rubber-like elastomers based on thermodynamic theory. Mater. Des. 2019, 178, 107876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannarelli, A.; Niasar, M.G.; Ross, R. The effects of static pre-stretching on the short and long-term reliability of dielectric elastomer actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 125014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Betts, A.; Kennedy, D.; Jerrams, S. Eliminating electromechanical instability in dielectric elastomers by employing pre-stretch. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 265401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Wu, J.; Chen, F. Optimal biaxial prestretch ratios of soft dielectric elastomer actuators for maximal voltage-induced displacement. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2023, 66, 2871–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Santo, V.; Goerig, E.; Wainwright, D.K.; Akanyeti, O.; Liao, J.C.; Castro-Santos, T.; Lauder, G.V. Convergence of undulatory swimming kinematics across a diversity of fishes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2113206118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Naskar, S.; Mukhopadhyay, T. Multi-Physically Programmable Tubular Origami Metamaterials: Exploitable Nexus of Geometry, Folding Mechanics and Stimuli-Responsive Physics. Adv. Sci. 2025, e05089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duduta, M.; Hajiesmaili, E.; Zhao, H.; Wood, R.J.; Clarke, D.R. Realizing the potential of dielectric elastomer artificial muscles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 2476–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duduta, M.; Berlinger, F.C.J.; Nagpal, R.; Clarke, D.R.; Wood, R.J.; Temel, F.Z. Electrically-latched compliant jumping mechanism based on a dielectric elastomer actuator. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 09LT01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Moghani, M.; Li, A.; Duduta, M. A Small Steerable Tip Based on Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 6531–6538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Suzuki, S.; Nabae, H.; Miyagawa, S.; Suzumori, K.; Maeda, S. Machine learning-enhanced soft robotic system inspired by rectal functions to investigate fecal incontinence. Bio-Des. Manuf. 2025, 8, 482–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, P.; Hong, R.; Yang, B.; Zhang, G.; Shao, Y.; Ding, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Zhong, H. Diagnosis analysis of rectal function through using ensemble empirical mode decomposition–deep belief networks algorithm. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2021, 92, 064102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Suzuki, S.; Wiranata, A.; Ohgi, J.; Miyagawa, S. Power, Control, and Data Acquisition Systems for Rectal Simulator Integrated with Soft Pouch Actuators. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.15473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruntu, D.I.; Botello, M.A.; Reyes, C.A.; Beatriz, J. Frequency–amplitude response of superharmonic resonance of second order of electrostatically actuated MEMS cantilever resonators. Int. J. Non-Linear Mech. 2021, 133, 103719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, B.; Li, X.; Dong, L.; Zhang, M.; Zou, J.; Gu, G. Dexterous electrical-driven soft robots with reconfigurable chiral-lattice foot design. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, F.; Jing, Z.; Yu, F.; Chen, Y. A Hybrid Territorial Aquatic Bionic Soft Robot with Controllable Transition Capability. J. Bionic Eng. 2023, 20, 568–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitler, W.J.; Fraser, K.; Ferrero, E.A. Escape Behaviour in the Stomatopod Crustacean Squilla Mantis, and the Evolution of the Caridoid Escape Reaction. J. Exp. Biol. 2000, 203, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izadi, H.; Stewart, K.M.E.; Penlidis, A. Role of contact electrification and electrostatic interactions in gecko adhesion. J. R. Soc. Interface 2014, 11, 20140371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Xie, X.; Zhu, J.; Wu, K.; Wang, C. Biomimetic Crawling Robot Based on Dielectric Elastomer: Design, Modeling and Experiment. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2024, 9, 9669–9676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, J.; Xu, F.; Wang, H. Small-Scale Soft Terrestrial Robot with Electrically Driven Multi-Modal Locomotion Capability. Soft Robot. 2025, 12, 387–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Huang, B.; McCoul, D.; Li, M.; Mu, L.; Zhao, J. A soft breaststroke-inspired swimming robot actuated by dielectric elastomers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 045006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Hayashi, T.; Isaka, T. Simulating vortex generation to investigate the propulsive and braking mechanisms of breaststroke kick using computational fluid dynamics on a breaststroke swimmer. J. Biomech. 2024, 176, 112329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, T.; Shintake, J. Rolled Dielectric Elastomer Antagonistic Actuators for Biomimetic Underwater Robots. Polymers 2022, 14, 4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Arase, C.; Ren, Z.; Chirarattananon, P. Design, Characterization, and Liftoff of an Insect-Scale Soft Robotic Dragonfly Powered by Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Sun, M. Dynamic flight stability of a hovering model dragonfly. J. Theor. Biol. 2014, 348, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Wu, X.; Xue, J.; Chen, X.; Cao, C.; Gao, X. A Soft Robot Driven by a Spring-Rolling Dielectric Elastomer Actuator with Two Bristles. Micromachines 2023, 14, 618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, J.O.; Gorb, S.N. Radial arrangement of Janus-like setae permits friction control in spiders. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Lv, J.; Huang, Y.; Gai, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lee, P.S.; Xu, H.; Wu, D. Multilayer Dielectric Elastomer with Reconfigurable Electrodes for Artificial Muscle. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, 2206094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Kim, S.; Ji, X.; Zhu, W.; Niroui, F.; Kong, J.; Chen, Y. A High-Lift Micro-Aerial-Robot Powered by Low-Voltage and Long-Endurance Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2106757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Qin, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Liu, L. Soft Manta Ray Robot Based on Bilateral Bionic Muscle Actuator. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2024, 9, 7723–7730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, H.; Abbaspour, M.; Darbandi, M. Numerical study to evaluate the important parameters affecting the hydrodynamic performance of manta ray’s in flapping motion. Appl. Ocean Res. 2021, 109, 102559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, F.E.; Kolpas, A.; Crossett, A.; Dudas, M.A.; Moored, K.W.; Bart-Smith, H. Kinematics of swimming of the manta ray: Three-dimensional analysis of open-water maneuverability. J. Exp. Biol. 2018, 221, jeb166041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Zhang, C.; Tan, W.; Yang, J.; Lin, D.; Liu, L. Electroactive Polymer-Based Soft Actuator with Integrated Functions of Multi-Degree-of-Freedom Motion and Perception. Soft Robot. 2022, 10, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Griethuijsen, L.I.; Trimmer, B.A. Locomotion in caterpillars. Biol. Rev. 2014, 89, 656–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metallo, C.; Mukherjee, R.; Trimmer, B.A. Stepping pattern changes in the caterpillar Manduca sexta: The effects of orientation and substrate. J. Exp. Biol. 2020, 223, jeb220319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skov, A.L.; Yu, L. Optimization Techniques for Improving the Performance of Silicone-Based Dielectric Elastomers. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1700762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladman, N.W.; Askew, G.N. The hydrodynamics of jet propulsion swimming in hatchling and juvenile European common cuttlefish, Sepia officinalis. J. Exp. Biol. 2023, 226, jeb246225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staaf, D.J.; Gilly, W.F.; Denny, M.W. Aperture effects in squid jet propulsion. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 217, 1588–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaqubi, S.; Dardel, M.; Daniali, H.M.; Ghasemi, M.H. Modeling and control of crank–slider mechanism with multiple clearance joints. Multibody Syst. Dyn. 2016, 36, 143–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, W.; Li, S.; Jiang, Y.; Zang, W.; Fu, W.; Hao, X.; Ning, N.; Tian, M.; Zhang, L. A Soft Mimic Robotic Arm Powered by Dielectric Elastomer Actuator. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2411229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Li, B.; Yu, Y.; Yu, M.; Ma, J.; Yang, W.; Wang, P.; Jiao, Z. A Jumping Robot Driven by a Dielectric Elastomer Actuator. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.T.; Phung, H.; Nguyen, T.D.; Lee, C.; Kim, U.; Lee, D.; Moon, H.; Koo, J.; Nam, J.-d.; Choi, H.R. A small biomimetic quadruped robot driven by multistacked dielectric elastomer actuators. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 065005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhuo, J.; Peng, J.; Dong, H.; Jiang, S.; Shi, Y. A Stretchable Soft Pump Driven by a Heterogeneous Dielectric Elastomer Actuator. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2411160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Godaba, H.; Ren, H.; Zhu, J. Bioinspired Soft Actuators for Eyeball Motions in Humanoid Robots. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2019, 24, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Xu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Shan, J. Development of a Stick-Slip Dielectric Elastomer Actuator for Robotic Applications. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters. 2025, 10, 11371–11378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Xue, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Du, Q.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, J. A soft gripper driven by conical dielectric elastomer actuator to achieve displacement amplification and compliant grips. Intell. Serv. Robot. 2024, 17, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, J.-H.; Koh, J.-S.; Kyung, K.-U. Soft Polymer-Actuated Compliant Microgripper with Adaptive Vibration-Controlled Grasp and Release. Soft Robot. 2024, 11, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sheng, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, L.; Zhao, J.; Chen, H. Temperature effect on electromechanical properties of polyacrylic dielectric elastomer: An experimental study. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 047002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, C.; Li, G. Compressible dielectric elastomer actuators in high hydrostatic pressures: Models and experiments. Phys. Rev. E 2024, 110, L052501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Yi, L.; Chen, X.; Yang, Q.; Xu, W.; Wang, A.; et al. Concerning the stability of seawater electrolysis: A corrosion mechanism study of halide on Ni-based anode. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shintake, J.; Cacucciolo, V.; Shea, H.; Floreano, D. Soft Biomimetic Fish Robot Made of Dielectric Elastomer Actuators. Soft Robot. 2018, 5, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, G.; Liang, Y.; Cheng, T.; Dai, J.; Yang, X.; Liu, B.; Zeng, Z.; Huang, Z.; Luo, Y.; et al. Fast-moving soft electronic fish. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1602045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, M.; Li, S.; Wong, T.-W.; Wang, Y.; Li, T.; et al. A soft artificial muscle driven robot with reinforcement learning. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drebushchak, V. Heat capacity increases with pressure. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2009, 95, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, B.; Li, W.; Zu, L.; Tang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Bioinspired Triboelectric Soft Robot Driven by Mechanical Energy. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2104770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, W.; Gu, G.; Zhang, W.; Luo, H.; Wang, T.; Zhang, B.; Guo, J.; Cui, P.; Yang, F.; Cheng, G.; et al. Rotational pulsed triboelectric nanogenerators integrated with synchronously triggered mechanical switches for high efficiency self-powered systems. Nano Energy 2021, 82, 105725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, P.; Dong, Z.; Dai, X.; Qiu, X. Flexible Polydimethylsiloxane-Based Porous Polyimide Films with an Ultralow Dielectric Constant and Remarkable Water Resistance. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 2597–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, J.D.; Poukens, V.; Baker, R.S.; Demer, J.L. Structure-function correlations in the human medial rectus extraocular muscle pulleys. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1996, 37, 468–472. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Bao, Q.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Q. Highly Transparent and Long-Term Stable Dielectric Elastomer Composites Enabled by Poly(ionic liquid) Inclusion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2401901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gupta, A.; Lu, Q.; Wu, W.; Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Hu, X.; Lee, P.S. Ultrasoft and fast self-healing poly(ionic liquid) electrode for dielectric elastomer actuators. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 7405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Kang, G.; Hu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Li, T.; Qu, S. Low-cycle electro-mechanical fatigue of dielectric elastomers: Pure-shear experiments and life-prediction model. Int. J. Fatigue 2021, 148, 106220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannarelli, A.; Ghaffarian Niasar, M.; Ross, R. Electrode interface polarization formation in dielectric elastomer actuators. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2020, 312, 111992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Basir, A.; Avila, R.; Lim, J.; Hong, S.W.; Choe, G.; Shin, J.H.; Hwang, J.H.; Park, S.Y.; Joo, J.; et al. Strain-invariant stretchable radio-frequency electronics. Nature 2024, 629, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, W. Non-monotonic electromechanical deformation of dielectric elastomer actuators with different surface densities of carbon nanotubes. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 015909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Qiu, J.; Zhu, K.; Li, J. Electro-mechanical performance of polyurethane dielectric elastomer flexible micro-actuator composite modified with titanium dioxide-graphene hybrid fillers. Mater. Des. 2016, 90, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Actuation Mechanism | Response Speed | Maximum Strain | Typical Motion Modes | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMA | Martensitic transformation | Second level (1 s–5 s) | 60% | Linear motion, bending, twisting | [40,41,42] |
| Hydrogel | Ion migration and solvent redistribution | Second level (140 ms–2 s) | 1200% | Volume expansion and contraction, bending | [43,44,45] |
| DEAs | Maxwell’s stress effect | Millisecond level (10 ms–500 ms) | 1600% | Planar expansion, linear contraction, bending | [46,47,48] |
| Pneumatic | Pressure change | Millisecond level (100 ms–2 s) | 300% | Bending, stretching, and twisting | [49,50,51] |
| IPMCs | Ion migration induced by an electric field | Second level (500 ms–5 s) | 5% | Large-amplitude bending and swinging | [52,53,54] |
| Maximum Strain | Output Force | Response Frequency | Environmental Adaptability | Manufacturing Difficulty | Typical Motion Modes | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Planar Type | 400% | 8.8 N | 100 Hz | Poor | Easy | Bending, linear motion | [55,116,117] |
| Saddle-Shaped Type | 500% | 0.6 N | 30 Hz | Medium | Medium | Bending, swinging | [61] |
| Cylindrical Type | 500% | 3.9 N | 400 Hz | Excellent (easy to encapsulate) | Difficult | Bending, swinging, linear motion | [60,102,118] |
| Conical Type | 400% | 30 N | 80 Hz | Good | Medium-Difficult | Linear motion | [119,120,121] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Gao, Z.; Yang, W.; Wang, R.; Zhang, L. Recent Advances in Dielectric Elastomer Actuator-Based Soft Robots: Classification, Applications, and Future Perspectives. Gels 2025, 11, 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11110844
Li S, Gao Z, Yang W, Wang R, Zhang L. Recent Advances in Dielectric Elastomer Actuator-Based Soft Robots: Classification, Applications, and Future Perspectives. Gels. 2025; 11(11):844. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11110844
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Shuo, Zhizheng Gao, Wenguang Yang, Ruiqian Wang, and Lei Zhang. 2025. "Recent Advances in Dielectric Elastomer Actuator-Based Soft Robots: Classification, Applications, and Future Perspectives" Gels 11, no. 11: 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11110844
APA StyleLi, S., Gao, Z., Yang, W., Wang, R., & Zhang, L. (2025). Recent Advances in Dielectric Elastomer Actuator-Based Soft Robots: Classification, Applications, and Future Perspectives. Gels, 11(11), 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels11110844






