The Influence of Particle Size and Calcium Content on Performance Characteristics of Metakaolin- and Fly-Ash-Based Geopolymer Gels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Setting Time and Fluidity
2.2. Morphology from Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) and Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.4. Pore Structure Analysis from Low-Field Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (LF-NMR)
2.5. Influence of Particle Size and Calcium Content on Compressive Strengths
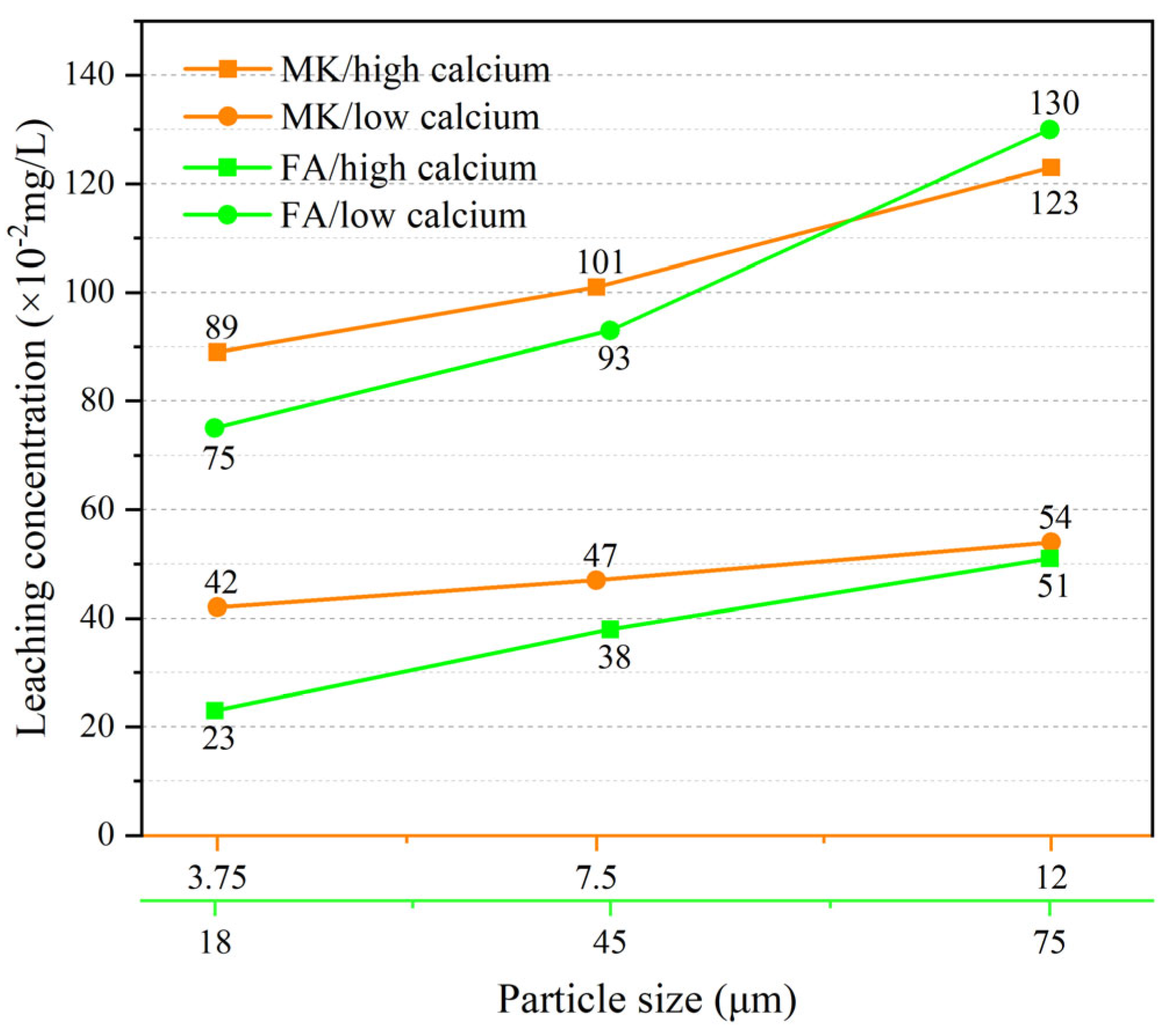
2.6. Influence of Particle Size and Calcium Content on Cr3+ Leaching Behavior
3. Conclusions
- The smaller particles of both binders with higher calcium content slowed down the setting time of geopolymers and deteriorated the flow of the slurries, suggesting a trade-off between achieving desired setting times and maintaining optimal flow properties.
- There is a negative correlation between the raw material particle size and compressive strength, but a positive correlation with the leaching rate.
- An increase in reactive calcium ions led to a more complex geopolymerization reaction. Not only does the geopolymerization occur, but the Ca2+ ions also form a calcium-containing hydrated gel. This gel interweaves with the geopolymer gel, filling the microstructure more compactly, which enhances the curing performance by creating a denser pore structure.
- The differences between fly ash and metakaolin in their physicochemical properties exhibited different behaviors in systems with high calcium content. These variations influence how each material reacts within the geopolymer matrix, impacting the final material characteristics.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Synthesis of Geopolymeric Formulations
4.3. Characterizations
4.3.1. Accessibility of Gels
4.3.2. Microstructural Characteristics
4.3.3. Pore Structure
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, R.; Budarayavalasa, S. Solidification and stabilization of hazardous wastes using geopolymers as sustainable binders. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2021, 23, 1699–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zifang, X.; Dongdong, Y.; Tao, D.; Yan, D. Research on Preparation of Coal Waste-Based Geopolymer and Its Stabilization/Solidification of Heavy Metals. Integr. Ferroelectr. 2021, 217, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Zhi, T.; Liu, L.; Mi, J.; Zhang, M.; Tian, C.; Si, Z.; Liu, X.; Mu, Y. Solidification/stabilization of chromium slag in red mud-based geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 316, 125813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Meng, Y.; Ju, T.; Song, M.; Chen, Z.; Shen, P.; Du, Y.; Deng, Y.; Han, S.; Jiang, J. Manufacture of alkali-activated and geopolymer hybrid binder (AGHB) by municipal waste incineration fly ash incorporating aluminosilicate supplementary cementitious materials (ASCM). Chemosphere 2022, 303, 134978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sata, V.; Sathonsaowaphak, A.; Chindaprasirt, P. Resistance of lignite bottom ash geopolymer mortar to sulfate and sulfuric acid attack. Cement. Concr. Comp. 2012, 34, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, Y.-M.; Heah, C.-Y.; Mohd Mustafa, A.B.; Kamarudin, H. Structure and properties of clay-based geopolymer cements: A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 83, 595–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarian, M.; Tao, Z.; Adam, G.; Samali, B. Mechanical properties of ambient cured one-part hybrid OPC-geopolymer concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 186, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Occhicone, A.; Graziuso, S.G.; De Gregorio, E.; Montagnaro, F.; Ricciotti, L.; Tarallo, O.; Roviello, G.; Ferone, C. Synthesis and Characterization of New Acid-activated Red Mud-metakaolin Geopolymers and Comparison with their Alkaline Counterparts. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 435, 140492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, M.R.; Dong, Y.; Hamed, M.M.; El Abd, A.; Ibrahiem, H.H.; Gouda, M.M.; Mansy, M.S.; Hassan, A.M.A.; Rahman, R.O.A. Microstructural Insights of Magnetic γ-Fe2O3/geopolymer Nanocomposite for Prospective Green Removal of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solutions. Sep. Pur. Technol. 2024, 333, 125941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, M.R.; El-Masry, E.H.; El-Sadek, A.A. Assessment of Individual and Mixed Alkali Activated Binders for Solidification of a Nuclear Grade Organic Resin Loaded with 134Cs, 60Co and 152+154Eu Radionuclides. J. Haz. Mater. 2019, 375, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascensão, G.; Seabra, M.P.; Aguiar, J.B.; Labrincha, J.A. Red Mud-based Geopolymers with Tailored Alkali Diffusion Properties and pH Buffering Ability. J. Cleaner Prod. 2017, 148, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Ishwarya, G.; Gupta, M.; Bhattacharyya, S. Geopolymer concrete: A review of some recent developments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 85, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheimi, M.; Aziz, I.H.; Abdullah MM, A.B.; Almadani, M.; Abd Razak, R. Waste Material via Geopolymerization for Heavy-Duty Application: A Review. Materials 2022, 15, 3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsimbe, J.; Dinka, M.; Olukanni, D.; Musonda, I. Geopolymer: A Systematic Review of Methodologies. Materials 2022, 15, 6852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elyamany, E.H.; Elmoaty, A.M.E.A.; Elshaboury, M.A. Setting time and 7-day strength of geopolymer mortar with various binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 187, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.; Kumar, S. Role of particle fineness on engineering properties and microstructure of fly ash derived geopolymer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 233, 117294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chindaprasirt, P.; Chareerat, T.; Hatanaka, S.; Cao, T. High-Strength Geopolymer Using Fine High-Calcium Fly Ash. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2011, 23, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, R.M.; El-Dessouky, I.M. Re-use of waste glass in improving properties of metakaolin-based geopolymers: Mechanical and microstructure examinations. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 132, 543–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Chen, L.; Bu, B. Rheokinetics and fluidity modification of alkali activated ultrafine metakaolin based geopolymers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 269, 121268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huseien, G.F.; Mirza, J.; Ismail, M.; Hussin, M.W. Influence of different curing temperatures and alkali activators on properties of GBFS geopolymer mortars containing fly ash and palm-oil fuel ash. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 125, 1229–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nodehi, M.; Taghvaee, M.V. Alkali-Activated Materials and Geopolymer: A Review of Common Precursors and Activators Addressing Circular Economy. Circ. Econ. Sust. 2021, 2, 165–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Zhou, W.; Lyu, X.; Liu, X.; Su, H.; Li, C.; Wang, H. Comprehensive Utilization of Steel Slag: A review. Powder Technol. 2023, 422, 118449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayenko, S.; Svitlychnyi, Y.; Shkuropatenko, V.; Pancotti, F.; Sandalova, S.; Poulesquen, A.; Giboire, I.; Hasnaoui, A.; Cori, D.; Magugliani, G.; et al. Incorporation of Organic Liquid Waste in Alkali Activated Mixed Fly Ash/Blast Furnace Slag/Metakaolin-based Geopolymers. Nucl. Eng. Des. 2024, 429, 113608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.Z.; Hou, P.K.; Guo, T.T. Study on the Effects of Different Water-Cement Ratios on the Flow Pattern Properties of Cement Grouts. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2011, 1366, 1264–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Cui, C.; Cai, C.S.; Li, S.L.; Zhao, J.W. Mechanism of activator concentration influencing properties of metakaolin-based geopolymer. Acta Mater. Compos. Sin. 2016, 33, 2952–2960. [Google Scholar]
- El-Naggar, M.; Amin, M. Impact of alkali cations on properties of metakaolin and metakaolin/slag geopolymers: Microstructures in relation to sorption of 134 Cs radionuclide. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 344, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, C.; Lukey, G.; Deventer, V.J. The coexistence of geopolymeric gel and calcium silicate hydrate at the early stage of alkaline activation. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 35, 1688–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Zhang, C.; Sun, W. Fly ash effects: III. The microaggregate effect of fly ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 2061–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Zhang, C.; Sun, W. Fly ash effects: II. The microaggregate effect of fly ash. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 2057–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Hu, S.; Zhang, P.; Elmaadawy, K.; Ke, Y.; Li, J.; Li, M.; Hu, J.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; et al. Microwave enhanced solidification/stabilization of lead slag with fly ash based geopolymer. J. Cleaner Prod. 2020, 272, 122957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Library of Standards: GB/T 1346-2011. Available online: https://www.nssi.org.cn/nssi/front/77257743.html (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- National Library of Standards: GB/T 8077-2012. Available online: https://www.nssi.org.cn/nssi/front/124563566.html (accessed on 10 January 2024).
- Lin, B.Q.; Zhong, Y.T.; Cao, X.; Liu, T.; Wang, Y.H. Effect of microwave irradiation on pore and fracture evolutions of coal. J. Xi’an Univ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 41, 964–972. [Google Scholar]







| (wt.%) | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | Cl | CaO | SO3 | H2O | OH− | Na2O | LOI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fly ash | 46.6 | 38.2 | 3.2 | 0.015 | 4.2 | 2.1 | 0.85 | 1.2 | 2.8 | |
| Metakaolin | 53.00 | 41.50 | 0.80 | |||||||
| GGBFS | 33.58 | 15.22 | 0.62 | 33.41 | ||||||
| Water glass | 31.00 | 57.45 | 11.55 |
| Number | Raw Materials | Particle Size (μm) | Calcium Content (wt.%) | Heavy Metal Content |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GFMK-12 | MK | 12 | 6.42 | 0.1/wt.% |
| GFMK-7.5 | 7.5 | |||
| GFMK-3.75 | 3.75 | |||
| GFMK-12C | MK/GGBFS | 12 | 20 | |
| GFMK-7.5C | 7.5 | |||
| GFMK-3.75C | 3.75 | |||
| GFFA-75 | FA | 75 | 0.5 | |
| GFFA-45 | 45 | |||
| GFFA-18 | 18 | |||
| GFFA-75C | FA/GGBFS | 75 | 20 | |
| GFFA-45C | 45 | |||
| GFFA-18C | 18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Dong, Y.; El-Naggar, M.R.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Y. The Influence of Particle Size and Calcium Content on Performance Characteristics of Metakaolin- and Fly-Ash-Based Geopolymer Gels. Gels 2024, 10, 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10100639
Li Y, Dong Y, El-Naggar MR, Wang F, Zhao Y. The Influence of Particle Size and Calcium Content on Performance Characteristics of Metakaolin- and Fly-Ash-Based Geopolymer Gels. Gels. 2024; 10(10):639. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10100639
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yefan, Yanhui Dong, Mohamed R. El-Naggar, Fucheng Wang, and Yixin Zhao. 2024. "The Influence of Particle Size and Calcium Content on Performance Characteristics of Metakaolin- and Fly-Ash-Based Geopolymer Gels" Gels 10, no. 10: 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10100639
APA StyleLi, Y., Dong, Y., El-Naggar, M. R., Wang, F., & Zhao, Y. (2024). The Influence of Particle Size and Calcium Content on Performance Characteristics of Metakaolin- and Fly-Ash-Based Geopolymer Gels. Gels, 10(10), 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels10100639






