Enhancing the Mechanical Properties of Injectable Nanocomposite Hydrogels by Adding Boronic Acid/Boronate Ester Dynamic Bonds at the Nanoparticle–Polymer Interface
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
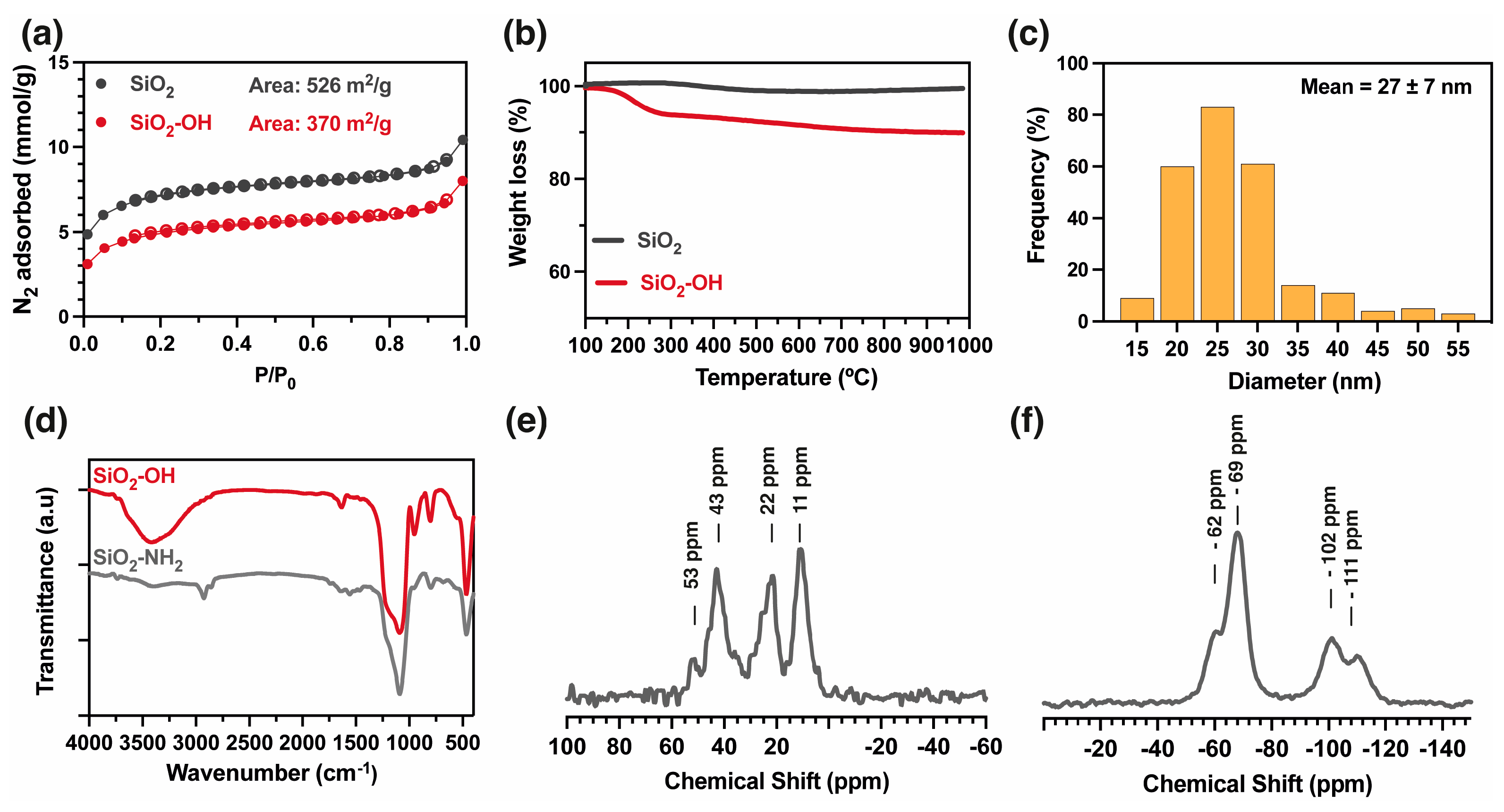
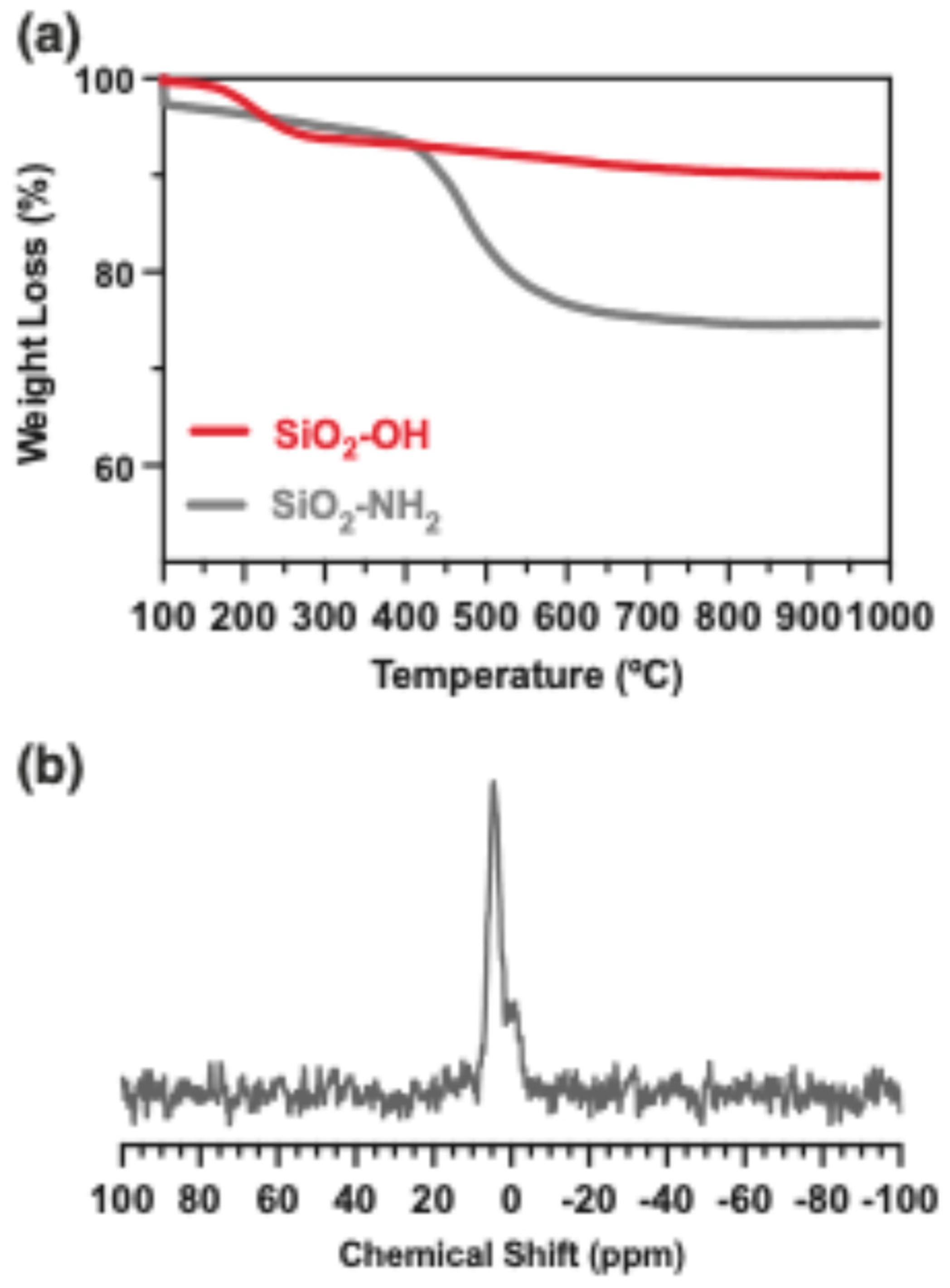
2.1. Activation and Functionalization of Nanoparticles
2.2. Obtaining the Nanocomposite Hydrogels
2.3. Injectability Test
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Activation, Functionalization, and Immobilization of Boronic Acid on SiO2 Nanoparticles
4.3. Synthesis of Modified Alginate with 4-Aminophenyl Boronic Acid (AlgBA)
4.4. Obtaining the Nanocomposite Hydrogels
4.5. Characterization Techniques
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Grimaudo, M.A.; Krishnakumar, G.S.; Giusto, E.; Furlani, F.; Bassi, G.; Rossi, A.; Molinari, F.; Lista, F.; Montesi, M.; Panseri, S. Bioactive injectable hydrogels for on demand molecule/cell delivery and for tissue regeneration in the central nervous system. Acta Biomater. 2022, 140, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketabat, F.; Khorshidi, S.; Karkhaneh, A. Application of minimally invasive injectable conductive hydrogels as stimulating scaffolds for myocardial tissue engineering. Polym. Int. 2018, 67, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, F.; Kehr, N.S. Recent Advances in Injectable Hydrogels for Controlled and Local Drug Delivery. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2021, 10, 2001341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, P.; Chatterjee, K. Injectable and self-healing double network polysaccharide hydrogel as a minimally-invasive delivery platform. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 291, 119585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Guo, W.; Wang, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yu, L.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; et al. An Injectable Asymmetric-Adhesive Hydrogel as a GATA6+ Cavity Macrophage Trap to Prevent the Formation of Postoperative Adhesions after Minimally Invasive Surgery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 32, 2110066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellati, A.; Hasanzadeh, E.; Gholipourmalekabadi, M.; Enderami, S.E. Injectable nanocomposite hydrogels as an emerging platform for biomedical applications: A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 131, 112489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phogat, K.; Ghosh, S.B.; Bandyopadhyay-Ghosh, S. Recent advances on injectable nanocomposite hydrogels towards bone tissue rehabilitation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2023, 140, e53362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, W.; Qian, J.; Wang, Y.; Hou, G.; Suo, A.; Ma, Y. Injectable hyaluronan/MnO2 nanocomposite hydrogel constructed by metal-hydrazide coordinated crosslink mineralization for relieving tumor hypoxia and combined phototherapy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 628, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, M.; Han, Y.; Lai, J.; Chen, J. Multistage-Targeted Gold/Mesoporous Silica Nanocomposite Hydrogel as in Situ Injectable Drug Release System for Chemophotothermal Synergistic Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.-Y.; Feng, X.-Q.; Lauke, B.; Mai, Y.-W. Effects of particle size, particle/matrix interface adhesion and particle loading on mechanical properties of particulate–polymer composites. Compos. Part B Eng. 2008, 39, 933–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiras, D.; Pessan, L.A. Mechanical properties of polypropylene/calcium carbonate nanocomposites. Mater. Res. 2009, 12, 517–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Tjiu, W.C.; Tong, Y.; He, C.; Goh, S.S.; Chung, T.-S. Morphology and fracture behavior of intercalated epoxy/clay nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 94, 1236–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H. The essential work of fracture of polyamide 66 filled with TiO2 nanoparticles. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2005, 65, 2374–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaresimin, M.; Schulte, K.; Zappalorto, M.; Chandrasekaran, S. Toughening mechanisms in polymer nanocomposites: From experiments to modelling. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2016, 123, 187–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salviato, M.; Zappalorto, M.; Quaresimin, M. Plastic shear bands and fracture toughness improvements of nanoparticle filled polymers: A multiscale analytical model. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2013, 48, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowan, N.; Cox, L.M.; Shah, P.K.; Song, H.B.; Stansbury, J.W.; Bowman, C.N. Dynamic Covalent Chemistry at Interfaces: Development of Tougher, Healable Composites through Stress Relaxation at the Resin–Silica Nanoparticles Interface. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 5, 1800511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowan, N.; Dobson, A.; Podgorski, M.; Bowman, C.N. Dynamic covalent chemistry (DCC) in dental restorative materials: Implementation of a DCC-based adaptive interface (AI) at the resin–filler interface for improved performance. Dent. Mater. 2020, 36, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowan, N.; Lu, Y.; Kolb, K.J.; Cox, L.M.; Long, R.; Bowman, C.N. Enhancing the toughness of composites via dynamic thiol–thioester exchange (TTE) at the resin–filler interface. Polym. Chem. 2020, 11, 4760–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diodati, L.E.; Liu, S.; Rinaldi-Ramos, C.M.; Sumerlin, B.S. Magnetic Nanoparticles Improve Flow Rate and Enable Self-Healing in Covalent Adaptable Networks. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 32957–32966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakma, P.; Konkolewicz, D. Dynamic Covalent Bonds in Polymeric Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 9682–9695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, T. Dual-Triggered and Thermally Reconfigurable Shape Memory Graphene-Vitrimer Composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 21691–21699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, A.; Soulié-Ziakovic, C. Silica–Epoxy Vitrimer Nanocomposites. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 5893–5902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz de Luzuriaga, A.; Martin, R.; Markaide, N.; Rekondo, A.; Cabañero, G.; Rodríguez, J.; Odriozola, I. Epoxy resin with exchangeable disulfide crosslinks to obtain reprocessable, repairable and recyclable fiber-reinforced thermoset composites. Mater. Horiz. 2016, 3, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgórski, M.; Fairbanks, B.D.; Kirkpatrick, B.E.; McBride, M.; Martinez, A.; Dobson, A.; Bongiardina, N.J.; Bowman, C.N. Toward Stimuli-Responsive Dynamic Thermosets through Continuous Development and Improvements in Covalent Adaptable Networks (CANs). Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufort, B.M.; Tibbitt, M.W. Design of moldable hydrogels for biomedical applications using dynamic covalent boronic esters. Mater. Today Chem. 2019, 12, 16–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, T.; Das, A.K. Dynamic boronate esters cross-linked guanosine hydrogels: A promising biomaterial for emergent applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 488, 215170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, W.L.A.; Sumerlin, B.S. Synthesis and Applications of Boronic Acid-Containing Polymers: From Materials to Medicine. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 1375–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, C.H.; Oportus, M.; Torres, C.; Urbina, C.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Reyes, P. Enantioselective hydrogenation of 1-phenyl-propane-1,2-dione on immobilised cinchonidine Pt/SiO2 catalysts. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2011, 348, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmar, L.; Toledo, L.; Sánchez, S.A.; Urbano, B.F. Fluorescent nanotubes in PHEMA hydrogels: Visualizing aggregation and distribution by confocal fluorescence microscopy. Mater. Today Commun. 2018, 16, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentz, K.C.; Savin, D.A. Chain Dispersity Effects on Brush Properties of Surface-Grafted Polycaprolactone-Modified Silica Nanoparticles: Unique Scaling Behavior in the Concentrated Polymer Brush Regime. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 5565–5573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glynn, S.J.; Gaffney, K.J.; Sainz, M.A.; Louie, S.G.; Petasis, N.A. Molecular characterization of the boron adducts of the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib with epigallocatechin-3-gallate and related polyphenols. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2015, 13, 3887–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colthup, N. Introduction to Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Pettignano, A.; Grijalvo, S.; Häring, M.; Eritja, R.; Tanchoux, N.; Quignard, F.; Díaz Díaz, D. Boronic acid-modified alginate enables direct formation of injectable, self-healing and multistimuli-responsive hydrogels. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 3350–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, W.L.A.; Deng, C.C.; Sumerlin, B.S. Structure–Reactivity Relationships in Boronic Acid–Diol Complexation. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 17863–17870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baby, D.K. Chapter 9—Rheology of hydrogels. In Rheology of Polymer Blends and Nanocomposites; Thomas, S., Sarathchandran, C., Chandran, N., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 193–204. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.H.; Wang, L.L.; Chung, J.J.; Kim, Y.-H.; Atluri, P.; Burdick, J.A. Methods To Assess Shear-Thinning Hydrogels for Application As Injectable Biomaterials. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 3146–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sánchez, J.; Ulloa, J.; Oyarzún, Y.; Ceballos, M.; Ruiz, C.; Boury, B.; Urbano, B.F. Enhancing the Mechanical Properties of Injectable Nanocomposite Hydrogels by Adding Boronic Acid/Boronate Ester Dynamic Bonds at the Nanoparticle–Polymer Interface. Gels 2024, 10, 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10100638
Sánchez J, Ulloa J, Oyarzún Y, Ceballos M, Ruiz C, Boury B, Urbano BF. Enhancing the Mechanical Properties of Injectable Nanocomposite Hydrogels by Adding Boronic Acid/Boronate Ester Dynamic Bonds at the Nanoparticle–Polymer Interface. Gels. 2024; 10(10):638. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10100638
Chicago/Turabian StyleSánchez, Jesús, Jose Ulloa, Yessenia Oyarzún, Matías Ceballos, Carla Ruiz, Bruno Boury, and Bruno F. Urbano. 2024. "Enhancing the Mechanical Properties of Injectable Nanocomposite Hydrogels by Adding Boronic Acid/Boronate Ester Dynamic Bonds at the Nanoparticle–Polymer Interface" Gels 10, no. 10: 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10100638
APA StyleSánchez, J., Ulloa, J., Oyarzún, Y., Ceballos, M., Ruiz, C., Boury, B., & Urbano, B. F. (2024). Enhancing the Mechanical Properties of Injectable Nanocomposite Hydrogels by Adding Boronic Acid/Boronate Ester Dynamic Bonds at the Nanoparticle–Polymer Interface. Gels, 10(10), 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10100638






